Is the Globe Warming? Is there Evidence in the Great Lakes Region?
|
|
|
- Darcy McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Is the Globe Warming? Is there Evidence in the Great Lakes Region? Objectives Teacher's Notes Graphing Ideas Students can plot increments of 0.1 degree on the Y axis and years on the X axis. The last point of their actual data should be on the line that divides the right side of the graph from the left projection side. The actual graphs are found on subsequent pages set aside for the teacher s use. Students typically project steep increases from their small data sets. Basis of Data Global temperature anomaly data are based on Jones and Wigley's work using both land and marine data. Researchers have compiled global average surface air temperature data from land stations, a few fixed position weather ships, and many moving ships. Temperature Anomalies are listed relative to a reference period for Global and a reference period for Great Lakes Data. Anomalies are variations from average values. Limitations of Data Students should discuss the limitations of the data set. If measurements were more heavily weighted on land data, that might contribute to greater extremes than if they were collected over water. Also, the data from ships leave many large data gaps over the oceans. There may be no way to tell just by looking at the data what limitations exist. To become good consumers of scientific information, students must consider the limitations of any data set. After completing this activity, students will be able to: Critically interpret graphic data. Evaluate and discuss the difficulties inherent in interpreting and forecasting long- and short-term trends. Analyze data, draw conclusions about whether there is evidence of global warming, and defend their conclusions. Procedure In preparation, cut apart the sections of the Global Temperature and Great Lakes Temperature lists (p. 9 and p.12) so each group will see only one segment of each. Make a copy of the graph scale for each team to graph its data. 1. Have students read Ohio Sea Grant s Global Change Scenarios Introduction: Understanding Climate Models. 2. Divide the class into five groups that will work separately. Each group will receive a copy of one global temperature data set (28 years) and colored pencils. Students should graph their set of data on the scale provided. As they observe how readings fluctuate from year to year, students can theorize whether there is any evidence that the global temperature was rising, falling, or remaining constant during the period they are studying. They should be able to back up their conclusions with data from their sample graphs. 3. The students then project what the graph of global surface air temperature will be 30 years into the future (from the last year of their graph), based on the trends and periodicities they observe in their individual data set. This should be drawn on the right side of the graph in a different color. 4. Repeat the exercise (Steps 2 3) using temperature data from the Great Lakes. Plot the data on the same graph sheets used for the global data, but this time using new colors so that four different colors appear on the graph. Have the class agree to use similar colors. How do Great Lakes temperature variations compare with those of the whole world? Did they always show parallel trends? How does the complete regional graph compare to the global graph? (Procedure continues) Issues G101
2 GLOBAL ANNUAL TEMPERATURE ANOMALY DATA (Cº) Year Temperature Anomaly Year Temperature Anomaly Year Temperature Anomaly To The Teacher: Give one set of data to each group of students. Jones, P.D., T.M.L. Wigley and K.R. Briffa Global and hemispheric temperature anomalies land and marine instrumental records. In, T.A. Boden, D.P. Kaiser, R.J. Sepanski and F.W. Stoss (eds.), Trends '93: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. ORNL/CDIAC-65. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN. pp G102
3 Teacher's Page: Graph of Global Annual Temperature Anomaly Data TEMPERATURE ANOMALY (ºC) GLOBAL ANNUAL TEMPERATURE ANOMALIES YEAR G103
4 Graph for Global and Great Lakes Temperature Activity 0 Actual Projection Temperature Anomalies relative to a reference period for Global and a reference period for Great Lakes data Temperature Anomalies ( C) G104
5 GREAT LAKES ANNUAL MEAN TEMPERATURE ANOMALY DATA (ºC) Year Mean Temperature Anomaly Year Mean Temperature Anomaly Year Mean Temperature Anomaly To The Teacher: Give one set of data to each group of students. Karl, T.R., D.R. Easterling, R.W. Knight and P.Y. Hughes U.S. national and regional temperature anomalies. In, T.A. Boden, D.P. Kaiser, R.J. Sepanski and F.W. Stoss (eds.), Trends '93: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. ORNL/CDIAC-65. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN. pp G105
6 Teacher's Page: Graph of Great Lakes Mean Temperature Anomaly Data TEMPERATURE ANOMALY (ºC) GREAT LAKES ANNUAL TEMPERATURE ANOMALIES YEAR G106
7 If the graphs of the same years are compared on different scales, it appears that variations in Great Lakes temperatures were large in comparison to global temperatures. Why are there more extremes in the Great Lakes data set? Global temperatures are a combination of values across the earth. Extremes are averaged out. Large variations are not as visible as they are in a regional data set like that of the Great Lakes. Regional data will often show a larger range of highs and lows because these extremes aren t hidden as well by averaging. Answers to Questions 1. a. The more data, the more certain we can be about trends. In this case, centuries of data are needed. b. No, data collection methods have varied over the years. c. They are the only information we have, and something is better than nothing. They do need to be used with caution, however. d. Accept many answers human error, instrument failure, and effects of cities, cars, and industries, which can generate heat and may affect the surrounding climate. 2. Answers will vary based on class projections. 3. Answers will vary based on readings and student knowledge, but should include things like vegetation effects, arctic permafrost effects, ocean circulation, greenhouse gases, cloud effects, etc. 5. Each group, beginning with the first ( ) temperature chart, should present their data, along with predictions for average global and Great Lakes temperatures 30 years in the future. Compile the graphs of each group into a single graph to show the class. The first group hangs its graph on the front wall. The next group then covers the previous group s predictions with the actual data. Some teachers create a data timeline along the classroom wall or in a hallway. Students can compare their estimates with the actual data. Questions for Discussion 1. Groups should consider their predictions and answer the following: a. How much data do we need to plot a trend? b. Were weather collection methods the same for all data sets being reviewed? (e.g., how were weather data collected in 1885?) c. Even if the data are old, do they have value? d. Besides measurement techniques, what other factors may influence the reported data? 2. In 1995 the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change established predictions about future global warming. Their results are based on a scenario of business as usual, in which no changes are made in government regulations about greenhouse gas emissions. The predictions are that, as a result of enhanced greenhouse warming, the global mean temperature will rise 1.0 to 3.5ºC by the year 2100 with a best estimate of 2ºC. How do predictions made in the class compare with these predictions? 3. Based on information in the background readings, discuss what factors are involved in global climate change besides just temperature. What kinds of data should scientists combine into a model to get a more complete picture of the Earth System changes involved in global warming? A teachable moment for graph scales! Have students compare the two bar graphs on overhead transparencies. The Y-axis of the global temperature graph extends from 0.5 C to -0.5 C, while the Y-axis of the Great Lakes temperature graph extends from 2.5 C to -2.5 C. What we are experiencing is an error of scale. Plotting the two sets on the same axis, one for global and one for the Great Lakes, shows the true magnitude of the variation! Sometimes people who report science choose their graph scales in such a way that data are distorted vertically. They can then claim that the trend is not as great as it was feared, or is even worse than anyone imagined. Students should be alert to how data are portrayed in the media, so they can become wise consumers of science information. G107
8 Review Questions 1. How reliable were the five sets of predictions in Activity A? Discuss the implications of basing conclusions on limited data and the patterns that could be inferred from considering each of these subsets. 2. How much data is needed to make reliable predictions? What kinds of data might be combined for a more reliable picture of global climate change? 3. Thinking back to your history classes, can you recall any events, inventions, or discoveries that may have contributed to increased temperatures? 4. Were the data used in this exercise collected by experimentation? Sometimes we learn about the scientific method and assume that the only way to do science is by experiments. Often in reality, more can be learned about Earth Systems through historical data that are mainly descriptive. To the following list add some observable data about the Earth Systems or the Great Lakes in particular that might be classified as: Historical/Descriptive Phosphorus loading to each lake over the years Amount of toxin in birds in different regions Lake level changes Flood periods Experimental It may be difficult to find experimental data! Fish growing experiments based on Great Lakes fishes Answers to Review Questions 1. In trying to make predictions or conclusions based on limited data, it is hard to see the whole picture. As the Great Lakes graph shows, conditions are more variable over short distances than when averaged worldwide. Also, trends are difficult to determine when data are only available from a limited time period. For instance, flooding may have been prevalent in a specific region over a period of 2-3 years. In looking at a graph of floods for a 10-year period, one might conclude that floods occur in an area two or three years out of every 10, when actually they occur only two or three out of every 100 years. 2. In order to make a reliable prediction, data should be obtained from as many years as possible using both human records and proxy data (data from which other information can be inferred, such as tree rings and fossil pollen as indicators of past climate conditions). In doing so, the researcher can better generalize data to a longer time frame. If just a few years of data are used, the researcher must list the limitations of data from a short time span. 3. Several events occurred after the late 1800s that created greater levels of pollution, including the levels of greenhouse gases. For example, the industrial revolution occurred in the late 1800s. Additionally, the automobile, invented in 1885, began to be mass produced in WW1 may have had effects also either directly from fires and other factors, or indirectly from technological developments during the war. G108
9 Extensions 1. Local temperature variation may be different than either regional or global variation. Obtain local temperature data and plot this on a similar graph. How does it compare to the other data? What factors could cause differences between the data sets? 2. Working in groups, do research on the history of legislation regarding atmospheric conditions, such as those banning CFCs. Do you feel that these laws have had an effect? Explain your answer. 3. Do library research on the phenomenon of El Niño and its effects on global temperature. 4. Review the data provided on greenhouse gas concentrations (Activity B), and the changes in their levels over time. What relationships do you see between changes in global temperature and the levels of these gases? Global and Great Lakes temperature data can be downloaded in the following manner: ftp cdiac.esd.ornl.gov Name: anonymous Password: YOU@your address Guest login ok, access restrictions apply. ftp> cd /pub/trends93 ftp> dir ftp> cd temp ftp> get glakes721 (or use "ftp> get jones606" for global anomalies) ftp> quit ftp> Goodbye Access to CDIAC's anonymous FTP area is also available on the Internet: CDP@ORNL.GOV References Aspen Global Change Institute Is it Getting Hot or Not? How When Affects What: Part II. Ground Truth Studies. Aspen, CO. Boden, T. A., Kaiser D.P., Sepanski R.J. and Stoss F.W Trends 93: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. Oak Ridge, TN: Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center. 984 pp. Environment Canada Climate Change and Canadian Impacts: The Scientific Perspective, Climate Change Digest #CCD NOAA Reports to the Nation On Our Changing Planet: The Climate System Silver Spring, MD: U.S. Department of Commerce. G109
10 Revised Great Lakes Annual Temperature Anomaly Data [C] Anomalies are now provided as departures from the 20th century average ( ). From the National Climatic Data Center, calculated February 6, 2007, at gcag/gcag.html using Longitude -84 to -90 (W) and Latitude 40 to 50 N Teacher: Please give one set of data to each group of students for graphing ACTUAL anomalies. Be sure all groups use the same scales on the graph axes G109a
11 Revised Global Annual Temperature Anomaly Data [C] Anomalies are now provided as departures from the 20th century average ( ). From the National Climatic Data Center, accessed May 30, 2006 at ftp://ftp.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/ anomalies/annual.land_and_ocean.90s.90n.df_ mean.dat Teacher: Please give one set of data to each group of students for graphing ACTUAL anomalies. Be sure all groups use the same scales on the graph axes G109b
What is Climate? Climate Change Evidence & Causes. Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing?
 What is Climate? 1 Climate Change Evidence & Causes Refers to the average environmental conditions (i.e. temperature, precipitation, extreme events) in a given location over many years Climate is what
What is Climate? 1 Climate Change Evidence & Causes Refers to the average environmental conditions (i.e. temperature, precipitation, extreme events) in a given location over many years Climate is what
Get the Picture: Climate Models
 Students will review scientific infographics to test their understanding of the role, contribution, and limitations of climate models in helping us understand Earth s past, present, and future climate
Students will review scientific infographics to test their understanding of the role, contribution, and limitations of climate models in helping us understand Earth s past, present, and future climate
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Overview: Students will learn about global climate change, what causes global warming, and scientific projections about climate change in the near future. Levels V-VI Grades 9-12
Global Climate Change Overview: Students will learn about global climate change, what causes global warming, and scientific projections about climate change in the near future. Levels V-VI Grades 9-12
Weather and climate. reflect. what do you think? look out!
 reflect You re going on vacation in a week and you have to start thinking about what clothes you re going to pack for your trip. You ve read the weather reports for your vacation spot, but you know that
reflect You re going on vacation in a week and you have to start thinking about what clothes you re going to pack for your trip. You ve read the weather reports for your vacation spot, but you know that
Climate Change or Climate Variability?
 Climate Change or Climate Variability? Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Climate Climate change Climate variability Climate zones Precipitation Temperature Water cycle Weather WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will
Climate Change or Climate Variability? Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Climate Climate change Climate variability Climate zones Precipitation Temperature Water cycle Weather WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will
Chapter Introduction. Earth. Change. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Climates of Earth Chapter Wrap-Up Climate Cycles Recent Climate Change What is climate and how does it impact life on Earth? What do you think? Before you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Climates of Earth Chapter Wrap-Up Climate Cycles Recent Climate Change What is climate and how does it impact life on Earth? What do you think? Before you
Climate Discovery Teacher s Guide
 Unit:Little Ice Age Lesson: 1 Materials & Preparation Time: Introduction: 30 min Data collection: 10 minutes daily (for one or more weeks) Part 1 graphing/analysis: 45 min Part 2 graphing/analysis: 45
Unit:Little Ice Age Lesson: 1 Materials & Preparation Time: Introduction: 30 min Data collection: 10 minutes daily (for one or more weeks) Part 1 graphing/analysis: 45 min Part 2 graphing/analysis: 45
IMPACTS OF A WARMING ARCTIC
 The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
Relative and Absolute Directions
 Relative and Absolute Directions Purpose Learning about latitude and longitude Developing math skills Overview Students begin by asking the simple question: Where Am I? Then they learn about the magnetic
Relative and Absolute Directions Purpose Learning about latitude and longitude Developing math skills Overview Students begin by asking the simple question: Where Am I? Then they learn about the magnetic
Activity 2 Changes Close to Home
 Activity 2 Changes Close to Home Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 2 >> Page 1 ACTIVITY 2 CHANGES CLOSE TO HOME ORAL CLIMATE HISTORY PROJECT Documenting Cultural Knowledge, Savoonga, Alaska Smithsonian
Activity 2 Changes Close to Home Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 2 >> Page 1 ACTIVITY 2 CHANGES CLOSE TO HOME ORAL CLIMATE HISTORY PROJECT Documenting Cultural Knowledge, Savoonga, Alaska Smithsonian
LAB 15. Lab 15. Air Masses and Weather Conditions: How Do the Motions and Interactions of Air Masses Result in Changes in Weather Conditions?
 Lab Handout Lab 15. Air Masses and Weather Conditions: How Do the Motions and Interactions of Air Masses Result in Changes in Weather Conditions? Introduction Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere.
Lab Handout Lab 15. Air Masses and Weather Conditions: How Do the Motions and Interactions of Air Masses Result in Changes in Weather Conditions? Introduction Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere.
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Simulating Future Climate Change Using A Global Climate Model
 Simulating Future Climate Change Using A Global Climate Model Introduction: (EzGCM: Web-based Version) The objective of this abridged EzGCM exercise is for you to become familiar with the steps involved
Simulating Future Climate Change Using A Global Climate Model Introduction: (EzGCM: Web-based Version) The objective of this abridged EzGCM exercise is for you to become familiar with the steps involved
Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years. Statement of
 Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years Statement of Gerald R. North, Ph.D. Chairman, Committee on Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years National Research Council
Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years Statement of Gerald R. North, Ph.D. Chairman, Committee on Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years National Research Council
THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS
 THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS As Canada s climate changes, and weather patterns shift, Canadian climate models provide guidance in an uncertain future. CANADA S CLIMATE IS CHANGING
THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS As Canada s climate changes, and weather patterns shift, Canadian climate models provide guidance in an uncertain future. CANADA S CLIMATE IS CHANGING
Activity 3 Arctic Heat Wave?
 Activity 3 Arctic Heat Wave? Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 3 >> Page 1 ACTIVITY 3 ARCTIC HEAT WAVE? THE RATE OF CLIMATE CHANGE Are Ice Caps Melting Faster? From 1979 to 2002, seasonal melting
Activity 3 Arctic Heat Wave? Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 3 >> Page 1 ACTIVITY 3 ARCTIC HEAT WAVE? THE RATE OF CLIMATE CHANGE Are Ice Caps Melting Faster? From 1979 to 2002, seasonal melting
Weather Review. Use this graph to answer the next questions. A B C D
 Weather Review 1. Which of the following lists elements of the weather? a. Radiation, Wind Speed, Precipitation b. Soil type, Plate type, Water type c. Temperature, Precipitation, Air Pressure d. Ocean
Weather Review 1. Which of the following lists elements of the weather? a. Radiation, Wind Speed, Precipitation b. Soil type, Plate type, Water type c. Temperature, Precipitation, Air Pressure d. Ocean
Outline 24: The Holocene Record
 Outline 24: The Holocene Record Climate Change in the Late Cenozoic New York Harbor in an ice-free world (= Eocene sea level) Kenneth Miller, Rutgers University An Ice-Free World: eastern U.S. shoreline
Outline 24: The Holocene Record Climate Change in the Late Cenozoic New York Harbor in an ice-free world (= Eocene sea level) Kenneth Miller, Rutgers University An Ice-Free World: eastern U.S. shoreline
[1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing
![[1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing [1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing](/thumbs/81/84565805.jpg) The science and policy of climate change is based on four major pieces of evidence [1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 195 1953 1956 1959 1962 1965 1968 1971 1974 1977 198
The science and policy of climate change is based on four major pieces of evidence [1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 195 1953 1956 1959 1962 1965 1968 1971 1974 1977 198
Map Skills Lesson 1. Materials: maps, pencils, Lesson 1 Worksheet, strips of paper, grid paper
 Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference)
 Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference) Teacher Notes: Evidence for Climate Change PowerPoint Slide 1 Slide 2 Introduction Image 1 (Namib Desert, Namibia) The sun is on the horizon
Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference) Teacher Notes: Evidence for Climate Change PowerPoint Slide 1 Slide 2 Introduction Image 1 (Namib Desert, Namibia) The sun is on the horizon
WHAT YOU WILL LEARN. Key Concepts: TitleTitle Volcanoes and Global Warming. Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfate aerosols Greenhouse effect
 TitleTitle Volcanoes and Global Warming Key Concepts: Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfate aerosols Greenhouse effect WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will identify materials ejected by volcanic activity. 2.
TitleTitle Volcanoes and Global Warming Key Concepts: Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfate aerosols Greenhouse effect WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will identify materials ejected by volcanic activity. 2.
DOWNLOAD PDF READING CLIMATE MAPS
 Chapter 1 : Template:Climate chart/how to read a climate chart - Wikipedia Maps don't just tell you which way to go they can tell you practically everything about an area of land, even the weather. Learn
Chapter 1 : Template:Climate chart/how to read a climate chart - Wikipedia Maps don't just tell you which way to go they can tell you practically everything about an area of land, even the weather. Learn
8.1 CHANGES IN CHARACTERISTICS OF UNITED STATES SNOWFALL OVER THE LAST HALF OF THE TWENTIETH CENTURY
 8.1 CHANGES IN CHARACTERISTICS OF UNITED STATES SNOWFALL OVER THE LAST HALF OF THE TWENTIETH CENTURY Daria Scott Dept. of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences St. Could State University, St. Cloud, MN Dale Kaiser*
8.1 CHANGES IN CHARACTERISTICS OF UNITED STATES SNOWFALL OVER THE LAST HALF OF THE TWENTIETH CENTURY Daria Scott Dept. of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences St. Could State University, St. Cloud, MN Dale Kaiser*
Flags of the Sea. Standards : Numbers and Operations, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Problem Solving, Communication, and Connections.
 Part 1 Standards : Numbers and Operations, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Problem Solving, Communication, and Connections. There are flags everywhere you go. You see them in front of buildings.
Part 1 Standards : Numbers and Operations, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Problem Solving, Communication, and Connections. There are flags everywhere you go. You see them in front of buildings.
Sunspot Cycles source: NOAA
 Sunspots and Global Warming Charlie Nelson November 23 There is a statistically significant correlation between the amplitude of the sunspot cycle and the temperature of the atmosphere. This relationship
Sunspots and Global Warming Charlie Nelson November 23 There is a statistically significant correlation between the amplitude of the sunspot cycle and the temperature of the atmosphere. This relationship
Climate Change. Unit 3
 Climate Change Unit 3 Aims Is global warming a recent short term phenomenon or should it be seen as part of long term climate change? What evidence is there of long-, medium-, and short- term climate change?
Climate Change Unit 3 Aims Is global warming a recent short term phenomenon or should it be seen as part of long term climate change? What evidence is there of long-, medium-, and short- term climate change?
THE SUN, THE MOON AND OUR SOLAR SYSTEM TEACHER NOTES TO SHARE WITH STUDENTS
 THE SUN, THE MOON AND OUR SOLAR SYSTEM TEACHER NOTES TO SHARE WITH STUDENTS The Sun is the biggest feature in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar
THE SUN, THE MOON AND OUR SOLAR SYSTEM TEACHER NOTES TO SHARE WITH STUDENTS The Sun is the biggest feature in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar
Project-Based Inquiry Science: Air Quality Storyline. Air Quality: What s the Big Question? How Can You Improve Air Quality in Your Community?
 Project-Based Inquiry Science: Air Quality Storyline Air Quality: What s the Big Question? How Can You Improve Air Quality in Your Community? In the Introduction to Air Quality, students read a parable
Project-Based Inquiry Science: Air Quality Storyline Air Quality: What s the Big Question? How Can You Improve Air Quality in Your Community? In the Introduction to Air Quality, students read a parable
Severe Weather and weather mapping Remediation Assignment. Once the page has been approved, Mrs. Blinka will sign here:
 Severe Weather and weather mapping Remediation Assignment Part I: Complete the remediation page attached This will be a single page (front and back) that helps your organize the most important information
Severe Weather and weather mapping Remediation Assignment Part I: Complete the remediation page attached This will be a single page (front and back) that helps your organize the most important information
Digging into the Past Pre-Visit Materials
 Digging into the Past Pre-Visit Materials Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Digging into the Past Pre-Visit The Pre-visit activities are linked to the pre-requisite skills and knowledge
Digging into the Past Pre-Visit Materials Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Digging into the Past Pre-Visit The Pre-visit activities are linked to the pre-requisite skills and knowledge
Shepard Glacier-2005 Glacier National Park, Montana
 To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture, click Options in the Message Bar, and then click Enable
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture, click Options in the Message Bar, and then click Enable
Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do?
 Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do? Lesson 1.1 What is History? I. Why Study History? A. History is the study of the of the past. History considers both the way things
Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do? Lesson 1.1 What is History? I. Why Study History? A. History is the study of the of the past. History considers both the way things
SHAPING OUR FUTURE: THE CLIMATE CHALLENGE KS3 LESSON 1 TEACHER GUIDE HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING?
 SHAPING OUR FUTURE: THE CLIMATE CHALLENGE KS3 LESSON 1 TEACHER GUIDE HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING? KS3 LESSON 1 TEACHER GUIDE HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING? Learning objective: To understand, through the
SHAPING OUR FUTURE: THE CLIMATE CHALLENGE KS3 LESSON 1 TEACHER GUIDE HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING? KS3 LESSON 1 TEACHER GUIDE HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING? Learning objective: To understand, through the
Climate Change Lecture Notes
 Climate Change Lecture Notes (Topic 12A) page 1 Climate Change Lecture Notes Learning Outcomes for the Climate Change Unit 1. Students can list observations which suggest that the world is warming, and
Climate Change Lecture Notes (Topic 12A) page 1 Climate Change Lecture Notes Learning Outcomes for the Climate Change Unit 1. Students can list observations which suggest that the world is warming, and
Lesson IV. TOPEX/Poseidon Measuring Currents from Space
 Lesson IV. TOPEX/Poseidon Measuring Currents from Space The goal of this unit is to explain in detail the various measurements taken by the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. Keywords: ocean topography, geoid,
Lesson IV. TOPEX/Poseidon Measuring Currents from Space The goal of this unit is to explain in detail the various measurements taken by the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. Keywords: ocean topography, geoid,
Annex I to Target Area Assessments
 Baltic Challenges and Chances for local and regional development generated by Climate Change Annex I to Target Area Assessments Climate Change Support Material (Climate Change Scenarios) SWEDEN September
Baltic Challenges and Chances for local and regional development generated by Climate Change Annex I to Target Area Assessments Climate Change Support Material (Climate Change Scenarios) SWEDEN September
NSF Expeditions in Computing. Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach. Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota
 NSF Expeditions in Computing Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota kumar@cs.umn.edu www.cs.umn.edu/~kumar Vipin Kumar UCC Aug 15, 2011 Climate Change:
NSF Expeditions in Computing Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota kumar@cs.umn.edu www.cs.umn.edu/~kumar Vipin Kumar UCC Aug 15, 2011 Climate Change:
C1: From Weather to Climate Looking at Air Temperature Data
 C1: From Weather to Climate Looking at Air Temperature Data Purpose Students will work with short- and longterm air temperature data in order to better understand the differences between weather and climate.
C1: From Weather to Climate Looking at Air Temperature Data Purpose Students will work with short- and longterm air temperature data in order to better understand the differences between weather and climate.
Southington Public Schools Curriculum Map Subject: Science Grade: 6
 Southington Public Schools Curriculum Map Subject: Science Grade: 6 UNIT TITLE #1 Heat Energy / Weather # 2 Solar System #3 Energy in the Earth s System #4 Erosion #5 Water: Human Impact TIMELINE Sept.
Southington Public Schools Curriculum Map Subject: Science Grade: 6 UNIT TITLE #1 Heat Energy / Weather # 2 Solar System #3 Energy in the Earth s System #4 Erosion #5 Water: Human Impact TIMELINE Sept.
El Niño / Southern Oscillation
 El Niño / Southern Oscillation Student Packet 2 Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents Introduction on
El Niño / Southern Oscillation Student Packet 2 Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents Introduction on
Motivating Questions: How many hurricanes happen in a year? Have the number of hurricanes per year changed over time?
 Hurricanes Over Time Materials For the leader: Projector Whiteboard to project data graph onto For the activity: Graphing paper Markers Globe Copy of data cards Overview Hurricanes occur in the North Atlantic
Hurricanes Over Time Materials For the leader: Projector Whiteboard to project data graph onto For the activity: Graphing paper Markers Globe Copy of data cards Overview Hurricanes occur in the North Atlantic
As the World Turns. Vocabulary rotate, revolve, tilt, frame of reference, spin, axis. Science Enhanced Scope and Sequence Grade 3
 As the World Turns Strand Earth Patterns, Cycles, and Change Topic Seasons, day and night Primary SOL 3.8 The student will investigate and understand basic patterns and cycles occurring in nature. Key
As the World Turns Strand Earth Patterns, Cycles, and Change Topic Seasons, day and night Primary SOL 3.8 The student will investigate and understand basic patterns and cycles occurring in nature. Key
FOLLOW THE ENERGY! EARTH S DYNAMIC CLIMATE SYSTEM
 Investigation 1B FOLLOW THE ENERGY! EARTH S DYNAMIC CLIMATE SYSTEM Driving Question How does energy enter, flow through, and exit Earth s climate system? Educational Outcomes To consider Earth s climate
Investigation 1B FOLLOW THE ENERGY! EARTH S DYNAMIC CLIMATE SYSTEM Driving Question How does energy enter, flow through, and exit Earth s climate system? Educational Outcomes To consider Earth s climate
Warm Up Vocabulary Check
 Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Meteorology B Wright State Invite Team Name Team # Student Members: &
 1 Meteorology B Team Name Team # Student Members: & Raw Score: / 126 Rank: Part I. Multiple Choice. Answer the following questions by selecting the best answer. 2 points each. 1. All of the following are
1 Meteorology B Team Name Team # Student Members: & Raw Score: / 126 Rank: Part I. Multiple Choice. Answer the following questions by selecting the best answer. 2 points each. 1. All of the following are
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Ice Cores: Modeling Ice Sheets
 Details Completion Time: About 1 period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Ice Cores: Modeling Ice Sheets Overview Working in groups students will use common materials to create layers of snow and
Details Completion Time: About 1 period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Ice Cores: Modeling Ice Sheets Overview Working in groups students will use common materials to create layers of snow and
LAB 19. Lab 19. Differences in Regional Climate: Why Do Two Cities Located at the Same Latitude and Near a Body of Water Have Such Different Climates?
 Lab Handout Lab 19. Differences in Regional Climate: Why Do Two Cities Located at the Same Latitude and Near a Body of Water Have Such Different Climates? Introduction Weather describes the current atmospheric
Lab Handout Lab 19. Differences in Regional Climate: Why Do Two Cities Located at the Same Latitude and Near a Body of Water Have Such Different Climates? Introduction Weather describes the current atmospheric
Ocean Temperatures. Key Words: No new key words.
 Key Words: No new key words. Ocean Temperatures Getting Started: 1. In this activity, you will simulate the work of climatologists who sample ocean surface temperatures and compile that data to investigate
Key Words: No new key words. Ocean Temperatures Getting Started: 1. In this activity, you will simulate the work of climatologists who sample ocean surface temperatures and compile that data to investigate
Global Climate Change - What evidence have scientists collected to support global climate change? Why? Model 1 Earth s Surface Temperatures.
 Name Blk Global Climate Change - What evidence have scientists collected to support global climate change? Obj/Module 63. Evidence of Global Warming Why? Global climate change is a topic that is frequently
Name Blk Global Climate Change - What evidence have scientists collected to support global climate change? Obj/Module 63. Evidence of Global Warming Why? Global climate change is a topic that is frequently
Teacher s Guide For. Measuring the Earth s Temperature
 Teacher s Guide For Measuring the Earth s Temperature For grade 7 - College Program produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William V. Ambrose Teacher's
Teacher s Guide For Measuring the Earth s Temperature For grade 7 - College Program produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William V. Ambrose Teacher's
Critical Thinking Review
 Critical Thinking Review (wk3) Cognitive Skill of the Week: Analysis Analysis is the examination of a system (or complex), its components (or ingredients), and the linkages among these components. One
Critical Thinking Review (wk3) Cognitive Skill of the Week: Analysis Analysis is the examination of a system (or complex), its components (or ingredients), and the linkages among these components. One
STATE OF THE CLIMATE IN 2017
 STATE OF THE CLIMATE IN 2017 Today s Presenters Jeff Rosenfeld Editor-In-Chief, Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society Boston, MA Deke Arndt Chief, Monitoring Branch, NOAA s National Centers for
STATE OF THE CLIMATE IN 2017 Today s Presenters Jeff Rosenfeld Editor-In-Chief, Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society Boston, MA Deke Arndt Chief, Monitoring Branch, NOAA s National Centers for
Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect 8.
 Matching (2 points each) 1. weather 2. climate 3. Greenhouse Effect 4. Convection Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect
Matching (2 points each) 1. weather 2. climate 3. Greenhouse Effect 4. Convection Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect
Climate Change. Grades 5-8. Written by Darcy J. Gentleman Illustrated by S&S Learning Materials. ISBN Copyright 2008
 Climate Change Grades 5-8 Written by Darcy J. Gentleman Illustrated by S&S Learning Materials About the author: Darcy J. Gentleman has a Ph.D. in analytical chemistry from Arizona State University. His
Climate Change Grades 5-8 Written by Darcy J. Gentleman Illustrated by S&S Learning Materials About the author: Darcy J. Gentleman has a Ph.D. in analytical chemistry from Arizona State University. His
Surface Processes and the Hydrosphere Unit Heating the Earth s Atmosphere Chapter 11 (pg )
 Name: Block: Surface Processes and the Hydrosphere Unit Heating the Earth s Atmosphere Chapter 11 (pg. 352 385) 11.1: Focus on the Atmosphere: Weather and Climate What is the difference between the weather
Name: Block: Surface Processes and the Hydrosphere Unit Heating the Earth s Atmosphere Chapter 11 (pg. 352 385) 11.1: Focus on the Atmosphere: Weather and Climate What is the difference between the weather
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty
 Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Appendix A. Linear Relationships in the Real World Unit
 Appendix A The Earth is like a giant greenhouse. The sun s energy passes through the atmosphere and heats up the land. Some of the heat escapes back into space while some of it is reflected back towards
Appendix A The Earth is like a giant greenhouse. The sun s energy passes through the atmosphere and heats up the land. Some of the heat escapes back into space while some of it is reflected back towards
Hudson River Estuary Climate Change Lesson Project. Grades 5-8 Teacher s Packet. Lesson 3. Climate Change in My City
 Grades 5-8 Teacher s Packet Lesson 3 Climate Change in My City Teacher s Packet 2 Climate Change in My City NYS Intermediate Level Science Standard 1: Analysis, Inquiry and Design/Scientific Inquiry S1.3
Grades 5-8 Teacher s Packet Lesson 3 Climate Change in My City Teacher s Packet 2 Climate Change in My City NYS Intermediate Level Science Standard 1: Analysis, Inquiry and Design/Scientific Inquiry S1.3
Activity 1 Eyewitnesses to Change
 Activity 1 Eyewitnesses to Change Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 1 >> Page 1 EYEWITNESSES TO CHANGE NATIVE PEOPLES OBSERVE CLIMATE CHANGES IN THE ARCTIC Living With Change Sachs Harbour, Canada
Activity 1 Eyewitnesses to Change Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 1 >> Page 1 EYEWITNESSES TO CHANGE NATIVE PEOPLES OBSERVE CLIMATE CHANGES IN THE ARCTIC Living With Change Sachs Harbour, Canada
Science Standard 1: Students analyze monthly precipitation and temperature records, displayed in bar charts, collected in metric units (mm).
 Title: Precipitation Patterns across the Globe NSF GK-12 Fellow: Terry Legg Type of Lesson: STEM Grade Level(s): 4 th - 7 th grade This activity can be tailored to older, more advanced students by having
Title: Precipitation Patterns across the Globe NSF GK-12 Fellow: Terry Legg Type of Lesson: STEM Grade Level(s): 4 th - 7 th grade This activity can be tailored to older, more advanced students by having
Lab 21. Forecasting Extreme Weather: When and Under What Atmospheric Conditions Are Tornadoes Likely to Develop in the Oklahoma City Area?
 Forecasting Extreme Weather When and Under What Atmospheric Conditions Are Tornadoes Likely to Develop in the Oklahoma City Area? Lab Handout Lab 21. Forecasting Extreme Weather: When and Under What Atmospheric
Forecasting Extreme Weather When and Under What Atmospheric Conditions Are Tornadoes Likely to Develop in the Oklahoma City Area? Lab Handout Lab 21. Forecasting Extreme Weather: When and Under What Atmospheric
Global Temperature. James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo
 Global Temperature James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo November 3, 2005 This note responds to recent inquiries about 2005 global temperature, the inquiries stimulated by a 13 October Washington
Global Temperature James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo November 3, 2005 This note responds to recent inquiries about 2005 global temperature, the inquiries stimulated by a 13 October Washington
Temperature Changes OBJECTIVES PREPARATION SCHEDULE MATERIALS. The students. For each student. For each team of two. For the class
 activity 3 Temperature Changes OBJECTIVES Students observe changes in air temperature and discover the role of the Sun in heating Earth. The students measure and record outdoor air temperature at three
activity 3 Temperature Changes OBJECTIVES Students observe changes in air temperature and discover the role of the Sun in heating Earth. The students measure and record outdoor air temperature at three
Section 20: Arrow Diagrams on the Integers
 Section 0: Arrow Diagrams on the Integers Most of the material we have discussed so far concerns the idea and representations of functions. A function is a relationship between a set of inputs (the leave
Section 0: Arrow Diagrams on the Integers Most of the material we have discussed so far concerns the idea and representations of functions. A function is a relationship between a set of inputs (the leave
Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map
 Subject Area Grade First Grade Date June 2005, reviewed June 2009 Unit Content Standards Addressed Skills/Benchmarks Essential Questions Assessments Unit 1 Here We Are and Our Class Our School Our Families
Subject Area Grade First Grade Date June 2005, reviewed June 2009 Unit Content Standards Addressed Skills/Benchmarks Essential Questions Assessments Unit 1 Here We Are and Our Class Our School Our Families
2. There may be large uncertainties in the dating of materials used to draw timelines for paleo records.
 Limitations of Paleo Data A Discussion: Although paleoclimatic information may be used to construct scenarios representing future climate conditions, there are limitations associated with this approach.
Limitations of Paleo Data A Discussion: Although paleoclimatic information may be used to construct scenarios representing future climate conditions, there are limitations associated with this approach.
Climate Change: Global Warming Claims
 Climate Change: Global Warming Claims Background information (from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change): The climate system is a complex, interactive system consisting of the atmosphere, land surface,
Climate Change: Global Warming Claims Background information (from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change): The climate system is a complex, interactive system consisting of the atmosphere, land surface,
Global Paleogeography
 Global Paleogeography Overview of Global Paleogeography Paleogeography is the study of how the Earth s geography has changed during the course of history. Using geological data, scientists reconstruct
Global Paleogeography Overview of Global Paleogeography Paleogeography is the study of how the Earth s geography has changed during the course of history. Using geological data, scientists reconstruct
L ESSON P LAN:DETERMINING THE E FFECT OF D ISTANCE (PART 1) AND I NCLINATION (PART 2)
 L ESSON P LAN:DETERMINING THE E FFECT OF D ISTANCE (PART 1) AND I NCLINATION (PART 2) In the activity at the heart of this lesson, the students will measure the effect of distance and inclination on the
L ESSON P LAN:DETERMINING THE E FFECT OF D ISTANCE (PART 1) AND I NCLINATION (PART 2) In the activity at the heart of this lesson, the students will measure the effect of distance and inclination on the
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1
 The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
CLIMATE. SECTION 14.1 Defining Climate
 Date Period Name CLIMATE SECTION.1 Defining Climate In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual
Date Period Name CLIMATE SECTION.1 Defining Climate In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual
Environments and Ecosystems
 Environments and Ecosystems A habitat is a place where organisms naturally live and grow. Habitats include biotic, living factors, such as plants and animals and abiotic, non-living factors, such as rocks,
Environments and Ecosystems A habitat is a place where organisms naturally live and grow. Habitats include biotic, living factors, such as plants and animals and abiotic, non-living factors, such as rocks,
Elementary Science: Curriculum Map for Grade 5
 Second Nine Weeks Earth Science Guiding Question: How are the physical characteristics of each planet different? GLE0507.6.1 Compare planets based on their known characteristics. GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore
Second Nine Weeks Earth Science Guiding Question: How are the physical characteristics of each planet different? GLE0507.6.1 Compare planets based on their known characteristics. GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore
Subject: Science, Biology, History, Geography
 Digging for Evidence Author: Jacqueline D. Grade Span: 6-8 Assignment Type: Individual, Small Group State: South Carolina Subject: Science, Biology, History, Geography Recommended Time Frame: 9 class periods
Digging for Evidence Author: Jacqueline D. Grade Span: 6-8 Assignment Type: Individual, Small Group State: South Carolina Subject: Science, Biology, History, Geography Recommended Time Frame: 9 class periods
Climate. What is climate? STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Name Class Date
 Climate SECTION 14.1 What is climate? In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual wind speed 4.
Climate SECTION 14.1 What is climate? In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual wind speed 4.
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Betty LaDuke. Biomes of the World PRESERVATION OF OREGON S ARTISTIC HERITAGE PROJECT. Grade Level no grade level listed on the word document
 Betty LaDuke PRESERVATION OF OREGON S ARTISTIC HERITAGE PROJECT Biomes of the World Grade Level no grade level listed on the word document Theme The artist in his or her environment Curriculum Framework
Betty LaDuke PRESERVATION OF OREGON S ARTISTIC HERITAGE PROJECT Biomes of the World Grade Level no grade level listed on the word document Theme The artist in his or her environment Curriculum Framework
The of that surrounds the Earth. Atmosphere. A greenhouse that has produced the most global. Carbon Dioxide
 Name: Date: # Weather and Climate Unit Review Directions: Complete this packet to help you prepare for your unit test by filling in the blanks to complete the definitions. Then if no picture is provided,
Name: Date: # Weather and Climate Unit Review Directions: Complete this packet to help you prepare for your unit test by filling in the blanks to complete the definitions. Then if no picture is provided,
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes!
 Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic
 Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic 1. Large amounts of ice form in some seasons in the oceans near the North Pole and the South Pole (the Arctic Ocean and the Southern Ocean). This ice,
Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic 1. Large amounts of ice form in some seasons in the oceans near the North Pole and the South Pole (the Arctic Ocean and the Southern Ocean). This ice,
National Center for Atmospheric Research: Climate Discovery Teacher s Guide
 Lesson Summary Students use a photo of the Bhutan glaciers in order to investigate the different effects albedo has on solar absorption. Prior Knowledge & Skills Graphing skills Data collection skills
Lesson Summary Students use a photo of the Bhutan glaciers in order to investigate the different effects albedo has on solar absorption. Prior Knowledge & Skills Graphing skills Data collection skills
Planetary Atmospheres (Chapter 10)
 Planetary Atmospheres (Chapter 10) Based on Chapter 10 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 11 and 13 on Jovian planet systems and Extrasolar planets Chapters 4, 5, and 8 on Momentum,
Planetary Atmospheres (Chapter 10) Based on Chapter 10 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 11 and 13 on Jovian planet systems and Extrasolar planets Chapters 4, 5, and 8 on Momentum,
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere
 Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Impact of Climate Change on Chinook Salmon
 Region: Western Coastlines Grade Level(s): 5-8 Impact of Climate Change on Chinook Salmon Time Required: 2-3 class periods Focus Question(s): How will long term climate changes impact northwest Pacific
Region: Western Coastlines Grade Level(s): 5-8 Impact of Climate Change on Chinook Salmon Time Required: 2-3 class periods Focus Question(s): How will long term climate changes impact northwest Pacific
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test
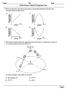 Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology.
 What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
Thank you for choosing AIMS!
 Thank you for choosing AIMS! Please use this free activity in your classroom, and watch your students begin to experience the "Aha!" moments of real learning. We like hearing from you. Like us and share
Thank you for choosing AIMS! Please use this free activity in your classroom, and watch your students begin to experience the "Aha!" moments of real learning. We like hearing from you. Like us and share
ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models
 ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models Jennifer Fletcher Day 27: July 29, 2010 Using Climate Models to Build Understanding Often climate models are thought of as forecast tools (what s the climate going
ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models Jennifer Fletcher Day 27: July 29, 2010 Using Climate Models to Build Understanding Often climate models are thought of as forecast tools (what s the climate going
In this activity, students will compare weather data from to determine if there is a warming trend in their community.
 Overview: In this activity, students will compare weather data from 1910-2000 to determine if there is a warming trend in their community. Objectives: The student will: use the Internet to locate scientific
Overview: In this activity, students will compare weather data from 1910-2000 to determine if there is a warming trend in their community. Objectives: The student will: use the Internet to locate scientific
Curriculum Map. Essential Questions (Questions for students that reflect the skills we want them to learn) What are the science skills?
 Curriculum Map Name of Teacher: Michelle Thomson Grade: Sixth grade Subject of Course: Science August - September Content (The What of Teaching: Topics, Themes, Issues, Concepts) Scientific methods and
Curriculum Map Name of Teacher: Michelle Thomson Grade: Sixth grade Subject of Course: Science August - September Content (The What of Teaching: Topics, Themes, Issues, Concepts) Scientific methods and
Global Warming and Changing Sea Level. Name: Part 1: Am I part of the problem?!
 Part 1: Am I part of the problem?! Name: The consumption of energy in the form of fossil fuel combustion is the largest single contributor to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. and the
Part 1: Am I part of the problem?! Name: The consumption of energy in the form of fossil fuel combustion is the largest single contributor to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. and the
Alliance Created State Giant Traveling Map Lesson
 Title: Comparing Arizona s Temperatures Recommended Grades: 4 th 5 th Time Needed: 30 minutes Objectives: Students will: Compare and contrast the geographic features of Arizona by researching seasonal
Title: Comparing Arizona s Temperatures Recommended Grades: 4 th 5 th Time Needed: 30 minutes Objectives: Students will: Compare and contrast the geographic features of Arizona by researching seasonal
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Climate Change. Model-Evidence Link Diagram (MEL) MEL Key Points Model A: Current climate. released from the Sun.
 A Content Secondary Science Newsletter from the Southern Nevada Regional Professional Development Program Science Dissected Climate Change Model-Evidence Link Diagram (MEL) Earth s climate is a complex
A Content Secondary Science Newsletter from the Southern Nevada Regional Professional Development Program Science Dissected Climate Change Model-Evidence Link Diagram (MEL) Earth s climate is a complex
ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION. A Collection of Learning Experiences WEATHER Weather Student Activity Book
 ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION A Collection of Learning Experiences WEATHER Weather Student Activity Book Name This learning experience activity book is yours to keep.
ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION A Collection of Learning Experiences WEATHER Weather Student Activity Book Name This learning experience activity book is yours to keep.
Effects of Global Warming on Coastal Cities: A Katrina Case Study
 Effects of Global Warming on Coastal Cities: A Katrina Case Study Introduction This lesson was created to discuss the possible effects of temperatures increasing worldwide, with a focus on the events that
Effects of Global Warming on Coastal Cities: A Katrina Case Study Introduction This lesson was created to discuss the possible effects of temperatures increasing worldwide, with a focus on the events that
