Ocean mesoscale, surface heat fluxes and surface convergence
|
|
|
- Edgar Daniels
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NSF/NCAR DOE BER SCIDAC NASA Vector winds NASA Physical Oceanography Ocean mesoscale, surface heat fluxes and surface convergence Justin Small Frank Bryan, Stu Bishop, Bob Tomas Larry O Neill Thanks to Shang-Ping Xie, Meghan Cronin, Dudley Chelton for early inspiration And to many others for discussions and results Apologies in advance: I may not mention your favorite paper too many papers to mention all!
2 Outline 1. Surface turbulent heat flux response to eddies 2. Models for response of atmosphere boundary layer to SST fronts and eddies 3. Surface convergence over western boundary currents 4. Some discussion points I will not cover remote atmosphere response to boundary currents and eddies Claude Frankignoul and Mike Alexander wrote a review on this for a paper I have been leading for last 5 years. Not yet finished/published Nor will I cover feedback to ocean (see Ma et al and others) Also not cover Lagrangian tracking/compositing of eddies E.g. Frenger et al., Ma et al., Gaube et al.
3 Part 1. Mesoscale SST and surface heat flux Will focus on turbulent heat flux Main contributor to heat flux response to SST Dominated in turn by latent heat flux Use various observed heat fluxes products and CESM model simulations
4 Stochastic model of air-sea interaction Frankignoul, Hasselmann 1977 Barsugli and Battisti 1998 Wu et al Smirnov et al 2014 Zhang et al 2017 Bishop et al From Bishop et al 2017 Increasing ocean noise Increasing ocean noise Correlation between SST and surface heat flux. Positive heat flux out of ocean. Correlation between SST tendency and surface heat flux.
5 Fig. 4. Monthly: SST-LHFLX correlations a) OAFLUX b) OAFLUX c) J-OFURO-v d) SEAFLUX e) HIGH RESOLUTION CESM f) LOW RESOLUTION CESM
6 Fig. 5. Monthly: SST tendency -LHFLX correlations a) J-OFURO-v b) SEAFLUX c) HIGH RESOLUTION CESM d) LOW RESOLUTION CESM
7 Scale dependence in OAFLUX data Increasing spatial scale Increasing spatial scale From Bishop et al 2017
8 Part 2. Models of wind response to fronts Lindzen Nigam 1987 Hayes et al 1989, Wallace et al 1989 Feliks et al 2004, 2007 Takatama et al 2011, 2015 Schneider and Qiu 2015 Gemmrich, Monahan, this conference Pressure adjustment mechanism/ Ekman-balanced-mass-adjustment Vertical mixing mechanism Pressure adjustment mechanism boundary layer+ QG free trop. Combined model Combined model Stochastic model
9 Convergence ~ -Laplacian(SST ) Boundary Layer Model (1) Takatama et al. 2011, 2015 Under approximation of no advection (A terms=0), negligible stress at height Z (tau(z)=0) We can derive Convergence ~ -Laplacian(SLP) Lindzen and Nigam 1987, Minobe et al 2008 Underlying assumption that air temperature, moisture anomalies follow underlying SST anomalies so that e.g. p ~ -SST
10 Boundary Layer Model (2) Linear response to a weak SST front Linearised about background Ekman spiral Also includes backpressure effect Schneider and Qiu 2015
11 Boundary Layer Model (2) Linear response to a weak SST front Linearised about background Ekman spiral Also includes backpressure effect Surface convergence (& vertical motion) has a component due to: 1. Laplacian (surface air temperature) 2. Downwind surface air temperature gradient Gradients in surface air temperature driven by gradients in SST
12 Part 3. Low level Convergence over mesoscale features and western boundary currents I will focus on Gulf Stream mean state and variability This includes eddies but is not exclusively focused on eddies (sorry) Next slide: sequence of papers related to convergence over the Gulf Stream
13 LOTS OF PAPERS!!!! Pressure adjustment mechanism Surface convergence and deep precipitation over Gulf Stream - Pressure adjustment mechanism? Nakamura 2004 baroclinicity set by ocean? Storm tracks co-located with Gulf Stream at least in boundary layer Atmospheric fronts modified by Gulf Stream Warm conveyor belt modified by Gulf Stream (unstable lower trop.) Surface convergence over Gulf Stream - Pressure adjustment mechanism + synoptic storms Decomposed convergence and curl in terms of pressure/vertical mixing Surface convergence in cold sector of storm over Gulf Stream - Pressure adjustment mechanism including moisture Surface convergence over Gulf Stream mainly due to some extreme storms. Highly skewed distribution. Median is weak divergence, not convergence.
14 Storm Tracks and Atmosphere Fronts Surface Storm Track From Booth et al 2010 Surface storm track defined as band-pass filtered meridional wind standard deviation.white line if Gulf Stream mean position Proposed mechanisms include 1) SST front setting atmosphere baroclinicity 2) vertical mixing of momentum 3) enhanced surface latent heat flux over fronts e.g. Nakamura 2004 Booth et al 2010, 2017 Joyce and Kwon 2009 Small et al 2014 See also Ogawa-san presentation this week: mean sensible heat flux governed by meridional wind variance Cold front frequency From Parfitt et al Atmosphere cold front frequency (as a fraction) in a control high resolution model. Thermal damping and strengthening
15 Long-term mean properties surface convergence etc. Minobe et al Note: sign convention opposite to Minobe et al O Neill et al. 2017, JCLIM. Results from COAMPS simulations, 1- year mean.
16 So everyone is in agreement then pressure adjustment mechanism drives convergence over the Gulf Stream Keep listening
17 Look what happens when you remove the most extreme storms, which occur in only about 5% of data. Also, median conditions are surface divergence The field of Laplacian of SST is similar on all days but convergence only occurs on a small amount of days Is there an anchoring effect? O Neill et al. 2017, JCLIM. QuiKSCAT data.
18 What s going on then? Feliks et al. 2004, 2007, Brachet et al boundary-layer temperature Convergence driven by sea level pressure Laplacian has components due to upper vorticity (e.g. from storms) and also due to boundary layer temperature.
19 Daily timeseries at points in WBCs Lap(SST)-surface Convergence relationship Timeseries of Lap(SST) and surface convergence from daily data From 7 years of daily data of CAM/CESM. Correlations (in red boxes) are very low.
20 Can we detect any influence of Lap(SST) on variability of surface convergence? Assume daily variability of surface convergence driven by synoptic storms and atmosphere fronts So look at longer timescales Monthly to interannual to 5 year Investigate relationship between SST, Tair(2m), sea level pressure, and convergence at bottom model level Standard correlation/covariance analysis at each point More sophisticated methods should be used! Data is high pass box-car filtered to show 10deg. Scale or less I use 40 years of monthly data from high-resolution coupled CESM. As it is a coupled model it has a not perfect Gulf Stream separation, but does not greatly affect the following results
21 Sign convention In following panels: Negative correlations are consistent with SST/Tair forcing boundary layer response Except for correlation of Lap(sea level pressure) and Convergence Positive correlations consistent with SLP forcing convergence
22 Results: North Atlantic Correlation, SST and sea level pressure Correlation, T(air) and sea level pressure Correlation, Lap(T(air)) and Lap(SLP) Correlation, Convergence and Lap(SLP) Correlation, Lap(SST) and Convergence Correlation, Lap(T(air)) and Convergence Note reduced color bars in last two panels
23 Results: North Pacific Correlation, SST and sea level pressure Correlation, T(air) and sea level pressure Correlation, Lap(T(air)) and Lap(SLP) Correlation, Convergence and Lap(SLP) Correlation, Lap(SST) and Convergence Correlation, Lap(T(air)) and Convergence Note reduced color bars in last two panels
24 Results: Agulhas return Current Correlation, SST and sea level pressure Correlation, T(air) and sea level pressure Correlation, Lap(T(air)) and Lap(SLP) Correlation, Convergence and Lap(SLP) Correlation, Lap(SST) and Convergence Correlation, Lap(T(air)) and Convergence Note reduced color bars in last two panels
25 Summary of monthly+ analysis of lap(ta) and surface convergence Tropics high correlation low covariance Western boundary currents, sharp fronts High correlations in narrow regions, high covariance Broad eddying region (i.e. region of large ocean EKE) High covariance Weak correlation Time-scale dependence Correlations get stronger for longer timescales (e.g. interannual) But statistical significance less as sample size shorter
26 Let s return to time-mean convergence
27 O Neill et al. 2017, JCLIM. QuiKSCAT data.
28 Fig.4. The estimated surface convergence response to Laplacian of: top: surface pressure second row: boundary layer pressure increment, third row: deep pressure. Final row: full model surface convergence. Courtesy Bob Tomas. See also Minobe/Takatama/Terray.
29 Three Discussion Slides
30 Discussion slide: What drives deep response to Gulf Stream Boundary layer processes directly drive deep response? Feliks et al. 2004, 2007 Minobe et al 2008 Synoptic Storms? Extreme storms? Atmospheric Fronts? boundary layer modifies storm track (indirect effect)? Air-sea heat fluxes at fronts dictating baroclinicity (Nakamura 2004, Small et al 2014) Vertical motion from boundary layer? (Feliks et al) Atmosphere fronts affected by surface heat fluxes (Parfitt et al.)
31 Discussion slide: Scale dependence and coupling coefficients O Neill et al illustrate scale-dependence of SST-wind coupling Schneider et al analyse scale-dependence Coupling coefficients Traditional SST-wind speed etc coefficients (Chelton et al., O Neill et al.) Or more sophisticated wavenumber approach (Schneider and Qiu) with background wind and wind speed dependence?
32 What ocean scales affect the atmosphere And what atmosphere grid scale is needed? See also Bryan et al 2010
U.S. CLIVAR Western Boundary Current Workshop January 2009 Phoenix, Arizona. Wyndham Phoenix 50 East Adams Street
 U.S. CLIVAR Western Boundary Current Workshop 15-17 January 2009 Phoenix, Arizona Wyndham Phoenix 50 East Adams Street January 15 (Thursday) Session 1: Findings from the KESS and CLIMODE programs; Co-coveners:
U.S. CLIVAR Western Boundary Current Workshop 15-17 January 2009 Phoenix, Arizona Wyndham Phoenix 50 East Adams Street January 15 (Thursday) Session 1: Findings from the KESS and CLIMODE programs; Co-coveners:
Atmospheric responses to oceanic eddies in the Kuroshio Extension region
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Vertical momentum mixing mechanism is dominant in surface wind changes Atmospheric responses to oceanic eddies are
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Vertical momentum mixing mechanism is dominant in surface wind changes Atmospheric responses to oceanic eddies are
Using Ensemble Sensitivity to Understand the Role of Sea Surface Temperatures in Midlatitude Storm Development in the Gulf Stream Region
 Using Ensemble Sensitivity to Understand the Role of Sea Surface Temperatures in Midlatitude Storm Development in the Gulf Stream Region Jimmy Booth, Susan Bates, LuAnne Thompson, Kathie Kelly University
Using Ensemble Sensitivity to Understand the Role of Sea Surface Temperatures in Midlatitude Storm Development in the Gulf Stream Region Jimmy Booth, Susan Bates, LuAnne Thompson, Kathie Kelly University
C
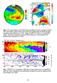 C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
The role of the midlatitude ocean in sub-seasonal prediction
 The role of the midlatitude ocean in sub-seasonal prediction R. Saravanan Xiaohui Ma, Xue Liu, J. Steinweg-Woods J. Kurian, R. Montuoro, P. Chang, I. Szunyogh Yinglai Jia, Ocean University of China J.
The role of the midlatitude ocean in sub-seasonal prediction R. Saravanan Xiaohui Ma, Xue Liu, J. Steinweg-Woods J. Kurian, R. Montuoro, P. Chang, I. Szunyogh Yinglai Jia, Ocean University of China J.
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa
 John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
Wind, Current, Wave, and Stress Coupling in the Boundary Layer and A Plan for Observing This Coupling from Space
 Wind, Current, Wave, and Stress Coupling in the Boundary Layer and A Plan for Observing This Coupling from Space Mark A. Bourassa and Qi Shi COAPS, EOAS & GFDI, Florida State University With input from
Wind, Current, Wave, and Stress Coupling in the Boundary Layer and A Plan for Observing This Coupling from Space Mark A. Bourassa and Qi Shi COAPS, EOAS & GFDI, Florida State University With input from
Use of Satellite Observations to Measure Air-Sea Coupling and to Validate Its Estimates from Numerical Atmospheric Models
 Use of Satellite Observations to Measure Air-Sea Coupling and to Validate Its Estimates from Numerical Atmospheric Models Natalie Perlin, Dudley Chelton, Simon de Szoeke College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric
Use of Satellite Observations to Measure Air-Sea Coupling and to Validate Its Estimates from Numerical Atmospheric Models Natalie Perlin, Dudley Chelton, Simon de Szoeke College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric
P R O L O G U E CORRELATION COEF. dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology)
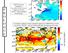 P R O L O G U E dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology) Correlation between total precipitable water (from NVAP-M) and total cloud (from
P R O L O G U E dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology) Correlation between total precipitable water (from NVAP-M) and total cloud (from
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
A new century-long high-resolution global climate run using the Community Earth System Model.
 Office of Science (BER) and NERSC and DOE/UCAR Co-operative Agreement US Department of Energy NCAR-Wyoming Supercomputer Center National Science Foundation A new century-long high-resolution global climate
Office of Science (BER) and NERSC and DOE/UCAR Co-operative Agreement US Department of Energy NCAR-Wyoming Supercomputer Center National Science Foundation A new century-long high-resolution global climate
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Effect of Sea Surface Temperature Wind Stress Coupling on Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean
 1092 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 37 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Effect of Sea Surface Temperature Wind Stress Coupling on Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean MICHAEL A.
1092 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 37 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Effect of Sea Surface Temperature Wind Stress Coupling on Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean MICHAEL A.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Downscaling Global Warming with a Regional Ocean- Atmosphere Model over the Tropical Atlantic
 Downscaling Global Warming with a Regional Ocean- Atmosphere Model over the Tropical Atlantic Role of equatorial ocean dynamics: equatorial upwelling and ocean mesoscale variability Hyodae Seo and Shang-Ping
Downscaling Global Warming with a Regional Ocean- Atmosphere Model over the Tropical Atlantic Role of equatorial ocean dynamics: equatorial upwelling and ocean mesoscale variability Hyodae Seo and Shang-Ping
Mid-latitude Ocean Influence on North Pacific Sector Climate Variability
 Mid-latitude Ocean Influence on North Pacific Sector Climate Variability Guidi Zhou 1, Mojib Latif 1,2, Richard Greatbatch 1,2, Wonsun Park 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz-Centre for Ocean Research Kiel 2 Kiel University
Mid-latitude Ocean Influence on North Pacific Sector Climate Variability Guidi Zhou 1, Mojib Latif 1,2, Richard Greatbatch 1,2, Wonsun Park 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz-Centre for Ocean Research Kiel 2 Kiel University
What governs the location of the Southern Ocean deep winter mixing in CESM
 NSF NCAR WYOMING SUPERCOMPUTER CENTER DOE SCIDAC FUNDED PROJECT What governs the location of the Southern Ocean deep winter mixing in CESM Justin Small Dan Whitt Alice DuVivier Matt Long Acknowledging:
NSF NCAR WYOMING SUPERCOMPUTER CENTER DOE SCIDAC FUNDED PROJECT What governs the location of the Southern Ocean deep winter mixing in CESM Justin Small Dan Whitt Alice DuVivier Matt Long Acknowledging:
Observations and Modeling of SST Influence on Surface Winds
 Observations and Modeling of SST Influence on Surface Winds Dudley B. Chelton and Qingtao Song College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331-5503 chelton@coas.oregonstate.edu,
Observations and Modeling of SST Influence on Surface Winds Dudley B. Chelton and Qingtao Song College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331-5503 chelton@coas.oregonstate.edu,
COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE INTERACTION AT OCEANIC MESOSCALES
 THE FUTURE OF OCEANOGRAPHY FROM SPACE COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE INTERACTION AT OCEANIC MESOSCALES ABSTRACT. Satellite observations have revealed a remarkably strong positive correlation between sea surface
THE FUTURE OF OCEANOGRAPHY FROM SPACE COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE INTERACTION AT OCEANIC MESOSCALES ABSTRACT. Satellite observations have revealed a remarkably strong positive correlation between sea surface
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction at Oceanic Mesoscales
 Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction at Oceanic Mesoscales Dudley B. Chelton, Distinguished Professor of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences chelton@coas.oregonstate.edu College of Oceanic and Atmospheric
Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction at Oceanic Mesoscales Dudley B. Chelton, Distinguished Professor of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences chelton@coas.oregonstate.edu College of Oceanic and Atmospheric
Inter-model variations in projected precipitation. change over the North Atlantic: Sea surface. temperature effect
 1 1 2 3 Inter-model variations in projected precipitation change over the North Atlantic: Sea surface temperature effect 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Shang-Min LONG 1, 2* and Shang-Ping XIE 1, 2 1 Physical
1 1 2 3 Inter-model variations in projected precipitation change over the North Atlantic: Sea surface temperature effect 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Shang-Min LONG 1, 2* and Shang-Ping XIE 1, 2 1 Physical
North Pacific Decadal Varibility: Current Understanding and Unresolved Issues
 North Pacific Decadal Varibility: Current Understanding and Unresolved Issues Arthur J. Miller, Emanuele Di Lorenzo, Shoshiro Minobe, Niklas Schneider SIO/UCSD Georgia Tech Hokkaido IPRC/Hawaii W8 POC
North Pacific Decadal Varibility: Current Understanding and Unresolved Issues Arthur J. Miller, Emanuele Di Lorenzo, Shoshiro Minobe, Niklas Schneider SIO/UCSD Georgia Tech Hokkaido IPRC/Hawaii W8 POC
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Eastern boundary upwelling in CORE vs JRA55 ocean-ice simulations
 Eastern boundary upwelling in CORE vs JRA55 ocean-ice simulations Justin Small Steve Yeager, Gokhan Danabasoglu, Bill Large, Who Kim NCAR Hiroyuki Tsujino, JMA Ocean-ice simulations CORE forcing T62, ~1.8deg.
Eastern boundary upwelling in CORE vs JRA55 ocean-ice simulations Justin Small Steve Yeager, Gokhan Danabasoglu, Bill Large, Who Kim NCAR Hiroyuki Tsujino, JMA Ocean-ice simulations CORE forcing T62, ~1.8deg.
Figure 2. Time series of the standard deviation of spatial high pass filtered QuikSCAT wind stress (solid) and AMSR SST (dashed) for (top to bottom)
 a) Figure 1. Spatial high pass filtered a) QuikSCAT wind stress (colors) and AMSR SST (contours), QuikSCAT wind stress divergence (colors) and AMSR downwind SST gradient (contours) and QuikSCAT wind stress
a) Figure 1. Spatial high pass filtered a) QuikSCAT wind stress (colors) and AMSR SST (contours), QuikSCAT wind stress divergence (colors) and AMSR downwind SST gradient (contours) and QuikSCAT wind stress
Florida State University Libraries
 Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2014 The Effects of Sea Surface Temperature Gradients on Surface Turbulent Fluxes John Steffen Follow
Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2014 The Effects of Sea Surface Temperature Gradients on Surface Turbulent Fluxes John Steffen Follow
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B
 Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
On the Coupling of Wind Stress and Sea Surface Temperature
 15 APRIL 2006 S A M E L S O N E T A L. 1557 On the Coupling of Wind Stress and Sea Surface Temperature R. M. SAMELSON, E. D. SKYLLINGSTAD, D. B. CHELTON, S. K. ESBENSEN, L. W. O NEILL, AND N. THUM College
15 APRIL 2006 S A M E L S O N E T A L. 1557 On the Coupling of Wind Stress and Sea Surface Temperature R. M. SAMELSON, E. D. SKYLLINGSTAD, D. B. CHELTON, S. K. ESBENSEN, L. W. O NEILL, AND N. THUM College
LETTERS. North Atlantic Atmosphere Ocean Interaction on Intraseasonal Time Scales
 VOL. 17, NO. 8 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 APRIL 2004 LETTERS North Atlantic Atmosphere Ocean Interaction on Intraseasonal Time Scales LAURA M. CIASTO AND DAVID W. J. THOMPSON Department of Atmospheric Science,
VOL. 17, NO. 8 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 APRIL 2004 LETTERS North Atlantic Atmosphere Ocean Interaction on Intraseasonal Time Scales LAURA M. CIASTO AND DAVID W. J. THOMPSON Department of Atmospheric Science,
Ocean surface circulation
 Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
NW Atlantic warming under climate change: new simulations with high-resolution CESM
 NW Atlantic warming under climate change: new simulations with high-resolution CESM Justin Small John Truesdale, Susan Bates, Gary Strand, Jerry Meehl, Don Wuebbles Acknowledging: Mike Alexander, Andrew
NW Atlantic warming under climate change: new simulations with high-resolution CESM Justin Small John Truesdale, Susan Bates, Gary Strand, Jerry Meehl, Don Wuebbles Acknowledging: Mike Alexander, Andrew
Surface Circulation. Key Ideas
 Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Two Types of Surface Wind Response to the East China Sea Kuroshio Front*
 8616 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Two Types of Surface Wind Response to the East China Sea Kuroshio Front* JING-WU LIU AND SU-PING ZHANG Physical Oceanography Laboratory, and Ocean Atmosphere
8616 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Two Types of Surface Wind Response to the East China Sea Kuroshio Front* JING-WU LIU AND SU-PING ZHANG Physical Oceanography Laboratory, and Ocean Atmosphere
Currents & Gyres Notes
 Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
The response of the Pacific storm track and atmospheric circulation to Kuroshio Extension variability
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2014) DOI:10.1002/qj.2334 The response of the Pacific storm track and atmospheric circulation to Kuroshio Extension variability
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2014) DOI:10.1002/qj.2334 The response of the Pacific storm track and atmospheric circulation to Kuroshio Extension variability
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
PV Generation in the Boundary Layer
 1 PV Generation in the Boundary Layer Robert Plant 18th February 2003 (With thanks to S. Belcher) 2 Introduction How does the boundary layer modify the behaviour of weather systems? Often regarded as a
1 PV Generation in the Boundary Layer Robert Plant 18th February 2003 (With thanks to S. Belcher) 2 Introduction How does the boundary layer modify the behaviour of weather systems? Often regarded as a
On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time
 Hamburg Workshop 215 On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time Xiaoming Zhai Centre for Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia With David Marshall,
Hamburg Workshop 215 On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time Xiaoming Zhai Centre for Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia With David Marshall,
Global Circulation. Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern
 Global Circulation Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern Wind rose shows % frequency of winds around the compass 1 Global Circulation
Global Circulation Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern Wind rose shows % frequency of winds around the compass 1 Global Circulation
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Empirical climate models of coupled tropical atmosphere-ocean dynamics!
 Empirical climate models of coupled tropical atmosphere-ocean dynamics! Matt Newman CIRES/CDC and NOAA/ESRL/PSD Work done by Prashant Sardeshmukh, Cécile Penland, Mike Alexander, Jamie Scott, and me Outline
Empirical climate models of coupled tropical atmosphere-ocean dynamics! Matt Newman CIRES/CDC and NOAA/ESRL/PSD Work done by Prashant Sardeshmukh, Cécile Penland, Mike Alexander, Jamie Scott, and me Outline
Analysis of Mixing and Dynamics Associated with the Dissolution of Hurricane-Induced Cold Wakes
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Analysis of Mixing and Dynamics Associated with the Dissolution of Hurricane-Induced Cold Wakes Carol Anne Clayson Dept.
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Analysis of Mixing and Dynamics Associated with the Dissolution of Hurricane-Induced Cold Wakes Carol Anne Clayson Dept.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1353 Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents Lixin Wu 1, Wenju Cai 2, Liping Zhang 1, Hisashi Nakamura 3, Axel Timmermann 4,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1353 Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents Lixin Wu 1, Wenju Cai 2, Liping Zhang 1, Hisashi Nakamura 3, Axel Timmermann 4,
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development
 Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
Western Boundary Currents and Frontal Air Sea Interaction: Gulf Stream and Kuroshio Extension
 5644 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 23 Western Boundary Currents and Frontal Air Sea Interaction: Gulf Stream and Kuroshio Extension KATHRYN A. KELLY,* R. JUSTIN SMALL, 1 R. M. SAMELSON, # BO QIU,
5644 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 23 Western Boundary Currents and Frontal Air Sea Interaction: Gulf Stream and Kuroshio Extension KATHRYN A. KELLY,* R. JUSTIN SMALL, 1 R. M. SAMELSON, # BO QIU,
Coupling between Sea Surface Temperature and Low-Level Winds in Mesoscale Numerical Models
 146 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Coupling between Sea Surface Temperature and Low-Level Winds in Mesoscale Numerical Models QINGTAO SONG AND DUDLEY B. CHELTON College of Oceanic and Atmospheric
146 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Coupling between Sea Surface Temperature and Low-Level Winds in Mesoscale Numerical Models QINGTAO SONG AND DUDLEY B. CHELTON College of Oceanic and Atmospheric
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
UC Irvine Faculty Publications
 UC Irvine Faculty Publications Title A linear relationship between ENSO intensity and tropical instability wave activity in the eastern Pacific Ocean Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5w9602dn
UC Irvine Faculty Publications Title A linear relationship between ENSO intensity and tropical instability wave activity in the eastern Pacific Ocean Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5w9602dn
Atmospheric Response to North Pacific SST: The Role of Ocean Atmosphere Coupling*
 1MAY 2004 LIU AND WU 1859 Atmospheric Response to North Pacific SST: The Role of Ocean Atmosphere Coupling* ZHENGYU LIU AND LIXIN WU Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison,
1MAY 2004 LIU AND WU 1859 Atmospheric Response to North Pacific SST: The Role of Ocean Atmosphere Coupling* ZHENGYU LIU AND LIXIN WU Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison,
Sea Surface Temperature impact on the Sea Level Changes Over North Pacific
 Sea Surface Temperature impact on the Sea Level Changes Over North Pacific Xichen Li; Jiang Zhu; Shang-Ping Xier; Shan Li Institute of Atmospheric Physics I. Tropical Polar Teleconnections Observed Changes
Sea Surface Temperature impact on the Sea Level Changes Over North Pacific Xichen Li; Jiang Zhu; Shang-Ping Xier; Shan Li Institute of Atmospheric Physics I. Tropical Polar Teleconnections Observed Changes
On the relationship between Synoptic Wintertime Atmospheric Variability and path shifts in the Gulf Stream and the Kuroshio Extension
 On the relationship between Synoptic Wintertime Atmospheric Variability and path shifts in the Gulf Stream and the Kuroshio Extension Terrence M. Joyce Young-Oh Kwon Lisan Yu WHOI 2 nd Revision 5 Dec.
On the relationship between Synoptic Wintertime Atmospheric Variability and path shifts in the Gulf Stream and the Kuroshio Extension Terrence M. Joyce Young-Oh Kwon Lisan Yu WHOI 2 nd Revision 5 Dec.
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Understanding Predictability and Model Errors Through Light, Portable Pseudo-Assimilation and Experimental Prediction Techniques
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding Predictability and Model Errors Through Light, Portable Pseudo-Assimilation and Experimental Prediction Techniques
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding Predictability and Model Errors Through Light, Portable Pseudo-Assimilation and Experimental Prediction Techniques
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
Air-Sea Coupling in an Eastern Boundary Current Region
 Air-Sea Coupling in an Eastern Boundary Current Region Eric D. Skyllingstad CEOAS, Oregon State University Roger M. Samelson D. B. Chelton, A. Kurapov CEOAS, Oregon State University N. Perlin RSMAS, University
Air-Sea Coupling in an Eastern Boundary Current Region Eric D. Skyllingstad CEOAS, Oregon State University Roger M. Samelson D. B. Chelton, A. Kurapov CEOAS, Oregon State University N. Perlin RSMAS, University
Atmosphere Ocean Interaction on Weekly Timescales in the North Atlantic and Pacific
 MARCH 1997 DESER AND TIMLIN 393 Atmosphere Ocean Interaction on Weekly Timescales in the North Atlantic and Pacific CLARA DESER AND MICHAEL S. TIMLIN CIRES, University of Colorado, Boulder, Boulder, Colorado
MARCH 1997 DESER AND TIMLIN 393 Atmosphere Ocean Interaction on Weekly Timescales in the North Atlantic and Pacific CLARA DESER AND MICHAEL S. TIMLIN CIRES, University of Colorado, Boulder, Boulder, Colorado
Propagation of wind and buoyancy forced density anomalies in the North Pacific: Dependence on ocean model resolution
 Ocean Modelling 16 (2007) 277 284 Short Communication Propagation of wind and buoyancy forced density anomalies in the North Pacific: Dependence on ocean model resolution LuAnne Thompson *, Jordan Dawe
Ocean Modelling 16 (2007) 277 284 Short Communication Propagation of wind and buoyancy forced density anomalies in the North Pacific: Dependence on ocean model resolution LuAnne Thompson *, Jordan Dawe
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY
 NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Non-linear patterns of eddy kinetic energy in the Japan/East Sea
 Non-linear patterns of eddy kinetic energy in the Japan/East Sea O.O. Trusenkova, D.D. Kaplunenko, S.Yu. Ladychenko, V.B. Lobanov V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia
Non-linear patterns of eddy kinetic energy in the Japan/East Sea O.O. Trusenkova, D.D. Kaplunenko, S.Yu. Ladychenko, V.B. Lobanov V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia
Abstract Mechanisms of the internally generated decadal-to-multidecadal. variability of SST in the Atlantic Ocean in a coupled GCM
 Clim Dyn DOI 10.1007/s00382-015-2660-8 Mechanisms of internally generated decadal to multidecadal variability of SST in the Atlantic Ocean in a coupled GCM Hua Chen 1 Edwin K. Schneider 2,3 Zhiwei Wu 1
Clim Dyn DOI 10.1007/s00382-015-2660-8 Mechanisms of internally generated decadal to multidecadal variability of SST in the Atlantic Ocean in a coupled GCM Hua Chen 1 Edwin K. Schneider 2,3 Zhiwei Wu 1
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO
 11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS 587.. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). (+) ( ) EOF 1 of SST (+)
11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS 587.. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). (+) ( ) EOF 1 of SST (+)
Ocean Dynamics. The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai
 Ocean Dynamics The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai LO: integrate relevant oceanographic processes with factors influencing survival and growth of fish larvae Physics Determining Ocean Dynamics 1. Conservation
Ocean Dynamics The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai LO: integrate relevant oceanographic processes with factors influencing survival and growth of fish larvae Physics Determining Ocean Dynamics 1. Conservation
Coupling of Extratropical Mesoscale Eddies in the Ocean to Westerly Winds in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer
 1095 Coupling of Extratropical Mesoscale Eddies in the Ocean to Westerly Winds in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer WARREN B. WHITE AND JEFFREY L. ANNIS Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of
1095 Coupling of Extratropical Mesoscale Eddies in the Ocean to Westerly Winds in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer WARREN B. WHITE AND JEFFREY L. ANNIS Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of
Frictional Damping of Baroclinic Waves
 Frictional Damping of Baroclinic Waves HHH, 26th May 2006 Bob Plant With thanks to Stephen Belcher, Brian Hoskins, Dan Adamson Motivation Control simulation, T+60 Simulation with no boundary layer turbulence,
Frictional Damping of Baroclinic Waves HHH, 26th May 2006 Bob Plant With thanks to Stephen Belcher, Brian Hoskins, Dan Adamson Motivation Control simulation, T+60 Simulation with no boundary layer turbulence,
Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator
 Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator Group Representative Hideharu
Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator Group Representative Hideharu
Which Climate Model is Best?
 Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Dynamics of annual cycle/enso interactions
 Dynamics of annual cycle/enso interactions A. Timmermann (IPRC, UH), S. McGregor (CCRC), M. Stuecker (Met Dep., UH) F.-F. Jin (Met Dep., UH), K. Stein (Oce Dep., UH), N. Schneider (IPRC, UH), ENSO and
Dynamics of annual cycle/enso interactions A. Timmermann (IPRC, UH), S. McGregor (CCRC), M. Stuecker (Met Dep., UH) F.-F. Jin (Met Dep., UH), K. Stein (Oce Dep., UH), N. Schneider (IPRC, UH), ENSO and
Global sea surface temperature October 25 th 2007
 The VOCALS Regional Experiment Aerosols, clouds, and precipitation in southeast Pacific stratocumulus Robert Wood Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Global sea surface temperature October 25
The VOCALS Regional Experiment Aerosols, clouds, and precipitation in southeast Pacific stratocumulus Robert Wood Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Global sea surface temperature October 25
TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction and Tropical Climate Shang-Ping Xie OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE INTERACTION AND TROPICAL CLIMATE
 OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE INTERACTION AND TROPICAL CLIMATE Shang-Ping Xie International Pacific Research Center and Department of Meteorology University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA Keywords: ocean-atmospheric
OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE INTERACTION AND TROPICAL CLIMATE Shang-Ping Xie International Pacific Research Center and Department of Meteorology University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA Keywords: ocean-atmospheric
Basic Ocean Current Systems. Basic Ocean Structures. The State of Oceans. Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate. Temperature.
 Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
The Forcing of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
 The Forcing of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation Schneider and Cornuelle, 2005 Patrick Shaw 3/29/06 Overlying Questions What processes statistically influence variability in the PDO? On what time scales
The Forcing of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation Schneider and Cornuelle, 2005 Patrick Shaw 3/29/06 Overlying Questions What processes statistically influence variability in the PDO? On what time scales
An Empirical Model for Surface Wind Stress Response to SST Forcing Induced by Tropical Instability Waves (TIWs) in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific
 JUNE 2009 Z H A N G A N D B U S A L A C C H I 2021 An Empirical Model for Surface Wind Stress Response to SST Forcing Induced by Tropical Instability Waves (TIWs) in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific RONG-HUA
JUNE 2009 Z H A N G A N D B U S A L A C C H I 2021 An Empirical Model for Surface Wind Stress Response to SST Forcing Induced by Tropical Instability Waves (TIWs) in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific RONG-HUA
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities
 WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Supplementary Material for. Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability
 1 2 Supplementary Material for Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability 3 4 Jie He 1, Clara Deser 2 & Brian J. Soden 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. Princeton University, and NOAA/Geophysical
1 2 Supplementary Material for Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability 3 4 Jie He 1, Clara Deser 2 & Brian J. Soden 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. Princeton University, and NOAA/Geophysical
The Gulf Stream signature on SST: observations and impact on the North Atlantic storm-track
 The Gulf Stream signature on SST: observations and impact on the North Atlantic storm-track Arnaud Czaja & Alison Cobb, Luke Sheldon at Imperial College, Rhys Parfitt (WHOI) & Benoit Vannière (Reading
The Gulf Stream signature on SST: observations and impact on the North Atlantic storm-track Arnaud Czaja & Alison Cobb, Luke Sheldon at Imperial College, Rhys Parfitt (WHOI) & Benoit Vannière (Reading
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN
 JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium
 Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium Meng Zuo, Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: zuomeng@lasg.iap.ac.cn Sixth WMO International
Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium Meng Zuo, Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: zuomeng@lasg.iap.ac.cn Sixth WMO International
JRA-55CHS: An Atmospheric Reanalysis Produced with High-Resolution SST. Satoru Okajima 1
 SOLA, XXXX, Vol.X, XXX-XXX, doi: 0./sola.XXXX-XXX JRA-CHS: An Atmospheric Reanalysis Produced with High-Resolution SST Ryusuke Masunaga,, Hisashi Nakamura, Hirotaka Kamahori, Kazutoshi Onogi and Satoru
SOLA, XXXX, Vol.X, XXX-XXX, doi: 0./sola.XXXX-XXX JRA-CHS: An Atmospheric Reanalysis Produced with High-Resolution SST Ryusuke Masunaga,, Hisashi Nakamura, Hirotaka Kamahori, Kazutoshi Onogi and Satoru
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 45 (2008) 274 319 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dynatmoce Air sea interaction
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 45 (2008) 274 319 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dynatmoce Air sea interaction
SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate
 SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate Chris Reason Oceanography Dept, Univ. Cape Town Overview of southern African climate and tropical Atlantic SST South American monsoon, Benguela
SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate Chris Reason Oceanography Dept, Univ. Cape Town Overview of southern African climate and tropical Atlantic SST South American monsoon, Benguela
Contribution of the cold sector of extratropical cyclones to mean state features over the Gulf Stream in winter
 Contribution of the cold sector of extratropical cyclones to mean state features over the Gulf Stream in winter Benoît Vannière a Arnaud Czaja a Helen F Dacre b a Physics Department, Imperial College London,
Contribution of the cold sector of extratropical cyclones to mean state features over the Gulf Stream in winter Benoît Vannière a Arnaud Czaja a Helen F Dacre b a Physics Department, Imperial College London,
Variations of total heat flux during typhoons in the South China Sea
 78 Variations of total heat flux during typhoons in the South China Sea Wan Ruslan Ismail 1, and Tahereh Haghroosta 2,* 1 Section of Geography, School of Humanities, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden,
78 Variations of total heat flux during typhoons in the South China Sea Wan Ruslan Ismail 1, and Tahereh Haghroosta 2,* 1 Section of Geography, School of Humanities, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden,
- tornadoes. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. -tropical storms. -Storm surge
 (1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 12) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their relationship to air masses Also
(1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 12) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their relationship to air masses Also
Numerical Experiments of Tropical Cyclone Seasonality over the Western North Pacific
 Numerical Experiments of Tropical Cyclone Seasonality over the Western North Pacific Dong-Kyou Lee School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Seoul National University, Korea Contributors: Suk-Jin Choi,
Numerical Experiments of Tropical Cyclone Seasonality over the Western North Pacific Dong-Kyou Lee School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Seoul National University, Korea Contributors: Suk-Jin Choi,
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.
![Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz. Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.](/thumbs/88/117265944.jpg) Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
How Volcanism Impacts on Tropical Atlantic PPT. Luciana F. Prado Ilana Wainer
 How Volcanism Impacts on Tropical Atlantic PPT Luciana F. Prado Ilana Wainer Two leading modes of Tropical Atlantic SST variability Equatorial Zonal Mode (zonal) ( Atlantic Mode Niño ~38% Meridional Mode
How Volcanism Impacts on Tropical Atlantic PPT Luciana F. Prado Ilana Wainer Two leading modes of Tropical Atlantic SST variability Equatorial Zonal Mode (zonal) ( Atlantic Mode Niño ~38% Meridional Mode
Pacific Decadal Variability: The Tropical Pacific Mode and the North Pacific Mode*
 VOL. 16, NO. 8 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 APRIL 2003 Pacific Decadal Variability: The Tropical Pacific Mode and the North Pacific Mode* L. WU, Z.LIU, AND R. GALLIMORE Center for Climatic Research, University
VOL. 16, NO. 8 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 APRIL 2003 Pacific Decadal Variability: The Tropical Pacific Mode and the North Pacific Mode* L. WU, Z.LIU, AND R. GALLIMORE Center for Climatic Research, University
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region
 Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical marine stratus and stratocumulus regions
 Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
An observational study of the impact of the North Pacific SST on the atmosphere
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18611, doi:10.1029/2006gl026082, 2006 An observational study of the impact of the North Pacific SST on the atmosphere Qinyu Liu, 1 Na
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18611, doi:10.1029/2006gl026082, 2006 An observational study of the impact of the North Pacific SST on the atmosphere Qinyu Liu, 1 Na
