Isomerism - Stereoisomers
|
|
|
- Job Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isomerism - Stereoisomers 6 CN ; Octahedron, Triethylentetraamine H 2 N H N N H NH 2 No coplanar rings Two coplanar rings Three coplanar rings
2 Isomerism - Stereoisomers Number of possible Isomers
3 Isomerism - Stereoisomers Number of possible Isomers Ma 3 bcd a facial d a c a b no mirror plane meridional a a a a a b d c a d a d a b a b a c c a b d a c
4 Isomerism - Stereoisomers Number of possible Isomers
5 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Combination of Chelate Rings (, ) Handedness of chelate Rings Lambda Delta
6 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Combination of Chelate Rings (, ) [Co(en) 3 ] 3+
7 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Combination of Chelate Rings (, ) Procedure for Determining Handedness
8 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Combination of Chelate Rings (, ) CoEDTA - Not coplanar, not connected at the same atom X X R1: R2, R3, R4, R5 X X X R2: R1, R3, R4, R5,, or
9 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Lignad Ring Conformation 6 CN ; Octahedron, Triethylentetraamine H 2 N H N N H NH 2 S S S S R R R R
10 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Lignad Ring Conformation Chelate Ring Conformation (λ, δ)
11 Isomerism Stereoisomers: Lignad Ring Conformation 6 CN ; Octahedron, Triethylentetraamine Chelate Ring Conformation (λ, δ)
12 Isomerism Constitutional Isomers: Hydrate Isomers Hydrate Isomers: having water as either a ligand or an added part of the crystal structure
13 Isomerism Constitutional Isomers: Ionization Isomerism Ionization Isomers: Exchange of ions between inside and outside coordination sphere
14 Isomerism Constitutional Isomers: Coordination Isomerism Coordination Isomers: require at least two metal
15 Isomerism Constitutional Isomers: Linkage (ambidentate) Isomerism Linkage Isomers: Compounds containing ambidentate ligand thiocyanate thiocyano isothiocyano nitrite nitro nitrito
16 Isomerism Separation and Identification of Isomers Separation Fractional Crystalization packing, solubility, size, charge Chiral Isomers Resolution chiral counterions Identification X-ray crystallography Optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) Circular dichroism (CD)
17 Coordination Numbers and Structures Structures vs Properties. Factors for Structures 1. Number of Bonds Bond formation is usually exothermic. So stability 2. VSEPR 3. Occupancy of d orbitals Square-planar vs Tetrahedral 4. Steric Effects 5. Crystal Packing Effects Crystalline Lattice vs Solution What is common thing? Which one is a dominant factor? CN Geometries Rare Linear Trigonal-plane Tetrahedron, Square-plane Trigonal bipyramid, Square pyramid Octahedron, Trigonal prosm Pentagonal bipyramid, Capped trigonal prism, Capped octahedron Known up to 16 CN
18 Coordination Numbers and Structures Oxidation States of Transition Metals
19 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 1,2, and 3 CN = 1, Rare
20 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 1,2, and 3 CN = 2, Rare, Linear (D h ) Mostly d 10 metals, Ag(I), Cu(I), Au(I), Hg(II) d 5, d 6, d 7 Examples of CN = 2 Large Ligands can induce a linear arrangement
21 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 1,2, and 3 CN = 3, Rare, Trigonal planar (D 3h ) Mostly d 10, PPh 3, N(SiMe 3 ) 2, Bulky enough, Steric effect vs Electroic structure
22 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 4 CN = 4, Tetrahedral (T d ) Squre-planar(D 4h ) Tetrahedral (T d ) ; very common,
23 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 4 CN = 4, Tetrahedral (T d ) Squre-planar(D 4h ) Squre-planar(D 4h ) ; mostly d 8 (Pd(II), Pt(II), Ni(II), Ag(III), Ir(I) Rh(I)) Tetrahedral vs Square-planar Counterion, Crystal Packing Cl Cl Cu Cl Cl 2Cs
24 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 4 CN = 4, Tetrahedral (T d ) Squre-planar(D 4h ) Squre-planar(D 4h ) ; mostly d 8 (Pd(II), Pt(II), Ni(II), Ag(III), Ir(I) Rh(I)) Tetrahedral vs Square-planar Counterion, Crystal Packing E is not big.
25 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 5 CN = 5, Trigonal bipyramid (D 3h ), Square pyramid (C 4v ) Fluxional behavior.
26 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 6 CN = 6, Octahedral (O h ) most common O h to D 4h
27 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 6 CN = 6, Octahedral (O h ) to Trigonal Prism (D 3h ) Usually with three bidentate ligands
28 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 7 CN = 7, Pentagonal bipyramid (O h ), Capped trigonal prism, Capped octahedron Capped trigonal prism Pentagonal bipyramid Capped octahedron Different counterion, steric requirment
29 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN = 8 CN = 8, Square antiprism, Dodecahedron Eight coordination is rare in the first row transition metals Square antiprism Why? Central ion must be large in order to accommodate eightcoordination Dodecahedron
30 Coordination Numbers and Structures CN 8 CN 8, known up to 16, not common
31 Multimetallic Compexes Without direct M-M bond With direct M-M bond
9-4 Coordination Numbers and Structure
 Chapter 9 Coordination Chemistry I: Structure and Isomers 9-1 History 9-2 Nomenclature 9-3 Isomerism 9-4 Coordination Numbers and Structure History What is coordination compound? Coordniantion compounds
Chapter 9 Coordination Chemistry I: Structure and Isomers 9-1 History 9-2 Nomenclature 9-3 Isomerism 9-4 Coordination Numbers and Structure History What is coordination compound? Coordniantion compounds
9-4 Coordination Numbers and Structure
 Chapter 9 Coordination Chemistry I: Structure and Isomers 9-1 History 9-2 Nomenclature 9-3 Isomerism 9-4 Coordination Numbers and Structure History What is coordination compound? Coordniantion compounds
Chapter 9 Coordination Chemistry I: Structure and Isomers 9-1 History 9-2 Nomenclature 9-3 Isomerism 9-4 Coordination Numbers and Structure History What is coordination compound? Coordniantion compounds
Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes)
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7: Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal 20: Isomerism part
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7: Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal 20: Isomerism part
Coordination Number 2
 Page 1 of 11 Coordination Numbers and Geometry Lecture 2. CHEM1902 (C 10K) Coordination Chemistry The total number of points of attachment to the central element is termed the coordination number and this
Page 1 of 11 Coordination Numbers and Geometry Lecture 2. CHEM1902 (C 10K) Coordination Chemistry The total number of points of attachment to the central element is termed the coordination number and this
Coordination compounds - Isomerism
 Coordination compounds - Isomerism K.Sridharan Dean School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1 Types of isomerism... 3 1.1 Types of isomerism...
Coordination compounds - Isomerism K.Sridharan Dean School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1 Types of isomerism... 3 1.1 Types of isomerism...
Chapter 25 Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds Part 1
 Chapter 25 Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds Part 1 Introduction The transition elements are defined as: those metallic elements that have a partially but incompletely filled d subshell or easily
Chapter 25 Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds Part 1 Introduction The transition elements are defined as: those metallic elements that have a partially but incompletely filled d subshell or easily
Chapter 19 d-block metal chemistry: general considerations
 Chapter 19 d-block metal chemistry: general considerations Ground state electronic configurations Reactivity, characteristic properties Electroneutrality principle Kepert Model Coordination Numbers Isomerism
Chapter 19 d-block metal chemistry: general considerations Ground state electronic configurations Reactivity, characteristic properties Electroneutrality principle Kepert Model Coordination Numbers Isomerism
Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes)
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7: Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal 22: Isomerism part
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7: Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal 22: Isomerism part
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 24: Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 24: Chemistry of Coordination Compounds Metal compounds with complex assemblies of metals surrounded by molecules and ions are called coordination compounds 24.3:
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 24: Chemistry of Coordination Compounds Metal compounds with complex assemblies of metals surrounded by molecules and ions are called coordination compounds 24.3:
The d-block elements. Transition metal chemistry is d-orbitals/electrons
 The d-block elements d-block elements include Sc-Zn, Y-Cd, a(or u)-hg. Transition metal chemistry is d-orbitals/electrons H&S, Fig 1.1, p. 15 Properties of transition metal ions are very sensitive to the
The d-block elements d-block elements include Sc-Zn, Y-Cd, a(or u)-hg. Transition metal chemistry is d-orbitals/electrons H&S, Fig 1.1, p. 15 Properties of transition metal ions are very sensitive to the
Downloaded from
 1 Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 9: Coordination Compounds 1. Difference between coordination compound and double bond: Coordination compound A coordination compound contains a central metal atom or ion
1 Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 9: Coordination Compounds 1. Difference between coordination compound and double bond: Coordination compound A coordination compound contains a central metal atom or ion
Coordination Chemistry: Bonding Theories. Crystal Field Theory. Chapter 20
 Coordination Chemistry: Bonding Theories Crystal Field Theory Chapter 0 Review of the Previous Lecture 1. We discussed different types of isomerism in coordination chemistry Structural or constitutional
Coordination Chemistry: Bonding Theories Crystal Field Theory Chapter 0 Review of the Previous Lecture 1. We discussed different types of isomerism in coordination chemistry Structural or constitutional
CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Co-ordination Compounds
 CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Co-ordination Compounds Co-ordination compounds: a) A coordination compound contains a central metal atom or ion surrounded by number of oppositely
CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Co-ordination Compounds Co-ordination compounds: a) A coordination compound contains a central metal atom or ion surrounded by number of oppositely
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
CHEMISTRY PAPER No. : 7 MODULE No. : 23 (Optical Isomerism)
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7 : Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes) 23
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7 : Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes) 23
Drawing Lewis Structures
 Chapter 2 - Basic Concepts: molecules Bonding models: Valence-Bond Theory (VB) and Molecular Orbital Theory (MO) Lewis acids and bases When both of the electrons in the covalent bond formed by a Lewis
Chapter 2 - Basic Concepts: molecules Bonding models: Valence-Bond Theory (VB) and Molecular Orbital Theory (MO) Lewis acids and bases When both of the electrons in the covalent bond formed by a Lewis
Pauli Principle. ! This requirement (which has no theoretical proof) does not change the overall state of the system.
 Pauli Principle! The complete wave function for a system of electrons in a multielectron atom depends upon orbital (spatial) and spin contributions; i.e., ψ = ψ orb ψ spin = ψ(n,l,m l )ψ(m s ).! All electrons
Pauli Principle! The complete wave function for a system of electrons in a multielectron atom depends upon orbital (spatial) and spin contributions; i.e., ψ = ψ orb ψ spin = ψ(n,l,m l )ψ(m s ).! All electrons
RDCH 702 Lecture 4: Orbitals and energetics
 RDCH 702 Lecture 4: Orbitals and energetics Molecular symmetry Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating
RDCH 702 Lecture 4: Orbitals and energetics Molecular symmetry Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating
Coordination Compounds
 Coordination Compounds 1. What is a coordination compound composed of? a. Metal Ion b. Ligand c. Counter Ion 2. What is a complex ion? The metal ion and ligand combination. 3. What is a counter ion? An
Coordination Compounds 1. What is a coordination compound composed of? a. Metal Ion b. Ligand c. Counter Ion 2. What is a complex ion? The metal ion and ligand combination. 3. What is a counter ion? An
Ch. 23: Transition metals and Coordination Chemistry
 Ch. 23: Transition metals and Coordination Chemistry Learning goals and key skills: Determine the oxidation number and number of d electrons for metal ions in complexes Name coordination compounds given
Ch. 23: Transition metals and Coordination Chemistry Learning goals and key skills: Determine the oxidation number and number of d electrons for metal ions in complexes Name coordination compounds given
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry
 Advanced Inorganic Chemistry Alireza Gorji Department of Chemistry, Yazd University Isomerism 20_441 Isomers (same formula but different properties) ایزومری Structural isomers (different bonds) Stereoisomers
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry Alireza Gorji Department of Chemistry, Yazd University Isomerism 20_441 Isomers (same formula but different properties) ایزومری Structural isomers (different bonds) Stereoisomers
Transition Metal Complexes
 2P32 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. Pilkington Lecture 4 - Transition Metal Complexes Transition Metal Complexes: Definitions and Terminology. Isomerism in Transition Metal Complexes: Structural
2P32 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. Pilkington Lecture 4 - Transition Metal Complexes Transition Metal Complexes: Definitions and Terminology. Isomerism in Transition Metal Complexes: Structural
Chemistry 324 Midterm 1 KEY Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Instructor: D. J. Berg
 Chem 324 Midterm 1 Fall 2011 Version 1 Page 1 of 9 Chemistry 324 Midterm 1 KEY Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Instructor: D. J. Berg Name: Answer all questions on the paper (use the back if necessary). There
Chem 324 Midterm 1 Fall 2011 Version 1 Page 1 of 9 Chemistry 324 Midterm 1 KEY Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Instructor: D. J. Berg Name: Answer all questions on the paper (use the back if necessary). There
The d -Block Elements & Coordination Chemistry
 Chapter The d -Block Elements & ordination Chemistry Hill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th Ed. The d-block Elements Groups 3-1 in the Periodic chart associated with the filling of the 3d, 4d, 5d electronic
Chapter The d -Block Elements & ordination Chemistry Hill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th Ed. The d-block Elements Groups 3-1 in the Periodic chart associated with the filling of the 3d, 4d, 5d electronic
8.3 Bonding Theories > Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding. 8.3 Bonding Theories. 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry. 1. In the transition metals section chemical similarities are found within a and across a.
 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry 1. In the transition metals section chemical similarities are found within a and across a. 2. What are 2 transition metals that have unique electron configurations?
Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry 1. In the transition metals section chemical similarities are found within a and across a. 2. What are 2 transition metals that have unique electron configurations?
Coordination Number Six
 Coordination Number Six 241 Octahedral is a very important geometry. It is the starting point for the shapes of most transition metal complexes. 1. Regular octahedron all distances are EQUIVALENT 2. Distorted
Coordination Number Six 241 Octahedral is a very important geometry. It is the starting point for the shapes of most transition metal complexes. 1. Regular octahedron all distances are EQUIVALENT 2. Distorted
Transition Metal Chemistry
 APPLIED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Transition Metal Chemistry CHEM261HC/SS1/01 Periodic Table Elements are divided into four categories Main-group elements (S-Block) Transition metals 1.
APPLIED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Transition Metal Chemistry CHEM261HC/SS1/01 Periodic Table Elements are divided into four categories Main-group elements (S-Block) Transition metals 1.
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 101 Midterm Test 2 November 21, pm (60 minutes) DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD ON THE TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW
 Version A UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 101 Midterm Test 2 November 21, 2014 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version A DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD ON THE TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
Version A UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 101 Midterm Test 2 November 21, 2014 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version A DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD ON THE TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
Coordination compounds
 Coordination compounds Multiple choice questions 1. In the complex formation, the central metal atom / ion acts as a) Lewis base b) Bronsted base c) Lewis acid d) Bronsted acid 2. The groups satisfying
Coordination compounds Multiple choice questions 1. In the complex formation, the central metal atom / ion acts as a) Lewis base b) Bronsted base c) Lewis acid d) Bronsted acid 2. The groups satisfying
Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
 Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Some History In the 19 th century, chemists started to prepare colored compounds containing transition metals and other substances like ammonia,
Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Some History In the 19 th century, chemists started to prepare colored compounds containing transition metals and other substances like ammonia,
Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
 Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Some History In the 19 th century, chemists started to prepare colored compounds containing transition metals and other substances like ammonia,
Chapter 21 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Some History In the 19 th century, chemists started to prepare colored compounds containing transition metals and other substances like ammonia,
The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model
 1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
The d-block elements. Transition metal chemistry is d-orbitals/electrons
 The d-block elements d-block elements include Sc-Zn, Y-Cd, a(or u)-hg. Valence orbitals for d-block elements: Transition elements: Why transition metals? ns, (n-1)d, np H&S, Fig 1.13, p. 23 atom has an
The d-block elements d-block elements include Sc-Zn, Y-Cd, a(or u)-hg. Valence orbitals for d-block elements: Transition elements: Why transition metals? ns, (n-1)d, np H&S, Fig 1.13, p. 23 atom has an
Transition Metals * Mary McHale. 1 Transitions Metals: Synthesis of an Inorganic Compound (trans-dinitrobis(ethylenediamine) nitrate)
 OpenStax-CNX module: m15503 1 Transition Metals * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Transitions Metals: Synthesis of an
OpenStax-CNX module: m15503 1 Transition Metals * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Transitions Metals: Synthesis of an
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. Molecular Shapes. Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Ligands: an ion or molecule capable of donating a pair of electrons to the central atom via a donor atom.
 Ligands: an ion or molecule capable of donating a pair of electrons to the central atom via a donor atom. Unidentate ligands: Ligands with only one donor atom, e.g. NH3, Cl -, F - etc. Bidentate ligands:
Ligands: an ion or molecule capable of donating a pair of electrons to the central atom via a donor atom. Unidentate ligands: Ligands with only one donor atom, e.g. NH3, Cl -, F - etc. Bidentate ligands:
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Chapter 9
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 16. Transition Metals Complexes: Structure and Isomers
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 16. Transition Metals Complexes: Structure and Isomers Topics: Name(s): Element: 1. Periodic trends and the transition metals 4. Polydentate ligands
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 16. Transition Metals Complexes: Structure and Isomers Topics: Name(s): Element: 1. Periodic trends and the transition metals 4. Polydentate ligands
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Chang & Goldsby Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Chang & Goldsby Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Chapter 6 PRETEST: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 PRETEST: Chemical In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.The charge on an ion is a. always positive.
Chapter 6 PRETEST: Chemical In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.The charge on an ion is a. always positive.
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory No. 1 of 10 1. Which shape would have sp 3 hybridization? (A) Linear (B) Bent (C) Tetrahedron (D) Trigonal planar (E) Octahedron C. Correct.
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory No. 1 of 10 1. Which shape would have sp 3 hybridization? (A) Linear (B) Bent (C) Tetrahedron (D) Trigonal planar (E) Octahedron C. Correct.
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 101 Midterm Test 2 November 21, pm (60 minutes) DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD ON THE TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW
 Version B UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 101 Midterm Test 2 November 21, 2014 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version B DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD ON THE TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
Version B UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 101 Midterm Test 2 November 21, 2014 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version B DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD ON THE TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015
 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015 This week, we ll use ball and stick models to explore molecular structure. At the end of the lab period, hand in the completed packet of Molecular
10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015 This week, we ll use ball and stick models to explore molecular structure. At the end of the lab period, hand in the completed packet of Molecular
Atomic orbitals, symmetry, and coordination polyhedra
 Coordination Chemistry Reviews 197 (2000) 141 168 www.elsevier.com/locate/ccr Atomic orbitals, symmetry, and coordination polyhedra R. Bruce King * Department of Chemistry, Uni ersity of Georgia, Athens,
Coordination Chemistry Reviews 197 (2000) 141 168 www.elsevier.com/locate/ccr Atomic orbitals, symmetry, and coordination polyhedra R. Bruce King * Department of Chemistry, Uni ersity of Georgia, Athens,
Orbitals and energetics
 Orbitals and energetics Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating radionuclide complexes Structure
Orbitals and energetics Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating radionuclide complexes Structure
Coordination Chemistry Prof. Debashis Ray Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture - 10 Coordination Number - IV
 Coordination Chemistry Prof. Debashis Ray Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 10 Coordination Number - IV (Refer Slide Time: 00:28) Good evening everybody. So, we
Coordination Chemistry Prof. Debashis Ray Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 10 Coordination Number - IV (Refer Slide Time: 00:28) Good evening everybody. So, we
Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory Electronic Structure of Six and Four-Coordinate Complexes Using Crystal Field Theory, we can generate energy level
Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory Electronic Structure of Six and Four-Coordinate Complexes Using Crystal Field Theory, we can generate energy level
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 21. Transition Metals Complexes V: Reaction Mechanisms
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 21. Transition Metals Complexes V: Reaction Mechanisms Name(s): Element: Topics: 1. Substitution reactions: dissociative v. associative 4. Pseudorotation
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 21. Transition Metals Complexes V: Reaction Mechanisms Name(s): Element: Topics: 1. Substitution reactions: dissociative v. associative 4. Pseudorotation
Coordination chemistry and organometallics
 Coordination chemistry and organometallics Double salt and Complex salt A salt that keeps its identity only in solid state is called a double salt. In solution they dissociate into component ions. E.g.:
Coordination chemistry and organometallics Double salt and Complex salt A salt that keeps its identity only in solid state is called a double salt. In solution they dissociate into component ions. E.g.:
Chapter 24. Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds. Lecture Presentation. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 24 Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Gemstones The colors of rubies and emeralds are both due to the presence of Cr 3+
Lecture Presentation Chapter 24 Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Gemstones The colors of rubies and emeralds are both due to the presence of Cr 3+
UNIT IX COORDINATION COMPOUNDS ( 3 : MARKS)
 TEACHER ORIENTED UNIT IX COORDINATION COMPOUNDS ( 3 : MARKS) 1) Coordination compounds - introduction, 2) Ligands, 3) Coordination number, 4) Colour, 5) Magnetic properties and shapes, 6) IUPAC nomenclature
TEACHER ORIENTED UNIT IX COORDINATION COMPOUNDS ( 3 : MARKS) 1) Coordination compounds - introduction, 2) Ligands, 3) Coordination number, 4) Colour, 5) Magnetic properties and shapes, 6) IUPAC nomenclature
Transition Metal Chemistry
 APPLIED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Transition Metal Chemistry CHEM261HC/SS1/01 Periodic table Elements are divided into four categories 1.Main-group elements 2.Transition metals 3.Lanthanides
APPLIED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Transition Metal Chemistry CHEM261HC/SS1/01 Periodic table Elements are divided into four categories 1.Main-group elements 2.Transition metals 3.Lanthanides
NAME: Chapter 12, Test 1: Chemical Bonding. Total Question(s): 20 Here are the quiz answers, in review:
 NAME: Chapter 12, Test 1: Chemical Bonding Total Question(s): 20 Here are the quiz s, in review: 1.Elements whose electronegativities are similar will form bonds that are. (A) ionic (B) polar covalent
NAME: Chapter 12, Test 1: Chemical Bonding Total Question(s): 20 Here are the quiz s, in review: 1.Elements whose electronegativities are similar will form bonds that are. (A) ionic (B) polar covalent
Chapter 21: Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
 Chapter 21: Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Mg, Cr, V, Co Pt Fe complexes O2 Mo and Fe complexes: nitrogen fixation Zn: 150 Cu, Fe: Co: B12 21.1 Transition Metals show great similarities within
Chapter 21: Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Mg, Cr, V, Co Pt Fe complexes O2 Mo and Fe complexes: nitrogen fixation Zn: 150 Cu, Fe: Co: B12 21.1 Transition Metals show great similarities within
Transition Metal Chemistry and Coordination Compounds
 Transition Metal Chemistry and Coordination Compounds Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Properties of the Transition Metals All transition metals
Transition Metal Chemistry and Coordination Compounds Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Properties of the Transition Metals All transition metals
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
The Transition Metals
 The Transition Metals d electrons in group 3 are readily removed via ionization. d electrons in group 11 are stable and generally form part of the core electron configuration. Transition Metal Valence
The Transition Metals d electrons in group 3 are readily removed via ionization. d electrons in group 11 are stable and generally form part of the core electron configuration. Transition Metal Valence
Transition Metal Chemistry
 APPLIED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Transition Metal Chemistry CHEM261HC/SS1/01 Periodic table Elements are divided into four categories Main-group elements Transition metals 1. Main-group
APPLIED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Transition Metal Chemistry CHEM261HC/SS1/01 Periodic table Elements are divided into four categories Main-group elements Transition metals 1. Main-group
Quiz 5 R = lit-atm/mol-k 1 (25) R = J/mol-K 2 (25) 3 (25) c = X 10 8 m/s 4 (25)
 ADVANCED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 and FINAL December 18, 2012 INSTRUCTIONS: PRINT YOUR NAME > NAME. QUIZ 5 : Work 4 of 1-5 (The lowest problem will be dropped) FINAL: #6 (10 points ) Work 6 of 7 to 14
ADVANCED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 and FINAL December 18, 2012 INSTRUCTIONS: PRINT YOUR NAME > NAME. QUIZ 5 : Work 4 of 1-5 (The lowest problem will be dropped) FINAL: #6 (10 points ) Work 6 of 7 to 14
Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
 VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
 Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry What is inorganic chemistry? Inorganic Chemistry Organimetallic Bioinorganic Organic vs Inorganic Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry Organic vs Inorganic Introduction
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry What is inorganic chemistry? Inorganic Chemistry Organimetallic Bioinorganic Organic vs Inorganic Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry Organic vs Inorganic Introduction
Chapter 13: Phenomena
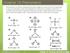 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Bonding in Coordination Compounds. Crystal Field Theory. Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes
 Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes 1) Crystal Field Theory (ligand field theory) Crystal Field Theory Treat igands as negative charges (they repel the e- in the d orbitals deals only with d orbitals
Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes 1) Crystal Field Theory (ligand field theory) Crystal Field Theory Treat igands as negative charges (they repel the e- in the d orbitals deals only with d orbitals
Structure of Coordination Compounds
 Chapter 22 COORDINATION CHEMISTRY (Part II) Dr. Al Saadi 1 Structure of Coordination Compounds The geometry of coordination compounds plays a significant role in determining their properties. The structure
Chapter 22 COORDINATION CHEMISTRY (Part II) Dr. Al Saadi 1 Structure of Coordination Compounds The geometry of coordination compounds plays a significant role in determining their properties. The structure
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 21 Coordination chemistry: reactions of complexes
 CHEM 511 chapter 21 page 1 of 7 Chapter 21 Coordination chemistry: reactions of complexes Reactions of Complexes Typically measure ligand substitution reactions in solution (usually water) Lability and
CHEM 511 chapter 21 page 1 of 7 Chapter 21 Coordination chemistry: reactions of complexes Reactions of Complexes Typically measure ligand substitution reactions in solution (usually water) Lability and
Chemistry 324 Final Examination
 Chem 324 Final Examination 2008 December 11, 2008 Page 1 of 8 Chemistry 324 Final Examination Thursday, December 11, 2008 Instructor: Dave Berg Answer all questions in the booklet provided; additional
Chem 324 Final Examination 2008 December 11, 2008 Page 1 of 8 Chemistry 324 Final Examination Thursday, December 11, 2008 Instructor: Dave Berg Answer all questions in the booklet provided; additional
The Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds
 Chapter 22 The Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds Concept Check 22.1 Another complex studied by Werner had a composition corresponding to the formula PtCl 4 2KCl. From electrical-conductance
Chapter 22 The Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds Concept Check 22.1 Another complex studied by Werner had a composition corresponding to the formula PtCl 4 2KCl. From electrical-conductance
Chapter 10 Practice Problems
 Chapter 10 Practice Problems Q 10.1 0-1 -1-1 S +2 +2 S S +2 0-1 -1-1 0 C in S - 6 6 1 2 1 2 C in S = 6 4 1 4 0 2 C S 6 0 1 8 2 2 Q 10.2 Correct Answer: B Two oxygen atoms will have a formal charge of 1
Chapter 10 Practice Problems Q 10.1 0-1 -1-1 S +2 +2 S S +2 0-1 -1-1 0 C in S - 6 6 1 2 1 2 C in S = 6 4 1 4 0 2 C S 6 0 1 8 2 2 Q 10.2 Correct Answer: B Two oxygen atoms will have a formal charge of 1
CHEM1101 Worksheet 6: Lone Pairs and Molecular Geometry
 CHEM1101 Worksheet 6: Lone Pairs and Molecular Geometry Model 1: Oxidation numbers Oxidation numbers are a useful accountancy tool to help keep track of electrons in compounds and reactions. This is particularly
CHEM1101 Worksheet 6: Lone Pairs and Molecular Geometry Model 1: Oxidation numbers Oxidation numbers are a useful accountancy tool to help keep track of electrons in compounds and reactions. This is particularly
Section 6 Questions from Shriver and Atkins
 Section 6 Questions from Shriver and tkins 4.35 Remember, softness increases as you go down a group, and both Zn and Hg are in Group 12. Hg 2+ is a very soft acid, so it is only realistically able to form
Section 6 Questions from Shriver and tkins 4.35 Remember, softness increases as you go down a group, and both Zn and Hg are in Group 12. Hg 2+ is a very soft acid, so it is only realistically able to form
CHAPTER - 9 ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
 CHAPTER - 9 CO-O ORDINATION COMPOUNDS Formulas for coordinationn compounds: Tetraamineaquachloridocobalt (III) chloride ---- [Co(NH 3 ) 4 (H 2 O) Cl]Cl 2 Potassium tetrahydroxozincate (II) ------- K 2
CHAPTER - 9 CO-O ORDINATION COMPOUNDS Formulas for coordinationn compounds: Tetraamineaquachloridocobalt (III) chloride ---- [Co(NH 3 ) 4 (H 2 O) Cl]Cl 2 Potassium tetrahydroxozincate (II) ------- K 2
Chapter 13: Phenomena
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
MC Molecular Structures, Dipole Moments, Geometry, IMF Name: Date:
 MC Molecular Structures, Dipole Moments, Geometry, IMF Name: Date: 2008 22. Which of the following is a nonpolar molecule that contains polar bonds? (A) F 2 (B) CHF 3 (C) CO 2 (D) HCl (E) NH 3 28. Which
MC Molecular Structures, Dipole Moments, Geometry, IMF Name: Date: 2008 22. Which of the following is a nonpolar molecule that contains polar bonds? (A) F 2 (B) CHF 3 (C) CO 2 (D) HCl (E) NH 3 28. Which
Chapter 23 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
 Chapter 23 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Many compounds of transition metals are colored (used in paints and to stain glass; produce color in gemstones). 23.1 The Transition Metals Most
Chapter 23 Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry Many compounds of transition metals are colored (used in paints and to stain glass; produce color in gemstones). 23.1 The Transition Metals Most
51. Pi bonding occurs in each of the following species EXCEPT (A) CO 2 (B) C 2 H 4 (C) CN (D) C 6 H 6 (E) CH 4
 Name AP Chemistry: Bonding Multiple Choice 41. Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length? (A) N 2 (B) O 2 (C) Cl 2 (D) Br 2 (E) I 2 51. Pi bonding occurs in each of the following species
Name AP Chemistry: Bonding Multiple Choice 41. Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length? (A) N 2 (B) O 2 (C) Cl 2 (D) Br 2 (E) I 2 51. Pi bonding occurs in each of the following species
Transition Metals and Complex Ion Chemistry
 Transition Metals and mplex Ion Chemistry Definitions mplex ion - a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A mplex (or ordination compound) is a compound consisting
Transition Metals and mplex Ion Chemistry Definitions mplex ion - a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A mplex (or ordination compound) is a compound consisting
Review questions CHAPTER 5. Practice exercises 5.1 F F 5.3
 CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture
 Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture Dr. Namphol Sinkaset Chapter 23 Study Guide Concepts 1. In the transition metals, the ns orbital fills before the (n-1)d orbitals. However, the ns orbital
Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture Dr. Namphol Sinkaset Chapter 23 Study Guide Concepts 1. In the transition metals, the ns orbital fills before the (n-1)d orbitals. However, the ns orbital
11/9/15. Intermolecular hydrogen bond: Hydrogen bond: Intramolecular hydrogen bond: Induced dipole moment, polarisability
 Induced dipole moment, polarisability in electric field: Van der Waals forces Intermolecular forces other than covalent bonds or other than electrostatic interactions of ions induced d. moment µ * = α
Induced dipole moment, polarisability in electric field: Van der Waals forces Intermolecular forces other than covalent bonds or other than electrostatic interactions of ions induced d. moment µ * = α
Assignment 09 A. 2- The image below depicts a seesaw structure. Which of the following has such a structure?
 Assignment 09 A 1- Give the total number of electron domains, the number of bonding and nonbonding domains, and the molecular geometry, respectively, for the central atom of P 3. a) four electron domains,
Assignment 09 A 1- Give the total number of electron domains, the number of bonding and nonbonding domains, and the molecular geometry, respectively, for the central atom of P 3. a) four electron domains,
Transition Metal Elements and Their Coordination Compounds
 Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). Transition Metal Elements and Their Coordination Compounds 2 Compounds. Naming and Geometry. 1 3 p.1046a 4 Fig.
Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). Transition Metal Elements and Their Coordination Compounds 2 Compounds. Naming and Geometry. 1 3 p.1046a 4 Fig.
Chapter 24. Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
 Chapter 24. Chemistry of Coordination Compounds 24.1 Metal Complexes Metal complexes (or complexes) have a metal ion (which can have a 0 oxidation state) bonded to a number of molecules or ions. If the
Chapter 24. Chemistry of Coordination Compounds 24.1 Metal Complexes Metal complexes (or complexes) have a metal ion (which can have a 0 oxidation state) bonded to a number of molecules or ions. If the
Chapters 8 and 9. Octet Rule Breakers Shapes
 Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
9 Molecular Structures II: Compounds of Transition Metals
 7 9 Molecular tructures II: Compounds of Transition Metals 9.1 Ligand ield Theory The mutual interaction between bonding electron pairs is the same for transition metal compounds as for compounds of main
7 9 Molecular tructures II: Compounds of Transition Metals 9.1 Ligand ield Theory The mutual interaction between bonding electron pairs is the same for transition metal compounds as for compounds of main
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
Electronic structure Crystal-field theory Ligand-field theory. Electronic-spectra electronic spectra of atoms
 Chapter 19 d-metal complexes: electronic structure and spectra Electronic structure 19.1 Crystal-field theory 19.2 Ligand-field theory Electronic-spectra 19.3 electronic spectra of atoms 19.4 electronic
Chapter 19 d-metal complexes: electronic structure and spectra Electronic structure 19.1 Crystal-field theory 19.2 Ligand-field theory Electronic-spectra 19.3 electronic spectra of atoms 19.4 electronic
Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)!
 Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)! 15 C 4+ 42 Si 4+ Size of atoms! Hefferan and O Brien, 2010; Earth Materials Force balance! Crystal structure (Chap. 4)!
Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)! 15 C 4+ 42 Si 4+ Size of atoms! Hefferan and O Brien, 2010; Earth Materials Force balance! Crystal structure (Chap. 4)!
Chapter 19: Phenomena
 Chapter 19: Phenomena Phenomena: Transition metal complexes are often used in paints for coloration due to their wide range of colors. Using the data below identify any patterns in the colors of compounds.
Chapter 19: Phenomena Phenomena: Transition metal complexes are often used in paints for coloration due to their wide range of colors. Using the data below identify any patterns in the colors of compounds.
Practice Problems: Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry. # Ligands Coordination # Oxidation #
 Practice Problems: Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry 1. Complete the valence level orbital notation for the following monatomic ions. KEY CHEM 1B a) Ag + b) Co 3+ 4d 5s 3d 4s c) Fe 3+ d) Cr
Practice Problems: Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry 1. Complete the valence level orbital notation for the following monatomic ions. KEY CHEM 1B a) Ag + b) Co 3+ 4d 5s 3d 4s c) Fe 3+ d) Cr
Chapter 19: Phenomena
 Chapter 19: Phenomena Phenomena: Transition metal complexes are often used in paints for coloration due to their wide range of colors. Using the data below identify any patterns in the colors of compounds.
Chapter 19: Phenomena Phenomena: Transition metal complexes are often used in paints for coloration due to their wide range of colors. Using the data below identify any patterns in the colors of compounds.
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
UNIT 9 Topic: Coordination Compounds
 UNIT 9 Topic: Coordination Compounds 1. State the postulates of Werner s theory of coordination compounds. Postulates: 1. Central metal ion in a complex shows two types of valences - primary valence and
UNIT 9 Topic: Coordination Compounds 1. State the postulates of Werner s theory of coordination compounds. Postulates: 1. Central metal ion in a complex shows two types of valences - primary valence and
TRANSITION METAL COMPLEXES Chapter 25, VB/CF Handout
 TRANSITION METAL COMPLEXES Chapter 25, VB/CF Handout The energy of a covalent bond is largely the energy of resonance of two electrons between two atoms the resonance energy increases in magnitude with
TRANSITION METAL COMPLEXES Chapter 25, VB/CF Handout The energy of a covalent bond is largely the energy of resonance of two electrons between two atoms the resonance energy increases in magnitude with
Inorganic Chemistry 411/511 Final Exam Name 115 minutes; 200 points total Show your work for partial credit.
 Inorganic Chemistry 411/511 Final Exam Name 115 minutes; 200 points total Show your work for partial credit. 1 1. Draw the molecular geometry and indicate any deviations from ideal VSEPR coordination angles.
Inorganic Chemistry 411/511 Final Exam Name 115 minutes; 200 points total Show your work for partial credit. 1 1. Draw the molecular geometry and indicate any deviations from ideal VSEPR coordination angles.
Coordination Compounds. Suggested reading: Shriver & Atkins, Chapter 7
 Lecture 15 Coordination Compounds Suggested reading: Shriver & Atkins, Chapter 7 From last lectures: 3 classes of nanomaterials Alex Zettl with a carbon nanotube Metallic Nanoparticles Semiconducting Nanocrystals
Lecture 15 Coordination Compounds Suggested reading: Shriver & Atkins, Chapter 7 From last lectures: 3 classes of nanomaterials Alex Zettl with a carbon nanotube Metallic Nanoparticles Semiconducting Nanocrystals
