ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE HEAVIEST JUNE PRECIPITATION IN SOUTHEASTERN CHINA SINCE 1961
|
|
|
- Tyler Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE HEAVIEST JUNE PRECIPITATION IN SOUTHEASTERN CHINA SINCE 1961 Ying Sun, Siyan Dong, Xuebin Zhang, Peter Stott, and Ting Hu Anthropogenic influence has increased the chance of an extreme heavy precipitation event like that in June 2017 in southeastern China by about twofold, from a 0.6% probability to a 1.2% probability. INTRODUCTION. In June 2017, southeastern China experienced heavy and long-lasting precipitation. The total precipitation amount was the highest on record since 1961 (Fig. 1) and was about 60% more than the average for June in the region. The normalized precipitation departure exceeds 3.0 sigma from the mean. In Hunan province, which is located in central southeastern China, the persistent heavy rainfall at the end of June affected more than 7.8 million people, with 34 fatalities and about 0.8 million people displaced. The affected area of the crops was 605,000 hectares, with a total of 116,000 hectares without harvest. A total of 32,000 houses collapsed and 41,000 were severely damaged. The direct economic loss was billion Chinese Yuan (CMA 2017; NCC 2017). It is therefore important to provide a timely answer as to the reasons for this heavy precipitation and if it is related to human influence. AFFILIATIONS: Sun National Climate Center, Laboratory for Climate Studies, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing, and Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China; Dong and Hu National Climate Center, Laboratory for Climate Studies, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing, China; Zhang Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada, Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter, United Kingdom CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Ying Sun, sunying@cma.gov.cn The abstract for this article can be found in this issue, following the table of contents. DOI: /BAMS-D A supplement to this article is available online ( /BAMS-D ) American Meteorological Society For information regarding reuse of this content and general copyright information, consult the AMS Copyright Policy. Human-induced increases in greenhouse gases have contributed to the observed intensification of heavy precipitation events in many land areas (Zhang et al. 2007; Min et al. 2011; Zhang et al. 2013). Several studies have investigated the influence of external forcing on some heavy precipitation events in China (e.g., Zhou et al. 2013; Burke et al. 2016). In one case, human influence may have contributed to the occurrence probability of heavy precipitation in southeastern China in May (Burke et al. 2016) whereas in another case there was no clear evidence of human influence of heavy precipitation in northern China (Zhou et al. 2013). There is also evidence of human influence that results in a shift toward heavy precipitation over eastern China (Ma et al. 2017). Here, we use outputs from the large ensemble simulations conducted with the Canadian Earth System Model version 2 (CanESM2; Arora et al. 2011) to investigate possible human influence on heavy precipitation like the June 2017 precipitation event in southeastern China. DATA AND METHODS. The precipitation event mainly covered the area N, E (box in Fig. 1). We use gauge observations of precipitation (SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_DAY_V3.0; that have been collected and rigorously quality controlled (Cao et al. 2016) at the China National Meteorological Information Center (NMIC). Since most Chinese stations were established after the late 1950s and the data become reliable and continuous after 1961, we use the station data in the region at about 600 stations for the period We divide the region into multiple grid boxes at resolution, roughly consistent with the CanESM2 model grids. We average station precipitation amount within each grid. These gridded values are then averaged to obtain regional S1
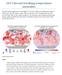
2 Fig. 1. Observed June percentage precipitation anomaly (PPA). (a) PPA (in percentage, relative to average) in June 2017 in China. The region defined as southeastern China is represented by the boxed areas. (b) Regional average of PPA in June in southeastern China during averages that are finally used to compute the percentage precipitation anomaly (PPA) relative to the base period. CanESM2 was run at T63 resolution (~2.8 longitude/latitude) and included interactive atmosphere, ocean, sea ice, land, and carbon cycle components (Arora et al. 2011). Two large initial-condition ensembles, each consisting of 50 simulations, were randomly initiated from the conditions on 1 January Two sets of experiments forced with the historical anthropogenic (greenhouse gases combined with aerosols, land use changes, etc.) and natural forcing (ALL) and with natural forcing only (NAT) were conducted. The ALL experiments finished at the end of 2004 and the RCP8.5 scenario was used to extend the ALL simulations from January 2005 onward (Fyfe et al. 2017). The NAT experiments were driven by the solar and volcanic forcings from 1950 to The solar forcing for all years after 2005 replicated the forcing data from the last solar cycle observed before 2006 and there is no explosive volcanoes forcing after S2 DECEMBER 2018 The CanESM2 has a relatively high transient climate response (TCR) of 2.4 C (IPCC 2013), leading to higher global mean surface temperature (GMST) increase than the observations. To take this higher sensitivity into account and also make the results comparable with other models, we consider simulation over a 20-yr period ( ) for which the CanESM2 simulated mean GMST is 1 C above the preindustrial level as simulated for the current climate. This is because Earth s surface has warmed about 1 C by In the following, the event probabilities in model simulations are computed based on data from the period of Our analyses include the following steps: 1) Compute the regional percentage precipitation anomaly (PPA) in June for observations and for individual ALL and NAT forcing runs during ) Estimate the probability (P OBS ) for the observed June 2017 precipitation in the observational data using an empirical probability formula (Bonsal et al. 2001). This method is easy to implement and does not assume a probability distribution for the data. 3) Pool the 51 years ( ) of data that occur before GMST rises by 1 C from each of the 50 ALL runs together and then estimate the PPA magnitude (PPA ALL ) in the pooled data corresponding to the event probability P OBS, using the same probability formula. 4) Pool the 20 years ( ) of data corresponding to the current climate from each of the 50 NAT runs and then estimate the probability of PPA ALL in NAT simulations (P NAT ). 5) Compute the risk ratio RR = P ALL /P NAT. 6) Use a bootstrap method to estimate the confidence interval of the risk ratio. This involves three steps: (a) draw 50 samples of 57- yr data from the 50 ALL runs with replacement and then compute PPA ALL ; (b) draw 50 samples of 20 years of data from the 50 NAT runs with replacement and then compute P NAT ; and (c) compute risk ratio from the bootstrapped samples and repeat the bootstrap
3 Fig. 2. Observed and simulated regional precipitation anomaly in June and relevant statistics. (a) Observed and simulated PPA for southeastern China. The black line shows the observations while the red, blue, and orange lines display the multimodel ensemble mean under ALL, NAT, and RCP8.5 forcings, respectively. Shadings indicate the ensemble spread by the 50 members. (b) Histograms of observed (black) and simulated percentage precipitation anomalies for driven by ALL (purple) and NAT (blue) forcings. (c) Histograms of percentage precipitation anomaly simulated by CanESM2 under ALL (red) and RCP8.5 scenario for the future periods in (brown), (light blue), and (orange). procedure 1000 times. For the future climate under RCP8.5 scenario, the three time periods , , and are selected to compute the occurrence probability of the events like 2017 PPA ALL. The P RCP can be obtained with the same method as the probability calculation P NAT. Then the risk ratios for future climate are calculated as compared with the climate without anthropogenic forcing under NAT forcing (P RCP /P NAT ) and with the current observational world (P RCP /P OBS ). RESULTS. Figure 1a shows that the June 2017 anomalous heavy precipitation was centered in southeastern China, especially in the region south of the Yangtze River Valley. Other areas in China experienced below-normal precipitation during this month. In the studied region, the percentage precipitation anomaly in many stations (135 stations; 22% in the studied region) is higher than 100% with some stations experiencing a record-breaking amount of precipitation. The three stations with the highest June PPA (233%, 217%, and 210%) were all located in Hunan Province, where the most serious flooding disaster caused various problems for human life and society. Figure 1b shows the regional mean series for southeastern China. It is apparent that June has been very wet since the early 1990s and the June 2017 was the wettest since 1961, with a PPA OBS value of 61.9%. The probability for a 2017-like event is 1.2% (P OBS = 0.012) in the observational data, which corresponds to 1-in-83-yr event. The second largest PPA OBS occurred in 1998 with a PPA value of 57.9%. Figure 2a shows the observed (black) and simulated June precipitation anomalies under ALL (red), NAT S3
4 (blue), and RCP8.5 (orange) in southeastern China in and the years after 2018 till The simulated June precipitation amount mm ( mm; Fig. ES1) is smaller than the observation (247.4 mm), but the standard deviation of June precipitation in the simulation (20.5 mm, with a 5% 95% range of mm) is more comparable with the observed one (20.9 mm). This means that the normalized PPA would have slightly larger variations in the models than those observed. Figure 2a shows that the model results under ALL and NAT forcings cover the observed range. The ensemble mean values under ALL and NAT forcing are small, suggesting that the response of precipitation to external forcing is still very small compared with the natural internal variability. Figure 2b shows the PDF distribution of observed and simulated PPA. The observed data slightly skew rightward but this cannot be seen in the models. For the observed 2017-like event probability P OBS = 0.012, the corresponding PPA magnitude under ALL forcing (PPA ALL ) is 46.5% [90% confidence interval (CI): 44.3% 52.3%]. The probability of a PPA of 46.5% under NAT forcing is 0.6% (p = 0.006) (90% CI: ), which is a 1-in yr event (90% CI: yr). Correspondingly, we can estimate that the risk ratio (RR) is 2.1 (90% CI: ), indicating that human-induced climate change may have increased the probability of a 2017-like event by about twofold. Under the future RCP8.5 scenario, the ensemble mean of regional percentage precipitation anomalies simulated by CanESM2 show a clear increasing trend (Fig. 2a). Additionally, the PDFs of PPA in the early ( ), middle ( ), and late twenty-first century ( ) clearly shift rightward (Fig. 2c). The distribution becomes wider and shorter compared with the observation, especially in The probabilities of PPA ALL in three future stages are (90% CI: ), (90% CI: ), and (90% CI: ), respectively. These correspond to 1-in-22.6-yr (90% CI: yr), 1-in-11.3-yr (90% CI: yr), and 1-in-5.1-yr (90% CI: yr) events. Compared with the NAT experiments, the estimated risk ratios are 7.6 (90% CI: ), 15.2 (90% CI: ), and 33.8 (90% CI: ). If we compare the increased probability of such an event with those that occurred in the current observational world (P OBS ), the risk ratio would be 3.7 (90% CI: ), 7.3 (90% CI: ), and 16.3 (90% CI: ) under the influence of future increased human activities. All these indicate that the occurrence risk of 2017-like events will increase with the increased anthropogenic forcing. As CanESM2 has larger sensitivities, the projected changes would be larger than median projection by CMIP5 models. The projected changes would also be less under other RCP scenarios with various mitigation efforts such as RCP4.5 or RCP2.6. CONCLUSIONS. The human influence on the heaviest June precipitation since 1961 in southeastern China is analyzed with the observational and CanESM2 model data. The results show that the probability of extreme June precipitation that is as rare as or rarer than the June 2017 event in the ALL simulations has increased by about twofold when compared with the NAT simulations. This indicates that the anthropogenic influence may have increased the chance for such an event happening. Additionally, the model suggests that increases in regional precipitation will become more likely and probabilities for a similar event are projected to increase progressively more with future anthropogenic warming. These future projections provide additional support for the conclusion that the occurrence probability of such heavy precipitation may already be increasing due to human influence. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS. Y.S., S. D., and T. H. are supported by China funding agencies through multiple grants: China 2018YFA , NSFC and , and CCSF PAS was supported by the UK China Research and Innovation Partnership Fund through the Met Office Climate Science for Service Partnership (CSSP) China as part of the Newton Fund, the EUCLEIA project funded by the European Union s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/ ) under Grant Agreement , and the Joint UK DECCBEIS/Defra Met Office Hadley Centre Climate Programme (GA01101). REFERENCES Arora, V. K., and Coauthors, 2011: Carbon emission limits required to satisfy future representative concentration pathways of greenhouse gases. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L05805, Bonsal, B. R., X. Zhang, L. A. Vincent, and W. D. Hogg, 2001: Characteristics of daily and extreme temperatures over Canada. J. Climate, 14, , doi.org/ / (2001)014<1959:codae T>2.0.CO;2. Burke, C., P. Stott, Y. Sun, and A. Ciavarella, 2016: Attribution of extreme rainfall in South East China during May 2015 [in Explaining Extremes of 2015 from a Climate Perspective ]. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 97, S92 S96, Cao, L., Y. Zhu, G. Tang, F. Yuan, and Z. Yan, 2016: Climatic warming in China according to a homogenized S4 DECEMBER 2018
5 data set from 2419 stations. Int. J. Climatol., 36, , CMA, 2017: China Climate Bulletin 2017 (in Chinese with English abstract). China Meteorological Administration, 54 pp., /auto13139/201801/t _ html. Fyfe, J. C., and Coauthors, 2017: Large near-term projected snowpack loss over the western United States. Nat. Commun., 8, 14996, /ncomms IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. T. F. Stocker et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, 1535 pp. Ma, S., and Coauthors, 2017: Detectable anthropogenic shift toward heavy precipitation over eastern China. J. Climate, 30, , /JCLI-D Min, S.-K., X. B. Zhang, F. W. Zwiers, and G. C. Hegerl, 2011: Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature, 470, , NCC, 2017: China Monthly Climate Bulletin for June National Climate Center of China Meteorological Administration, 18 pp, /influ/moni_china.php. Zhang, X., F. W. Zwiers, G. C. Hegerl, F. H. Lambert, N. P. Gillett, S. Solomon, P. Stott, and T. Nozawa, 2007: Detection of human influence on twentieth-century precipitation trends. Nature, 448, , doi.org/ /nature06025., H. Wan, F. W. Zwiers, G. C. Hegerl, and S.-K. Min, 2013: Attributing intensification of precipitation extremes to human influence. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, , Zhou, T. J., F. F. Song, R. P. Lin, X. L. Chen, and X. Y. Chen, 2013: The 2012 North China floods: Explaining an extreme rainfall event in the context of a longer-term drying tendency [in Explaining Extreme Events of 2012 from a Climate Perspective ]. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 94, S49 S51, S5
18. ATTRIBUTION OF EXTREME RAINFALL IN SOUTHEAST CHINA DURING MAY 2015
 18. ATTRIBUTION OF EXTREME RAINFALL IN SOUTHEAST CHINA DURING MAY 2015 Claire Burke, Peter Stott, Ying Sun, and Andrew Ciavarella Anthropogenic climate change increased the probability that a short-duration,
18. ATTRIBUTION OF EXTREME RAINFALL IN SOUTHEAST CHINA DURING MAY 2015 Claire Burke, Peter Stott, Ying Sun, and Andrew Ciavarella Anthropogenic climate change increased the probability that a short-duration,
22. DO CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF YANGTZE RIVER EXTREME RAINFALL?
 22. DO CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF YANGTZE RIVER EXTREME RAINFALL? Xing Yuan, Shanshan Wang, and Zeng-Zhen Hu Anthropogenic climate change has increased the risk of 216 Yangtze River
22. DO CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF YANGTZE RIVER EXTREME RAINFALL? Xing Yuan, Shanshan Wang, and Zeng-Zhen Hu Anthropogenic climate change has increased the risk of 216 Yangtze River
19. RECORD-BREAKING HEAT IN NORTHWEST CHINA IN JULY 2015: ANALYSIS OF THE SEVERITY AND UNDERLYING CAUSES
 19. RECORD-BREAKING HEAT IN NORTHWEST CHINA IN JULY 2015: ANALYSIS OF THE SEVERITY AND UNDERLYING CAUSES Chiyuan Miao, Qiaohong Sun, Dongxian Kong, and Qingyun Duan The record-breaking heat over northwest
19. RECORD-BREAKING HEAT IN NORTHWEST CHINA IN JULY 2015: ANALYSIS OF THE SEVERITY AND UNDERLYING CAUSES Chiyuan Miao, Qiaohong Sun, Dongxian Kong, and Qingyun Duan The record-breaking heat over northwest
ANTHROPOGENIC CONTRIBUTION TO THE 2017 EARLIEST SUMMER ONSET IN SOUTH KOREA
 ANTHROPOGENIC CONTRIBUTION TO THE 2017 EARLIEST SUMMER ONSET IN SOUTH KOREA Seung-Ki Min, Yeon-Hee Kim, In-Hong Park, Donghyun Lee, Sarah Sparrow, David Wallom, and Dáithí Stone Large-ensemble RCM and
ANTHROPOGENIC CONTRIBUTION TO THE 2017 EARLIEST SUMMER ONSET IN SOUTH KOREA Seung-Ki Min, Yeon-Hee Kim, In-Hong Park, Donghyun Lee, Sarah Sparrow, David Wallom, and Dáithí Stone Large-ensemble RCM and
20. EXTREME RAINFALL (R20MM, RX5DAY) IN YANGTZE HUAI, CHINA, IN JUNE JULY 2016: THE ROLE OF ENSO AND ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE
 20. EXTREME RAINFALL (R20MM, RX5DAY) IN YANGTZE HUAI, CHINA, IN JUNE JULY 2016: THE ROLE OF ENSO AND ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE Qiaohong Sun and Chiyuan Miao Both the 2015/16 strong El Niño and anthropogenic
20. EXTREME RAINFALL (R20MM, RX5DAY) IN YANGTZE HUAI, CHINA, IN JUNE JULY 2016: THE ROLE OF ENSO AND ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE Qiaohong Sun and Chiyuan Miao Both the 2015/16 strong El Niño and anthropogenic
ATTRIBUTION OF THE PERSISTENT SPRING SUMMER HOT AND DRY EXTREMES OVER NORTHEAST CHINA IN 2017
 ATTRIBUTION OF THE PERSISTENT SPRING SUMMER HOT AND DRY EXTREMES OVER NORTHEAST CHINA IN 2017 Shanshan Wang, Xing Yuan, and Renguang Wu Anthropogenic climate change has increased the risk of 2017 northeast
ATTRIBUTION OF THE PERSISTENT SPRING SUMMER HOT AND DRY EXTREMES OVER NORTHEAST CHINA IN 2017 Shanshan Wang, Xing Yuan, and Renguang Wu Anthropogenic climate change has increased the risk of 2017 northeast
Future Changes of Drought and Flood Events in China under a Global Warming Scenario
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2013, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 8 13 Future Changes of Drought and Flood Events in China under a Global Warming Scenario CHEN Huo-Po 1, SUN Jian-Qi 1, and CHEN Xiao-Li 2 1
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2013, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 8 13 Future Changes of Drought and Flood Events in China under a Global Warming Scenario CHEN Huo-Po 1, SUN Jian-Qi 1, and CHEN Xiao-Li 2 1
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA
 27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
23. HUMAN INFLUENCE ON THE RECORD-BREAKING COLD EVENT IN JANUARY OF 2016 IN EASTERN CHINA
 23. HUMAN INFLUENCE ON THE RECORD-BREAKING COLD EVENT IN JANUARY OF 2016 IN EASTERN CHINA Cheng Qian, Jun Wang, Siyan Dong, Hong Yin, Claire Burke, Andrew Ciavarella, Buwen Dong, Nicolas Freychet, Fraser
23. HUMAN INFLUENCE ON THE RECORD-BREAKING COLD EVENT IN JANUARY OF 2016 IN EASTERN CHINA Cheng Qian, Jun Wang, Siyan Dong, Hong Yin, Claire Burke, Andrew Ciavarella, Buwen Dong, Nicolas Freychet, Fraser
S16. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 2014 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT
 S6. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 204 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT Chris Funk, Shraddhanand Shukla, Andy Hoell, and Ben Livneh This document is a supplement
S6. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 204 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT Chris Funk, Shraddhanand Shukla, Andy Hoell, and Ben Livneh This document is a supplement
Operational event attribution
 Operational event attribution Peter Stott, NCAR, 26 January, 2009 August 2003 Events July 2007 January 2009 January 2009 Is global warming slowing down? Arctic Sea Ice Climatesafety.org climatesafety.org
Operational event attribution Peter Stott, NCAR, 26 January, 2009 August 2003 Events July 2007 January 2009 January 2009 Is global warming slowing down? Arctic Sea Ice Climatesafety.org climatesafety.org
9. THE 2015 EXTREME DROUGHT IN WESTERN CANADA
 9. THE 2015 EXTREME DROUGHT IN WESTERN CANADA Kit Szeto, Xuebin Zhang, Robert Edward White, and Julian Brimelow Analysis results indicate that the 2015 extreme drought in western Canada was likely an outcome
9. THE 2015 EXTREME DROUGHT IN WESTERN CANADA Kit Szeto, Xuebin Zhang, Robert Edward White, and Julian Brimelow Analysis results indicate that the 2015 extreme drought in western Canada was likely an outcome
ANTHROPOGENIC WARMING HAS SUBSTANTIALLY INCREASED THE LIKELIHOOD OF JULY 2017 LIKE HEAT WAVES OVER CENTRAL EASTERN CHINA
 ANTHROPOGENIC WARMING HAS SUBSTANTIALLY INCREASED THE LIKELIHOOD OF JULY 2017 LIKE HEAT WAVES OVER CENTRAL EASTERN CHINA Yang Chen, Wei Chen, Qin Su, Feifei Luo, Sarah Sparrow, Fangxing Tian, Buwen Dong,
ANTHROPOGENIC WARMING HAS SUBSTANTIALLY INCREASED THE LIKELIHOOD OF JULY 2017 LIKE HEAT WAVES OVER CENTRAL EASTERN CHINA Yang Chen, Wei Chen, Qin Su, Feifei Luo, Sarah Sparrow, Fangxing Tian, Buwen Dong,
Anthropogenic warming of central England temperature
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 7: 81 85 (2006) Published online 18 September 2006 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).136 Anthropogenic warming of central England temperature
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 7: 81 85 (2006) Published online 18 September 2006 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).136 Anthropogenic warming of central England temperature
2. MULTIMODEL ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON RECORD GLOBAL AND REGIONAL WARMTH DURING 2015
 2. MULTIMODEL ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON RECORD GLOBAL AND REGIONAL WARMTH DURING 2015 Jonghun Kam, Thomas R. Knutson, Fanrong Zeng, and Andrew T. Wittenberg In 2015, record warm surface
2. MULTIMODEL ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON RECORD GLOBAL AND REGIONAL WARMTH DURING 2015 Jonghun Kam, Thomas R. Knutson, Fanrong Zeng, and Andrew T. Wittenberg In 2015, record warm surface
7. CMIP5 MODEL-BASED ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON HIGHLY ANOMALOUS ARCTIC WARMTH DURING NOVEMBER DECEMBER 2016
 7. CMIP5 MODEL-BASED ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON HIGHLY ANOMALOUS ARCTIC WARMTH DURING NOVEMBER DECEMBER 2016 Jonghun Kam, Thomas R. Knutson, Fanrong Zeng, and Andrew T. Wittenberg According
7. CMIP5 MODEL-BASED ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON HIGHLY ANOMALOUS ARCTIC WARMTH DURING NOVEMBER DECEMBER 2016 Jonghun Kam, Thomas R. Knutson, Fanrong Zeng, and Andrew T. Wittenberg According
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
THE EXTREMELY WET MARCH OF 2017 IN PERU
 THE EXTREMELY WET MARCH OF 2017 IN PERU Nikolaos Christidis, Richard A. Betts, and Peter A. Stott While extreme rainfall of March 2017 in Peru was favored by the anomalously warm ocean, human influence
THE EXTREMELY WET MARCH OF 2017 IN PERU Nikolaos Christidis, Richard A. Betts, and Peter A. Stott While extreme rainfall of March 2017 in Peru was favored by the anomalously warm ocean, human influence
Current and future climate of the Cook Islands. Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program
 Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Penrhyn Pukapuka Nassau Suwarrow Rakahanga Manihiki N o r t h e r n C o o k I s l a nds S o u t h e Palmerston r n C o o k I s l
Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Penrhyn Pukapuka Nassau Suwarrow Rakahanga Manihiki N o r t h e r n C o o k I s l a nds S o u t h e Palmerston r n C o o k I s l
Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, UK.
 Temperature Extremes, the Past and the Future. S Brown, P Stott, and R Clark Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, UK. Tel: +44 (0)1392 886471 Fax
Temperature Extremes, the Past and the Future. S Brown, P Stott, and R Clark Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, UK. Tel: +44 (0)1392 886471 Fax
Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events over Canada
 1MAY 2001 ZHANG ET AL. 1923 Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events over Canada XUEBIN ZHANG, W.D.HOGG, AND ÉVA MEKIS Climate Research Branch, Meteorological Service of Canada,
1MAY 2001 ZHANG ET AL. 1923 Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events over Canada XUEBIN ZHANG, W.D.HOGG, AND ÉVA MEKIS Climate Research Branch, Meteorological Service of Canada,
Projected change in extreme rainfall events in China by the end of the 21st century using CMIP5 models
 Article SPECIAL ISSUE: Extreme Climate in China April 2013 Vol.58 No.12: 1462 1472 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5612-2 Projected change in extreme rainfall events in China by the end of the 21st century using
Article SPECIAL ISSUE: Extreme Climate in China April 2013 Vol.58 No.12: 1462 1472 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5612-2 Projected change in extreme rainfall events in China by the end of the 21st century using
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 5, May ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 1 Projection of Changes in Monthly Climatic Variability at Local Level in India as Inferred from Simulated Daily
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 1 Projection of Changes in Monthly Climatic Variability at Local Level in India as Inferred from Simulated Daily
Climate outlook, longer term assessment and regional implications. What s Ahead for Agriculture: How to Keep One of Our Key Industries Sustainable
 Climate outlook, longer term assessment and regional implications What s Ahead for Agriculture: How to Keep One of Our Key Industries Sustainable Bureau of Meteorology presented by Dr Jeff Sabburg Business
Climate outlook, longer term assessment and regional implications What s Ahead for Agriculture: How to Keep One of Our Key Industries Sustainable Bureau of Meteorology presented by Dr Jeff Sabburg Business
Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L11705, doi:10.1029/2007gl029631, 2007 Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during 1961 2005 Weihong Qian, 1 Jiaolan
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L11705, doi:10.1029/2007gl029631, 2007 Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during 1961 2005 Weihong Qian, 1 Jiaolan
ATTRIBUTION OF A RECORD-BREAKING HEATWAVE EVENT IN SUMMER 2017 OVER THE YANGTZE RIVER DELTA
 ATTRIBUTION OF A RECORD-BREAKING HEATWAVE EVENT IN SUMMER 2017 OVER THE YANGTZE RIVER DELTA Chunlüe Zhou, Kaicun Wang, Dan Qi, and Jianguo Tan The occurrence probability of the record-breaking Yangtze
ATTRIBUTION OF A RECORD-BREAKING HEATWAVE EVENT IN SUMMER 2017 OVER THE YANGTZE RIVER DELTA Chunlüe Zhou, Kaicun Wang, Dan Qi, and Jianguo Tan The occurrence probability of the record-breaking Yangtze
Supplementary Material for: Coordinated Global and Regional Climate Modelling
 1 Supplementary Material for: Coordinated Global and Regional Climate Modelling 2 a. CanRCM4 NARCCAP Analysis 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 As CanRCM4 is a new regional model
1 Supplementary Material for: Coordinated Global and Regional Climate Modelling 2 a. CanRCM4 NARCCAP Analysis 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 As CanRCM4 is a new regional model
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA
 FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
Attribution of anthropogenic influence on seasonal sea level pressure
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L23709, doi:10.1029/2009gl041269, 2009 Attribution of anthropogenic influence on seasonal sea level pressure N. P. Gillett 1 and P. A.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L23709, doi:10.1029/2009gl041269, 2009 Attribution of anthropogenic influence on seasonal sea level pressure N. P. Gillett 1 and P. A.
Climate Risk Profile for Samoa
 Climate Risk Profile for Samoa Report Prepared by Wairarapa J. Young Samoa Meteorology Division March, 27 Summary The likelihood (i.e. probability) components of climate-related risks in Samoa are evaluated
Climate Risk Profile for Samoa Report Prepared by Wairarapa J. Young Samoa Meteorology Division March, 27 Summary The likelihood (i.e. probability) components of climate-related risks in Samoa are evaluated
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
Ellen L. Mecray NOAA Regional Climate Services Director, Eastern Region Taunton, MA
 Ellen L. Mecray NOAA Regional Climate Services Director, Eastern Region Taunton, MA Regions of the US National Climate Assessment What we Observe: Climate changes and impacts Increasing temperature Increasingly
Ellen L. Mecray NOAA Regional Climate Services Director, Eastern Region Taunton, MA Regions of the US National Climate Assessment What we Observe: Climate changes and impacts Increasing temperature Increasingly
How can we explain possible human contribution to weather events?
 WMO-IPCC Tokyo workshop for weather presenters, November 11, 2015 How can we explain possible human contribution to weather events? Masahiro Watanabe Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute University
WMO-IPCC Tokyo workshop for weather presenters, November 11, 2015 How can we explain possible human contribution to weather events? Masahiro Watanabe Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute University
Zambia. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G.
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Zambia C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Zambia C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
9th Scientific Statement. Recent Irish weather extremes and climate change Ray McGrath, Rowan Fealy and Tom Sheridan
 9th Scientific Statement Recent Irish weather extremes and climate change Ray McGrath, Rowan Fealy and Tom Sheridan In November 2009 Ireland experienced unusually wet weather that caused widespread flooding.
9th Scientific Statement Recent Irish weather extremes and climate change Ray McGrath, Rowan Fealy and Tom Sheridan In November 2009 Ireland experienced unusually wet weather that caused widespread flooding.
Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for August 2015 January 2016
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for August 2015 January 2016 BUSAN, 24 July 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for August 2015 January 2016 (ASONDJ) at the APEC Climate
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for August 2015 January 2016 BUSAN, 24 July 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for August 2015 January 2016 (ASONDJ) at the APEC Climate
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
Changes in Daily Climate Extremes of Observed Temperature and Precipitation in China
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2013, VOL. 6, NO. 5, 312 319 Changes in Daily Climate Extremes of Observed Temperature and Precipitation in China WANG Ai-Hui and FU Jian-Jian Nansen-Zhu International
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2013, VOL. 6, NO. 5, 312 319 Changes in Daily Climate Extremes of Observed Temperature and Precipitation in China WANG Ai-Hui and FU Jian-Jian Nansen-Zhu International
Monsoon Activities in China Tianjun ZHOU
 Monsoon Activities in China Tianjun ZHOU Email: zhoutj@lasg.iap.ac.cn CLIVAR AAMP10, Busan,, Korea 18-19 19 June 2010 Outline Variability of EASM -- Interdecadal variability -- Interannual variability
Monsoon Activities in China Tianjun ZHOU Email: zhoutj@lasg.iap.ac.cn CLIVAR AAMP10, Busan,, Korea 18-19 19 June 2010 Outline Variability of EASM -- Interdecadal variability -- Interannual variability
Figure ES1 demonstrates that along the sledging
 UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
SUPPLEMENT EXPLAINING EXTREME EVENTS OF 2016 FROM A CLIMATE PERSPECTIVE
 SUPPLEMENT EXPLAINING EXTREME EVENTS OF 2016 FROM A CLIMATE PERSPECTIVE Editors Stephanie C. Herring, Nikolaos Christidis, Andrew Hoell, James P. Kossin, Carl J. Schreck III, and Peter A. Stott Special
SUPPLEMENT EXPLAINING EXTREME EVENTS OF 2016 FROM A CLIMATE PERSPECTIVE Editors Stephanie C. Herring, Nikolaos Christidis, Andrew Hoell, James P. Kossin, Carl J. Schreck III, and Peter A. Stott Special
Update on Climate Science. Professor Richard Betts, Met Office
 Update on Climate Science Professor Richard Betts, Met Office The science of climate change Crown copyright Met Office Prof Richard Betts Head of Climate Impacts Research Crown copyright Met Office Observing
Update on Climate Science Professor Richard Betts, Met Office The science of climate change Crown copyright Met Office Prof Richard Betts Head of Climate Impacts Research Crown copyright Met Office Observing
25. THE HOT AND DRY APRIL OF 2016 IN THAILAND
 25. THE HOT AND DRY APRIL OF 2016 IN THAILAND Nikolaos Christidis, Kasemsan Manomaiphiboon, Andrew Ciavarella, and Peter A. Stott The record temperature of April 2016 in Thailand would not have occurred
25. THE HOT AND DRY APRIL OF 2016 IN THAILAND Nikolaos Christidis, Kasemsan Manomaiphiboon, Andrew Ciavarella, and Peter A. Stott The record temperature of April 2016 in Thailand would not have occurred
The Canadian Climate Model 's Epic Failure November 2016
 The Canadian Climate Model 's Epic Failure November 2016 By: Ken Gregory The Canadian Centre for Climate Modeling and Analysis located at the University of Victoria in British Columbia submitted five runs
The Canadian Climate Model 's Epic Failure November 2016 By: Ken Gregory The Canadian Centre for Climate Modeling and Analysis located at the University of Victoria in British Columbia submitted five runs
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China
 Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China Xu Ming Shanghai Typhoon Institute November,25 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Typhoon disasters in China 3. Climatology and climate change of typhoon affecting
Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China Xu Ming Shanghai Typhoon Institute November,25 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Typhoon disasters in China 3. Climatology and climate change of typhoon affecting
Precipitation changes in the mid-latitudes of the Chinese mainland during
 J Arid Land (2017) 9(6): 924 937 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0105-4 Science Press Springer-Verlag Precipitation changes in the mid-latitudes of the Chinese mainland during 1960 2014 HU Yuling 1,
J Arid Land (2017) 9(6): 924 937 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0105-4 Science Press Springer-Verlag Precipitation changes in the mid-latitudes of the Chinese mainland during 1960 2014 HU Yuling 1,
Northern Rockies Adaptation Partnership: Climate Projections
 Northern Rockies Adaptation Partnership: Climate Projections Contents Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Region... 2 Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Central Subregion... 8 Observed
Northern Rockies Adaptation Partnership: Climate Projections Contents Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Region... 2 Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Central Subregion... 8 Observed
Water cycle changes during the past 50 years over the Tibetan Plateau: review and synthesis
 130 Cold Region Hydrology in a Changing Climate (Proceedings of symposium H02 held during IUGG2011 in Melbourne, Australia, July 2011) (IAHS Publ. 346, 2011). Water cycle changes during the past 50 years
130 Cold Region Hydrology in a Changing Climate (Proceedings of symposium H02 held during IUGG2011 in Melbourne, Australia, July 2011) (IAHS Publ. 346, 2011). Water cycle changes during the past 50 years
IAP Dynamical Seasonal Prediction System and its applications
 WCRP Workshop on Seasonal Prediction 4-7 June 2007, Barcelona, Spain IAP Dynamical Seasonal Prediction System and its applications Zhaohui LIN Zhou Guangqing Chen Hong Qin Zhengkun Zeng Qingcun Institute
WCRP Workshop on Seasonal Prediction 4-7 June 2007, Barcelona, Spain IAP Dynamical Seasonal Prediction System and its applications Zhaohui LIN Zhou Guangqing Chen Hong Qin Zhengkun Zeng Qingcun Institute
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Climate Change Scenario, Climate Model and Future Climate Projection
 Training on Concept of Climate Change: Impacts, Vulnerability, Adaptation and Mitigation 6 th December 2016, CEGIS, Dhaka Climate Change Scenario, Climate Model and Future Climate Projection A.K.M. Saiful
Training on Concept of Climate Change: Impacts, Vulnerability, Adaptation and Mitigation 6 th December 2016, CEGIS, Dhaka Climate Change Scenario, Climate Model and Future Climate Projection A.K.M. Saiful
Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh
 24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015?
 24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015? Pandora Hope, Guomin Wang, Eun-Pa Lim, Harry H. Hendon, and Julie M. Arblaster Using a seasonal forecasting framework for attribution,
24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015? Pandora Hope, Guomin Wang, Eun-Pa Lim, Harry H. Hendon, and Julie M. Arblaster Using a seasonal forecasting framework for attribution,
Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for May - October 2015
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for May - October 2015 BUSAN, 23 April 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for May - October 2015 (MJJASO) at the APEC Climate Center
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for May - October 2015 BUSAN, 23 April 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for May - October 2015 (MJJASO) at the APEC Climate Center
CLIVAR International Climate of the Twentieth Century (C20C) Project
 CLIVAR International Climate of the Twentieth Century (C20C) Project Chris Folland, UK Met office 6th Climate of the Twentieth Century Workshop, Melbourne, 5-8 Nov 2013 Purpose and basic methodology Initially
CLIVAR International Climate of the Twentieth Century (C20C) Project Chris Folland, UK Met office 6th Climate of the Twentieth Century Workshop, Melbourne, 5-8 Nov 2013 Purpose and basic methodology Initially
Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for July December 2017
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for July December 2017 BUSAN, 26 June 2017 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for July December 2017 (JASOND) at the APEC Climate Center
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for July December 2017 BUSAN, 26 June 2017 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for July December 2017 (JASOND) at the APEC Climate Center
Figure 1. Carbon dioxide time series in the North Pacific Ocean (
 Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Current and future climate of Vanuatu. Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program
 Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Hiu Torres Islands Vanua Lava Gaua Banks Islands Espiritu Santo Malekula Ambae Épi Maéwo Pentecost Ambrym Shepherd Islands Éfate
Pacific-Australia Climate Change Science and Adaptation Planning Program Hiu Torres Islands Vanua Lava Gaua Banks Islands Espiritu Santo Malekula Ambae Épi Maéwo Pentecost Ambrym Shepherd Islands Éfate
A Study of the Uncertainty in Future Caribbean Climate Using the PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 A Study of the Uncertainty in Future Caribbean Climate Using the PRECIS Regional Climate Model by Abel Centella and Arnoldo Bezanilla Institute of Meteorology, Cuba & Kenrick R. Leslie Caribbean Community
A Study of the Uncertainty in Future Caribbean Climate Using the PRECIS Regional Climate Model by Abel Centella and Arnoldo Bezanilla Institute of Meteorology, Cuba & Kenrick R. Leslie Caribbean Community
30. FUTURE CHALLENGES IN EVENT ATTRIBUTION METHODOLOGIES
 30. FUTURE CHALLENGES IN EVENT ATTRIBUTION METHODOLOGIES Peter A. Stott, Nikos Christidis, Stephanie C. Herring, Andrew Hoell, James P. Kossin, and Carl J. Schreck III Since these reports began five years
30. FUTURE CHALLENGES IN EVENT ATTRIBUTION METHODOLOGIES Peter A. Stott, Nikos Christidis, Stephanie C. Herring, Andrew Hoell, James P. Kossin, and Carl J. Schreck III Since these reports began five years
Assessment of Snow Cover Vulnerability over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(2): 93 100, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00093 ARTICLE Assessment of Snow Cover Vulnerability over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Lijuan Ma 1,
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(2): 93 100, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00093 ARTICLE Assessment of Snow Cover Vulnerability over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Lijuan Ma 1,
Was the Amazon Drought of 2005 Human-Caused? Peter Cox Met Office Chair in Climate System Dynamics. Outline
 Was the Amazon Drought of 2005 Human-Caused? Peter Cox Met Office Chair in Climate System Dynamics With thanks to : Phil Harris, Chris Huntingford, Chris Jones, Richard Betts, Matthew Collins, Jose Marengo,
Was the Amazon Drought of 2005 Human-Caused? Peter Cox Met Office Chair in Climate System Dynamics With thanks to : Phil Harris, Chris Huntingford, Chris Jones, Richard Betts, Matthew Collins, Jose Marengo,
Supplementary Information for:
 Supplementary Information for: Linkage between global sea surface temperature and hydroclimatology of a major river basin of India before and after 1980 P. Sonali, Ravi S. Nanjundiah, & D. Nagesh Kumar
Supplementary Information for: Linkage between global sea surface temperature and hydroclimatology of a major river basin of India before and after 1980 P. Sonali, Ravi S. Nanjundiah, & D. Nagesh Kumar
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation
 Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Detection and Attribution of Climate Change
 Detection and Attribution of Climate Change What is D&A? Global Mean Temperature Extreme Event Attribution Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, Sjoukje Philip (KNMI) Definitions Detection: demonstrating that climate
Detection and Attribution of Climate Change What is D&A? Global Mean Temperature Extreme Event Attribution Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, Sjoukje Philip (KNMI) Definitions Detection: demonstrating that climate
2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies
 2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies June 2015 global temperature was the highest in 136 (since 1880) years reaching an average of 0.88 C above the 20 th century average. This is an increase of 0.12
2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies June 2015 global temperature was the highest in 136 (since 1880) years reaching an average of 0.88 C above the 20 th century average. This is an increase of 0.12
The importance of sampling multidecadal variability when assessing impacts of extreme precipitation
 The importance of sampling multidecadal variability when assessing impacts of extreme precipitation Richard Jones Research funded by Overview Context Quantifying local changes in extreme precipitation
The importance of sampling multidecadal variability when assessing impacts of extreme precipitation Richard Jones Research funded by Overview Context Quantifying local changes in extreme precipitation
Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2820 Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss Kelly E. McCusker 1,2, John C. Fyfe 2 & Michael Sigmond 2 1 School
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2820 Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss Kelly E. McCusker 1,2, John C. Fyfe 2 & Michael Sigmond 2 1 School
How advances in atmospheric modelling are used for improved flood forecasting. Dr Michaela Bray Cardiff University
 How advances in atmospheric modelling are used for improved flood forecasting Dr Michaela Bray Cardiff University Overview of current short term rainfall forecasting Advancements and on going research
How advances in atmospheric modelling are used for improved flood forecasting Dr Michaela Bray Cardiff University Overview of current short term rainfall forecasting Advancements and on going research
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW
 2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic Background during
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
Regional climate change in Tibet: past and future
 Symposium on Advanced Assimilation and Uncertainty Quantification in Big Data Research for Weather, Climate and Earth System Monitoring and Prediction May 23-24, 2016, State College. photos: www.dawide.com
Symposium on Advanced Assimilation and Uncertainty Quantification in Big Data Research for Weather, Climate and Earth System Monitoring and Prediction May 23-24, 2016, State College. photos: www.dawide.com
Duration and Seasonality of Hourly Extreme Rainfall in the Central Eastern China
 NO.6 LI Jian, YU Rucong and SUN Wei 799 Duration and Seasonality of Hourly Extreme Rainfall in the Central Eastern China LI Jian 1 ( ), YU Rucong 1 ( ), and SUN Wei 2,3 ( ) 1 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
NO.6 LI Jian, YU Rucong and SUN Wei 799 Duration and Seasonality of Hourly Extreme Rainfall in the Central Eastern China LI Jian 1 ( ), YU Rucong 1 ( ), and SUN Wei 2,3 ( ) 1 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 2, 87 92 The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model WEI Chao 1,2 and DUAN Wan-Suo 1 1
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 2, 87 92 The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model WEI Chao 1,2 and DUAN Wan-Suo 1 1
EUROPE ATTRIBUTION STATEMENT for 2014 TEMPS. 1. UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE: European record 2014 temperatures in CMIP5
 METHODOLOGY 1. UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE: European record 2014 temperatures in CMIP5 Contacts: David Karoly - dkaroly@unimelb.edu.au; Andrew King - andrew.king@unimelb.edu.au; Sophie Lewis - sophie.lewis@anu.edu.au
METHODOLOGY 1. UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE: European record 2014 temperatures in CMIP5 Contacts: David Karoly - dkaroly@unimelb.edu.au; Andrew King - andrew.king@unimelb.edu.au; Sophie Lewis - sophie.lewis@anu.edu.au
22. CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF INDONESIAN HEAT AND DROUGHT
 22. CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF INDONESIAN HEAT AND DROUGHT Andrew D. King, Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, and David J. Karoly El Niño and human-induced climate change have substantially
22. CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF INDONESIAN HEAT AND DROUGHT Andrew D. King, Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, and David J. Karoly El Niño and human-induced climate change have substantially
Training: Climate Change Scenarios for PEI. Training Session April Neil Comer Research Climatologist
 Training: Climate Change Scenarios for PEI Training Session April 16 2012 Neil Comer Research Climatologist Considerations: Which Models? Which Scenarios?? How do I get information for my location? Uncertainty
Training: Climate Change Scenarios for PEI Training Session April 16 2012 Neil Comer Research Climatologist Considerations: Which Models? Which Scenarios?? How do I get information for my location? Uncertainty
Suriname. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G.
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Suriname C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Suriname C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Schema8c Global Climate Model
 Schema8c Global Climate Model Horizontal Grid (Latitude-Longitude) Vertical Grid (Height or Pressure) NOAA/ GFDL s CLIMATE and EARTH SYSTEM MODELING Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Understanding
Schema8c Global Climate Model Horizontal Grid (Latitude-Longitude) Vertical Grid (Height or Pressure) NOAA/ GFDL s CLIMATE and EARTH SYSTEM MODELING Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Understanding
Changes in Weather and Climate Extremes and Their Causes. Xuebin Zhang (CRD/ASTD) Francis Zwiers (PCIC)
 www.ec.gc.ca Changes in Weather and Climate Extremes and Their Causes Xuebin Zhang (CRD/ASTD) Francis Zwiers (PCIC) Outline What do we mean by climate extremes Changes in extreme temperature and precipitation
www.ec.gc.ca Changes in Weather and Climate Extremes and Their Causes Xuebin Zhang (CRD/ASTD) Francis Zwiers (PCIC) Outline What do we mean by climate extremes Changes in extreme temperature and precipitation
Climpact2 and regional climate models
 Climpact2 and regional climate models David Hein-Griggs Scientific Software Engineer 18 th February 2016 What is the Climate System?? What is the Climate System? Comprises the atmosphere, hydrosphere,
Climpact2 and regional climate models David Hein-Griggs Scientific Software Engineer 18 th February 2016 What is the Climate System?? What is the Climate System? Comprises the atmosphere, hydrosphere,
Historical and Modelled Climate Data issues with Extreme Weather: An Agricultural Perspective. Neil Comer, Ph.D.
 Historical and Modelled Climate Data issues with Extreme Weather: An Agricultural Perspective Neil Comer, Ph.D. When Crops are in the fields it s looking good: Trend in Summer Temperature (L) & Summer
Historical and Modelled Climate Data issues with Extreme Weather: An Agricultural Perspective Neil Comer, Ph.D. When Crops are in the fields it s looking good: Trend in Summer Temperature (L) & Summer
Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
Appendix 1: UK climate projections
 Appendix 1: UK climate projections The UK Climate Projections 2009 provide the most up-to-date estimates of how the climate may change over the next 100 years. They are an invaluable source of information
Appendix 1: UK climate projections The UK Climate Projections 2009 provide the most up-to-date estimates of how the climate may change over the next 100 years. They are an invaluable source of information
Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future. warming scenarios
 Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future warming scenarios Liang Ning 1,2,3* and Raymond S. Bradley 2 1 Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment of Ministry
Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future warming scenarios Liang Ning 1,2,3* and Raymond S. Bradley 2 1 Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment of Ministry
Forecast system development: what next?
 Forecast system development: what next? Doug Smith, Adam Scaife, Nick Dunstone, Leon Hermanson, Rosie Eade, Vikki Thompson, Martin Andrews, Jeff Knight, Craig MacLachlan, and many others Improved models
Forecast system development: what next? Doug Smith, Adam Scaife, Nick Dunstone, Leon Hermanson, Rosie Eade, Vikki Thompson, Martin Andrews, Jeff Knight, Craig MacLachlan, and many others Improved models
Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation in East China from 1880 to 1999
 CLIMATE RESEARCH Vol. 32: 29 218, 26 Published October 26 Clim Res Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation in East China from 188 to 1999 Weihong Qian 1, *, Zicheng Yu 2, Yafen Zhu 1 1 Monsoon
CLIMATE RESEARCH Vol. 32: 29 218, 26 Published October 26 Clim Res Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation in East China from 188 to 1999 Weihong Qian 1, *, Zicheng Yu 2, Yafen Zhu 1 1 Monsoon
11. WAS THE JANUARY 2016 MID-ATLANTIC SNOWSTORM JONAS SYMPTOMATIC OF CLIMATE CHANGE?
 11. WAS THE JANUARY 2016 MID-ATLANTIC SNOWSTORM JONAS SYMPTOMATIC OF CLIMATE CHANGE? Klaus Wolter, Martin Hoerling, Jon K. Eischeid, and Dave Allured Model simulations indicate that anthropogenic climate
11. WAS THE JANUARY 2016 MID-ATLANTIC SNOWSTORM JONAS SYMPTOMATIC OF CLIMATE CHANGE? Klaus Wolter, Martin Hoerling, Jon K. Eischeid, and Dave Allured Model simulations indicate that anthropogenic climate
Seamless weather and climate for security planning
 Seamless weather and climate for security planning Kirsty Lewis, Principal Climate Change Consultant, Met Office Hadley Centre 28 June 2010 Global Climate Models Mitigation timescale changes could be avoided
Seamless weather and climate for security planning Kirsty Lewis, Principal Climate Change Consultant, Met Office Hadley Centre 28 June 2010 Global Climate Models Mitigation timescale changes could be avoided
9. ANTHROPOGENIC AND NATURAL INFLUENCES ON RECORD 2016 MARINE HEAT WAVES
 9. ANTHROPOGENIC AND NATURAL INFLUENCES ON RECORD 2016 MARINE HEAT WAVES Eric C. J. Oliver, Sarah E. Perkins-Kirkpatrick, Neil J. Holbrook, and Nathaniel L. Bindoff Two of the longest and most intense
9. ANTHROPOGENIC AND NATURAL INFLUENCES ON RECORD 2016 MARINE HEAT WAVES Eric C. J. Oliver, Sarah E. Perkins-Kirkpatrick, Neil J. Holbrook, and Nathaniel L. Bindoff Two of the longest and most intense
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
PERSPECTIVES ON FOCUSED WORKSHOP QUESTIONS
 PERSPECTIVES ON FOCUSED WORKSHOP QUESTIONS REGARDING PAST ECONOMIC IMPACTS OF STORMS OR FLOODS Tom Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 1. According
PERSPECTIVES ON FOCUSED WORKSHOP QUESTIONS REGARDING PAST ECONOMIC IMPACTS OF STORMS OR FLOODS Tom Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 1. According
Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S.
 Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S. Sam Iacobellis and Dan Cayan Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Sponsors: NOAA RISA
Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S. Sam Iacobellis and Dan Cayan Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Sponsors: NOAA RISA
Air Quality Modelling under a Future Climate
 Air Quality Modelling under a Future Climate Rachel McInnes Met Office Hadley Centre Quantifying the impact of air pollution on health - Fri 12th Sep 2014 Crown copyright Met Office Rachel.McInnes@metoffice.gov.uk
Air Quality Modelling under a Future Climate Rachel McInnes Met Office Hadley Centre Quantifying the impact of air pollution on health - Fri 12th Sep 2014 Crown copyright Met Office Rachel.McInnes@metoffice.gov.uk
INCREASING HURRICANES, DROUGHTS, & WILDFIRES. Paul H. Carr AF Research Laboratory Emeritus
 INCREASING HURRICANES, DROUGHTS, & WILDFIRES Paul H. Carr AF Research Laboratory Emeritus www.mirrorofnature.org INCREASING HURRICANES, DROUGHTS, & WILDFIRES By Paul H. Carr, NES American Physical Society,
INCREASING HURRICANES, DROUGHTS, & WILDFIRES Paul H. Carr AF Research Laboratory Emeritus www.mirrorofnature.org INCREASING HURRICANES, DROUGHTS, & WILDFIRES By Paul H. Carr, NES American Physical Society,
Early benefits of mitigation in risk of regional climate extremes
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3259 Early benefits of mitigation in risk of regional climate extremes Andrew Ciavarella 1 *, Peter Stott 1,2 and Jason Lowe 1,3
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3259 Early benefits of mitigation in risk of regional climate extremes Andrew Ciavarella 1 *, Peter Stott 1,2 and Jason Lowe 1,3
Climate Outlook for October 2017 March 2018
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for October 2017 March 2018 BUSAN, 25 September 2017 The synthesis of the latest model forecasts for October 2017 to March 2018 (ONDJFM) from the APEC Climate Center
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for October 2017 March 2018 BUSAN, 25 September 2017 The synthesis of the latest model forecasts for October 2017 to March 2018 (ONDJFM) from the APEC Climate Center
Understanding Weather and Climate Risk. Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017
 Understanding Weather and Climate Risk Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017 What is risk in a weather and climate context? Hazard: something with the
Understanding Weather and Climate Risk Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017 What is risk in a weather and climate context? Hazard: something with the
