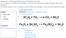
2. Is this balanced or not? 2 LiCl + Br 2 2 LiBr + Cl 2 3. Summarize notes from last assignment.
|
|
|
- Egbert Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assignment #3 Temperature in Reactions LO: To recognize how to tell if a chemical reaction has occurred. EQ: Compare and contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions. Give examples of each. AGENDA 1. Discussion 2. video HOMEWORK 1. Finish Worksheet LEVEL ZERO VOICE Catalyst (10 minutes, individual work): 1. Is it a physical or chemical change? Why? Glass breaking Burn book Make lemonade Cook waffle Staple paper 2. Is this balanced or not? 2 LiCl + Br 2 2 LiBr + Cl 2 3. Summarize notes from last assignment.
2 Chemical Equations: Equations that show reactants and products in a chemical reaction Reactant: starting materials (left side of equation) Products: the new substance(s) formed (right side)
3 tin + oxygen gas tin oxide (reactants) (product) 2 Sn + O2 2 SnO (reactants) (product)
4 2H2O 2H2 + O2 Coefficient: how many molecules or atoms (comes before the atom or molecule) Subscript: the little number in a chemical formula that tells how many atoms of an element are in a molecule
5 Law of Conservation of Mass: the total mass before a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass after the reaction In a chemical reaction, atoms are REARRANGED, not destroyed In all chemical reactions, the amount of matter is the same before and after the change takes place No atoms are lost, no atoms are gained
6 Balance a Chemical Equation When you are writing a chemical equation: 1. Make sure the symbols and formulas for the reactants and products are correct 2. Check to make sure both sides are balanced (same number of each atom appears on each side of the equation reactants and products) - compare the number of one atom on both sides of the arrow to make sure it s the same on both sides
7 Parentheses in Chemical Equations When you count atoms inside a parentheses, the subscript following the parentheses multiplies all the atoms inside. Ca (OH) 2 Count the atoms: 1 Ca atoms 2 O atoms 2H atoms
8 Parentheses in Chemical Equations When you count atoms inside a parentheses, the subscript following the parentheses multiplies all the atoms inside. Ca (OH) 2 Count the atoms: 1 Ca atoms 2 O atoms 2H atoms
9 Quickwrite: How do you know when a chemical reaction has taken place?
10 Quickwrite: How do you know when a chemical reaction has taken place?
11 Observations: detailed observations (no more than two lines)
12 Cl.Ev.Re.: Prove whether the reaction you witnessed was a chemical or a physical change. Claim: Write your claim. (Was it a chem rxn?) Evidence: What is your evidence to support your claim? State evidence without reasoning. List lines of evidence. Reasoning: Explain why your evidence supports your claim.
13 What do you think these words mean? Exothermic Endothermic
14 Let s break it down Exo Endo - Thermo -
15 So what do you guys think endothermic means? What do you think exothermic means?
16 Video:
17 In your glossary write: Endo: absorbing, within Exo: outwards Thermo: heat
18 In your NOTES write: Exothermic reaction heat is released The actual particles are losing heat to the surrounding Surroundings feel warmer
19 In your NOTES write: Endothermic reaction heat is absorbed The actual particles are gaining heat Surroundings feel cooler because it is losing heat
20 Assignment #3 Temperature in Reactions LO: To recognize how to tell if a chemical reaction has occurred. EQ: Compare and contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions. Give examples of each. AGENDA 1. Discussion 2. Exploration HOMEWORK 1. Finish Worksheet LEVEL ZERO VOICE PROCESSING TASK (10 minutes, individual work): 8 flips Exothermic (define) Energy is. (released/absorbed) Heat is. (gained/lost) Feels. (warm/cold) Endothermic (define) Energy is. (released/absorbed) Heat is. (gained/lost) Feels. (warm/cold)
Why do cold packs get cold?
 Assignment #5 Temperature in Reactions LO: To determine which solute dissolves most endothermically and exothermically in water. EQ: What makes an endothermic reaction feel cold? (explain using bonds and
Assignment #5 Temperature in Reactions LO: To determine which solute dissolves most endothermically and exothermically in water. EQ: What makes an endothermic reaction feel cold? (explain using bonds and
8.1 Chemical Properties and Changes. chemical property chemical change dissolving
 8.1 Chemical Properties and Changes chemical property chemical change dissolving Ability to Change 8.1 Chemical Properties and Changes In a chemical change, the properties that give a substance its identity
8.1 Chemical Properties and Changes chemical property chemical change dissolving Ability to Change 8.1 Chemical Properties and Changes In a chemical change, the properties that give a substance its identity
Chemical Equilibrium
 Chemical Equilibrium Forward Rxn: A + B C + D Reverse Rxn: A + B C + D Written as: A + B C + D OR A + B C + D A reversible reaction has both an endothermic rxn and an exothermic rxn Reactants Exothermic
Chemical Equilibrium Forward Rxn: A + B C + D Reverse Rxn: A + B C + D Written as: A + B C + D OR A + B C + D A reversible reaction has both an endothermic rxn and an exothermic rxn Reactants Exothermic
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. Counting atoms
 Assignment 4 Chemical Detectives at the Molecular Level LO: To explain the differences between chemical and physical changes through observable evidence. EQ: What evidence can be used to tell the difference
Assignment 4 Chemical Detectives at the Molecular Level LO: To explain the differences between chemical and physical changes through observable evidence. EQ: What evidence can be used to tell the difference
Chemical Symbols & Formulas
 + Chemical Symbols & Formulas + Chemical Symbols All elements in the Periodic Table have symbols that are recognized world wide. It does not matter which country you are in or the language you speak. Example:
+ Chemical Symbols & Formulas + Chemical Symbols All elements in the Periodic Table have symbols that are recognized world wide. It does not matter which country you are in or the language you speak. Example:
Chemical Reactions. Section 7.1: Nature of Reactions
 Chemical Reactions Section 7.1: Nature of Reactions When do chemical reactions take place? What is the role of energy in chemical reactions? 1 Chemical Reactions It is a change in matter that produces
Chemical Reactions Section 7.1: Nature of Reactions When do chemical reactions take place? What is the role of energy in chemical reactions? 1 Chemical Reactions It is a change in matter that produces
10.1 Chemical Equations
 Section 10.1 Equations 10.1 Equations Developing the language of chemistry reactions and change Think of the element symbols as the alphabet of chemistry and the formulas as the words of chemistry. s are
Section 10.1 Equations 10.1 Equations Developing the language of chemistry reactions and change Think of the element symbols as the alphabet of chemistry and the formulas as the words of chemistry. s are
1. Parts of Chemical Reactions. 2 H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2 H 2 O(g) How to read a chemical equation
 Unit 6 Chemical Reactions 1. Parts of a Chemical Reaction 2. Indicators of a Chemical Reaction 3. Enthalpy 4. Balancing Chemical Equations 5. Word Equations 6. Classifying Chemical Reactions 7. Predicting
Unit 6 Chemical Reactions 1. Parts of a Chemical Reaction 2. Indicators of a Chemical Reaction 3. Enthalpy 4. Balancing Chemical Equations 5. Word Equations 6. Classifying Chemical Reactions 7. Predicting
Chemical Bonds And Equations
 Chemical Bonds And Equations Intro to Chemical Bonds EQ: Why do atoms have a strong desire to form chemical bonds in nature? What are these called when different types of atoms bond to form a chemically
Chemical Bonds And Equations Intro to Chemical Bonds EQ: Why do atoms have a strong desire to form chemical bonds in nature? What are these called when different types of atoms bond to form a chemically
Notes: Balancing Chemical Equations
 Notes: Balancing Chemical Equations Effects of chemical reactions: Chemical reactions rearrange atoms in the reactants to form new products. The identities and properties of the products are completely
Notes: Balancing Chemical Equations Effects of chemical reactions: Chemical reactions rearrange atoms in the reactants to form new products. The identities and properties of the products are completely
Energy Changes in Reactions p
 Energy Changes in Reactions p.126 210 Heat vs. temperature: Heat is a form of energy, it is transferred from one system to another Temperature is an indication of the intensity of heat, it measures the
Energy Changes in Reactions p.126 210 Heat vs. temperature: Heat is a form of energy, it is transferred from one system to another Temperature is an indication of the intensity of heat, it measures the
Ionic Covalent Metallic
 3 Types of Chemical Bonds Ionic Covalent Metallic What can you describe about each of these bonds just by looking at the name? Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bond A force of attraction that holds
3 Types of Chemical Bonds Ionic Covalent Metallic What can you describe about each of these bonds just by looking at the name? Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bond A force of attraction that holds
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Understanding Chemical Reactions Lesson 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Lesson 3 Energy Changes and Chemical Reactions
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Understanding Chemical Reactions Lesson 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Lesson 3 Energy Changes and Chemical Reactions Chapter Wrap-Up Changes in Matter A physical change does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Understanding Chemical Reactions Lesson 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Lesson 3 Energy Changes and Chemical Reactions Chapter Wrap-Up Changes in Matter A physical change does
The car has set out on the trip and has been driving for a while. Cruise control is set for a constant speed.
 161 ChemQuest 53 Name: Date: Hour: Information: Internal Thermodynamics involves the study of the energy and disorder of a system. Every system has internal energy. Internal energy is the total amount
161 ChemQuest 53 Name: Date: Hour: Information: Internal Thermodynamics involves the study of the energy and disorder of a system. Every system has internal energy. Internal energy is the total amount
Chemical Bonds & Reactions
 Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bond A force of attraction that holds two atoms together Involves the valence electrons (they determine the chemical characteristics of the atom!) Valence Electrons
Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bond A force of attraction that holds two atoms together Involves the valence electrons (they determine the chemical characteristics of the atom!) Valence Electrons
States & Properties of Matter. Unit 1 Topics 4 & 5
 States & Properties of Matter Unit 1 Topics 4 & 5 Pure Substances Topic 4 - Elements and Compounds Elements Pure substances that only contain one kind of atom and cannot be separated into a simpler substance.
States & Properties of Matter Unit 1 Topics 4 & 5 Pure Substances Topic 4 - Elements and Compounds Elements Pure substances that only contain one kind of atom and cannot be separated into a simpler substance.
Science 1206 Chemistry Unit #10
 Science 1206 Chemistry Unit #10 Introduction to Chemical Equations Communicating Chemical Changes Chemical change occurs when matter changes into a new and different form. The new form has a new make up
Science 1206 Chemistry Unit #10 Introduction to Chemical Equations Communicating Chemical Changes Chemical change occurs when matter changes into a new and different form. The new form has a new make up
Chapter 9 Practice Test
 Chapter 9 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following describes a chemical reaction? a) A gas is given off when
Chapter 9 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following describes a chemical reaction? a) A gas is given off when
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions Chemical Equation --> is a representation of a chemical reaction in which the reactants and products are expressed as formulas Reactants --> substances that undergo change
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions Chemical Equation --> is a representation of a chemical reaction in which the reactants and products are expressed as formulas Reactants --> substances that undergo change
Balancing Equations. Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve
 Balancing Equations Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve changes in the chemical composition of matter the making of new
Balancing Equations Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve changes in the chemical composition of matter the making of new
CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS Section 1: Forming New Substances Chemical Changes are responsible for leaf coloring Chemical Reactions Process of one or more substance undergoes change to produce one or
CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS Section 1: Forming New Substances Chemical Changes are responsible for leaf coloring Chemical Reactions Process of one or more substance undergoes change to produce one or
Choose the answer that best completes each statement.
 Name Date CHAPTER TEST: CHEMICAL BONDS AND EQUATIONS Multiple Choice Choose the answer that best completes each statement. 1. Magnesium bromide is an ionic compound with the chemical formula MgBr2. What
Name Date CHAPTER TEST: CHEMICAL BONDS AND EQUATIONS Multiple Choice Choose the answer that best completes each statement. 1. Magnesium bromide is an ionic compound with the chemical formula MgBr2. What
Chemical Reactions. A. Chemical Reactions And The Law Of Conservation Of Mass
 Chemical Reactions A. Chemical Reactions And The Law Of Conservation Of Mass 1. A CHEMICAL REACTION is a change that produces new materials with different properties from the starting materials. Various
Chemical Reactions A. Chemical Reactions And The Law Of Conservation Of Mass 1. A CHEMICAL REACTION is a change that produces new materials with different properties from the starting materials. Various
Chemical Bonds & Reactions
 Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bond A force of attraction that holds two atoms together Has a significant effect on chemical and physical properties of compounds involves the valence electrons Valence
Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bond A force of attraction that holds two atoms together Has a significant effect on chemical and physical properties of compounds involves the valence electrons Valence
Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Guided Notes
 Name: Period: What is a Chemical Reaction and how do they occur? Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Guided Notes A chemical reaction is a process that involves of atoms Law of Conservation of : Mass is neither
Name: Period: What is a Chemical Reaction and how do they occur? Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Guided Notes A chemical reaction is a process that involves of atoms Law of Conservation of : Mass is neither
Heat can be thought of as the flow of energy between two bodies because of a difference in temperature
 Why? The amount of heat energy released or absorbed by a chemical or physical change can be measured using an instrument called a calorimeter. This measurement is based on the law of energy conservation.
Why? The amount of heat energy released or absorbed by a chemical or physical change can be measured using an instrument called a calorimeter. This measurement is based on the law of energy conservation.
Introduction to Chemical Reactions. Making new substances
 Introduction to Chemical Reactions Making new substances Main Ideas Chemical Reactions are represented by Chemical Equations. Chemical Equations are balanced to show the same number of atoms of each element
Introduction to Chemical Reactions Making new substances Main Ideas Chemical Reactions are represented by Chemical Equations. Chemical Equations are balanced to show the same number of atoms of each element
Student Exploration: Chemical Changes
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Chemical Changes Vocabulary: acid, base, catalyst, chemical change, coefficient, conservation of matter, decomposition, dissolve, double replacement, endothermic, exothermic,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Chemical Changes Vocabulary: acid, base, catalyst, chemical change, coefficient, conservation of matter, decomposition, dissolve, double replacement, endothermic, exothermic,
Physical Change - alters the form or appearance of a substance but does not change it into a new, different substance
 Chemical Reactions Physical Change - alters the form or appearance of a substance but does not change it into a new, different substance Chemical Change - forms one or more new substances with properties
Chemical Reactions Physical Change - alters the form or appearance of a substance but does not change it into a new, different substance Chemical Change - forms one or more new substances with properties
Ch. 8 Notes ~ CHEMICAL REACTIONS NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics.
 Ch. 8 Notes ~ CHEMICAL REACTIONS NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Chemical Reactions (rxns.) A. chemical reaction an expression showing the conversion
Ch. 8 Notes ~ CHEMICAL REACTIONS NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Chemical Reactions (rxns.) A. chemical reaction an expression showing the conversion
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work):
 Assignment #6 Review States LO: To identify areas of weakness. EQ: Describe the three states of matter in depth. Write the main force responsible in bold color. 4/27-4/28 AGENDA 1. CST Review 2. Phases
Assignment #6 Review States LO: To identify areas of weakness. EQ: Describe the three states of matter in depth. Write the main force responsible in bold color. 4/27-4/28 AGENDA 1. CST Review 2. Phases
Chemical Equations and Reactions
 Chemical Equations and Reactions 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing substances; 8.5F
Chemical Equations and Reactions 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing substances; 8.5F
Energy Changes, Reaction Rates and Equilibrium. Thermodynamics: study of energy, work and heat. Kinetic energy: energy of motion
 Energy Changes, Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Thermodynamics: study of energy, work and heat Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position, stored energy Chemical reactions involve
Energy Changes, Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Thermodynamics: study of energy, work and heat Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position, stored energy Chemical reactions involve
Chemistry. Friday, March 30 th Monday, April 9 th, 2018
 Chemistry Friday, March 30 th Monday, April 9 th, 2018 Do-Now: BrainPOP: Heat 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes. 3. What is the specific heat of water?
Chemistry Friday, March 30 th Monday, April 9 th, 2018 Do-Now: BrainPOP: Heat 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes. 3. What is the specific heat of water?
Chemical Reactions: The Law of Conservation of Mass
 Chemical Reactions: The Law of Conservation of Mass What happens in a Chemical Reaction? Chemical bonds in the reactants are broken, then atoms are rearranged to form new substances (products). Reactants
Chemical Reactions: The Law of Conservation of Mass What happens in a Chemical Reaction? Chemical bonds in the reactants are broken, then atoms are rearranged to form new substances (products). Reactants
7.1 Describing Reactions
 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions 7.1 Describing Reactions Chemical Equations Equation states what a reaction starts with, and what it ends with. Reactants the starting materials that undergo change. (On the
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions 7.1 Describing Reactions Chemical Equations Equation states what a reaction starts with, and what it ends with. Reactants the starting materials that undergo change. (On the
The Question (Learning Goals)
 The Question (Learning Goals) What is the Law of Conservation of Mass (or atoms)? What is a balanced Chemical Reaction? How do we balance a chemical reaction?? (A Level) Review: Chemical Reactions Chemical
The Question (Learning Goals) What is the Law of Conservation of Mass (or atoms)? What is a balanced Chemical Reaction? How do we balance a chemical reaction?? (A Level) Review: Chemical Reactions Chemical
Section 1 Forming New Substances
 Section 1 Forming New Substances Key Concept During chemical reactions, atoms rearrange to form new substances that have different properties than the original substances had. What You Will Learn Four
Section 1 Forming New Substances Key Concept During chemical reactions, atoms rearrange to form new substances that have different properties than the original substances had. What You Will Learn Four
Chemical formula - tells you how many atoms of each element are in a compound example: CO 2 (carbon dioxide) has one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms
 Chemical Reactions Chemical formula - tells you how many atoms of each element are in a compound example: CO 2 (carbon dioxide) has one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms 2 points Chemical Equation - a short,
Chemical Reactions Chemical formula - tells you how many atoms of each element are in a compound example: CO 2 (carbon dioxide) has one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms 2 points Chemical Equation - a short,
PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL CHANGES
 PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL CHANGES The characteristics of a substance are called its properties. Physical properties are those that describe the matter without changing its composition. Examples are density,
PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL CHANGES The characteristics of a substance are called its properties. Physical properties are those that describe the matter without changing its composition. Examples are density,
Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Funsheets
 Name: Period: Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Funsheets Part A: Reaction Diagrams 1) Answer the following questions based on the potential energy diagram shown here: a. Does the graph represent an endothermic
Name: Period: Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Funsheets Part A: Reaction Diagrams 1) Answer the following questions based on the potential energy diagram shown here: a. Does the graph represent an endothermic
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Unit 2 What are we made of? Unit 2.2 Test Review
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: TEKS covered: Unit 2 What are we made of? Unit 2.2 Test Review 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each
Name: Class Period: Due Date: TEKS covered: Unit 2 What are we made of? Unit 2.2 Test Review 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each
Chapter 17: Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 17: Chemical Reactions Section 1: Chemical Formulas and Equations Chemical Equations Balancing Chemical Equations Law of Conservation of Mass Evidences of Chemical Reactions Symbols to represent
Chapter 17: Chemical Reactions Section 1: Chemical Formulas and Equations Chemical Equations Balancing Chemical Equations Law of Conservation of Mass Evidences of Chemical Reactions Symbols to represent
Student Exploration: Chemical Equations - PAP Login to to complete this assignment.
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Chemical Equations - PAP Login to www.explorelearning.com to complete this assignment. Define the following terms on a separate paper by 10/1: Coefficient, Conservation
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Chemical Equations - PAP Login to www.explorelearning.com to complete this assignment. Define the following terms on a separate paper by 10/1: Coefficient, Conservation
Chemical Equations. Physical Science
 Chemical Equations Physical Science Chemical Equations A chemical equation is a shorthand way of expressing a chemical reaction. CHEMICAL REACTIONS Reactants: Zn + I 2 Product: Zn I 2 Chemical reactions
Chemical Equations Physical Science Chemical Equations A chemical equation is a shorthand way of expressing a chemical reaction. CHEMICAL REACTIONS Reactants: Zn + I 2 Product: Zn I 2 Chemical reactions
Honors text: Ch 10 & 12 Unit 06 Notes: Balancing Chemical Equations
 Notes: Balancing Chemical Equations Effects of chemical reactions: Chemical reactions rearrange atoms in the reactants to form new products. The identities and properties of the products are completely
Notes: Balancing Chemical Equations Effects of chemical reactions: Chemical reactions rearrange atoms in the reactants to form new products. The identities and properties of the products are completely
THERMODYNAMICS. Dear Reader
 THERMODYNAMICS Dear Reader You are familiar with many chemical reactions which are accompanied by the absorption or release of energy. For example, when coal burns in air, a lot of heat is given out. Another
THERMODYNAMICS Dear Reader You are familiar with many chemical reactions which are accompanied by the absorption or release of energy. For example, when coal burns in air, a lot of heat is given out. Another
Observing Chemical Change - 5.1
 Observing Chemical Change - 5.1 Vocabulary: Physical change - Chemical change - Reactant Product Precipitate Exothermic reaction - Endothermic reaction - Properties of matter: Two kinds of properties of
Observing Chemical Change - 5.1 Vocabulary: Physical change - Chemical change - Reactant Product Precipitate Exothermic reaction - Endothermic reaction - Properties of matter: Two kinds of properties of
Section 1 Chemical Changes
 Chemical Reactions Section 1 Chemical Changes What You ll Learn: How to identify the reactants & products in a chemical reaction How a chemical reaction follows the law of conservation of mass How chemists
Chemical Reactions Section 1 Chemical Changes What You ll Learn: How to identify the reactants & products in a chemical reaction How a chemical reaction follows the law of conservation of mass How chemists
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. atom ion molecule
 Section 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. VOCABULARY atom ion molecule element ionic bond compound covalent bond MAIN IDEA: Living things
Section 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. VOCABULARY atom ion molecule element ionic bond compound covalent bond MAIN IDEA: Living things
Thermodynamics: Enthalpy
 Name: Band: Date: Thermodynamics: Enthalpy Big Idea: Spontaneity A spontaneous change is a change that occurs without outside intervention. All spontaneous changes lead to equilibrium. Identify each change
Name: Band: Date: Thermodynamics: Enthalpy Big Idea: Spontaneity A spontaneous change is a change that occurs without outside intervention. All spontaneous changes lead to equilibrium. Identify each change
2.1. All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements.
 SECTION 2.1 ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES Study Guide KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. VOCABULARY atom ion molecule element ionic bond compound covalent bond Living
SECTION 2.1 ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES Study Guide KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. VOCABULARY atom ion molecule element ionic bond compound covalent bond Living
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (4 minutes, individual work): How do plants grow? What do plants eat?
 Assignment #5 Photosynthesis LO: To understand the process of photosynthesis. EQ: Explain the light dependent and light independent reactions. Include where they take place. (4-5 sentences) AGENDA 2/6-2/7
Assignment #5 Photosynthesis LO: To understand the process of photosynthesis. EQ: Explain the light dependent and light independent reactions. Include where they take place. (4-5 sentences) AGENDA 2/6-2/7
Chemical reactions. C2- Topic 5
 Chemical reactions C2- Topic 5 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a change that takes place when one or more substances (called reactants) form one or more new substances (called products)
Chemical reactions C2- Topic 5 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a change that takes place when one or more substances (called reactants) form one or more new substances (called products)
Changes & Chemical Reactions. Unit 5
 Changes & Chemical Reactions Unit 5 5 Types of Chemical Reactions Double Decomposition Replacement 1 2 3 4 5 Synthesis Single Replacement Combustion Continue Synthesis 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Menu Decomposition
Changes & Chemical Reactions Unit 5 5 Types of Chemical Reactions Double Decomposition Replacement 1 2 3 4 5 Synthesis Single Replacement Combustion Continue Synthesis 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Menu Decomposition
Chemical Reactions Chapter 2 L book pages L44 - L73. examples?
 Name: Period: Chemical Reactions Chapter 2 L book pages L44 - L73 Vocabulary Word What is this? (definition) What are some examples? What does it look like? (draw a picture or diagram) Physical property
Name: Period: Chemical Reactions Chapter 2 L book pages L44 - L73 Vocabulary Word What is this? (definition) What are some examples? What does it look like? (draw a picture or diagram) Physical property
video 6.1 types of bonds
 video 6.1 types of bonds what is a bond? Intramolecular force that holds one to another in a compound The energy stored in a bond is energy 1 why do atoms bond? Atoms bond together to get 8 valence electrons
video 6.1 types of bonds what is a bond? Intramolecular force that holds one to another in a compound The energy stored in a bond is energy 1 why do atoms bond? Atoms bond together to get 8 valence electrons
2. Indicators of Chemical Rxns. Abbreviations of State (g) gas (l) liquid (s) solid (aq) aqueous a substance dissolved in water
 Unit 6 Chemical Reactions 1. Parts of a Chemical Reaction 2. Indicators of a Chemical Reaction 3. Enthalpy 4. Balancing Chemical Equations 5. Word Equations 6. Classifying Chemical Reactions 7. Predicting
Unit 6 Chemical Reactions 1. Parts of a Chemical Reaction 2. Indicators of a Chemical Reaction 3. Enthalpy 4. Balancing Chemical Equations 5. Word Equations 6. Classifying Chemical Reactions 7. Predicting
Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Name Date Chemical Reactions and Equations What happens to atoms and energy during a chemical reaction? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about chemical reactions Record
Name Date Chemical Reactions and Equations What happens to atoms and energy during a chemical reaction? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about chemical reactions Record
11B, 11E Temperature and heat are related but not identical.
 Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
E20: BALANCING EQUATIONS
 E20: BALANCING EQUATIONS Before we can talk about balancing equations, we need to know how to READ an equation. We've already talked about symbols (like H or Na), and you should know how to read a formula
E20: BALANCING EQUATIONS Before we can talk about balancing equations, we need to know how to READ an equation. We've already talked about symbols (like H or Na), and you should know how to read a formula
Practice Packet Unit 7: Heat
 Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 7: Heat Review (Things you need to know in order to understand the new stuff ) Particle Diagrams Draw a particle diagram of a compound of CaCl2, using
Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 7: Heat Review (Things you need to know in order to understand the new stuff ) Particle Diagrams Draw a particle diagram of a compound of CaCl2, using
Chapter 7: Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 7: Chemical Reactions Physical Science C. Goodman, Doral Academy Charter High School, 2012-2013 Based on a presentation by Holt, Rinehart and Winston Section 7.1 Essential questions 1. What is
Chapter 7: Chemical Reactions Physical Science C. Goodman, Doral Academy Charter High School, 2012-2013 Based on a presentation by Holt, Rinehart and Winston Section 7.1 Essential questions 1. What is
Chemical Reactions. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 Name Date Class Chemical Reactions Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Chemistry is a. a characteristic of a substance that can be observed
Name Date Class Chemical Reactions Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Chemistry is a. a characteristic of a substance that can be observed
Chemical Bonds & Reactions
 Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bonding Do you understand how it works? What do you think when I pull out a bag of candy? I want that candy cause I don t have any! Does everyone think the same thing?
Chemical Bonds & Reactions Chemical Bonding Do you understand how it works? What do you think when I pull out a bag of candy? I want that candy cause I don t have any! Does everyone think the same thing?
Surface Area (not in book) Reality Check: What burns faster, large or small pieces of wood?
 Concentration Flammable materials burn faster in pure oxygen than in air because the of O 2 is greater. Hospitals must make sure that no flames are allowed near patients receiving oxygen. Surface Area
Concentration Flammable materials burn faster in pure oxygen than in air because the of O 2 is greater. Hospitals must make sure that no flames are allowed near patients receiving oxygen. Surface Area
TOPIC. Chemical Formulas. Essential Question: What is the law of conservation of mass, and how does it apply to chemical equations?
 TPIC Chemical Formulas Essential Question: What is the law of conservation of mass, and how Chemical formulas are written using an element s chemical symbol from the periodic table. They are used to identify
TPIC Chemical Formulas Essential Question: What is the law of conservation of mass, and how Chemical formulas are written using an element s chemical symbol from the periodic table. They are used to identify
Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chemical Formulas and Equations 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing substances; 8.5F
Chemical Formulas and Equations 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing substances; 8.5F
Word Equations. Symbols used in equations. Unit 7: Chemical Reactions. hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
 Unit 7: Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions involve a reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. Can be represented in different ways 1 Word Equations hydrogen peroxide reacts to produce
Unit 7: Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions involve a reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. Can be represented in different ways 1 Word Equations hydrogen peroxide reacts to produce
Which of the following is NOT an example of a chemical reaction? A. Milk turning sour B. Food being digested C. A match burning D.
 Chemical Reactions Which of the following is NOT an example of a chemical reaction? A. Milk turning sour B. Food being digested C. A match burning D. Ice melting Which of the following is NOT an example
Chemical Reactions Which of the following is NOT an example of a chemical reaction? A. Milk turning sour B. Food being digested C. A match burning D. Ice melting Which of the following is NOT an example
Balancing CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
 Balancing CHEMICAL EQUATIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS involves a chemical change in the identity of one or more chemical species Ex. Rusting of iron (Fe): chemical rxn btwn water and iron involve the breaking
Balancing CHEMICAL EQUATIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS involves a chemical change in the identity of one or more chemical species Ex. Rusting of iron (Fe): chemical rxn btwn water and iron involve the breaking
Careful observations led to the discovery of the conservation of mass.
 Chapter 7, Section 2 Key Concept: The masses of reactants and products are equal. BEFORE, you learned Chemical reactions turn reactants into products by rearranging atoms Chemical reactions can be observed
Chapter 7, Section 2 Key Concept: The masses of reactants and products are equal. BEFORE, you learned Chemical reactions turn reactants into products by rearranging atoms Chemical reactions can be observed
7.4 Potential Energy Diagrams
 Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations Remember: 7.4 Potential Energy Diagrams Chemical reactions can react in both the and directions All chemical reactions need Reactions can either
Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations Remember: 7.4 Potential Energy Diagrams Chemical reactions can react in both the and directions All chemical reactions need Reactions can either
Unit 7 Part I: Introductions to Biochemistry
 Unit 7 Part I: Introductions to Biochemistry Chemical Reactions, Enzymes and ATP 19-Mar-14 Averett 1 Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions Process by which one set of chemicals is changed into another
Unit 7 Part I: Introductions to Biochemistry Chemical Reactions, Enzymes and ATP 19-Mar-14 Averett 1 Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions Process by which one set of chemicals is changed into another
Unit 3 Lesson 2: Chemical Reactions Please Complete an Audio Setup Grab you SUPER FANTASTIC Science Notebook!
 Unit 3 Lesson 2: Chemical Reactions Please Complete an Audio Setup Grab you SUPER FANTASTIC Science Notebook! Review for Unit 3 Lesson 1: Bonding What type of bond share electrons? What type of bond gain
Unit 3 Lesson 2: Chemical Reactions Please Complete an Audio Setup Grab you SUPER FANTASTIC Science Notebook! Review for Unit 3 Lesson 1: Bonding What type of bond share electrons? What type of bond gain
Section 1 Chemical Changes
 Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions Section1 Chemical Reactions slides 3-20 Section 2 Chemical Equations slides 21-34 Section 3 Classifying Chemical Reactions slides 35-46 Sections 4 Chemical Reactions
Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions Section1 Chemical Reactions slides 3-20 Section 2 Chemical Equations slides 21-34 Section 3 Classifying Chemical Reactions slides 35-46 Sections 4 Chemical Reactions
ALE 4. Effect of Temperature and Catalysts on the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
 Name Chem 163 Section: Team Number: ALE 4. Effect of Temperature and Catalysts on the Rate of a Chemical Reaction (Reference: 16.5 16.6 & 16.8 Silberberg 5 th edition) Why do reaction rates increase as
Name Chem 163 Section: Team Number: ALE 4. Effect of Temperature and Catalysts on the Rate of a Chemical Reaction (Reference: 16.5 16.6 & 16.8 Silberberg 5 th edition) Why do reaction rates increase as
Chapter 7 An Introduction to Chemical Reactions. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Chapter 7 An Introduction to Chemical Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Chemical Reaction A chemical change or chemical reaction is a process in which one or more pure substances
Chapter 7 An Introduction to Chemical Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Chemical Reaction A chemical change or chemical reaction is a process in which one or more pure substances
Science 1206 Unit 3: Chemical Reactions Page 1 of 15
 Science 1206 Unit 3: Chemical Reactions Page 1 of 15 Introduction to Chemical Reactions Notes Part II TEXT p. 218-219 (word equations) There are many chemical reactions too many to count in fact! Like
Science 1206 Unit 3: Chemical Reactions Page 1 of 15 Introduction to Chemical Reactions Notes Part II TEXT p. 218-219 (word equations) There are many chemical reactions too many to count in fact! Like
Lesson 01 and 02: Introduction to Chemical Reaction Equations. 01 Chemical Reactions
 Chemistry 11, Chemical Reactions, Unit 05 1 Lesson 01 and 02: Introduction to Chemical Reaction Equations 01 Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process by which one or more substances may be transformed
Chemistry 11, Chemical Reactions, Unit 05 1 Lesson 01 and 02: Introduction to Chemical Reaction Equations 01 Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process by which one or more substances may be transformed
Moles. Balanced chemical equations Molar ratios Mass Composition Empirical and Molecular Mass Predicting Quantities
 Moles Balanced chemical equations Molar ratios Mass Composition Empirical and Molecular Mass Predicting Quantities Micro World atoms & molecules Macro World grams Atomic mass is the mass of an atom in
Moles Balanced chemical equations Molar ratios Mass Composition Empirical and Molecular Mass Predicting Quantities Micro World atoms & molecules Macro World grams Atomic mass is the mass of an atom in
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 12, sections 1 and 2: Heat in Chemical Reactions
 Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 12, sections 1 and 2: Heat in Chemical Reactions Terms, definitions, topics Joule, calorie (Re-read p 57-58) Thermochemistry Exothermic reaction Endothermic reaction
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 12, sections 1 and 2: Heat in Chemical Reactions Terms, definitions, topics Joule, calorie (Re-read p 57-58) Thermochemistry Exothermic reaction Endothermic reaction
UNIT 5. Chemical Equations
 UNIT 5 Chemical Equations Do Now Monday Determine the chemical formula of the following: 1. Calcium Oxide 2. Aluminum Sulfide 3. Diphosphorus tetraoxide Announcements / Reminders Today Begin Unit 5, Homework
UNIT 5 Chemical Equations Do Now Monday Determine the chemical formula of the following: 1. Calcium Oxide 2. Aluminum Sulfide 3. Diphosphorus tetraoxide Announcements / Reminders Today Begin Unit 5, Homework
CHAPTER 8 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 8 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS Occurs when matter combines or breaks apart to produce new kinds of matter with different properties with a change in energy. EVIDENCE FOR
CHAPTER 8 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS Occurs when matter combines or breaks apart to produce new kinds of matter with different properties with a change in energy. EVIDENCE FOR
Chapter 7 TEST CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE.
 Chapter 7 TEST CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE. 1. Which of these is not a sign of a chemical reaction? a. A gas is given off. c. Heat is released. b. The material dissolves. d. A color change
Chapter 7 TEST CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE. 1. Which of these is not a sign of a chemical reaction? a. A gas is given off. c. Heat is released. b. The material dissolves. d. A color change
Skill Building UNDERSTANDING AND BALANCING EQUATIONS
 Skill Building UNDERSTANDING AND BALANCING EQUATIONS Equations are the language of chemistry, and they are important in helping us understand how atoms and molecules form new substances. It has been said
Skill Building UNDERSTANDING AND BALANCING EQUATIONS Equations are the language of chemistry, and they are important in helping us understand how atoms and molecules form new substances. It has been said
General Physical Science. Chemical and Physical Properties. Chemical and Physical Properties. Chapter 13 Chemical Reactions. Physical properties
 General Physical Science Chapter 13 Chemical Reactions Chemical and Physical Properties Physical properties Observations about a substance changes that do not involve a change in the arrangement of the
General Physical Science Chapter 13 Chemical Reactions Chemical and Physical Properties Physical properties Observations about a substance changes that do not involve a change in the arrangement of the
Ch & 12 Test. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Ch 10 11 & 12 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many valence electrons does Argon, a noble gas, have? a. 1 b.
Name: Class: Date: Ch 10 11 & 12 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many valence electrons does Argon, a noble gas, have? a. 1 b.
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes
 Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
a) Write the equation for the overall reaction. (Using steps 1 and 2)
 Chemistry 12 Reaction Mechanisms Worksheet Name: Date: Block: 1. It is known that compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (C.F.C.s) (eg. CFCl3) will break up in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, such
Chemistry 12 Reaction Mechanisms Worksheet Name: Date: Block: 1. It is known that compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (C.F.C.s) (eg. CFCl3) will break up in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, such
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transferred or transformed, but cannot be created or destroyed. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the first law of thermodynamics
The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transferred or transformed, but cannot be created or destroyed. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the first law of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes
 Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes Date Topics Video cast DUE Assignment during class time One Review of thermodynamics ONE and TWO Review of thermo Wksheet Two 19.1-4; state function THREE
Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes Date Topics Video cast DUE Assignment during class time One Review of thermodynamics ONE and TWO Review of thermo Wksheet Two 19.1-4; state function THREE
4 Energy and Rates of Chemical Reactions
 CHAPTER 14 4 and Rates of Chemical Reactions SECTION Chemical Reactions BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How is energy involved in a chemical reaction?
CHAPTER 14 4 and Rates of Chemical Reactions SECTION Chemical Reactions BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How is energy involved in a chemical reaction?
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Unit 2 It s Elemental Test Review
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: TEKS covered: Unit 2 It s Elemental Test Review 8.5A describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations of protons, electrons and nucleus
Name: Class Period: Due Date: TEKS covered: Unit 2 It s Elemental Test Review 8.5A describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations of protons, electrons and nucleus
Thermochemistry. Mr.V
 Thermochemistry Mr.V Introduction to Energy changes System Surroundings Exothermic Endothermic Internal energy Enthalpy Definitions System A specified part of the universe which is under investigation
Thermochemistry Mr.V Introduction to Energy changes System Surroundings Exothermic Endothermic Internal energy Enthalpy Definitions System A specified part of the universe which is under investigation
Chemistry of Life Essential Questions
 Chemistry of Life Essential Questions VMHS Standards 8.6b; 8.6c; 1h; 4e; 4f; 5a;1b; 1. What is an atom? What are elements? An atom is the basic unit of o Consist of,, and An element is a type of atom o
Chemistry of Life Essential Questions VMHS Standards 8.6b; 8.6c; 1h; 4e; 4f; 5a;1b; 1. What is an atom? What are elements? An atom is the basic unit of o Consist of,, and An element is a type of atom o
Unit 5: Chemical Reactions. Chapter 11
 Unit 5: Chemical Reactions Chapter 11 Objectives 35 Identify the five types of chemical reactions 36 Write word and chemical equations based on chemical reactions 37 Balance chemical equations 38 Predict
Unit 5: Chemical Reactions Chapter 11 Objectives 35 Identify the five types of chemical reactions 36 Write word and chemical equations based on chemical reactions 37 Balance chemical equations 38 Predict
Conservation of Mass
 Conservation of Mass 1 of 35 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Conservation of Mass 2 of 35 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is a chemical reaction? 3 of 35 Boardworks Ltd 2016 A chemical reaction is a change that takes place
Conservation of Mass 1 of 35 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Conservation of Mass 2 of 35 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is a chemical reaction? 3 of 35 Boardworks Ltd 2016 A chemical reaction is a change that takes place
CHEM3.4 Demonstrate understanding of thermochemical principles and the properties of particles and substances
 CHEM3.4 Demonstrate understanding of thermochemical principles and the properties of particles and substances We have covered the underlined part so far. This is: Electron configurations with s, p, d orbitals
CHEM3.4 Demonstrate understanding of thermochemical principles and the properties of particles and substances We have covered the underlined part so far. This is: Electron configurations with s, p, d orbitals
S T A T I O N 1 E X O T H E R M I C / E N D O T H E R M I C P R O C E S S E S
 Name Period Date S T A T I O N 1 E X O T H E R M I C / E N D O T H E R M I C P R O C E S S E S Determine if each statement describes an exothermic process (EXO) or endothermic process (ENDO). _EXO EXO_
Name Period Date S T A T I O N 1 E X O T H E R M I C / E N D O T H E R M I C P R O C E S S E S Determine if each statement describes an exothermic process (EXO) or endothermic process (ENDO). _EXO EXO_
