STCE Newsletter. 18 May May 2015
|
|
|
- Rosamond Webb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published by the STCE - this issue : 29 May Available online at The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium. Content Page 1. Layer upon layer 2 2. Curious about GIC, power-grid and pipelines? 3 3. Or more interested in Solar and Astrophysical Modeling? 4 4. ESWW12 registration is open 5 5. PROBA2 Observations () 6 6. Review of solar activity 8 7. Review of geomagnetic activity 9 8. Geomagnetic Observations at Dourbes () Review of ionospheric activity () Future Events 13 Final Editor : Contact : Petra Vanlommel R. Van der Linden, General Coordinator STCE, Ringlaan Avenue Circulaire, 1180 Brussels, Belgium Page 1 of 19
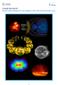
2 1. Layer upon layer Last week, the sunspot activity was again all but exciting. Only a few, very small, and mostly inactive sunspot groups were visible in white light. In H-alpha, which is a filter showing the "cold" inner atmosphere of the Sun, the Sun's outlook was dominated by some long filaments. These are local belts of plasma squeezed together by opposite polarity magnetic fields (see Moving up to the hot outer solar atmosphere, the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) imagery from SDO showed darkish patches. Some of those patches contain the filaments seen in H-alpha and are called filament channels. Others are indicative of low density areas and correspond to coronal holes, allowing the fast solar wind to escape into space. At even higher temperatures, x-ray imagery show these coronal holes even more prominently, though part of them sometimes correspond to areas where there are simply little active (hot) areas - see this of 7 December 2012 at welcome.html for more details. The image above shows the Sun on 25 May in the 4 above-mentioned filters. All images were taken between 09:10 and 09:16UT, so the locations of the different features correlate very well. The solar outlook changes dramatically when moving from the solar surface (white light) all the way up to the very hot solar atmosphere. This can also be seen in this gif animation at Page 2 of 19
3 All the relevant features can also be brought together on one image, as is done below. The basic image is a white light disk image on which the filaments (red, fat lines) are indicated. The dashed green lines indicate the somewhat dark areas seen in the EUV images. The prominent dark patches seen in x-ray imagery are indicated in blue. The bright areas are indicative of active regions, not necessarily sunspot groups, and are represented by the dashed white contours. The whole has been overlaid on the x-ray image showing the hot outer solar atmosphere. Clearly, the Sun's atmospheric structure is much more complex than a simple white light image would suggest. Credits - Images were taken from SDO ( GONG H-alpha Network ( and GOES/SXI ( 2. Curious about GIC, power-grid and pipelines? Here is your chance to learn more about it. Go to Page 3 of 19
4 3. Or more interested in Solar and Astrophysical Modeling? No problem, we have it all: Page 4 of 19
5 Absolutely worth a trip to Germany from September, ESWW12 registration is open One more announcement: we will meet in Ostend, at the sea. Bring your swimming suit! Don't forget to submit your abstract before June 1. Page 5 of 19
6 5. PROBA2 Observations () Solar Activity Solar flare activity fluctuated between very low and low during the week. In order to view the activity of this week in more detail, we suggest to go to the following website from which all the daily (normal and difference) movies can be accessed: This page also lists the recorded flaring events. A weekly overview movie can be found here (SWAP week 269). Details about some of this week s events, can be found further below. Page 6 of 19
7 Wednesday May 20 Failed eruption on the southeast 08:17 SWAP image Find a movie of the event here (SWAP movie) Page 7 of 19
8 Friday May 22 Eruption on the west 09:29 SWAP image Find a movie of the event here (SWAP movie) 6. Review of solar activity Solar activity has been very low for the entire week with just some occasional low level C flares (10 in total, all below C3 level). Active region 2349 was the most active source with 2351 contributing earlier in the week and 2353 (which developed on disk) later in the week. Page 8 of 19
9 The background X-ray flux was situated in the B-level as can be seen in the graph below showing the X-ray flux measured by the satellite GOES. Some smaller filament eruptions were detected earlier in the week, but none generated significant or Earth-ward CME's. 7. Review of geomagnetic activity The week started with the arrival of the May 12 CME on May 18, which with its low speed caused just a minor transient in the solar wind. It was followed by a sector boundary crossing and the subsequent arrival of a high speed stream from a positive polarity coronal hole (CH) - green encircled in the SDO/ AIA 193 image, near the central meridian. Page 9 of 19
10 Solar wind velocity increased to around 550 km/s. Total magnetic field reached a peak of 19nT around 1:00UT May 19 after which it steadily decreased to nominal values. Some periods of pronounced negative Bz were recorded, down to -15nT. Page 10 of 19
11 The negative Bz came associated with some minor geomagnetic storm conditions around midnight May 18 to 19 (NOAA Kp 5, though local K Dourbes did not exceed K=4). Solar wind conditions then returned to nominal with associated quiet to unsettled geomagnetic conditions. 8. Geomagnetic Observations at Dourbes (18 May May 2015) Page 11 of 19
12 9. Review of ionospheric activity () The figure shows the time evolution of the Vertical Total Electron Content (VTEC) (in red) during the last week at three locations: a) in the northern part of Europe(N61, 5 E) b) above Brussels(N50.5, 4.5 E) c) in the southern part of Europe(N36, 5 E) This figure also shows (in grey) the normal ionospheric behaviour expected based on the median VTEC from the 15 previous days. The VTEC is expressed in TECu (with TECu=10^16 electrons per square meter) and is directly related to the signal propagation delay due to the ionosphere (in figure: delay on GPS L1 frequency). The Sun's radiation ionizes the Earth's upper atmosphere, the ionosphere, located from about 60km to 1000km above the Earth's surface.the ionization process in the ionosphere produces ions and free electrons. These electrons perturb the propagation of the GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signals by inducing a so-called ionospheric delay. Page 12 of 19
13 See for some more explanations ; for detailed information, see Future Events For more details, see Solar Influences on the Magnetosphere, Ionosphere and Atmosphere in Sunny Beach, Bulgaria Start : End : Check the website for more information. Los Alamos Space Weather Summer School, in Los Alamos, NM, USA Start : End : The Space Weather Summer School at Los Alamos National Laboratory, established in 2011 under the founding Director Josef Koller, is dedicated to space weather, space science and applications. Every year we solicit applications for the Los Alamos Space Weather Summer School. This summer school is sponsored and supported by a number or organizations at LANL. This year our top sponsors include the Los Alamos Institute of Geophysics, Planetary Physics and Signatures (IGPPS) and the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Office (LDRD). The summer school brings together top space science students with internationally recognized researchers at LANL in an educational and collaborative atmosphere. RadioSun4 Workshop & Summer School in Irkutsk, Russia Start : End : The RadioSun Workshop and Summer School 2015 is the fourth international academic seminar supported by the International Research Staff Exchange Scheme of the Seventh Fromework Programme of the European Union (FP7-IRSES RADIOSUN). The aims of this project are to establish close research interaction and collaboration between the key EU and non-eu research groups involved in the research of the Sun in the radio band; qualitatively advance our knowledge of the physical processes operating in the solar atmosphere, the basic mechanisms responsible for its evolution and dynamics and its effect on the Earth; and provide younger researchers with extensive training in relevant research techniques and with universal transfer. Solar dynamo frontier workshop in Boulder, CO (USA) Start : End : The last five years have seen substantial progress in our understanding of the solar dynamo, fueled by continuing advances in observations and modeling. With the launch of NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) in 2010 came an unprecedented window on the evolving magnetic topology of the Sun, highlighting its intricate 3D structure and global connectivity. The Helioseismic Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on SDO in particular has provided potentially transformative yet enigmatic insights into the internal dynamics of the solar convection zone that underlie the dynamo. Attempts to detect subsurface convective motions from helioseismic inversions have yielded only upper limits on the largescale convective amplitude, challenging our understanding of global solar convection. Yet, potential signatures of giant cells have been detected in photospheric Dopplergrams. Estimates of the meridional flow from HMI and complementary instruments (SOHO/MDI and GONG) have been equally tantalizing Page 13 of 19
14 and enigmatic. Several disparate techniques, including local and global helioseismic inversions and correlation tracking of surface features, have yielded evidence of a multi-cellular meridional flow but they differ on the detailed flow structure and amplitude. This multi-cellular meridional flow has potentially profound implications for flux-transport dynamo models that previously assumed a very different structure with a single circulation cell per hemisphere. National Astronomy Meeting 2015 in Llandudno, UK Start : End : We would like to invite you to submit contributed abstracts to the parallel session "The science of space weather: progressing our understanding" at the 2015 UK National Astronomy Meeting from 5-9 July ( The abstract-submission deadline is 1 April Observers, modellers, and theoreticians are all welcome. We also welcome participation from end users interested in how the science of space weather is advancing. The science of space weather: progressing our understanding The goal of this session is to provide an opportunity to discuss the scientific research that underpins space weather and how a new generation of operational space weather measurements could best be utilised to further progress our understanding. Specific topics are likely to include 1) gaps in our understanding of space weather and how to resolve them, 2) new space and ground-based data that are needed, 3) new science that can be carried out with the operational space weather measurements being planned today. This session is motivated by the fact that the UK has a strong heritage in the science of the coupled Sun-Earth system, from both an observational and theoretical perspective. This research is increasingly being applied to the area of space weather monitoring and forecasting, a topic that is now nationally recognised as an important natural hazard for the UK (highly ranked in the National Risk Register) and the subsequent opening of the Met Office Space Weather Operations Centre in Up until now, both the research and the space weather monitoring and forecasting have utilised mainly data from instrumentation (both space- and ground-based) designed to answer pertinent scientific questions, though some operational instruments (e.g. the X-ray and particle detectors on NOAA's GOES spacecraft) are also widely exploited for scientific use. However, there is now growing interest in deploying more instruments, in space and on the ground, designed to support operational space weather services. Such operational measurements can facilitate new science, as demonstrated by the extensive research use of GOES data, but it is important that the limitations imposed by operational needs are discussed. CISM Space Weather Summer School in Boulder, CO, USA Start : End : The CISM Summer School is intended to give students a comprehensive immersion in the subject of space weather: what it is, what it does, and what can be done about it. Space weather is many things: beautiful when seen through the eyes of a sun-viewing telescope, fascinating when studied for its alien worlds of magnetic structures and phenomena, awesome when witnessed as a solar eruption or auroral storm, and devastating to the users of services it disrupts. Space weather links the Sun, the Earth, and the space in between in a branching chain of consequences. Weather systems on the Sun can spawn interplanetary storms of colossal size and energy that envelop the whole planet in electrical hurricanes. Such storms attack high-tech, complex, and expensive technological systems that provide much of the infrastructure that allows modern society to function. Loops7: Heating of the Magnetically Closed Corona in Cambridge, UK Start : End : Page 14 of 19
15 The conference will review past and recent achievements, as well as future challenges in the field of solar coronal loop physics. Heliophysics Summer Schoool 2015: Seasons in Space: Cycles of variability of Sun-Planet systems, in Boulder, CO, USA Start : End : Heliophysics is all of the science common to the field of the Sun-Earth connections. This fast-developing field of research covers many traditional sub-disciplines of space physics, astrophysics, and climate studies. The NASA Living with a Star program, with its focus on the basic science underlying all aspects of space weather, acts as a catalyst to bring the many research disciplines together to deepen our understanding of the system of systems formed by the Sun-Earth connection. 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC) in The Hague, The Netherlands Start : End : The 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC) will be held from July 30 to August 6, 2015, in The Hague, The Netherlands. It is an important and large conference in the field of Astroparticle Physics. The ICRC covers: cosmic-ray physics, solar and heliospheric physics, gamma-ray astronomy, neutrino astronomy, and dark matter physics. SOLARNET III / HELAS VII: The Sun, the stars, and solar-stellar relations, in Freiburg (Germany) Start : End : The purpose of this conference is to discuss the latest questions and results in solar and stellar physics. Solar and stellar seismology will be one particular focus but contributions on all aspects of solar-stellar relations will be welcome. We aim to establish links and synergies between the day- and night-time fields of astrophysics. 1st Joint Solar Probe Plus-Solar Orbiter Workshop, in Florence (Italy) Start : End : The Workshop will address how the joint exploration of the corona and inner heliosphere will lead to advances in our understanding of coronal heating and solar wind acceleration, the magnetic and plasma structure of the heliosphere, and the acceleration of energetic particles at shocks and flares. The workshop will inspire research that will make use of SO and SPP observations within the context of the NASA Heliophysics Observatory System and identify key areas for preparatory research. Synergistic observations from other ground based and space based assets will also be addressed. International Workshop and School on Solar System plasma in Mamaia, Romania Start : End : The International Workshop and School on solar system plasma turbulence, intermittency and multifractals (STORM 2015) focus on the quantitative experimental, theoretical and numerical investigation of turbulence, intermittency, fractal/multifractal features, waves and coherent structures Page 15 of 19
16 interaction, criticality and non-linear cross-scale coupling. As widely documented by in-situ satellite measurements and remote or ground-based observations, turbulence, intermittency and dynamical complexity are quite ubiquitous processes observed in the dynamics of solar, planetary and interplanetary plasmas, as well as in the dynamical evolution of proxies linked to magnetospheric and ionospheric variability. Unfolding the spatio-temporal structure of magnetic field and plasma fluctuations from experimental observations and numerical simulations provides further insight on the structure of plasma turbulence and intermittency. On the theoretical side, the understanding of such complex dynamical behavior cannot be simply surmised from the basic fluid/kinetic equations, but instead requires novel theoretical, experimental and data analysis approaches. The workshop is a forum to present and discuss latest results in these fields. The purpose of the school is to give to a young audience of Graduate, Ph.D. students, and postdoc scientists, which ideally represents the next generation of scholars in the physics of space plasmas, an overall view of both theoretical and data analysis tools apt to fully exploit unique and unprecedented observations that will be provided by future upcoming mission like Solar Orbiter and Solar Probe Plus. 3rd UK-Ukraine-Spain meeting on solar physics and space science in Lviv, Ukraine Start : End : The meeting will cover various aspects of solar physics and space weather related processes. The special emphasis will be paid to progress in data-driven simulations and high-resolution spectropolarimetry as powerful diagnostic techniques to unravel information about magnetic fields in the photosphere and chromosphere of the Sun. Hinode 9 - International Science Meeting in Belfast, UK Start : End : Hinode is a solar satellite funded jointly by JAXA, NASA, ESA and STFC/UKSA that has entered its ninth year of operations. It has had a major impact across many areas of solar physics and facilitated many fundamental discoveries. These findings are documented in over 850 papers in the refereed literature and hundreds of papers in conference proceedings. With 96 refereed publications in 2013 and more than 81 papers in 2014, Hinode has remained scientifically highly productive. A non-exhaustive list indicates over 100 students globally who are undertaking or have completed PhDs using Hinode data. With the Solar Orbiter on the horizon, there is a good chance that the two missions will operate at the same time. The meeting will help the solar physics community to maximise the science return from the Orbiter. RADECS-2015 in Moscow, Russia Start : End : The aim of RADECS conferences is to provide an annual European forum for the presentation and discussion of the latest advances in the field of radiation effects on electronic and photonic materials, devices, circuits, sensors, and systems. The scope of the conference encompasses technological processes and design techniques for producing radiation tolerant systems for space, aeronautical or terrestrial applications, as well as relevant methodologies for their characterization and qualification. The conference features a technical program, an Industrial Exhibition, and one day tutorial or "short course" on radiation effects. The technical program includes oral and poster sessions and round tables. Page 16 of 19
17 Heliospheric physical processes for understanding Solar-Terrestrial Relations in L'Aquila, Italie Start : End : A good understanding of solar-terrestrial processes is fundamental to modelling the influence of solar variability on the Earth's environment and climate. To capture all the physical aspects of the solar windmagnetosphere-ionosphere-atmosphere interaction, and also the impact of solar variability on climate, the Sun-Earth system has to be studied as a whole. The main purpose of this school is to provide graduate, PhD students and also young post-doc researchers with a global view of the main physical processes by which solar variability affects the Earth's environment. In addition, an overview of different data analysis and methods for describing solar-terrestrial relations will be given. The school will provide a mix of lectures and activities requiring students participation. Ground-based Solar Observations in the Space Instrumentation Era in Coimbra, Portugal Start : End : This CSPM-2015 scientific meeting will cover various aspects of solar dynamic and magnetic phenomena which are observed over the entire electromagnetic spectrum: white-light, Hα, Ca II, and radio from ground and in a variety of other wavelengths (white light, UV and EUV, and X-rays) from space. Emphasis will also be placed on instrumentation, observing techniques, and solar image processing techniques, as well as theory and modelling through detailed radiative transfer in increasingly realistic MHD models. The long-term (cyclic) evolution of solar magnetism and its consequence for the solar atmosphere, eruptive phenomena, solar irradiation variations, and space weather, will be in focus. Here, special attention will be devoted to the long-term observations made in Coimbra and also to the results of the SPRING / SOLARNET and SCOSTEP VarSITI studies. In particular, the weak solar activity during the current solar maximum will be discussed. Finally, since this meeting is organised around the 90th anniversary of performing the first spectroheliographic observations in Coimbra, a session will be specially dedicated to new solar instruments (both ground-based and space-borne) that will give access to unexplored solar atmospheric features and dynamic phenomena over the coming years. AMS-02 Energetic Particle Workshop in Hawaii, USA Start : End : The workshop aims to bring together experts in the field of cosmic rays and solar energetic particles with an additional focus on their propagation inside the heliosphere and their interaction with the magnetosphere. The talks will present the most recent results related to solar energetic particles (SEPs), solar modulation, space radiation and related phenomena. Third Remote Sensing of the Inner Heliosphere and Space Weather Applications Workshop in Morelai, Michoacan (Mexico) Start : End : The workshop aims to gather experts from the various fields of remoteâ sensing observations of the inner heliosphere, including whiteâ light, EUV, and radio observation, together with modellers in order to tackle key outstanding science and spaceâ weather operational issues, establish closer working relations, and devise the best ways to move the field forward as a whole. In addition, the science learned from remote Âsensing observations is critical to improving our capabilities of spaceâ weather forecasting. The workshop aims to look at ways in which we can more easily and efficiently share and access the various types of data between individual groups and subâcommunities and to officially launch the IPS Common Page 17 of 19
18 Data Format v1.0 (IPSCDFv1.0) now in use. It also aims to allow investigations into ways in which we model the inner heliosphere looking at the advantages and disadvantages of the available modelling, updates on present and future remoteâsensing capabilities, and investigating further the ways in which these data sets all complement each other and are necessary to gain knowledge and understanding of the fundamental physical processes that occur within the inner heliosphere. These are critical processes that are key to both Heliophysics science as well as to spaceâweather operations and forecasting. 12th Potsdam Thinkshop in Potsdam, Germany Start : End : In the tradition of the series of »Potsdam Thinkshops«, we invite instrument specialists, observers, modellers, and theorists to exchange ideas, to stimulate discussion, to initiate future collaborations among participants, and to attract new users of instruments by showcasing the capabilities. The aim is to make progress towards a comprehensive description of solar eruptive events effectively aggregating their global properties as well as their highly dynamic fine structure. SEST/MiniMax Workshop in Mexico City, Mexico Start : End : The workshop is to improve the scientific understanding of the origin and propagation of solar transients, and develop the prediction capacity of these transients' arrival and potential impact on the Earth. The workshop engages coordinated international activities in observation, theory and modeling, and involves scientists in both developed and developing countries, and provides an online platform for educational opportunities for students Sun-Climate Symposium in Savannah, Georgia, USA Start : End : Observations of the Sun and Earth from space have revolutionized our view and understanding about impacts of solar variability and anthropogenic forcing on Earth climate. For more than three solar cycles since 1978, the total and spectral solar irradiance (TSI and SSI) and global terrestrial atmosphere/surface have been observed continuously, enabling unprecedented quality data for Sunclimate studies. The primary objective of this symposium is to convene climate scientists, solar physicists, and experimentalists together for a better understanding how Earth climate system changes and responds to solar variability. European Space Weather Week in Belgium Start : End : The European Space Weather Week (ESWW) is the European forum for Space Weather users, forecasters, scientists and the involved industries, as proven by the high attendance to the ESWW 11 in November The ESWW 12 will be held in Belgium in November, 23-27, 2015 and its organisation has already started and is benefiting from the experience and inputs from the past editions. AGU Chapman Conference on Currents in Geospace and Beyond in Dubrovnik, Croatia Start : End : Page 18 of 19
19 Electric currents are fundamental to the structure and dynamics of space plasmas, including our own near-earth space environment (also called "geospace"). This recognition is one of the great achievements in space research, going back to the beginning of the last century. With the current multispacecraft missions, such as Cluster, THEMIS and Swarm, we have unprecedented opportunities to unravel many of the intriguing puzzles about electric currents. The conference will provide a forum in which various space science communities can come together to discuss recent achievements of observational, theoretical, and modelling studies. The emphasis will be on cross-disciplinary science sessions. 41st COSPAR Scientific Assembly in Istanbul, Turkey Start : End : The 41st COSPAR Scientific Assembly will be held in Istanbul, Turkey from 30 July - 7 August This Assembly is open to all bona fide scientists. IAU Symposium 327: Fine Structure and Dynamics of the Solar Atmosphere in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia Start : End : The scientific goal of this symposium is to discuss recent results on the processes shaping the structure of the solar atmosphere and driving plasma eruptions and explosive events. Activity of the solar atmosphere entails numerous multi-scale processes. State-of-the-art solar instrumentation is revealing the dynamics of the Sun with unprecedented temporal and spatial resolutions. Together with advanced numerical simulations these investigations are making new steps in our understanding of the complex dynamical structure of the solar atmosphere. Major unsolved problems of astrophysics such as how the solar corona is heated and how the solar wind and heliosphere are powered have their roots in the origin of small-scale magnetic fields constituting the Sun's 'magnetic carpet' in the photosphere and appearing as 'magnetic canopy' in the chromosphere. Page 19 of 19
STCE Newsletter. 25 May May 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 5 Jun 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 5 Jun 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 1 Jun Jun 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 11 Jun 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 11 Jun 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 7 Dec Dec 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 18 Dec 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 18 Dec 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 11 Jan Jan 2016
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 21 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 21 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 7 May May 2018
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 18 May 2018. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 18 May 2018. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 4 Jan Jan 2016
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 15 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 15 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 5 Sep Sep 2016
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 16 Sep 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 16 Sep 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 6 Jan Jan 2014
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 16 Jan 2014. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 16 Jan 2014. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 28 Dec Jan 2016
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 8 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 8 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 18 Jan Jan 2016
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 29 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 29 Jan 2016. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 29 Jan Feb 2018
 STCE Newsletter 29 Jan 2018-4 Feb 2018 Published by the STCE - this issue : 8 Feb 2018. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative
STCE Newsletter 29 Jan 2018-4 Feb 2018 Published by the STCE - this issue : 8 Feb 2018. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative
STCE Newsletter. 31 Aug Sep 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 10 Sep 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 10 Sep 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 9 Jun Jun 2014
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 19 Jun 2014. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 19 Jun 2014. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
STCE Newsletter. 24 Aug Aug 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 4 Sep 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 4 Sep 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
AIA DATA ANALYSIS OVERVIEW OF THE AIA INSTRUMENT
 AIA DATA ANALYSIS OVERVIEW OF THE AIA INSTRUMENT SDO SUMMER SCHOOL ~ August 2010 ~ Yunnan, China Marc DeRosa (LMSAL) ~ derosa@lmsal.com WHAT IS SDO? The goal of Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is to understand:
AIA DATA ANALYSIS OVERVIEW OF THE AIA INSTRUMENT SDO SUMMER SCHOOL ~ August 2010 ~ Yunnan, China Marc DeRosa (LMSAL) ~ derosa@lmsal.com WHAT IS SDO? The goal of Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is to understand:
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge. Chi Wang. National Space Science Center, CAS
 Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
STCE Newsletter. 26 Jun Jul 2017
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 7 Jul 2017. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 7 Jul 2017. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
SOTERIA. Giovanni Lapenta for the Soteria Consortium. Centrum voor Plasma-Astrofysica Katholieke Universiteit Leuven BELGIUM
 SOTERIA Giovanni Lapenta for the Soteria Consortium Centrum voor Plasma-Astrofysica Katholieke Universiteit Leuven BELGIUM This research has received funding from the European Commission's Seventh Framework
SOTERIA Giovanni Lapenta for the Soteria Consortium Centrum voor Plasma-Astrofysica Katholieke Universiteit Leuven BELGIUM This research has received funding from the European Commission's Seventh Framework
STCE Newsletter. 10 Aug Aug 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 21 Aug 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 21 Aug 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
First European Space Weather Week. Space weather - atmospheres, drag, global change future needs. 29 November-3 December 2004
 First European Space Weather Week Space weather - atmospheres, drag, global change future needs 29 November-3 December 2004 Timescales of important phenomena Weather Climate No single statement of requirement
First European Space Weather Week Space weather - atmospheres, drag, global change future needs 29 November-3 December 2004 Timescales of important phenomena Weather Climate No single statement of requirement
Sun Earth Connection Missions
 Sun Earth Connection Missions ACE Advanced Composition Explorer The Earth is constantly bombarded with a stream of accelerated particles arriving not only from the Sun, but also from interstellar and galactic
Sun Earth Connection Missions ACE Advanced Composition Explorer The Earth is constantly bombarded with a stream of accelerated particles arriving not only from the Sun, but also from interstellar and galactic
THE SOLAR WIND & SOLAR VARIABILITY
 The Sun-Earth System: CONTENTS AN OVERVIEW The Stars Around Us 1 Our Dependence on the Sun 3 The Sun s Inconstancy 3 Intruders from Afar 5 What Gets By 5 Voyages of Discovery in an Age of Exploration 6
The Sun-Earth System: CONTENTS AN OVERVIEW The Stars Around Us 1 Our Dependence on the Sun 3 The Sun s Inconstancy 3 Intruders from Afar 5 What Gets By 5 Voyages of Discovery in an Age of Exploration 6
Center Data Analysis Service supported by the FAGS
 Solar Influences Data analysis Center Data Analysis Service supported by the FAGS SUNSPOT BULLETIN 2 n Provisional international and normalized hemispheric daily sunspot numbers for September 2 computed
Solar Influences Data analysis Center Data Analysis Service supported by the FAGS SUNSPOT BULLETIN 2 n Provisional international and normalized hemispheric daily sunspot numbers for September 2 computed
Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather. Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia
 Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia Planets Comets Solar wind Interplanetary magnetic field Cosmic rays Satellites Astronauts HELIOSPHERE
Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia Planets Comets Solar wind Interplanetary magnetic field Cosmic rays Satellites Astronauts HELIOSPHERE
Chapter 8 Geospace 1
 Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02
 Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02 Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 96822, HI, US E-mail: bindi@hawaii.edu AMS-02 collaboration The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02 Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 96822, HI, US E-mail: bindi@hawaii.edu AMS-02 collaboration The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
INTERPLANETARY ASPECTS OF SPACE WEATHER
 INTERPLANETARY ASPECTS OF SPACE WEATHER Richard G. Marsden Research & Scientific Support Dept. of ESA, ESTEC, P.O. Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, NL, Email: Richard.Marsden@esa.int ABSTRACT/RESUME Interplanetary
INTERPLANETARY ASPECTS OF SPACE WEATHER Richard G. Marsden Research & Scientific Support Dept. of ESA, ESTEC, P.O. Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, NL, Email: Richard.Marsden@esa.int ABSTRACT/RESUME Interplanetary
The Magnetic Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
Toward Interplanetary Space Weather: Strategies for Manned Missions to Mars
 centre for fusion, space and astrophysics Toward Interplanetary Space Weather: Strategies for Manned Missions to Mars Presented by: On behalf of: Jennifer Harris Claire Foullon, E. Verwichte, V. Nakariakov
centre for fusion, space and astrophysics Toward Interplanetary Space Weather: Strategies for Manned Missions to Mars Presented by: On behalf of: Jennifer Harris Claire Foullon, E. Verwichte, V. Nakariakov
Solar eruptive phenomena
 Solar eruptive phenomena Andrei Zhukov Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium 26/01/2018 1 Eruptive solar activity Solar activity exerts continous influence on the solar
Solar eruptive phenomena Andrei Zhukov Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium 26/01/2018 1 Eruptive solar activity Solar activity exerts continous influence on the solar
1-4-1A. Sun Structure
 Sun Structure A cross section of the Sun reveals its various layers. The Core is the hottest part of the internal sun and is the location of nuclear fusion. The heat and energy produced in the core is
Sun Structure A cross section of the Sun reveals its various layers. The Core is the hottest part of the internal sun and is the location of nuclear fusion. The heat and energy produced in the core is
Cosmic Rays. Cooperation at the Space Pole. D. Sapundjiev, T. Verhulst, M. Dierckxsens, E. De Donder, N. Crosby, K. Stegen, and S.
 Cosmic Rays Cooperation at the Space Pole D. Sapundjiev, T. Verhulst, M. Dierckxsens, E. De Donder, N. Crosby, K. Stegen, and S. Stankov Excellence (STCE) Ringlaan 3, B-1180 Brussels, Belgium Stan Stankov
Cosmic Rays Cooperation at the Space Pole D. Sapundjiev, T. Verhulst, M. Dierckxsens, E. De Donder, N. Crosby, K. Stegen, and S. Stankov Excellence (STCE) Ringlaan 3, B-1180 Brussels, Belgium Stan Stankov
The Structure of the Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
10:10-10 :35 P.K.Manoharan National Centre for Radio Astrophysics
 23 rd November, 2011 10:10-10 :35 P.K.Manoharan National Centre for Radio Astrophysics Radio observations, combined with the groundbased optical observations and spacebased data can provide a crossreferenced
23 rd November, 2011 10:10-10 :35 P.K.Manoharan National Centre for Radio Astrophysics Radio observations, combined with the groundbased optical observations and spacebased data can provide a crossreferenced
Imaging the Earth from the Moon FUV Imaging of the Earth s Space Weather. Dr. Larry J. Paxton (office)
 Imaging the Earth from the Moon FUV Imaging of the Earth s Space Weather Dr. Larry J. Paxton 240 228 6871 (office) Larry.paxton@jhuapl.edu Making Observations of the Earth from the Moon Makes Sense Once
Imaging the Earth from the Moon FUV Imaging of the Earth s Space Weather Dr. Larry J. Paxton 240 228 6871 (office) Larry.paxton@jhuapl.edu Making Observations of the Earth from the Moon Makes Sense Once
STCE Newsletter. 22 Jul Jul 2013
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 1 Aug 2013. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 1 Aug 2013. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Solar Orbiter. T.Appourchaux, L.Gizon and the SO / PHI team derived from M.Velli's and P.Kletzkine's presentations
 Solar Orbiter T.Appourchaux, L.Gizon and the SO / PHI team derived from M.Velli's and P.Kletzkine's presentations 2 nd Solar-C definition meeting, Tokyo, Japan Content Science Objectives of Solar Orbiter
Solar Orbiter T.Appourchaux, L.Gizon and the SO / PHI team derived from M.Velli's and P.Kletzkine's presentations 2 nd Solar-C definition meeting, Tokyo, Japan Content Science Objectives of Solar Orbiter
CESAR BOOKLET General Understanding of the Sun: Magnetic field, Structure and Sunspot cycle
 CESAR BOOKLET General Understanding of the Sun: Magnetic field, Structure and Sunspot cycle 1 Table of contents Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium... 3 A short introduction
CESAR BOOKLET General Understanding of the Sun: Magnetic field, Structure and Sunspot cycle 1 Table of contents Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium... 3 A short introduction
Solar Magnetic Fields Jun 07 UA/NSO Summer School 1
 Solar Magnetic Fields 1 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO Summer School 1 If the sun didn't have a magnetic field, then it would be as boring a star as most astronomers think it is. -- Robert Leighton 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO
Solar Magnetic Fields 1 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO Summer School 1 If the sun didn't have a magnetic field, then it would be as boring a star as most astronomers think it is. -- Robert Leighton 11 Jun 07 UA/NSO
Solar Activity during the Rising Phase of Solar Cycle 24
 International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
SPACE WEATHER: STORMS FROM THE SUN
 GIFT 2013 - Natural Hazards Vienna, Austria, 10 April 2013 SPACE WEATHER: STORMS FROM THE SUN Norma B. Crosby Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy Ringlaan-3-Avenue Circulaire, B-1180 Brussels, Belgium
GIFT 2013 - Natural Hazards Vienna, Austria, 10 April 2013 SPACE WEATHER: STORMS FROM THE SUN Norma B. Crosby Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy Ringlaan-3-Avenue Circulaire, B-1180 Brussels, Belgium
The Frequency Agile Solar Radiotelescope
 The Frequency Agile Solar Radiotelescope Associated Universities, Inc. National Radio Astronomy Observatory University of California, Berkeley California Institute of Technology New Jersey Institute of
The Frequency Agile Solar Radiotelescope Associated Universities, Inc. National Radio Astronomy Observatory University of California, Berkeley California Institute of Technology New Jersey Institute of
The Sun sends the Earth:
 The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
Report from Finland. Kirsti Kauristie Finnish Meteorological Institute
 Report from Finland Kirsti Kauristie Finnish Meteorological Institute IPT-SWeISS-2, Tokyo, Japan, 21-23 May 2018 Current SWE activities Contributors: Universities Aalto Helsinki (UH) Oulu (UO) Turku (UTU)
Report from Finland Kirsti Kauristie Finnish Meteorological Institute IPT-SWeISS-2, Tokyo, Japan, 21-23 May 2018 Current SWE activities Contributors: Universities Aalto Helsinki (UH) Oulu (UO) Turku (UTU)
The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp
 The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp Teknisk fysik '07 1 Contents History... 3 Introduction... 3 Two types of solar winds... 4 Effects of the solar wind... 5 Magnetospheres... 5 Atmospheres... 6 Solar storms...
The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp Teknisk fysik '07 1 Contents History... 3 Introduction... 3 Two types of solar winds... 4 Effects of the solar wind... 5 Magnetospheres... 5 Atmospheres... 6 Solar storms...
Solar eruptive filament studies at USO for the COMESEP project
 International Symposium on Solar Terrestrial Physics ASI Conference Series, 2013, Vol. 10, pp 67 71 Edited by N. Gopalswamy, S. S. Hasan, P. B. Rao and Prasad Subramanian Solar eruptive filament studies
International Symposium on Solar Terrestrial Physics ASI Conference Series, 2013, Vol. 10, pp 67 71 Edited by N. Gopalswamy, S. S. Hasan, P. B. Rao and Prasad Subramanian Solar eruptive filament studies
Space Weather Effects of Coronal Mass Ejection
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2006) 27, 219 226 Space Weather Effects of Coronal Mass Ejection K. N. Iyer 1,, R. M. Jadav 1, A. K. Jadeja 1, P. K. Manoharan 2, Som Sharma 3 and Hari Om Vats 3 1 Department of Physics,
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2006) 27, 219 226 Space Weather Effects of Coronal Mass Ejection K. N. Iyer 1,, R. M. Jadav 1, A. K. Jadeja 1, P. K. Manoharan 2, Som Sharma 3 and Hari Om Vats 3 1 Department of Physics,
Space Weather and Satellite System Interaction
 Space Engineering International Course, Kyutech, 4 th Quarter Semester 2017 Space Weather and Satellite System Interaction Lecture 2: Space Weather Concept, Reporting and Forecasting Assoc. Prof. Ir. Dr.
Space Engineering International Course, Kyutech, 4 th Quarter Semester 2017 Space Weather and Satellite System Interaction Lecture 2: Space Weather Concept, Reporting and Forecasting Assoc. Prof. Ir. Dr.
Geomagnetic storms. Measurement and forecasting
 Geomagnetic storms. Measurement and forecasting Anna Gustavsson 17 October 2006 Project of the Space Physics Course 2006 Umeå University 1 Introduction Effects of magnetic storms on technology Geomagnetic
Geomagnetic storms. Measurement and forecasting Anna Gustavsson 17 October 2006 Project of the Space Physics Course 2006 Umeå University 1 Introduction Effects of magnetic storms on technology Geomagnetic
History and modernity of the study of Space Weather in Russia
 History and modernity of the study of Space Weather in Russia Klimov, S.I., A.A. Petrukovich Space Research Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences (IKI RAN), 117997, 84/32 Profsoyuznaya str., Moscow, Russia
History and modernity of the study of Space Weather in Russia Klimov, S.I., A.A. Petrukovich Space Research Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences (IKI RAN), 117997, 84/32 Profsoyuznaya str., Moscow, Russia
STCE Newsletter. 28 Oct Nov 2013
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 8 Nov 2013. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 8 Nov 2013. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Logistics 2/13/18. Topics for Today and Thur+ Helioseismology: Millions of sound waves available to probe solar interior. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 9 Tues 13 Feb 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur+ Helioseismology:
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 9 Tues 13 Feb 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur+ Helioseismology:
Swedish Institute of Space Physics Research Strategies
 Dnr 1.1-147/14 (replaces Dnr 1-309/04) Swedish Institute of Space Physics Research Strategies The Swedish Institute of Space Physics (IRF) is a national research institute under the auspices of the Swedish
Dnr 1.1-147/14 (replaces Dnr 1-309/04) Swedish Institute of Space Physics Research Strategies The Swedish Institute of Space Physics (IRF) is a national research institute under the auspices of the Swedish
Guidepost. Chapter 08 The Sun 10/12/2015. General Properties. The Photosphere. Granulation. Energy Transport in the Photosphere.
 Guidepost The Sun is the source of light an warmth in our solar system, so it is a natural object to human curiosity. It is also the star most easily visible from Earth, and therefore the most studied.
Guidepost The Sun is the source of light an warmth in our solar system, so it is a natural object to human curiosity. It is also the star most easily visible from Earth, and therefore the most studied.
Chapter 1. Introduction. 1.1 Why study the sun?
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Why study the sun? The sun is an ordinary main-sequence star of spectral type G2V. From the human perspective it is the most important star in the universe. It provides the earth
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Why study the sun? The sun is an ordinary main-sequence star of spectral type G2V. From the human perspective it is the most important star in the universe. It provides the earth
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths
 1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT
![Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT](/thumbs/89/99030303.jpg) Space Weather S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Outline Overview of Space Weather I. Space disasters II. Space weather III. Sun IV. Solar wind (interplanetary space) V. Magnetosphere VI. Recent Space
Space Weather S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Outline Overview of Space Weather I. Space disasters II. Space weather III. Sun IV. Solar wind (interplanetary space) V. Magnetosphere VI. Recent Space
Radio Observations and Space Weather Research
 Radio Observations and Space Weather Research Jasmina Magdalenić Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium What is space weather and why is it important? Eruptive processes:
Radio Observations and Space Weather Research Jasmina Magdalenić Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium What is space weather and why is it important? Eruptive processes:
NASA s Contribution to International Living With a Star
 NASA s Contribution to International Living With a Star Madhulika Guhathakurta Office of Space Science, CodeSS NASA Headquarters October 17,2002 Sun-Earth Connection (Sec) Program Planet Varying Radiation
NASA s Contribution to International Living With a Star Madhulika Guhathakurta Office of Space Science, CodeSS NASA Headquarters October 17,2002 Sun-Earth Connection (Sec) Program Planet Varying Radiation
8.2 The Sun pg Stars emit electromagnetic radiation, which travels at the speed of light.
 8.2 The Sun pg. 309 Key Concepts: 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some
8.2 The Sun pg. 309 Key Concepts: 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some
! The Sun as a star! Structure of the Sun! The Solar Cycle! Solar Activity! Solar Wind! Observing the Sun. The Sun & Solar Activity
 ! The Sun as a star! Structure of the Sun! The Solar Cycle! Solar Activity! Solar Wind! Observing the Sun The Sun & Solar Activity The Sun in Perspective Planck s Law for Black Body Radiation ν = c / λ
! The Sun as a star! Structure of the Sun! The Solar Cycle! Solar Activity! Solar Wind! Observing the Sun The Sun & Solar Activity The Sun in Perspective Planck s Law for Black Body Radiation ν = c / λ
Chapter 14 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Star Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is
Chapter 14 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is
Logistics 2/14/17. Topics for Today and Thur. Helioseismology: Millions of sound waves available to probe solar interior. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 9 Tues 14 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur Helioseismology:
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 9 Tues 14 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur Helioseismology:
What is COSPAR and why does it matter to CAPS? Gregg Vane 16 September 2015
 What is COSPAR and why does it matter to CAPS? Gregg Vane 16 September 2015 Topics Overview of COSPAR Relevance to CAPS How to engage in an effective way 2 Overview of COSPAR Origin: Established by the
What is COSPAR and why does it matter to CAPS? Gregg Vane 16 September 2015 Topics Overview of COSPAR Relevance to CAPS How to engage in an effective way 2 Overview of COSPAR Origin: Established by the
ILWS activity in Romania
 Institute of Space Science romanian space agency ILWS activity in Romania Dumitru HASEGAN 1,2. Octav MARGHITU 1 1-ISS, 2-ROSA Outline A. Introduction Historical synopsis B. Research themes 1. Solar-Terrestrial
Institute of Space Science romanian space agency ILWS activity in Romania Dumitru HASEGAN 1,2. Octav MARGHITU 1 1-ISS, 2-ROSA Outline A. Introduction Historical synopsis B. Research themes 1. Solar-Terrestrial
An Introduction to Space Weather. J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR
 An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
The Sun. Basic Properties. Radius: Mass: Luminosity: Effective Temperature:
 The Sun Basic Properties Radius: Mass: 5 R Sun = 6.96 km 9 R M Sun 5 30 = 1.99 kg 3.33 M ρ Sun = 1.41g cm 3 Luminosity: L Sun = 3.86 26 W Effective Temperature: L Sun 2 4 = 4πRSunσTe Te 5770 K The Sun
The Sun Basic Properties Radius: Mass: 5 R Sun = 6.96 km 9 R M Sun 5 30 = 1.99 kg 3.33 M ρ Sun = 1.41g cm 3 Luminosity: L Sun = 3.86 26 W Effective Temperature: L Sun 2 4 = 4πRSunσTe Te 5770 K The Sun
Chapter 9 The Sun. Nuclear fusion: Combining of light nuclei into heavier ones Example: In the Sun is conversion of H into He
 Our sole source of light and heat in the solar system A common star: a glowing ball of plasma held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion at its center. Nuclear fusion: Combining of
Our sole source of light and heat in the solar system A common star: a glowing ball of plasma held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion at its center. Nuclear fusion: Combining of
Marianna G. Shepherd Scientific Secretary Scientific Committee on Solar-Terrestrial Physics (SCOSTEP)
 51 st Scientific and Technical Subcommittee UN COPUOS Vienna, 12 February 2014 Marianna G. Shepherd Scientific Secretary Scientific Committee on Solar-Terrestrial Physics (SCOSTEP) STEP Solar- Terrestrial
51 st Scientific and Technical Subcommittee UN COPUOS Vienna, 12 February 2014 Marianna G. Shepherd Scientific Secretary Scientific Committee on Solar-Terrestrial Physics (SCOSTEP) STEP Solar- Terrestrial
Substorms at Mercury: Old Questions and New Insights. Daniel N. Baker Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP)
 Substorms at Mercury: Old Questions and New Insights Daniel N. Baker Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) Outline of Presentation Introduction Substorms in the Earth s Magnetosphere Prior
Substorms at Mercury: Old Questions and New Insights Daniel N. Baker Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) Outline of Presentation Introduction Substorms in the Earth s Magnetosphere Prior
ILWS Related Activities in Germany (Update) Prague, June 11-12, 2008
 ILWS Related Activities in Germany (Update) Prague, June 11-12, 2008 ILWS, DLR, Dr. Frings Overview Update is based on previous ILWS Presentations Focus on recent developments and achievements SOL-ACES
ILWS Related Activities in Germany (Update) Prague, June 11-12, 2008 ILWS, DLR, Dr. Frings Overview Update is based on previous ILWS Presentations Focus on recent developments and achievements SOL-ACES
Rationale for a European Space Weather Programme
 Rationale for a European Space Weather Programme Hannu Koskinen Finnish Meteorological Institute ESWS Final Presentation ESTEC, 6 December, 2001 Scope WP 300 of ESWS: Establishment of detailed rationale
Rationale for a European Space Weather Programme Hannu Koskinen Finnish Meteorological Institute ESWS Final Presentation ESTEC, 6 December, 2001 Scope WP 300 of ESWS: Establishment of detailed rationale
About the Van Allen Probes Mission
 Van Allen Probes Exploring th About the Van Allen Probes Mission To help us understand how Earth responds to changes in the sun s energy and how that response affects life and society, NASA launched the
Van Allen Probes Exploring th About the Van Allen Probes Mission To help us understand how Earth responds to changes in the sun s energy and how that response affects life and society, NASA launched the
Using This Flip Chart
 Using This Flip Chart Sunspots are the first indicators that a storm from the Sun is a possibility. However, not all sunspots cause problems for Earth. By following the steps in this flip chart you will
Using This Flip Chart Sunspots are the first indicators that a storm from the Sun is a possibility. However, not all sunspots cause problems for Earth. By following the steps in this flip chart you will
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 15 THE SUN: A GARDEN-VARIETY STAR PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 15 THE SUN: A GARDEN-VARIETY STAR PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 15.1 Our Star. The Sun our local star is quite average in many ways. However, that does not stop it from being a fascinating
ASTRONOMY Chapter 15 THE SUN: A GARDEN-VARIETY STAR PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 15.1 Our Star. The Sun our local star is quite average in many ways. However, that does not stop it from being a fascinating
What is COSPAR and! why does it matter to PSS?" Gregg Vane! 05 October 2015!
 What is COSPAR and why does it matter to PSS?" Gregg Vane 05 October 2015 Topics" Overview of COSPAR Relevance to PSS How to engage in an effective way 2 Overview of COSPAR Origin: Established by the International
What is COSPAR and why does it matter to PSS?" Gregg Vane 05 October 2015 Topics" Overview of COSPAR Relevance to PSS How to engage in an effective way 2 Overview of COSPAR Origin: Established by the International
AUTOMATIC PREDICTION OF SOLAR FLARES USING A NEURAL NETWORK. James Negus University of Chicago Mentor: Andrew Jones LASP
 AUTOMATIC PREDICTION OF SOLAR FLARES USING A NEURAL NETWORK James Negus University of Chicago Mentor: Andrew Jones LASP SOLAR FLARE A flare is defined as a sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness.
AUTOMATIC PREDICTION OF SOLAR FLARES USING A NEURAL NETWORK James Negus University of Chicago Mentor: Andrew Jones LASP SOLAR FLARE A flare is defined as a sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness.
The importance of ground-based observations of the solar corona
 The importance of ground-based observations of the solar corona J. Burkepile 1, S. Tomczyk 1, P. Nelson 1, A.G. dewijn 1, S. Sewell 1, D. Elmore 2, L. Sutherland 1, R. Summers 1, D. Kolinski 1, L. Sitongia
The importance of ground-based observations of the solar corona J. Burkepile 1, S. Tomczyk 1, P. Nelson 1, A.G. dewijn 1, S. Sewell 1, D. Elmore 2, L. Sutherland 1, R. Summers 1, D. Kolinski 1, L. Sitongia
Space Weather Activities in Switzerland
 Space Weather Activities in Switzerland Margit Haberreiter PMOD/WRC, Davos, Switzerland 1 Reports Space Research in Switzerland 2012-2014 In preparation: Space Research in Switzerland 2015-2017 2 Reports
Space Weather Activities in Switzerland Margit Haberreiter PMOD/WRC, Davos, Switzerland 1 Reports Space Research in Switzerland 2012-2014 In preparation: Space Research in Switzerland 2015-2017 2 Reports
Gaps in Space Weather Forecasting
 Gaps in Space Weather Forecasting Awareness Gap: Where is there uncertainty about how the scientific community can contribute to space weather operations? Areas With Good Awareness - All agencies recognize
Gaps in Space Weather Forecasting Awareness Gap: Where is there uncertainty about how the scientific community can contribute to space weather operations? Areas With Good Awareness - All agencies recognize
Sun-Earth Connection Missions
 ACE (1997 ) Cosmic and Heliospheric Study of the physics and chemistry Advanced Composition Explorer Learning Center of the solar corona, the solar wind, http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/ace/ http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov
ACE (1997 ) Cosmic and Heliospheric Study of the physics and chemistry Advanced Composition Explorer Learning Center of the solar corona, the solar wind, http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/ace/ http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov
Space environment (natural and artificial) Realtime solar activity and space environment information for spacecraft operation
 ISO 2008 All rights reserved ISO TC 20/SC 14 N873 Date: 2012-07-31 ISO/CDV 16709 ISO TC 20/SC 14/WG 4 Secretariat: Space environment (natural and artificial) Realtime solar activity and space environment
ISO 2008 All rights reserved ISO TC 20/SC 14 N873 Date: 2012-07-31 ISO/CDV 16709 ISO TC 20/SC 14/WG 4 Secretariat: Space environment (natural and artificial) Realtime solar activity and space environment
Geomagnetic Disturbances (GMDs) History and Prediction
 Geomagnetic Disturbances (GMDs) History and Prediction J. Patrick Donohoe, Ph.D., P.E. Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi State University Box 9571 Miss. State, MS 39762 donohoe@ece.msstate.edu
Geomagnetic Disturbances (GMDs) History and Prediction J. Patrick Donohoe, Ph.D., P.E. Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi State University Box 9571 Miss. State, MS 39762 donohoe@ece.msstate.edu
Space Weather and Amateur Radio: Science, Forecasting and Effects. The Aerospace Corporation Dayton Hamvention Antenna Forum 19 May 2017
 Space Weather and Amateur Radio: Science, Forecasting and Effects The Aerospace Corporation Dayton Hamvention Antenna Forum 19 May 2017 What is Space Weather? Essentially Space Weather is: A planet s interaction
Space Weather and Amateur Radio: Science, Forecasting and Effects The Aerospace Corporation Dayton Hamvention Antenna Forum 19 May 2017 What is Space Weather? Essentially Space Weather is: A planet s interaction
Announcements. - Homework #5 due today - Review on Monday 3:30 4:15pm in RH103 - Test #2 next Tuesday, Oct 11
 Announcements - Homework #5 due today - Review on Monday 3:30 4:15pm in RH103 - Test #2 next Tuesday, Oct 11 Review for Test #2 Oct 11 Topics: The Solar System and its Formation The Earth and our Moon
Announcements - Homework #5 due today - Review on Monday 3:30 4:15pm in RH103 - Test #2 next Tuesday, Oct 11 Review for Test #2 Oct 11 Topics: The Solar System and its Formation The Earth and our Moon
The Sun. 1a. The Photosphere. A. The Solar Atmosphere. 1b. Limb Darkening. A. Solar Atmosphere. B. Phenomena (Sunspots) C.
 The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2006Sep18 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind 3 1a. The
The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2006Sep18 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind 3 1a. The
Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program
 Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program The Sun Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun isn t actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun a giant ball of
Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program The Sun Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun isn t actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun a giant ball of
The Sun. 1a. The Photosphere. A. The Solar Atmosphere. 1b. Limb Darkening. A. Solar Atmosphere. B. Phenomena (Sunspots) C.
 The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2014Feb08 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind & earthly
The Sun 1 The Sun A. Solar Atmosphere 2 B. Phenomena (Sunspots) Dr. Bill Pezzaglia C. Interior Updated 2014Feb08 A. The Solar Atmosphere 1. Photosphere 2. Chromosphere 3. Corona 4. Solar Wind & earthly
Recent and future actions about Space Weather in Austria Manuela Temmer
 Recent and future actions about Space Weather in Austria Manuela Temmer Institute of Physics, University of Graz, Austria U.N. Space Weather Expert group Meeting and Workshop, Vienna, February 15 17, 2016
Recent and future actions about Space Weather in Austria Manuela Temmer Institute of Physics, University of Graz, Austria U.N. Space Weather Expert group Meeting and Workshop, Vienna, February 15 17, 2016
The Dancing Lights Program
 The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter?
 Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter? N. Ganushkina (1, 2), S. Dubyagin (1), I. Sillanpää (1), D.
Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter? N. Ganushkina (1, 2), S. Dubyagin (1), I. Sillanpää (1), D.
Exploring the Solar Wind with Ultraviolet Light
 Timbuktu Academy Seminar, Southern University and A&M College, November 19, 2003 Exploring the Solar Wind with Ultraviolet Light Steven R. Cranmer Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
Timbuktu Academy Seminar, Southern University and A&M College, November 19, 2003 Exploring the Solar Wind with Ultraviolet Light Steven R. Cranmer Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Earth Sun comparison. Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned.
 Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
Space Weather. ~ Affects of solar activities onto Earth. Cause-Effect Time Intervals range from immediate (precisely, 8 minutes) to several days.
 Space Weather ~ Affects of solar activities onto Earth Cause-Effect Time Intervals range from immediate (precisely, 8 minutes) to several days. days Two difficulties arise for forecasting (modelling):
Space Weather ~ Affects of solar activities onto Earth Cause-Effect Time Intervals range from immediate (precisely, 8 minutes) to several days. days Two difficulties arise for forecasting (modelling):
STCE Newsletter. 14 Jan Jan 2013
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 25 Jan 2013. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 25 Jan 2013. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Geomagnetic Disturbance Report Reeve Observatory
 Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Proton-proton cycle 3 steps PHYS 162 1
 Proton-proton cycle 3 steps PHYS 162 1 4 Layers of the Sun CORE : center, where fusion occurs RADIATION: energy transfer by radiation CONVECTION: energy transfer by convection PHOTOSPHERE: what we see
Proton-proton cycle 3 steps PHYS 162 1 4 Layers of the Sun CORE : center, where fusion occurs RADIATION: energy transfer by radiation CONVECTION: energy transfer by convection PHOTOSPHERE: what we see
Space Weather Awareness in the Arctic. Torsten Neubert Head of Section for Solar System Physics
 Space Weather Awareness in the Arctic Torsten Neubert Head of Section for Solar System Physics Technology in the Arctic There is significant potential Resources Tourism helped by receding ocean ice There
Space Weather Awareness in the Arctic Torsten Neubert Head of Section for Solar System Physics Technology in the Arctic There is significant potential Resources Tourism helped by receding ocean ice There
1 A= one Angstrom = 1 10 cm
 Our Star : The Sun )Chapter 10) The sun is hot fireball of gas. We observe its outer surface called the photosphere: We determine the temperature of the photosphere by measuring its spectrum: The peak
Our Star : The Sun )Chapter 10) The sun is hot fireball of gas. We observe its outer surface called the photosphere: We determine the temperature of the photosphere by measuring its spectrum: The peak
Indo-US Bilateral Cooperation Program in Heliophysics and Space Weather
 Indo-US Bilateral Cooperation Program in Heliophysics and Space Weather Dibyendu Nandy ~~ Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata What is Heliophysics? Solar variability forces space
Indo-US Bilateral Cooperation Program in Heliophysics and Space Weather Dibyendu Nandy ~~ Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata What is Heliophysics? Solar variability forces space
