RAINFALL CHARACTERIZATION IN AN ARID AREA
|
|
|
- Evelyn Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 4, 1991, p RAINFALL CHARACTERIZATION IN AN ARID AREA Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed Department of Civil Engineering Qatar University, Doha, Qatar. ABSTRACT The objective of this work is to characterize the rainfall in Doha which lies in an arid region. The rainfall data included daily rainfall depth since 1962 and the hyetographs of the individual storms since The rainfall is characterized by high variability and severe thunderstorms which are of limited geographical extent. Four probability distributions were used to fit the maximum rainfall in 24 hours and the annual rainfall depth. The extreme value distribution was found to have the best fit. The rainfall intensity-duration-frequency relationship has been developed which compares well with values obtained by other investigators in the Gulf area. INTRODUCTION A knowledge of the rainfall characteristics is of paramount importance in the design of hydrologic system whether the function of such a system is water control or water use and management. In some arid areas of the world failure to account for the drainage of storm water sometimes causes tremendous inconvenience. Presumably it was thought that an arid area hardly experiences any rain and therefore there is no need to worry about storm water. The definition of arid region is somewhat vague, but where the potential water loss by evaporation and transpiration exceeds the amount of water supplied by precipitation may be called an arid area. The maximum precipitation for an arid area is not constant since it varies with the geographic location and the temperature. Extremely arid areas are those where precipitation totally lacks any rhythm and remains at zero for at least twelve consecutive months (Macmillan, 1982). The purpose of this work is to characterize the rainfall in Doha which lies in an arid area. The rainfall data are analyzed to assess the variability and to develop relevant intensity-duration-frequency relationship with somewhat inadequate data. Doha is the capital of the State of Qatar, a peninsula in the Arabian Gulf. Since 1962 Doha International Airport meteorological station is operated by the Department of Meteorology of the Ministry of Communication and Transport and is considered to have the largest record in the State of Qatar. Available information 35
2 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed include daily rainfall depth since 1962 and the hyetographs of the individual storms since Daily rainfall data is processed by the Department of Meteorology to produce the summary of annual rainfall depth, maximum rainfall in 24 hours and the number of rainfall days in a year with a depth exceeding 1 mm. VARIABILITY OF RAINFALL Annual rainfall depth, maximum rainfall depth, maximum rainfall in 24 hours and number of rainfall days for 28 years ( ) are shown in Figures 1, 2 and 3 respectively. Maximum and minimum values are given in Table 1 together with the mean, the standard deviation and the coefficient of variation defined as the ratio of the standard deviation and the mean. These values indicate considerable variation in the rainfall amounts and events. The coefficient of variation of the rainfall depth was A very high value compared to the coefficient of variation for well-watered regions of the world where this coefficient can be as low as Since the true mean is not known, it is interesting to notice the importance of the length of the record on estimating the mean. Table 2 shows the variation in the mean of annual rainfall depth for different record lengths together with the percentage deviation of that mean from the true mean taken as the mean of the whole record (28 years). It indicates that in order to obtain a reasonable estimate of the mean annual rainfall depth, at least ten years record is needed. 350r , 300 e 2so :I: : Oa.ULLR.UUK.UUKAUUL.U_u ,66 19, , , YEARS Fig. 1: Annual Rainfall Depth 36
3 Rainfall Characterization in an Arid Area 100, , 9 L;tj uaa.ULUL.UUL.U , , YEARS Fig. 2: Maximum Rainfall in 24 Hours :a I c:i z YEARS Fig. 3: Number of Rainfall Days (Rainfall Depth > 1 mm) The mean anual rainfall depth for Doha is 77.2 mm, a small value compared to corresponding values for well watered areas of the world, (the average annual precipitation over the whole of the United Kingdom is of the order 1100 mm, 14 times that of Doha, and can be as high as 5000 mm in the mountainous regions of the North-West (Bartlett, 1981). From Figure 1, it is clear that in the years 1962, 1970, 1971 and 1985 the rainfall depth was less than 20% of the mean indicating relatively very dry years. 37
4 Abdallah S, Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed Table 1 Summary of Statistical Parameters for Rainfall Data ( ), Doha-Qatar. Maximum Minimum Mean Max. Standard CoetT. Variable Mean Deviation of Variation Annual Depth (mm) Maximum Rainfall in 24 hrs (mm) No. of Rainfall Days in excess of 1 mm 22 zero Table 2 Variation of the Mean Annual Rainfall Depth with the Length of the Record. Period Number of Mean % Deviation years (mm) of true mean zero Figure 4 shows the average monthly variation in the rainfall. It indicates that the months of June, July, August and September are dry. Most of the rain occurs in winter and early spring. Roughly 65% of the annual rainfall occurs in January, February and March. By including the months of December and April this would account for 90% of the total rainfall. It is observed that most of the lightning and thunders occur in March and April. A tally of storms that have occurred since 1975 up to the end of 1989 (14 years) would indicate that 75.6% of the storms produced a depth less than 10 mm, while 24.4% of the storms produced a depth greater than 10 38
5 Rainfall Characterization in an Arid Area 20r MONTH Fig. 4: Mean Monthly Rainfall Depth ' 10 z MONTH Fig. 5: Monthly Mean Daily Evaporation mm out of which 10.7% of the storms produced a depth greater than 20 mm and 5.3% of the storms produced a depth greater than 30 mm. A tally of those storms that produced a depth in excess of 10 mm would indicate that such storms usually occur in February and March. The probability of having at least one, two, three, four, and five storms in one year with a depth greater than 10 mm each is respectively 85.7%, 64.3%, 35.7%, 21.4% and 7.1 %. Standard pan evaporation data for the period 1976 to 1988 at the Doha International Airport were analyzed giving a mean daily rate of 8.6 mrnlday with a 39
6 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed standard deviation of This would result in a coefficient of variation of 0.068, indicating less variability in pan evaporation. The annual average evaporation depth is 3,139 mm, more than forty times the annual rainfall depth. Figure 5 shows the variation of the average monthly evaporation rate during 1976 through Maximum evaporation of 15.7 mrnld occurs in June while the minimum rate of 3.7 mrnld occurs in December. In 1978 a second climatological station was installed at the Doha Port within four kilometers from the main station at the International Airport. For comparison the annual rainfall depth, maximum rainfall depth in 24 hours and number of rainfall days having rainfall depth greater than 1 mm for the two stations over the period ( ) are given in Table 3. This table includes the correlation coefficient, the y intercept and the slope of the regression line. The highest observed deviation in both the annual rainfall depth and the maximum rainfall in 24 hours between the two stations occurred in In general correlation of the maximum rainfall in 24 hours between the two stations is low as compared to the annual rainfall depth. Table 3 Areal Variation of Rainfall Characteristics Year Annual Rainfall Max. Rainfall in No. of Rainfall Depth (mm) 24 hrs. (mm) Days> I mm x 'y X y X y Mean Correlation Coefficient y intercept (a) Slope (b) 'y : Doha Port Station 2 x : Doha International Airport Station y=a+bx 40
7 Rainfall Characterization in an Arid Area EXTREME-VALUE ANALYSIS Hydrologic systems are sometimes impacted by severe storms. The magnitude of a storm is inversely related to its frequency of occurrence, very severe events occurring less frequently than moderate events. The objective of frequency analysis of hydrologic data is to relate the magnitude of extreme events to their frequency of occurrence through the use of probability distributions. Four types of probability distributions namely: the normal distribution, the log normal distribution, log Pearson type III distribution and the extreme value (Gumbel) distribution were fitted to the annual series of maximum rainfall in 24 hours over the period of In order to perform the analysis, an order (m) is assigned to each individual recorded event according to the magnitude (m=1 for the highest rainfall in 24 hrs). The probability of an event of the same magnitude or higher occurring may then be calculated by: P = (m/n+1) where N is the total number of events recorded in the data series, herein 27 years. The calculated frequency of an event of the same magnitude or higher is given by; Tr = (lip) Tr is called the return period or the recurrence interval and is defined again as the average time interval between storms that are equal to or greater than a specific value. The arranged data for the maximum rainfall in 24 hours annual series together with the corresponding probability of excedence (p) is plotted on log-probability paper as shown on Figure 6. Procedures to fit the four probability distributions to the data are clearly outlined in Prashun (1987) and Chow et al. (1988). The goodness of fit for the four distributions was tested using the Chi-square test statistics (Chow et al., 1988 and Haan, 1977). The same steps were followed for the total annual depth series. The results are presented in Figure 7. It was found that the extreme value (Gumbel) distribution provided the best fit for the two series. The calculated skewness coefficient required by the log-pearson type-iii distribution for the two series was close to ( -2.0). The curves representing this distribution both on Figures 6 and 7 correspond to a skewness coefficient of ( -1.0). The later value provided a better fit for the data values of the larger magnitude and lower probability of exceedence. This end of the series is of more concern. It is clear from Figures 6 and 7 that the normal distribution deviates from the data points at its two ends, i.e. extreme low and high values. The normal distribution provided a better fit for the annual total rainfall series than the annual maximum 41
8 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed GUMBEL LOG. NORMAL LOG. PEARSON 50 f-----'-=-=-=-=-=-=-= NORMAL PROBABILITY OF EXCEEDENCE 7. Fig. 6: Probability Distributions of the Maximum Rainfall in 24 Hours rainfall in 24 hours. The problem with most hydrologic data is that an equal spread does not occur above and below the mean. The lower side is limited to the range from the mean to zero, while there is theoretically no limitation on the upper range. This contributes to what is called a skewed distribution. INTENSITY-DURATION-FREQUENCY RELATIONSHIP One of the most important rainfall characteristics is the rainfall intensity, usually expressed in mm/hr. Average annual rainfall has only a limited bearing on the 42
9 Rainfall Characterization in an Arid Area ----GUMBEL =-=-===:-c-- LOG. NORMAL LOG. PEARSON NORMAL I E E 100 t t 50 U.l Ci -l -l -l 10 :l z 5 NORMAL '-1-.f----- LOG. PEARSON (----:;o::::==f==== LOG. NORMAL i / / GUMBEL PROBABILITY OF EXCEEDENCE % Fig. 7: Probability Distributions of the Annual Rainfall Depth design of surface water sewerage schemes. Storms of high intensity generally last for fairly short periods and cover smaller areas. Therefore in applying statistical methods to rainfall data the analysis should include the intensity as well as the oveall depth. The analysis should provide the average period of time within which the depth of rainfall for a given duration will be equalled or exceeded. In order to establish the relationship among rainfall intensity, duration and return period available rainfall hyetographs over the period (13 years) were analyzed. Because of the limited number of rainfall events, it was not possible to determine the complete relationship using rigorous statistical procedures as outlined by Fair et al. (1977) and Chow et al. (1988). Therefore the procedure outlined in Al-Layla et al. (1980) was followed to determine the intensity-duration- 43
10 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed frequency relationship with inadequate data. The procedure depends on the use of the coefficients given in Tables 4 and 5. While Table 4 relates the one-hour rainfall with different return periods to the one-hour, two year rainfall, Table 5 relates the rainfall of different durations to the one hour rainfall depth of the same return period. The available hyetographs were scanned to determine the maximum rainfall depth that has occurred in one hour over 13 years. The storm on 12/3/1982 shown in Figure 8 produced the largest depth of 26 mm in one hour and was assigned a return period of 14 years. Figures 9 and 10 show the hyetographs of the storms which produced the second and third largest depth in one hour over 13 years. These depths were respectively 21 mm and 17.5 mm. The corresponding return periods would be then 7 and 5. Both the cumulative rainfall depth and intensity are portrayed on the hyetographs. Table 4 Ratio of the 2 Y r, 1 Hr. Rainfall to the 1 Hr. Rainfall of Different Return Period* Return Period (Years) Ratio Al-Layla et al. (1980) Table 5 Ratio of. the 1 Hr, Rainfall Depth to the Rainfall Depth of Different Duration for the Same Return Period*. Country Duration (Minutes) 5 10 IS USA Australia USSR Al-Layla et al. (1980) The intensity-duration-frequency relationship developed was based on the critical storm on 12/3/1982, (depth= 26 mm, duration= 60 min, return period= 14 yr). By interpolating the coefficients given in Table 4, the ratio of 1 hr, 14 yr rainfall 44
11 Rainfall Characterization in an Arid Area?Or , c: 40 Q.. <I) Cl ==L '1'DOI:,Boun Fig. 8: Rainfall Hyetograph, 12/3/ (0-30 J I 25 e 20..c: Q.. <I) 15 Cl TDCE, Boun 8 10 Fig. 9: Rainfall Hyetograph, 21/2/ r ,30 30 e 25 e 'E. 20 <I) Cl o := o TIKB,Boun Fig. 10: Rainfall Hyetograph, 15/12/
12 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed to 1 hr, 2 yr rainfall is Hence, the 1 hr, 2 yr rainfall depth is estimated as 15.3 mm. Similarly the 1 hr rainfall depths for 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 year return periods were obtained. The ratios given in Table 5 for USA was used to determine the rainfall depths for different storm durations namely, 5, 10, 15, 30, 120 minutes based on the one-hour depth for each return period. The resulting depths are included in Table 6. The intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) relationship is obtained by dividing each depth by the corresponding duration. The developed IDF relationship was compared to an IDF presented by Eccleston et al. (1981) which was based on a limited data ( ) collected for three recording rainfall gauges at Rowdaht al Faras, Abu Nakhla, and Abu-Samara (three inland sites in the State of Qatar). The results are given in Table 7 together with the corresponding data for Bahrain, a neighboring state in the Gulf area known to have longer rainfall record of approximately fifty years. As an independent check on the developed IDF relationship, the 1 hr, 5 yr rainfall depth from Table 6 is 20.6 mm. The corresponding values from the hyetographs of Figures 9 and 10 are a depth of 21 mm for 1 hr, 7 yr storm of 2112/1988 and 17.5 mm for 1 hr, 5 yr storm of 15/ In the absence of 1 hr rainfall records, one may use rainfall records of 24 hrs. which are generally available. The ratio between 2 yr, 1 hr rainfall to 2 yr, 24 hr rainfall varies between 0.35 to 0.5 (Al-Layla et al. 1980). An average value of was used to convert the maximum rainfall in 24 hrs observed over a period of 28 years to 1 hr rainfall. The resulting 1 hr, 28 yr rainfall depth will be 34 mm. The ratio to convert 1 hr, 28 yr rainfall depth to 1 hr, 2 yr rainfall depth is obtained by interpolation from Table 4 as 1.9. This would give 1 hr, 2 yr depth of 17.9 mm compared to 15.3 mm as obtained from the critical storm of 12/ Table 6 Depth-Duration-Frequency Relationship Based on the Critical Storm of 12/ (Doha-Qatar). Rainfall Depth (mm) Return Period (Years) Duration (Minutes)
13 Table 7 Comparison of Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Relationships (Doha-Qatar) -1>- -.1 Duration (Minutes) (1) (2) Rainfall Intensity (mm/hr) Return Period Tr (Years) Tr = 2 Tr = 5 Tr = 10 (3) (4) (1) (2) (3) (4) (1) (1) Developed IDF based on the critical storm of 12/3/1982, inadequate data procedure. (2) Eccleston et al., (1981). (3) Bahrain, Pencol (1981) (4) U.K., Simple Ministry-type formulae, Bartlett (1981) (2) (3) (4) (1) s "' to> ::::: Q ill "' Tr = 25..., l'b (2) (3) (4) - "' g ::1 s "' 1:: ) :J. Q )... "'
14 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed The intensity-duration-frequency relationship based on the critical storm of 12/3/1982 was fitted by an equation of the form; i in which i is the rainfall intensity in mrnlhr, Tr is the return period in years and t is the storm duration in minutes. C,m,d and n are fitting parameters. The best fit of the developed IDF relationship was for the following values of the parameters; (C = -UO, m = 0.206, d = 10, and n = 0.787) The IDF relationship is shown in Figure 11. Table 7 includes also the rainfall IDF values relevant to the United Kingdom for comparison purposes. These values were computed using simple "Ministry-type" formulae based on work originally published by Norris in 1948 (Bartlett, 1981) c e E > t: V'} z IJ.l E z DEVELOPED IDF Tr= Tr= 5 + Tr= 10 -B- Tr= 25 "'* Tr= 50 + Tr= 100 o DURATION Minutes Fig. 11: Intensity-Duration-Frequency Relationship CONCLUSIONS The State of Qatar can be taken to represent an arid area since the average annual evaporation loss greatly exceeds the average annual rainfall gain. The mean annual rainfall depth based on a record of 28 years in Doha, the state capital, was 48
15 Rai;;fa/1 Characterization in an Arid Area 77.2 mm, while the maximum annual depth observed was mm in There are only few days in the year when precipitation take place (8 to 9 days) between November and April. Thunder storms may occur once or twice a year and can contribute significantly to the total annual rainfall depth. The maximum rainfall in 24 hrs so far recorded was 80.1 mm. The rainfall is characterized by high variability. In order: to obtain a reasonable estimate of a representative mean of the annual rainfall depth the length of the record need to be at least ten years. Although the correlation of the annual rainfall depth and the number of rainfall days was adequate for two closely spaced stations, the correlation of the maximum rainfall in 24 hrs was not as good. This shows that severe thunderstorms are of limited geographic extent. Four probability distributions were used to fit the maximum rainfall in 24 hrs and the annual rainfall depth. The (Gumbel) extreme-value distribution was found to have the best fit. The rainfall intensity-duration frequency (IDF) relationship for Doha has been developed based on the analysis of the hyetographs of few critical storms and compared with the maximum 24 hrs rainfall data. The developed relationship seems adequate when further compared with values obtained by other investigators for the State of Qatar and for Bahrain a neighbouring state in the Gulf area where longer rainfall record is available. While the annual rainfall depth in an arid area can be small compared to well watered areas of the world, the intensities of the storms in an arid region may be high over short durations. Rainfall is scarce in an arid area but some events are severe and can cause inconvenience. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We wish to acknowledge with thanks the help and cooperation extended by the Department of Meteorology, Ministry of Communication and Transport, State of Qatar, for providing the rainfall data. REFERENCES 1. Al-Layla, M.A., Ahmed, S. and Middlebrooks, E.J., 1980, Handbook of Wastewater Collection and Treatment, Garland STPM Press, New York. 2. Bartlett, R.E., 1981, Surface Water Sewerage. Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London. 3. Chow, V.T., Maidment, D.R. and Mays, L.W., 1988, Applied Hydrology. McGraw Hill Book Company, New York. 49
16 Abdallah S. Bazaraa and Shamim Ahmed 4. Department of Meteorology, Ministry of Communication and Transport, Long Period Means and Extremes of Climatological Elements, Doha International Airport ( )., State of Qatar. 5. Department of Meteorology, Ministry of Communication and Transport, Long Period Means and Extremes of Climatological Elements, Doha Port ( ), State of Qatar. 6. Eccleston, B., Pikes, J.G. and Harhash, I., 1981, The Water Resources of Qatar and Their Development. Technical Report No. 5, Ministry of Industry and Agriculture, State of Qatar. 7. Fair, G.M., Geyer, J.C. and Okun, D.A., 1971, Elements of Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal, John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York. 8. Haan, C.T., 1977, Statistical Methods in Hydrology. Iowa State University Press, Ames,. Iowa. 9. Macmillan Family Encyclopedia, 1982, Macmillan, London. 10. Prashun, A.L., 1987, Fundamentals of Hydraulic Engineering. Hot Rinehart and Winston, New York. 11. Pencol, J.T. and Sons, 1981, Doha Storm Water and Land Drainage Master Plan. Draft Report, Ministry of Public Works, State of Qatar. 12. Pilgrim, D.H., 1987, (Editor), Australian Rainfall and Runoff, A Guide to Flood Estimation. The Institution of Engineers, Barton, Australia. 13. Reich, B.M., 1963, Short-Duration Rainfall-Intensity Estimates and Other Design Aids for Regions of Sparse Data. Journal of Hydrology, Vol. (1), pp Yevjevich, V., 1972, Probability and Statistics in Hydrology. Water Resources Publications, Fort Colins, Colarado, USA. 50
Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves Example
 Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves Example Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) curves describe the relationship between rainfall intensity, rainfall duration, and return period (or its inverse, probability
Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves Example Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) curves describe the relationship between rainfall intensity, rainfall duration, and return period (or its inverse, probability
Modeling Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency (R-IDF) Relationship for Seven Divisions of Bangladesh
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 5/ August 2015 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Modeling Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency (R-IDF) Relationship
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 5/ August 2015 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Modeling Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency (R-IDF) Relationship
Establishment of Intensity-Duration- Frequency Formula for Precipitation in Puthimari Basin, Assam
 Establishment of Intensity-Duration- Frequency Formula for Precipitation in Puthimari Basin, Assam Tinku Kalita 1, Bipul Talukdar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Assam Engineering College,
Establishment of Intensity-Duration- Frequency Formula for Precipitation in Puthimari Basin, Assam Tinku Kalita 1, Bipul Talukdar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Assam Engineering College,
Range Cattle Research and Education Center January CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2012 Range Cattle Research and Education Center.
 1 Range Cattle Research and Education Center January 2013 Research Report RC-2013-1 CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2012 Range Cattle Research and Education Center Brent Sellers Weather conditions strongly influence
1 Range Cattle Research and Education Center January 2013 Research Report RC-2013-1 CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2012 Range Cattle Research and Education Center Brent Sellers Weather conditions strongly influence
CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2002
 Range Cattle Research and Education Center Research Report RC-2003-1 February 2003 CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2002 Range Cattle Research and Education Center R. S. Kalmbacher Professor, IFAS, Range Cattle Research
Range Cattle Research and Education Center Research Report RC-2003-1 February 2003 CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2002 Range Cattle Research and Education Center R. S. Kalmbacher Professor, IFAS, Range Cattle Research
Lecture 2: Precipitation
 2-1 GEOG415 Lecture 2: Precipitation Why do we study precipitation? Precipitation measurement -- depends on the study purpose. Non-recording (cumulative) Recording (tipping bucket) Important parameters
2-1 GEOG415 Lecture 2: Precipitation Why do we study precipitation? Precipitation measurement -- depends on the study purpose. Non-recording (cumulative) Recording (tipping bucket) Important parameters
Solution: The ratio of normal rainfall at station A to normal rainfall at station i or NR A /NR i has been calculated and is given in table below.
 3.6 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA Data for the period of missing rainfall data could be filled using estimation technique. The length of period up to which the data could be filled is dependent on individual
3.6 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA Data for the period of missing rainfall data could be filled using estimation technique. The length of period up to which the data could be filled is dependent on individual
Effect of Storm Separation Time on Rainfall Characteristics-A Case Study of Johor, Malaysia
 European Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-216X Vol.45 No.2 (2010), pp.162-167 EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2010 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm Effect of Storm Separation Time on Rainfall
European Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-216X Vol.45 No.2 (2010), pp.162-167 EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2010 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm Effect of Storm Separation Time on Rainfall
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY. Lecture -29 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc.
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -29 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Goodness of fit Chi-square test χ
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -29 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Goodness of fit Chi-square test χ
Developing Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency Models for Calabar City, South-South, Nigeria.
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-06, pp-19-24 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Developing Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-06, pp-19-24 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Developing Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency
A Study on Storm Water Drainage System of Annanagara and Ashokanagara of Shimoga City Karnataka India
 A Study on Storm Water Drainage System of Annanagara and Ashokanagara of Shimoga City Karnataka India Veena D Savanth Lecturer, Department of Civil Engineering Jain Institute of Technology, Davanagere,
A Study on Storm Water Drainage System of Annanagara and Ashokanagara of Shimoga City Karnataka India Veena D Savanth Lecturer, Department of Civil Engineering Jain Institute of Technology, Davanagere,
University of East London Institutional Repository:
 University of East London Institutional Repository: http://roar.uel.ac.uk This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
University of East London Institutional Repository: http://roar.uel.ac.uk This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Hydro-meteorological Aspect. 3.3 Rain Gauge Stations
 3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
Keywords: rainfall variation, extreme rainfall, intensity frequency duration, Eastern Australia
 Secular Variation in Rainfall and Intensity-Frequency-Duration Curves in Eastern Australia Yi-Ru Chen 1, Bofu Yu and Graham Jenkins Griffith University, QLD, Australia Abstract Rainfall intensity-frequency-duration
Secular Variation in Rainfall and Intensity-Frequency-Duration Curves in Eastern Australia Yi-Ru Chen 1, Bofu Yu and Graham Jenkins Griffith University, QLD, Australia Abstract Rainfall intensity-frequency-duration
"ESTIMATES OF POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION OVER THE STATE OF QATAR"
 Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 2, 1989. "ESTMATES OF POTENTAL EVAPOTRANSPRATON OVER THE STATE OF QATAR" By Abdallah Sadik Bazaraa Department of Civil Engineering University of Qatar, Doha
Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 2, 1989. "ESTMATES OF POTENTAL EVAPOTRANSPRATON OVER THE STATE OF QATAR" By Abdallah Sadik Bazaraa Department of Civil Engineering University of Qatar, Doha
Range Cattle Research and Education Center January CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2016 Range Cattle Research and Education Center.
 1 Range Cattle Research and Education Center January 2017 Research Report RC-2017-1 CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2016 Range Cattle Research and Education Center Brent Sellers Weather conditions strongly influence
1 Range Cattle Research and Education Center January 2017 Research Report RC-2017-1 CLIMATOLOGICAL REPORT 2016 Range Cattle Research and Education Center Brent Sellers Weather conditions strongly influence
Rainfall Analysis. Prof. M.M.M. Najim
 Rainfall Analysis Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Estimate long term mean rainfall for a new station Describe the usage of a hyetograph Define recurrence
Rainfall Analysis Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Estimate long term mean rainfall for a new station Describe the usage of a hyetograph Define recurrence
LITERATURE REVIEW. History. In 1888, the U.S. Signal Service installed the first automatic rain gage used to
 LITERATURE REVIEW History In 1888, the U.S. Signal Service installed the first automatic rain gage used to record intensive precipitation for short periods (Yarnell, 1935). Using the records from this
LITERATURE REVIEW History In 1888, the U.S. Signal Service installed the first automatic rain gage used to record intensive precipitation for short periods (Yarnell, 1935). Using the records from this
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY. Lecture -27 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc.
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -27 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Frequency factors Normal distribution
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -27 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Frequency factors Normal distribution
Rainfall variation and frequency analysis study in Dharmapuri district, India
 Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol. 45 (11), November 216, pp. 156-1565 Rainfall variation and frequency analysis study in Dharmapuri district, India V. Rajendran 1*, R. Venkatasubramani 2 & G.
Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol. 45 (11), November 216, pp. 156-1565 Rainfall variation and frequency analysis study in Dharmapuri district, India V. Rajendran 1*, R. Venkatasubramani 2 & G.
Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC
 Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC This threat overview relies on projections of future climate change in the Mekong Basin for the period 2045-2069 compared to a baseline of 1980-2005.
Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC This threat overview relies on projections of future climate change in the Mekong Basin for the period 2045-2069 compared to a baseline of 1980-2005.
Intensity-Duration-Frequency Analysis of Rainfall for a Site in Chennai City
 Intensity-Duration-Frequency Analysis of Rainfall for a Site in Chennai City James Jesudasan Julius Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Coimbatore IRCC Intern, Indian Institute of Technology
Intensity-Duration-Frequency Analysis of Rainfall for a Site in Chennai City James Jesudasan Julius Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Coimbatore IRCC Intern, Indian Institute of Technology
DETERMINATION OF PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FOR DATA ON RAINFALL AND FLOOD LEVELS IN BANGLADESH
 061-072 Determination 9/26/05 5:28 PM Page 61 DETERMINATION OF PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FOR DATA ON RAINFALL AND FLOOD LEVELS IN BANGLADESH M Ferdows *1, Masahiro OTA 1, Roushan Jahan 1, MNA Bhuiyan 2,
061-072 Determination 9/26/05 5:28 PM Page 61 DETERMINATION OF PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION FOR DATA ON RAINFALL AND FLOOD LEVELS IN BANGLADESH M Ferdows *1, Masahiro OTA 1, Roushan Jahan 1, MNA Bhuiyan 2,
Design Storms for Hydrologic Analysis
 Design Storms for Hydrologic Analysis Course Description This course is designed to fulfill two hours of continuing education credit for Professional Engineers. Its objective is to provide students with
Design Storms for Hydrologic Analysis Course Description This course is designed to fulfill two hours of continuing education credit for Professional Engineers. Its objective is to provide students with
Dependence of evaporation on meteorological variables at di erent time-scales and intercomparison of estimation methods
 Hydrological Processes Hydrol. Process. 12, 429±442 (1998) Dependence of evaporation on meteorological variables at di erent time-scales and intercomparison of estimation methods C.-Y. Xu 1 and V.P. Singh
Hydrological Processes Hydrol. Process. 12, 429±442 (1998) Dependence of evaporation on meteorological variables at di erent time-scales and intercomparison of estimation methods C.-Y. Xu 1 and V.P. Singh
Reprinted from MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW, Vol. 109, No. 12, December 1981 American Meteorological Society Printed in I'. S. A.
 Reprinted from MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW, Vol. 109, No. 12, December 1981 American Meteorological Society Printed in I'. S. A. Fitting Daily Precipitation Amounts Using the S B Distribution LLOYD W. SWIFT,
Reprinted from MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW, Vol. 109, No. 12, December 1981 American Meteorological Society Printed in I'. S. A. Fitting Daily Precipitation Amounts Using the S B Distribution LLOYD W. SWIFT,
Climate Change Impact on Intensity-Duration- Frequency Curves in Ho Chi Minh city
 Climate Change Impact on Intensity-Duration- Frequency Curves in Ho Chi Minh city Minh Truong Ha Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate Change, Hanoi, Vietnam Kuala Lumpur, 06-2018 Rationale Unpredictable
Climate Change Impact on Intensity-Duration- Frequency Curves in Ho Chi Minh city Minh Truong Ha Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate Change, Hanoi, Vietnam Kuala Lumpur, 06-2018 Rationale Unpredictable
Rainfall is the major source of water for
 RESEARCH PAPER: Assessment of occurrence and frequency of drought using rainfall data in Coimbatore, India M. MANIKANDAN AND D.TAMILMANI Asian Journal of Environmental Science December, 2011 Vol. 6 Issue
RESEARCH PAPER: Assessment of occurrence and frequency of drought using rainfall data in Coimbatore, India M. MANIKANDAN AND D.TAMILMANI Asian Journal of Environmental Science December, 2011 Vol. 6 Issue
Module 1. Lecture 2: Weather and hydrologic cycle (contd.)
 Lecture 2: Weather and hydrologic cycle (contd.) Hydrology Hydor + logos (Both are Greek words) Hydor means water and logos means study. Hydrology is a science which deals with the occurrence, circulation
Lecture 2: Weather and hydrologic cycle (contd.) Hydrology Hydor + logos (Both are Greek words) Hydor means water and logos means study. Hydrology is a science which deals with the occurrence, circulation
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL
 MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL Bahari Meymandi.A Department of Hydraulic Structures, college of
MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL Bahari Meymandi.A Department of Hydraulic Structures, college of
CFCAS project: Assessment of Water Resources Risk and Vulnerability to Changing Climatic Conditions. Project Report II.
 CFCAS project: Assessment of Water Resources Risk and Vulnerability to Changing Climatic Conditions Project Report II. January 2004 Prepared by and CFCAS Project Team: University of Western Ontario Slobodan
CFCAS project: Assessment of Water Resources Risk and Vulnerability to Changing Climatic Conditions Project Report II. January 2004 Prepared by and CFCAS Project Team: University of Western Ontario Slobodan
A Report on a Statistical Model to Forecast Seasonal Inflows to Cowichan Lake
 A Report on a Statistical Model to Forecast Seasonal Inflows to Cowichan Lake Prepared by: Allan Chapman, MSc, PGeo Hydrologist, Chapman Geoscience Ltd., and Former Head, BC River Forecast Centre Victoria
A Report on a Statistical Model to Forecast Seasonal Inflows to Cowichan Lake Prepared by: Allan Chapman, MSc, PGeo Hydrologist, Chapman Geoscience Ltd., and Former Head, BC River Forecast Centre Victoria
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development NATIONAL CONFERENCE ON APPLICATIONS OF
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development NATIONAL CONFERENCE ON APPLICATIONS OF
STUDY OF FIXED-DURATION DESIGN RAINFALLS IN AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL RUNOFF AND JOINT PROBABILITY BASED DESIGN RAINFALLS
 STUDY OF FIXED-DURATION DESIGN RAINFALLS IN AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL RUNOFF AND JOINT PROBABILITY BASED DESIGN RAINFALLS ABDUR RAUF and ATAUR RAHMAN School of Engineering and Industrial Design, University of
STUDY OF FIXED-DURATION DESIGN RAINFALLS IN AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL RUNOFF AND JOINT PROBABILITY BASED DESIGN RAINFALLS ABDUR RAUF and ATAUR RAHMAN School of Engineering and Industrial Design, University of
Frequency analysis of rainfall deviation in Dharmapuri district in Tamil Nadu
 Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol.46 (8), August 217, pp. 171-1714 Frequency analysis of rainfall deviation in Dharmapuri district in Tamil Nadu V. Rajendran 1* & R. Venkatasubramani 2 1 Department
Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol.46 (8), August 217, pp. 171-1714 Frequency analysis of rainfall deviation in Dharmapuri district in Tamil Nadu V. Rajendran 1* & R. Venkatasubramani 2 1 Department
PLANNED UPGRADE OF NIWA S HIGH INTENSITY RAINFALL DESIGN SYSTEM (HIRDS)
 PLANNED UPGRADE OF NIWA S HIGH INTENSITY RAINFALL DESIGN SYSTEM (HIRDS) G.A. Horrell, C.P. Pearson National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA), Christchurch, New Zealand ABSTRACT Statistics
PLANNED UPGRADE OF NIWA S HIGH INTENSITY RAINFALL DESIGN SYSTEM (HIRDS) G.A. Horrell, C.P. Pearson National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA), Christchurch, New Zealand ABSTRACT Statistics
Geostatistical Analysis of Rainfall Temperature and Evaporation Data of Owerri for Ten Years
 Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2012, 2, 196-205 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2012.22020 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) Geostatistical Analysis of Rainfall Temperature
Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2012, 2, 196-205 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2012.22020 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) Geostatistical Analysis of Rainfall Temperature
Essential Maths Skills. for AS/A-level. Geography. Helen Harris. Series Editor Heather Davis Educational Consultant with Cornwall Learning
 Essential Maths Skills for AS/A-level Geography Helen Harris Series Editor Heather Davis Educational Consultant with Cornwall Learning Contents Introduction... 5 1 Understanding data Nominal, ordinal and
Essential Maths Skills for AS/A-level Geography Helen Harris Series Editor Heather Davis Educational Consultant with Cornwall Learning Contents Introduction... 5 1 Understanding data Nominal, ordinal and
A Near Real-time Flood Prediction using Hourly NEXRAD Rainfall for the State of Texas Bakkiyalakshmi Palanisamy
 A Near Real-time Flood Prediction using Hourly NEXRAD for the State of Texas Bakkiyalakshmi Palanisamy Introduction Radar derived precipitation data is becoming the driving force for hydrological modeling.
A Near Real-time Flood Prediction using Hourly NEXRAD for the State of Texas Bakkiyalakshmi Palanisamy Introduction Radar derived precipitation data is becoming the driving force for hydrological modeling.
Analysis of Rainfall and Other Weather Parameters under Climatic Variability of Parbhani ( )
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.295
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.295
Hourly Rainfall Distribution Pattern in the Northern Coast of Bolaang Mongondow
 Hourly Rainfall Distribution Pattern in the Northern Coast of Bolaang Mongondow Jeffry S. F. Sumarauw #1, Sisca V. Pandey *2, Roski R. I. Legrans #3 #1 Principal Investigator, Civil Engineering Dept.,
Hourly Rainfall Distribution Pattern in the Northern Coast of Bolaang Mongondow Jeffry S. F. Sumarauw #1, Sisca V. Pandey *2, Roski R. I. Legrans #3 #1 Principal Investigator, Civil Engineering Dept.,
Rainfall Analysis for the Northern Wadis of United Arab Emirates: A Case Study
 Rainfall Analysis for the Northern s of United Arab Emirates: A Case Study Mohsen Sherif 1 ; Salem Akram 2 ; and Amapr Shetty 3 Downloaded from ascelibrary.org by United Arab Emirates University on 10/22/17.
Rainfall Analysis for the Northern s of United Arab Emirates: A Case Study Mohsen Sherif 1 ; Salem Akram 2 ; and Amapr Shetty 3 Downloaded from ascelibrary.org by United Arab Emirates University on 10/22/17.
Rainfall Observations in the Loxahatchee River Watershed
 Rainfall Observations in the Loxahatchee River Watershed Richard C. Dent Loxahatchee River District September 1997 Introduction Rain is a common occurrence in south Florida, yet its presence or absence
Rainfall Observations in the Loxahatchee River Watershed Richard C. Dent Loxahatchee River District September 1997 Introduction Rain is a common occurrence in south Florida, yet its presence or absence
ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL DATA FROM EASTERN IRAN ABSTRACT
 ISSN 1023-1072 Pak. J. Agri., Agril. Engg., Vet. Sci., 2013, 29 (2): 164-174 ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL DATA FROM EASTERN IRAN 1 M. A. Zainudini 1, M. S. Mirjat 2, N. Leghari 2 and A. S. Chandio 2 1 Faculty
ISSN 1023-1072 Pak. J. Agri., Agril. Engg., Vet. Sci., 2013, 29 (2): 164-174 ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL DATA FROM EASTERN IRAN 1 M. A. Zainudini 1, M. S. Mirjat 2, N. Leghari 2 and A. S. Chandio 2 1 Faculty
MODELLING FROST RISK IN APPLE TREE, IRAN. Mohammad Rahimi
 WMO Regional Seminar on strategic Capacity Development of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in RA II (Opportunity and Challenges in 21th century) Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 3-4 December 2008
WMO Regional Seminar on strategic Capacity Development of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in RA II (Opportunity and Challenges in 21th century) Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 3-4 December 2008
Technical Memorandum. City of Salem, Stormwater Management Design Standards. Project No:
 Technical Memorandum 6500 SW Macadam Avenue, Suite 200 Portland, Oregon, 97239 Tel: 503-244-7005 Fax: 503-244-9095 Prepared for: Project Title: City of Salem, Oregon City of Salem, Stormwater Management
Technical Memorandum 6500 SW Macadam Avenue, Suite 200 Portland, Oregon, 97239 Tel: 503-244-7005 Fax: 503-244-9095 Prepared for: Project Title: City of Salem, Oregon City of Salem, Stormwater Management
Best Fit Probability Distributions for Monthly Radiosonde Weather Data
 Best Fit Probability Distributions for Monthly Radiosonde Weather Data Athulya P. S 1 and K. C James 2 1 M.Tech III Semester, 2 Professor Department of statistics Cochin University of Science and Technology
Best Fit Probability Distributions for Monthly Radiosonde Weather Data Athulya P. S 1 and K. C James 2 1 M.Tech III Semester, 2 Professor Department of statistics Cochin University of Science and Technology
The Development of Intensity-Duration Frequency Curve for Ulu Moyog and Kaiduan Station of Sabah
 Transactions on Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 2, 149-156, 2017 The Development of Intensity-Duration Frequency Curve for Ulu Moyog and Kaiduan Station of Sabah Nicklos Jefrin 1 *, Nurmin Bolong 1,
Transactions on Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 2, 149-156, 2017 The Development of Intensity-Duration Frequency Curve for Ulu Moyog and Kaiduan Station of Sabah Nicklos Jefrin 1 *, Nurmin Bolong 1,
Development of Pakistan s New Area Weighted Rainfall Using Thiessen Polygon Method
 Pakistan Journal of Meteorology Vol. 9, Issue 17: July 2012 Technical Note Development of Pakistan s New Area Weighted Rainfall Using Thiessen Polygon Method Faisal, N. 1, 2, A. Gaffar 2 ABSTRACT In this
Pakistan Journal of Meteorology Vol. 9, Issue 17: July 2012 Technical Note Development of Pakistan s New Area Weighted Rainfall Using Thiessen Polygon Method Faisal, N. 1, 2, A. Gaffar 2 ABSTRACT In this
RAINFALL INTENSITY-DURATION-FREQUENCY RELATIONSHIP FOR SOME REGIONS IN SAUDI ARABIA
 Academic Journal of Science CD-ROM. ISSN: 165-68 :: 1(1):41 55 (01) RAINFALL INTENSITY-DURATION-FREQUENCY RELATIONSHIP FOR SOME REGIONS IN SAUDI ARABIA Ibrahim H. Elsebaie King Saud University, Kingdom
Academic Journal of Science CD-ROM. ISSN: 165-68 :: 1(1):41 55 (01) RAINFALL INTENSITY-DURATION-FREQUENCY RELATIONSHIP FOR SOME REGIONS IN SAUDI ARABIA Ibrahim H. Elsebaie King Saud University, Kingdom
Rainfall Analysis in Mumbai using Gumbel s Extreme Value Distribution Model
 Rainfall Analysis in Mumbai using Gumbel s Extreme Value Distribution Model S. Sangita Mishra 1, M. Solapure 2, R. Satpathy 3, K. Phadtare 4, S. Pawar 5 1 Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 Undergraduate students
Rainfall Analysis in Mumbai using Gumbel s Extreme Value Distribution Model S. Sangita Mishra 1, M. Solapure 2, R. Satpathy 3, K. Phadtare 4, S. Pawar 5 1 Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 Undergraduate students
Drought Monitoring in Mainland Portugal
 Drought Monitoring in Mainland Portugal 1. Accumulated precipitation since 1st October 2014 (Hydrological Year) The accumulated precipitation amount since 1 October 2014 until the end of April 2015 (Figure
Drought Monitoring in Mainland Portugal 1. Accumulated precipitation since 1st October 2014 (Hydrological Year) The accumulated precipitation amount since 1 October 2014 until the end of April 2015 (Figure
Estimating Design Rainfalls Using Dynamical Downscaling Data
 Estimating Design Rainfalls Using Dynamical Downscaling Data Ke-Sheng Cheng Department of Bioenvironmental Systems Engineering Mater Program in Statistics National Taiwan University Introduction Outline
Estimating Design Rainfalls Using Dynamical Downscaling Data Ke-Sheng Cheng Department of Bioenvironmental Systems Engineering Mater Program in Statistics National Taiwan University Introduction Outline
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 3.1 Synoptic Patterns Precipitation and Topography Precipitation Regionalization... 11
 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... iii 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 DATA SOURCES AND METHODS... 2 2.1 Data Sources... 2 2.2 Frequency Analysis... 2 2.2.1 Precipitation... 2 2.2.2 Streamflow... 2 2.3 Calculation of
TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... iii 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 DATA SOURCES AND METHODS... 2 2.1 Data Sources... 2 2.2 Frequency Analysis... 2 2.2.1 Precipitation... 2 2.2.2 Streamflow... 2 2.3 Calculation of
PRELIMINARY DRAFT FOR DISCUSSION PURPOSES
 Memorandum To: David Thompson From: John Haapala CC: Dan McDonald Bob Montgomery Date: February 24, 2003 File #: 1003551 Re: Lake Wenatchee Historic Water Levels, Operation Model, and Flood Operation This
Memorandum To: David Thompson From: John Haapala CC: Dan McDonald Bob Montgomery Date: February 24, 2003 File #: 1003551 Re: Lake Wenatchee Historic Water Levels, Operation Model, and Flood Operation This
Terrestrial Flood Risk and Climate Change in the Yallahs River, Jamaica. An assessment of future flood risk. projections of future climate
 Terrestrial Flood Risk and Climate Change in the Yallahs River, Jamaica An assessment of future flood risk using hydrodynamic models driven by projections of future climate Matthew Wilson1, Arpita Mandal2,
Terrestrial Flood Risk and Climate Change in the Yallahs River, Jamaica An assessment of future flood risk using hydrodynamic models driven by projections of future climate Matthew Wilson1, Arpita Mandal2,
Investigation IV: Seasonal Precipitation and Seasonal Surface Runoff in the US
 Investigation IV: Seasonal Precipitation and Seasonal Surface Runoff in the US Purpose Students will consider the seasonality of precipitation and surface runoff and think about how the time of year can
Investigation IV: Seasonal Precipitation and Seasonal Surface Runoff in the US Purpose Students will consider the seasonality of precipitation and surface runoff and think about how the time of year can
RAINFALL DISTRIBUTION AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS IN MAKKAH AL-MUKARRAMAH REGION, SAUDI ARABIA
 - 4129 - RAINFALL DISTRIBUTION AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS IN MAKKAH AL-MUKARRAMAH REGION, SAUDI ARABIA BAHRAWI, J. A. Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Management, Faculty of Meteorology, Environment
- 4129 - RAINFALL DISTRIBUTION AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS IN MAKKAH AL-MUKARRAMAH REGION, SAUDI ARABIA BAHRAWI, J. A. Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Management, Faculty of Meteorology, Environment
Presented at WaPUG Spring Meeting 1 st May 2001
 Presented at WaPUG Spring Meeting 1 st May 21 Author: Richard Allitt Richard Allitt Associates Ltd 111 Beech Hill Haywards Heath West Sussex RH16 3TS Tel & Fax (1444) 451552 1. INTRODUCTION The Flood Estimation
Presented at WaPUG Spring Meeting 1 st May 21 Author: Richard Allitt Richard Allitt Associates Ltd 111 Beech Hill Haywards Heath West Sussex RH16 3TS Tel & Fax (1444) 451552 1. INTRODUCTION The Flood Estimation
Wind Resource Modelling using the Markov Transition Probability Matrix Method
 Twelfth LACCEI Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCEI 214) Excellence in Engineering To Enhance a Country s Productivity July 22-24, 214 Guayaquil, Ecuador. Wind
Twelfth LACCEI Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCEI 214) Excellence in Engineering To Enhance a Country s Productivity July 22-24, 214 Guayaquil, Ecuador. Wind
Estimation of the probable maximum precipitation in Barcelona (Spain)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 31: 1322 1327 (2011) Published online 14 April 2010 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/joc.2149 Estimation of the probable
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 31: 1322 1327 (2011) Published online 14 April 2010 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/joc.2149 Estimation of the probable
MET 3102-U01 PHYSICAL CLIMATOLOGY (ID 17901) Lecture 14
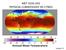 MET 3102-U01 PHYSICAL CLIMATOLOGY (ID 17901) Lecture 14 The hydrologic cycle evaporation vapor transport precipitation precipitation evaporation runoff Evaporation, precipitation, etc. in cm Vapor transported
MET 3102-U01 PHYSICAL CLIMATOLOGY (ID 17901) Lecture 14 The hydrologic cycle evaporation vapor transport precipitation precipitation evaporation runoff Evaporation, precipitation, etc. in cm Vapor transported
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Drought Characterization. Examination of Extreme Precipitation Events
 Drought Characterization Examination of Extreme Precipitation Events Extreme Precipitation Events During the Drought For the drought years (1999-2005) daily precipitation data was analyzed to find extreme
Drought Characterization Examination of Extreme Precipitation Events Extreme Precipitation Events During the Drought For the drought years (1999-2005) daily precipitation data was analyzed to find extreme
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Mean annual precipitation (MAP) is perhaps the most widely used variable in hydrological design, water resources planning and agrohydrology. In the past two decades one of the basic
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Mean annual precipitation (MAP) is perhaps the most widely used variable in hydrological design, water resources planning and agrohydrology. In the past two decades one of the basic
Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh
 24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
SWIM and Horizon 2020 Support Mechanism
 SWIM and Horizon 2020 Support Mechanism Working for a Sustainable Mediterranean, Caring for our Future REG-7: Training Session #1: Drought Hazard Monitoring Example from real data from the Republic of
SWIM and Horizon 2020 Support Mechanism Working for a Sustainable Mediterranean, Caring for our Future REG-7: Training Session #1: Drought Hazard Monitoring Example from real data from the Republic of
CHARACTERISTICS OF MONTHLY AND ANNUAL RAINFALL OF THE UPPER BLUE NILE BASIN
 CHARACTERISTICS OF MONTHLY AND ANNUAL RAINFALL OF THE UPPER BLUE NILE BASIN Wossenu Abtew 1, Assefa M. Melesse 2 and Tibebe Dessalegne 1 Principal Engineer, South Florida Water Management District, West
CHARACTERISTICS OF MONTHLY AND ANNUAL RAINFALL OF THE UPPER BLUE NILE BASIN Wossenu Abtew 1, Assefa M. Melesse 2 and Tibebe Dessalegne 1 Principal Engineer, South Florida Water Management District, West
Champaign-Urbana 1999 Annual Weather Summary
 Champaign-Urbana 1999 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer A major snowstorm kicked off the new
Champaign-Urbana 1999 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer A major snowstorm kicked off the new
Hydrologic Overview & Quantities
 Hydrologic Overview & Quantities It is important to understand the big picture when attempting to forecast. This includes the interactive components and hydrologic quantities. Hydrologic Cycle The complexity
Hydrologic Overview & Quantities It is important to understand the big picture when attempting to forecast. This includes the interactive components and hydrologic quantities. Hydrologic Cycle The complexity
DROUGHT MONITORING BULLETIN
 DROUGHT MONITORING BULLETIN 24 th November 2014 Hot Spot Standardized Precipitation Index for time period from November 2013 to April 2014 was, due to the lack of precipitation for months, in major part
DROUGHT MONITORING BULLETIN 24 th November 2014 Hot Spot Standardized Precipitation Index for time period from November 2013 to April 2014 was, due to the lack of precipitation for months, in major part
Table (6): Annual precipitation amounts as recorded by stations X and Y. No. X Y
 Example: X and Y are two neighboring rainfall stations. Station X has complete records and station Y has some missing values. Find the linear correlation equation between the two series as mentioned in
Example: X and Y are two neighboring rainfall stations. Station X has complete records and station Y has some missing values. Find the linear correlation equation between the two series as mentioned in
Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Precipitation Data in a mountainous Region (Upper Indus Basin-UIB)
 Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Precipitation Data in a mountainous Region (Upper Indus Basin-UIB) AsimJahangir Khan, Doctoral Candidate, Department of Geohydraulicsand Engineering Hydrology, University
Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Precipitation Data in a mountainous Region (Upper Indus Basin-UIB) AsimJahangir Khan, Doctoral Candidate, Department of Geohydraulicsand Engineering Hydrology, University
Precipitation Extremes in the Hawaiian Islands and Taiwan under a changing climate
 Precipitation Extremes in the Hawaiian Islands and Taiwan under a changing climate Pao-Shin Chu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Hawaii-Manoa Y. Ruan, X. Zhao, D.J. Chen, and P.L. Lin December
Precipitation Extremes in the Hawaiian Islands and Taiwan under a changing climate Pao-Shin Chu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Hawaii-Manoa Y. Ruan, X. Zhao, D.J. Chen, and P.L. Lin December
Current Climate Trends and Implications
 Current Climate Trends and Implications Dr. Mark Seeley Professor emeritus Department of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota St Paul, MN 55108 Crop Insurance Conference September 12, 2018
Current Climate Trends and Implications Dr. Mark Seeley Professor emeritus Department of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota St Paul, MN 55108 Crop Insurance Conference September 12, 2018
Three main areas of work:
 Task 2: Climate Information 1 Task 2: Climate Information Three main areas of work: Collect historical and projected weather and climate data Conduct storm surge and wave modeling, sea-level rise (SLR)
Task 2: Climate Information 1 Task 2: Climate Information Three main areas of work: Collect historical and projected weather and climate data Conduct storm surge and wave modeling, sea-level rise (SLR)
Extreme Rain all Frequency Analysis for Louisiana
 78 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1420 Extreme Rain all Frequency Analysis for Louisiana BABAK NAGHAVI AND FANG XIN Yu A comparative study of five popular frequency distributions and three parameter estimation
78 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1420 Extreme Rain all Frequency Analysis for Louisiana BABAK NAGHAVI AND FANG XIN Yu A comparative study of five popular frequency distributions and three parameter estimation
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Analysis of real-time prairie drought monitoring and forecasting system. Lei Wen and Charles A. Lin
 Analysis of real-time prairie drought monitoring and forecasting system Lei Wen and Charles A. Lin Back ground information A real-time drought monitoring and seasonal prediction system has been developed
Analysis of real-time prairie drought monitoring and forecasting system Lei Wen and Charles A. Lin Back ground information A real-time drought monitoring and seasonal prediction system has been developed
Rainfall variation and frequency analysis study of Salem district Tamil Nadu
 Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol. 46 (1), January 217, pp. 213-218 Rainfall variation and frequency analysis study of Salem district Tamil Nadu Arulmozhi.S 1* & Dr. Prince Arulraj.G 2 1 Department
Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol. 46 (1), January 217, pp. 213-218 Rainfall variation and frequency analysis study of Salem district Tamil Nadu Arulmozhi.S 1* & Dr. Prince Arulraj.G 2 1 Department
Unit 2 Text Worksheet # 2
 Unit 2 Text Worksheet # 2 Read Pages 74-77 1. Using fig. 5.1 on page 75 identify: Climatic Region the most widespread climatic region in the low latitudes two climatic subregions with dry conditions for
Unit 2 Text Worksheet # 2 Read Pages 74-77 1. Using fig. 5.1 on page 75 identify: Climatic Region the most widespread climatic region in the low latitudes two climatic subregions with dry conditions for
SPATIO-TEMPORAL CHARACTERISTICS OF RAINFALL AND TEMPERATURE IN BANGLADESH
 SPATIO-TEMPORAL CHARACTERISTICS OF RAINFALL AND TEMPERATURE IN BANGLADESH K. Roy *, M. Kumruzzaman & A. Hossain Department of Civil Engineering, Rajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, Rajshahi,
SPATIO-TEMPORAL CHARACTERISTICS OF RAINFALL AND TEMPERATURE IN BANGLADESH K. Roy *, M. Kumruzzaman & A. Hossain Department of Civil Engineering, Rajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, Rajshahi,
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD,
 J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
Lecture 6: Precipitation Averages and Interception
 Lecture 6: Precipitation Averages and Interception Key Questions 1. How much and when does Whatcom County receive rain? 2. Where online can you find rainfall data for the state? 3. How is rainfall averaged
Lecture 6: Precipitation Averages and Interception Key Questions 1. How much and when does Whatcom County receive rain? 2. Where online can you find rainfall data for the state? 3. How is rainfall averaged
A summary of the weather year based on data from the Zumwalt weather station
 ZUMWALT PRAIRIE WEATHER 2016 A summary of the weather year based on data from the Zumwalt weather station Figure 1. An unusual summer storm on July 10, 2016 brought the second-largest precipitation day
ZUMWALT PRAIRIE WEATHER 2016 A summary of the weather year based on data from the Zumwalt weather station Figure 1. An unusual summer storm on July 10, 2016 brought the second-largest precipitation day
New average divisional daily temperature normals, shown in Table 2, range. Lawrence A. Schaal
 The New Decade and Changing Normals of Temperature and Precipitation in Indiana Lawrence A. Schaal Department of Agronomy Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907 Introduction "Normals" of temperature
The New Decade and Changing Normals of Temperature and Precipitation in Indiana Lawrence A. Schaal Department of Agronomy Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907 Introduction "Normals" of temperature
The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis
 The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis Beth Ebert and Gary Weymouth Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia e.ebert@bom.gov.au Daily rainfall data and analysis procedure
The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis Beth Ebert and Gary Weymouth Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia e.ebert@bom.gov.au Daily rainfall data and analysis procedure
The Climate of Kiowa County
 The Climate of Kiowa County Kiowa County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 24 inches in northwestern
The Climate of Kiowa County Kiowa County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 24 inches in northwestern
ANALYSIS OF DEPTH-AREA-DURATION CURVES OF RAINFALL IN SEMIARID AND ARID REGIONS USING GEOSTATISTICAL METHODS: SIRJAN KAFEH NAMAK WATERSHED, IRAN
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 14 2006 ANALYSIS OF DEPTH-AREA-DURATION
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 14 2006 ANALYSIS OF DEPTH-AREA-DURATION
Chapter- Three GEOMORPHOLOGY AND RAINFALL PATTERN
 Chapter- Three GEOMORPHOLOGY AND RAINFALL PATTERN 3.1 INTRODUCTION Geomorphology and its slope as a basic and applied science in general and as tool for searching groundwater resources in efficient geomorphological
Chapter- Three GEOMORPHOLOGY AND RAINFALL PATTERN 3.1 INTRODUCTION Geomorphology and its slope as a basic and applied science in general and as tool for searching groundwater resources in efficient geomorphological
The Climate of Payne County
 The Climate of Payne County Payne County is part of the Central Great Plains in the west, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Payne County is also part of the Crosstimbers in the
The Climate of Payne County Payne County is part of the Central Great Plains in the west, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Payne County is also part of the Crosstimbers in the
Storm rainfall. Lecture content. 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given
 Storm rainfall Lecture content 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given max rainfall depth 1 rainfall duration and return period à Depth-Duration-Frequency curves 2
Storm rainfall Lecture content 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given max rainfall depth 1 rainfall duration and return period à Depth-Duration-Frequency curves 2
November 2018 Weather Summary West Central Research and Outreach Center Morris, MN
 November 2018 Weather Summary Lower than normal temperatures occurred for the second month. The mean temperature for November was 22.7 F, which is 7.2 F below the average of 29.9 F (1886-2017). This November
November 2018 Weather Summary Lower than normal temperatures occurred for the second month. The mean temperature for November was 22.7 F, which is 7.2 F below the average of 29.9 F (1886-2017). This November
Changes to Extreme Precipitation Events: What the Historical Record Shows and What It Means for Engineers
 Changes to Extreme Precipitation Events: What the Historical Record Shows and What It Means for Engineers Geoffrey M Bonnin National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Weather Service Office
Changes to Extreme Precipitation Events: What the Historical Record Shows and What It Means for Engineers Geoffrey M Bonnin National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Weather Service Office
4. THE HBV MODEL APPLICATION TO THE KASARI CATCHMENT
 Application of HBV model to the Kasari River, 1994 Page 1 of 6 Application of the HBV model to the Kasari river for flow modulation of catchments characterised by specific underlying features by R. Vedom,
Application of HBV model to the Kasari River, 1994 Page 1 of 6 Application of the HBV model to the Kasari river for flow modulation of catchments characterised by specific underlying features by R. Vedom,
THE DEVELOPMENT OF RAIN-BASED URBAN FLOOD FORECASTING METHOD FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT PRACTICE USING X-MP RADAR OBSERVATION
 Research Paper Advances in River Engineering, JSCE, Vol.19, 2013,June THE DEVELOPMENT OF RAIN-BASED URBAN FLOOD FORECASTING METHOD FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT PRACTICE USING X-MP RADAR OBSERVATION Seongsim YOON
Research Paper Advances in River Engineering, JSCE, Vol.19, 2013,June THE DEVELOPMENT OF RAIN-BASED URBAN FLOOD FORECASTING METHOD FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT PRACTICE USING X-MP RADAR OBSERVATION Seongsim YOON
Depth-Duration Frequency (DDF) and Depth-Area- Reduction Factors (DARF)
 Spatial Analysis of Storms Using GIS Brian Hoblit, Steve Zelinka, Cris Castello, and David Curtis Abstract Point data from rain gages have been historically used to develop depth-area relationships, design
Spatial Analysis of Storms Using GIS Brian Hoblit, Steve Zelinka, Cris Castello, and David Curtis Abstract Point data from rain gages have been historically used to develop depth-area relationships, design
138 ANALYSIS OF FREEZING RAIN PATTERNS IN THE SOUTH CENTRAL UNITED STATES: Jessica Blunden* STG, Inc., Asheville, North Carolina
 138 ANALYSIS OF FREEZING RAIN PATTERNS IN THE SOUTH CENTRAL UNITED STATES: 1979 2009 Jessica Blunden* STG, Inc., Asheville, North Carolina Derek S. Arndt NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville,
138 ANALYSIS OF FREEZING RAIN PATTERNS IN THE SOUTH CENTRAL UNITED STATES: 1979 2009 Jessica Blunden* STG, Inc., Asheville, North Carolina Derek S. Arndt NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville,
Climate Change Impact on Intensity-Duration- Frequency Curves in Ho Chi Minh city
 Climate Change Impact on Intensity-Duration- Frequency Curves in Ho Chi Minh city Khiem Van Mai, Minh Truong Ha, Linh Nhat Luu Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate Change, Hanoi, Vietnam Hanoi,
Climate Change Impact on Intensity-Duration- Frequency Curves in Ho Chi Minh city Khiem Van Mai, Minh Truong Ha, Linh Nhat Luu Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate Change, Hanoi, Vietnam Hanoi,
