Conversion Technologies Chemical and Catalytical Processing: Gas phase route
|
|
|
- Clare Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 st Brazil-U.S. Biofuels Short Course: Providing Interdisciplinary Education in Biofuels Technology July 27 - August 7, 2009 University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil Conversion Technologies Chemical and Catalytical Processing: Gas phase route Ricardo Reis Soares School of Chemical Engineering Federal University of Uberlandia rrsoares@ufu.br
2 Uberlandia?! Where is it?
3 utline bjectives General Background Glycerol as a block molecule Synthesis gas by low gas-phase glycerol aqueous solution reforming at low temperature Coupling the reforming and WGS for H 2 production Coupling the reforming and FTS for liquid fuel production Partial Conclusions Direct Sugar/Polyol Conversion New Biorefinery approach Integration of Reforming and Deoxygenation reactions C-C coupling reactions Partial Conclusions Conclusions Acknowledgements
4 Main bjective Chemical and Catalytical processing Platform Prof. Ulf Lecture Cellulosic derivatives Sugars This Lecture: Gas phase route Dr. Yuryi Lecture: HMF-based route Biomass Platform 1: Ethanol Platform 2: Thermochemical Fuels Chemicals/Commodities Energy Plastics and Polymers Dr. Lawrence Russo (U.S. Department of Energy) Seminar (Monday/27-July)
5 Heuristics for Chemical and Catalytical Processing Biomass Limit the number of processing steps Less operations = lower cost Use renewable reagents/solvents Minimize solvent use Use concentrated feeds Efficient product separation Spontaneous separation of hydrophobic products Cascades of flow reactors Facilitate transport between processing steps Integrated Processes Energy Balance & Thermodynamics Find good catalyst(s)
6 utline bjective General Background Glycerol as a block molecule Synthesis gas by low gas-phase glycerol aqueous solution reforming at low temperature Coupling the reforming and WGS for H 2 production Coupling the reforming and FTS for liquid fuel production Partial Conclusions Direct Sugar/Polyol Conversion New Biorefinery approach Integration of Reforming and Deoxygenation reactions C-C coupling reactions Partial Conclusions Conclusions Acknowledgements
7 Current proven processes using biomass feedstock Vegetable oils and animal fats Transesterification Fermentation (1) Cellulosic Carbohydrates Aqueous Ethanol (8 wt %) Distillation ($$$) Waste Glycerol Aqueous Glycerol (25-80 wt %) Fuel-Grade Ethanol Biodiesel Low Temperature Gas-Phase Processing Hydrogen GAL Syngas C + H 2 Water-Gas Shift Reaction Methanol Methanol Synthesis Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis (FTS) Chemicals Liquid Hydrocarbons (diesel, light naphta) Di-Methyl Ether (DME) (1) C. S. Gong, J. X. Du, N. J. Cao, G. T. Tsao, Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2000, 84-86,
8 Vegetable oils and animal fats Transesterification Waste Glycerol Biomass Feedstock Sorbitol (3) Aqueous Glycerol (25-80 wt %) (2) Prof. Ulf class Sugars (Hexoses) Biodiesel Low Temperature Gas-Phase Processing Hydrogen GAL Syngas C + H 2 Water-Gas Shift Reaction Methanol Methanol Synthesis Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis (FTS) Chemicals Liquid Hydrocarbons (diesel, light naphta) Di-Methyl Ether (DME) (2) Gallezot et al., Appl. Catal., A: General, v 331, p , 2007 (3) E. Tronconi et al.; Chem. Eng. Sci., 47(9-11), ,1992
9 Catalytic testing units - UFU
10 Catalyst Screening (T = 623 K, P = 1 bar, and 30 wt% Glycerol) Conversion to Ga as Phase (%) Pt/C H TF (m min -1 ) Pt/Ce 2 -Zr 2 Pt/Ce 2 -Zr 2 Pt/Al 2 3 Pt/Zr 2 Pt/Mg-Zr 2 Time on stream (h) Pt/C Pt/Mg-Zr 2 Pt/Al 2 3 Time on stream (h) Pt/Zr 2 From R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, J. A. Dumesic, Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2006, 45,
11 4 Catalyst Screening (T = 623 K, P = 1 bar, and 30 wt% Glycerol) (H 2 /C) mo olar ratio Pt/Al 2 3 Pt/Ce 2 -Zr 2 Pt/C Pt/Zr 2 C 3 H 8 3 3C + 4H 2 [H 2 /C] = 1.33 nly Glycerol decomposition takes place WGS takes place on the oxide-supported catalysts Time on stream (h) The WGS sites are blocked. Pt/Mg-Zr 2 From R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, J. A. Dumesic, Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2006, 45,
12 18 16 Catalyst Screening (T = 623 K, P = 1 bar, and 30 wt% Glycerol) (C 2 TF/ H 2 TF) X It suggests that one of the modes of catalyst deactivation is the coke formation by dehydration reactions Time on stream (h) From R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, J. A. Dumesic, Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2006, 45,
13 Pt/C stability at different reaction conditions Conversion to Ga as Phase (%) wt%, 1 bar 50 wt%, 1 bar 30 wt%, 20 bar Time (h) Molar Ra atio wt%, 1 bar 30 wt%, 1 bar 30 wt%, 20 bar C/C 2 H 2 /C Time (h) From R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, J. A. Dumesic, Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2006, 45,
14 Results from Initial Kinetics Measurements Pt/C (inert support) showed The best stability High activity and selectivity Support plays important role: Water-gas shift Deactivation However, for fuel and chemicals production: Can we carry out two reactions at same conditions (T,P) over either consecutive beds or in separate reactors?
15 What do we need to do? Find a catalyst that works in the T and P range of FT What is the problem? Pt/C shows low activity below 573 K and under pressure Θ C increases as T decreases (and P increases) What is a potential solution? Additive to weaken adsorption of C on Pt
16 DFT : C Adsorption on Near Surface Alloys Greeley & Mavrikakis, Catal. Today 111,, 52 (2006) Pt Good candidates! Pt/Ru Pt/Re Large BE gap Cu is not a good catalyst
17 Bimetallic catalyst screening (P = 1 bar and 30 wt% Glycerol) Glycerol Reactivity and Selectivity over Pt-Me/C bimetallic catalysts K 573K 548K 100 Gas phase carbon selectivity at 623K Conversion to gas pha ase (%) Gas phase carbon selec ctivity (%) Alkanes C2 C 0 Pt PtRu PtRe PtFe PtCu PtSn PtIr PtCo PtNi PtRh Pts Catalyst 0 Pt PtRu PtRe PtFe PtCu PtSn PtIr PtCo PtNi PtRh Pts Catalyst From E. L. Kunkes, R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, and J. A. Dumesic,; Applied Catalysis B, 90 (2009)
18 Bimetallic catalyst screening (P = 1 bar and 30 wt% Glycerol) Apparent Activation Energies measurements from Pt-Me/C bimetallic catalysts 6,5 6,0 5,5 E a =35 kj/mol ln C TF (min -1 ) 5,0 4,5 4,0 Pt PtCu PtRu PtRe E a =43 kj/mol E a =84 kj/mol 3,5 E a =93 kj/mol 3,0 0, , , , , , /T (1/K) Reaction mechanism may proceed differently on the Ru and Re promoted catalyst From E. L. Kunkes, R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, and J. A. Dumesic,; Applied Catalysis B, 90 (2009)
19 Glycerol Conversion to Synthesis Gas (Pt-Re/C with 30% Glycerol at 548 K and 8.3 bar) C/C 2 H 2 /C
20 Vegetable oils and animal fats Transesterification Advances in Biofuel production Fermentation Cellulosic Carbohydrates Aqueous Ethanol (8 wt %) Aqueous Ethanol Distillation (8 wt ($$$) %) Waste Glycerol Aqueous Glycerol (25-80 wt %) Fuel-Grade Ethanol Biodiesel Low Temperature Gas-Phase Processing Coupling: Syngas formation and FTS Hydrogen GAL Syngas C + H 2 Water-Gas Shift Reaction Methanol Methanol Synthesis Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis (FTS) Chemicals Liquid Hydrocarbons (diesel, light naphta) Di-Methyl Ether (DME)
21 Advances in Biofuel production Coupling Gasification & FT Synthesis Advantage: Heat integration 1 3C+4H C H 2.24C+4.48H 0.28C H +2.24H 0.28(C H +H C H ) 0.76(C+H C +H ) C H C H C H +0.76C +1.48H 3C +4H kcal/mol -81 kcal/mol -10 kcal/mol -7 kcal/mol -15 kcal/mol -354 kcal/mol From R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, J. A. Dumesic, Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2006, 45,
22 Heat Integration Glycerol/Water Glycerol Reformer Heat in = 242 kcal/mol Heat out = 99 kcal/mol Net heat = 143 kcal/mol Fischer-Tropsch Converter Synthesis gas Synthesis gas & water T = 275 o C P = 10 bar 30 wt% Glycerol H c = 354 kcal/mol Process heat 149 kcal/mol 24 kcal/mol 173 kcal/mol Water Combustion gases Water E out E in = 2.4 Liquid alkanes
23 Advances in Biofuel production Two-bed system : Glycerol + H 2 (30-80 wt%) Syngas formation & FTS X C = 30% Pt-Re/C 0,1 0,01 T = 548 K P tot = 8 bar H 2 :C = 2 S C5+ S CH4 S C2 C5+ = 38% S CH4 = 15% C2 = 4.5% C+H 2 + H 2 + xygenates 548 K 8 bar S /n cn 1E-3 1E-4 1E-5 α=0.8 Ru/Ti 2 1E n Liquid Fuel This method may allow for economic operation of a small-scale scale FT reactor by having a heat-integrated catalytic process. From D. A. Simonetti, J Rass-Hansen, E. L. Kunkes, R. R. Soares, and J. A. Dumesic, Green Chemistry,9, 2007,
24
25 Vegetable oils and animal fats Transesterification Advances in Biofuel production Fermentation Cellulosic Carbohydrates Aqueous Ethanol (8 wt %) Aqueous Ethanol Distillation (8 wt ($$$) %) Waste Glycerol Aqueous Glycerol (25-80 wt %) Fuel-Grade Ethanol Biodiesel Low Temperature Gas-Phase Processing Coupling: Syngas formation and WGS Hydrogen GAL Syngas C + H 2 Water-Gas Shift Reaction Methanol Methanol Synthesis Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis (FTS) Chemicals Liquid Hydrocarbons (diesel, light naphta) Di-Methyl Ether (DME)
26 Advantages: Heat Integration Net energy (kj / mol.glycerol) Reaction at 573 K with C combustion without C combustion Net energy = H (reforming) + H (glyc.+h 2 gasification) - H (products combustion) A maximum energy balance at 60 wt% glycerol A positive energy balance for glycerol concentration higher than 18 wt% wt% of glycerol in aqueous solution From E. L. Kunkes, R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, and J. A. Dumesic,; Applied Catalysis B, 90 (2009)
27 Results Two-beds system : Syngas formation & WGS Conversion to gas phase co onversion (%) wt% glycerol conversion at 573K 60 Conversion H 2 /C H2 /C Pt-Re/C C+H 2 +H 2 Glycerol + H 2 (80 wt%) 573 K Pt/CeZr Time on stream (hr) H 2 /C From E. L. Kunkes, R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, and J. A. Dumesic,; Applied Catalysis B, 90 (2009)
28 Results Two-beds system : Syngas formation & WGS wt% glycerol conversion at 573K Glycerol + H 2 (30 wt%) Conversion to gas phase con nversion (%) Conversion H 2 /C H2 /C Pt-Re/C C+H 2 +H 2 Pt/CeZr 573 K Time on stream (hr) H 2 /C 2 From E. L. Kunkes, R. R. Soares, D. A. Simonetti, and J. A. Dumesic,; Applied Catalysis B, 90 (2009)
29 Results Summary of the results of the coupled reactions Glycerol (wt %) Carbon Conversion (%) Alkane Selectivity (%) H 2 /C ratio H 2 Yield (%)
30 Partial Conclusions We showed that liquid fuels and chemicals can be produced from glycerol via a two-step gas-phase process that involves the catalytic conversion of glycerol to H 2 and C combined with subsequent water-gas shift and Fischer- Tropsch synthesis. The experimental results validated the Rational Design approach of the catalyst selection by using DFT simulations. This two-step process serves as an energy-efficient efficient alternative to current biomass-based based processes to produce fuels and chemicals. We showed that valuable chemicals can be produced from glycerol via one-step aqueous-phase reforming.
31 utline bjectives General Background Glycerol as a block molecule Synthesis gas by low gas-phase glycerol aqueous solution reforming at low temperature Coupling the reforming and WGS for H 2 production Coupling the reforming and FTS for liquid fuel production Partial Conclusions Direct Sugar/Polyol Conversion New Biorefinery approach Integration of Reforming and Deoxygenation reactions C-C coupling reactions Partial Conclusions Conclusions Acknowledgements E. L. Kunkes et al.; SCIENCE, 2008 Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe
32 Integration of reforming and deoxygenation 60 wt% Sorbitol C 6 H H 2 C 2 10 wt % Pt-Re/C 503 K 18 bar H 2, C x, Alkanes Acids H C 6 H 14 6 Alcohols 13H 2 C 4 -C 6 H 70-80% of H 2 from reforming is used in de-oxygenation C 6 H y z + H 2 Heterocyclics Ketones H 2 H 2 rearrangement H 2 H 2 cyclization H H H H Water Pt-Re chemistry H Sugar/Polyol H H H E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) H H * H 2 C -H cleavage H H 2 H 2 H H * * C - cleavage H H H H * * * * H H 2 +C 2 water-gas shift H 2 H 2 C -C cleavage * * * Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe C C C
33 Some facts Intermediate pressures and temperatures Provide the greatest yields of monofunctional products 60 wt% sorbitol conversion at 503K and 18 bar 1 kg of organic phase (sorb_503_18) for every 3.5 kg of sorbitol 70 % of maximum possible efficiency (complete balance between reforming and deoxygantion) Sorb_503_18 retains 65% of the energy in sorbitol feed Monofucntional hydrocarbons can be used directly Solvents, chemical intermediates, fuels and fuel additives C 6 is the limit? (C-C coupling processes) Gasoline additives (aromatics) Diesel and Jet fuels C 8 -C 12 E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe
34 Coupling of alkenes C-C C coupling Reactions R' H R" H + 500K R' R" + H 2 Dehydration H + R + R' R 523K R' Coupling R + R' + R" R H + 623K R" + H 2 Aromatization R' R R + H + 623K Alkylation E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe
35 Hydrogenation-Aromatization Sorb_503_18 (Active components) H H Ru/C 423K 50 bar H 2 H_Sorb_503_18 H H H 2 HZSM-5 673K 1 bar Aromatics and olefins 40 % conversion of Sorb_503_18 into fuel grade aromatics 29.4% C4 6.8% C % Benzene 14.3% Toluene 11.0% Xylenes and Ethylbenzene E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) % C3 1.1% C % C3-6 Substituted benzene
36 C-C C coupling Reactions (contd.) Aldol condensation-dehydration-hydrogenation R H - + H + + R' R R' R R' H H 2 Pd/Cu H K With H 2 co-feed Ketonization of carboxylic acids R R' R' + R H + /H - R' R H H + H 2 + C 2 E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe
37 Vapor phase aldol condensation Sorb_503_18 (Active components) H CuMg 10 Al 7 x 5 bar 573K H 2 Condensation products Pt/NbP 4 40 bar 523K H 2 Singly-branched C 8 -C 12 alkanes H 2 H 2 H Acid Neutralization Required acids deactivate basic catalyst! 6.2% C 8 7.9% C % C 10 ~40% conversion to C 8 -C % C 11 ~85% conversion of 2-ketones 28.8% C 6 8.2% C 12 E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe 25.8% C 4-5
38 Ketonization and Condensation 30.5% C 6 Gluc_483_18 (Active components) H H 7.7% C 7 H 2 C 2 Glucose-derived 100 % conversion organic: to C 7 -C35% 11 acids Ketonized Gluc_483_18 (Active components) Pd/CeZr x 5 bar 623K H 2 CeZr x H 20 bar 623K % C % C 9 H 10.1% C 7 C 7 -C 12 Linear and branched ketones 57% C 7+ products 12.5% 8.7% C C % C % C % C 4-5 E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) % C % C % C % C % C % C 12+ Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe
39 Partial Conclusions Strategy: Remove oxygen but retain some functionality Sugar/polyol conversion involves a balance between C-C C and C- cleavage reactions Endothermic C-C C cleavage (reforming) provides H 2 Exothermic C- cleavage (deoxygenation deoxygenation) consumes H 2 PtRe/C catalyzes both reactions (heat and H 2 integration in single reactor) Intermediate temperatures and pressures achieve maximum yield of mono-functional products High temperatures and pressures alkanes (non-functional) Low temperatures/pressures oxygenated aq. products Targeted C-C C coupling reactions yield fuel grade products E.L. Kunkes et al. Science (2008) Slides from E.L. Kunkes presented at 2008 AICHe
40 Conclusion : Chemical and Catalytic Platform will be an alternative for future biorefineries Fermentation BIETHANL Bagasse Trans and/or esterification of vegetable, edible oils and fatty acids Biodiesel Pyrolysis BIMASS Sugars Glycose Fructose Lactose Arabinose Sucrose Xylose Starch Polyol (Glicerol and Sorbitol) Syngas (C + H 2 ) Bio-oil ENERGY (Fuels) Acid hydrolysis (hemi) and Cellulose Biomass Residues (as bagasse) Chemicals
41 Acknowledgements U.S. Department of Energy (DE), ffice of Basic Energy Sciences, Chemical Sciences Division CAPES and UW for post-doctoral grants PETRBRAS and CBMM for FT financial support FAPEMIG and PETRBRAS for UFU Biofuel Research FULBRIGHT (THAIS CSER et al.) Catalytic Bio-Reforming Team Dante A Simonetti Prof. James A Dumesic Edward L Kunkes
42 Thank you! Questions?
43 The Reaction Network H H H 2 H 2 H 2 H H C-C Cleavage *CH x H2 C WGS H 2 C 2 H H H 2 Metal Methanation H 2 F-T Synthesis H 2 C- Cleavage (Dehydration) H 2 H H H H H H H H H H H H H H (Alkane precursors) C-C C Cleavage C- Cleavage H 2 H 2 CH 4 C 2 H 6
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Glycerol as a Source for Fuels and Chemicals by Low-Temperature Catalytic Processing Ricardo R. Soares, Dante A. Simonetti, and James A. Dumesic*
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Glycerol as a Source for Fuels and Chemicals by Low-Temperature Catalytic Processing Ricardo R. Soares, Dante A. Simonetti, and James A. Dumesic*
CATALYSTS FOR SELECTIVE CONVERSION OF PLANT CELL WALL POLYSACCHARIDES
 CATALYSTS FOR SELECTIVE CONVERSION OF PLANT CELL WALL POLYSACCHARIDES Nathan S. Mosier Associate Professor, Ag. and Bio. Engineering Purdue University 2014 Frontiers in Biorefining St. Simons Island, Georgia
CATALYSTS FOR SELECTIVE CONVERSION OF PLANT CELL WALL POLYSACCHARIDES Nathan S. Mosier Associate Professor, Ag. and Bio. Engineering Purdue University 2014 Frontiers in Biorefining St. Simons Island, Georgia
Sustainable Energy Technologies
 Sustainable Energy Technologies Molecular Heterogeneous Catalysis Hydrogen Technology Renewable feedstocks Fuel cell catalysis Prof. Dr. Emiel Hensen Prof. Dr. Peter Notten Prof. Dr. Jaap Schouten Chemical
Sustainable Energy Technologies Molecular Heterogeneous Catalysis Hydrogen Technology Renewable feedstocks Fuel cell catalysis Prof. Dr. Emiel Hensen Prof. Dr. Peter Notten Prof. Dr. Jaap Schouten Chemical
Biomass to Liquid OVERVIEW: RESEARCH TEAMS & THRUSTS. Page 266
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA Production of Liquid Fuels Biomass via Thermo-Chemical Conversion Processes PI: B. Joseph, USF; Co-PI s: Y. Goswami, V. Bhethanabotla, J. Wolan, V. Gupta Students: Ali Gardezi,
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA Production of Liquid Fuels Biomass via Thermo-Chemical Conversion Processes PI: B. Joseph, USF; Co-PI s: Y. Goswami, V. Bhethanabotla, J. Wolan, V. Gupta Students: Ali Gardezi,
CONVERSION OF CROP OIL TO AROMATICS OVER DOPED ZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 CNVERSIN F CRP IL T ARMATICS VER DPED ZSM-5 CATALYSTS Presented by: Swapnil Fegade Department of Chemical Engineering University of North Dakota Contributors: Swastika Bithi Dr. Brian Tande Dr. Wayne Seames
CNVERSIN F CRP IL T ARMATICS VER DPED ZSM-5 CATALYSTS Presented by: Swapnil Fegade Department of Chemical Engineering University of North Dakota Contributors: Swastika Bithi Dr. Brian Tande Dr. Wayne Seames
Methane Oxidation Reactions
 Methane Oxidation Reactions CH 4 + 2 O -> CO 2 2 + 2 H 2 O Total Oxidation (Combustion) CH 4 + 0.5 O -> CO 2 + 2 H 2 CO + 0.5 O -> CO 2 2 H 2 + 0.5 O -> H 2 2 O CH 4 + H 2 O->CO + 3 H 2 Partial Oxidation
Methane Oxidation Reactions CH 4 + 2 O -> CO 2 2 + 2 H 2 O Total Oxidation (Combustion) CH 4 + 0.5 O -> CO 2 + 2 H 2 CO + 0.5 O -> CO 2 2 H 2 + 0.5 O -> H 2 2 O CH 4 + H 2 O->CO + 3 H 2 Partial Oxidation
Aqueous-phase reforming a pathway to chemicals and fuels
 Alexey Kirilin Aqueous-phase reforming a pathway to chemicals and fuels Laboratory of Industrial Chemistry and Reaction Engineering Process Chemistry Centre Åbo Akademi Agenda 2 Short Introduction, biomass,
Alexey Kirilin Aqueous-phase reforming a pathway to chemicals and fuels Laboratory of Industrial Chemistry and Reaction Engineering Process Chemistry Centre Åbo Akademi Agenda 2 Short Introduction, biomass,
15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions
 15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions Halogenation An alkane will react with a halogen to produce a halalkane and the corresponding hydrogen halide. The catalyst is ultraviolet radiation. Reaction 1 methane chlorine
15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions Halogenation An alkane will react with a halogen to produce a halalkane and the corresponding hydrogen halide. The catalyst is ultraviolet radiation. Reaction 1 methane chlorine
Production of Renewable Chemicals. Pieter. C. A. Bruijnincx, Joseph Zakzeski, Anna L. Jongerius, and Bert M. Weckhuysen
 Catalytic Conversion of Lignin and its Derivatives for the Production of Renewable Chemicals Pieter. C. A. Bruijnincx, Joseph Zakzeski, Anna L. Jongerius, j p g and Bert M. Weckhuysen Catalytic Biomass
Catalytic Conversion of Lignin and its Derivatives for the Production of Renewable Chemicals Pieter. C. A. Bruijnincx, Joseph Zakzeski, Anna L. Jongerius, j p g and Bert M. Weckhuysen Catalytic Biomass
GCSE Chemistry. Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know. Name: Science Group: Teacher:
 GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
Chemistry 106 Fall 2006 Exam 1 Form A 1. Does this molecule have both cis and trans isomers?
 1. Does this molecule have both cis and trans isomers? Cl A. No, it has only the cis isomer. B. Yes, this is the cis isomer. C. Yes, this is the trans isomer. D. No. E. No, it has only the trans isomer
1. Does this molecule have both cis and trans isomers? Cl A. No, it has only the cis isomer. B. Yes, this is the cis isomer. C. Yes, this is the trans isomer. D. No. E. No, it has only the trans isomer
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10
 video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
Propylene: key building block for the production of important petrochemicals
 Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Le Lycee Mauricien. Proposed Syllabus Chemistry (5070) - Form 5
 Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
The Chemistry and Energy of Life
 2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Chapter 2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Key Concepts 2.1 Atomic Structure Is the Basis for Life s Chemistry 2.2 Atoms Interact and Form Molecules 2.3 Carbohydrates
2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Chapter 2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Key Concepts 2.1 Atomic Structure Is the Basis for Life s Chemistry 2.2 Atoms Interact and Form Molecules 2.3 Carbohydrates
Electrofuels Electrochemistry as a tool for a sustainable biofuel synthesis
 Electrofuels Electrochemistry as a tool for a sustainable biofuel synthesis Uwe Schröder, Nachhaltige Chemie und Energieforschung, Institut für ökologische Chemie Uwe Schröder, Institut für Ökologische
Electrofuels Electrochemistry as a tool for a sustainable biofuel synthesis Uwe Schröder, Nachhaltige Chemie und Energieforschung, Institut für ökologische Chemie Uwe Schröder, Institut für Ökologische
Conversion of Methane and Light Alkanes to Chemicals over Heterogeneous Catalysts Lessons Learned from Experiment and Theory
 Conversion of Methane and Light Alkanes to Chemicals over Heterogeneous Catalysts Lessons Learned from Experiment and Theory March 8, 201 6 Alexis T. Bell Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Conversion of Methane and Light Alkanes to Chemicals over Heterogeneous Catalysts Lessons Learned from Experiment and Theory March 8, 201 6 Alexis T. Bell Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Organic Chemistry. QuickTime and a are needed to see this picture.
 QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Organic Chemistry QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Organic Chemistry Has
QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Organic Chemistry QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Organic Chemistry Has
The Simplest Alkanes. Physical Properties 2/16/2012. Butanes are still gases. bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 n-pentane.
 The Simplest Alkanes Butanes are still gases Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 8 ) n-butane CH 2 CH 2 Isobutane ( ) 3 CH bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C bp -0.4 C bp -10.2 C Branched isomer
The Simplest Alkanes Butanes are still gases Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 8 ) n-butane CH 2 CH 2 Isobutane ( ) 3 CH bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C bp -0.4 C bp -10.2 C Branched isomer
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
Dr Panagiotis Kechagiopoulos. Lecturer in Chemical Engineering. School of Engineering
 Catalytic reforming of biomass derived oxygenates for sustainable hydrogen production: Experimental investigations, microkinetic modelling and reactor design Dr Panagiotis Kechagiopoulos Lecturer in Chemical
Catalytic reforming of biomass derived oxygenates for sustainable hydrogen production: Experimental investigations, microkinetic modelling and reactor design Dr Panagiotis Kechagiopoulos Lecturer in Chemical
An Alternative Biofuel: LPG from Biomass- Derived Organic Acids TIE Graduate Research Fellowship Report
 An Alternative Biofuel: LPG from Biomass- Derived Organic Acids 2010-2011 TIE Graduate Research Fellowship Report Branko Zugic Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Tufts University, Medford
An Alternative Biofuel: LPG from Biomass- Derived Organic Acids 2010-2011 TIE Graduate Research Fellowship Report Branko Zugic Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Tufts University, Medford
C11.1 Organic Chemistry Quiz Questions & Answers. Parts 1 & 2; all sets Parts 3 & 4; Sets 1 & 2 only
 C11.1 Organic Chemistry Quiz Questions & Answers Parts 1 & 2; all sets Parts 3 & 4; Sets 1 & 2 only C11.1 Organic Chemistry Part 1 1. Define a mixture. 2. Define crude oil. 3. Define a hydrocarbon. 4.
C11.1 Organic Chemistry Quiz Questions & Answers Parts 1 & 2; all sets Parts 3 & 4; Sets 1 & 2 only C11.1 Organic Chemistry Part 1 1. Define a mixture. 2. Define crude oil. 3. Define a hydrocarbon. 4.
Organic Chemistry. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers
 Chapter Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers Ch 1-Structure and bonding Ch 2-Polar covalent bonds: Acids and bases McMurry, J. (2004) Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition
Chapter Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers Ch 1-Structure and bonding Ch 2-Polar covalent bonds: Acids and bases McMurry, J. (2004) Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition
Overview. July 24, Catalysis Center for Energy Innovation
 verview July 24, 2017 CCEI is an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, ffice of Basic Sciences Mission, PIs, and Institutions Mission: CCEI is a transformative catalysis
verview July 24, 2017 CCEI is an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, ffice of Basic Sciences Mission, PIs, and Institutions Mission: CCEI is a transformative catalysis
PETE 203: Properties of oil
 PETE 203: Properties of oil Prepared by: Mr. Brosk Frya Ali Koya University, Faculty of Engineering, Petroleum Engineering Department 2013 2014 Lecture no. (2): Crude oil chemistry and composition 5. Crude
PETE 203: Properties of oil Prepared by: Mr. Brosk Frya Ali Koya University, Faculty of Engineering, Petroleum Engineering Department 2013 2014 Lecture no. (2): Crude oil chemistry and composition 5. Crude
Organic Chemistry. Alkanes are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds.
 Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS
 SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS QUESTION 1 The equation describing the production of butyl ethanoate is given below. Catalyst C4H 9OH CH 3COOH CH 3COOC 4H 9 H 2O( l ) 0.0500
SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS QUESTION 1 The equation describing the production of butyl ethanoate is given below. Catalyst C4H 9OH CH 3COOH CH 3COOC 4H 9 H 2O( l ) 0.0500
Synthesis of mixed alcohols over K-Ni-MoS 2 catalysts
 Synthesis of mixed alcohols over K-Ni-MoS 2 catalysts Rodrigo Suárez París Supervisors: Magali Boutonnet, Sven Järås Division of Chemical Technology, KTH OUTLINE Introduction and objective Experimental
Synthesis of mixed alcohols over K-Ni-MoS 2 catalysts Rodrigo Suárez París Supervisors: Magali Boutonnet, Sven Järås Division of Chemical Technology, KTH OUTLINE Introduction and objective Experimental
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
CATALYTIC STEAM REFORMING OF TOLUENE POST- GASIFICATION USING AS MODEL COMPOUND OF TAR PRODUCED BY BIOMASS GASIFICATION
 CATALYTIC STEAM REFORMING OF TOLUENE POST- GASIFICATION USING AS MODEL COMPOUND OF TAR PRODUCED BY BIOMASS GASIFICATION J. D. SILVA, C.C.B. OLIVEIRA AND C. A. M. ABREU 1 Polytechnic School UPE, Laboratory
CATALYTIC STEAM REFORMING OF TOLUENE POST- GASIFICATION USING AS MODEL COMPOUND OF TAR PRODUCED BY BIOMASS GASIFICATION J. D. SILVA, C.C.B. OLIVEIRA AND C. A. M. ABREU 1 Polytechnic School UPE, Laboratory
E (mol NO 2) L 1 s 1. C (mol NO 2) L 1 s 1. D (mol NO 2) L 1 s 1. Answer: B
 CH302 Spring 2008 Practice Exam 3 [Q1] Multiple Choice - 1 point 1) The rate of formation of oxygen in the reaction 2N 2 O 5 (g) 4NO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) is 2.28 (mol O 2 ) L 1 s 1. What is the rate of formation
CH302 Spring 2008 Practice Exam 3 [Q1] Multiple Choice - 1 point 1) The rate of formation of oxygen in the reaction 2N 2 O 5 (g) 4NO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) is 2.28 (mol O 2 ) L 1 s 1. What is the rate of formation
Catalytic Aromatization of Methane
 Catalytic Aromatization of Methane N.I.FAYZULLAYEV* 1, S.M.TUROBJONOV 2 1 Department of Natural Sciences, Division of Chemistry, Samarkand State University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan 2 Tashkent chemistry-technology
Catalytic Aromatization of Methane N.I.FAYZULLAYEV* 1, S.M.TUROBJONOV 2 1 Department of Natural Sciences, Division of Chemistry, Samarkand State University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan 2 Tashkent chemistry-technology
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
1. What is the letter of the alphabet in parentheses that follows EXAM I in the title above? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e
 HEM 102, EXAM I ( a ) 1. What is the letter of the alphabet in parentheses that follows EXAM I in the title above? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e 2. Which compound has the most constitutional isomers? a. 2 H
HEM 102, EXAM I ( a ) 1. What is the letter of the alphabet in parentheses that follows EXAM I in the title above? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e 2. Which compound has the most constitutional isomers? a. 2 H
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Alcohols. Ethanol Production. 182 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 25
 3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
Mechanocatalytic Approaches to Biomass Conversion
 Mechanocatalytic Approaches to Biomass Conversion Carsten Sievers March 10, 2015 Atlanta, GA Sievers Research Group Catalytic Routes for Sustainable Production of Fuels and Chemicals Synthesis Characterization
Mechanocatalytic Approaches to Biomass Conversion Carsten Sievers March 10, 2015 Atlanta, GA Sievers Research Group Catalytic Routes for Sustainable Production of Fuels and Chemicals Synthesis Characterization
OH, is an important feedstock for the chemical industry.
 1 Methanol, CH 3 OH, is an important feedstock for the chemical industry. In the manufacture of methanol, carbon dioxide and hydrogen are reacted together in the reversible reaction shown below. CO 2 (g)
1 Methanol, CH 3 OH, is an important feedstock for the chemical industry. In the manufacture of methanol, carbon dioxide and hydrogen are reacted together in the reversible reaction shown below. CO 2 (g)
SINOPEC MTP and MTX technologies
 COPYRIGHT@SUNJUNNAN COPYRIGHT@SUNJUNNAN 18-19 th, July, 2016, Parsian Azadi Hotel, Tehran, Iran Methanol+Toluene to Xylenes SINOPEC MTP and MTX technologies July 18 th, 2016 CONTENT MTP Introduction S-MTP
COPYRIGHT@SUNJUNNAN COPYRIGHT@SUNJUNNAN 18-19 th, July, 2016, Parsian Azadi Hotel, Tehran, Iran Methanol+Toluene to Xylenes SINOPEC MTP and MTX technologies July 18 th, 2016 CONTENT MTP Introduction S-MTP
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas
 , July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas Ditlhobolo Seanokeng, Achtar Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract This study aimed at investigating
, July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas Ditlhobolo Seanokeng, Achtar Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract This study aimed at investigating
1 What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen. oxygen only. steam. yeast
 What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen oxygen only steam yeast 2 Which term describes the formation of ethanol from glucose? cracking distillation polymerisation 3 Which
What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen oxygen only steam yeast 2 Which term describes the formation of ethanol from glucose? cracking distillation polymerisation 3 Which
Abstracts. p67. X. Tan, H. Lv, and X. Zhang. R. Hudson and A. Moores
 IX 1.1.1 omogeneous Reduction of Alkenes X. Tan,. Lv, and X. Zhang p7 This chapter is focused on recent progress in the asymmetric hydrogenation of substituted alkenes, and the application of this methodology
IX 1.1.1 omogeneous Reduction of Alkenes X. Tan,. Lv, and X. Zhang p7 This chapter is focused on recent progress in the asymmetric hydrogenation of substituted alkenes, and the application of this methodology
Sectional Solutions Key
 Sectional Solutions Key 1. For the equilibrium: 2SO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2SO 3 (g) + 188 kj, the number of moles of sulfur trioxide will increase if: a. the temperature of the system is increased (at constant
Sectional Solutions Key 1. For the equilibrium: 2SO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2SO 3 (g) + 188 kj, the number of moles of sulfur trioxide will increase if: a. the temperature of the system is increased (at constant
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Contents and Concepts Understanding Heats of Reaction The first part of the chapter lays the groundwork for understanding what we mean by heats of reaction. 1. Energy and Its
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Contents and Concepts Understanding Heats of Reaction The first part of the chapter lays the groundwork for understanding what we mean by heats of reaction. 1. Energy and Its
Chemistry 2 Summer 2008 Exam 3 KEY Chapters 11, 13, & 15
 Chemistry 2 Summer 2008 Exam 3 KEY Chapters 11, 13, & 15 You might find the following useful. Answer the following by writing the word, words, letter, letters or number in each blank that best completes
Chemistry 2 Summer 2008 Exam 3 KEY Chapters 11, 13, & 15 You might find the following useful. Answer the following by writing the word, words, letter, letters or number in each blank that best completes
Lecture Outline. 5.1 The Nature of Energy. Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy. 1 mv
 Chapter 5. Thermochemistry Common Student Misconceptions Students confuse power and energy. Students confuse heat with temperature. Students fail to note that the first law of thermodynamics is the law
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry Common Student Misconceptions Students confuse power and energy. Students confuse heat with temperature. Students fail to note that the first law of thermodynamics is the law
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Timing Department: Science Year Group: 0 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Chemistry (Combined) C/C States of matter/methods of Separating and purifying substances C3 Atomic structure
Timing Department: Science Year Group: 0 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Chemistry (Combined) C/C States of matter/methods of Separating and purifying substances C3 Atomic structure
Non-oxidative methane aromatization in a catalytic membrane reactor
 Non-oxidative methane aromatization in a catalytic membrane reactor Olivier RIVAL, Bernard GRANDJEAN, Abdelhamid SAYARI, Faïçal LARACHI Department of Chemical Engineering and CERPIC Université Laval, Ste-Foy,
Non-oxidative methane aromatization in a catalytic membrane reactor Olivier RIVAL, Bernard GRANDJEAN, Abdelhamid SAYARI, Faïçal LARACHI Department of Chemical Engineering and CERPIC Université Laval, Ste-Foy,
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. Itispossiblethatinthenextseveraldecadeswemayhavetoshifttowardothercarbonsources for these
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. Itispossiblethatinthenextseveraldecadeswemayhavetoshifttowardothercarbonsources for these
Study on the Production of Gamma valerolactone from Hybrid Poplar
 Study on the Production of Gamma valerolactone from Hybrid Poplar Troy Runge, Chunhui Zhang March 16, 2011 Topics of my Talk Bioenergy Gamma valerolactone background Pentose & Hexose hydrolysis Levulinic
Study on the Production of Gamma valerolactone from Hybrid Poplar Troy Runge, Chunhui Zhang March 16, 2011 Topics of my Talk Bioenergy Gamma valerolactone background Pentose & Hexose hydrolysis Levulinic
The lifetime of the catalyst, and therefore its stability, are measured in terms of its TN.
 A catalyst may be defined by its Turnover Number (TN). Each time the complete catalyst cycle occurs, we consider one catalytic turnover to have been completed (one mole of product formed per mole of catalyst).
A catalyst may be defined by its Turnover Number (TN). Each time the complete catalyst cycle occurs, we consider one catalytic turnover to have been completed (one mole of product formed per mole of catalyst).
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life I. Concept 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules a. Atoms Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry i. Atom: _ ii. (They are SUPER small! It would take 3 million carbon
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life I. Concept 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules a. Atoms Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry i. Atom: _ ii. (They are SUPER small! It would take 3 million carbon
Hydrogenation of CO Over a Cobalt/Cerium Oxide Catalyst for Production of Lower Olefins
 Hydrogenation of CO Over a Cobalt/Cerium Oxide Catalyst for Production of Lower Olefins Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Hydrogenation of
Hydrogenation of CO Over a Cobalt/Cerium Oxide Catalyst for Production of Lower Olefins Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Hydrogenation of
Core. Topic 10: Organic chemistry. Essential idea: Organic chemistry focuses on the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
 Core Chemistry guide 67 Essential idea: Organic chemistry focuses on the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Nature of science: Serendipity and scientific discoveries
Core Chemistry guide 67 Essential idea: Organic chemistry focuses on the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Nature of science: Serendipity and scientific discoveries
The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
 The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry By Ball, Hill and Scott Download PDF at https://open.umn.edu/opentextbooks/bookdetail.aspx?bookid=40 Page 5 Chapter 1 Chemistry, Matter, and Measurement
The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry By Ball, Hill and Scott Download PDF at https://open.umn.edu/opentextbooks/bookdetail.aspx?bookid=40 Page 5 Chapter 1 Chemistry, Matter, and Measurement
Catalytic Technique of Bio oil Conversion to Valuable Chemicals
 American Journal of Chemical Engineering 2017; 5(2-1): 1-5 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajche doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.s.2017050201.11 ISSN: 2330-8605 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8613 (Online) Catalytic
American Journal of Chemical Engineering 2017; 5(2-1): 1-5 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajche doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.s.2017050201.11 ISSN: 2330-8605 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8613 (Online) Catalytic
Thrust Area 3: Biomass (Thermo-Chemical Conversion) Progress Summary
 Thrust Area 3: Biomass (Thermo-Chemical Conversion) Production of Liquid Fuels Biomass via Thermo-Chemical Conversion Processes PI: Babu Joseph Co-PIs: Yogi Goswami, Venkat Bhethanabotla, John Wolan, Vinay
Thrust Area 3: Biomass (Thermo-Chemical Conversion) Production of Liquid Fuels Biomass via Thermo-Chemical Conversion Processes PI: Babu Joseph Co-PIs: Yogi Goswami, Venkat Bhethanabotla, John Wolan, Vinay
Salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol from fermentation broth
 Salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol from fermentation broth Beata RUKOWICZ, Krzysztof ALEJSKI, Ireneusz MIESIĄC Keywords: 1,3-propanediol; fermentation broth; solvent extraction Abstract: 1,3-propanediol
Salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol from fermentation broth Beata RUKOWICZ, Krzysztof ALEJSKI, Ireneusz MIESIĄC Keywords: 1,3-propanediol; fermentation broth; solvent extraction Abstract: 1,3-propanediol
`1AP Biology Study Guide Chapter 2 v Atomic structure is the basis of life s chemistry Ø Living and non- living things are composed of atoms Ø
 `1AP Biology Study Guide Chapter 2 v Atomic structure is the basis of life s chemistry Ø Living and non- living things are composed of atoms Ø Element pure substance only one kind of atom Ø Living things
`1AP Biology Study Guide Chapter 2 v Atomic structure is the basis of life s chemistry Ø Living and non- living things are composed of atoms Ø Element pure substance only one kind of atom Ø Living things
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
3.2 Alkanes. Refining crude oil. N Goalby chemrevise.org 40 C 110 C 180 C. 250 C fuel oil 300 C 340 C. Fractional Distillation: Industrially
 3.2 Alkanes Refining crude oil Fractional Distillation: Industrially Petroleum is a mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons Petroleum fraction: mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length
3.2 Alkanes Refining crude oil Fractional Distillation: Industrially Petroleum is a mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons Petroleum fraction: mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length
Research Article Thermodynamic Equilibrium Analysis of Methanol Conversion to Hydrocarbons Using Cantera Methodology
 Thermodynamics Volume 212, Article ID 1246, 7 pages doi:1.11/212/1246 Research Article Thermodynamic Equilibrium Analysis of Methanol Conversion to Hydrocarbons Using Cantera Methodology Duminda A. Gunawardena
Thermodynamics Volume 212, Article ID 1246, 7 pages doi:1.11/212/1246 Research Article Thermodynamic Equilibrium Analysis of Methanol Conversion to Hydrocarbons Using Cantera Methodology Duminda A. Gunawardena
Application Note. Authors. Abstract. Energy & Chemicals, Biofuels & Alternative Energy
 Analytical Quantification of Deoxygenated Compounds in Catalytic Reaction Samples as an Evaluation Technique to Detere Reaction Conversion from a Bioderived Oil in Novel Biofuel Testing Application Note
Analytical Quantification of Deoxygenated Compounds in Catalytic Reaction Samples as an Evaluation Technique to Detere Reaction Conversion from a Bioderived Oil in Novel Biofuel Testing Application Note
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
Q.1 Which of the structures is/are classified as phenols?
 Alcohols 1 ALOOLS Aliphatic Aromatic general formula n 2n+1 O - provided there are no rings named as substituted alkanes by removing the final -e and adding -ol for isomers the position of the O is given
Alcohols 1 ALOOLS Aliphatic Aromatic general formula n 2n+1 O - provided there are no rings named as substituted alkanes by removing the final -e and adding -ol for isomers the position of the O is given
Energy, Enthalpy and Thermochemistry. Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat
 9 Energy, Enthalpy and Thermochemistry Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat The law of conservation of energy Energy can be converted but the total is a constant Two types of energy: Kinetic
9 Energy, Enthalpy and Thermochemistry Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat The law of conservation of energy Energy can be converted but the total is a constant Two types of energy: Kinetic
1 Compound Q decolourises bromine water. Compound Q has two carbon atoms in each molecule. Which statement about compound Q is correct?
 1 ompound Q decolourises bromine water. ompound Q has two carbon atoms in each molecule. Which statement about compound Q is correct? It contains carbon-hydrogen double bonds. It has six hydrogen atoms
1 ompound Q decolourises bromine water. ompound Q has two carbon atoms in each molecule. Which statement about compound Q is correct? It contains carbon-hydrogen double bonds. It has six hydrogen atoms
Slide 1 / 97. Organic Chemistry: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
 Slide 1 / 97 Organic Chemistry: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Slide 2 / 97 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Organic compounds range from simple molecules
Slide 1 / 97 Organic Chemistry: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Slide 2 / 97 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Organic compounds range from simple molecules
Catalytic Hydrodesulfurisation
 CHAPTER 2 Catalytic Hydrodesulfurisation 1 The Process Although some of the organic sulfur compounds found in oil and other feedstocks can be removed by the absorption, adsorption and oxidation processes
CHAPTER 2 Catalytic Hydrodesulfurisation 1 The Process Although some of the organic sulfur compounds found in oil and other feedstocks can be removed by the absorption, adsorption and oxidation processes
Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether
 Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
Energy & Environmental Science
 Energy & Environmental Science Accepted Manuscript This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted
Energy & Environmental Science Accepted Manuscript This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted
Introduction to Chemical Reactions. Chapter 6
 Introduction to Chemical Reactions Chapter 6 Instructional Goals 1. Given the reactants and product in a chemical reaction, the student will be able to write and balance chemical equations. 2. Identify
Introduction to Chemical Reactions Chapter 6 Instructional Goals 1. Given the reactants and product in a chemical reaction, the student will be able to write and balance chemical equations. 2. Identify
Naming Organic Halides. Properties of Organic Halides
 Organic Compounds Organic Halides A hydrocarbon in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by halogen atoms Freons (chlorofluorocarbons) in refrigeration and air conditioning Teflon (polytetrafluoroethane)
Organic Compounds Organic Halides A hydrocarbon in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by halogen atoms Freons (chlorofluorocarbons) in refrigeration and air conditioning Teflon (polytetrafluoroethane)
Objectives. Organic molecules. Carbon. Hydrocarbon Properties. Organic Chemistry Introduction. Organic versus Hydrocarbon 1/1/17
 Objectives Organic Chemistry Introduction 8.1 To determine the properties of organic molecules and recognize a hydrocarbon. Use table P and Q to write structural and molecular formulas for hydrocarbons.
Objectives Organic Chemistry Introduction 8.1 To determine the properties of organic molecules and recognize a hydrocarbon. Use table P and Q to write structural and molecular formulas for hydrocarbons.
Gestão de Sistemas Energéticos 2017/2018
 Gestão de Sistemas Energéticos 2017/2018 Exergy Analysis Prof. Tânia Sousa taniasousa@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Conceptualizing Chemical Exergy C a H b O c enters the control volume at T 0, p 0. O 2 and CO 2,
Gestão de Sistemas Energéticos 2017/2018 Exergy Analysis Prof. Tânia Sousa taniasousa@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Conceptualizing Chemical Exergy C a H b O c enters the control volume at T 0, p 0. O 2 and CO 2,
Grade 12 Chemistry, University I
 Grade 12 Chemistry, University I Monarch Park Collegiate SCH 4U Credit Value: 1 Course Outline prepared by: Monarch Park Chemistry Teachers Text Book: Nelson "Chemistry 12" Department Head: G. Nakashima
Grade 12 Chemistry, University I Monarch Park Collegiate SCH 4U Credit Value: 1 Course Outline prepared by: Monarch Park Chemistry Teachers Text Book: Nelson "Chemistry 12" Department Head: G. Nakashima
UNIT 3 CHEMISTRY. Fundamental Principles in Chemistry
 UNIT 3 CHEMISTRY NOTE: This list has been compiled based on the topics covered in the 2016 Master Class program. Once all of the 2017 Chemistry program materials have been finalised, this summary will
UNIT 3 CHEMISTRY NOTE: This list has been compiled based on the topics covered in the 2016 Master Class program. Once all of the 2017 Chemistry program materials have been finalised, this summary will
Ch120 Lecture: The BiMoO x Story
 Ch120 Lecture: The Bi x Story Heterogeneous selective (amm)oxidation of propene. Kimberly Chenoweth November 28, 2007 What do these processes have in common? Late 1800s Early 1900s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s
Ch120 Lecture: The Bi x Story Heterogeneous selective (amm)oxidation of propene. Kimberly Chenoweth November 28, 2007 What do these processes have in common? Late 1800s Early 1900s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s
AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri. Chapter 4 Stoichiometry and MB with Reactions
 AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri Chapter 4 Stoichiometry and MB with Reactions Stoichiometry Stoichiometry provides a quantitative means of relating the amount of
AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri Chapter 4 Stoichiometry and MB with Reactions Stoichiometry Stoichiometry provides a quantitative means of relating the amount of
Kinetics of the Fischer-Tropsch Reaction over a Ru- Promoted Co/Al 2 o 3 Catalyst
 Kinetics of the Fischer-Tropsch Reaction over a Ru- Promoted Co/Al o 3 Catalyst Tejas Bhatelia 1, Wenping Ma, Burtron Davis, Gary Jacobs and Dragomir Bukur 1* 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Texas
Kinetics of the Fischer-Tropsch Reaction over a Ru- Promoted Co/Al o 3 Catalyst Tejas Bhatelia 1, Wenping Ma, Burtron Davis, Gary Jacobs and Dragomir Bukur 1* 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Texas
Combined Science: Trilogy
 Co-teaching GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy This high level co-teaching guide will help you plan your route through the course. You ll be able to see what common themes and topics span
Co-teaching GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy This high level co-teaching guide will help you plan your route through the course. You ll be able to see what common themes and topics span
Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Ethylene Glycol Over Supported Platinum Catalysts
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of George W. Huber 2003 Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Ethylene Glycol Over Supported Platinum Catalysts George W Huber, University of Massachusetts
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of George W. Huber 2003 Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Ethylene Glycol Over Supported Platinum Catalysts George W Huber, University of Massachusetts
GTC Technology. Rethinking Xylenes Production via Toluene Methylation
 GTC Technology Rethinking Xylenes Production via Toluene Methylation Joseph C. Gentry Director, Global Licensing IOCL Petrochemical Conclave New Delhi February 7, 2014 Re-thinking Xylenes Para-dimethylbenzene
GTC Technology Rethinking Xylenes Production via Toluene Methylation Joseph C. Gentry Director, Global Licensing IOCL Petrochemical Conclave New Delhi February 7, 2014 Re-thinking Xylenes Para-dimethylbenzene
Unit 5 Test. Name: Score: 37 / 37 points (100%)
 Name: Score: 37 / 37 points (100%) Unit 5 Test Matching (1 point each) Match each item with the correct statement below a activity series j product b chemical equation k reactant c coefficient l reduction
Name: Score: 37 / 37 points (100%) Unit 5 Test Matching (1 point each) Match each item with the correct statement below a activity series j product b chemical equation k reactant c coefficient l reduction
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
Study Guide: Basic Chemistry, Water, Life Compounds and Enzymes
 Study Guide: Basic Chemistry, Water, Life Compounds and Enzymes 1. Lipids are good energy-storage molecules because a) the can absorb a large amount of energy while maintaining a constant temperature b)
Study Guide: Basic Chemistry, Water, Life Compounds and Enzymes 1. Lipids are good energy-storage molecules because a) the can absorb a large amount of energy while maintaining a constant temperature b)
Role of products and intermediates in bioethanol conversion to hydrocarbons on H-ZSM-5: A time-resolved study
 Role of products and intermediates in bioethanol conversion to hydrocarbons on H-ZSM-5: A time-resolved study Rakesh Batchu, Vladimir V. Galvita, Konstantinos Alexopoulos, Kristof Van der Borght, Hilde
Role of products and intermediates in bioethanol conversion to hydrocarbons on H-ZSM-5: A time-resolved study Rakesh Batchu, Vladimir V. Galvita, Konstantinos Alexopoulos, Kristof Van der Borght, Hilde
Part B: Unraveling the mechanism of catalytic reactions through kinetics and thermodynamics
 Part B: Unraveling the mechanism of catalytic reactions through kinetics and thermodynamics F.C. Meunier, J. Scalbert and F. Thibault-Starzyk Appl. Catal. A: Gen. (2015), in press, doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2014.12.028
Part B: Unraveling the mechanism of catalytic reactions through kinetics and thermodynamics F.C. Meunier, J. Scalbert and F. Thibault-Starzyk Appl. Catal. A: Gen. (2015), in press, doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2014.12.028
MICROSTRUCTURE-BASED PROCESS ENGINEERING AND CATALYSIS
 MICROSTRUCTURE-BASED PROCESS ENGINEERING AND CATALYSIS 1 2 APPLICATION PORTFOLIO Fine chemistry We design chemical processes from lab to pilot scale in a safe, efficient and flexible way: using micro-
MICROSTRUCTURE-BASED PROCESS ENGINEERING AND CATALYSIS 1 2 APPLICATION PORTFOLIO Fine chemistry We design chemical processes from lab to pilot scale in a safe, efficient and flexible way: using micro-
Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example)
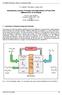 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction
 Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Experiment Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial Rate
![Experiment Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial Rate Experiment Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial Rate](/thumbs/77/75974637.jpg) Chem 120 Practice Final Winter 2014 1 of 14 1. The following are initial rate data for: A + 2 B C + 2 D Experiment Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial Rate 1 0.10 0.10 0.300 2 0.20 0.10 0.600 3 0.10 0.20 1.200
Chem 120 Practice Final Winter 2014 1 of 14 1. The following are initial rate data for: A + 2 B C + 2 D Experiment Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial Rate 1 0.10 0.10 0.300 2 0.20 0.10 0.600 3 0.10 0.20 1.200
PROCESS TECHNOLOGY- ORGANIC II. 51. Gas phase dehydrogenation of ethyl-benzene to styrene occurs over catalyst based on
 PROCESS TECHNOLOGY- ORGANIC II 51. Gas phase dehydrogenation of ethyl-benzene to styrene occurs over catalyst based on (a) iron oxide, (b) silica alumina, (c) titanium dioxide, (d) sodium silicate, 52.
PROCESS TECHNOLOGY- ORGANIC II 51. Gas phase dehydrogenation of ethyl-benzene to styrene occurs over catalyst based on (a) iron oxide, (b) silica alumina, (c) titanium dioxide, (d) sodium silicate, 52.
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Understanding Chemical Reactions through Computer Modeling. Tyler R. Josephson University of Delaware 4/21/16
 Understanding Chemical Reactions through Computer Modeling Tyler R. Josephson University of Delaware 4/21/16 A little about me B.S. in Chem E from U of M, 2011 Currently, Ph.D. student at University of
Understanding Chemical Reactions through Computer Modeling Tyler R. Josephson University of Delaware 4/21/16 A little about me B.S. in Chem E from U of M, 2011 Currently, Ph.D. student at University of
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Hangzhou , PR China
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Influence of Ni based catalysts on CH 4 -CO 2 reforming reaction Hangjie Li 1, Dongming Shen 2, Xikun Gai 3,
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Influence of Ni based catalysts on CH 4 -CO 2 reforming reaction Hangjie Li 1, Dongming Shen 2, Xikun Gai 3,
