Dalton Transactions Accepted Manuscript
|
|
|
- Brittany Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dalton Transactions Accepted Manuscript This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted Manuscripts are published online shortly after acceptance, before technical editing, formatting and proof reading. Using this free service, authors can make their results available to the community, in citable form, before we publish the edited article. We will replace this Accepted Manuscript with the edited and formatted Advance Article as soon as it is available. You can find more information about Accepted Manuscripts in the Information for Authors. Please note that technical editing may introduce minor changes to the text and/or graphics, which may alter content. The journal s standard Terms & Conditions and the Ethical guidelines still apply. In no event shall the Royal Society of Chemistry be held responsible for any errors or omissions in this Accepted Manuscript or any consequences arising from the use of any information it contains.
2 Page 1 of 7 Journal Name Dalton Transactions Dynamic Article Links Cite this: DOI: /c0xx00000x ARTICLE TYPE Uniform Iron Oxide Hollow Spheres for High-performance Delivery of Insoluble Anticancer Drugs Yichen Zhu, a Jie Lei, b* Ye Tian a* Received (in XXX, XXX) Xth XXXXXXXXX 20XX, Accepted Xth XXXXXXXXX 20XX 5 DOI: /b000000x As an intrinsic character of many anticancer drugs, low solubility in physiological condition always limited the usage of these active ingredients in clinic. To overcome this bottleneck, we attempt to design and construct a high-performance magnetic-targeted delivery system based on uniform iron oxide hollow spheres. Via a facile one-pot solvothermal route, well-defined iron oxide hollow spheres were prepared 10 with inexpensive inhesion. Compared with previously reported mesoporous Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles, our iron oxide hollow spheres with larger void space endowed the structures with high storage capacity of guest molecules. To confirm the efficiency of drug-loading and chemotherapy in vitro, camptothecin (CPT) was selected as a model insoluble anticancer drug in our present work. Detailed anticancer efficacy were further investigated by using MTT assays and microscope image method, indicating these iron oxide 15 hollow spheres promising for insoluble drug delivery Introduction Cancer has become the leading cause of death worldwide in accordance with the World Cancer Report. 1, 2 Along with the rapid development of modern medicine, chemotherapy, surgery, and radiotherapy have been considered as main therapies and applied widely in clinic. However, low solubility of anticancer drug in physiological condition always limits their usages for efficient treatment in anticancer programs. 3-6 For instance, intravenous administration of these insoluble chemical entities will form large aggregates in blood and induce serious side effect. More importantly, low solubility will cause insufficient drug accumulation around tumour sites and weaken chemotherapeutic efficiency. 7 Recently, significant progress has been made to design novel drug delivery system (DDS) to enhance the bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs Towards this goal, various micro/nano carriers including mesoporous particles, liposomes, and micelles have been constructed and applied for anticancer therapy by taking advantages of their rational biodistribution, minimal toxicity upon normal tissues, ease of surface functionality, as well as active target ability Among all these biomedicine materials, magnetic nanostructures have achieved much more attentions because of their potential applications in hyperthermia therapy, pre-clinical contrast agents, magnetic separation of biomolecules, as well as targeted drug delivery Compared with other magnetic materials, nanoparticles based on iron oxide a Department of Urology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, (P. R. China). tianyebfh@gmail.com b Department of MRI, Fourth Hosipital of Jilin University, Changchun, (P. R. China). lei_jie_1@hotmail.com Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: supporting figures. See DOI: /b000000x/ have been investigated the most owing to their chemical stability in physiological environment and high magnetic saturation For example, nanoballs containing Fe 3 O 4 particles has been applied as FDA-approved magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Moreover, considerable approaches have been presented by integrating several advantages within one material for both diagnosis and therapy In Addition, particles containing magnetic section and mesoporous section have also been wellprepared by several groups Although promising, disadvantages, such as limited drug storage efficacy, poor response towards assistant magnet, and time-consuming synthesis still hamper these materials to be high-performance carriers in biomedicine applications. Thereby, the development of magnetic nanocarriers via a facile route, excellent internality, and high drug-loading capability is still urgently needed. Current studies have demonstrated the preparation of various magnetic hollow structures, which extremely aroused extensive interest in fields of high drug-loading delivery systems. 5,41 Inspired by these previous reports, herein, water-stable magnetic hollow spheres based on iron oxide were synthesized via a facile strategy, which could acted as a high-performance delivery platform for insoluble anticancer drugs. Fig. 1 illustrated the onepot fabrication approach of our well-designed magnetic hollow spheres and their usage as drug-carriers to chemotherapeutics. Detailed solvent effect in solvothermal process was discussed, indicating the important role of ETA during the conformation course of hollow structure. In vitro toxicity studies promised their superior biocompatibility and neglectable cytoxicity of magnetic hollow spheres. As a routinely used hydrophobic drug in clinic, camptothecin was selected to investigate the drug delivery efficiency, the drug release properties, as well as the anticancer effectiveness upon 786-O cells. Taking together, results obtained This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year] [journal], [year], [vol],
3 Dalton Transactions Page 2 of from our present work indicated that CPT-magnetic hollow spheres showed a high drug-loading capacity, nearly zero-release property in extracellular condition and high anticancer efficiency. Materials and methods Materials Ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl 3 6H 2 O), anhydrous sodium acetate (NaOAc), polyethylene glycolethylene (PEG-2000), glycol (EG), ethanolamine (ETA), and ethanol were purchased from Beijing Chemicals. Camptothecin (CPT) was purchased from Aladdin Reagent. All chemical agents used in these experiments were of analytical grade and used directly without further purification. Preparation of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres The monodisperse Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were synthesized by one-pot solvothermal method. In detail, 1.5 g of FeCl 3 6H 2 O was dissolved in 40 ml of solvent containing EG (30 ml) and ETA (10 ml) to form a stable orange solution. 4.0 g of NaAc and 1.0 g PEG-2000 were added into the above solution under vigorously magnetic stirring until completely dissolved. The obtained homogeneous solution was transferred to a Teflon-lined stainlesssteel autoclave (50 ml) and sealed to heat at 200 ºC. After reaction for 8 h, the autoclave was cooled to ambient temperature naturally. The obtained magnetite particles were washed with ethanol and deionized water in sequence, and then dried in vacuum at 60 ºC for 12 h. With different amount of EG and ETA, solvent effect of ETA in solvothermal process was investigated in detail. Loading of CPT and in vitro drug release Camptothecin (CPT) loading was achieved by incubating CPT 30 with Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres. Firstly, CPT powder was first dissolved in chloroform, making a saturated CPT solution at a concentration of 4 mg ml -1. Above solution mixed with Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres (10 mg) was placed under stirring for 24 h. In this condition, Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were filled with CPT. Then, the 35 drug-loaded spheres were centrifuged, wash with PBS several times, and dried under vacuum at 70 ºC overnight. The supernatant and washed solutions were collected and the residual drug content was determined by UV-vis method to calculate the drug-loading capacity of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres. In vitro release 40 experiments were performed under different solvent conditions. Detailedly, 1 mg of CPT-Fe 3 O 4 were resuspended in a centrifuge tube (10 ml) containing 5 ml PBS or DMSO. At certain time intervals, Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were centrifuged, and 0.5 ml release medium containing the free drug was transferred out to 45 determine the concentration of CPT. 50 Cell cultures 786-O cells (human kidney carcinoma cell line), NIH3T3 cells (mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line), HepG2 cells, and Hela cells were supplied by American Type Culture Collection. 786-O cells were cultured in 1640 medium containing penicillin (100 U ml -1 ), streptomycin (100 U ml -1 ), and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in a humidified incubator at 37 ºC and 5% CO 2. NIH3T3 cells were cultured in DMEM containing penicillin (100 U ml -1 ), streptomycin (100 U ml -1 ), and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in a humidified incubator at 37 ºC and 5% CO 2. Both cells were harvested by the use of trypsin and were resuspended in fresh complete medium before plating. In vitro cytotoxicity studies MTT assays were performed to quantify the cytotoxicity of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres. Typically, 786-O cells and NIH3T3 cells were cultured in 96-well plates with a density of per well for 12 h to allow the cells to attach. Serial dilutions of different formulations containing Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were added to the culture medium. At the end of the incubation time, medium containing Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were removed, and cell samples were treated with MTT for another 4 h, which was followed by the addition of DMSO to dissolve the formazan crystals. Bio-Rad model-680 microplate reader was applied to measure the absorbance at a wavelength of 570 nm. Six replicates were done for each treatment group and percent viability was normalized to cell viability in the absence of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres. In vitro anticancer activity MTT assays were further carried out to evaluate the cytotoxicity of CPT-Fe 3 O 4. Briefly, 786-O cells, HepG2 cells, and Hela cells 75 were respectively seeded in 96-well plates with a density of per well for 12 h to allow the cells to attach. CPT and CPT-Fe 3 O 4 with expected formulations were added to the medium. Cells were incubated in 5% CO 2 at 37 ºC for 24 h. At the end of incubation time, cell samples were treated via MTT 80 assay Cellular modality and observation For microscope imaging, 786-O cells with a density of were plated in a 24-well plate for 4 h to allow the cells to attach. After the cells were washed twice by cool phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres, CPT, and CPT-Fe 3 O 4 with a concentration of 25 µg ml -1 were added to the culture medium. After incubating for 24 h, cells were washed again with PBS several times to remove the remaining nanoparticles. In order to nucleus labeling, nuclei was stained with Hoechst (20 mg ml -1 in PBS) for 10 min, rinsed with PBS, and then observed under an Olympus BX-51 optical system microscopy. In addition, 786-O cells were stained with trypan blue for 15 min, washed with PBS, and then imaged by a digital microscope. Pictures were then taken with an Olympus digital camera. Detection of Fe 3+ in 786-O cells To detection the amount of Fe 3+ in cells, 786-O cells were plated in a 24-well plate for 4 h to allow the cells to attach. Then, Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres and CPT-Fe 3 O 4 were added to the culture medium with a concentration of 25 µg ml -1 (1mL). After 24 h incubation, cells were washed with PBS several times to remove the remaining nanoparticles. Then concentrated HCl was added to above systems to obtain cell lysis for ICP-MS analysis. Statistical analysis All data were expressed in this article as mean result ± standard deviation (SD). The statistical analysis was performed by using Origin 8.0 software. 2 Journal Name, [year], [vol], This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year]
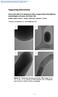
4 Page 3 of 7 Dalton Transactions Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of one-pot synthesis of Fe 3O 4 hollow spheres and their applications to chemotherapeutics. Results and discussion The synthesis of uniform magnetic hollow spheres was carried out using a modified facile solvothermal method. 31 Detailed morphological and structural features of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were examined via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) at first. As exhibited in Fig. 2A, Fig. 2B, and Fig. S1, Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres with uniform and non-aggregated nature revealed a relatively coarse surface and a mean diameter of ~ 200 nm, which were composed of small primary nanoparticles with an average size of nm. The roughness of surface should be attributed to the accumulation effect of small nanocrystals. Careful observation of a single hollow sphere based on high-magnification SEM image shown in Fig. 2A additionally revealed that the magnetic hollow sphere was constructed of smaller nanocrystals. As illustrated in Fig. 2C, wide-angle XRD pattern of the magnetic hollow spheres revealed the characteristic broad diffraction peaks of well-defined magnetite phase (JCPDS ). As shown in Fig. 2D, EDS results originated from point scan indicated that the sample mainly contained Fe and O elements. The graft of PEG molecules on nanocarriers could extremely enhance their biocompatibility, mondispersity, and hydrophilicity In our present work, PEG was introduced and applied to form PEG-modified magnetic hollow spheres. Based on our thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) result, the content of PEG molecules was calculated to be 7.21% (Fig. S2). Multifunctional nanomaterials with excellent response towards assistant magnet have gained much attention due to their unique magnetic-separable and magnetic-targeted features As illustrated in Fig. 2E, the magnetic property collected on a SQUID magnetometer at room temperature demonstrated the magnetization saturation value of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres was emu g -1. Photograph shown in Fig. 2F revealed an admirable dissolution and a visible response of the as-prepared hollow spheres towards an appropriate magnet. The nitrogen absorption/desorption isotherms of our magnetic hollow spheres was illustrated in Fig. S3. It could be seen that the sample exhibited typical Ⅳ-typed isotherms with H1-hysteresis loops, indicating the presence of mesopores. BET surface area and total pore volume were calculated to be m 2 g -1 and cm 3 g -1, respectively. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis of these Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres in PBS containing 10% FBS illustrated an average diameter of 224 nm, which was larger than that of TEM observation and thus indicated the successful modification of PEG molecules on the surface of the spheres. Otherwise, the zeta potential of these Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres was mv. To sum up, these well-defined Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres promised more potential for biomedicine applications. To investigate the solvent effect of ETA in the formation process, control experiments were carried out additionally. As illustrated in Fig. 3A, no hollow structures were obtained except for solid magnetic nanoparticles. When the amount of ETA was 55 Fig. 2 SEM micrograph (a), TEM image (b), wide-angle XRD pattern (c), EDS spectrum (d), room-temperature field-dependent magnetization curve (e), as well as visible magnetic-response process (f) of Fe 3O 4 hollow spheres. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year] Journal Name, [year], [vol],
5 Dalton Transactions Page 4 of 7 Fig. 3 SEM images and wide-angle XRD patterns (d) of Fe 3O 4 obtained upon different solvent conditions: without ETA (a and black), ETA:EG = 5 1:1 (band red ), as well as ETA:EG = 3:1 (c and blue) (scale bar: 1 µm). increased to half of the total, nanocrystal with an average size of 30 nm could be achieved (Fig. 3B). However, amorphous products with agglomerate magnetic materials were gained while 10 ETA increased to three-quarter content (Fig. 3C). The formation mechanism of magnetic hollow spheres was attributed to the intense coordination between amido of ETA and Fe 3+. Complex composed with ETA and Fe 3+ could limit the rapid growth of nanoparticles, resulting in the formation of smaller nanocrystals. 15 Under proper solvent condition, smaller nanocrystals assembled into hollow spheres as expected. Wide-angle XRD patterns shown in Fig. 3D further indicated the magnetite phase of all these products. Cell viability under the co-incubation with nanoparticles was 20 evaluated at first to examine the feasibility of obtained magnetic hollow spheres in a drug delivery system. As shown in Fig. 4A, Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres did not present cytotoxicity against 786-O cells. Significantly, the cell viability still remained above 95% even under a high concentration of 200 µg ml -1. Otherwise, we 25 selected NIH3T3 cells (a normal cell line) to investigate the in vitro toxicity of magnetic hollow spheres. As illustrated in Fig. S4, cell viabilities were not hindered by Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres up to a concentration of 200µg ml -1. In addition, long-term dialysis against natural PBS containing 10% fetal bovine serum was 30 performed to examine the stability of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres in physiological condition. Result revealed that there was no leaching of free Fe 3+ from the magnetic hollow spheres, indicating their excellent stability. However, when experiment was carried out under acid condition (ph = 4.5), result of the 35 dialysis demonstrated the dissolution of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres and the presence of Fe 3+ achieved via ICP-MS method. On the basis of these results, it could be inferred that our magnetic nanocarriers decomposed during endocytosis, released drug in cytoplasm, and resulted in the high-performance cancer treatment. 40 To date, lack of aqueous solubility always limited their practical applications of many anticancer drugs in clinic. 3,5,18 To overcome this bottleneck, hollow materials with large space for storing guest molecules held more potential for the development of novel delivery systems. With the unique hollow feature of our Fe 3 O 4 particles, it was highly desired to apply Fe 3 O 4 hollow structures as efficient nanocarriers of hydrophobic drugs in cancer therapy. Camptothecin (CPT) was employed as a model hydrophobic anticancer drug in our current study. The Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres were loaded with CPT molecules by soaking them in DMSO containing CPT 24 h. After CPT-Fe 3 O 4 was removed via careful centrifugation, CPT-Fe 3 O 4 was washed twice with PBS to confirm that there was no additional adsorbed drug on the surface of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres. Detected via UV-vis method, approximate 120 µg of CPT molecules were stored inside 1 mg of hollow spheres, demonstrating the high loading capacity of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres (Fig. S5). Fig. 4B revealed the released amounts of CPT when the CPT-Fe 3 O 4 were dispersed in PBS (ph = 7.4) and DMSO with different incubation periods, respectively. Less than 3% of the stored CPT could be released into the supernatant when CPT-Fe 3 O 4 was dispersed in PBS and left in suspension for up to 4 h. However, once CPT-Fe 3 O 4 was dispersed in DMSO for 0.5 h, most of CPT could be released and detected in the supernatant. Above results suggested the negligible drug leakage in PBS of CPT-Fe 3 O 4 and great significance in the minimization of side effects. Viabilities of 786-O cells against CPT and CPT- Fe 3 O 4 after incubation for 24 h were present in Fig. 4C. Compared with control group, both CPT and CPT-Fe 3 O 4 exhibited toxicity towards 786-O cells. Slight cytotoxicities of free CPT were probably in accordance with the low solubility of CPT in hydrophilic medium. Much higher cytotoxic efficacy of CPT-Fe 3 O 4 further made out the efficient drug-delivery capability by using carriers. Due to the presence of hydrophobic sections in cells, CPT-Fe 3 O 4 could rationally release CPT at these active sites, which played an important role to kill cancer cells. To confirm the internalization route of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres and CPT-Fe 3 O 4 composites, we investigated the amount of Fe 3+ in 786-O cells via ICP-MS method. Nearly 70% of the initial Fe 3+ content could be detected both in Fe 3 O 4 and CPT-Fe 3 O 4 groups (184 µg well -1 for Fe 3 O 4 and 176 µg well -1 for CPT-Fe 3 O 4 ), which indicated that the loading process of CPT presented no effect on the endocytosis of nanocarriers. To obtain a generalized conclusion, another two kinds of carcinoma cell lines including HepG2 cells and Hela cells were selected to investigate the delivery efficiency of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres. As exhibited in Fig. S6, CPT-Fe 3 O 4 could kill more cells than CPT only based on both mentioned cell lines, which foretold that the magnetic hollow spheres could act as high-performance carriers during the drug delivery system. In addition, morphological change of cell nuclei observed via fluorescence microscope imaging was investigated to provide a systemic explanation for above excellent anticancer efficiency. As shown in Fig. 4D, all the nuclei revealed normal morphology without any accumulation of chromatin, indicating our Fe 3 O 4 showed nearly no toxicity towards cells. On the contrary, obvious nuclear fragmentation and accumulation of chromatin could occur in most of 786-O cells incubated upon CPT-Fe 3 O 4, while fewer condensed nuclei presented in 786-O cells incubated with CPT only. To further demonstrate the performance of Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres in drug delivery system, Journal Name, [year], [vol], This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year]
6 Page 5 of 7 Dalton Transactions Fig. 4 Effect of Fe 3O 4 hollow spheres on the viability of 786-O cells under 24 h of incubation (a), release amounts of CPT from CPT-Fe 3O 4 complex measured via UV-vis method (b), viability of 786-O cells incubated with CPT and CPT-Fe 3O 4 upon different incubation concentrations (c), as well as 5 microscope imaging photos of stained nuclei of 786-O cells (d) (scale bar: 50 µm) tryblue staining shown in Fig. S7 also indicated our above description. There were more death occurred in CPT-Fe 3 O 4 group than CPT group. More importantly, nearly no death occurred in Fe 3 O 4 group, indicating neglectable toxicity in vitro. Thus, it could be deduced that well-prepared Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres could potentially be applied as effective vehicles to store and deliver highly toxic and water-insoluble anticancer drug for cancer treatment. Conclusions In summary, monodisperse magnetic hollow spheres based no iron oxide with excellent magnetic response have been successfully designed and constructed via a facile one-pot solvothermal route. The amount of ETA in solvent played an important role during the formation od Fe 3 O 4 hollow structure, indicating the solvent effect in preparation of nanomaterials. These well-prepared Fe 3 O 4 hollow spheres could effectively deliver insoluble anticancer drug to the cancer cells due to the presence of large inner cavity. Otherwise, CPT-Fe 3 O 4 composites demonstrated a much higher anticancer activity than single CPT in accordance with its low solubility in physiological condition. Above results indicated our magnetic hollow spheres promised the potentials in anticancer drug delivery and cancer treatment in vitro. References 1 R. Bardhan, S. Lal, A. Joshi, N. Halas, Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, D. Yoo, J. Lee, T. Shin, J. Cheon, Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, W. Wei, Z. Yue, J. Qu, H. Yue, Z. Su, G. Ma, Nanomedicine 2010, 35 5, C. Lipinski, Am. Pharm. Rev. 2002, 5, Z. Yue, W. Wei, Z. You, Q. Yang, H. Yue, Z. Su, G. Ma, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, C. Wischke, S. Schwendeman, Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, C. Lipinski, F. Lombardo, B. Dominy, P. Feeney, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3. 8 B. Parakhonskiy, A. Haase, R. Antolini, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, P. Yang, Z. Quan, C. Li, X. Kang, H. Lian, J. Lin, Biomaterials , 29, M. Melancon, A. Elliott, A. Shetty, Q. Huang, R. Stafford, C. Li, J. Controlled Release 2011, 156, W. Zhao, H. Chen, Y. Li, L. Li, M. Lang, J. Shi, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, Y. Zhu, T. Ikoma, N. Hanagata, S. Kaskel, Small 2010, 6, R. Hao, R. Xing, Z. Xu, Y. Hou, S. Gao, S. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, X. Lou, L. Archer, Z. Yang, Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, D. Yang, X. Kang, P. Ma, Y. Dai, Z. Hou, Z. Cheng, C. Li, J. Lin, 55 Biomaterials 2013, 34, H. Liu, D. Chen, L. Lin, T. Liu, L. Tan, X. Wu, F. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, Y. Chen, H. Chen, J. Shi, Acc. Chem. Res. DOI: /ar400091e Z. Liu, X. Liu, Q. Yuan, K. Dong, L. Jiang, Z. Li, J. Ren, X. Qu, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, S. Skrabalak, J. Chen, Y. Sun, X. Lu, L. Au, C. Cobley, Y. Xia, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, M. Ambrogio, C. Thomas, Y. Zhao, J. Zink, J. Stoddart, Acc. Chem. 65 Res. 2011, 44, W. Dong, Y. Li, D. Niu, Z. Ma, J. Gu, Y. Chen, W. Zhao, X. Liu, C. Liu, J. Shi, Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, S. Selvan, P. Patra, C. Ang, J. Ying, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, J. Ge, Q. Zhang, T. Zhang, Y. Yin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, H. Wu, S. Zhang, J. Zhang, G. Liu, J. Shi, L. Zhang, X. Cui, M. Ruan, Q. He, W. Bu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year] Journal Name, [year], [vol],
7 Dalton Transactions Page 6 of 7 25 B. Kim, N. Lee, H. Kim, K. An, Y. Park, Y. Choi, K. Shin, Y. Lee, S. Kwon, H. Na, J. Park, T. Ahn, Y. Kim, W. Moon, S. Choi, T. Hyeon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, N. Frey, S. Peng, K. Cheng, S. Sun, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, C. Xu, Z. Yuan, N. Kohler, J. Kim, M. Chung, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, Z. Liu, M. Li, X. Yang, M. Yin, J. Ren, X. Qu, Biomaterials 2011, 32, W. Seo, J. Lee, X. Sun, Y. Suzuki, D. Mann, Z. Liu, M. Terashima, P. Yang, M. Mcconnell, D. Nishimura, H. Dai, Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, K. Yan, H. Li, P. Li, H. Zhu, J. Shen, C. Yi, S. Wu, K. Yeung, Z. Xu, H. Xu, P. Chu, Biomaterials 2014, 35, H. Deng, X. Li, Q. Peng, X. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, W. Cheng, K. Tang, J. Sheng, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, P. Yang, Z. Quan, Z. Hou, C. Li, X. Kang, Z. Cheng, J. Lin, Biomaterials 2009, W. Ma, Y. Zhang, L. Li, L. You, P. Zhang, Y. Zhang, J. Li, M. Yu, J. Guo, H. Lu, C. Wang, ACS Nano 2012, 6, S. Liu, H. Chen, X. Lu, C. Deng, X. Zhang, P. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, J. Kim, H. Kim, N. Lee, T. Kim, H. Kim, T. Yu, I. Song, W. Moon, 25 T. Hyeon, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, J. Choi, Y. Jun, S. Yeon, H. Kim, J. Shin, J. Cheon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, M. Liong, J. Lu, M. Kovochich, T. Xia, S. Ruehm, A. Nel, F. Tamanoi, J. Zink, ACS Nano 2008, 2, C. Thomas, D. Ferris, J. Lee, E. Choi, M. Cho, E. Kim, J. Stoddart, J. Shin, J. Cheon, J. Zink, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, Y. Zhao, L. Lin, Y. Lu, H. Gao, S. Chen, P. Yang, S. Yu, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2012, 1, X. Kang, Y. dai, P. Ma, D. Yang, C. Li, Z. Hou, Z. Cheng, J. Lin, 35 Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, S. Guo, D. Li, L. Zhang, J. Li, E. Wang, Biomaterials 2009, 30, F. Wang, X. Chen, Z. Zhao, S. Tang, X. Huang, C. Lin, C. Cai, N. Zheng, J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, M. Zhu, G. Nie, H. Meng, T. Xia, A. Nel, Y. Zhao, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, Z. Liu, J. robinson, X. Sun, H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, Z. Liu, F. Pu, S. Huang, Q. Yuan, J. Ren, X. Qu, Biomaterials 2013, 45 34, Y. Jun, J. Seo, J. Cheon, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, S. Hu, K. Kuo, W. Tung, D. Liu, S. Chen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, C. Xu, K. Xu, H. Gu, R. Zheng, H. Liu, X. Zhang, Z. Guo, B. Xu, J. 50 Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, S. Gai, P. Yang, C. Li, W. Wang, Y. Dai, N. Niu, J. Lin, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, Journal Name, [year], [vol], This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year]
8 Page 7 of 7 Dalton Transactions Table of Contents Uniform Iron Oxide Hollow Spheres for High-performance Delivery of Insoluble Anticancer Drugs 5 Novel magnetic hollow spheres based on iron oxide have been desiged and synthesized via a facile and cost-effective one-pot solvothermal route, which successfully acted as nanocarriers for the high-performance delivery of insoluble anticancer drugs in vitro. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry [year] Journal Name, [year], [vol],
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Supporting Information. Carbon Imidazolate Framework-8 Nanoparticles for
 Supporting Information Carbon Nanodots@Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous ph-responsive Drug Delivery and Fluorescence Imaging Liu He, a Tingting Wang, b Jiping An, c Xiaomeng
Supporting Information Carbon Nanodots@Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous ph-responsive Drug Delivery and Fluorescence Imaging Liu He, a Tingting Wang, b Jiping An, c Xiaomeng
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Self-Sacrificial Template-Induced Modulation of Conjugated Microporous Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Self-Sacrificial Template-Induced Modulation of Conjugated Microporous Polymer
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Surfactant-Free Preparation of Au@Resveratrol Hollow Nanoparticles with Photothermal Performance and Antioxidant Activity Wenjing Wang, Qi Tang, Tianrong Yu, Xing Li, Yang Gao, Jing
Supporting Information Surfactant-Free Preparation of Au@Resveratrol Hollow Nanoparticles with Photothermal Performance and Antioxidant Activity Wenjing Wang, Qi Tang, Tianrong Yu, Xing Li, Yang Gao, Jing
High Yield Synthesis of Bracelet-like Hydrophilic Ni-Co Magnetic Alloy Flux-closure Nanorings
 Supporting information High Yield Synthesis of Bracelet-like Hydrophilic Ni-Co Magnetic Alloy Flux-closure Nanorings Ming-Jun Hu, Yang Lu, Sen Zhang, Shi-Rui Guo, Bin Lin, Meng Zhang, Shu-Hong Yu* Experimental
Supporting information High Yield Synthesis of Bracelet-like Hydrophilic Ni-Co Magnetic Alloy Flux-closure Nanorings Ming-Jun Hu, Yang Lu, Sen Zhang, Shi-Rui Guo, Bin Lin, Meng Zhang, Shu-Hong Yu* Experimental
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Functionalized Nano-MoS 2 with Peroxidase Catalytic and Near- Infrared Photothermal Activities for Safe and Synergetic Wound Antibacterial Applications Wenyan Yin, a,#, * Jie Yu,
Supporting Information Functionalized Nano-MoS 2 with Peroxidase Catalytic and Near- Infrared Photothermal Activities for Safe and Synergetic Wound Antibacterial Applications Wenyan Yin, a,#, * Jie Yu,
General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported. Bicomponent Metal Monoxides as Alternative High- Performance Li-Ion Anodes to Binary Spinel Oxides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Multilayer CuO@NiO Hollow Spheres: Microwave-Assisted Metal-Organic-Framework Derivation and Highly Reversible Structure-Matched Stepwise Lithium Storage Wenxiang Guo, Weiwei
Supporting Information for Multilayer CuO@NiO Hollow Spheres: Microwave-Assisted Metal-Organic-Framework Derivation and Highly Reversible Structure-Matched Stepwise Lithium Storage Wenxiang Guo, Weiwei
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Complex Bioactive Delivery Vehicles
 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Complex Bioactive Delivery Vehicles Kathleen Eggleson, Ph.D. Center for Nano Science and Technology University of Notre Dame Characteristics of mesoporous materials Material
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Complex Bioactive Delivery Vehicles Kathleen Eggleson, Ph.D. Center for Nano Science and Technology University of Notre Dame Characteristics of mesoporous materials Material
Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug Delivery
 Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials: Tannic acid (TA), silver nitrate
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials: Tannic acid (TA), silver nitrate
A project report on SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERISATION OF COPPER NANOPARTICLE-GRAPHENE COMPOSITE. Submitted by Arun Kumar Yelshetty Roll no 410 CY 5066
 A project report on SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERISATION OF COPPER NANOPARTICLE-GRAPHENE COMPOSITE Submitted by Arun Kumar Yelshetty Roll no 410 CY 5066 Under the guidance of Prof. (Ms). Sasmita Mohapatra Department
A project report on SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERISATION OF COPPER NANOPARTICLE-GRAPHENE COMPOSITE Submitted by Arun Kumar Yelshetty Roll no 410 CY 5066 Under the guidance of Prof. (Ms). Sasmita Mohapatra Department
Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with. Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang Yang, Pu-Can Guo, Han-Qing Yu*
 Supporting Information for Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn 1.8 Fe 1.2 O 4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang
Supporting Information for Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn 1.8 Fe 1.2 O 4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang
Supporting Information for:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Multifunctional PB@mSiO 2 -PEG/DOX Nanoplatform for Combined Photothermal-Chemotherapy of Tumor Yun Yan Su a#, Zhaogang Teng a#, Hui Yao b, Shou Ju Wang a, Ying Tian a, Yun Lei
Supporting Information A Multifunctional PB@mSiO 2 -PEG/DOX Nanoplatform for Combined Photothermal-Chemotherapy of Tumor Yun Yan Su a#, Zhaogang Teng a#, Hui Yao b, Shou Ju Wang a, Ying Tian a, Yun Lei
Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries
 Supporting Information for Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries Zhu-Yin Sui, Pei-Ying Zhang,, Meng-Ying Xu,
Supporting Information for Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries Zhu-Yin Sui, Pei-Ying Zhang,, Meng-Ying Xu,
Multifunctional polyphosphazene-coated multi-walled carbon. nanotubes for the synergistic treatment of redox-responsive
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for Multifunctional polyphosphazene-coated multi-walled carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for Multifunctional polyphosphazene-coated multi-walled carbon
The Biological Effect of Iron Oxide and its Hydrate Nanoparticles
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 121-123 (2007) pp 735-738 Online available since 2007/Mar/15 at www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.121-123.735
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 121-123 (2007) pp 735-738 Online available since 2007/Mar/15 at www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.121-123.735
Supporting Information. Oxalate-Assisted Formation of Uniform Carbon-Confined SnO 2 Nanotubes with Enhanced Lithium Storage
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Oxalate-Assisted Formation of Uniform Carbon-Confined SnO 2 Nanotubes with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Oxalate-Assisted Formation of Uniform Carbon-Confined SnO 2 Nanotubes with
Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal. Nanoparticles-Infinite Coordination Polymers as a Specific
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Infinite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Infinite
External Magnetic Field Enhanced Chemo-Photothermal Combination Tumor. Therapy via Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
 Supporting information External Magnetic Field Enhanced Chemo-Photothermal Combination Tumor Therapy via Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Xiaomeng Guo, Wei Li, Lihua Luo, Zuhua Wang, Qingpo Li, Fenfen Kong, Hanbo
Supporting information External Magnetic Field Enhanced Chemo-Photothermal Combination Tumor Therapy via Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Xiaomeng Guo, Wei Li, Lihua Luo, Zuhua Wang, Qingpo Li, Fenfen Kong, Hanbo
One-pot synthesis of bi-metallic PdRu tripods as an efficient catalyst for. electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction to ammonia
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for One-pot synthesis of bi-metallic PdRu tripods
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for One-pot synthesis of bi-metallic PdRu tripods
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Hybrid Gold Superstructures: Synthesis and. Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications
 Supporting Information Hybrid Gold Nanocube@Silica@Graphene-Quantum-Dot Superstructures: Synthesis and Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications Liu Deng, Ling Liu, Chengzhou Zhu, Dan Li and Shaojun
Supporting Information Hybrid Gold Nanocube@Silica@Graphene-Quantum-Dot Superstructures: Synthesis and Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications Liu Deng, Ling Liu, Chengzhou Zhu, Dan Li and Shaojun
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Mesoporous C-coated SnO x nanosheets
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Mesoporous C-coated SnO x nanosheets
Gold Nanoshell Coated Thermo-pH Dual Responsive Liposomes for Resveratrol Delivery and Chemophotothermal
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Gold Nanoshell Coated Thermo-pH
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Gold Nanoshell Coated Thermo-pH
Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene. quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Supporting Information. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Polymer-coated spherical mesoporous silica for ph-controlled delivery of insulin Sae Rom Choi a,, Dong-jin Jang b,, Sanghyun Kim a, Sunhyung An c, Jinwoo Lee c, Euichaul
Electronic Supplementary Information Polymer-coated spherical mesoporous silica for ph-controlled delivery of insulin Sae Rom Choi a,, Dong-jin Jang b,, Sanghyun Kim a, Sunhyung An c, Jinwoo Lee c, Euichaul
Supporting information
 Supporting information Manipulating the Concavity of Rhodium Nanocubes Enclosed with High-index Facets via Site-selective Etching Yumin Chen, Qing-Song Chen, Si-Yan Peng, Zhi-Qiao Wang, Gang Lu, and Guo-Cong
Supporting information Manipulating the Concavity of Rhodium Nanocubes Enclosed with High-index Facets via Site-selective Etching Yumin Chen, Qing-Song Chen, Si-Yan Peng, Zhi-Qiao Wang, Gang Lu, and Guo-Cong
Kinetically-Enhanced Polysulfide Redox Reactions by Nb2O5. Nanocrystal for High-Rate Lithium Sulfur Battery
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Kinetically-Enhanced Polysulfide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Kinetically-Enhanced Polysulfide
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials Nanjing Hao, Kalana W. Jayawardana, Xuan Chen
Supporting Information One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials Nanjing Hao, Kalana W. Jayawardana, Xuan Chen
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Highly efficient and recyclable triple-shelled Ag@Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 @TiO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Highly efficient and recyclable triple-shelled Ag@Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 @TiO
The cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles is dispersitydependent
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles is dispersitydependent Dengtong Huang, Hualu
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles is dispersitydependent Dengtong Huang, Hualu
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Surfactant-Free Assembly of Mesoporous Carbon Hollow Spheres with Large Tunable Pore Sizes Hongwei Zhang, Owen Noonan, Xiaodan Huang, Yannan Yang, Chun Xu, Liang Zhou, and Chengzhong
Supporting Information Surfactant-Free Assembly of Mesoporous Carbon Hollow Spheres with Large Tunable Pore Sizes Hongwei Zhang, Owen Noonan, Xiaodan Huang, Yannan Yang, Chun Xu, Liang Zhou, and Chengzhong
Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation. and Elimination of Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
Fully Zwitterionic Nanoparticle Antimicrobial Agents through Tuning of Core Size and Ligand Structure
 Supporting Information Fully Zwitterionic Nanoparticle Antimicrobial Agents through Tuning of Core Size and Ligand Structure Shuaidong Huo,,,, Ying Jiang,, Akash Gupta, Ziwen Jiang, Ryan Landis, Singyuk
Supporting Information Fully Zwitterionic Nanoparticle Antimicrobial Agents through Tuning of Core Size and Ligand Structure Shuaidong Huo,,,, Ying Jiang,, Akash Gupta, Ziwen Jiang, Ryan Landis, Singyuk
Tuning the Shell Number of Multi-Shelled Metal Oxide. Hollow Fibers for Optimized Lithium Ion Storage
 Supporting Information Tuning the Shell Number of Multi-Shelled Metal Oxide Hollow Fibers for Optimized Lithium Ion Storage Jin Sun, Chunxiao Lv, Fan Lv, ǁ Shuai Chen, Daohao Li, Ziqi Guo, Wei Han, Dongjiang
Supporting Information Tuning the Shell Number of Multi-Shelled Metal Oxide Hollow Fibers for Optimized Lithium Ion Storage Jin Sun, Chunxiao Lv, Fan Lv, ǁ Shuai Chen, Daohao Li, Ziqi Guo, Wei Han, Dongjiang
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C. composites for photodegradation of organic dye
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C composites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C composites
Digitized single scattering nanoparticles for probing molecular binding
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Digitized single scattering nanoparticles for probing molecular binding Yue Liu a, Cheng Zhi Huang a,b* a Education Ministry Key Laboratory on Luminescence and
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Digitized single scattering nanoparticles for probing molecular binding Yue Liu a, Cheng Zhi Huang a,b* a Education Ministry Key Laboratory on Luminescence and
RSC Advances.
 This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted Manuscripts are published online shortly after
This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted Manuscripts are published online shortly after
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Eco-friendly Composite of Fe 3 O 4 -Reduced Grapene Oxide Particles for Efficient Enzyme Immobilization Sanjay K. S. Patel a,, Seung Ho Choi b,, Yun Chan Kang b,*, Jung-Kul Lee a,*
Supporting Information Eco-friendly Composite of Fe 3 O 4 -Reduced Grapene Oxide Particles for Efficient Enzyme Immobilization Sanjay K. S. Patel a,, Seung Ho Choi b,, Yun Chan Kang b,*, Jung-Kul Lee a,*
bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Hierarchical Ni/NiTiO 3 derived from NiTi LDHs: a bifunctional electrocatalyst
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Hierarchical Ni/NiTiO 3 derived from NiTi LDHs: a bifunctional electrocatalyst
New Journal of Chemistry Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 New Journal of Chemistry Electronic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 New Journal of Chemistry Electronic
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information MoSe2 embedded CNT-Reduced Graphene Oxide (rgo) Composite Microsphere with Superior Sodium Ion Storage and Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performances Gi Dae Park, Jung Hyun
Supporting Information MoSe2 embedded CNT-Reduced Graphene Oxide (rgo) Composite Microsphere with Superior Sodium Ion Storage and Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performances Gi Dae Park, Jung Hyun
In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to synthesis sulfide-graphene nanocomposites
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
1 Synthesis and characterization of the amphiphilic ionic dendrimers
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary information 1 Synthesis and characterization of the amphiphilic ionic dendrimers
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary information 1 Synthesis and characterization of the amphiphilic ionic dendrimers
Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Hematite) Nanocrystals. Z.H. Lee
 ABSTRACT Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Hematite) Nanocrystals Z.H. Lee Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge, Singapore 119260 Monodispersed iron oxide
ABSTRACT Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Hematite) Nanocrystals Z.H. Lee Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge, Singapore 119260 Monodispersed iron oxide
Supporting Information. Phenolic/resin assisted MOFs derived hierarchical Co/N-doping carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Interaction effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different morphologies on human red blood cells Madhura Joglekar, Robert A. Roggers, Yannan Zhao, and Brian G. Trewyn
Supporting Information Interaction effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different morphologies on human red blood cells Madhura Joglekar, Robert A. Roggers, Yannan Zhao, and Brian G. Trewyn
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information 1. Synthesis of perovskite materials CH 3 NH 3 I
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information 1. Synthesis of perovskite materials CH 3 NH 3 I
Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water. (a) A typical photograph of fullerence (C60), C60S nanoparticles,
Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water. (a) A typical photograph of fullerence (C60), C60S nanoparticles,
A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal
 Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Materials Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs, φ = 10-30 nm) were purchased from Nanotech Port Co. Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, >98 %), Triton X-100 and
Supporting Information Materials Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs, φ = 10-30 nm) were purchased from Nanotech Port Co. Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, >98 %), Triton X-100 and
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Nanosized metal organic framework of Fe-MIL-88NH 2 as a novel peroxidase mimic and used for colorimetric detection of glucose
 Supplementary Information for Nanosized metal organic framework of Fe-MIL-88NH 2 as a novel peroxidase mimic and used for colorimetric detection of glucose Ya Li Liu, a Xi Juan Zhao, a Xiao Xi Yang b and
Supplementary Information for Nanosized metal organic framework of Fe-MIL-88NH 2 as a novel peroxidase mimic and used for colorimetric detection of glucose Ya Li Liu, a Xi Juan Zhao, a Xiao Xi Yang b and
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Near-infrared light and ph-responsive
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Near-infrared light and ph-responsive Au@carbon/calcium
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Near-infrared light and ph-responsive Au@carbon/calcium
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
for highly efficient and stable corrosive-water evaporation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of mesoporous Fe 3 Si aerogel
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of mesoporous Fe 3 Si aerogel
Engineering of Hollow Core-Shell Interlinked Carbon Spheres for Highly Stable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Engineering of Hollow Core-Shell Interlinked Carbon Spheres for Highly Stable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Qiang Sun, Bin He, Xiang-Qian Zhang, and An-Hui Lu* State Key Laboratory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Engineering of Hollow Core-Shell Interlinked Carbon Spheres for Highly Stable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Qiang Sun, Bin He, Xiang-Qian Zhang, and An-Hui Lu* State Key Laboratory
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Hollow Microporous Organic Capsules Buyi Li, Xinjia Yang, Lingling Xia, Muhammad Irfan Majeed and Bien Tan* Both Buyi Li and Xinjia Yang contributed equally to this work School
Supplementary Information Hollow Microporous Organic Capsules Buyi Li, Xinjia Yang, Lingling Xia, Muhammad Irfan Majeed and Bien Tan* Both Buyi Li and Xinjia Yang contributed equally to this work School
Please do not adjust margins. Flower stamen-like porous boron carbon nitride nanoscrolls for water cleaning
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Flower stamen-like porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Flower stamen-like porous
Lotus root-like porous carbon nanofiber anchored with CoP nanoparticles as all-ph hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Material Lotus root-like porous carbon nanofiber anchored with CoP nanoparticles as all-ph hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts Hengyi Lu 1, Wei Fan 2 ( ), Yunpeng Huang 1, and
Electronic Supplementary Material Lotus root-like porous carbon nanofiber anchored with CoP nanoparticles as all-ph hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts Hengyi Lu 1, Wei Fan 2 ( ), Yunpeng Huang 1, and
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Supporting Information. Sol gel Coating of Inorganic Nanostructures with Resorcinol Formaldehyde Resin
 Supporting Information Sol gel Coating of Inorganic Nanostructures with Resorcinol Formaldehyde Resin Na Li, a,b Qiao Zhang, b Jian Liu, c Jibong Joo, b Austin Lee, b Yang Gan,* a Yadong Yin *b a School
Supporting Information Sol gel Coating of Inorganic Nanostructures with Resorcinol Formaldehyde Resin Na Li, a,b Qiao Zhang, b Jian Liu, c Jibong Joo, b Austin Lee, b Yang Gan,* a Yadong Yin *b a School
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals
 A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
Supporting Information. Co 4 N Nanosheets Assembled Mesoporous Sphere as a Matrix for Ultrahigh Sulfur Content Lithium Sulfur Batteries
 Supporting Information Co 4 N Nanosheets Assembled Mesoporous Sphere as a Matrix for Ultrahigh Sulfur Content Lithium Sulfur Batteries Ding-Rong Deng, Fei Xue, Yue-Ju Jia, Jian-Chuan Ye, Cheng-Dong Bai,
Supporting Information Co 4 N Nanosheets Assembled Mesoporous Sphere as a Matrix for Ultrahigh Sulfur Content Lithium Sulfur Batteries Ding-Rong Deng, Fei Xue, Yue-Ju Jia, Jian-Chuan Ye, Cheng-Dong Bai,
In Situ Gelation-Induced Death of Cancer Cells Based on Proteinosomes
 Supporting information for In Situ Gelation-Induced Death of Cancer Cells Based on Proteinosomes Yuting Zhou, Jianmin Song, Lei Wang*, Xuting Xue, Xiaoman Liu, Hui Xie*, and Xin Huang* MIIT Key Laboratory
Supporting information for In Situ Gelation-Induced Death of Cancer Cells Based on Proteinosomes Yuting Zhou, Jianmin Song, Lei Wang*, Xuting Xue, Xiaoman Liu, Hui Xie*, and Xin Huang* MIIT Key Laboratory
1 Supporting Information. 2 Reconfigurable and resettable arithmetic logic units based. 4 Siqi Zhang a, Kun Wang a, Congcong Huang b and Ting Sun a*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 1 Supporting Information 2 Reconfigurable and resettable arithmetic logic units based 3 on magnetic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 1 Supporting Information 2 Reconfigurable and resettable arithmetic logic units based 3 on magnetic
Electronic Supplementary Material. Methods. Synthesis of reference samples in Figure 1(b) Nano Res.
 Electronic Supplementary Material Shaped Pt Ni nanocrystals with an ultrathin Pt-enriched shell derived from one-pot hydrothermal synthesis as active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction Jun Gu 1,, Guangxu
Electronic Supplementary Material Shaped Pt Ni nanocrystals with an ultrathin Pt-enriched shell derived from one-pot hydrothermal synthesis as active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction Jun Gu 1,, Guangxu
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Precisely Controllable Core-Shell Ag@Carbon Dots Nanoparticles: Application to in Situ Super-Sensitive Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions Jing Jin, Shoujun Zhu, Yubin Song, Hongyue
Supporting Information Precisely Controllable Core-Shell Ag@Carbon Dots Nanoparticles: Application to in Situ Super-Sensitive Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions Jing Jin, Shoujun Zhu, Yubin Song, Hongyue
Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni foam for solar thermal water evaporation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 The supporting information for Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 The supporting information for Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni
Supplementary Material for. Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive Nitrogen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Supporting Information. for. Advanced Materials, adma Wiley-VCH 2006
 Supporting Information for Advanced Materials, adma.200601546 Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting Information Synthesis of Magnetic Microspheres with Immobilized Metal Ions for Enrichment
Supporting Information for Advanced Materials, adma.200601546 Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting Information Synthesis of Magnetic Microspheres with Immobilized Metal Ions for Enrichment
A Scalable Synthesis of Few-layer MoS2. Incorporated into Hierarchical Porous Carbon. Nanosheets for High-performance Li and Na Ion
 Supporting Information A Scalable Synthesis of Few-layer MoS2 Incorporated into Hierarchical Porous Carbon Nanosheets for High-performance Li and Na Ion Battery Anodes Seung-Keun Park, a,b Jeongyeon Lee,
Supporting Information A Scalable Synthesis of Few-layer MoS2 Incorporated into Hierarchical Porous Carbon Nanosheets for High-performance Li and Na Ion Battery Anodes Seung-Keun Park, a,b Jeongyeon Lee,
Supplementary Figure 1. (a-b) EDX of Mo 2 and Mo 2
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a-b) EDX of Mo 2 C@NPC/NPRGO and Mo 2 C@NPC. Supplementary Figure 2. (a) SEM image of PMo 12 2-PPy, (b) TEM, (c) HRTEM, (d) STEM image and EDX elemental mapping of C, N, P, and
Supplementary Figure 1. (a-b) EDX of Mo 2 C@NPC/NPRGO and Mo 2 C@NPC. Supplementary Figure 2. (a) SEM image of PMo 12 2-PPy, (b) TEM, (c) HRTEM, (d) STEM image and EDX elemental mapping of C, N, P, and
Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution
 Electronic Supplementary Material Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution Jiaqing Zhu 1, Zhiyu Ren 1 ( ), Shichao Du 1, Ying Xie 1, Jun Wu 1,2, Huiyuan
Electronic Supplementary Material Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution Jiaqing Zhu 1, Zhiyu Ren 1 ( ), Shichao Du 1, Ying Xie 1, Jun Wu 1,2, Huiyuan
Supporting Information. Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive Photocatalyst for the Suzuki Coupling Reaction**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion. Batteries
 Layered-Structure SbPO 4 /Reduced Graphene Oxide: An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion Batteries Jun Pan, Shulin Chen, # Qiang Fu, Yuanwei Sun, # Yuchen Zhang, Na Lin, Peng Gao,* # Jian Yang,* and
Layered-Structure SbPO 4 /Reduced Graphene Oxide: An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion Batteries Jun Pan, Shulin Chen, # Qiang Fu, Yuanwei Sun, # Yuchen Zhang, Na Lin, Peng Gao,* # Jian Yang,* and
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Au-HKUST-1 Composite Nanocapsules: Synthesis with a Coordination Replication Strategy and Catalysis on CO Oxidation Yongxin Liu, 1 Jiali Zhang, 1 Lingxiao Song, 1 Wenyuan Xu, 1 Zanru
Supporting Information Au-HKUST-1 Composite Nanocapsules: Synthesis with a Coordination Replication Strategy and Catalysis on CO Oxidation Yongxin Liu, 1 Jiali Zhang, 1 Lingxiao Song, 1 Wenyuan Xu, 1 Zanru
Fabrication of Metallic Nickel-Cobalt Phosphide Hollow Microspheres for. High-Rate Supercapacitors
 Supporting Information Fabrication of Metallic Nickel-Cobalt Phosphide Hollow Microspheres for High-Rate Supercapacitors Miao Gao, Wei-Kang Wang, Xing Zhang, Jun Jiang, Han-Qing Yu CAS Key Laboratory of
Supporting Information Fabrication of Metallic Nickel-Cobalt Phosphide Hollow Microspheres for High-Rate Supercapacitors Miao Gao, Wei-Kang Wang, Xing Zhang, Jun Jiang, Han-Qing Yu CAS Key Laboratory of
Supporting Information. Simple Bacterial Detection and High-Throughput Drug Screening. Based on Graphene-Enzyme Complex
 Supporting Information Simple Bacterial Detection and High-Throughput Drug Screening Based on Graphene-Enzyme Complex Juan-Li, Ling-Jie Wu, Shan-Shan Guo, Hua-E Fu, Guo-Nan Chen* and Huang-Hao Yang* The
Supporting Information Simple Bacterial Detection and High-Throughput Drug Screening Based on Graphene-Enzyme Complex Juan-Li, Ling-Jie Wu, Shan-Shan Guo, Hua-E Fu, Guo-Nan Chen* and Huang-Hao Yang* The
Immobilization of BiOX (X=Cl, Br) on activated carbon fibers as
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Immobilization of BiOX (X=Cl, Br) on activated carbon fibers as recycled photocatalysts
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Immobilization of BiOX (X=Cl, Br) on activated carbon fibers as recycled photocatalysts
Supplementary Information. Pluronic polymer capped biocompatible mesoporous silica nanocarriers
 Supplementary Information Pluronic polymer capped biocompatible mesoporous silica nanocarriers Adem Yildirim,* ab Gokcen Birlik Demirel, bc Rengin Erdem, ab Berna Senturk, ab Turgay Tekinay, ab and Mehmet
Supplementary Information Pluronic polymer capped biocompatible mesoporous silica nanocarriers Adem Yildirim,* ab Gokcen Birlik Demirel, bc Rengin Erdem, ab Berna Senturk, ab Turgay Tekinay, ab and Mehmet
Hierarchical MoO 2 /Mo 2 C/C Hybrid Nanowires for High-Rate and. Long-Life Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Hierarchical MoO 2 /Mo 2 C/C Hybrid Nanowires for High-Rate and Long-Life Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries Lichun Yang, a Xiang Li, a Yunpeng Ouyang, a Qingsheng Gao, b Liuzhang
Supporting Information Hierarchical MoO 2 /Mo 2 C/C Hybrid Nanowires for High-Rate and Long-Life Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries Lichun Yang, a Xiang Li, a Yunpeng Ouyang, a Qingsheng Gao, b Liuzhang
Ratiometric Detection of Intracellular Lysine and ph with One-Pot Synthesized Dual Emissive Carbon Dots
 Supporting Information Ratiometric Detection of Intracellular Lysine and ph with One-Pot Synthesized Dual Emissive Carbon Dots Wei Song, 1 Wenxiu Duan, 2 Yinghua Liu, 1 Zhongju Ye, 3 Yonglei Chen, 1 Hongli
Supporting Information Ratiometric Detection of Intracellular Lysine and ph with One-Pot Synthesized Dual Emissive Carbon Dots Wei Song, 1 Wenxiu Duan, 2 Yinghua Liu, 1 Zhongju Ye, 3 Yonglei Chen, 1 Hongli
Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric
 Modern Applied Science January, 2009 Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric Fan Zhang & Junling Yang School of Material Science and Chemical Engineer Tianjin Polytechnic
Modern Applied Science January, 2009 Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric Fan Zhang & Junling Yang School of Material Science and Chemical Engineer Tianjin Polytechnic
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information One-Dimensional MoO2-Co2Mo3O8@C Nanorods: A Novel and High
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information One-Dimensional MoO2-Co2Mo3O8@C Nanorods: A Novel and High
Supplementary Figure 1. SEM and TEM images of the metal nanoparticles (MNPs) and metal oxide templates.
 Supplementary Figure 1. SEM and TEM images of the metal nanoparticles (MNPs) and metal oxide templates. (a) 13 nm Au, (b) 60 nm Au, (c) 3.3 nm Pt, (d) ZnO spheres, (e) Al 2O 3 spheres and (f) Cu 2O cubes.
Supplementary Figure 1. SEM and TEM images of the metal nanoparticles (MNPs) and metal oxide templates. (a) 13 nm Au, (b) 60 nm Au, (c) 3.3 nm Pt, (d) ZnO spheres, (e) Al 2O 3 spheres and (f) Cu 2O cubes.
Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance. absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive ions from.
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
Self-assembled pancake-like hexagonal tungsten oxide with ordered mesopores for supercapacitors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information Self-assembled pancake-like hexagonal
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information Self-assembled pancake-like hexagonal
A Simple Fluorescein Derived Colorimetric and Fluorescent off - on Sensor For The Detection of Hypochlorite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information A Simple Fluorescein Derived Colorimetric and Fluorescent off
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information A Simple Fluorescein Derived Colorimetric and Fluorescent off
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nest-like NiCoP for Highly Efficient Overall Water Splitting Cheng Du, a Lan Yang, a Fulin Yang, a Gongzhen Cheng a and Wei Luo a,b* a College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,
Supporting Information Nest-like NiCoP for Highly Efficient Overall Water Splitting Cheng Du, a Lan Yang, a Fulin Yang, a Gongzhen Cheng a and Wei Luo a,b* a College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,
