Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics. Mechanisms ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE. H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl. Margaret A. Daugherty.
|
|
|
- Paulina Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
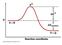
1 Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products In the transition state (denoted by X ), the chemistry is intermediate between reactant and product. The substrates are strained hence chemistry can occur. Enzymes work to reduce G, the barrier between substrate and transition state.
2 REGULATION AND RECOGNITION LOCK & KEY Lysozyme binding to an antibody INDUCED FIT (enzymes) Hexokinase binding it s substrate glucose BIOC 205 ENZYME-SUBSTRATE INTERACTIONS THE LOCK & KEY MODEL A perfect match between enzyme and substrate can explain enzyme specificity does not explain enzymatic catalysis If everything is such a perfect fit, how does the chemistry occur? How do we go from substrate to product? Implies a rigid, inflexible enzyme
3 ENZYME-SUBSTRATE INTERACTIONS THE INDUCED FIT MODEL KEY FEATURES: ENZYME STRUCTURE CHANGES IN PRESENCE OF SUBSTRATE --- BRINGS CATALYTIC GROUPS INTO CORRECT POSITION TO DO CHEMISTRY ---SUBSTRATE IS FORCED INTO TRANSITION STATE CONFORMATION ACCOUNTS FOR SPECIFITY AND FOR CATALYSIS Intermediate State in Catalysis uncatalyzed reaction Catalyzed reaction: 2 low barriers replacing 1 high barrier. Lower activation energy; reaction goes faster ES complex with low energy EX complex with lower energy than X sec Enzymes stabilize transition state more than ES complex
4 LARGE RATE ACCELERATIONS: ENZYME STRUCTURE AND MECHANISM MECHANISMS OF CATALYSIS 1). Entropy loss in the formation of ES 2). Destabilization of ES due to strain, desolvation or electrostatic effects 3). Proximity and orientation 4). Covalent catalysis (an example of the serine proteases) 5). Metal ion catalysis 6). General acid or base catalysis Any or all of this things can contribute to catalytic rate acceleration Active Site Small compared to the protein; 3D entity, usually found in a cleft or crevice; Size, shape, charge, non-covalent interactions are all important! Binding is via multiple interactions; Specificity achieved by the arrangement of the active site; Converts substrate to product. Active site
5 ENZYME ACTIVE SITES BIND THE TRANSITION STATE BETTER THAN SUBSTRATE OR PRODUCT Goal: Perform chemistry! Fast! Binding of Substrate must be favorable;...but not too favorable! Destabilization of ES relative to the transition state, EX Loss of entropy on formation of ES Destabilization of ES by Strain Distortion Desolvation Fig 14.2 Favorable binding energy destabilized by entropy loss, strain, distortion, desolvation! FORMATION OF ES: LOSS OF ENTROPY MAIN POINTS: 2 reactants --> 1 product Lose translational and rotational entropy Entropy offset by favorable H (chemical interactions) No further loss of entropy in going to EX Note: orientation: the active site has the catalytic groups in the most effective orientation to carry out the needed chemistry.
6 DESTABILIZATION OF ES: Strain, Desolvation, Electrostatic Effects + MAIN POINTS 1). Active site is specialized to bind transition state to carry out chemistry; in order to make a fit the ES complex is strained or destabilized. 2). When charged groups move from solvent to active site, they often become desolvated - this makes them less stable, hence more reactive. DESTABILIZATION OF ES: Strain, Desolvation, Electrostatic Effects MAIN POINT Charged groups on S may be forced to interact with like charges. This is unfavorable and destabilizes S. Reaction pathway acts to remove stress - hence faster rates result. Note: proximity Bringing the substrate together with the catalytic groups on the enzyme results in an effective concentration increase relative to the concentration of substrates in solution. Hence faster reaction rates.
7 STUDYING TRANSITION STATE - TRANSITION STATE ANALOGS: High affinity (10-14 M) substrates that mimic the transition state; transition state analogs are stable and only mimic the actual TS. As such they never bind as tightly as the TS itself! AAs Frequently Involved in Catalysis
8 CATALYTIC FUNCTIONS OF REACTIVE GROUPS OF IONIZABLE AMINO ACIDS O R-C- Acyl group COVALENT CATALYSIS A covalent bond is formed between enzyme and substrate BX + Enzyme E-B + X + Y Enz + BY serine proteases: coming right up!
9 Acid-Base Catalysis Specific vs. general Specific Acid-Base Catalysis: H + or OH - accelerates the reaction; donated from H 2 0 In this case, the reaction will be ph dependent; However buffers that can donate or accept H + /OH - will not affect the reaction rate: Acid-Base Catalysis General Acid-Base Catalysis: in which an acid or base other than H + or OH - (other than H 2 O) accelerates the reaction; reactive groups in the enzymes active sites; These are characterized by changes in rate with increasing buffer concentrations - i.e., there is some other group available to act as an general acid or general base. Histidine plays a major role as a general acid or base. pka ~ 7.0
10 Enolase: Lys - general base; abstracts H+ Glu - general acid; Donating proton to OH --> H 2 0 Metal Ion Catalysis Metalloenzymes: bind metal tightly require metal for 3-D structure Transition metal ions Fe 2+, Fe 3+, Zn 2+, Mn 2+ or Co 2+ Metal activated enzymes: bind metals weakly; usually only during catalysis - play a structural role; bind metals from solution alkali and alkaline earth metals Na +, K +, Mg ++ or Ca ++ Roles: Bind to substrates and orient the substrates Mediate redox reactions through reversible changes in the metals oxidation state Electrostatically shield or stabilize negative charges.
11 Human Carbonic Anhydrase: A Zinc containing enzyme CO 2 + H 2 O <---> HCO H + Zinc is tetrahedrally coordinated H 2 O is polarized! Im = imidazole of histidine THE SERINE PROTEASES Trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, thrombin, subtilisin, plasmin, TPA All involve serine in their catalytic mechanism; Serine is part of a catalytic triad of Ser, His, Asp All serine proteases are homologous, but locations of the three critical residues vary. By convention, numbering of critical residues is always the same: His-57, Asp-102 and Ser-195
12 PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF SERINE PROTEASES ZYMOGENS ARE CLEAVED TO THEIR ACTIVE CONFORMATION
13 ACTIVE SITE: A DEPRESSION ON PROTEIN SURFACE Chymotrypsin in complex with eglin C depth of active site depression depends on reaction Chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase blue yellow green All three proteases show: similar backbone conformations active site residue orientations yet. All three exhibit different cleavage specificity Chymotrpysin: aromatics; trypsin: basic & elastase: gly & alanine
14 SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY shallow hydrophobic deep hydrophobic deep negatively charged Small differences in the nature of the binding pocket give rise to substrate specificity in the proteases. ARTIFICIAL SUBSTRATES PROVIDE INSIGHT INTO MECHANISM
15 EVENTS AT THE ACTIVE SITE: MECHANISM COVALENT & GENERAL ACID-BASE CHEMISTRY 1). Asp-102 functions to orient His-57 2). His-57 acts as a general acid and a general base. 3). Ser-195 covalently binds the peptide to be cleaved 4). Covalent bond formation turns a trigonal C into a tetrahedral carbon 5). A tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate is stabilized by NH s of Gly193 and Ser195. MECHANISM I: BINDING OF SUBSTRATE Asp-102 immobilizes His57 via H-bond His acts as general base; deprotonates Ser; Via nucleophilic reaction, serine attacks C=O Covalent intermediate with protonated amine; negative charge on O is unstable His acts as general acid; donates H to amide nitrogen
16 Oxyanion Hole Major Role in Transition State Stabilization Recall: binding site is relatively hydrophobic; need to neutralize charges Substrate C=0 hydrogen bonds to amide Hs of G193 and S195 Enhanced stabilization: 1). C-O - bond longer than C=O bond; Amide H s and O closer together 2). O - hydrogen bonds stronger than C=O hydrogen bonds 3). Side chain interactions MECHANISM II: ATTACK OF WATER; RELEASE OF AMINO PRODUCT From last slide: C-N bond cleavage and release of amino product ; resulting acyl intermediate is relatively stable His acts as general base, accepting proton from water; Water attacks (nucleophilic) on carbonyl.
17 MECHANISM III: COLLAPSE OF TETRAHEDRAL INTERMEDIATE From last slide Transient tetrahedral intermediate; with collapse of tetrahedral intermediate assisted by His donating a proton to Ser (concerted). MECHANISM IV: RELEASE OF CARBOXYL PRODUCT Final step: Deprotonation of carboxyl group; with departure of carboxyl product from active site.
18 Serine Protease Mechanism Review 1). Enzymes stabilize transition state more than ES complex. 2). There are a limited number of factors that contribute to catalysis. 3). Destabilization of ES relative to the transition state occurs via: Loss of entropy on forming ES Strain on the ES complex Distortion of the ES complex Desolvation of the ES complex 4). Catalysis is also achieved through orientation of the chemically reactive groups on the enzyme in close proximity with the substrate. 5). Transition state analogs are a way of studying enzyme mechanism. 6). The serine proteases have a catalytic triad that consists of Ser, His and Asp. The job of Asp102 is to correctly position His57 in the active site. His57 acts both as a general acid and a general base. Serine covalently binds the substrate. Water is involved in the mechanism.
Enzyme function: the transition state. Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms. Catalytic Reactions. Margaret A. Daugherty A B. Lecture 16: Fall 2003
 Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Catalytic Reactions. Intermediate State in Catalysis. Lecture 16: Catalyzed reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction. Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms
 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
It s the amino acids!
 Catalytic Mechanisms HOW do enzymes do their job? Reducing activation energy sure, but HOW does an enzyme catalysis reduce the energy barrier ΔG? Remember: The rate of a chemical reaction of substrate
Catalytic Mechanisms HOW do enzymes do their job? Reducing activation energy sure, but HOW does an enzyme catalysis reduce the energy barrier ΔG? Remember: The rate of a chemical reaction of substrate
4 Examples of enzymes
 Catalysis 1 4 Examples of enzymes Adding water to a substrate: Serine proteases. Carbonic anhydrase. Restrictions Endonuclease. Transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to a nucleotide. Nucleoside monophosphate
Catalysis 1 4 Examples of enzymes Adding water to a substrate: Serine proteases. Carbonic anhydrase. Restrictions Endonuclease. Transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to a nucleotide. Nucleoside monophosphate
Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism
 Mechanisms of Enzymes BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
Mechanisms of Enzymes BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Mechanisms of Enzymes Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6, 7, 8 Enzymes Enzyme Mechanism 1 Mechanisms of Enzymes Energy diagrams Binding modes of enzyme catalysis Chemical modes of enzyme catalysis Acid-Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Binding
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis
 Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Key Concepts.
 Lectures 13-14: Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 9, pp. 241-254 Updated on: 2/7/07 at 9:15 pm movie of chemical mechanism of serine proteases (from Voet & Voet,
Lectures 13-14: Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 9, pp. 241-254 Updated on: 2/7/07 at 9:15 pm movie of chemical mechanism of serine proteases (from Voet & Voet,
Acid/Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Electrostatic catalysis Proximity and orientation Preferential binding of the transition
 Enzyme catalysis Factors that contribute to catalytic power of enzymes Acid/Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Electrostatic catalysis Proximity and orientation Preferential binding
Enzyme catalysis Factors that contribute to catalytic power of enzymes Acid/Base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Electrostatic catalysis Proximity and orientation Preferential binding
C a h p a t p e t r e r 6 E z n y z m y e m s
 Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility
 (P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
(P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
Lecture 14 (10/18/17) Lecture 14 (10/18/17)
 Lecture 14 (10/18/17) Reading: Ch6; 190-191, 194-195, 197-198 Problems: Ch6 (text); 7, 24 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 4, 13 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 198-203 Ch6; Box 6-1 Problems: Ch6 (text); 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
Lecture 14 (10/18/17) Reading: Ch6; 190-191, 194-195, 197-198 Problems: Ch6 (text); 7, 24 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 4, 13 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 198-203 Ch6; Box 6-1 Problems: Ch6 (text); 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
Two requirements for life: Self-replication and appropriate catalysis. A. Most enzymes (def.: biological catalysts) are proteins
 Enzymes We must be able to enhance the rates of many physical and chemical processes to remain alive and healthy. Support for that assertion: Maladies of genetic origin. Examples: Sickle-cell anemia (physical)
Enzymes We must be able to enhance the rates of many physical and chemical processes to remain alive and healthy. Support for that assertion: Maladies of genetic origin. Examples: Sickle-cell anemia (physical)
Mechanisms of catalysis
 Mechanisms of catalysis Proximity and orientation effects Proximity: Reaction between bound molecules doesn't require an improbable collision of 2 molecules -- they're already in "contact" (increases the
Mechanisms of catalysis Proximity and orientation effects Proximity: Reaction between bound molecules doesn't require an improbable collision of 2 molecules -- they're already in "contact" (increases the
[Urea] (M) k (s -1 )
![[Urea] (M) k (s -1 ) [Urea] (M) k (s -1 )](/thumbs/89/98097251.jpg) BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
Chapter 14. Outline. How Much Enzyme-Induced Rate Accelerations?
 Chapter 14 Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham Mechanisms of Enzyme Action http://lms.ls.ntou.edu.tw/course/106 hanjia@mail.ntou.edu.tw il t Essential Questions Before this class, ask your self the
Chapter 14 Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham Mechanisms of Enzyme Action http://lms.ls.ntou.edu.tw/course/106 hanjia@mail.ntou.edu.tw il t Essential Questions Before this class, ask your self the
Enzymes I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Enzymes I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources Mark's Basic Medical Biochemistry Other resources NCBI Bookshelf: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=books The Medical Biochemistry
Enzymes I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources Mark's Basic Medical Biochemistry Other resources NCBI Bookshelf: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=books The Medical Biochemistry
[Urea] (M) k (s -1 )
![[Urea] (M) k (s -1 ) [Urea] (M) k (s -1 )](/thumbs/96/126856044.jpg) BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
BMB178 Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 Due: 10/26/2018, noon Office hour: 10/25/2018, SFL GSR218 7 9 pm Problem 1. Transition state theory (20 points): Consider a unimolecular reaction where a substrate S is converted
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 6 Enzymes
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 6 Enzymes CHAPTER 6 Enzymes Key topics about enzyme function: Physiological significance of enzymes Origin of catalytic power of enzymes Chemical mechanisms of catalysis
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 6 Enzymes CHAPTER 6 Enzymes Key topics about enzyme function: Physiological significance of enzymes Origin of catalytic power of enzymes Chemical mechanisms of catalysis
Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: 2. Peripheral proteins: 3. Amphitropic proteins:
 Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: proteins that insert into/span the membrane bilayer; or covalently linked to membrane lipids. (Interact with the hydrophobic part of the membrane) 2. Peripheral
Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: proteins that insert into/span the membrane bilayer; or covalently linked to membrane lipids. (Interact with the hydrophobic part of the membrane) 2. Peripheral
Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems
 Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems Introduction Enzymes are Biological Catalysis A catalyst is a substance
Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems Introduction Enzymes are Biological Catalysis A catalyst is a substance
Chapters 5-6 Enzymes. Catalyst: A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not itself consumed.
 hapters 56 Enzymes atalyst: A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not itself consumed. Most biological catalysts are proteins but some RA are catalysts too. e.g. Peptide bonds
hapters 56 Enzymes atalyst: A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not itself consumed. Most biological catalysts are proteins but some RA are catalysts too. e.g. Peptide bonds
Chemistry Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class.
 Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. Name 1. There is a real enzyme called cocaine esterase that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme
Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. Name 1. There is a real enzyme called cocaine esterase that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme
Enzymes! Accelerate reactions by x 10 6 (and up to x ) Specific with respect to reaction catalized.
 Enzymes! Accelerate reactions by x 10 6 (and up to x 10 19 ) Specific with respect to reaction catalized. Selective with respect to reagent recognized. Cartoon Guide to Genetics Gonick & Wheelis 1 Microreview
Enzymes! Accelerate reactions by x 10 6 (and up to x 10 19 ) Specific with respect to reaction catalized. Selective with respect to reagent recognized. Cartoon Guide to Genetics Gonick & Wheelis 1 Microreview
Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
 Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Review: Garrett and Grisham, Enzyme Specificity and Regulation (Chapt. 13) and Mechanisms of Enzyme
Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Review: Garrett and Grisham, Enzyme Specificity and Regulation (Chapt. 13) and Mechanisms of Enzyme
Enzyme Kinetics 2014
 V 41 Enzyme Kinetics 2014 Atkins Ch.23, Tinoco 4 th -Ch.8 Enzyme rxn example Catalysis/Mechanism: E + S k -1 ES k 1 ES E is at beginning and k 2 k -2 E + P at end of reaction Catalyst: No consumption of
V 41 Enzyme Kinetics 2014 Atkins Ch.23, Tinoco 4 th -Ch.8 Enzyme rxn example Catalysis/Mechanism: E + S k -1 ES k 1 ES E is at beginning and k 2 k -2 E + P at end of reaction Catalyst: No consumption of
What is an enzyme? Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall General Properties
 Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 ENZYMES: Why, what, when, where, how? All but the who! What: proteins that exert kinetic control over
Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 ENZYMES: Why, what, when, where, how? All but the who! What: proteins that exert kinetic control over
Reading for today: Chapter 16 (selections from Sections A, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 17 (Diffusion)
 Lecture 29 Enzymes Reading for today: Chapter 6 (selections from Sections, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 7 (Diffusion) 4/3/6 Today s Goals Michaelis-Menten mechanism for simple enzyme reactions:
Lecture 29 Enzymes Reading for today: Chapter 6 (selections from Sections, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 7 (Diffusion) 4/3/6 Today s Goals Michaelis-Menten mechanism for simple enzyme reactions:
G. GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS
 G. GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS Towards a Better Chemical Mechanism via Catalysis There are two types of mechanisms we ll be discussing this semester. Kinetic mechanisms are concerned with rate constants
G. GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS Towards a Better Chemical Mechanism via Catalysis There are two types of mechanisms we ll be discussing this semester. Kinetic mechanisms are concerned with rate constants
2. Which of the following are nucleophiles and which are electrophiles?
 Life Sciences 1a ractice roblems 7 1. a) ow many intermediates are there in the reaction? b) ow many transition states are there? c) What is the fastest step in the reaction? d) Which is more stable, A
Life Sciences 1a ractice roblems 7 1. a) ow many intermediates are there in the reaction? b) ow many transition states are there? c) What is the fastest step in the reaction? d) Which is more stable, A
4. What is the general expression Keq (the equilibrium constant) in terms of product and reactant concentration? tell us about the enzyme.
 Section 8 Enzyme Kinetics Pre-Activity Assignment 1. Produce a reading log for the sections in your text that discuss the Michaelis-Menten equation and including kcat. 2. Focus on the derivation of the
Section 8 Enzyme Kinetics Pre-Activity Assignment 1. Produce a reading log for the sections in your text that discuss the Michaelis-Menten equation and including kcat. 2. Focus on the derivation of the
Catalytic power of enzymes
 Enzyme catalysis Catalytic power of enzymes Enzymatic reactions are involved in most biological processes. There is a major practical and fundamental interest in finding out what makes enzymes so efficient
Enzyme catalysis Catalytic power of enzymes Enzymatic reactions are involved in most biological processes. There is a major practical and fundamental interest in finding out what makes enzymes so efficient
What is an enzyme? Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 KEY FEATURES OF ENZYMES
 Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 What is an enzyme? General Properties Mostly proteins, but some are actually RNAs Biological catalysts
Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 What is an enzyme? General Properties Mostly proteins, but some are actually RNAs Biological catalysts
Lecture 11: Enzymes: Kinetics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 8, pp
![Lecture 11: Enzymes: Kinetics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 8, pp Lecture 11: Enzymes: Kinetics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 8, pp](/thumbs/74/70848503.jpg) Lecture 11: Enzymes: Kinetics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 8, pp. 216-225 Updated on: 2/4/07 at 9:00 pm Key Concepts Kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Study of enzyme kinetics
Lecture 11: Enzymes: Kinetics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 8, pp. 216-225 Updated on: 2/4/07 at 9:00 pm Key Concepts Kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Study of enzyme kinetics
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells
 Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells Transferases and hydrolases catalyze group transfer reactions Acyl transfer: Hexokinase catalyzes a phosphoryl transfer from ATP to
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells Transferases and hydrolases catalyze group transfer reactions Acyl transfer: Hexokinase catalyzes a phosphoryl transfer from ATP to
Lecture # 3, 4 Selecting a Catalyst (Non-Kinetic Parameters), Review of Enzyme Kinetics, Selectivity, ph and Temperature Effects
 1.492 - Integrated Chemical Engineering (ICE Topics: Biocatalysis MIT Chemical Engineering Department Instructor: Professor Kristala Prather Fall 24 Lecture # 3, 4 Selecting a Catalyst (Non-Kinetic Parameters,
1.492 - Integrated Chemical Engineering (ICE Topics: Biocatalysis MIT Chemical Engineering Department Instructor: Professor Kristala Prather Fall 24 Lecture # 3, 4 Selecting a Catalyst (Non-Kinetic Parameters,
Biologic catalysts 1. Shared properties with chemical catalysts a. Enzymes are neither consumed nor produced during the course of a reaction. b.
 Enzyme definition Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes,
Enzyme definition Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes,
CHEM 3653 Exam # 1 (03/07/13)
 1. Using phylogeny all living organisms can be divided into the following domains: A. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Vertebrate B. Archaea and Eukarya C. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea D. Eukarya and Bacteria
1. Using phylogeny all living organisms can be divided into the following domains: A. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Vertebrate B. Archaea and Eukarya C. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea D. Eukarya and Bacteria
BSc and MSc Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BSc and MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BSc and MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking
Exam 3 11/10/2014 Last Name (PRINT): First Name: Pg Topic Pts Total possible 3 Multiple. 12 choice 4 Multiple. 9 choice 5 Multiple
 Last Name (PRINT): First Name: Pg Topic Pts Total possible 3 Multiple 12 choice 4 Multiple 9 choice 5 Multiple 12 choice 6 Multiple 16 choice, start T/F 7 T/F and Fill in Blank 22 8 Binding problems 12
Last Name (PRINT): First Name: Pg Topic Pts Total possible 3 Multiple 12 choice 4 Multiple 9 choice 5 Multiple 12 choice 6 Multiple 16 choice, start T/F 7 T/F and Fill in Blank 22 8 Binding problems 12
NAME. EXAM I I. / 36 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BICH421/621 III. / 38 TOTAL /100
 EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
Enzymes as machines: how they work
 Enzymes as machines: how they work Biophysical Society Summer Course 26 June 2014 Charlie Carter They are Just as Scared of You, As You are of Them Adapted from: Steve Cote, Chapel Hill artist Readings
Enzymes as machines: how they work Biophysical Society Summer Course 26 June 2014 Charlie Carter They are Just as Scared of You, As You are of Them Adapted from: Steve Cote, Chapel Hill artist Readings
It is generally believed that the catalytic reactions occur in at least two steps.
 Lecture 16 MECHANISM OF ENZYME ACTION A chemical reaction such as A ----> P takes place because a certain fraction of the substrate possesses enough energy to attain an activated condition called the transition
Lecture 16 MECHANISM OF ENZYME ACTION A chemical reaction such as A ----> P takes place because a certain fraction of the substrate possesses enough energy to attain an activated condition called the transition
From Friday s material
 5.111 Lecture 35 35.1 Kinetics Topic: Catalysis Chapter 13 (Section 13.14-13.15) From Friday s material Le Chatelier's Principle - when a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium tends
5.111 Lecture 35 35.1 Kinetics Topic: Catalysis Chapter 13 (Section 13.14-13.15) From Friday s material Le Chatelier's Principle - when a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium tends
Catalysis. Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica
 Catalysis Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica References: Biochemistry" by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet Biochemistry" by Christopher K. Mathews, K. E. Van Hold and Kevin
Catalysis Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica References: Biochemistry" by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet Biochemistry" by Christopher K. Mathews, K. E. Van Hold and Kevin
Overview of Kinetics
 Overview of Kinetics [P] t = ν = k[s] Velocity of reaction Conc. of reactant(s) Rate of reaction M/sec Rate constant sec -1, M -1 sec -1 1 st order reaction-rate depends on concentration of one reactant
Overview of Kinetics [P] t = ν = k[s] Velocity of reaction Conc. of reactant(s) Rate of reaction M/sec Rate constant sec -1, M -1 sec -1 1 st order reaction-rate depends on concentration of one reactant
Chapter 15. Enzymatic Catalysis
 Chapter 15. Enzymatic Catalysis Catalytic mechanisms Acid-base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Proximity and orientation effects Stabilization of the transition state Acid-base catalysis
Chapter 15. Enzymatic Catalysis Catalytic mechanisms Acid-base catalysis Covalent catalysis Metal ion catalysis Proximity and orientation effects Stabilization of the transition state Acid-base catalysis
Exam 4 April 15, 2005 CHEM 3511 Print Name: KEY Signature
 1) (8 pts) General Properties of Enzymes. Give four properties of enzymaticallycatalyzed reactions. The answers should indicate how enzymatic reactions differ from non-enzymatic reactions. Write four only
1) (8 pts) General Properties of Enzymes. Give four properties of enzymaticallycatalyzed reactions. The answers should indicate how enzymatic reactions differ from non-enzymatic reactions. Write four only
Enzyme reactions mechanisms and Immobilization of enzymes
 Enzyme reactions mechanisms and Immobilization of enzymes Lecture 18.11.2016 CHEM-E3140 Bioprocess Technology II Aalto University School of Chemical Technology Ossi Turunen 1 Reaction mechanisms 1) General
Enzyme reactions mechanisms and Immobilization of enzymes Lecture 18.11.2016 CHEM-E3140 Bioprocess Technology II Aalto University School of Chemical Technology Ossi Turunen 1 Reaction mechanisms 1) General
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013
 Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 9 Biochemical Transformations I. Carbon-carbon bond forming and cleaving reactions in Biology (see the Lexicon). Enzymes catalyze a limited
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 9 Biochemical Transformations I. Carbon-carbon bond forming and cleaving reactions in Biology (see the Lexicon). Enzymes catalyze a limited
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties
 1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
CHEM April 10, Exam 3
 Name CHEM 3511 April 10, 2009 Exam 3 Name Page 1 1. (12 points) Give the name of your favorite Tech professor and in one sentence describe why you like him/her. 2. (10 points) An enzyme cleaves a chemical
Name CHEM 3511 April 10, 2009 Exam 3 Name Page 1 1. (12 points) Give the name of your favorite Tech professor and in one sentence describe why you like him/her. 2. (10 points) An enzyme cleaves a chemical
CHAPTER 29 HW: AMINO ACIDS + PROTEINS
 CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
Chapter 8. Enzymes: basic concept and kinetics
 Chapter 8 Enzymes: basic concept and kinetics Learning objectives: mechanism of enzymatic catalysis Michaelis -Menton Model Inhibition Single Molecule of Enzymatic Reaction Enzymes: catalysis chemical
Chapter 8 Enzymes: basic concept and kinetics Learning objectives: mechanism of enzymatic catalysis Michaelis -Menton Model Inhibition Single Molecule of Enzymatic Reaction Enzymes: catalysis chemical
BMB Lecture Covalent Catalysis 2. General Acid-base catalysis
 BMB 178 2017 Lecture 3 1. Covalent Catalysis 2. General Acid-base catalysis Evidences for A Covalent Intermediate Direct Evidences: Direct observation of formation and disappearance of an intermediate
BMB 178 2017 Lecture 3 1. Covalent Catalysis 2. General Acid-base catalysis Evidences for A Covalent Intermediate Direct Evidences: Direct observation of formation and disappearance of an intermediate
Chapter 6: Outline-2. Chapter 6: Outline Properties of Enzymes. Introduction. Activation Energy, E act. Activation Energy-2
 Chapter 6: Outline- Properties of Enzymes Classification of Enzymes Enzyme inetics Michaelis-Menten inetics Lineweaver-Burke Plots Enzyme Inhibition Catalysis Catalytic Mechanisms Cofactors Chapter 6:
Chapter 6: Outline- Properties of Enzymes Classification of Enzymes Enzyme inetics Michaelis-Menten inetics Lineweaver-Burke Plots Enzyme Inhibition Catalysis Catalytic Mechanisms Cofactors Chapter 6:
C a h p a t p e t r e r 6 E z n y z m y e m s
 Chapter 6 Enzymes 1. An Introduction to Enzymes Enzymes are catalytically active biological macromolecules Enzymes are catalysts of biological systems Almost every biochemical reaction is catalyzed by
Chapter 6 Enzymes 1. An Introduction to Enzymes Enzymes are catalytically active biological macromolecules Enzymes are catalysts of biological systems Almost every biochemical reaction is catalyzed by
Biomolecules: lecture 9
 Biomolecules: lecture 9 - understanding further why amino acids are the building block for proteins - understanding the chemical properties amino acids bring to proteins - realizing that many proteins
Biomolecules: lecture 9 - understanding further why amino acids are the building block for proteins - understanding the chemical properties amino acids bring to proteins - realizing that many proteins
Catalysis is Necessary for Life. Chapter 6 Enzymes. Why Study Enzymes? Enzymes are Biological Catalysts
 Chapter 6 Enzymes Catalysis is Necessary for Life Definition: a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, while emerging unchanged at the end Corollary A: a catalyst is never used up,
Chapter 6 Enzymes Catalysis is Necessary for Life Definition: a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, while emerging unchanged at the end Corollary A: a catalyst is never used up,
Chapter 6 Overview. Enzymes. Catalysis most important function of proteins. Globular protein Increase rate of metabolic processes
 Chapter 6 Overview Enzymes Catalysis most important function of proteins n Enzymes protein catalysts Globular protein Increase rate of metabolic processes Enzymes kinetics info on reaction rates & measure
Chapter 6 Overview Enzymes Catalysis most important function of proteins n Enzymes protein catalysts Globular protein Increase rate of metabolic processes Enzymes kinetics info on reaction rates & measure
Lecture 16 (10/23/17) Lecture 16 (10/23/17)
 Lecture 16 (10/23/17) Reading: Ch6; 207-210 Ch6; 192-193, 195-196, 205-206 Problems: Ch6 (text); 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 9, 11 Ch6 (study guide-applying); 2 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 213-218
Lecture 16 (10/23/17) Reading: Ch6; 207-210 Ch6; 192-193, 195-196, 205-206 Problems: Ch6 (text); 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 9, 11 Ch6 (study guide-applying); 2 NEXT Reading: Ch6; 213-218
Protein Folding & Stability. Lecture 11: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a
 Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology
 L28-1 Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology Bovine Pancreatic RNase A Biochemistry, Life, and all that L28-2 A brief word about biochemistry traditionally, chemical engineers used organic and inorganic chemistry
L28-1 Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology Bovine Pancreatic RNase A Biochemistry, Life, and all that L28-2 A brief word about biochemistry traditionally, chemical engineers used organic and inorganic chemistry
Biochemistry. Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics
 Biochemistry Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase -
Biochemistry Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase -
489--Lectures 3 and 4. Fundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry
 489--Lectures 3 and 4 Fundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry (with special relevance to biological systems) Some slides courtesy of Prof. Xuan Zhao (U. Memphis) and Prof. Yi Lu (U. Illinois) Fundamentals
489--Lectures 3 and 4 Fundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry (with special relevance to biological systems) Some slides courtesy of Prof. Xuan Zhao (U. Memphis) and Prof. Yi Lu (U. Illinois) Fundamentals
Biochemistry Enzyme kinetics
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Enzyme Kinetics Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 2. Enzymes as biological catalyst 3. Enzyme Catalysis 4. Understanding
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Enzyme Kinetics Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 2. Enzymes as biological catalyst 3. Enzyme Catalysis 4. Understanding
Chapter 16. Examples of nutcracker mechanisms.
 Protein Primer, Lumry, Draft-{6-15-03) Chapter 16, Nutcracker mechanisms, 16-1 Chapter 16. Examples of nutcracker mechanisms. Hemoglobin, cytochrome C and chymotrypsin were the first proteins to be used
Protein Primer, Lumry, Draft-{6-15-03) Chapter 16, Nutcracker mechanisms, 16-1 Chapter 16. Examples of nutcracker mechanisms. Hemoglobin, cytochrome C and chymotrypsin were the first proteins to be used
Kinetics Catalysis y Enzymes
 Kinetics Catalysis Enzymes Catalysis involves lowering of the energy barrier ΔH ΔH A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation
Kinetics Catalysis Enzymes Catalysis involves lowering of the energy barrier ΔH ΔH A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation
Dental Biochemistry EXAM I
 Dental Biochemistry EXAM I August 29, 2005 In the reaction below: CH 3 -CH 2 OH -~ ethanol CH 3 -CHO acetaldehyde A. acetoacetate is being produced B. ethanol is being oxidized to acetaldehyde C. acetaldehyde
Dental Biochemistry EXAM I August 29, 2005 In the reaction below: CH 3 -CH 2 OH -~ ethanol CH 3 -CHO acetaldehyde A. acetoacetate is being produced B. ethanol is being oxidized to acetaldehyde C. acetaldehyde
Problems from Previous Class
 1 Problems from Previous lass 1. What is K m? What are the units of K m? 2. What is V max? What are the units of V max? 3. Write down the Michaelis-Menten equation. 4. What order of reaction is the reaction
1 Problems from Previous lass 1. What is K m? What are the units of K m? 2. What is V max? What are the units of V max? 3. Write down the Michaelis-Menten equation. 4. What order of reaction is the reaction
MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4
 MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
!n[a] =!n[a] o. " kt. Half lives. Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure of methyl isonitrile as a function of time!
![!n[a] =!n[a] o. kt. Half lives. Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure of methyl isonitrile as a function of time! !n[a] =!n[a] o. kt. Half lives. Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure of methyl isonitrile as a function of time!](/thumbs/77/76481346.jpg) Half lives Half life: t 1/2 t 1/2 is the time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to drop to half of its initial value. For the reaction A! products Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure
Half lives Half life: t 1/2 t 1/2 is the time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to drop to half of its initial value. For the reaction A! products Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure
Final Chem 4511/6501 Spring 2011 May 5, 2011 b Name
 Key 1) [10 points] In RNA, G commonly forms a wobble pair with U. a) Draw a G-U wobble base pair, include riboses and 5 phosphates. b) Label the major groove and the minor groove. c) Label the atoms of
Key 1) [10 points] In RNA, G commonly forms a wobble pair with U. a) Draw a G-U wobble base pair, include riboses and 5 phosphates. b) Label the major groove and the minor groove. c) Label the atoms of
Introduction and. Properties of Enzymes
 Unit-III Enzymes Contents 1. Introduction and Properties of enzymes 2. Nomenclature and Classification 3. Mechanism of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 4. Kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 5. Inhibition
Unit-III Enzymes Contents 1. Introduction and Properties of enzymes 2. Nomenclature and Classification 3. Mechanism of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 4. Kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 5. Inhibition
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR
 THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA 1 November 1, 2016 Mid-Term EXAMINATION PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR EXAMINATION:
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA 1 November 1, 2016 Mid-Term EXAMINATION PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR EXAMINATION:
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge. FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison
 BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
A) at equilibrium B) endergonic C) endothermic D) exergonic E) exothermic.
 CHEM 2770: Elements of Biochemistry Mid Term EXAMINATION VERSION A Date: October 29, 2014 Instructor: H. Perreault Location: 172 Schultz Time: 4 or 6 pm. Duration: 1 hour Instructions Please mark the Answer
CHEM 2770: Elements of Biochemistry Mid Term EXAMINATION VERSION A Date: October 29, 2014 Instructor: H. Perreault Location: 172 Schultz Time: 4 or 6 pm. Duration: 1 hour Instructions Please mark the Answer
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability
 Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents the lowest energy state for a
Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents the lowest energy state for a
Protein Folding & Stability. Lecture 11: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Protein Folding: What we know. Protein Folding
 Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Structure - Function Protein Folding: What we know 1). Amino acid sequence dictates structure. 2). The native structure represents
CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS
 CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS EM 1 2012/13 ERT 317 BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING Course details Credit hours/units : 4 Contact hours : 3 hr (L), 3 hr (P) and 1 hr (T) per week Evaluations Final
CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS EM 1 2012/13 ERT 317 BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING Course details Credit hours/units : 4 Contact hours : 3 hr (L), 3 hr (P) and 1 hr (T) per week Evaluations Final
4. The Michaelis-Menten combined rate constant Km, is defined for the following kinetic mechanism as k 1 k 2 E + S ES E + P k -1
 Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Course Goals for CHEM 202
 Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Dana Alsulaibi. Jaleel G.Sweis. Mamoon Ahram
 15 Dana Alsulaibi Jaleel G.Sweis Mamoon Ahram Revision of last lectures: Proteins have four levels of structures. Primary,secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Primary structure is the order of amino acids
15 Dana Alsulaibi Jaleel G.Sweis Mamoon Ahram Revision of last lectures: Proteins have four levels of structures. Primary,secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Primary structure is the order of amino acids
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of
 Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
Peptides And Proteins
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Proton Acidity. (b) For the following reaction, draw the arrowhead properly to indicate the position of the equilibrium: HA + K + B -
 Proton Acidity A01 Given that acid A has a pk a of 15 and acid B has a pk a of 10, then: (a) Which of the two acids is stronger? (b) For the following reaction, draw the arrowhead properly to indicate
Proton Acidity A01 Given that acid A has a pk a of 15 and acid B has a pk a of 10, then: (a) Which of the two acids is stronger? (b) For the following reaction, draw the arrowhead properly to indicate
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. 6 elements make up 99% of all living things
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. 6 elements make up 99% of all living things
Lecture 12. Metalloproteins - II
 Lecture 12 Metalloproteins - II Metalloenzymes Metalloproteins with one labile coordination site around the metal centre are known as metalloenzyme. As with all enzymes, the shape of the active site is
Lecture 12 Metalloproteins - II Metalloenzymes Metalloproteins with one labile coordination site around the metal centre are known as metalloenzyme. As with all enzymes, the shape of the active site is
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
BMB Lecture 2
 BMB 178 2018 Lecture 2 How to map transition state Covalent Catalysis How to Map Transition States 1. Linear Free Energy Relationship 2. Kinetic Isotope Effects 3. Transition state analogues Linear Free
BMB 178 2018 Lecture 2 How to map transition state Covalent Catalysis How to Map Transition States 1. Linear Free Energy Relationship 2. Kinetic Isotope Effects 3. Transition state analogues Linear Free
Enzymes are macromolecules (proteins) that act as a catalyst
 Chapter 8.4 Enzymes Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers Even though a reaction is spontaneous (exergonic) it may be incredibly slow Enzymes cause hydrolysis to occur at a faster
Chapter 8.4 Enzymes Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers Even though a reaction is spontaneous (exergonic) it may be incredibly slow Enzymes cause hydrolysis to occur at a faster
Conformational Analysis
 Conformational Analysis C01 3 C C 3 is the most stable by 0.9 kcal/mole C02 K eq = K 1-1 * K 2 = 0.45-1 * 0.048 = 0.11 C04 The intermediate in the reaction of 2 has an unfavorable syn-pentane interaction,
Conformational Analysis C01 3 C C 3 is the most stable by 0.9 kcal/mole C02 K eq = K 1-1 * K 2 = 0.45-1 * 0.048 = 0.11 C04 The intermediate in the reaction of 2 has an unfavorable syn-pentane interaction,
Biotechnology of Proteins. The Source of Stability in Proteins (III) Fall 2015
 Biotechnology of Proteins The Source of Stability in Proteins (III) Fall 2015 Conformational Entropy of Unfolding It is The factor that makes the greatest contribution to stabilization of the unfolded
Biotechnology of Proteins The Source of Stability in Proteins (III) Fall 2015 Conformational Entropy of Unfolding It is The factor that makes the greatest contribution to stabilization of the unfolded
B O C 4 H 2 O O. NOTE: The reaction proceeds with a carbonium ion stabilized on the C 1 of sugar A.
 hbcse 33 rd International Page 101 hemistry lympiad Preparatory 05/02/01 Problems d. In the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond, the glycosidic bridge oxygen goes with 4 of the sugar B. n cleavage, 18 from
hbcse 33 rd International Page 101 hemistry lympiad Preparatory 05/02/01 Problems d. In the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond, the glycosidic bridge oxygen goes with 4 of the sugar B. n cleavage, 18 from
Previous Class. Today. Cosubstrates (cofactors)
 Previous Class Cosubstrates (cofactors) Today Proximity effect Basic equations of Kinetics Steady state kinetics Michaelis Menten equations and parameters Enzyme Kinetics Enzyme kinetics implies characterizing
Previous Class Cosubstrates (cofactors) Today Proximity effect Basic equations of Kinetics Steady state kinetics Michaelis Menten equations and parameters Enzyme Kinetics Enzyme kinetics implies characterizing
Class Business. I will have Project I graded by the end of the week. The discussion groups for Project 2 are cancelled
 Quiz 1 Class Business I will have Project I graded by the end of the week. Project 2 is due on 11/15 The discussion groups for Project 2 are cancelled There is additional reading for classes held on 10/30
Quiz 1 Class Business I will have Project I graded by the end of the week. Project 2 is due on 11/15 The discussion groups for Project 2 are cancelled There is additional reading for classes held on 10/30
Ch. 3 Metabolism and Enzymes
 Ch. 3 Metabolism and Enzymes Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions that enable energy to flow through
Ch. 3 Metabolism and Enzymes Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions that enable energy to flow through
Answers to Chapter 6 (in-text & asterisked problems)
 Introduction to Bioorganic Chemistry and Chemical Biology 1 Answers to Chapter 6 (intext & asterisked problems) Answer 6.1 olve the equation. Convert temperature in C to K by adding 273. Plug the numbers
Introduction to Bioorganic Chemistry and Chemical Biology 1 Answers to Chapter 6 (intext & asterisked problems) Answer 6.1 olve the equation. Convert temperature in C to K by adding 273. Plug the numbers
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
