Screening Aid. Pine Sawyer Beetles Monochamus sutor (Linnaeus) and M. alternatus Hope. Joseph Benzel
|
|
|
- Anne Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Screening Aid Joseph Benzel 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research Boulevard, Suite 108, Fort Collins, Colorado U.S.A. ( itp@usda.gov) Version 3 6 July 2015 This CAPS (Cooperative Agricultural Pest Survey) screening aid produced for and distributed by: USDA-APHIS-PPQ National Identification Services (NIS) This and other identification resources are available at: The pine sawyer beetles (Monochamus spp.) are a widespread genus of longhorn beetles with several members of economic importance. Within this group are two species that are considered potentially invasive pests: the small white-marmorated longhorned beetle (Monochamus sutor) (Fig. 1) and the Japanese pine sawyer (Monochamus alternatus) (Fig. 2). Monochamus alternatus feeds primarily on pines (Pinus) but will attack a variety of conifers and some deciduous trees. Monochamus sutor attacks a variety of conifer species including fir (Abies), larch (Larix), and spruce (Picea). Both species are known to carry the pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) and other phytoparasitic nematodes that are capable of killing trees and spreading bacterial diseases. The beetle itself feeds on the phloem as a larvae and in the crown as an adult (Figs. 3-4) but is unlikely to directly kill its host. Monochamus belongs to the family, which are known as the longhorned beetles. Members of this family are recognized by their highly elongate antennae, in males sometimes reaching twice the length of body. Monochamus belongs to the subfamily Lamiinae which is distinguished by its hypognathus head, acute palpi, and obliquely sulcate anterior tibia. Fig. 1: Monochamus sutor on tree (photo by Stanislaw Kinelski, Bugwood.org). The genus Monochamus contains over 100 species and is found worldwide. Eight species and six additional subspecies occur in the U.S. Monochamus adults are identified by large acute lateral tubercles on the pronotum, coursely rougose elytral bases, and elongate front legs in the male. Neither M. alternatus nor M. sutor have been detected in the United States. This aid is designed to assist in the sorting and screening of M. alternatus and M. sutor suspect adults collected in Lindgren funnel traps and by visual surveys in the continental United States. It covers basic Sorting of traps, First Level, and Second Level screening, all based on morphological characters. Basic knowledge of morphology is necessary to screen for M. alternatus and M. sutor suspects. Fig. 2: Monochamus alternatus on tree (photo by William M. Ciesla, Forest Health Management International, Bugwood.org). 1
2 Sorting Insects collected during Monochamus surveys should be sorted initially for the presence of beetles of the appropriate size, color, and shape. 1. Beetles are between 15 mm (0.6 inches) and 28 mm (1.1 inches) in length. 2. Beetles have highly elongate antennae, over twice body length (Fig. 5). 3. Beetles are black, or mottled brown with white patches (Figs. 11 & 14). Beetles meeting these requirements should be forwarded to Level 1 Screening (Page 3). Fig. 5: male Monochamus sp. Fig. 3-4: Monochamus sp. galleries infected with bluestain fungi and containing larvae (top) and pupae (bottom). Despite their large size, Monochamus do little direct damage the host tree. They burrow in the phloem and heartwood where they feed on wood and symbiotic fungi. Most trees that are killed die as the result of infection by parasites vectored by the beetle. These include bluestain fungus, the pine wood nematode, and a variety of pathogenic bacteria (photos by Lacy L. Hyche, Auburn University, Bugwood.org). Fig. 6: female Monochamus sp. Fig. 5-6: Lateral views of male (top) and female (bottom) Monochamus sp. Monochamus is a sexually dimorphic genus with males having antennae and forelegs significantly longer than those of females. Conversely, the overall body size of females is usually greater than that of males, although some overlap does occur. 2
3 Level 1 Screening Suspect adults should be pinned and properly labeled. Level 1 Screening is based on characteristics of the head, tarsal claws, general dorsal surface, and antennae. It is designed to separate Monochamus from related genera. Head The heads of the subfamily Lamiinae are vertical with the genial margin directed posteriorly rather than ventrally (Fig 7). Tarsal Claws The tarsal claws of Monochamus are divergent (Fig. 8) rather than being divaricate or bifid. Fig. 7: Head of Monochamus sp. In the Lamiinae the head is vertically oriented with the mouthparts directed ventrally, and the genal margin is directed posteriorly. Antennae The antennal scape of Monochamus has a distinct carinate ring called a circatrix at the apex (Fig. 9). General Dorsal Features The prothorax of Monochamus bears a pair of large prominent lateral tubercles (Fig. 10). The elytral bases are coarsely rougose and the elytra themselves are uniformly covered with pubescence (Fig. 10). The related genus Anoplophora (which includes the Asian longhorned beetle - ALB) is always black in color and has pubecence only in distinct patches. Specimens meeting these requirements should be forwarded to Level Two Screening. Fig. 10: Dorsal view of Monochamus marmorator. Note the pair of large horns on the pronotum (circled), the coarsely rougose elytral bases, and the uniformly pubescent elytra. Many species have elaborately patterned pubescence. Fig. 8: Tarsal claws of Monochamus sp. Fig. 9: Antennal base of Monochamus sp. The scape has a distinct cicatrix at its apex (circled). 3
4 Level 2 Screening Level 2 screening is designed to separate M. alternatus and M. sutor suspects from native Monochamus. Screening is based on characters of the elytra and scutellum as well as general notes on size. Monochamus spp. are sexually dimorphic (Figs. 5-6), with the male having antennae twice as long as the body and females having antennae 1.5 times as long as the body. Monochamus sutor Monochamus sutor (Fig. 11) bears a close resemblence to the native M. scutellatus (Fig. 12). Both beetles are black in color which distinguishes them from other native Monochamus (Fig. 13). The apices of their elytra are rounded and unarmed by spines at the suture (Fig. 20). The two species can be distinguished by the larger amounts of pubescence on the elytra of M. sutor. Usually this pubescence is yellow in color and occurs in dense patches. In M. scutellatus the pubescence is more evenly distributed and is snow white in color. Both species have a densley pubescent scutellum where the difference in color of the pubescence can be easily observed (Figs ). Monochamus alternatus The elytral apex of M. alternatus (Fig. 21) is more narrowly rounded than that of M. sutor (Fig. 20). Monochamus alternatus is reddish brown to black in color with two broken stripes of orange pubescence on the pronotum (Fig. 27). Two native species, M. carolinensis (Fig. 15) and M. titillator (Fig. 16) bear a close resemblence to M. alternatus (Fig. 14). The three can be distinguished by the unarmed and somewhat flattened elytral apicies of M. alternatus compared to the broad tooth seen in M. carolinensis and the narrow conical tooth of M. titillator (Figs ). Other non-target species (Figs ) lack the tooth entirely (e.g., Fig. 24). Fig. 11: Monochamus sutor (target) Fig. 12: Monochamus scutellatus Fig. 13: Monochamus obtusus 4
5 Level 2 Non-targets Fig. 14: Monochamus alternatus (target) (Photo by Steven Valley, Oregon Department of Agriculture, Bugwood.org). Fig. 15: Monochamus carolinensis. Fig. 16: Monochamus titillator. Fig. 17: Monochamus mutator. Fig. 18: Monochamus clamator. 5 Fig. 19: Monochamus notatus.
6 Level 2 Non-targets Fig. 20: Monochamus sutor (target). Fig. 21: Monochamus alternatus (target). (Photo by Steven Valley, Oregon Department of Agriculture, Bugwood.org). Fig. 22: Monochamus carolinensis. Figs : Elytral apicies of various Monochamus spp. The apex of M. sutor is broadly rounded while that of most other Monochamus are more acute and often armed with spines as seen with M. carolinensis and M. titillator. The apex of M. alternatus is narrowed but unarmed. Fig. 23: Monochamus titillator. Fig. 24: Monochamus clamator Figs (left): Scutellums of M. sutor and M. scutellatus. Note the difference in the color of the pubescence. Fig. 25: Monochamus sutor (target). Fig. 26: Monochamus scutellatus. Suspect M. sutor (black cerambycids with vertical heads, a circatrix on the antennae, broadly rounded elytral apicies, and small spots of yellow pubescence) and M. alternatus (red-brown cerambycids with vertical heads, a circatrix on the antennae, narrowed but unarmed elytral apicies, and two stripes of orange pubescence on the pronotum) should be sent forward for identification. Specimens must be labeled and carefully packed to avoid damage during shipping. Fig. 27 (below) Pronotum of Monochamus alternatus. Note the two stripes of orange pubecence. (Photo by Steven Valley, Oregon Department of Agriculture, Bugwood.org). 6
7 Key and References Key to Sort and Screen M. sutor and M. alternatus Suspects in the United States 1. Beetles approxmately mm long; antennae significanly longer than body and with distinct. circatrix on scape (Fig. 9); coloration black or red-brown with uniformly pubescent elytra, mouthparts directed ventrally (Fig. 7); tarsal claws divergent (Fig. 8) Beetles larger or smaller than mm long; antennae not significantly longer than body or without distict circatrix; color not black or red brown or without uniformly distributed pubescence on the elytra; mouthparts directed forward; or tarsal claws divaricate or bifid... Not suspect 2. Elytral apices rounded (Fig. 20); body usually black Elytral apices flattened or armed with tooth (Fig. 21); body usually reddish brown Body with large amount of pubescence; patches of pubescence yellow in color (Fig. 25)...M. sutor suspect 3. Body with less pubescence, patches of pubescence white in color (Fig. 26)... Not suspect 4. Pronotum with two stripes of orange pubescence (Fig. 27); elytral apices not armed with tooth (Fig. 21)...M. alternatus suspect 4. Pronotum without stripes of orange pubescence; elytral apex armed with tooth (of various forms) (Figs )... Not suspect Citation Benzel, J. S Screening aid: Pine sawyer beetles,. Identification Technology Program (ITP), USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T, Fort Collins, CO. 7 pp. References for more information on Monochamus sutor, M. alternatus, and non-targets CERIS Exotic Wood Borer/Bark Beetle Survey Reference: Monochamus sutor. CERIS Exotic Wood Borer/Bark Beetle Survey Reference: Monochamus alternatus. node/506. Lingafelter, S. W Illustrated key to the longhorned woodboring beetles of the eastern United States. The Coleopterists Society. North Potomac. Maryland. pp Lingafelter, S. W. and Hoebeke, E. R Revision of the genus Anoplophora (: ). The Entomological Society of Washington. Washington D.C. pp Linsley, E. G. and Chemsak, J. A The of North America, Part VII, No. 1: Taxonomy and Classification of the Subfamily Lamiinae, Tribes Parmennini Through Acanthoderini. Entomology: Volume 102. University of California Press. Berkeley, California pp Turnbow, R. H. and Thomas, M. C Family 120., pp In, Arnett R. H., American Beetles: Volume II. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida. Acknowledgments Funding for this project was provided to J. S. Benzel through section of the FY2014 Farm Bill. I would like thank Terrence Walters (USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T ITP) and USDA-APHIS-PPQ National Identification Services for support of this work and access to imaging equipment. Boris Kondratieff, Donald Bright, and Todd Gilligan (Colorado State University) provided advice on species identification, image editing, and screening aid formatting. 7
Screening Aid. Six-toothed Bark Beetle Ips sexdentatus (Börner) Joseph Benzel
 Screening Aid Joseph Benzel 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research Boulevard, Suite 108, Fort Collins, Colorado
Screening Aid Joseph Benzel 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research Boulevard, Suite 108, Fort Collins, Colorado
Screening Aid. Asiatic Rice Borer Chilo suppressalis (Walker) Todd M. Gilligan 1 and Steven C. Passoa 2
 Screening Aid Todd M. Gilligan 1 and Steven C. Passoa 2 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research Boulevard, Suite
Screening Aid Todd M. Gilligan 1 and Steven C. Passoa 2 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research Boulevard, Suite
Screening Aid. Yellow Peach Moth Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenée) Hanna R. Royals 1, Todd M. Gilligan 1 and Steven C. Passoa 2
 Screening Aid Hanna R. Royals 1, Todd M. Gilligan 1 and Steven C. Passoa 2 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research
Screening Aid Hanna R. Royals 1, Todd M. Gilligan 1 and Steven C. Passoa 2 1) Identification Technology Program (ITP) / Colorado State University, USDA-APHIS-PPQ-Science & Technology (S&T), 2301 Research
A Strange New Genus and Species of Mesosini from North Thailand (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Lamiinae) [Studies on Asian Mesosini, VII]
![A Strange New Genus and Species of Mesosini from North Thailand (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Lamiinae) [Studies on Asian Mesosini, VII] A Strange New Genus and Species of Mesosini from North Thailand (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Lamiinae) [Studies on Asian Mesosini, VII]](/thumbs/94/118924602.jpg) Elytra, Tokyo, New Series, 1(1): 119 123 July 31, 2011 A Strange New Genus and Species of Mesosini from North Thailand (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Lamiinae) [Studies on Asian Mesosini, VII] Junsuke YAMASAKO
Elytra, Tokyo, New Series, 1(1): 119 123 July 31, 2011 A Strange New Genus and Species of Mesosini from North Thailand (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Lamiinae) [Studies on Asian Mesosini, VII] Junsuke YAMASAKO
Two new species of Cryptophagus HERBST, 1792 (Coleoptera: Cryptophagidae) from New Mexico (United States of America)
 Linzer biol. Beitr. 49/1 571-576 28.7.2017 Two new species of Cryptophagus HERBST, 1792 (Coleoptera: Cryptophagidae) from New Mexico (United States of America) Jens ESSER A b s t r a c t : Two new species
Linzer biol. Beitr. 49/1 571-576 28.7.2017 Two new species of Cryptophagus HERBST, 1792 (Coleoptera: Cryptophagidae) from New Mexico (United States of America) Jens ESSER A b s t r a c t : Two new species
Gypsy Moth Defoliation Harpers Ferry, Va
 Gypsy Moth Defoliation Harpers Ferry, Va Common Bad Bugs Eastern Tent Caterpillar Bagworm Japanese Beetles Aphids Scale Insects Borers Eastern Tent Caterpillar Bagworm Japanese Beetles Aphids Soft Scales
Gypsy Moth Defoliation Harpers Ferry, Va Common Bad Bugs Eastern Tent Caterpillar Bagworm Japanese Beetles Aphids Scale Insects Borers Eastern Tent Caterpillar Bagworm Japanese Beetles Aphids Soft Scales
Invasive Species Test. 30 Stations 90 seconds each -or- 15 stations (2/seat) 3 minutes each
 Invasive Species Test 30 Stations 90 seconds each -or- 15 stations (2/seat) 3 minutes each Station 1 A. The insect transmits Huanglongbing killing the plant upon which it feeds. How was this species introduced
Invasive Species Test 30 Stations 90 seconds each -or- 15 stations (2/seat) 3 minutes each Station 1 A. The insect transmits Huanglongbing killing the plant upon which it feeds. How was this species introduced
Do we understand how pinewood nematode kills trees? Some hypotheses
 Do we understand how pinewood nematode kills trees? Some hypotheses Hugh Evans, Sam Evans & Makihiko Ikegami Forest Research, the research agency of the Forestry Commission, UK Adults emerge carrying nematodes
Do we understand how pinewood nematode kills trees? Some hypotheses Hugh Evans, Sam Evans & Makihiko Ikegami Forest Research, the research agency of the Forestry Commission, UK Adults emerge carrying nematodes
Todd A.Steinlage, Alaska Department of Natural Resources, Division of Agriculture, Plant Materials Center
 Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus in Alaska Greenhouses and Nurseries Todd A.Steinlage, Alaska Department of Natural Resources, Division of Agriculture, Plant Materials Center Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV)
Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus in Alaska Greenhouses and Nurseries Todd A.Steinlage, Alaska Department of Natural Resources, Division of Agriculture, Plant Materials Center Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV)
Biology and Ecology of Forest Health. Climate Change and Tree Health
 Biology and Ecology of Forest Health Climate Change and Tree Health Assume classic UKCIP scenario: ca 3 o C warming in 50-80 yrs; warmer winters/summers; increased winter rain and summer drought; perturbations
Biology and Ecology of Forest Health Climate Change and Tree Health Assume classic UKCIP scenario: ca 3 o C warming in 50-80 yrs; warmer winters/summers; increased winter rain and summer drought; perturbations
COMMON CONIFERS OF THE PNW
 COMMON CONIFERS OF THE PNW The common conifers in the Pacific Northwest belong to the following genera: Abies, Calocedrus, Callitropsis, Juniperus, Larix, Picea, Pinus, Pseudotsuga, Taxus, Thuja, and Tsuga.
COMMON CONIFERS OF THE PNW The common conifers in the Pacific Northwest belong to the following genera: Abies, Calocedrus, Callitropsis, Juniperus, Larix, Picea, Pinus, Pseudotsuga, Taxus, Thuja, and Tsuga.
Kansas State University Department of Entomology Newsletter
 Kansas State University Department of Entomology Newsletter For Agribusinesses, Applicators, Consultants, Extension Personnel & Homeowners Department of Entomology 123 West Waters Hall K-State Research
Kansas State University Department of Entomology Newsletter For Agribusinesses, Applicators, Consultants, Extension Personnel & Homeowners Department of Entomology 123 West Waters Hall K-State Research
Musk thistle and Canada thistle
 Musk thistle and Canada thistle Musk thistle, Carduus nutans Identification & origins Eurasian origin Sometimes called the nodding thistle : long slender stems bear heavy flowers Flowers are broader at
Musk thistle and Canada thistle Musk thistle, Carduus nutans Identification & origins Eurasian origin Sometimes called the nodding thistle : long slender stems bear heavy flowers Flowers are broader at
Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 15(3). p173-
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A New Species of Nocticanace from D Canaceidae) Miyagi, Ichiro Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 15(3). p173- Issue Date 1973-10-20 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/4146
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A New Species of Nocticanace from D Canaceidae) Miyagi, Ichiro Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 15(3). p173- Issue Date 1973-10-20 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/4146
Pest Species of Copitarsia Hampson in the Neotropics: Identification and Hosts
 Pest Species of Copitarsia Hampson in the Neotropics: Identification and Hosts D R. M I C H A E L G. P O G U E U S D A S Y S T E M A T I C E N T O M O L O G Y L A B S M I T H S O N I A N I N S T I T U
Pest Species of Copitarsia Hampson in the Neotropics: Identification and Hosts D R. M I C H A E L G. P O G U E U S D A S Y S T E M A T I C E N T O M O L O G Y L A B S M I T H S O N I A N I N S T I T U
a. Identify the genus and species: (1 pt) b. Explain how and why this species was introduced to America: (2 pts)
 1 NOTE: ONE SECTION OF THIS TEST REQUIRES A CALCULATOR Section 1: a. Identify the genus and species: (1 pt) b. Explain how and why this species was introduced to America: (2 pts) c. Explain why this species
1 NOTE: ONE SECTION OF THIS TEST REQUIRES A CALCULATOR Section 1: a. Identify the genus and species: (1 pt) b. Explain how and why this species was introduced to America: (2 pts) c. Explain why this species
It is one of the most serious oak diseases in the United States, killing thousands of trees each year.
 1 Oak Wilt is the disease caused by the pathogenic non-native fungus Ceratocystis fagacearum that affects oaks. Oaks in the red oak group (those with sharply pointed tips- like pin oak and red oak) are
1 Oak Wilt is the disease caused by the pathogenic non-native fungus Ceratocystis fagacearum that affects oaks. Oaks in the red oak group (those with sharply pointed tips- like pin oak and red oak) are
Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. from North Thailand (Odonata: Gomphidae) MATTI HAMALAINEN
 Entomol. Z., 106(5), 1996 177 Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. from North Thailand (Odonata: Gomphidae) MATTI HAMALAINEN With 8 figures Abstract: A new dragonfly species, Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. (holotype
Entomol. Z., 106(5), 1996 177 Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. from North Thailand (Odonata: Gomphidae) MATTI HAMALAINEN With 8 figures Abstract: A new dragonfly species, Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. (holotype
Banana t hri p s i n t he We s t I ndi e s
 Thrips are tiny (1-2 mm), slender insects with typical long fringes on the margins of their narrow wings. Adults may cause major damage by puncturing the fruit epidermis to suck out the contents. The fruit
Thrips are tiny (1-2 mm), slender insects with typical long fringes on the margins of their narrow wings. Adults may cause major damage by puncturing the fruit epidermis to suck out the contents. The fruit
GHABBOUR, M.W. Plant Protection Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Ministry of Agriculture, Dokki, Egypt.
 Entomologica, Bari, 33, (1999): 73-83 GHABBOUR, M.W. Plant Protection Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Ministry of Agriculture, Dokki, Egypt. DESCRIPTIONS OF THE FIRST-INSTAR NYMPHS OF
Entomologica, Bari, 33, (1999): 73-83 GHABBOUR, M.W. Plant Protection Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Ministry of Agriculture, Dokki, Egypt. DESCRIPTIONS OF THE FIRST-INSTAR NYMPHS OF
Invasive Ambrosia Beetle Conference The Situation in California August 14, 2012 PUBLIC MEETING
 Invasive Ambrosia Beetle Conference The Situation in California August 14, 2012 PUBLIC MEETING Meeting sponsored by: The Hofshi Foundation University of California, Riverside UC Center for Invasive Pest
Invasive Ambrosia Beetle Conference The Situation in California August 14, 2012 PUBLIC MEETING Meeting sponsored by: The Hofshi Foundation University of California, Riverside UC Center for Invasive Pest
Investigating Use of Biocontrol Agents to Control Spotted Knapweed
 Investigating Use of Biocontrol Agents to Control Spotted Knapweed Target Grade Level: 5 th Created and Adapted by: Rachel Loehman UNIVERSITY OF MONTANA GK-12 PROGRAM 1 Investigating Use of Biocontrol
Investigating Use of Biocontrol Agents to Control Spotted Knapweed Target Grade Level: 5 th Created and Adapted by: Rachel Loehman UNIVERSITY OF MONTANA GK-12 PROGRAM 1 Investigating Use of Biocontrol
Oak Ambrosia Beetle, Platypus quercivorus
 Oak Ambrosia Beetle, Platypus quercivorus (Murayama), Phenology (Degree-Day) Model Analysis by Len Coop, Integrated Plant Protection Center, Oregon State University, July 22, 2016 Summary of model version
Oak Ambrosia Beetle, Platypus quercivorus (Murayama), Phenology (Degree-Day) Model Analysis by Len Coop, Integrated Plant Protection Center, Oregon State University, July 22, 2016 Summary of model version
NORTH AMERICAN SCIARIDAE (Diptera). 1. A NEW SPECIES OF SCATOPSCIARA AND LECTOTYPE DESIGNATION OF EUGNORISTE OCCIDENTALIS COQUILLETT 1
 Pacific Insects 10 (1) : 37-41 10 May 1968 NORTH AMERICAN SCIARIDAE (Diptera). 1. A NEW SPECIES OF SCATOPSCIARA AND LECTOTYPE DESIGNATION OF EUGNORISTE OCCIDENTALIS COQUILLETT 1 By Wallace A. Steffan BISHOP
Pacific Insects 10 (1) : 37-41 10 May 1968 NORTH AMERICAN SCIARIDAE (Diptera). 1. A NEW SPECIES OF SCATOPSCIARA AND LECTOTYPE DESIGNATION OF EUGNORISTE OCCIDENTALIS COQUILLETT 1 By Wallace A. Steffan BISHOP
Mosquito Systematics Vol. 6(Z) June 1974
 Mosquito Systematics Vol. 6(Z) June 1974 93 Research on the Mosquitoes of Angola. VII - Redescription of the Larva of Aedes durbanensis durbanensis (Theo., 1903) and Description of Aedes durbanensis angozae
Mosquito Systematics Vol. 6(Z) June 1974 93 Research on the Mosquitoes of Angola. VII - Redescription of the Larva of Aedes durbanensis durbanensis (Theo., 1903) and Description of Aedes durbanensis angozae
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN PRESS
 OCCASIONAL PAPERS OF THE MUSEUM OF ZOOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ANN ARBOR, MICHIQAN UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN PRESS A NEW SPECIES OF ARCISILESTES FROM MEXICO (ODONATA : LESTINAE ) IN the fall of 1938, H.
OCCASIONAL PAPERS OF THE MUSEUM OF ZOOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ANN ARBOR, MICHIQAN UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN PRESS A NEW SPECIES OF ARCISILESTES FROM MEXICO (ODONATA : LESTINAE ) IN the fall of 1938, H.
Soybean stem fly outbreak in soybean crops
 Soybean stem fly outbreak in soybean crops By Kate Charleston Published: April 10, 2013 An estimated 4,000 ha of soybeans near Casino in Northern NSW have been affected to varying degrees by soybean stem
Soybean stem fly outbreak in soybean crops By Kate Charleston Published: April 10, 2013 An estimated 4,000 ha of soybeans near Casino in Northern NSW have been affected to varying degrees by soybean stem
Vegetable Diagnostics 101: Insects and Diseases
 Vegetable Diagnostics 101: Insects and Diseases The 2013 Educational Program Committee is pleased to share conference educational materials with you under the condition that they are used without alteration
Vegetable Diagnostics 101: Insects and Diseases The 2013 Educational Program Committee is pleased to share conference educational materials with you under the condition that they are used without alteration
Student Name: Teacher: Date: Test: 9_12 Agriculture AP41 - Horticulture I Test 2 Description: Pest Management District: Wake County Form: 501
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: Test: 9_12 Agriculture AP41 - Horticulture I Test 2 Description: Pest Management District: Wake County Form: 501 1. Aimee uses traps in her garden to: 2. Which is MOST true
Student Name: Teacher: Date: Test: 9_12 Agriculture AP41 - Horticulture I Test 2 Description: Pest Management District: Wake County Form: 501 1. Aimee uses traps in her garden to: 2. Which is MOST true
DESCRIPTIONS OF HORSEFLIES FROM MIDDLE AMERICA. I.*
 DESCRIPTIONS OF HORSEFLIES FROM MIDDLE AMERICA. I.* JAMES S, HINE. During the continuance of my studies of North American Tabanidae more or less material has come to hand from southern localities. Panama
DESCRIPTIONS OF HORSEFLIES FROM MIDDLE AMERICA. I.* JAMES S, HINE. During the continuance of my studies of North American Tabanidae more or less material has come to hand from southern localities. Panama
Thaumatotibia leucotreta I'. Bottom edge of hindwing lacking circular patch of black scent scales; tibia of hindleg not heavily tufted 2
 SCREENNG KEY FOR CAPS TARGET TORTRCDAE N THE EASTERN AND MDWESTERN UNTED STATES (MALES) 1. Bottom edge of hindwing with circular patch of black scent scales; tibia of hindleg heavily tufted (false codling
SCREENNG KEY FOR CAPS TARGET TORTRCDAE N THE EASTERN AND MDWESTERN UNTED STATES (MALES) 1. Bottom edge of hindwing with circular patch of black scent scales; tibia of hindleg heavily tufted (false codling
A new species of the genus Oxyomus Dejean, 1833 from Thailand (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Aphodiinae) Łukasz MINKINA INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHODS
 Studies and Reports Taxonomical Series 14 (1): 145-149, 2018 A new species of the genus Oxyomus Dejean, 1833 from Thailand (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Aphodiinae) Łukasz MINKINA os. Polana Szaflarska 4/39,
Studies and Reports Taxonomical Series 14 (1): 145-149, 2018 A new species of the genus Oxyomus Dejean, 1833 from Thailand (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Aphodiinae) Łukasz MINKINA os. Polana Szaflarska 4/39,
Dectes Stem Borer: A Summertime Pest of Soybeans
 Dectes Stem Borer: A Summertime Pest of Soybeans Veronica Johnson* and Cerruti R 2 Hooks $ University of Maryland Dept. of Entomology * Graduate student and $ Associate professor and Extension Specialist
Dectes Stem Borer: A Summertime Pest of Soybeans Veronica Johnson* and Cerruti R 2 Hooks $ University of Maryland Dept. of Entomology * Graduate student and $ Associate professor and Extension Specialist
Forest Entomology. Forest Insects
 6 Forest Insects 7 Insects kill more trees in the U.S. each year than any other forest stress agent. In addition, they can cause significant growth loss, degrade lumber, make trees vulnerable to attack
6 Forest Insects 7 Insects kill more trees in the U.S. each year than any other forest stress agent. In addition, they can cause significant growth loss, degrade lumber, make trees vulnerable to attack
28. Genus Xoanon Semenov Fig. C28.1 (female dorsal habitus) Fig. C28.2 (female lateral habitus) Fig. C28.3 (male dorsal habitus)
 28. Genus Xoanon Semenov Fig. C28.1 (female dorsal habitus) Fig. C28.2 (female lateral habitus) Fig. C28.3 (male dorsal habitus) Xoanon Semenov, 1921: 87. Type species: Xoanon mysta Semenov, by original
28. Genus Xoanon Semenov Fig. C28.1 (female dorsal habitus) Fig. C28.2 (female lateral habitus) Fig. C28.3 (male dorsal habitus) Xoanon Semenov, 1921: 87. Type species: Xoanon mysta Semenov, by original
Unit G: Pest Management. Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
ENIGMADIPLOSIS AGAPANTHI, A NEW GENUS AND SPECIES OF GALL MIDGE (DIPTERA, CECIDOMYIIDAE) DAMAGING
 ENIGMADIPLOSIS AGAPANTHI, A NEW GENUS AND SPECIES OF GALL MIDGE (DIPTERA, CECIDOMYIIDAE) DAMAGING AGAPANTHUS FLOWERS IN ENGLAND I Keith M. Harris, 81 Linden Way, Ripley, Woking, Surrey, GU23 6LP, and Andrew
ENIGMADIPLOSIS AGAPANTHI, A NEW GENUS AND SPECIES OF GALL MIDGE (DIPTERA, CECIDOMYIIDAE) DAMAGING AGAPANTHUS FLOWERS IN ENGLAND I Keith M. Harris, 81 Linden Way, Ripley, Woking, Surrey, GU23 6LP, and Andrew
A NEW GENUS, SPECIES, AND SUBTRIBE OF TERMITOPHILOUS STAPHYLINIDAE FROM AUSTRALIA (Coleoptera)
 Pacific Insects 12 (3): 499-596 30 October 1970 A NEW GENUS, SPECIES, AND SUBTRIBE OF TERMITOPHILOUS STAPHYLINIDAE FROM AUSTRALIA (Coleoptera) With a Description of its Glands 1 By David H. Kistner 2 Abstract:
Pacific Insects 12 (3): 499-596 30 October 1970 A NEW GENUS, SPECIES, AND SUBTRIBE OF TERMITOPHILOUS STAPHYLINIDAE FROM AUSTRALIA (Coleoptera) With a Description of its Glands 1 By David H. Kistner 2 Abstract:
PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A
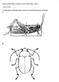 1 PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST 2006 - PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A B 2 C D 2. These are chewing mouthparts. Name their parts (=
1 PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST 2006 - PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A B 2 C D 2. These are chewing mouthparts. Name their parts (=
Certified Arborist. Diagnosis and Plant Disorders. What is a healthy plant?
 Certified Arborist Diagnosis and Plant Disorders What is a healthy plant? Vitality Ability to deal with stress Vigor Genetic ability to deal with stress 1 Many things combine to cause decline! Plant Health
Certified Arborist Diagnosis and Plant Disorders What is a healthy plant? Vitality Ability to deal with stress Vigor Genetic ability to deal with stress 1 Many things combine to cause decline! Plant Health
Boxwood Blight. Enhanced First Detector Training
 Boxwood Blight Enhanced First Detector Training Boxwood Blight Presented by Margery Daughtrey Cornell University, LIHREC Boxwood blight Potential impact Pathways Identification & pathogen biology Hosts
Boxwood Blight Enhanced First Detector Training Boxwood Blight Presented by Margery Daughtrey Cornell University, LIHREC Boxwood blight Potential impact Pathways Identification & pathogen biology Hosts
Project. Aim: How does energy flow in Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems? Explore. The four food webs are:
 Name: Date: Aim: How does energy flow in Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems? Explore The four food webs are: o Antarctic Marine Food Web o Arctic Marine Food Web o Tundra Land Food Web o Tundra Freshwater
Name: Date: Aim: How does energy flow in Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems? Explore The four food webs are: o Antarctic Marine Food Web o Arctic Marine Food Web o Tundra Land Food Web o Tundra Freshwater
CAMBIUM, meristem, heartwood, and lenticel are
 Examining the Structures of a Tree CAMBIUM, meristem, heartwood, and lenticel are some terms that may be new to you. These terms are used to describe various tree structures. Not surprisingly, many terms
Examining the Structures of a Tree CAMBIUM, meristem, heartwood, and lenticel are some terms that may be new to you. These terms are used to describe various tree structures. Not surprisingly, many terms
(Bulletin of FFPRI), Vol.2, No.4 (No.389), , December,
 (Bulletin of FFPRI), Vol., No. (No.89), -6, December, 00 Preliminary release experiments in laboratory and outdoor cages of Dastarcus helophoroides (Fairmaire) (Coleoptera: Bothrideridae) for biological
(Bulletin of FFPRI), Vol., No. (No.89), -6, December, 00 Preliminary release experiments in laboratory and outdoor cages of Dastarcus helophoroides (Fairmaire) (Coleoptera: Bothrideridae) for biological
Mountain Pine Beetle. Yukon Forest Health Forest insect and disease. Energy, Mines and Resources Forest Management Branch
 Mountain Pine Beetle Yukon Forest Health Forest insect and disease 13 Energy, Mines and Resources Forest Management Branch Introduction The mountain pine beetle, (Dendroctonus ponderosae) is a native North
Mountain Pine Beetle Yukon Forest Health Forest insect and disease 13 Energy, Mines and Resources Forest Management Branch Introduction The mountain pine beetle, (Dendroctonus ponderosae) is a native North
(69) THE GENUS EUPHALERUS IN AMERICA NORTH OF MEXICO (PSYLLIDAE: HOMOPTERA)
 VOL. 10 JOURNAL KANS. ENT. SOC, APRIL, 1937. NO. 2. L lestaceipennis THE GENUS EUPHALERUS IN AMERICA NORTH OF MEXICO (PSYLLIDAE: HOMOPTERA) L. D. TUTHILL, Iowa State College, Ames, Iowa The Psyllidae (Chermidae)
VOL. 10 JOURNAL KANS. ENT. SOC, APRIL, 1937. NO. 2. L lestaceipennis THE GENUS EUPHALERUS IN AMERICA NORTH OF MEXICO (PSYLLIDAE: HOMOPTERA) L. D. TUTHILL, Iowa State College, Ames, Iowa The Psyllidae (Chermidae)
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet
 Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-22 Selerotinia Diseases of Vegetable and Field Crops in Florida Ken Pernezny and L. H. Purdy, Professor, Everglades Research and Education Center, Belle Glade; and Professor,
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-22 Selerotinia Diseases of Vegetable and Field Crops in Florida Ken Pernezny and L. H. Purdy, Professor, Everglades Research and Education Center, Belle Glade; and Professor,
LIFE CYCLE AND LABORATORY REARING OF LACCOTREPHES MACULATES (HEMIPTERA:NEPIDAE) FROM JAMMU (J & K, INDIA)
 790 LIFE CYCLE AND LABORATORY REARING OF LACCOTREPHES MACULATES (HEMIPTERA:NEPIDAE) FROM JAMMU (J & K, INDIA) Ramnik Kour*, J. S. Tara, Sheetal Sharma and Shivani Kotwal * Department of Zoology, University
790 LIFE CYCLE AND LABORATORY REARING OF LACCOTREPHES MACULATES (HEMIPTERA:NEPIDAE) FROM JAMMU (J & K, INDIA) Ramnik Kour*, J. S. Tara, Sheetal Sharma and Shivani Kotwal * Department of Zoology, University
Scheme of Examination (B.Sc. (Hons.) Agriculture) ( )
 Scheme of Examination (B.Sc. (Hons.) Agriculture) (2016-2020) 20 Marks (Internal) + 80 marks (External) 20% Internal Examination 20 Marks (Mid term examination/internal assessment) 1). Internal theory
Scheme of Examination (B.Sc. (Hons.) Agriculture) (2016-2020) 20 Marks (Internal) + 80 marks (External) 20% Internal Examination 20 Marks (Mid term examination/internal assessment) 1). Internal theory
Diagnosing Plant Problems. A strategy to get started
 + Diagnosing Plant Problems A strategy to get started + Causes of plant damage Living factors Pests such as insects, mites, rodents, mammals Pathogens that cause disease such as fungi, bacteria, viruses,
+ Diagnosing Plant Problems A strategy to get started + Causes of plant damage Living factors Pests such as insects, mites, rodents, mammals Pathogens that cause disease such as fungi, bacteria, viruses,
Review of the genus Trogoderma from Madagascar (Coleoptera: Dermestidae: Megatominae)
 Baltic J. Coleopterol. 9(2) 2009 ISSN 1407-8619 Review of the genus Trogoderma from Madagascar (Coleoptera: Dermestidae: Megatominae) Jiří Háva Háva J. 2009. Review of the genus Trogoderma from Madagascar
Baltic J. Coleopterol. 9(2) 2009 ISSN 1407-8619 Review of the genus Trogoderma from Madagascar (Coleoptera: Dermestidae: Megatominae) Jiří Háva Háva J. 2009. Review of the genus Trogoderma from Madagascar
PSYCHE A NEW GENUS AND SPECIES OF. Vertex with vestiges of ocelli. Antennae with first segment very
 PSYCHE Vol. 70 December, 963 No. 4 A NEW GENUS AND SPECIES OF NEOTROPICAL HORSEFLY (DIPTERA: TABANIDAE) * BY G. B. FAIRCHILD Gorgas Memorial Laboratory, Panama, R. de P. The Neotropical Tabanidae are remarkable
PSYCHE Vol. 70 December, 963 No. 4 A NEW GENUS AND SPECIES OF NEOTROPICAL HORSEFLY (DIPTERA: TABANIDAE) * BY G. B. FAIRCHILD Gorgas Memorial Laboratory, Panama, R. de P. The Neotropical Tabanidae are remarkable
Beneficial Insects. PJ Liesch UW-Madison: Insect Diagnostic Lab
 1 Beneficial Insects PJ Liesch UW-Madison: pliesch@wisc.edu Twitter: @WiBugGuy What are Beneficial Insects? 2! Insects that provide ecosystem services to humans! Benefits provided to humans by nature!
1 Beneficial Insects PJ Liesch UW-Madison: pliesch@wisc.edu Twitter: @WiBugGuy What are Beneficial Insects? 2! Insects that provide ecosystem services to humans! Benefits provided to humans by nature!
Department of Entomology University of New Hampshire Durham, New Hampshire 03824
 LARVAE OF WRACK COLEOPTERA IN THE FAMILIES CORYLOPHIDAE, RHIZOPHAGIDAE, AND LATHRIDIIDAE* BY DONALD S. CHANDLER Department of Entomology University of New Hampshire Durham, New Hampshire 03824 Wrack studies
LARVAE OF WRACK COLEOPTERA IN THE FAMILIES CORYLOPHIDAE, RHIZOPHAGIDAE, AND LATHRIDIIDAE* BY DONALD S. CHANDLER Department of Entomology University of New Hampshire Durham, New Hampshire 03824 Wrack studies
Dermestid Beetles: A Self-Tutorial for PPQ Identifiers (Part 2)
 Dermestid Beetles: A Self-Tutorial for PPQ Identifiers (Part 2) Charles F. Brodel, Ph.D. Collateral National Coleoptera Specialist USDA APHIS - PPQ Miami Inspection Station Miami, Florida August, 2008
Dermestid Beetles: A Self-Tutorial for PPQ Identifiers (Part 2) Charles F. Brodel, Ph.D. Collateral National Coleoptera Specialist USDA APHIS - PPQ Miami Inspection Station Miami, Florida August, 2008
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 7: Introduction to Plant Diseases and Insects.
 Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 7: Introduction to Plant Diseases and Insects. 1 After completing this module you should: 1. Understand the causes of abssiotic
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 7: Introduction to Plant Diseases and Insects. 1 After completing this module you should: 1. Understand the causes of abssiotic
PSYCHE A RE-EVALUATION OF THE CHECKERED BEETLES FROM THE UPPER MIOCENE OF FLORISSANT, COLORADO (COLEOPTERA: CLERIDAE)
 PSYCHE Vol. 99 1992 No. 2-3 A RE-EVALUATION OF THE CHECKERED BEETLES FROM THE UPPER MIOCENE OF FLORISSANT, COLORADO (COLEOPTERA: CLERIDAE) BY JONATHAN MAWDSLEY Department of Entomology Museum of Comparative
PSYCHE Vol. 99 1992 No. 2-3 A RE-EVALUATION OF THE CHECKERED BEETLES FROM THE UPPER MIOCENE OF FLORISSANT, COLORADO (COLEOPTERA: CLERIDAE) BY JONATHAN MAWDSLEY Department of Entomology Museum of Comparative
Title. Author(s)Lewvanich, Angoon. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information SCHOENOBIINAE)
 Title TWO NEW SPECIES OF THE GENUS SCIRPOPHAGA FROM NEPAL SCHOENOBIINAE) Author(s)Lewvanich, Angoon Insecta matsumurana. New series : journal of the Fac Citation17-27 Issue Date 1981-07 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/9815
Title TWO NEW SPECIES OF THE GENUS SCIRPOPHAGA FROM NEPAL SCHOENOBIINAE) Author(s)Lewvanich, Angoon Insecta matsumurana. New series : journal of the Fac Citation17-27 Issue Date 1981-07 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/9815
Managing Mycological Mysteries
 Managing Mycological Mysteries (Systematics and the Identification of Fungi) NPDN meeting March 2016 Megan Romberg USDA APHIS PPQ PHP NIS APHIS NIS Beltsville APHIS CPHST Beltsville APHIS NIS (Mycology)
Managing Mycological Mysteries (Systematics and the Identification of Fungi) NPDN meeting March 2016 Megan Romberg USDA APHIS PPQ PHP NIS APHIS NIS Beltsville APHIS CPHST Beltsville APHIS NIS (Mycology)
PR1VATE LIBRARY OE WILLIAM L P.EIER_.S
 PR1VATE LIBRARY OE WILLIAM L P.EIER_.S PENTAGENllDAE: A NEW FAMILY OF EPHEMEROIDEA (EPHEMEROPTERA) 1 2 W. P. McCAFFERTY 3 Department of Entomology University of Georgia Athens, Georgia 30601 ABSTRACT On
PR1VATE LIBRARY OE WILLIAM L P.EIER_.S PENTAGENllDAE: A NEW FAMILY OF EPHEMEROIDEA (EPHEMEROPTERA) 1 2 W. P. McCAFFERTY 3 Department of Entomology University of Georgia Athens, Georgia 30601 ABSTRACT On
History INVASIVE INSECTS THREATENING YOUR BACKYARD: BROWN MARMORATED STINK BUG & VIBURNUM LEAF BEETLE. Identification. Common Look-A-Likes 1/12/2015
 History INVASIVE INSECTS THREATENING YOUR BACKYARD: BROWN MARMORATED STINK BUG & VIBURNUM LEAF BEETLE Native to Asia First discovered in Pennsylvania, 1998 David R. Lance, USDA APHIS PPQ Adults emerge
History INVASIVE INSECTS THREATENING YOUR BACKYARD: BROWN MARMORATED STINK BUG & VIBURNUM LEAF BEETLE Native to Asia First discovered in Pennsylvania, 1998 David R. Lance, USDA APHIS PPQ Adults emerge
Managing stink bugs through cultural practices
 Managing stink bugs through cultural practices Rachael Long, Farm Advisor, UC Cooperative Extension Yolo, Solano, Sacramento Counties, http://ceyolo.ucanr.edu Common stink bugs: Southern green (Africa
Managing stink bugs through cultural practices Rachael Long, Farm Advisor, UC Cooperative Extension Yolo, Solano, Sacramento Counties, http://ceyolo.ucanr.edu Common stink bugs: Southern green (Africa
STUDIES OF THE GENUS EMPOASCA (HOMOPTERA, CICADELLIDAE)
 STUDIES OF THE GENUS EMPOASCA (HOMOPTERA, CICADELLIDAE) PART VI TWENTY-TWO NEW SPECIES OF EMPOASCA FROM NORTH AMERICA RALPH H. DAVIDSON AND DWIGHT M. DELONG Ohio State University Empoasca necyla n. sp.
STUDIES OF THE GENUS EMPOASCA (HOMOPTERA, CICADELLIDAE) PART VI TWENTY-TWO NEW SPECIES OF EMPOASCA FROM NORTH AMERICA RALPH H. DAVIDSON AND DWIGHT M. DELONG Ohio State University Empoasca necyla n. sp.
Description of Haliplus larvae from Lebanon (Coleoptera: Haliplidae)
 Koleopterologische Rundschau 81 41 54 Wien, September 2011 Description of Haliplus larvae from Lebanon (Coleoptera: Haliplidae) B.J. van VONDEL Abstract The third instar larvae of Haliplus kulleri VONDEL
Koleopterologische Rundschau 81 41 54 Wien, September 2011 Description of Haliplus larvae from Lebanon (Coleoptera: Haliplidae) B.J. van VONDEL Abstract The third instar larvae of Haliplus kulleri VONDEL
ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN
 ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN UITGEGEVEN DOOR HET RIJKSMUSEUM VAN NATUURLIJKE HISTORIE TE LEIDEN (MINISTERIE VAN CULTUUR, RECREATIE EN MAATSCHAPPELIJK WERK) Deel 49 no. 3 4 april 1975 TELOCHILUS FREYI, A NEW
ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN UITGEGEVEN DOOR HET RIJKSMUSEUM VAN NATUURLIJKE HISTORIE TE LEIDEN (MINISTERIE VAN CULTUUR, RECREATIE EN MAATSCHAPPELIJK WERK) Deel 49 no. 3 4 april 1975 TELOCHILUS FREYI, A NEW
Biological Control of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Prospects and Procedures
 Biological Control of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Prospects and Procedures Brian Cutting Christine Dieckhoff Kim Hoelmer USDA-ARS Beneficial Insects Introduction Research, Newark, DE The Brown Marmorated
Biological Control of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Prospects and Procedures Brian Cutting Christine Dieckhoff Kim Hoelmer USDA-ARS Beneficial Insects Introduction Research, Newark, DE The Brown Marmorated
Part 1: Naming the cultivar
 REGISTRATION FORM FOR a CULTIVAR NAME of POPULUS L. Sub-Committee for Nomenclature and Registration FAO - International Poplar Commission (appointed in 1958 as the ICRA for the genus Populus) Addresses
REGISTRATION FORM FOR a CULTIVAR NAME of POPULUS L. Sub-Committee for Nomenclature and Registration FAO - International Poplar Commission (appointed in 1958 as the ICRA for the genus Populus) Addresses
What is insect forecasting, and why do it
 Insect Forecasting Programs: Objectives, and How to Properly Interpret the Data John Gavloski, Extension Entomologist, Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Initiatives Carman, MB R0G 0J0 Email: jgavloski@gov.mb.ca
Insect Forecasting Programs: Objectives, and How to Properly Interpret the Data John Gavloski, Extension Entomologist, Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Initiatives Carman, MB R0G 0J0 Email: jgavloski@gov.mb.ca
Terrestrial Invasive Species - An Overview
 Terrestrial Invasive Species - An Overview Angie Ambourn Entomologist March 6, 2018 Optional Tagline Goes Here mn.gov/websiteurl Definition of Invasive species non-native to the ecosystem under consideration;
Terrestrial Invasive Species - An Overview Angie Ambourn Entomologist March 6, 2018 Optional Tagline Goes Here mn.gov/websiteurl Definition of Invasive species non-native to the ecosystem under consideration;
Factors that potentially mediate the ecological host range of Trissolcus japonicus
 Factors that potentially mediate the ecological host range of Trissolcus japonicus Paul S. Botch & Ernest S. Delfosse Department of Entomology Michigan State University Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (BMSB)
Factors that potentially mediate the ecological host range of Trissolcus japonicus Paul S. Botch & Ernest S. Delfosse Department of Entomology Michigan State University Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (BMSB)
SIMPLE GUIDE TO IRISH HOVERFLY SPECIES
 SIMPLE GUIDE TO IRISH HOVERFLY SPECIES This guide has been put together by the National Biodiversity Data Centre with text provided by Dr Tom Gittings 2013 Identifying syrphid species in Ireland Syrphids
SIMPLE GUIDE TO IRISH HOVERFLY SPECIES This guide has been put together by the National Biodiversity Data Centre with text provided by Dr Tom Gittings 2013 Identifying syrphid species in Ireland Syrphids
This module will highlight what you should look for in detecting ALB
 Early detection of Asian Longhorned Beetle (ALB) infestations in North America is critical to the overall success of eradication programs both in terms of time and money. This module will highlight what
Early detection of Asian Longhorned Beetle (ALB) infestations in North America is critical to the overall success of eradication programs both in terms of time and money. This module will highlight what
Phytophthora ramorum What Every Georgia Nursery Should Know
 Phytophthora ramorum What Every Georgia Nursery Should Know Mike Evans Plant Protection Division Who Does P. ramorum Affect? Any Business that Imports or Exports Plant Material Any Business that Purchases
Phytophthora ramorum What Every Georgia Nursery Should Know Mike Evans Plant Protection Division Who Does P. ramorum Affect? Any Business that Imports or Exports Plant Material Any Business that Purchases
Growth and Development of Ooencyrtus sp.
 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Growth and Development of Ooencyrtus sp. Danarun S. and S. Bumroongsook * Department of Plant Production Technology, Faculty of Agricultural Technology,
Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Growth and Development of Ooencyrtus sp. Danarun S. and S. Bumroongsook * Department of Plant Production Technology, Faculty of Agricultural Technology,
Department of Entomology, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C Eomichla hallwachsae, new species (Figs. 1-3)
 Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 37(2), 1983, 155-159 A NEW SPECIES OF EOMICHLA FROM COSTA RICA (OECOPHORIDAE) J. F. GATES CLARKE Department of Entomology, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 37(2), 1983, 155-159 A NEW SPECIES OF EOMICHLA FROM COSTA RICA (OECOPHORIDAE) J. F. GATES CLARKE Department of Entomology, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
Lesson 3 Classification of Insects
 Lesson 3 Classification of Insects Timeframe 1 Fifty minute class period Target Audience Middle School (6-8) Life Science but easily adapted to Grades 4-12 Materials - Petri Dishes - Magnifying Lenses
Lesson 3 Classification of Insects Timeframe 1 Fifty minute class period Target Audience Middle School (6-8) Life Science but easily adapted to Grades 4-12 Materials - Petri Dishes - Magnifying Lenses
An Introduction to Natural Enemies for Biological Control of Pest Insects
 An Introduction to Natural Enemies for Biological Control of Pest Insects Anna Fiedler, Doug Landis, Rufus Isaacs, Julianna Tuell Dept. of Entomology, Michigan State University Biological control Use of
An Introduction to Natural Enemies for Biological Control of Pest Insects Anna Fiedler, Doug Landis, Rufus Isaacs, Julianna Tuell Dept. of Entomology, Michigan State University Biological control Use of
Entomology Research Laboratory The University of Vermont South Burlington, Vermont USA
 THE LIFE CYCLE OF PEAR THRIPS, Taeniothrips inconsequens (Uzel) IN VERMONT Margaret Skinner, Bruce L. Parker and Sandra H. ~ilmot' Entomology Research Laboratory The University of Vermont South Burlington,
THE LIFE CYCLE OF PEAR THRIPS, Taeniothrips inconsequens (Uzel) IN VERMONT Margaret Skinner, Bruce L. Parker and Sandra H. ~ilmot' Entomology Research Laboratory The University of Vermont South Burlington,
Unit 6 Populations Dynamics
 Unit 6 Populations Dynamics Define these 26 terms: Commensalism Habitat Herbivory Mutualism Niche Parasitism Predator Prey Resource Partitioning Symbiosis Age structure Population density Population distribution
Unit 6 Populations Dynamics Define these 26 terms: Commensalism Habitat Herbivory Mutualism Niche Parasitism Predator Prey Resource Partitioning Symbiosis Age structure Population density Population distribution
Application of Remote Sensing and Global Positioning Technology for Survey and Monitoring of Plant Pests
 Application of Remote Sensing and Global Positioning Technology for Survey and Monitoring of Plant Pests David Bartels, Ph.D. USDA APHIS PPQ CPHST Mission Texas Laboratory Spatial Technology and Plant
Application of Remote Sensing and Global Positioning Technology for Survey and Monitoring of Plant Pests David Bartels, Ph.D. USDA APHIS PPQ CPHST Mission Texas Laboratory Spatial Technology and Plant
FOSS California Environments Module Glossary 2007 Edition. Adult: The last stage in a life cycle when the organism is mature and can reproduce.
 FOSS California Environments Module Glossary 2007 Edition Adult: The last stage in a life cycle when the organism is mature and can reproduce. Algae: A large group of water organisms. Amphibian: An organism,
FOSS California Environments Module Glossary 2007 Edition Adult: The last stage in a life cycle when the organism is mature and can reproduce. Algae: A large group of water organisms. Amphibian: An organism,
Comparative Mouthpart Morphology and Evolution of the Carnivorous Heptageniidae (Ephemeroptera) 1
 l Aquatic Insects, Vol. 8 (1986). No. 2, pp. 83-89 0165-0424/86/0802-0083 $3.00 Swets & Zeitlinger Comparative Mouthpart Morphology and Evolution of the Carnivorous Heptageniidae (Ephemeroptera) 1 by W.
l Aquatic Insects, Vol. 8 (1986). No. 2, pp. 83-89 0165-0424/86/0802-0083 $3.00 Swets & Zeitlinger Comparative Mouthpart Morphology and Evolution of the Carnivorous Heptageniidae (Ephemeroptera) 1 by W.
28 3 Insects Slide 1 of 44
 1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
CBA Practice Exam - Ecology
 CBA Practice Exam - Ecology For the following two questions, use the diagram below: 1. (TEKS 11B) The organisms in the illustration are all part of a pond community. What would likely happen to the fish
CBA Practice Exam - Ecology For the following two questions, use the diagram below: 1. (TEKS 11B) The organisms in the illustration are all part of a pond community. What would likely happen to the fish
Investigating San Jose scale in northwest Michigan sweet cherries
 Investigating San Jose scale in northwest Michigan sweet cherries E. A. Pochubay and N. L. Rothwell Michigan State University Extension, AgBioResearch January 13-14, 2015 Northwest Michigan Orchard and
Investigating San Jose scale in northwest Michigan sweet cherries E. A. Pochubay and N. L. Rothwell Michigan State University Extension, AgBioResearch January 13-14, 2015 Northwest Michigan Orchard and
CMG GardenNotes #171 Identifying Trees and Shrubs
 CMG GardenNotes #171 Identifying Trees and Shrubs Outline: I. Introduction II. Plant Identification Tools, page 1 a. Plant Identification Keys, page 2 III. Terminology, page 3 IV. Plant Identification
CMG GardenNotes #171 Identifying Trees and Shrubs Outline: I. Introduction II. Plant Identification Tools, page 1 a. Plant Identification Keys, page 2 III. Terminology, page 3 IV. Plant Identification
WSU and UI Master Gardeners March 1, 2016 Philip Shinn
 WSU and UI Master Gardeners March 1, 2016 Philip Shinn What is a Woody Plant? Tree Biology CODIT Planting & Pruning Tree Triage C 9 H 10 O 2 Strengthens cell walls in Xylem Sequesters carbon 30% of
WSU and UI Master Gardeners March 1, 2016 Philip Shinn What is a Woody Plant? Tree Biology CODIT Planting & Pruning Tree Triage C 9 H 10 O 2 Strengthens cell walls in Xylem Sequesters carbon 30% of
A NEW SPECIES OF ZELANDOBIUS (PLECOPTERA: GRIPOPTERYGIDAE: ANTARCTOPERLINAE) FROM NEW ZEALAND
 A NEW SPECIES OF ZELANDOBIUS (PLECOPTERA: GRIPOPTERYGIDAE: ANTARCTOPERLINAE) FROM NEW ZEALAND R.G. DEATH Department of Zoology, University of Canterbury, Christchurch 1, New Zealand. (Received and accepted
A NEW SPECIES OF ZELANDOBIUS (PLECOPTERA: GRIPOPTERYGIDAE: ANTARCTOPERLINAE) FROM NEW ZEALAND R.G. DEATH Department of Zoology, University of Canterbury, Christchurch 1, New Zealand. (Received and accepted
Leica EZ4D Scope Training
 Leica EZ4D Scope Training By: Ryan S. Davis Arthropod Diagnostician UPPDL Fine tuning your photographic skills, and taking pictures of what s important Lecture Preparing insects for photographing Ways
Leica EZ4D Scope Training By: Ryan S. Davis Arthropod Diagnostician UPPDL Fine tuning your photographic skills, and taking pictures of what s important Lecture Preparing insects for photographing Ways
Description of a new genus of Doryctinae wasps (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) from Brazil
 Description of a new genus of Doryctinae wasps (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) from Brazil S.A.G. Gomes & A.M. Penteado-Dias Gomes, S.A.G. & A.M. Penteado-Dias. Description of a new genus of Doryctinae wasps
Description of a new genus of Doryctinae wasps (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) from Brazil S.A.G. Gomes & A.M. Penteado-Dias Gomes, S.A.G. & A.M. Penteado-Dias. Description of a new genus of Doryctinae wasps
Station 1. Note: There are no samples at this station. 1. True or False: Odonata use their superior flying abilities as a defense.
 Station 1 Note: There are no samples at this station. 1. True or False: Odonata use their superior flying abilities as a defense. 2. What do Orthopterans use for defense? A. Stink glands B. Eye spots C.
Station 1 Note: There are no samples at this station. 1. True or False: Odonata use their superior flying abilities as a defense. 2. What do Orthopterans use for defense? A. Stink glands B. Eye spots C.
Sun Helps Geraniums Poison Japanese Beetles
 April, 1929 71 Sun Helps Geraniums Poison Japanese Beetles An insect poison that seems to need the aid of the sun to develop its best effects has been observed in connection with the campaign against the
April, 1929 71 Sun Helps Geraniums Poison Japanese Beetles An insect poison that seems to need the aid of the sun to develop its best effects has been observed in connection with the campaign against the
Tree and Shrub Insects
 Aphids Aphids are small soft-bodied insects that suck plant juices. High aphid populations can cause leaves to yellow, curl, or drop early. The most bothersome aspect of aphids is the honeydew they produce.
Aphids Aphids are small soft-bodied insects that suck plant juices. High aphid populations can cause leaves to yellow, curl, or drop early. The most bothersome aspect of aphids is the honeydew they produce.
Parasitic Diseases. Plants killing plants
 Parasitic Diseases Plants killing plants Parasitic Plants According to the American Heritage Dictionary a parasite is- An organism that grows, feeds, and is sheltered on or in a different organism while
Parasitic Diseases Plants killing plants Parasitic Plants According to the American Heritage Dictionary a parasite is- An organism that grows, feeds, and is sheltered on or in a different organism while
Field Identification Guide
 Field Identification Guide Oriental Chestnut Gall Wasp Image: Gyorgy Csoka Hungary Forest Research Institute, Bugwood.org Funded by the EU s LIFE programme Oriental Chestnut Gall Wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus
Field Identification Guide Oriental Chestnut Gall Wasp Image: Gyorgy Csoka Hungary Forest Research Institute, Bugwood.org Funded by the EU s LIFE programme Oriental Chestnut Gall Wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus
Seasonal Variation in a Hymenopterous Parasitoid, Holcotetrastichus rhosaces
 Advances in Entomology, 2014, 2, 176-179 Published Online October 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ae http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ae.2014.24026 Seasonal Variation in a Hymenopterous Parasitoid,
Advances in Entomology, 2014, 2, 176-179 Published Online October 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ae http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ae.2014.24026 Seasonal Variation in a Hymenopterous Parasitoid,
APHODIINAE. Presentation APHODIINAE 1/25/2012
 APHODIINAE Paul E. Skelley Florida State Collection of Arthropods Florida Department of Agriculture Gainesville, Florida, USA Presentation Part 1: Aphodiinae Part 2: Collecting techniques Part 3: Test
APHODIINAE Paul E. Skelley Florida State Collection of Arthropods Florida Department of Agriculture Gainesville, Florida, USA Presentation Part 1: Aphodiinae Part 2: Collecting techniques Part 3: Test
Parasites of larval black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Thailand
 Parasites of larval black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Thailand Sanae Jitklang 1, Arunee Ahantarig 2, Chaliow Kuvangkadilok 2, Visut Baimai 2, and Peter H. Adler 3 1 Conservation Biology Program, Division
Parasites of larval black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Thailand Sanae Jitklang 1, Arunee Ahantarig 2, Chaliow Kuvangkadilok 2, Visut Baimai 2, and Peter H. Adler 3 1 Conservation Biology Program, Division
Bee common name. Search
 Bee common name Search Bees are flying insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their role in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the European honey bee. Managed Website
Bee common name Search Bees are flying insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their role in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the European honey bee. Managed Website
