BMB Lecture 2
|
|
|
- Thomasine Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BMB Lecture 2 How to map transition state Covalent Catalysis
2 How to Map Transition States 1. Linear Free Energy Relationship 2. Kinetic Isotope Effects 3. Transition state analogues
3 Linear Free Energy Relationship Correlate reaction rate with other equilibrium processes DG = -RT lnk DG = -RT lnk = -RT ln k To the extent that such a correlation holds, it may be inferred that the same factors contribute to both processes. Brønsted equation: log k = b pk a + C Brønsted slope Measures the amount of bond formation/breakage in
4 Example: Phosphoryl Transfer b nuc => Little bond formation with incoming nucleophile Herschlag & Jencks, JACS 1989 Factors other than pk a dictate nucleophilic reactivity - polarizability (softness) - oxidation potential - size - electronegativity
5 Example: Phosphoryl Transfer b LG b LG 1.2 Extensive bond breaking with leaving group
6 Reaction Coordinate Diagram for Phosphoryl Transfer (Associative, Pentavalent transition state) (Dissociative, metaphosphate-like transition state)
7 Kinetic Isotope Effects Infrared stretching frequencies: n = 2900 cm -1 (4.15 kcal/mol) for C-H bonds n = 2100 cm -1 (3.0 kcal/mol) for C-D bonds } => k H /k D 7
8 Types of Isotope Effects Solvent vs Substrate Isotope Effects exchangeable protons (O-H, N-H, S-H) non-exchangeable protons (C-H) Heavy Atom Isotope effects 13 C/ 12 C = 1.06; 18 O/ 16 O = 1.06; 15 N/ 14 N = 1.04 Primary vs Secondary Isotope Effects extent of bond breaking bond order/re-hybridization If (1) the bond is completely broken in ; (2) occurs during the rate-limiting step
9 Example 1. Hydrolysis of Aryl Phosphates Spontaneous hydrolysis: k ( 16 O) / k ( 18 O) = Substantial P-O bond breaking to b-g bridge oxygen in the transition state
10 Example 2. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 18 O nonbridge measures bond order metaphosphate-like small inverse IE pentavalent (associative) normal IE 18 O bridge measures extent of P-O bond cleavage 15 N measures charge developed on leaving group
11 KIE for hydrolysis of pnpp in solution 2% KIE on 18 O bridge - substantial P-O bond cleavage in Hengge et al, JACS 116, 5045 (1994)
12 KIE for hydrolysis of pnpp in solution 2% KIE on 18 O bridge - substantial P-O bond cleavage in Small, inverse KIE on 18 O nonbridge - metaphosphate-like Hengge et al, JACS 116, 5045 (1994)
13 KIE for hydrolysis of pnpp in solution 2% KIE on 18 O bridge - substantial P-O bond cleavage in Small, inverse KIE on 18 O nonbridge - metaphosphate-like KIE on 15 N substantial charge accumulation on O bridge Hengge et al, JACS 116, 5045 (1994)
14 KIE for hydrolysis of pnpp in solution 2% KIE on 18 O bridge - substantial P-O bond cleavage in Small, inverse KIE on 18 O nonbridge - metaphosphate-like KIE on 15 N substantial charge accumulation on O bridge 15 N and 18 O bridge KIE decreases upon protonation of g- phosphate proton migration from O nonbridge to O bridge (acid catalysis renders more associative) Hengge et al, JACS 116, 5045 (1994)
15 KIE on Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1.8% KIE on 18 O bridge substantial P-O bond cleavage in Small, inverse KIE on 18 O nonbridge metaphosphate-like No 15 N KIE negative charge on leaving group is neutralized 15 N and 18 O bridge KIE increases upon mutation of D181, suggesting that D181 acts as a general acid to protonate leaving group Hengge et al, Biochemistry 34, (1995)
16 ATP / GTP hydrolysis Admiraal & Herschlag, Chem. Biol. 2: 729 (1995)
17 Evaluation of Catalytic Models 1. General Base Catalysis? For reaction involving a dissociative, reaction has little dependence on basicity of the nucleophile Proton transfer from HOH (pk a 14) to Gln61 (pk a -2) is very unfavorable Role of Gln61? - positioning - facilitate proton transfer after
18 Evaluation of Catalytic Models 2. Phosphoryl Group Acts as A General Base? Proton donation to phosphoryl oxygen will destabilize a dissociative
19 Evaluation of Catalytic Models 3. Stabilization of charge on g-phosphoryl? Negative charge does not accumulate on g- phosphoryl oxygen in a dissociative
20 Evaluation of Catalytic Models 4. Stabilization of charge on b-phosphoryl? Can provide a small rate enhancement
21 Evaluation of Catalytic Models 4. Stabilization of charge on b-g bridge oxygen? Can potentially provide a large rate enhancement
22 Conserved Active Site Interactions with Bridge Oxygen GMPPNP GDP
23 F value Analysis to Study Protein Folding DDG U = DG U DG U = DG F - DG solv DDG U = DG U - DG U = DG F - DG F = DDG U /DDG U = (DG F DG )/(DG F DG solv ) Matouschek et al, Nature 340: 122 (1989)
24 F value Analysis to study Protein Folding F = DDG U /DDG U = (DG F DG )/(DG F DG solv ) 1. Target site is exposed to solvent in the to the same extent as in the unfolded state DG = DG solv => F = 1 2. Interaction energies in are similar to those in the folded state DG = DG F => F = 0 3. DG solv ~ 0 with small changes in hydrophobic side chains F = (DG F - DG ) / DG F
25 F value Analysis of Barnase folding
26 F value Analysis of Barnase folding
27 F value analysis of Barnase folding Structure of : hydrophobic core and secondary structure formed, but the N-cap and loops largely unfolded.
28 1. Best nucleophiles in biology: - Amines (RNH 2 ), alkoxides (RO - ), thiolates (RS - ), carbanions ( R 3 C - ) - Weaker but sometimes: carboxylates (RCO 2- ), phosphate (HPO 4 3- ) 2. Best electrophiles in Biology: - Phosphorus esters (HPO 3 -OR), - Carbonyls (RC=ONHR, RCO 2 R, etc.) 3. Good leaving groups in Biology: - Phosphates ( HPO 4 3- ), - Protonated amines ( NH 3+ ) - Protonated alcohols ( OH 2+ )
29
30 Strategies for Enzymatic Catalysis Covalent Catalysis General Acid-base Catalysis Metal Ions Electrostatics Entropy Putting it all together the intrinsic bind energy
31 Covalent Catalysis in the History of Enzymology enzymes are not chemical individuals, but that various kinds of bodies may have conferred upon them properties which cause them to behave like enzymes; so that we have to deal with properties rather than substances. The action can even be exerted at a distance. Balyliss, The Nature of Enzyme Action, 2nd ed. The assumption of this new force is detrimental to the progress of science, since it appears to satisfy the human spirit, and thus provides a limit to further research. Liebig, on Berzelius vitalistic theory of enzymes
32 Covalent Catalysis in the History of Enzymology The discovery that enzymes react chemically with their substrates to form covalent intermediates has done more than anything else to dispel mysterious mechanisms and vitalistic theories of enzyme action because it suggest that the mechanism of enzyme action is not fundamentally different from that of any other chemical reactions. The rapid progress in describing some enzymatic reactions in chemical terms and in the application of physical organic chemistry techniques to enzymoology has led to a swing of the pendulum of opinion W. P. Jencks, Catalysis in Chemistry and Enzymology, 2nd ed.
33 Covalent Catalysis 1. Demonstration of a covalent intermediate 2. Chemical and Energetic rationale
34 Initial Observation: An Initial Burst of Product Formation Stoichiometric with [E] Models: (1) Rate-limiting product release (2) Product Inhibition (3) Substrate-induced inactivation of enzyme (4) Two-step reaction with ratelimiting breakdown of Ac-E Hartley & Kilby, 1954
35 k cat is identical for substrates with fold difference in chemical reactivity Kirsch & Igelstrom, 1966
36 Direct Observation of Acyl-E at low ph ph 2.42, [E] > K S; [S] ~ 5[E] A. N-acetyl-L-tryp (P) B. N-acetyl-L-tryp-methyl ester Formation of Acyl-E k 2 = k cat deacylation of Acyl-E Kezdy et al, Biochemistry 86: 3690 (1964)
37 Crystal Structures of Acy-E Indoleacryloyl-a-chymotrypsin, ph 4.0 His57 Ser195 Henderson, J. Mol. Biol. 54: 341 (1970)
38 So Acyl-E is Demonstrated at low ph What about physiological reactions?
39 Millisecond kinetic measurement of the Chymotrypsin reaction Four kinetic phases: 1. Substrate binding to E: too fast to observe 2. Rapid formation of Acyl-E intermediate (< 0.5 sec) 3. Steady-state (0.5 5 sec) 4. Decomposition of Acyl-E (> 5 sec) McConn et al, JBC 246: 2918 (1971)
40 What if Acyl-E do Not Accumulate? Ester substrates: deacylation is rate-limiting Amide substrates: formation of acyl-e is rate-limiting Product Ratios from a Common Intermediate If the product ratios are the same for both amide and ester substrates, then reaction of both substrates involve a common intermediate
41 Product Partitioning in Chymotrypsin substrate Fastrez & Fersht, Biochemistry 12: 2025 (1973)
42 Evidences for A Covalent Intermediate Direct Evidences: Direct observation of formation and disappearance of an intermediate Kinetic competence: Rate constants for formation and disappearance of the intermediate must be at least as fast as the rate constant for the overall reaction Isolation and characterization of the intermediate The intermediate can be chased to the product with kinetic competence.
43 Evidences for A Covalent Intermediate Indirect Evidences: Different substrates with various reactivities form products at the same rate If different substrates share a common intermediate, product partitioning from E-I is the same for both substrates Stereochemistry: - Retention: 2-steps - Inversion: 1-step Parallel (ping-pong) kinetics
44 Why Is It Advantageous to Use Covalent Catalysis?
45 Chemical Logic to Use Covalent Catalysis 1. The catalyst has a higher nucleophilic reactivity than the final acceptor (X). 2. The Intermediate is more reactive than the substrate. 3. The Intermediate is less stable than the product.
46 Nucleophilic Catalysis by Imidazole 1. 3 amines are more reactive than OH - in nucleophilic attacks. 2. pk a ~ 7 the strongest base that can exist at neutral ph. 3. Acetylimidazole is highly susceptible to nuclephilic attacks. 4. Acetylimidazole is thermodynamically less stable compared to amines and esters.
47 Electrophilic Catalysis: Schiff base formation Activated nucleophile Electron sink
48 Example 1. Acetoacetate decarboxylase
49 Electrophilic Catalysis by Pyridoxal phosphate condense with Amino acid Pyridoxal phosphate Schiff base Each group around Ca can be cleaved; The anion is stabilized by the pyridine ring (electron sink)
50 Chemistry with pyridoxal schiff base Highly reactive intermediate 1. Racemization 2. Decarboxylation
51 Chemistry with pyridoxal schiff base 3. Interconversion of side chains RX = SH, OH, indole Allow interconversion of ser, thr, cys, trp, cystathione, etc.
52 but many enzymes don t use reactive nucleophiles or cofactors in covalent catalysis Positioning of the Nucleophile is Important
53 Nucleophilic Activation by Positioning in NDP Kinase Admiraal et al, Biochemistry 38: 4701 (1999)
54 Nucleophile Positioning and Thio-effects in NDP Kinase
55 Computationally designed Retroaldolase Lin et al, Science 319:1387 (2008)
56 Design motif 1 12 designs 2 with schiff base formation None reactive
57 Design motif 2 10 designs 1 with schiff base formation None reactive
58 Design motif 3 14 designs 10 with schiff base formation 8 had retroaldolase activity
59 Design motif 4 36 designs 20 with schiff base formation 23 had retroaldolase activity
60 How good are the designed enzymes?
61 What s wrong with RA 95.0? rosetta design crystal structure - Naphthal ring is rotated Largest deviation observed with Rosetta-designed loops (L1, L6, L7) that bracket the active site. - Substrate points away from water and Glu153
BMB Lecture Covalent Catalysis 2. General Acid-base catalysis
 BMB 178 2017 Lecture 3 1. Covalent Catalysis 2. General Acid-base catalysis Evidences for A Covalent Intermediate Direct Evidences: Direct observation of formation and disappearance of an intermediate
BMB 178 2017 Lecture 3 1. Covalent Catalysis 2. General Acid-base catalysis Evidences for A Covalent Intermediate Direct Evidences: Direct observation of formation and disappearance of an intermediate
4 Examples of enzymes
 Catalysis 1 4 Examples of enzymes Adding water to a substrate: Serine proteases. Carbonic anhydrase. Restrictions Endonuclease. Transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to a nucleotide. Nucleoside monophosphate
Catalysis 1 4 Examples of enzymes Adding water to a substrate: Serine proteases. Carbonic anhydrase. Restrictions Endonuclease. Transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to a nucleotide. Nucleoside monophosphate
A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility
 (P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
(P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013
 Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 9 Biochemical Transformations I. Carbon-carbon bond forming and cleaving reactions in Biology (see the Lexicon). Enzymes catalyze a limited
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 9 Biochemical Transformations I. Carbon-carbon bond forming and cleaving reactions in Biology (see the Lexicon). Enzymes catalyze a limited
It s the amino acids!
 Catalytic Mechanisms HOW do enzymes do their job? Reducing activation energy sure, but HOW does an enzyme catalysis reduce the energy barrier ΔG? Remember: The rate of a chemical reaction of substrate
Catalytic Mechanisms HOW do enzymes do their job? Reducing activation energy sure, but HOW does an enzyme catalysis reduce the energy barrier ΔG? Remember: The rate of a chemical reaction of substrate
[Urea] (M) k (s -1 )
![[Urea] (M) k (s -1 ) [Urea] (M) k (s -1 )](/thumbs/89/98097251.jpg) BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis
 Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Lecture 14 (10/18/17) Lecture 14 (10/18/17)
 Lecture 14 (10/18/17) Reading: Ch6; 190-191, 194-195, 197-198 Problems: Ch6 (text); 7, 24 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 4, 13 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 198-203 Ch6; Box 6-1 Problems: Ch6 (text); 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
Lecture 14 (10/18/17) Reading: Ch6; 190-191, 194-195, 197-198 Problems: Ch6 (text); 7, 24 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 4, 13 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 198-203 Ch6; Box 6-1 Problems: Ch6 (text); 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
Key Concepts.
 Lectures 13-14: Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 9, pp. 241-254 Updated on: 2/7/07 at 9:15 pm movie of chemical mechanism of serine proteases (from Voet & Voet,
Lectures 13-14: Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 9, pp. 241-254 Updated on: 2/7/07 at 9:15 pm movie of chemical mechanism of serine proteases (from Voet & Voet,
[Urea] (M) k (s -1 )
![[Urea] (M) k (s -1 ) [Urea] (M) k (s -1 )](/thumbs/96/126856044.jpg) BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 6 Enzymes
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 6 Enzymes CHAPTER 6 Enzymes Key topics about enzyme function: Physiological significance of enzymes Origin of catalytic power of enzymes Chemical mechanisms of catalysis
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 6 Enzymes CHAPTER 6 Enzymes Key topics about enzyme function: Physiological significance of enzymes Origin of catalytic power of enzymes Chemical mechanisms of catalysis
MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4
 MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Acid/Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Electrostatic catalysis Proximity and orientation Preferential binding of the transition
 Enzyme catalysis Factors that contribute to catalytic power of enzymes Acid/Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Electrostatic catalysis Proximity and orientation Preferential binding
Enzyme catalysis Factors that contribute to catalytic power of enzymes Acid/Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Electrostatic catalysis Proximity and orientation Preferential binding
Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics. Mechanisms ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE. H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl. Margaret A. Daugherty.
 Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products
Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products
Two requirements for life: Self-replication and appropriate catalysis. A. Most enzymes (def.: biological catalysts) are proteins
 Enzymes We must be able to enhance the rates of many physical and chemical processes to remain alive and healthy. Support for that assertion: Maladies of genetic origin. Examples: Sickle-cell anemia (physical)
Enzymes We must be able to enhance the rates of many physical and chemical processes to remain alive and healthy. Support for that assertion: Maladies of genetic origin. Examples: Sickle-cell anemia (physical)
Course Goals for CHEM 202
 Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
10/26/2010. An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene. to Ethylene
 6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
C a h p a t p e t r e r 6 E z n y z m y e m s
 Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism
 Mechanisms of Enzymes BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
Mechanisms of Enzymes BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Mechanisms of Enzymes Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Mechanisms of Enzymes Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
Enzyme function: the transition state. Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms. Catalytic Reactions. Margaret A. Daugherty A B. Lecture 16: Fall 2003
 Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Catalytic Reactions. Intermediate State in Catalysis. Lecture 16: Catalyzed reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction. Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms
 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
G. GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS
 G. GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS Towards a Better Chemical Mechanism via Catalysis There are two types of mechanisms we ll be discussing this semester. Kinetic mechanisms are concerned with rate constants
G. GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS Towards a Better Chemical Mechanism via Catalysis There are two types of mechanisms we ll be discussing this semester. Kinetic mechanisms are concerned with rate constants
Mechanisms of catalysis
 Mechanisms of catalysis Proximity and orientation effects Proximity: Reaction between bound molecules doesn't require an improbable collision of 2 molecules -- they're already in "contact" (increases the
Mechanisms of catalysis Proximity and orientation effects Proximity: Reaction between bound molecules doesn't require an improbable collision of 2 molecules -- they're already in "contact" (increases the
What is an enzyme? Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall General Properties
 Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 ENZYMES: Why, what, when, where, how? All but the who! What: proteins that exert kinetic control over
Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 ENZYMES: Why, what, when, where, how? All but the who! What: proteins that exert kinetic control over
Catalysis. Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica
 Catalysis Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica References: Biochemistry" by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet Biochemistry" by Christopher K. Mathews, K. E. Van Hold and Kevin
Catalysis Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica References: Biochemistry" by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet Biochemistry" by Christopher K. Mathews, K. E. Van Hold and Kevin
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
C a h p a t p e t r e r 6 E z n y z m y e m s
 Chapter 6 Enzymes 1. An Introduction to Enzymes Enzymes are catalytically active biological macromolecules Enzymes are catalysts of biological systems Almost every biochemical reaction is catalyzed by
Chapter 6 Enzymes 1. An Introduction to Enzymes Enzymes are catalytically active biological macromolecules Enzymes are catalysts of biological systems Almost every biochemical reaction is catalyzed by
Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems
 Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems Introduction Enzymes are Biological Catalysis A catalyst is a substance
Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems Introduction Enzymes are Biological Catalysis A catalyst is a substance
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry
 CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 2 Acids and Bases Central to Understanding Organic Chemistry Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 2 Acids and Bases Central to Understanding Organic Chemistry Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:
BMB Lecture 9
 BMB 178 2018 Lecture 9 Class 11, November 7, 2018 Steady-state kinetics (I) Case 3. Viscosity Variation If k cat /K m decreases with increasing viscosity, then the reaction is diffusion-limited (S binding
BMB 178 2018 Lecture 9 Class 11, November 7, 2018 Steady-state kinetics (I) Case 3. Viscosity Variation If k cat /K m decreases with increasing viscosity, then the reaction is diffusion-limited (S binding
Biologic catalysts 1. Shared properties with chemical catalysts a. Enzymes are neither consumed nor produced during the course of a reaction. b.
 Enzyme definition Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes,
Enzyme definition Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes,
BMB Lectures 9-10 October 25 and 27, Steady-state kinetics
 BMB 178 2017 Lectures 9-10 October 25 and 27, 2017 Steady-state kinetics Steady State Kinetics 1. Rate equations 2. Kinetic shortcuts 3. Positional isotope exchange 4. Inhibition Definition of steady state:
BMB 178 2017 Lectures 9-10 October 25 and 27, 2017 Steady-state kinetics Steady State Kinetics 1. Rate equations 2. Kinetic shortcuts 3. Positional isotope exchange 4. Inhibition Definition of steady state:
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
What is an enzyme? Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 KEY FEATURES OF ENZYMES
 Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 What is an enzyme? General Properties Mostly proteins, but some are actually RNAs Biological catalysts
Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 What is an enzyme? General Properties Mostly proteins, but some are actually RNAs Biological catalysts
Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
 Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Review: Garrett and Grisham, Enzyme Specificity and Regulation (Chapt. 13) and Mechanisms of Enzyme
Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Review: Garrett and Grisham, Enzyme Specificity and Regulation (Chapt. 13) and Mechanisms of Enzyme
Enzymes as machines: how they work
 Enzymes as machines: how they work Biophysical Society Summer Course 26 June 2014 Charlie Carter They are Just as Scared of You, As You are of Them Adapted from: Steve Cote, Chapel Hill artist Readings
Enzymes as machines: how they work Biophysical Society Summer Course 26 June 2014 Charlie Carter They are Just as Scared of You, As You are of Them Adapted from: Steve Cote, Chapel Hill artist Readings
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge. Biochemistry II. Bioenergetics
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge II. Bioenergetics Slide 1 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics is the quantitative study of energy relationships and energy conversion in biological
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge II. Bioenergetics Slide 1 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics is the quantitative study of energy relationships and energy conversion in biological
Chemistry Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class.
 Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. Name 1. There is a real enzyme called cocaine esterase that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme
Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. Name 1. There is a real enzyme called cocaine esterase that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme
Enzyme Kinetics 2014
 V 41 Enzyme Kinetics 2014 Atkins Ch.23, Tinoco 4 th -Ch.8 Enzyme rxn example Catalysis/Mechanism: E + S k -1 ES k 1 ES E is at beginning and k 2 k -2 E + P at end of reaction Catalyst: No consumption of
V 41 Enzyme Kinetics 2014 Atkins Ch.23, Tinoco 4 th -Ch.8 Enzyme rxn example Catalysis/Mechanism: E + S k -1 ES k 1 ES E is at beginning and k 2 k -2 E + P at end of reaction Catalyst: No consumption of
BI/CH421 Biochemistry I Exam 1 09/29/2014
 Part I: Multiple choice for each question, circle the choice that best answers the question. Do not write the letter in the margin to indicate your answer, circle it. 3 points each. 1. For a reaction with
Part I: Multiple choice for each question, circle the choice that best answers the question. Do not write the letter in the margin to indicate your answer, circle it. 3 points each. 1. For a reaction with
Catalytic power of enzymes
 Enzyme catalysis Catalytic power of enzymes Enzymatic reactions are involved in most biological processes. There is a major practical and fundamental interest in finding out what makes enzymes so efficient
Enzyme catalysis Catalytic power of enzymes Enzymatic reactions are involved in most biological processes. There is a major practical and fundamental interest in finding out what makes enzymes so efficient
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Resolving Apparent Conflicts between Theoretical and Experimental Models of Phosphate Monoester Hydrolysis
 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/jacs Resolving
This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/jacs Resolving
Lecture 12: Burst Substrates and the V vs [S] Experiment
![Lecture 12: Burst Substrates and the V vs [S] Experiment Lecture 12: Burst Substrates and the V vs [S] Experiment](/thumbs/95/124907449.jpg) Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2019 Lecture 12: Burst Substrates and the V vs [S] Experiment 14 February 2019 c David P. Goldenberg University of Utah goldenberg@biology.utah.edu
Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2019 Lecture 12: Burst Substrates and the V vs [S] Experiment 14 February 2019 c David P. Goldenberg University of Utah goldenberg@biology.utah.edu
Introductory Biochemistry
 Introductory Biochemistry Instructors Dr. Nafez Abu Tarboush Dr. Mamoun Ahram Recommended textbooks Biochemistry; Mary K. Campbell and Shawn O. Farrell, Brooks Cole; 6 th edition Recommended electronic
Introductory Biochemistry Instructors Dr. Nafez Abu Tarboush Dr. Mamoun Ahram Recommended textbooks Biochemistry; Mary K. Campbell and Shawn O. Farrell, Brooks Cole; 6 th edition Recommended electronic
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR
 THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA 1 November 1, 2016 Mid-Term EXAMINATION PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR EXAMINATION:
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA 1 November 1, 2016 Mid-Term EXAMINATION PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR EXAMINATION:
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
2. In regards to the fluid mosaic model, which of the following is TRUE?
 General Biology: Exam I Sample Questions 1. How many electrons are required to fill the valence shell of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 24? a. 0 the atom is inert b. 1 c. 2 d. 4 e. 6 2. In regards
General Biology: Exam I Sample Questions 1. How many electrons are required to fill the valence shell of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 24? a. 0 the atom is inert b. 1 c. 2 d. 4 e. 6 2. In regards
Enzymes and Protein Structure
 Enzymes and Protein Structure Last Week PTM s We (Re)Learned About Primary Structure And Tertiary Structure S-Q-D-A-G-M-Q-Q-G-A-D-M-D-Q-V-S-A Secondary Structure Enzymes What are these crazy things called
Enzymes and Protein Structure Last Week PTM s We (Re)Learned About Primary Structure And Tertiary Structure S-Q-D-A-G-M-Q-Q-G-A-D-M-D-Q-V-S-A Secondary Structure Enzymes What are these crazy things called
Supplemental Material: Annu. Rev. Biochem : doi: /annurev-biochem
 Supplemental Material: Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011. 80:669-702 doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060409-092741 Biological Phosphoryl Transfer Reactions: Understanding Mechanism and Catalysis Lassila, Zalatan,
Supplemental Material: Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011. 80:669-702 doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060409-092741 Biological Phosphoryl Transfer Reactions: Understanding Mechanism and Catalysis Lassila, Zalatan,
Lecture 16 (10/23/17) Lecture 16 (10/23/17)
 Lecture 16 (10/23/17) Reading: Ch6; 207-210 Ch6; 192-193, 195-196, 205-206 Problems: Ch6 (text); 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 9, 11 Ch6 (study guide-applying); 2 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 213-218
Lecture 16 (10/23/17) Reading: Ch6; 207-210 Ch6; 192-193, 195-196, 205-206 Problems: Ch6 (text); 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 9, 11 Ch6 (study guide-applying); 2 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 213-218
Biochemistry Enzyme kinetics
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Enzyme Kinetics Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 2. Enzymes as biological catalyst 3. Enzyme Catalysis 4. Understanding
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Enzyme Kinetics Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 2. Enzymes as biological catalyst 3. Enzyme Catalysis 4. Understanding
Amines Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Amines: structure and nomenclature
 Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.4 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
NAME. EXAM I I. / 36 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BICH421/621 III. / 38 TOTAL /100
 EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
Computational Biology 1
 Computational Biology 1 Protein Function & nzyme inetics Guna Rajagopal, Bioinformatics Institute, guna@bii.a-star.edu.sg References : Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4 th d. Alberts et. al. Pg. 129 190
Computational Biology 1 Protein Function & nzyme inetics Guna Rajagopal, Bioinformatics Institute, guna@bii.a-star.edu.sg References : Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4 th d. Alberts et. al. Pg. 129 190
Unit title: Chemistry for Applied Biologists
 Unit title: Chemistry for Applied Biologists Unit code: K/601/0292 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit covers bonding, thermodynamics, reaction rates, equilibrium, oxidation and reduction and organic
Unit title: Chemistry for Applied Biologists Unit code: K/601/0292 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit covers bonding, thermodynamics, reaction rates, equilibrium, oxidation and reduction and organic
Brønsted Acid Proton donor Base Proton acceptor O CH 3 COH + H H 3 O + + CH 3 CO -
 hap 7. Acid and Bases Brønsted Acid Proton donor Base Proton acceptor 3 3 3-2 acid base conj. acid conj. base 3 2 S 4 3 - S 4 base acid conj. acid conj. base 6 5 N 2 N 2 6 5 N - N 3 acid base conj. base
hap 7. Acid and Bases Brønsted Acid Proton donor Base Proton acceptor 3 3 3-2 acid base conj. acid conj. base 3 2 S 4 3 - S 4 base acid conj. acid conj. base 6 5 N 2 N 2 6 5 N - N 3 acid base conj. base
Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water
 Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water Biochemistry & Medicine Biochemistry can be defined as the science concerned with the chemical basis of life. Biochemistry can be described as the science concerned with the chemical
Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water Biochemistry & Medicine Biochemistry can be defined as the science concerned with the chemical basis of life. Biochemistry can be described as the science concerned with the chemical
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells
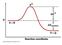 Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells Transferases and hydrolases catalyze group transfer reactions Acyl transfer: Hexokinase catalyzes a phosphoryl transfer from ATP to
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells Transferases and hydrolases catalyze group transfer reactions Acyl transfer: Hexokinase catalyzes a phosphoryl transfer from ATP to
CHEM 3653 Exam # 1 (03/07/13)
 1. Using phylogeny all living organisms can be divided into the following domains: A. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Vertebrate B. Archaea and Eukarya C. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea D. Eukarya and Bacteria
1. Using phylogeny all living organisms can be divided into the following domains: A. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Vertebrate B. Archaea and Eukarya C. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea D. Eukarya and Bacteria
BMB Lecture 1 September 27, 2017
 BMB 178 2017 Lecture 1 September 27, 2017 Introduction to Enzyme Catalysis Transition State Theory Welcome to BMB/Ch 178 Macromolecular function: Kinetics and Mechanisms Wednesdays and Fridays 10:30 am
BMB 178 2017 Lecture 1 September 27, 2017 Introduction to Enzyme Catalysis Transition State Theory Welcome to BMB/Ch 178 Macromolecular function: Kinetics and Mechanisms Wednesdays and Fridays 10:30 am
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution Reactions Substitution Reactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products
 hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
Bio-elements. Living organisms requires only 27 of the 90 common chemical elements found in the crust of the earth, to be as its essential components.
 Bio-elements Living organisms requires only 27 of the 90 common chemical elements found in the crust of the earth, to be as its essential components. Most of the chemical components of living organisms
Bio-elements Living organisms requires only 27 of the 90 common chemical elements found in the crust of the earth, to be as its essential components. Most of the chemical components of living organisms
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Key Concepts 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 8.2 The free-energy change of a reaction tells us
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Key Concepts 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 8.2 The free-energy change of a reaction tells us
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Water. Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD Lecture 2 MD summer Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan
 Water, DDS, PhD Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Lecture 2 MD summer 2014 1 Lecture Content Importance of water in biological systems Noncovalent interactions Water structure Water properties Water as a solvent
Water, DDS, PhD Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Lecture 2 MD summer 2014 1 Lecture Content Importance of water in biological systems Noncovalent interactions Water structure Water properties Water as a solvent
2017 Ebneshahidi. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi A. Introduction Chemistry science that deals with the composition of substances and the changes that take place in their composition. Organic chemistry chemistry that deals with organic
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi A. Introduction Chemistry science that deals with the composition of substances and the changes that take place in their composition. Organic chemistry chemistry that deals with organic
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways
 Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
BIOCHEMISTRY. František Vácha. JKU, Linz.
 BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
Exam II. Thursday in class Review Session Tuesday
 Exam II Thursday 10.30.08 in class Review Session Tuesday 10.28.08 Be able to draw a free energy diagram for an enzymatic reaction Know Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Understand the various types of inhibition
Exam II Thursday 10.30.08 in class Review Session Tuesday 10.28.08 Be able to draw a free energy diagram for an enzymatic reaction Know Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Understand the various types of inhibition
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - Organic Reactions I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. cleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a chemical
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. cleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a chemical
Biochemistry. Lecture 8
 Biochemistry Lecture 8 Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase - C - C - C Metabolites
Biochemistry Lecture 8 Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase - C - C - C Metabolites
Introduction into Biochemistry. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Lecture 1
 Introduction into Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Lecture 1 Course information Recommended textbooks Biochemistry; Mary K. Campbell and Shawn O. Farrell, Brooks Cole; 7 th edition Instructors Dr. Mamoun
Introduction into Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Lecture 1 Course information Recommended textbooks Biochemistry; Mary K. Campbell and Shawn O. Farrell, Brooks Cole; 7 th edition Instructors Dr. Mamoun
Biochemistry. Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics
 Biochemistry Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase -
Biochemistry Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase -
Alcohols. Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
 Alcohols Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group Uses: synthetic intermediate, cleanser, cosmetics, fuel, alcoholic beverages, etc. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
Alcohols Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group Uses: synthetic intermediate, cleanser, cosmetics, fuel, alcoholic beverages, etc. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
2054, Chap. 8, page 1
 2054, Chap. 8, page 1 I. Metabolism: Energetics, Enzymes, and Regulation (Chapter 8) A. Energetics and work 1. overview a. energy = ability to do work (1) chemical, transport, mechanical (2) ultimate source
2054, Chap. 8, page 1 I. Metabolism: Energetics, Enzymes, and Regulation (Chapter 8) A. Energetics and work 1. overview a. energy = ability to do work (1) chemical, transport, mechanical (2) ultimate source
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit. Lecture 2 (9/11/17)
 16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Chemistry of Microbiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology Atoms Matter anything that takes up space and has mass
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology Atoms Matter anything that takes up space and has mass
Free Energy. because H is negative doesn't mean that G will be negative and just because S is positive doesn't mean that G will be negative.
 Biochemistry 462a Bioenergetics Reading - Lehninger Principles, Chapter 14, pp. 485-512 Practice problems - Chapter 14: 2-8, 10, 12, 13; Physical Chemistry extra problems, free energy problems Free Energy
Biochemistry 462a Bioenergetics Reading - Lehninger Principles, Chapter 14, pp. 485-512 Practice problems - Chapter 14: 2-8, 10, 12, 13; Physical Chemistry extra problems, free energy problems Free Energy
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Isotope effects on enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions of phosphorothioates
 NUKLEONIKA 2002;47(Supplement 1):S17 S23 PROCEEDINGS Isotope effects on enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions of phosphorothioates Irina E. Catrina, Przemyslaw G. Czyryca, Alvan C. Hengge Abstract Kinetic
NUKLEONIKA 2002;47(Supplement 1):S17 S23 PROCEEDINGS Isotope effects on enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions of phosphorothioates Irina E. Catrina, Przemyslaw G. Czyryca, Alvan C. Hengge Abstract Kinetic
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry
 Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
ENZYME KINETICS. Medical Biochemistry, Lecture 24
 ENZYME KINETICS Medical Biochemistry, Lecture 24 Lecture 24, Outline Michaelis-Menten kinetics Interpretations and uses of the Michaelis- Menten equation Enzyme inhibitors: types and kinetics Enzyme Kinetics
ENZYME KINETICS Medical Biochemistry, Lecture 24 Lecture 24, Outline Michaelis-Menten kinetics Interpretations and uses of the Michaelis- Menten equation Enzyme inhibitors: types and kinetics Enzyme Kinetics
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry
 covered by A-Level Chemistry products Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant 1.1.1 Apply the mole concept to substances. Moles and Formulae 1.1.2 Determine the number
covered by A-Level Chemistry products Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant 1.1.1 Apply the mole concept to substances. Moles and Formulae 1.1.2 Determine the number
Reaction Thermodynamics
 Reaction Thermodynamics Thermodynamics reflects the degree to which a reaction is favored or disfavored Recall: G = Gibbs free energy = the energy available to do work ΔG = change in G of the system as
Reaction Thermodynamics Thermodynamics reflects the degree to which a reaction is favored or disfavored Recall: G = Gibbs free energy = the energy available to do work ΔG = change in G of the system as
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
A) at equilibrium B) endergonic C) endothermic D) exergonic E) exothermic.
 CHEM 2770: Elements of Biochemistry Mid Term EXAMINATION VERSION A Date: October 29, 2014 Instructor: H. Perreault Location: 172 Schultz Time: 4 or 6 pm. Duration: 1 hour Instructions Please mark the Answer
CHEM 2770: Elements of Biochemistry Mid Term EXAMINATION VERSION A Date: October 29, 2014 Instructor: H. Perreault Location: 172 Schultz Time: 4 or 6 pm. Duration: 1 hour Instructions Please mark the Answer
11/30/ Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions. Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions
 Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism. Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism. A. Energy and Energy Conversions. A. Energy and Energy Conversions
 Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism Lecture Series 6 Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism B. ATP: Transferring Energy in Cells D. Molecular Structure Determines Enzyme Fxn Energy is the capacity to do work (cause
Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism Lecture Series 6 Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism B. ATP: Transferring Energy in Cells D. Molecular Structure Determines Enzyme Fxn Energy is the capacity to do work (cause
Protein Folding & Stability. Lecture 11: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a
 Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Reading for today: Chapter 16 (selections from Sections A, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 17 (Diffusion)
 Lecture 29 Enzymes Reading for today: Chapter 6 (selections from Sections, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 7 (Diffusion) 4/3/6 Today s Goals Michaelis-Menten mechanism for simple enzyme reactions:
Lecture 29 Enzymes Reading for today: Chapter 6 (selections from Sections, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 7 (Diffusion) 4/3/6 Today s Goals Michaelis-Menten mechanism for simple enzyme reactions:
