Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation.
|
|
|
- Scott Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation. Olivier Pauluis Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Thanks to Arnaud Czaja, Robert Korty and Frederic Laliberte Sept. 1, 2009 Keck Institute for Space Studies, Caltech, CA
2 Entropy and circulation Entropy is a good quantity to analyze the global circulation: Heating and cooling maintain large-scale entropy gradient; entropy can be viewed as a conserved tracer; and entropy transport is tied to mechanical work. First order description of the circulation as reversible transport But not all processes are reversible!
3 Moist convection Cloud top height Moist adiabt S Photograph by Marco Lillini (
4
5 Not all processes involved with convection are reversible. Entrainment/ detrainment Precipitation Freezing/ melting Re-evaporation of precipitatio Mixing and entrainment in the boundary layer
6 Stormtracks
7 θ latitude Circulation on dry isentropes # " # ($,#) = ' 2% & # v # acos$ d# 0
8 θ 'Dry isentropes': " l = cst 'Moist isentropes': " e = cst Pressure(mb) θ θ e latitude latitude Instead of averaging the circulation on potential temperature surfaces, one can use surfaces of constant equivalent potential temperature. θ e includes a contribution from the latent heat content, and has often a minimum in the middle of the atmosphere.
9 Stream function on dry isentropes Stream function on moist isentropes θ θ e latitude latitude Same single cell structure But amplitude of the circulation differs!
10 In the Midlatitudes: DJF DJF θ θ e 40N 40N Circulation on moist isentropes is larger than that on dry isentropes.
11 Mass flux distribution at 40N - DJF Poleward flow θ e Equatorward flow Isentropic filaments that intercept the surface θ
12 Mass flux and stream function at 40N Stream function on dry isentropes: Stream function on moist isentropes: θ e θ e θ θ
13 θ e Isentropic filaments that intersect the surface Mass transport at 40N - DJF θ Portion of the mass transport included in the circulation on moist isentropes but not to that on dry isentropes The additional mass transport on moist isentropes takes place filaments near the Earth s surface. The equivalent potential temperature corresponds to upper tropospheric value of the potential temperature. This corresponds to a poleward flow of warm, moist air near the surface that is ready to rise into the upper troposphere.
14 Circulation on dry isentropes Moist branch: additional mass flow on moist isentropes In the midlatitudes, global circulation high entropy air poleward in two distinct branches: an upper tropospheric branch; an a lower branch of warm, most air that ascents into the upper troposphere within the stormtracks. Mass transport is comparable in each branch.
15 Entropy sources and sinks Governing equation for dry and moist entropy: Atmospheric Entropy transport Must balance sources And sinks d dt S m = L v T 0 E + Q T + "S irr Evaporation Is a source for S m d dt S l = L v T 0 P + Q T + "S irr Radiation and irreversible production are the same Precipitation Is a source for S l The right-hand side can be obtained from the streamfunction: " S S = #$ S(S,%) #%
16 Large source in the ITCZ Dry entropy sources: Large sink in the subtropics relatively weak sink in the midlatitudes θ Surface heating latitude
17 Weak source in the ITCZ Larger sink in the midlatitudes Moist entropy sources: Weak sink in the subtropics θ e Stronger surface source latitude
18 ERA40 (contour) NCEP-ERA40 (shading) JJA θ latitude ERA40 has stronger dry circulation both in the Tropics and in the midlatitudes of the Southern hemisphere
19 ERA40 (contour) NCEP-ERA40 (shading) JJA θ e latitude Smaller difference between circulation: NCEP makes up for a weaker dry circulation by transporting more moist air poleward
20 Extra-tropical recirculation is a common feature in many GCMs GFDL CM 2.1 ECHAM 5 But it is not present in neither CM2.1 nor the NCEP reanalysis
21 Conclusions Isentropic analysis can provide many insights on the dynamics of convection and the midlatitudes. Moist processes are important in both the tropics and the midlatitudes. Reversible adiabatic approach for the circulation offers a useful first order approximation, But there are key processes that do not fit into that mold.
22 Open questions: What is the nature of the midlatitude ascent (convection, slantwise ascent, moist conveyor belt )? How does it affect the transport of chemical tracers into the upper troposphere? What are the impacts of irreversible processes (precipitation, mixing and reevaporation) on the dynamics of midlatitude storms? What is the variability of the global circulation?
The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates
 1JUNE 2010 P A U L U I S E T A L. 3077 The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York New York
1JUNE 2010 P A U L U I S E T A L. 3077 The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York New York
Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations
 Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Monsoons- Past, Present and future May 20th, 2015 Caltech, Pasadena Outline Introduction Global monsoon in isentropic coordinates Dry ventilation
Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Monsoons- Past, Present and future May 20th, 2015 Caltech, Pasadena Outline Introduction Global monsoon in isentropic coordinates Dry ventilation
Thermodynamics of moist convection Part I: heat engine and buoyancy. Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Porquerolles
 Thermodynamics of moist convection Part I: heat engine and buoyancy Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Porquerolles Outline Introduction: the nature of the problem Entropy of moist air Heat engines and water vapor.
Thermodynamics of moist convection Part I: heat engine and buoyancy Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Porquerolles Outline Introduction: the nature of the problem Entropy of moist air Heat engines and water vapor.
Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes*
 MARCH 212 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 875 Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes* FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada TIFFANY
MARCH 212 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 875 Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes* FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada TIFFANY
Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean*
 JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
Dynamics of the Atmosphere. General circulation of the atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
Midlatitude Tropopause and Low-Level Moisture
 MARCH 2014 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1187 Midlatitude Tropopause and Low-Level Moisture YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, New York (Manuscript
MARCH 2014 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1187 Midlatitude Tropopause and Low-Level Moisture YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, New York (Manuscript
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan
 Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective!
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective!
A Theory for the Lower-Tropospheric Structure of the Moist Isentropic Circulation
 MARCH 213 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 843 A Theory for the Lower-Tropospheric Structure of the Moist Isentropic Circulation FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
MARCH 213 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 843 A Theory for the Lower-Tropospheric Structure of the Moist Isentropic Circulation FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
Tropical and Subtropical Meridional Latent Heat Transports by Disturbances to the Zonal Mean and Their Role in the General Circulation
 1872 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Tropical and Subtropical Meridional Latent Heat Transports by Disturbances to the Zonal Mean and Their Role in the General Circulation
1872 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Tropical and Subtropical Meridional Latent Heat Transports by Disturbances to the Zonal Mean and Their Role in the General Circulation
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS PART II
 Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS PART II The next chapter in the story: How differences in INSOLATION between low and high latitudes drive atmospheric circulation! pp 64 in Class Notes THE RADIATION BALANCE
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS PART II The next chapter in the story: How differences in INSOLATION between low and high latitudes drive atmospheric circulation! pp 64 in Class Notes THE RADIATION BALANCE
The general circulation: midlatitude storms
 The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
Isentropic Analysis applied to Convection, Hurricanes and Walker Circulation
 Isentropic Analysis applied to Convection, Hurricanes and Walker Circulation Olivier Pauluis, Agnieszka Mrowiec, Joanna Slawinska, and Fuqing Zhang Northeast Tropical Conference, May 27 2013 1 Introduction
Isentropic Analysis applied to Convection, Hurricanes and Walker Circulation Olivier Pauluis, Agnieszka Mrowiec, Joanna Slawinska, and Fuqing Zhang Northeast Tropical Conference, May 27 2013 1 Introduction
ATMO 436a. The General Circulation. Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it
 ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development
 Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport. Recall that the most primitive equilibrium climate model can be written
 2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment
 Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
CHAPTER 4. THE HADLEY CIRCULATION 59 smaller than that in midlatitudes. This is illustrated in Fig. 4.2 which shows the departures from zonal symmetry
 Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet
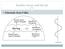 Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
no eddies eddies Figure 3. Simulated surface winds. Surface winds no eddies u, v m/s φ0 =12 φ0 =0
 References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
Isentropic analysis of convective motions. Olivier M. Pauluis. Agnieszka A. Mrowiec
 Generated using version 3.1.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 Isentropic analysis of convective motions 2 Olivier M. Pauluis Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science Courant Institute of Mathematical
Generated using version 3.1.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 Isentropic analysis of convective motions 2 Olivier M. Pauluis Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science Courant Institute of Mathematical
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems
 Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Mid-Latitude Dynamics and Atmospheric Rivers
 Mid-Latitude Dynamics and Atmospheric Rivers Session: Theory, Structure, Processes 1 Wednesday, 10 August 2016 Contribution from: Heini Werni Peter Knippertz Harold Sodemann Andreas Stohl Francina Dominguez
Mid-Latitude Dynamics and Atmospheric Rivers Session: Theory, Structure, Processes 1 Wednesday, 10 August 2016 Contribution from: Heini Werni Peter Knippertz Harold Sodemann Andreas Stohl Francina Dominguez
Hadley Circulation in Action. MET 200 Lecture 12! Global Winds: The General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Scales of Motion
 Hadley Circulation in Action MET 200 Lecture 12! Global Winds: The General Circulation of the Atmosphere 1 2 Previous Lecture Local Winds cales of Motion Eddies ea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook
Hadley Circulation in Action MET 200 Lecture 12! Global Winds: The General Circulation of the Atmosphere 1 2 Previous Lecture Local Winds cales of Motion Eddies ea Breeze Mountain-Valley Circulations Chinook
The meteorology of monsoons
 978--521-84799-5 - The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects 1 The meteorology of monsoons 1.1 Introduction Monsoon circulations are major features of the tropical atmosphere, which, primarily through
978--521-84799-5 - The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects 1 The meteorology of monsoons 1.1 Introduction Monsoon circulations are major features of the tropical atmosphere, which, primarily through
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes
 A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere
 DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere Lodovica Illari 1 Introduction What is responsible for stormy weather? What causes relatively warm temperatures one day and
DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere Lodovica Illari 1 Introduction What is responsible for stormy weather? What causes relatively warm temperatures one day and
Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences Isentropic analysis of moist convection
 Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences Isentropic analysis of moist convection --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Corresponding Author: Corresponding Author's Institution: First
Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences Isentropic analysis of moist convection --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Corresponding Author: Corresponding Author's Institution: First
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles. Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild
 The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
F = ma. ATS 150 Global Climate Change Winds and Weather. Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1. Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook
 Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Earth s Climate Patterns
 Earth s Climate Patterns Reading: Chapter 17, GSF 10/2/09 Also Jackson (linked on course web site) 1 What aspects of climate affect plant distributions? Climate: long-term distribution of weather in an
Earth s Climate Patterns Reading: Chapter 17, GSF 10/2/09 Also Jackson (linked on course web site) 1 What aspects of climate affect plant distributions? Climate: long-term distribution of weather in an
Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 2: Tropical General Circulation
 Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 2: Tropical General Circulation DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1-28-16 Today What determines
Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 2: Tropical General Circulation DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1-28-16 Today What determines
Atmospheric Circulation
 Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Atmospheric Circulation Introductory Oceanography Instructor: Ray Rector Atmospheric Circulation Key Topics Composition and Structure Solar Heating and Convection The Coriolis Effect Global Wind Patterns
Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere
 Climate Dynamics (Summer Semester 2017) J. Mülmenstädt Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere Reference Hartmann, Global Physical Climatology (1994), Ch. 2, 3, 6 Peixoto and
Climate Dynamics (Summer Semester 2017) J. Mülmenstädt Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere Reference Hartmann, Global Physical Climatology (1994), Ch. 2, 3, 6 Peixoto and
The role of land-sea contrast in the circulation response to seasonal insolation and global warming
 The role of land-sea contrast in the circulation response to seasonal insolation and global warming Tiffany A. Shaw Columbia University University of Chicago Thanks to A. Voigt, I Simpson, R. Seager What
The role of land-sea contrast in the circulation response to seasonal insolation and global warming Tiffany A. Shaw Columbia University University of Chicago Thanks to A. Voigt, I Simpson, R. Seager What
General Atmospheric Circulation
 General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
Radiative-Convective Models. The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation. Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1
 Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes
 Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes Iracema Fonseca de Albuquerque Cavalcanti National Institute for Space Research INPE Modes of variability- preferred patterns of variability.
Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes Iracema Fonseca de Albuquerque Cavalcanti National Institute for Space Research INPE Modes of variability- preferred patterns of variability.
Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Science 2 nd Edition: Article Template
 Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Science 2 nd Edition: Article Template Hadley Circulation (revised from I N James) Jian Lu 4400 University Drive MS 2B3 George Mason University Fairfax, VA 20330 USA E- mail:
Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Science 2 nd Edition: Article Template Hadley Circulation (revised from I N James) Jian Lu 4400 University Drive MS 2B3 George Mason University Fairfax, VA 20330 USA E- mail:
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate
 Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations. Cristiana Stan
 Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Isentropic Analysis. Much of this presentation is due to Jim Moore, SLU
 Isentropic Analysis Much of this presentation is due to Jim Moore, SLU Utility of Isentropic Analysis Diagnose and visualize vertical motion - through advection of pressure and system-relative flow Depict
Isentropic Analysis Much of this presentation is due to Jim Moore, SLU Utility of Isentropic Analysis Diagnose and visualize vertical motion - through advection of pressure and system-relative flow Depict
The Effective Static Stability Experienced by Eddies in a Moist Atmosphere
 JANUARY 2011 O G O R M A N 75 The Effective Static Stability Experienced by Eddies in a Moist Atmosphere PAUL A. O GORMAN Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts (Manuscript received
JANUARY 2011 O G O R M A N 75 The Effective Static Stability Experienced by Eddies in a Moist Atmosphere PAUL A. O GORMAN Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts (Manuscript received
AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY
 AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences EARLY ONLINE RELEASE This is a preliminary PDF of the author-produced manuscript that has been peer-reviewed and accepted for publication.
AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences EARLY ONLINE RELEASE This is a preliminary PDF of the author-produced manuscript that has been peer-reviewed and accepted for publication.
Atmospheric circulation
 Atmospheric circulation Trade winds http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2002/10apr_hawaii/ Atmosphere (noun) the envelope of gases (air) surrounding the earth or another planet Dry air:
Atmospheric circulation Trade winds http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2002/10apr_hawaii/ Atmosphere (noun) the envelope of gases (air) surrounding the earth or another planet Dry air:
The Relative Humidity in an Isentropic Advection Condensation Model: Limited Poleward Influence and Properties of Subtropical Minima
 The Relative Humidity in an Isentropic Advection Condensation Model: Limited Poleward Influence and Properties of Subtropical Minima The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share
The Relative Humidity in an Isentropic Advection Condensation Model: Limited Poleward Influence and Properties of Subtropical Minima The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
The Interannual Relationship between the Latitude of the Eddy-Driven Jet and the Edge of the Hadley Cell
 15 JANUARY 2011 K A N G A N D P O L V A N I 563 The Interannual Relationship between the Latitude of the Eddy-Driven Jet and the Edge of the Hadley Cell SARAH M. KANG Department of Applied Physics and
15 JANUARY 2011 K A N G A N D P O L V A N I 563 The Interannual Relationship between the Latitude of the Eddy-Driven Jet and the Edge of the Hadley Cell SARAH M. KANG Department of Applied Physics and
Midlatitude moisture contribution to recent Arctic tropospheric summertime variability
 Generated using V3.1.1 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! Midlatitude moisture contribution to recent Arctic tropospheric summertime variability
Generated using V3.1.1 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! Midlatitude moisture contribution to recent Arctic tropospheric summertime variability
Momentum Balance and Eliassen Palm Flux on Moist Isentropic Surfaces
 MARCH 216 Y A M A D A A N D P A U L U I S 1293 Momentum Balance and Eliassen Palm Flux on Moist Isentropic Surfaces RAY YAMADA Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York,
MARCH 216 Y A M A D A A N D P A U L U I S 1293 Momentum Balance and Eliassen Palm Flux on Moist Isentropic Surfaces RAY YAMADA Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York,
Reconstruction of Thermodynamic Cycles in a High-Resolution Simulation of a Hurricane
 OCTOBER 2017 P A U L U I S A N D Z H A N G 3367 Reconstruction of Thermodynamic Cycles in a High-Resolution Simulation of a Hurricane OLIVIER M. PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New
OCTOBER 2017 P A U L U I S A N D Z H A N G 3367 Reconstruction of Thermodynamic Cycles in a High-Resolution Simulation of a Hurricane OLIVIER M. PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature
 Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Influences on Insolation Absorption Reflection/Scattering Transmission 1 Absorption An absorber gains energy
Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Influences on Insolation Absorption Reflection/Scattering Transmission 1 Absorption An absorber gains energy
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why
 Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Seamless Poleward Atmospheric Energy Transports and Implications for the Hadley Circulation
 3706 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Seamless Poleward Atmospheric Energy Transports and Implications for the Hadley Circulation KEVIN E. TRENBERTH AND DAVID P. STEPANIAK National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
3706 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Seamless Poleward Atmospheric Energy Transports and Implications for the Hadley Circulation KEVIN E. TRENBERTH AND DAVID P. STEPANIAK National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
- tornadoes. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. - cyclones and anti-cyclones. -tropical storms. -Storm surge
 (1 of 16) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - cyclones and anti-cyclones - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 16) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their
(1 of 16) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - cyclones and anti-cyclones - tornadoes -tropical storms -Storm surge (2 of 16) Introduction Previously, We talked about fronts and their
CHAPTER 2 - ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION & AIR/SEA INTERACTION
 Chapter 2 - pg. 1 CHAPTER 2 - ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION & AIR/SEA INTERACTION The atmosphere is driven by the variations of solar heating with latitude. The heat is transferred to the air by direct absorption
Chapter 2 - pg. 1 CHAPTER 2 - ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION & AIR/SEA INTERACTION The atmosphere is driven by the variations of solar heating with latitude. The heat is transferred to the air by direct absorption
Isentropic Analysis of Convective Motions
 NOVEMBER 213 P A U L U I S A N D M R O W I E C 3673 Isentropic Analysis of Convective Motions OLIVIER M. PAULUIS Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science, Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York
NOVEMBER 213 P A U L U I S A N D M R O W I E C 3673 Isentropic Analysis of Convective Motions OLIVIER M. PAULUIS Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science, Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York
Tropical Meridional Circulations: The Hadley Cell
 Tropical Meridional Circulations: The Hadley Cell Introduction Throughout much of the previous sections, we have alluded to but not fully described the mean meridional overturning circulation of the tropics
Tropical Meridional Circulations: The Hadley Cell Introduction Throughout much of the previous sections, we have alluded to but not fully described the mean meridional overturning circulation of the tropics
Teleconnections between the tropical Pacific and the Amundsen- Bellinghausens Sea: Role of the El Niño/Southern Oscillation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006386, 2006 Teleconnections between the tropical Pacific and the Amundsen- Bellinghausens Sea: Role of the El Niño/Southern Oscillation Tom
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006386, 2006 Teleconnections between the tropical Pacific and the Amundsen- Bellinghausens Sea: Role of the El Niño/Southern Oscillation Tom
ATMO 551a Fall The Carnot Cycle
 What is a arnot ycle and Why do we care The arnot ycle arnot was a French engineer who was trying to understand how to extract usable mechanical work from a heat engine, that is an engine where a gas or
What is a arnot ycle and Why do we care The arnot ycle arnot was a French engineer who was trying to understand how to extract usable mechanical work from a heat engine, that is an engine where a gas or
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments
 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
GEO1010 tirsdag
 GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
Dynamics of the Atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
The effective static stability experienced by eddies in a moist atmosphere. Paul A. O Gorman
 Generated using V3. of the official AMS LATEX template The effective static stability experienced by eddies in a moist atmosphere Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Generated using V3. of the official AMS LATEX template The effective static stability experienced by eddies in a moist atmosphere Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts
PBL variability in the SEP during VOCALS-REx and its connection to synoptic and planetary scales
 PBL variability in the SEP during VOCALS-REx and its connection to synoptic and planetary scales Thomas Toniazzo S. Abel, R. Wood, C.R. Mechoso, G. Allen and L.C. Shaffrey Miami 22/3/2011 Toniazzo et al.
PBL variability in the SEP during VOCALS-REx and its connection to synoptic and planetary scales Thomas Toniazzo S. Abel, R. Wood, C.R. Mechoso, G. Allen and L.C. Shaffrey Miami 22/3/2011 Toniazzo et al.
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
The Hadley and Walker Circulation Changes in Global Warming Conditions Described by Idealized Atmospheric Simulations
 The Hadley and Walker Circulation Changes in Global Warming Conditions Described by Idealized Atmospheric Simulations Guillaume Gastineau, Laurent Li, Hervé Le Treut To cite this version: Guillaume Gastineau,
The Hadley and Walker Circulation Changes in Global Warming Conditions Described by Idealized Atmospheric Simulations Guillaume Gastineau, Laurent Li, Hervé Le Treut To cite this version: Guillaume Gastineau,
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine. The Atmospheric Heat Engine. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 1 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 1 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 1 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 1 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS continued (Part II) pp in Class Notes
 Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS continued (Part II) pp 61-67 in Class Notes To drive the circulation, the initial source of energy is from the Sun: Not to scale! EARTH- SUN Relationships 4 Things to Know
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS continued (Part II) pp 61-67 in Class Notes To drive the circulation, the initial source of energy is from the Sun: Not to scale! EARTH- SUN Relationships 4 Things to Know
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation
 The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
Topic # 12 How Climate Works
 Topic # 12 How Climate Works A Primer on How the Energy Balance Drives Atmospheric & Oceanic Circulation, Natural Climatic Processes pp 63-68 in Class Notes How do we get energy from this........ to drive
Topic # 12 How Climate Works A Primer on How the Energy Balance Drives Atmospheric & Oceanic Circulation, Natural Climatic Processes pp 63-68 in Class Notes How do we get energy from this........ to drive
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics
 Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
Winds and Currents in the Oceans
 Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Energy of Midlatitude Transient Eddies in Idealized Simulations of Changed Climates
 15 NOVEMBER 2008 O G O R M A N A N D S C H N E I D E R 5797 Energy of Midlatitude Transient Eddies in Idealized Simulations of Changed Climates PAUL A. O GORMAN* AND TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
15 NOVEMBER 2008 O G O R M A N A N D S C H N E I D E R 5797 Energy of Midlatitude Transient Eddies in Idealized Simulations of Changed Climates PAUL A. O GORMAN* AND TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005
 ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
Introduction to tropical meteorology and deep convection
 Introduction to tropical meteorology and deep convection TMD Lecture 1 Roger K. Smith University of Munich A satpix tour of the tropics The zonal mean circulation (Hadley circulation), Inter- Tropical
Introduction to tropical meteorology and deep convection TMD Lecture 1 Roger K. Smith University of Munich A satpix tour of the tropics The zonal mean circulation (Hadley circulation), Inter- Tropical
8/21/08. Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 4: Equatorial Wave Dynamics. Moisture and Equatorial Waves
 Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 4: Equatorial Wave Dynamics D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P
Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 4: Equatorial Wave Dynamics D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P
MAR 110 LECTURE #9 Earth s Heat Budget / Atmosphere Dynamics
 MAR 110: Lecture 9 Outline Heat Budget / Atmosphere Dynamics 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #9 Earth s Heat Budget / Atmosphere Dynamics External Energy Source-the Sun The portion of the sun s energy that is intercepted
MAR 110: Lecture 9 Outline Heat Budget / Atmosphere Dynamics 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #9 Earth s Heat Budget / Atmosphere Dynamics External Energy Source-the Sun The portion of the sun s energy that is intercepted
Isentropic Analysis of a Simulated Hurricane
 VOLUME 73 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S MAY 216 Isentropic Analysis of a Simulated Hurricane AGNIESZKA A. MROWIEC Center for Climate Systems Research, Columbia University,
VOLUME 73 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S MAY 216 Isentropic Analysis of a Simulated Hurricane AGNIESZKA A. MROWIEC Center for Climate Systems Research, Columbia University,
PHY2504 Course Project: Zonal Momentum Balance, Entropy Transport, and the Tropopause
 PHY2504 Course Project: Zonal Momentum Balance, Entropy Transport, and the Tropopause Andre R. Erler April 21 th, 2009 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Zonal Momentum Balance in Isentropic Mass Flux 4 2.1
PHY2504 Course Project: Zonal Momentum Balance, Entropy Transport, and the Tropopause Andre R. Erler April 21 th, 2009 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Zonal Momentum Balance in Isentropic Mass Flux 4 2.1
Surface Winds along Eastern Boundary Upwelling Systems in Future Climate Scenarios
 Surface Winds along Eastern Boundary Upwelling Systems in Future Climate Scenarios René D. Garreaud and Mark Falvey Department of Geophysics Universidad de Chile Outline EBUS Climate background Future
Surface Winds along Eastern Boundary Upwelling Systems in Future Climate Scenarios René D. Garreaud and Mark Falvey Department of Geophysics Universidad de Chile Outline EBUS Climate background Future
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for. monsoon research. H. Annamalai
 Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes
 Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman) Water vapor dynamics in warming
Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman) Water vapor dynamics in warming
Radiative Control of Deep Tropical Convection
 Radiative Control of Deep Tropical Convection Dennis L. Hartmann with collaboration of Mark Zelinka and Bryce Harrop Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Outline Review Tropical
Radiative Control of Deep Tropical Convection Dennis L. Hartmann with collaboration of Mark Zelinka and Bryce Harrop Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Outline Review Tropical
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The Tropical Response to Extratropical Thermal Forcing in an Idealized GCM: The Importance of Radiative Feedbacks and Convective Parameterization
 2812 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 66 The Tropical Response to Extratropical Thermal Forcing in an Idealized GCM: The Importance of Radiative Feedbacks and Convective
2812 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 66 The Tropical Response to Extratropical Thermal Forcing in an Idealized GCM: The Importance of Radiative Feedbacks and Convective
Weather Systems. Section
 Section 1 12.2 Objectives Compare and contrast the three major wind systems. Identify four types of fronts. Distinguish between highand low-pressure systems. Review Vocabulary convection: the transfer
Section 1 12.2 Objectives Compare and contrast the three major wind systems. Identify four types of fronts. Distinguish between highand low-pressure systems. Review Vocabulary convection: the transfer
