Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999
|
|
|
- Sybil Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999 Brandy Lumpkins Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison 8 May 2006
2 ABSTRACT A massive tornadic outbreak swept across Oklahoma and Texas on 3 May Nearly 70 individual tornadoes spun from 10 different supercells resulting in F4-F5 damage in some cities. This outbreak was partially due to dryline activity and partially due to the synoptic setup for the time period. The dry, well-mixed, unstably stratified air flowing east over the Rockies collided with moist, shallow, upslope air moving westward. The inversion over the moist air formed a cap that prevented convection until it was broken by the tropospheric jet and convergence along the dryline. 1. Introduction During the late afternoon and evening hours of 3 May 1999, a violent tornado outbreak swept across portions of Oklahoma and Kansas. A total of over 70 tornadoes were documented from the ten tornadic supercells (Fig 1) which developed over the southern plains that afternoon and evening. Fig 1 Storm tracks through the Texas region 3 May Long-lived, violent (F4-F5 damage) tornadoes occurred in the Oklahoma City, Oklahoma and Wichita, Kansas metropolitan areas, as well as in the small towns of Mulhall and Dover to the north and northwest of Oklahoma City. This study proposes that the magnitude of this outbreak is partially due to the dryline and partially due to the fierce synoptic setup. Data sources are addressed in section 2. The evolution of the synoptic-scale environment is presented in section 3, with specific emphasis on the distributions of moisture, instability, and vertical wind shear. Mesoscale features are discussed in section 4. Section 5 summarizes the important aspects of this major regional tornado outbreak and directs attention to the critical points of this study. 2. Data Data for this summary comes from a variety of sources. The National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) proved to be quite helpful. Figure 1 and statistical data from the tornado outbreak were obtained from the NOAA website. A number of figures were generated in garp and gempak. All of these utilize the eta model. This particular model was chosen because of its accepted accuracy. A majority of the information, including the cross sections and streamlines, comes from 0Z on 4 May This time falls in the midst of the outbreak. 3. Synoptic Overview A large-scale trough was located over the western United States at 12 UTC 3 May (Fig 2), with a smaller short wave trough over Arizona. The largescale trough amplified over the Rockies by 00 UTC 4 May, while the embedded short wave trough progressed from Arizona to western Oklahoma and Kansas.
3 streamlines of the 1000mb winds at the same time. Fig 2 Height and Winds In association with this deepening trough and southwesterly flow over the Rockies, a deepening surface low was located over the central high plains, with low-level southerly to southeasterly flow in the warm sector over Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. As destabilization continued over the southern plains, an upper-tropospheric jet streak moved east-northeast over Arizona and New Mexico, as shown in Fig 3. Fig 4 Streamlines 3 May Mesoscale Analysis Fig 5 is a two-panel cross section taken across the dryline from Albuquerque, NM to Little Rock, AK at 0Z on 4 May Figure 5a plots thetae and figure 5b is a plot of both theta and the mixing ratio (blue). The tight gradient of mixing ratio illustrates the dryline between Amarillo, TX and Norman, OK. By the mixing ratio values, it can be seen that the moist air is trapped under the area between 800mb and 700mb and that the values are relatively constant above that line. Fig 3 300mb Wind speeds from 3 May 1999 This region of diverging air helps to break the inversion and jumpstart intense convection. Even though flow along the dryline is generally from the south, the observed winds show a definite convergence. This flow can be seen in Fig 4, which illustrates the Fig 5a Vertical cross-section of theta contours
4 Fig 7a Dryline over Texas at 03Z Fig 5b Vertical cross-section of theta-e (black) and mixing ratio (blue) In figure 5a, this same barrier can be seen as a temperature inversion. To the west, a nearly adiabatic layer is observed immediately off the surface. In contrast, to the east, this well mixed layer is pushed up above the inversion into the mid-troposphere. Fig 7b Dryline over Texas at 09Z Fig 6 Conceptual model of a dryline It is known that one of the major causes of drylines is the collision of moist upslope flow with drier downslope flow over the mountains. A conceptual model can be seen in Fig 6. It is also quite typical of drylines to have a layer of decreased stability above the lowlevel inversion. Both of these factors are consistent with this cross section. Fig 7c Dryline over Texas at 15Z
5 Fig 8 shows the GOES-8 satellite imagery. It highlights convective activity through central Texas up through western Oklahoma. This thin line of convective clouds sits directly over or perhaps slightly east of, the dryline at this time. Fig 7d Dryline over Texas at 21Z Fig 7a-7d illustrate the motion of the dryline from 03Z through 21Z on 3 May. Location of the dryline was determined by a change in the mixing ratio over a small area. It is seen that as the night progresses, (Fig 6a-6c) the dryline progresses to the west. During the day there is a visible jump of the dryline to the east. However, the entire dryline does not move at the same speed and at times not even in the same direction. This diurnal trend, with its variance, is consistent with dryline motion. 5. Conclusion The 3 May 1999 tornadic outbreak was partially due to dryline activity and partially due to the synoptic setup for the time period. The dry, wellmixed, unstably stratified air flowing east over the Rockies collided with moist, shallow, upslope air moving westward. The inversion over the moist air formed a cap that prevented convection until it was broken by the tropospheric jet and convergence along the dryline. A combination of these factors made conditions right for one of the largest tornado outbreaks in Oklahoma s history. References GARP and Gempak Fig 8 Satellite over Texas and Oklahoma 3 May
The Jarrell Tornado of May 27, 1997
 The Jarrell Tornado of May 27, 1997 ANDREW MANKOWSKI University of Wisconsin Madison Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences ABSTRACT A tornado outbreak occurred over Central Texas on May 27, 1997. This outbreak
The Jarrell Tornado of May 27, 1997 ANDREW MANKOWSKI University of Wisconsin Madison Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences ABSTRACT A tornado outbreak occurred over Central Texas on May 27, 1997. This outbreak
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place"
 Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
Multi-day severe event of May 2013
 Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox
 Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin
 April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO
 WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO Charles D. Koch University of Wisconsin Madison AOS 453: Mesoscale Meteorology Professor Greg Tripoli 13 May
WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO Charles D. Koch University of Wisconsin Madison AOS 453: Mesoscale Meteorology Professor Greg Tripoli 13 May
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL. Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS
 P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments
 P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments Adam J. French and Matthew D. Parker North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION A principle
P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments Adam J. French and Matthew D. Parker North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION A principle
Talking points for Water Vapor Imagery Analysis for Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting.
 Talking points for Water Vapor Imagery Analysis for Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting. 1. Title. 2. Learning objectives. These are the topics we ll consider during this training session, the goal of the
Talking points for Water Vapor Imagery Analysis for Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting. 1. Title. 2. Learning objectives. These are the topics we ll consider during this training session, the goal of the
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology. Thunderstorms
 1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A thunderstorm is considered to be a weather system. a. synoptic-scale b. micro-scale c. meso-scale 2. By convention, the mature stage
CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A thunderstorm is considered to be a weather system. a. synoptic-scale b. micro-scale c. meso-scale 2. By convention, the mature stage
The Oakfield, Wisconsin, Tornado from July Brett Berenz Student at the University of Wisconsin
 The Oakfield, Wisconsin, Tornado from 18-19 July 1996 Brett Berenz Student at the University of Wisconsin Abstract On July 18 th, 1996 an F5 tornado affected the region of Oakfield, Wisconsin. Leading
The Oakfield, Wisconsin, Tornado from 18-19 July 1996 Brett Berenz Student at the University of Wisconsin Abstract On July 18 th, 1996 an F5 tornado affected the region of Oakfield, Wisconsin. Leading
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology. Lecture 8: September 16, AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2)
 MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event
 Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event The two events featured similar patterns but with much different results in central NC. The slides on
Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event The two events featured similar patterns but with much different results in central NC. The slides on
3A.4 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ELEVATED MIXED LAYER DURING THE SUPER TUESDAY OUTBREAK
 3A.4 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ELEVATED MIXED LAYER DURING THE SUPER TUESDAY OUTBREAK Christina C. Crowe* & John R. Mecikalski University of Alabama - Huntsville, Huntsville, Alabama 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Elevated
3A.4 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ELEVATED MIXED LAYER DURING THE SUPER TUESDAY OUTBREAK Christina C. Crowe* & John R. Mecikalski University of Alabama - Huntsville, Huntsville, Alabama 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Elevated
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
severe VOLUME 5, NUMBER 1, FEBRUARY 1980
 severe VOLUME 5, NUMBER 1, FEBRUARY 1980 TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM DEVELOPMENT IN WEST TEXAS 27 MAY 1978 by Richard E. Peterson Atmospheric Science Group Texas University Lubbock, TX and Alan Johnson National
severe VOLUME 5, NUMBER 1, FEBRUARY 1980 TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM DEVELOPMENT IN WEST TEXAS 27 MAY 1978 by Richard E. Peterson Atmospheric Science Group Texas University Lubbock, TX and Alan Johnson National
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE JUNE 1984 BARNEVELD, WI TORNADO
 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE JUNE 1984 BARNEVELD, WI TORNADO BRANDON SWEDLUND Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 13 May 2007 I. Introduction On the morning
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE JUNE 1984 BARNEVELD, WI TORNADO BRANDON SWEDLUND Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 13 May 2007 I. Introduction On the morning
1st Tornado Photograph
 Lecture 26 Part II Tornados Environment Storm Structure Life Cycle Source of Spin Forecasting Climatology Damage Marilee Thomas of Beaver City, NE took this photograph of her daughter Audra about two miles
Lecture 26 Part II Tornados Environment Storm Structure Life Cycle Source of Spin Forecasting Climatology Damage Marilee Thomas of Beaver City, NE took this photograph of her daughter Audra about two miles
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Dryline Convective Case Study: May 5th 2003 Severe Storm Outbreak
 Dryline Convective Case Study: May 5th 2003 Severe Storm Outbreak Abstract During the spring, thunderstorms develop ahead of a boundary called the dryline. This was the case with the May 4rd, 2003 Outbreak.
Dryline Convective Case Study: May 5th 2003 Severe Storm Outbreak Abstract During the spring, thunderstorms develop ahead of a boundary called the dryline. This was the case with the May 4rd, 2003 Outbreak.
Tropical Waves. John Cangialosi and Lixion Avila National Hurricane Center. WMO Region IV Tropical Cyclone Workshop
 Tropical Waves John Cangialosi and Lixion Avila National Hurricane Center WMO Region IV Tropical Cyclone Workshop Outline Basic definition Schematic diagrams/interactions Operational products/forecasts
Tropical Waves John Cangialosi and Lixion Avila National Hurricane Center WMO Region IV Tropical Cyclone Workshop Outline Basic definition Schematic diagrams/interactions Operational products/forecasts
P9.6 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS OF 3 APRIL 2004: AN EXAMINATION OF A DRY-SEASON SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN THE BORDERLAND
 P9.6 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS OF 3 APRIL 2004: AN EXAMINATION OF A DRY-SEASON SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN THE BORDERLAND 1. INTRODUCTION Michael P. Hardiman Joseph A. Rogash National Weather Service, Santa Teresa,
P9.6 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS OF 3 APRIL 2004: AN EXAMINATION OF A DRY-SEASON SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN THE BORDERLAND 1. INTRODUCTION Michael P. Hardiman Joseph A. Rogash National Weather Service, Santa Teresa,
A Preliminary Climatology of Tornado Events with Closed Cold Core 500 mb Lows in the Central and Eastern United States
 7B.4 A Preliminary Climatology of Tornado Events with Closed Cold Core 500 mb Lows in the Central and Eastern United States Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas Jared L. Guyer Storm
7B.4 A Preliminary Climatology of Tornado Events with Closed Cold Core 500 mb Lows in the Central and Eastern United States Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas Jared L. Guyer Storm
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
Tornado Dynamics. Readings:
 Tornado Dynamics Readings: Klemp (1987) Dynamics of Tornadic Thunderstorms (handout) Bluestein Vol II. Section 3.4.8. Rotunno, R., 1986: Tornadoes and tornadogenesis. In: P. Ray (Editor), Mesoscale Meteorology
Tornado Dynamics Readings: Klemp (1987) Dynamics of Tornadic Thunderstorms (handout) Bluestein Vol II. Section 3.4.8. Rotunno, R., 1986: Tornadoes and tornadogenesis. In: P. Ray (Editor), Mesoscale Meteorology
A Detailed Analysis of a Long-Tracked Supercell. Jason T. Martinelli and Andrew Elliott. Fred Glass
 A Detailed Analysis of a Long-Tracked Supercell Jason T. Martinelli and Andrew Elliott Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska Fred Glass National Weather Service Forecast
A Detailed Analysis of a Long-Tracked Supercell Jason T. Martinelli and Andrew Elliott Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska Fred Glass National Weather Service Forecast
The Greensburg, KS Tornado
 J2.4 The Greensburg, KS Tornado Daniel McCarthy NOAA Storm Prediction Center Norman, OK Larry Ruthi and Jeff Hutton NWS Weather Forecast Office Dodge City, KS 1. Background The tornado that moved through
J2.4 The Greensburg, KS Tornado Daniel McCarthy NOAA Storm Prediction Center Norman, OK Larry Ruthi and Jeff Hutton NWS Weather Forecast Office Dodge City, KS 1. Background The tornado that moved through
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
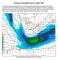 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak
 Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Analysis of Severe Storm Initiation Along Drylines in the Southern Plains
 Analysis of Severe Storm Initiation Along Drylines in the Southern Plains NICOLE L. BARBEE Meteorology Program, Iowa State University, Ames Mentor: Dr. William Gallus 1 1 Department of Geological and Atmospheric
Analysis of Severe Storm Initiation Along Drylines in the Southern Plains NICOLE L. BARBEE Meteorology Program, Iowa State University, Ames Mentor: Dr. William Gallus 1 1 Department of Geological and Atmospheric
Drylines and Convection: a Literature Review
 Drylines and Convection: a Literature Review ANDREW RYE AND JEFF DUDA Department of Geological Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa ABSTRACT Drylines are similar to fronts, but only
Drylines and Convection: a Literature Review ANDREW RYE AND JEFF DUDA Department of Geological Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa ABSTRACT Drylines are similar to fronts, but only
DRYLINE MAGIC by Tim Marshall (published in Weatherwise Magazine in 1992)
 DRYLINE MAGIC by Tim Marshall (published in Weatherwise Magazine in 1992) Every spring, veteran storm chasers head to West Texas to catch a weather show they call "dryline magic". The dryline is a boundary
DRYLINE MAGIC by Tim Marshall (published in Weatherwise Magazine in 1992) Every spring, veteran storm chasers head to West Texas to catch a weather show they call "dryline magic". The dryline is a boundary
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples Figure 1
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Ki-Hong Min 1*, Seonhee Choo 2, and Gyuwon Lee 1, and Kyung-Eak Kim 1,3
 Ki-Hong Min 1*, Seonhee Choo 2, and Gyuwon Lee 1, and Kyung-Eak Kim 1,3 1 School of Earth System Sciences, Major in Atmospheric Science, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea 2 Forecast Technology
Ki-Hong Min 1*, Seonhee Choo 2, and Gyuwon Lee 1, and Kyung-Eak Kim 1,3 1 School of Earth System Sciences, Major in Atmospheric Science, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea 2 Forecast Technology
Paul Yura*, Frank Alsheimer, and Joseph Calderone NOAA, National Weather Service Forecast Office, Charleston South Carolina 1.
 7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
THE DEEPENING OF A LOW-LEVEL TROUGH AS INDICATED BY DUST ALOFT IN GOES ' INFRARED PICTURES
 REFERENCES Baughman, R. G., and C. W. Schmid, Jr.: Lightning Storm Characteristics. U.S. Service, Intermountain Forest and Range ment Station, Research Paper in press. Davis, L. S., and R. W. Cooper, 1963:
REFERENCES Baughman, R. G., and C. W. Schmid, Jr.: Lightning Storm Characteristics. U.S. Service, Intermountain Forest and Range ment Station, Research Paper in press. Davis, L. S., and R. W. Cooper, 1963:
4/18/2010. National Weather Service. Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study
 National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes
 Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes VOLUME II Observations and Theory of Weather Systems HOWARD B. BLUESTEIN New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents 1. THE BEHAVIOR OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE,
Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes VOLUME II Observations and Theory of Weather Systems HOWARD B. BLUESTEIN New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents 1. THE BEHAVIOR OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE,
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801
 Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
MESOSCALE WINDS IN VICINITY OF CONVECTION AND WINTER STORMS. Robert M. Rabin
 MESOSCALE WINDS IN VICINITY OF CONVECTION AND WINTER STORMS Robert M. Rabin NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab (NSSL), Norman, OK Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS), Madison,
MESOSCALE WINDS IN VICINITY OF CONVECTION AND WINTER STORMS Robert M. Rabin NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab (NSSL), Norman, OK Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS), Madison,
The 13 April 2006 Severe Thunderstorm and Large Hail Event in Iowa & Wisconsin:A Case Study
 The 13 April 2006 Severe Thunderstorm and Large Hail Event in Iowa & Wisconsin:A Case Study David M. DeMeuse Undergraduate University of Wisconsin Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Science Mesoscale
The 13 April 2006 Severe Thunderstorm and Large Hail Event in Iowa & Wisconsin:A Case Study David M. DeMeuse Undergraduate University of Wisconsin Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Science Mesoscale
1. INTRODUCTION * Figure 1. National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center (SPC) storm reports for December 1, 2006.
 P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall ERTH FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP
 Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps
 Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes
 Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens ABSTRACT The North American low-level jet is known to have substantial impacts on the climatology of central and eastern regions of the United
Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens ABSTRACT The North American low-level jet is known to have substantial impacts on the climatology of central and eastern regions of the United
Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States
 Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States Kar retta Venable Jackson State University, Jackson, MS Mentors David Imy NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Storm
Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States Kar retta Venable Jackson State University, Jackson, MS Mentors David Imy NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Storm
WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA
 2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On
2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena
 The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
Mesoscale Convective Systems. The COMET Program March 2002
 Mesoscale Convective Systems The COMET Program March 2002 Overview! Introduction to MCSs! Squall Lines! Bow Echoes! Mesoscale Convective Complexes Introduction Definition! Mesoscale convective systems
Mesoscale Convective Systems The COMET Program March 2002 Overview! Introduction to MCSs! Squall Lines! Bow Echoes! Mesoscale Convective Complexes Introduction Definition! Mesoscale convective systems
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module 9: Air/sea interactions winter cyclogenesis
 Satellites, Weather and Climate Module 9: Air/sea interactions winter cyclogenesis Winter storms things to consider Deep moisture Thermal discontinuity Favorable surface and upper level features Geographical
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module 9: Air/sea interactions winter cyclogenesis Winter storms things to consider Deep moisture Thermal discontinuity Favorable surface and upper level features Geographical
Mature Tornado. Tornado funnel and debris cloud. Mature Tornado
 Mature Tornado Tornado funnel and debris cloud 43 Mature Tornado 44 Tornado in Final Rope Stage 45 Source of Spin 46 Source of Spin Updraft Stretches Rotating Column 47 Simulation of Tornado Formation
Mature Tornado Tornado funnel and debris cloud 43 Mature Tornado 44 Tornado in Final Rope Stage 45 Source of Spin 46 Source of Spin Updraft Stretches Rotating Column 47 Simulation of Tornado Formation
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
TOPOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON AMARILLO RADAR ECHO CLIMATOLOGY by Timothy P. Marshall and Richard E. Peterson
 TOPOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON AMARILLO RADAR ECHO CLIMATOLOGY by Timothy P. Marshall and Richard E. Peterson (Reprinted from preprint Volume: Eighth Conference on Weather Forecasting and Analysis, June 10-13,
TOPOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON AMARILLO RADAR ECHO CLIMATOLOGY by Timothy P. Marshall and Richard E. Peterson (Reprinted from preprint Volume: Eighth Conference on Weather Forecasting and Analysis, June 10-13,
The October 2015 Supercell Storm in Israel
 The October 2015 Supercell Storm in Israel Alissa Razy, Elyakom Vadislavsky, Anat Baharad, Noam Halfon, Itsik Carmona, Yoav Levi, Amit Savir Introduction A high-impact weather event associated with severe
The October 2015 Supercell Storm in Israel Alissa Razy, Elyakom Vadislavsky, Anat Baharad, Noam Halfon, Itsik Carmona, Yoav Levi, Amit Savir Introduction A high-impact weather event associated with severe
P1.3 Tornadoes in a Deceptively Small CAPE Environment: The 4/20/04 Outbreak in Illinois and Indiana
 P1.3 Tornadoes in a Deceptively Small CAPE Environment: The 4/20/04 Outbreak in Illinois and Indiana Albert E. Pietrycha* Jonathan M. Davies #, Mark Ratzer*, and Paul Merzlock* *National Weather Service,
P1.3 Tornadoes in a Deceptively Small CAPE Environment: The 4/20/04 Outbreak in Illinois and Indiana Albert E. Pietrycha* Jonathan M. Davies #, Mark Ratzer*, and Paul Merzlock* *National Weather Service,
The development and evolution of deep convection and heavy rainfall
 The development and evolution of deep convection and heavy rainfall Unique in spectra, space and time The spatial and temporal domains of the phenomena being investigated drive the satellite s spectral
The development and evolution of deep convection and heavy rainfall Unique in spectra, space and time The spatial and temporal domains of the phenomena being investigated drive the satellite s spectral
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Eastern United States Winter Storm and Severe Event of 28-29 February 2012 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Eastern United States Winter Storm and Severe Event of 28-29 February 2012 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event
 Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event Joshua M. Boustead National Weather Service Forecast Office Omaha, Nebraska Philip N. Schumacher National Weather Service Forecast
Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event Joshua M. Boustead National Weather Service Forecast Office Omaha, Nebraska Philip N. Schumacher National Weather Service Forecast
Hurricanes. April 14, 2009
 Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Case Study of the Record Hail Event and Severe Thunderstorm Outbreak in East-Central Nebraska on June 2003
 Case Study of the Record Hail Event and Severe Thunderstorm Outbreak in East-Central Nebraska on 22-23 June 2003 DANIEL C. HARTUNG Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison,
Case Study of the Record Hail Event and Severe Thunderstorm Outbreak in East-Central Nebraska on 22-23 June 2003 DANIEL C. HARTUNG Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison,
Some heavy precipitation issues. AOS C115/C228 Fall 2014
 Some heavy precipitation issues AOS C115/C228 Fall 2014 1 Heavy precipitation at a location = intensity x longevity 2 Common sources of heavy precipitation in U.S. Mesoscale convective systems and vortices
Some heavy precipitation issues AOS C115/C228 Fall 2014 1 Heavy precipitation at a location = intensity x longevity 2 Common sources of heavy precipitation in U.S. Mesoscale convective systems and vortices
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries
 11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters
 Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
A Mesoscale Analysis of the March 29, 1998 Comfrey Tornado
 A Mesoscale Analysis of the March 29, 1998 Comfrey Tornado Joseph D. Hoechst Undergraduate Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Email: hoechst@wisc.edu Department of Atmospheric
A Mesoscale Analysis of the March 29, 1998 Comfrey Tornado Joseph D. Hoechst Undergraduate Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Email: hoechst@wisc.edu Department of Atmospheric
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES 3. RESULTS
 16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains
 Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS), Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA Abstract A favorable
Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS), Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA Abstract A favorable
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002
 P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
National Severe Storms Laboratory and University of Oklahoma
 P5.23 OBSERVATIONS OF THE GREAT PLAINS DRYLINE UTILIZING MOBILE MESONET DATA Albert E. Pietrycha 1 and Erik N. Rasmussen 2 1 National Severe Storms Laboratory and Texas Tech University 2 Cooperative Institute
P5.23 OBSERVATIONS OF THE GREAT PLAINS DRYLINE UTILIZING MOBILE MESONET DATA Albert E. Pietrycha 1 and Erik N. Rasmussen 2 1 National Severe Storms Laboratory and Texas Tech University 2 Cooperative Institute
Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD
 P1.57 GOES WMSI PROGRESS AND DEVELOPMENTS Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. INTRODUCTION A multi-parameter index has
P1.57 GOES WMSI PROGRESS AND DEVELOPMENTS Kenneth L. Pryor* and Gary P. Ellrod Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS) Camp Springs, MD 1. INTRODUCTION A multi-parameter index has
Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
STATION If relative humidity is 60% and saturation vapor pressure is 35 mb, what is the actual vapor pressure?
 STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
THE MAP ROOM. BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall
 THE MAP ROOM BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall BY CHARLES E. GRAVES, JAMES T. MOORE, MARC J. SINGER, AND SAM NG AFFILIATIONS: GRAVES, MOORE, AND NG Department
THE MAP ROOM BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall BY CHARLES E. GRAVES, JAMES T. MOORE, MARC J. SINGER, AND SAM NG AFFILIATIONS: GRAVES, MOORE, AND NG Department
Observation Homework Due 11/24. Previous Lecture. Midlatitude Cyclones
 Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
P1.2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE SUMMER 2007 EXCESSIVE RAIN EVENT IN THE SOUTHERN PLAINS
 P1.2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE SUMMER 2007 EXCESSIVE RAIN EVENT IN THE SOUTHERN PLAINS Kevin H. Goebbert, Alexander D. Schenkman, Chad M. Shafer, and Nathan A. Snook University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE SUMMER 2007 EXCESSIVE RAIN EVENT IN THE SOUTHERN PLAINS Kevin H. Goebbert, Alexander D. Schenkman, Chad M. Shafer, and Nathan A. Snook University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 1. INTRODUCTION
Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011
 Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011 Instructions: Write your name (last name and first name) on your bubble sheet. Write your student identification number on the bubble sheet, and carefully and completely
Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011 Instructions: Write your name (last name and first name) on your bubble sheet. Write your student identification number on the bubble sheet, and carefully and completely
The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England
 P 1.5 22nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service,
P 1.5 22nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service,
Chapter 9. Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones
 Chapter 9 Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones Frontal Weather Fronts are boundary surfaces between different air masses. Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Drylines Frontal Weather
Chapter 9 Weather Patterns & Midlatitude Cyclones Frontal Weather Fronts are boundary surfaces between different air masses. Warm front Cold front Stationary front Occluded front Drylines Frontal Weather
The Glass Ceiling: Analysis of 19 July 2006 Western Iowa Null Severe Weather Event
 The Glass Ceiling: Analysis of 19 July 2006 Western Iowa Null Severe Weather Event Daniel R. Chavas, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI AOS 453 Final Case Study 13 May 2007 ABSTRACT On July 19
The Glass Ceiling: Analysis of 19 July 2006 Western Iowa Null Severe Weather Event Daniel R. Chavas, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI AOS 453 Final Case Study 13 May 2007 ABSTRACT On July 19
Meteorology. Chapter 10 Worksheet 2
 Chapter 10 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Downdrafts totally dominate the in the development of a thunderstorm. a) dissipating stage b) mature
Chapter 10 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Downdrafts totally dominate the in the development of a thunderstorm. a) dissipating stage b) mature
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Sensitivity of 24 h Forecast Dryline Position and Structure to Boundary Layer Parameterizations in Convection-allowing WRF Model Simulations
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 Sensitivity of 24 h Forecast Dryline Position and Structure to Boundary Layer Parameterizations
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 Sensitivity of 24 h Forecast Dryline Position and Structure to Boundary Layer Parameterizations
Quasi-Geostrophic Implications
 Chapter 10 Quasi-Geostrophic Implications When you look at a weather chart with all its isolines and plotted data, you need a framework upon which to interpret what you see. Quasi-geostrophic theory provides
Chapter 10 Quasi-Geostrophic Implications When you look at a weather chart with all its isolines and plotted data, you need a framework upon which to interpret what you see. Quasi-geostrophic theory provides
