This place covers: Electrolytic production of inorganic compounds, of non-metals and of organic compounds
|
|
|
- Gyles Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C25B ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF COMPOUNDS OR NON-METALS; APPARATUS THEREFOR (anodic or cathodic protection C23F 13/00; single-crystal growth C30B) Electrolytic production of inorganic compounds, of non-metals and of organic compounds Electrogenerative processes, i.e. processes for producing compounds in which simultaneously electricity is generated Electrophoretic production of compounds or non-metals Cells or assemblies of cells, constructional parts of cells, assemblies of constructional parts, e.g. electrode-diaphragm assemblies, as long as they are used in or suitable for one of the above production methods Electrodes, manufacture thereof not otherwise provided for, as long as they are used in or suitable for one of the above production methods Diaphragms, spacing elements, as long as they are used in or suitable for one of the above production methods Operating or servicing of cells, as long as this operating or servicing is part of one of the above production methods Relationships with other classification places The compounds of particular interest are also classified in the relevant classes, C01 (inorganic chemistry), C07 (organic chemistry), C07F (organo-metallic compounds ), and C08 (polymer chemistry ). Multi-step processes for surface treatment of metallic material involving at least one process provided for in class C23 and at least one process provided for in class C25 are classified in group C23F 17/00. Reversible fuel cells which act as electrolyzer, are classified in H01M 8/18. Production of dissolved species for purposes of water or waste water treatment is classified in C02F 1/46 and subgroups. The electrolytic or electrophoretic purification of materials is classified according to the nature of the liquid-material, e.g. water, electrolytes, processes solutions in the relevant places, e.g. A01K 63/00, C02F 1/46, C25B 15/08,C25D 21/16, C25F 7/02 Cold fusion method as such is classified in G21B 3/00 but electrodes and cells for the cold fusion are further classified in C25B. An electrothermal treatment of ores or metallurgical products for obtaining metals or alloys is classified in C22B 4/00 and does not involve an electrolytic process. Alloys as such, prepared by electrolytic methods are classified in C22C. 1
2 C25B (continued) Treating of water, waste water etc. by electrochemical methods, cells and electrodes therefor C02F 1/46 Separation or purification of peptides, e.g. of proteins, by electrophoresis C07K 1/26 Inhibiting corrosion of metals by anodic or cathodic protection C23F 13/00 Single crystal growth C30B Methods or apparatus for disinfecting or sterilising A61L 2/03, A61L 2/035 Making harmful compounds harmless by subjecting to electrochemical processes, electrodialysis A62D 3/11 Electrodialysis, electroosmosis B01D13/02, B01D 61/42 Gas separation, using electrochemical methods B01D 53/326 Separation, other than separation of solids, by electrophoresis B01D 61/42 Catalysts Processes employing the direct application of electric energy (i.e. electrochemical processes); Apparatus therefor Separation of hydrogen or hydrogen containing gases from gaseous mixtures B01J B01J 19/08 C01B 3/50 Carbon masses C01B 32/00, C04B 35/52 Electrochemical sensors G01N 27/00 Cold fusion, the method as such (however, cells and electrodes are classified in C25B) Electrochemical processes or apparatus for generating energy Semiconducting devices, photovoltaic cells as conversion devices, sources of energy (in particular for water electrolysis) G21B 3/00 H01M H02S 40/44 Special rules of classification Classification in C25B is always according to the last place priority rule. C25B concerns the production of compounds or non-metals, which includes separating the said products as such, or at least the possibility to separate them. Illustrative example: 1) Electrolysis of sodium chloride developing chlorine gas which is collected as a product is covered by C25B. 2) Electrolysis of water comprising sodium chloride which forms chlorine / hypochlorite in solution for disinfection is not covered by C25B. As a consequence, the electrolytic cells and parts of cells in case 1) are covered by C25B as well, while the electrolytic cells and parts of cells in case 2) are not. There are of course cases which are covered by C25B and another subclass or subgroup. 2
3 C25B (continued) Monopolar electrode Bipolar electrode Electrode which is connected to a power source and thus acts either as an anode or as a cathode Field electrode, i.e. an electrode which is positioned in the electrical field between a monopolar anode and a monopolar cathode without being itself connected to a power source. Through the action of the electrical field the side of the bipolar electrode which faces the cathode acts as an anode and the other side which faces the anode acts as a cathode Synonyms and Keywords In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used: Diaphragm MEA DSE DSA GDE Membrane Membrane Electrode Assembly Dimensionally Stable Electrode Dimensionally Stable Anode Gas Diffusion Electrode C25B 1/00 Electrolytic production of inorganic compounds or non-metals Electrolytic production of all those inorganic compounds or non metals which do not fall within the scope of one of the subgroups of C25B 1/00, e.g. electrolytic preparation of ammonia. Specific compounds like hydrogen, oxygen, silicon, ozone, alkali metal compounds, inorganic acida, per-compounds, etc are classified in the subgroups of C25B 1/00. C25B 1/003 {by photo-electrolysis with or without external current source} Photo-electrolysis process only. Photocatalysts B01J 35/004 Light-sensitive devices, e.g. panels or arrays of photoelectrochemical cells H01G 9/20 Photoelectrochemical cells H01M 14/005 3
4 C25B 1/003 (continued) Special rules of classification Distinction is to be done between a photoelectrolytic process or cell with two electrodes (even without externally applied voltage), and a photolytic process or cell with a single electrode where the process is catalyzed by a substance producing photoelectrons. C25B 1/02 of hydrogen or oxygen Electrolytic production of hydrogen or oxygen. Separation of hydrogen or hydrogen containing gases from gaseous mixtures, e.g. hydrogen electrochemical pumps Engines or plants characterised by use of other specific gases, e.g. oxyhydrogen (even when produced by an electrolytic cell) Engine-pertinent apparatus for supplying combustion engine with gas, e.g. hydrogen or oxygen, the apparatus having means for preparing such gas (even when the means is an electrolytic cell) C01B 3/50 F02B 43/10 F02M 25/12 Special rules of classification Only details of the electrolytic production process present in the document are classified. A simple reference to the presence of an electrolytic cell, or hydrogen produced by electrolysis, does not justify classification in C25B. C25B 1/04 by electrolysis of water Electrolysis of water with production of hydrogen and oxygen from water at the anode and cathode even when this water comprises an electroconductive additive, such as a hydroxide or an acid. Steam electrolysis is also covered. C25B 1/10 in diaphragm cells Electrolytic production of hydrogen or oxygen by electrolysis of water using diaphragm cells, the diaphragm being a barrier between electrodes, e.g. membrane,separator. 4
5 C25B 1/10 (continued) Reversible fuel cells H01M 8/18 C25B 1/12 in pressure cells Electrolytic production of hydrogen or oxygen by electrolysis of water using cells under pressure, e.g. high pressure water electrolysis system Reversible fuel cells H01M 8/18 C25B 1/13 of ozone Disinfecting / sterilising using electric current or electrolysis A02L/03, A02L/03E Disinfecting / sterilising with "dental water" A61C 1/0076 Production of dissolved species for treating of water, waste water etc. by electrochemical methods, cells and electrodes therefor C02F 1/467 C25B 1/24 of halogens or compounds thereof Production of dissolved species for treating of water, waste water etc. by electrochemical methods, cells and electrodes therefor C02F 1/467 5
6 C25B 1/28 of per-compounds Electrolytic production of per-compounds (per-compounds being defined in the glossary of terms). Disinfecting / sterilising using electric current or electrolysis A02L/03, A02L/03E Disinfecting / sterilising with "dental water" A61C 1/0076 Treatment of water and waste water by electrochemical disinfection C02F 1/4672 per-compounds compounds with oxyanions. When an element fors 4 oxyanions, the hypo and per prefexies are used in conjuntion with -ite or -ate suffixes, "per" being used to indicate more oxygen C25B 3/00 Electrolytic production of organic compounds Production of organic compounds by an electrolytic reaction. Electrolytic polymerization C08G 61/00 Production of hydrocarbons from hydrogen (even when produced by an electrolytic cell) and carbon monoxide Production of hydrocarbons from hydrogen (even when produced by an electrolytic cell) and carbon dioxide C10G 2/30 C10G 2/50 Electrocoating a substrate with an organic material C25D 9/02 Engines or plants characterised by use of other specific gases, e.g. oxyhydrogen (even when produced by an electrolytic cell) Engine-pertinent apparatus for supplying combustion engine with gas, e.g. hydrocarbon gas, the apparatus having means for preparing such gas (even when the means is an electrolytic cell) F02B 43/10 F02M 25/12 6
7 C25B 3/00 (continued) Oxidation and reduction Coupling oxidation or reduction directly at the organic molecule reaction without oxidation or reduction directly at the organic molecule, e.g. a Kolbe reaction C25B 5/00 Electrogenerative processes, i.e. processes for producing compounds in which simultaneously electricity is generated Processes when electricity is generated while a compound is produced other than water, e.g. hydrogen peroxide C25B 7/00 Electrophorectic production of compounds or non-metals (separation or purification of peptides, e.g. of proteins, by electrophoresis C07K 1/26) Production of compounds or non-metals where the process includes a step of reduction or oxidation of the material from which the compound or non-metals is formed, e.g. formation of a polymer. Separation or purification of peptides, e.g. of proteins, by electrophoresis C07K 1/26 Electrocoating, when the coating is only deposited and not produced by an electrolytic reaction C25D 13/04 C25B 9/00 Cells or assemblies of cells; Constructional parts of cells; Assemblies of constructional parts, e.g. electrode-diaphragm assemblies Cells, assembly of cells, assemblies of constructional parts used for the electrolytic production processes which are defined in other subgroups of C25B. 7
8 C25B 9/00 (continued) Devices for the electrolytic treatment of water or sewage C02F 1/46104 The combination of an electrolytic cell with a combustor to improve combustion. F02B 43/10 Electrolytic cells for electroplating C25D 17/00 Reversible fuel cells H01M 8/18 Grouping of such cells into batteries arranging plural cells such that they form a pile (not to form a storage battery) C25B 9/04 Devices for current supply (electrical connections in general H01R); Electrode connections; Electric inter-cell connections Devices and connections which are monopolar. Bipolar plates for electrolytic cells C25B 9/203 Electrical connections in fuel cells or storage batteries H01M 8/02, H01M 2/20 Electrical connections in general H01R 8
9 C25B 9/06 Cells comprising dimensionally-stable non-movable electrodes; Assemblies of constructional parts thereof Cells and their construction comprising electrodes that are not sacrificial. Dimensionally-stable electrode an electrode that is not intended to dissolve upon electrolysis (not a sacrificial electrode) C25B 9/063 {including bipolar electrodes} Cells and their construction comprising bipolar electrodes that are not sacrificial Bipolar electrode Field electrode, i.e. an electrode which is positioned in the electrical field between a monopolar anode and a monopolar cathode without being itself connected to a power source. Through the action of the electrical field the side of the bipolar electrode which faces the cathode acts as an anode and the other side which faces the anode acts as a cathode C25B 9/10 including an ion-exchange membrane in or on which electrode material is embedded Membrane-electrode assemblies (MEA). 9
10 C25B 9/12 Cells or assemblies of cells comprising at least one movable electrode, e.g. rotary electrodes; Assemblies of constructional parts thereof Movable electrode, be it electrodes that move in space or electrodes that move around an axis, such as rotary electrodes. C25B 9/16 Cells or assemblies of cells comprising at least one electrode made of particles; Assemblies of constructional parts thereof Electrodes comprising a bed of electrically conductive particles which are arranged such that they at least temporarily touch each other and an electrical conductor (a net, a plate etc.) which provides connection to a power source. Electrodes in particulate form for treatment of water or waste water or sewage C02F 1/46114 C25B 9/162 {comprising fluidised bed electrodes} Electrodes that comprise a bed of electrically conductive particles which are in motion, such that they only temporarily touch each other and the electrical conductor. C25B 9/166 {comprising static bed electrodes} Electrodes that comprise a bed of electrically conductive particles which rest, such that they continually touch each other and the electrical conductor. Synonyms and Keywords In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms: " fixed bed electrode " and " static bed electrode " 10
11 C25B 9/18 Assemblies comprising a plurality of cells ({C25B 9/005 takes precedence}; assemblies of cells with movable electrodes C25B 9/12; assemblies of cells with electrodes made of particles C25B 9/16) Assemblies of cells with movable electrodes C25B 9/12 Assemblies of cells with electrodes made of particles C25B 9/16 Special rules of classification C25B 9/005 takes precedence. C25B 9/20 of the filter-press type Stack of a plurality of cells in series, as in a filter press, e.g. electrodes are arranged vertically in a stack of vertical frames defining the electrolysis chamber(s) Filter-press type cells generally consist of a stack of vertical frames which define electrolysis chambers in which electrodes are arranged vertically C25B 9/203 {with bipolar electrodes} Stacks of a plurality of cells with bipolar electrodes, as in a filter press. Bipolar electrode field electrode, i.e. an electrode which is positioned in the electrical field between a monopolar anode and a monopolar cathode without being itself connected to a power source. Through the action of the electrical field the side of the bipolar electrode which faces the cathode acts as an anode and the other side which faces the anode acts as a cathode 11
12 C25B 11/00 Electrodes; Manufacture thereof not otherwise provided for Electrodes used for the electrolytic or electrochemical production processes which are defined somewhere in C25B. Electrodes for treatment of water or sewage C02F 1/46109 Photoelectrodes B01J 35/004 Electrodes for electrowinning C25C 7/02 Electrodes for electroplating C25D 17/10 Electrodes for storage batteries H01M 4/00 Electrodes for fuel cells H01M 4/86 Special rules of classification The electrodes corresponding to IPC C25B11/06 - C25B11/10 are classified in C25B 11/04. C25B 11/02 characterised by shape or form Special forms of electrodes, such a Venetian blinds, expandable electrodes. C25B 11/03 perforated or foraminous Perforated or foraminous structures, e.g. expandable metal. 12
13 C25B 11/035 {Porous electrodes} Gas diffusion electrodes (GDE) H01M 4/86, H01M 8/02 C25B 11/0405 {of electrodes having a substrate and a coating} Substrate Coating the bulk of the electrode, also including inevitable oxide layers which are present in particular on the valve metals all layers on the substrate, i.e. not only the electrocatalytic coating (which is usually on top and in contact with the electrolyte), but also intermediate layers (also those oxide layers which are not inevitable but formed on purpose on the substrate) C25B 11/12 Electrodes based on carbon (carbon masses in general C04B 35/52 ) {(C25B 11/0405 takes precedence)} Electrodes which have a carbon-based structure, e.g. carbon cloth. Diamond electrodes which are completely made of diamond, i.e. which are not a substrate with a diamond coating, are also covered Electrodes which comprise carbon either as the substrate or a coating C25B 11/0405 Diamond electrodes which comprise a diamond coating on a substrate C25B 11/0447 Diamond electrodes used in treatment of water, waste water etc. C02F 1/46109, C02F 2001/46133 Carbon masses C04B 35/52 13
14 C25B 11/16 Electrodes based on manganese dioxide or lead dioxide {(C25B 11/0405 takes precedence)} Electrodes which comprise manganese dioxide or lead dioxide either as the substrate or a coating C25B 11/0405 C25B 11/18 Mercury or amalgam electrodes {(C25B 11/0405 takes precedence)} Electrodes which comprise mercury or amalgam either as the substrate or a coating C25B 11/0405 C25B 13/00 Diaphragms; Spacing elements Structural material used to separate the electrodes of an electrolytic or electrophoretic cell, thereby forming two or more compartments, allowing the flow of an electrolytic solution or the migration of particular ions, but preventing the complete intermising of the two solutions of the migration of all kinds of ions. Membranes for separation processes B01D 67/00- B01D 71/00 Membranes for electrolytic production, recovery or refining of metals or alloys C25C 7/04 Membranes for fuel cells H01M 8/0289 Synonyms and Keywords In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms: "diaphragm " and " membrane" 14
15 C25B 13/04 characterised by the material Solid state electrolytes for fuel cells, characterized by the electrolyte material H01M 8/1016, H01M 2300/0088, H01M 2300/0065 C25B 13/08 based on organic materials Relationships with other classification places Organic polymer membranes when the emphasis is on the polymer electrolyte compound are classified in C08J 5/22, and in H01M 8/1018 or H01M 2300/0082 if the polymer electrolyte compound is used in fuel cells. C25B 15/00 Operating or servicing of cells Operating or servicing of cells when generally applied to a cell or in a process of C25B. When related to a specific process only, the operating or servicing is classified with the process, e.g. decomposition of amalgam which is process-related and therefore classified in C25B 1/42. C25B 15/02 Process control or regulation (controlling or regulating in general G05) Controlling or regulating in general G05 C25B 15/04 Regulation of the inter-electrode distance (electro-machining B23P) Relationships with other classification places Regulation of the inter-electrode distance in electrochemical machining, electrolytic grinding and electro-erosion is classified in B23H. 15
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 B03C MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS (filters making use of electricity or magnetism B01D 35/06; separating
B03C MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS (filters making use of electricity or magnetism B01D 35/06; separating
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 492 DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 PROJECT RP0508
 EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 492 The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) DEFINITIONS:
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 492 The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) DEFINITIONS:
INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE
 CPC - C05D - 2017.08 C05D INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE Fertiliser compositions containing potassium, calcium, magnesium and others, including
CPC - C05D - 2017.08 C05D INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE Fertiliser compositions containing potassium, calcium, magnesium and others, including
Chapter 18. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
Angel International SchoolManipay
 Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Proportions to find moles Correctly organized Example. Problem
 Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in grams Set
Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in grams Set
4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes. Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3. C2.1.1a Structure and bonding
 Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Name Date Class ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 21.1 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Section Review Objectives Use the activity series to identify which metal in a pair is more easily oxidized Identify the source of electrical energy in a voltaic cell Describe
21.1 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Section Review Objectives Use the activity series to identify which metal in a pair is more easily oxidized Identify the source of electrical energy in a voltaic cell Describe
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Reactions continued. And chemical review!!
 Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical reaction Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in
Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical reaction Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources)
 Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources) 1. Primary (single-discharge) batteries. => finite quantity of the reactants 2. Secondary or rechargeable batteries => regeneration of the original reactants by
Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources) 1. Primary (single-discharge) batteries. => finite quantity of the reactants 2. Secondary or rechargeable batteries => regeneration of the original reactants by
Electrolysis. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations. Score: /48. Percentage: /100
 Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
C01C. References. Limiting references CPC - C01C This place does not cover: Exceptions to the last appropriate place rule:
 C01C AMMONIA; CYANOGEN; COMPOUNDS THEREOF ({metal hydrides, monoborane, diborane or addition complexes thereof C01B 6/00}; salts of oxyacids of halogens C01B 11/00; peroxides, salts of peroxyacids C01B
C01C AMMONIA; CYANOGEN; COMPOUNDS THEREOF ({metal hydrides, monoborane, diborane or addition complexes thereof C01B 6/00}; salts of oxyacids of halogens C01B 11/00; peroxides, salts of peroxyacids C01B
Student Achievement. Chemistry 12
 Student Achievement Chemistry 12 Key Elements: Reaction Kinetics Estimated Time: 14 16 hours By the end of this course, students will be able to explain the significance of reaction rates, demonstrate
Student Achievement Chemistry 12 Key Elements: Reaction Kinetics Estimated Time: 14 16 hours By the end of this course, students will be able to explain the significance of reaction rates, demonstrate
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY
![MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY](/thumbs/90/103695152.jpg) MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet I Term I Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY 1. The diagram shows how aluminium is manufactured by electrolysis. What are the anode and
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet I Term I Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY 1. The diagram shows how aluminium is manufactured by electrolysis. What are the anode and
Two Types of Reactions. Chemistry Review. Hydronium Ion. Acid-Base Reactions. Acid-Base reactions Oxidation-Reduction reactions
 Two Types of Reactions Chemistry Review Acid-Base reactions Oxidation-Reduction reactions Chapter 18 Review Questions Will be EXTRA CREDIT Acid-Base Reactions Hydronium Ion Transfer of hydrogen ions protons
Two Types of Reactions Chemistry Review Acid-Base reactions Oxidation-Reduction reactions Chapter 18 Review Questions Will be EXTRA CREDIT Acid-Base Reactions Hydronium Ion Transfer of hydrogen ions protons
GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry. GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry. GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry. Bonding. GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry
 Particle Model and Atomic Structure The following symbols describe two different substances. Deduce all the information you can from these symbols. 13 C 12 6 6 C 1 Particle Model and Atomic Structure The
Particle Model and Atomic Structure The following symbols describe two different substances. Deduce all the information you can from these symbols. 13 C 12 6 6 C 1 Particle Model and Atomic Structure The
Elements,Compounds and Mixtures
 BASIC CONCEPTS: Elements,s and s 1. The smallest fundamental particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element is called an atom. 2. A pure substance that cannot be split up into
BASIC CONCEPTS: Elements,s and s 1. The smallest fundamental particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element is called an atom. 2. A pure substance that cannot be split up into
Today s Objectives: and an electrolytic cell. standard cell potentials. Section 14.3 (pp )
 Today s Objectives: 1. Identify the similarities and differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell 2. Predict the spontaneity of REDOX reactions based on standard cell potentials. 3. Recognize
Today s Objectives: 1. Identify the similarities and differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell 2. Predict the spontaneity of REDOX reactions based on standard cell potentials. 3. Recognize
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR (preparation of carboxylic acid esters by telomerisation C07C 67/47; telomerisation C08F)
 CPC - C07B - 2017.08 C07B GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR (preparation of carboxylic acid esters by telomerisation C07C 67/47; telomerisation C08F) General methods for the preparation
CPC - C07B - 2017.08 C07B GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR (preparation of carboxylic acid esters by telomerisation C07C 67/47; telomerisation C08F) General methods for the preparation
Chemistry Review. Chapter 18 Review Questions Will be EXTRA CREDIT
 Chemistry Review Chapter 18 Review Questions Will be EXTRA CREDIT Two Types of Reactions Acid-Base reactions Oxidation-Reduction reactions Acid-Base Reactions Transfer of hydrogen ions protons Makes water
Chemistry Review Chapter 18 Review Questions Will be EXTRA CREDIT Two Types of Reactions Acid-Base reactions Oxidation-Reduction reactions Acid-Base Reactions Transfer of hydrogen ions protons Makes water
In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium salt to produce potassium
 Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
CHLORINE PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM. Report No. 61A. Supplement A. by YEN CHEN YEN. May A private report by the STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Report No. 61A CHLORINE Supplement A by YEN CHEN YEN May 1074 A private report by the PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE I I MENLO PARK, CALIFORNIA CONTENTS 1 2 3 INTRODUCTION... 1 SUMMARY...
Report No. 61A CHLORINE Supplement A by YEN CHEN YEN May 1074 A private report by the PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE I I MENLO PARK, CALIFORNIA CONTENTS 1 2 3 INTRODUCTION... 1 SUMMARY...
Same theme covered in Combined but extra content Extra parts atomic symbols (first 20, Group 1 and Group 7)
 Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 17 Electrochemistry 17.1 Galvanic Cells A. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Rxns) 1. Oxidation = loss of electrons a. the substance oxidized is the reducing agent 2. Reduction = gain of electrons
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry 17.1 Galvanic Cells A. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Rxns) 1. Oxidation = loss of electrons a. the substance oxidized is the reducing agent 2. Reduction = gain of electrons
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/659.959 Filing Date 12 September 2000 Inventor Maria G. Medeiros Catherine L. Marsh James R. Moden Hubert G. Meunier NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing.
Serial Number 09/659.959 Filing Date 12 September 2000 Inventor Maria G. Medeiros Catherine L. Marsh James R. Moden Hubert G. Meunier NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing.
STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL
 STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL NEED TO KNOW SHEETS (BASED ON 1998 2006 EXAMS) TOPIC NO 1 -ide means two elements only ate/-ite means two elements + oxygen a solution contains a solid (solute)
STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL NEED TO KNOW SHEETS (BASED ON 1998 2006 EXAMS) TOPIC NO 1 -ide means two elements only ate/-ite means two elements + oxygen a solution contains a solid (solute)
for sodium ion (Na + )
 3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and recall names used for these inter-conversions
 Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST
 GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox)
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
KASSU JOINT EVALUATION EXAMINATION
 Name:... Index No.:... 233/1 CHEMISTRY Paper 1 THEORY JUNE 2016 Time: 2 hours Adm No:.. Candidate s Signature:... Date:... KASSU JOINT EVALUATION EXAMINATION Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education CHEMISTRY
Name:... Index No.:... 233/1 CHEMISTRY Paper 1 THEORY JUNE 2016 Time: 2 hours Adm No:.. Candidate s Signature:... Date:... KASSU JOINT EVALUATION EXAMINATION Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education CHEMISTRY
Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization.
 Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY T.Y.B.Sc Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization. Ans. The phenomenon of reverse e.m.f. brought about by the presence of product of electrolysis
Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY T.Y.B.Sc Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization. Ans. The phenomenon of reverse e.m.f. brought about by the presence of product of electrolysis
Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Method
 Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Method Ri Kwang Il, Kim Dok Sung, Pak Chol Min, YongSon Hong * Faculty of Chemistry, Kim Il Sung University, D.P.R.K Corresponding author.* E-mail address:
Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Method Ri Kwang Il, Kim Dok Sung, Pak Chol Min, YongSon Hong * Faculty of Chemistry, Kim Il Sung University, D.P.R.K Corresponding author.* E-mail address:
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Lesson Aiming for 4 Aiming for 6 Aiming for 8. I can use the periodic table to find the relative atomic mass of all elements.
 Chemical calculations C4.1 Relative masses and moles I can use the periodic table to identify the relative atomic mass for the first 20 elements. I can calculate the relative formula mass for familiar
Chemical calculations C4.1 Relative masses and moles I can use the periodic table to identify the relative atomic mass for the first 20 elements. I can calculate the relative formula mass for familiar
Chapter 7. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 7 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chapter Map Oxidation Historically oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn 2Zn 2+ + 4e O + 2e O 2 or O 2 + 4e 2O 2 Oxidation
Chapter 7 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chapter Map Oxidation Historically oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn 2Zn 2+ + 4e O + 2e O 2 or O 2 + 4e 2O 2 Oxidation
2) How is hydrogen formed at the cathode? Write a balanced half-equation for this reaction.
 Investigation 10 The Electrolysis Of Aqueous Sodium Chloride 48 In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, except in the exceptional case of using a mercury cathode, hydrogen is the product at the
Investigation 10 The Electrolysis Of Aqueous Sodium Chloride 48 In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, except in the exceptional case of using a mercury cathode, hydrogen is the product at the
MC 17 C - 6 SECTION - I
 SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Oxidation Historically, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn
Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Oxidation Historically, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 166 DATE: FEBRUARY 1, 2016 PROJECT RP0297 H01M 8/2405
 EUROPEA PATET OFFICE U.S. PATET AD TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC OTICE OF CHAGES 166 DATE: FEBRUARY 1, 2016 The following classification changes will be effected by this otice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s)
EUROPEA PATET OFFICE U.S. PATET AD TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC OTICE OF CHAGES 166 DATE: FEBRUARY 1, 2016 The following classification changes will be effected by this otice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s)
possesses negative potential & undergoes oxidation preferably act as ANODE
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Introduction: Electrochemistry is the area of Chemistry dealing with the interconversion of electrical energy and chemical energy. There are many applications of this in every day life.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Introduction: Electrochemistry is the area of Chemistry dealing with the interconversion of electrical energy and chemical energy. There are many applications of this in every day life.
Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Electrolysis 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are ionic compounds? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Ionic compounds are made up of positive ions and negative ions. What
Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Electrolysis 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are ionic compounds? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Ionic compounds are made up of positive ions and negative ions. What
National 5 Chemistry
 St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes & Structure Section 3: Bonding & Properties of Substances Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing
St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes & Structure Section 3: Bonding & Properties of Substances Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 270 DATE: NOVEMBER 1, 2016 PROJECT RP0259. Action Subclass Group(s)
 EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) Title wording changes: H01L 21/18 H01L
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) Title wording changes: H01L 21/18 H01L
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
Reducing Agent = a substance which "gives" electrons to another substance causing that substance to be reduced; a reducing agent is itself oxidized.
 Oxidation = a loss of electrons; an element which loses electrons is said to be oxidized. Reduction = a gain of electrons; an element which gains electrons is said to be reduced. Oxidizing Agent = a substance
Oxidation = a loss of electrons; an element which loses electrons is said to be oxidized. Reduction = a gain of electrons; an element which gains electrons is said to be reduced. Oxidizing Agent = a substance
Electrochemistry. Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions).
 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction: Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions). Half Reactions Method for Balancing Redox Equations: Acidic solutions: 1.
Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction: Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions). Half Reactions Method for Balancing Redox Equations: Acidic solutions: 1.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
 B05D PROCESSES FOR APPLYING LIQUIDS OR OTHER FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL (apparatus for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces B05B, B05C; {coating of foodstuffs A23P 20/17,
B05D PROCESSES FOR APPLYING LIQUIDS OR OTHER FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL (apparatus for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces B05B, B05C; {coating of foodstuffs A23P 20/17,
Matter Properties and Changes. Chemistry the study of matter and energy What is Matter?? What isn t Matter??
 Matter Properties and Changes Chemistry the study of matter and energy What is Matter?? What isn t Matter?? Matter? Name some matter Matter? Matter? I. Properties of Matter Chemistry is the study of matter
Matter Properties and Changes Chemistry the study of matter and energy What is Matter?? What isn t Matter?? Matter? Name some matter Matter? Matter? I. Properties of Matter Chemistry is the study of matter
These subclasses are to be used according to the following general rules:
 CPC - B03D - 2017.08 B03D FLOTATION; DIFFERENTIAL SEDIMENTATION (sedimentation in general B01D 21/00; in combination with other separation of solids B03B; sink-float separation B03B 5/28; detergents, soaps
CPC - B03D - 2017.08 B03D FLOTATION; DIFFERENTIAL SEDIMENTATION (sedimentation in general B01D 21/00; in combination with other separation of solids B03B; sink-float separation B03B 5/28; detergents, soaps
Chapter 32. Electrolysis
 Chapter 32 Electrolysis 32.1 Electrolysis a type of redox reactions 32.2 Predicting preferential discharge of ions 32.3 Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid 32.4 Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
Chapter 32 Electrolysis 32.1 Electrolysis a type of redox reactions 32.2 Predicting preferential discharge of ions 32.3 Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid 32.4 Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
Elements and Reactivity Revision Notes
 Elements and Reactivity Revision Notes Elements There are just over 100 elements in the Periodic Table. Elements are made up of one type of atom. Every element has a name, atomic number and symbol. Element
Elements and Reactivity Revision Notes Elements There are just over 100 elements in the Periodic Table. Elements are made up of one type of atom. Every element has a name, atomic number and symbol. Element
Matter Properties and Changes
 Matter Properties and Changes What is matter? anything that takes up space (volume) and has mass everything around you is made up of matter matter has 3 main states: solid, liquid, and gas Physical Property
Matter Properties and Changes What is matter? anything that takes up space (volume) and has mass everything around you is made up of matter matter has 3 main states: solid, liquid, and gas Physical Property
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Chemistry Paper 2
 AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.6 The rate and extent of chemical change Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction over time, using either the quantity of reactant used or the quantity of product
AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.6 The rate and extent of chemical change Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction over time, using either the quantity of reactant used or the quantity of product
National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions
 National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions Unit 1 Chemical changes 1. Describe how temperature, concentration and particle size affect the rate of a chemical reaction- mention collision theory in your
National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions Unit 1 Chemical changes 1. Describe how temperature, concentration and particle size affect the rate of a chemical reaction- mention collision theory in your
Option C: Chemistry in industry and technology
 Option C: Chemistry in industry and technology As one of the most important roles of chemistry is to make forms of matter that have never existed before, it plays a central role in any material revolution.
Option C: Chemistry in industry and technology As one of the most important roles of chemistry is to make forms of matter that have never existed before, it plays a central role in any material revolution.
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4335/1F London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry Paper 1F Foundation Tier Monday 10 November 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4335/1F London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry Paper 1F Foundation Tier Monday 10 November 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) To pic. Student Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Dr. Anand Gupta
 By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
Paper Atomic structure and the periodic table
 Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
 Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry Redox Reactions (19.1) Galvanic Cells (19.2) Standard Reduction Potentials (19.3) Thermodynamics of Redox Reactions (19.4) The
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry Redox Reactions (19.1) Galvanic Cells (19.2) Standard Reduction Potentials (19.3) Thermodynamics of Redox Reactions (19.4) The
Based on the work you have completed in S1 to S3, complete Prior Learning 3.1.
 3.2: Metals In this chapter you will learn about the structure of pure metals, alloys and how they react with other substances. You will develop skills in the correct use of the SQA data booklet to create
3.2: Metals In this chapter you will learn about the structure of pure metals, alloys and how they react with other substances. You will develop skills in the correct use of the SQA data booklet to create
Review Chemistry Paper 1
 Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Electrochemistry and battery technology Contents
 Electrochemistry and battery technology Contents Introduction Redox overview voltaic cells, electrolytic cells, fuel cells, Primary and secondary batteries. Other batteries; Construction, working and applications
Electrochemistry and battery technology Contents Introduction Redox overview voltaic cells, electrolytic cells, fuel cells, Primary and secondary batteries. Other batteries; Construction, working and applications
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Learning goals and key skills: Identify oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent in a chemical equation Complete and balance redox equations using the method
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Learning goals and key skills: Identify oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent in a chemical equation Complete and balance redox equations using the method
Solar Matters III Teacher Page
 Solar Matters III Teacher Page Electrolysis of Water Student Objective The student: will be able to design and conduct an experiment to electrolyze water into hydrogen and oxygen will be able to describe
Solar Matters III Teacher Page Electrolysis of Water Student Objective The student: will be able to design and conduct an experiment to electrolyze water into hydrogen and oxygen will be able to describe
SCHOOL YEAR CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12
 SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Activity. Modeling the Fuel Cell Reaction. Overview. Advance Preparation. Background Information
 4 Activity 1-2 class sessions Modeling the uel Cell Reaction 2011 Regents of the University of California Overview n order to understand the chemistry of fuel cells, students are introduced to oxidation-reduction
4 Activity 1-2 class sessions Modeling the uel Cell Reaction 2011 Regents of the University of California Overview n order to understand the chemistry of fuel cells, students are introduced to oxidation-reduction
5 Energy from chemicals
 5 Energy from chemicals Content 5.1 Enthalpy 5.2 Hydrogen fuel cell Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) describe the meaning of enthalpy change in terms of exothermic (H
5 Energy from chemicals Content 5.1 Enthalpy 5.2 Hydrogen fuel cell Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) describe the meaning of enthalpy change in terms of exothermic (H
5. Electrolytic Processes
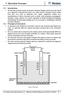 5.1 Introduction The fact that electrical energy can produce chemical changes and the processes based on it, called the electrolytic processes, are widely used for extraction of pure metals from their
5.1 Introduction The fact that electrical energy can produce chemical changes and the processes based on it, called the electrolytic processes, are widely used for extraction of pure metals from their
Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Process. The Galvanic Cell or Voltaic Cell
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5
 Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5 Lesson Specification learning outcomes Edexcel 360 Science Specification match Edexcel 360 Science GCSE Science Students Book page reference Additional information
Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5 Lesson Specification learning outcomes Edexcel 360 Science Specification match Edexcel 360 Science GCSE Science Students Book page reference Additional information
WHAT IS A BATTERY? way to store energy is through chemical bonds in substances, which is the basic
 WHAT IS A BATTERY? Energy cannot be destroyed or created, but it can be stored in various forms. One way to store energy is through chemical bonds in substances, which is the basic concept of fossil and
WHAT IS A BATTERY? Energy cannot be destroyed or created, but it can be stored in various forms. One way to store energy is through chemical bonds in substances, which is the basic concept of fossil and
CHEM 103 Aqueous Solutions
 CHEM 103 Aqueous Solut Lecture Notes February 28, 2006 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda What is a solution made of? Solubility of ionic compounds (salts), acids, and molecular compounds Exchange react that produce
CHEM 103 Aqueous Solut Lecture Notes February 28, 2006 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda What is a solution made of? Solubility of ionic compounds (salts), acids, and molecular compounds Exchange react that produce
C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you)
 Name: C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
Name: C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board. Class X Chemistry. Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
Electrochemistry. Galvanic Cell. Page 1. Applications of Redox
 Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Electrolysis. Introduction. Electrolysis APPENDIX. The key ideas required to understand this section are:
 Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
CARBON. Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA. Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California
 CARBON Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California A Wiley-Interscience Publicotion JOHN WILEY & SONS New York / Chichester / Brisbane
CARBON Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California A Wiley-Interscience Publicotion JOHN WILEY & SONS New York / Chichester / Brisbane
Electrochemical Cell
 Electrochemical Cell Construction of Voltaic Cells Notation for Voltaic Cells Cell Potential Standard Cell Potentials and Standard Electrode Potentials Equilibrium Constants from Cell Potentials Dependence
Electrochemical Cell Construction of Voltaic Cells Notation for Voltaic Cells Cell Potential Standard Cell Potentials and Standard Electrode Potentials Equilibrium Constants from Cell Potentials Dependence
Name... Index No... Candidate signature...
 Name.... Index No....... Candidate signature... Date:.. 233/1 CHEMISTRY Paper 1(THEORY) July / August 2018 Time: 2 Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Write your name and index number in the spaces provided
Name.... Index No....... Candidate signature... Date:.. 233/1 CHEMISTRY Paper 1(THEORY) July / August 2018 Time: 2 Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Write your name and index number in the spaces provided
8. Draw Lewis structures and determine molecular geometry based on VSEPR Theory
 Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620)
 www.xtremepapers.com Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620) Unit 11: Redox, electrochemistry and Group VII Recommended prior knowledge Students should have good understanding of the Periodic Table,
www.xtremepapers.com Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620) Unit 11: Redox, electrochemistry and Group VII Recommended prior knowledge Students should have good understanding of the Periodic Table,
11-1 Notes. Chemical Reactions
 11-1 Notes Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions In a chemical reaction 1 or more substances (the reactants) change into 1 or more new substances (the products). Reactants are always written on the left
11-1 Notes Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions In a chemical reaction 1 or more substances (the reactants) change into 1 or more new substances (the products). Reactants are always written on the left
Unit 12 Conduction in Liquids and Gases
 Conduction in Liquids and Gases Objectives: Define positive and negative ions. Discuss electrical conduction in gases. Discuss electrical conduction in a liquid. Discuss several of the ionization processes.
Conduction in Liquids and Gases Objectives: Define positive and negative ions. Discuss electrical conduction in gases. Discuss electrical conduction in a liquid. Discuss several of the ionization processes.
(i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of an atom is the number of...
 C2 Essential Questions Atomic Structure Q1.This question is about atomic structure and elements. (a) Complete the sentences. (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of
C2 Essential Questions Atomic Structure Q1.This question is about atomic structure and elements. (a) Complete the sentences. (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of
Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8. atom.
 Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
