Photoionization of trapped ions at synchrotrons and
|
|
|
- Bonnie Hunt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Photoionization of trapped ions at synchrotrons and free-electron electron X-ray X lasers José R. Crespo López-Urrutia Sascha W. Epp,, Martin C. Simon, Maria Schwarz, Christian Beilmann Max-Planck Planck-Institut für f r Kernphysik Heidelberg
3 Our closest highly ionized neighbor
4 Saariselkä at the other end...
5 Why highly charged ions (HCI)? Naturally abundant: warm hot intergalactic medium (WHIM, this backdrop) may comprise half of the missing baryonic matter! QED fully loaded electrons to benchmark relativistic ab initio theory Electron-electron correlations can be tuned from simple (H-like) to complex (He-like, etc.) Important for fusion research plasmas
6 Follow the bound-state QED experts...
7 QED scales with Z 4 only a few ev accuracy needed since effects are very large
8 Asymmetry due to quantum interference
9 1e QED 4 ev 2e QED 0.2 ev recoil 0.08 ev 0.04 ev uncertainty Mid-heavy ions studied with electrons, X rays
10 The He-like1s2p 1 P 1-1s 21 S 0 resonance line w Z Artemyev Drake Experiment Ref. This work Remarks (9) [1] (3) Absolute, 3x (38) [2] (4) Absolute, 10x (1) (200) [3] (13) Absolute, 7x (250) [4] In Fe 24+ contribution to this transition of: 4 ev QED, 200 mev screened QED, 100 mev nuclear recoil contributions vs. 13 mev uncertainty [1] L. Schleinkofer et al., Phys. Scr. 25, 917 (1982) [2] R. D. Deslattes, H. F. Beyer, and F. Folkmann, J. Phys. B 17, L689 (1984) [3] P. Beiersdorfer et al., Phys. Rev. A 40, 150 (1989) [4] J. P. Briand et al., Phys. Rev. A 29, 3143 (1984)
11 Two-electron QED Contributions to ground state in He-like Ar ev 5 ev 1 ev + + h. o. experimental error bar: 0.01 ev E nuclear recoil 0.06 ev higher orders ev 0.1 ev
12 Forbidden lines with laser spectroscopy
13 Relativistic nuclear recoil seen: 40 Ar/ 36 Ar isotopic shifts in forbidden transitions Ion Ion NMS SMS RNMS RSMS FS Total Ar Ar Normal mass shift (NMS), specific mass shift (SMS) and their relativistic corrections (RNMS, RSMS) are similar in size Theory λ (nm,air)* λ Observed (nm) Isotopic shifts ( 40 Ar/ 36 Ar) theory(nm) experiment(n m) Ar (27) (1) (2) Ar (30) (3) (7) Results agree with recent predictions (Shabaev)
14 CryPTEx: Cryogenic Paul trap for HCI spectroscopy Laser spectroscopy on sympathetically cooled HCI
15 Redistribution of energy by radiation Light is faster than shocks, even than relativistic jets X rays shift more energy around than visible light In astrophysics, parameter is the ratio of photon flux (ergs/cm 2 s) over electron density N =4 I/N ratio of photoionization over collisional ionization In astrophysics typically10< <10000 In laboratory up to <10 (lasers, Z pinches) With LCLS and EBIT, < possible (at low N)
16 Around black holes, neutron stars, X rays generated by infalling matter photoionize the surroundings: Photoabsorption is seen Black holes glow; Fe K-shell radiation is the last cry of matter
17 The identification problem Existing atomic models have large wavelength uncertainties and lack experimental confirmation Only 100 lines identified out of 950!
18 The Fe L-shell autoionizing resonances carry 60% of total PI strength, dominating over the direct channel PI cross section (cm 2 ) Integrated PI strength (cm 2 ev) x x x10-16 Direct PI cross section Total PI cross section Total strength Resonant strength Direct photoionization strength Planck continuum Cross section weighted with Planck continuum Photon energy (ev) Resonances dominate!
19 X-ray absorption spectra of quasars X-ray spectra of quasars show HCI in their outflows. Fe ions are prominent Uncertainties of different models for calculating spectra are too large for Doppler shift speed determinations
20 The warm-hot intergalactic medium (59 ± 9) % of baryons are missing 30 Mpsc To hot for visible light, too diffuse for direct X-ray detection Cosmological simulations (Cen & Ostriker) predict a warm-hot interstellar medium (WHIM) heated by gravitation to 10 6 K containing most of the missing baryons Discovery by Nicastro (2005)?
21 How to detect WHIM For very tenuous media, measurements in absorption are far more sensitive than those in emission Chandra Backlighting quasar medium absorbing radiation Spectrum shows absorption lines Details matter! You may miss half the mass of the universe!
22 WHIM and interstellar medium absorption Detective work: figure out red shift <z>, identify lines, determine temperature, infer density of metals, He + and H + Local Group WHIM <z>=0.011 WHIM <z>=0.027 WHIM
23 Details matter! You may miss half of the mass of the universe! Newer observations confirm WHIM (Fang et al.)
24 The opacity problem Radiation transport inside the Sun is determined by opacity of Fe, Ne, O at temperatures 200 to 500 ev Fe are essential Helioseismographic data disagree with models: opacities are only calculated!
25 Photonic interactions with HCI Combine novel high energy photon sources (free electron lasers, synchrotrons) with EBIT to measure excitation energies beyond current accuracy limits to study multiphoton processes to determine cross sections for photoexcitation, photoionization HCI benchmarking atomic theory
26 HCI production with electron beam ion trap I beam =450 ma radial potential electron beam space charge axial potential electrodes A/cm 2 n e e - /cm 3 Electron beam drives ionization and traps
27 Sascha s EBIT
28 z coordinate FEL principle Radiation field interacts with electron bunch and structures it Electron beam Radiation
29 Coherent superposition enhances intensity by a factor proportional to the number of charges in the bunch N e Dipole Wiggler Undulator Undulator Brilliance increases by many orders of magnitude
30 The free electron laser FLASH Accelerator hall Free electron LASer in Hamburg Undulator tunnel 240 m E max = 200 ev E/ΔE nat. 100 t pulse 2*10-14 s E pulse 50 μj 500 pulses/s 240 m Experimental hall
31 Photoexcitation of HCI in an EBIT photons/s ions/cm 2 1 count/s
32 Detail of the trapping region FEL excitation fluorescence detection
33 Soft X-ray laser spectroscopy at FLASH FEL 50 ev beam excites resonantly the 2s-2p transition in Li-like Fe 23+ 2p 2 P 3/2 excitation by FLASH 2p 2 P 1/2 detect fluorescence 1% QED contribution 2s 2 S 1/2 Li-like ions have highest relative QED contributions to transition energy (up to 15% for U 89+ )
34 Laser bandwidth reduced by scanning monochromator E/ΔE = 2000 E/ΔE = 70
35 Resonant laser fluorescence excitation Arrival time ( s) Integral counts on MCP(E,t) right scale x c = (11)(150) ev FWHM=0.0353(24) ev Photon energy (ev) Counts S. W. Epp et al., PRL 98, (2007)
36 Soft X-ray laser spectroscopy of Li-like Fe Fluorescence (counts) /DoF = R 2 = y ±0.3 x c ± w ± A 1.16 ±0.05 preliminary results 2 /DoF = R 2 = y ± 0.5 x c ± w ± A 1.37 ± Photon energy (ev) Resolving power E/ E currently:~2600 near future: evaporative + sympathetic cooling: no limits! Accuracy: ± 6 ppm QED contributions of ppm Δ exp =( ± 0.001) ev Δ lit = ev
37 Calibrations fail at the required level of accuracy
38 QED contributions to transition energy in Li-like HCI These results test recent QED calculations at the level of: 1,2,3 virtual photons exchange between bound electrons one loop self energy + vacuum polarization self-energy screening by core electrons nuclear size effects relativistic nuclear recoil CALIBRATION STANDARDS NOT GOOD ENOUGH!
39 (A) one, (B) two and (C) three virtual photon exchange between electrons. Radiative corrections: (D) one loop SE + VP (H-like), (E) screening of (D) by core electrons, (F) nuclear size, (G) relativistic nuclear recoil. Total rel. uncertainties (right scale): (H) theory; (black squares): experiment
40 Photoionization direct PI E=h E kin + E=h resonant PI L E binding L E res K K interference Fano profiles doubly excited autoionizing
41 Photoionization of ions: extremely difficult in lab Limitations of current techniques (merged beams): HCI with ionization potentials lower than 150 ev (Ce 9+ ) low charge state ions (Ne 3+, C 2+ ) photon energies < 300 ev Most astrophysically relevant ions excluded! Ion current: ~100 na Target density: < 10 6 cm -3 Interaction time: ~ μs H. Kjeldsen, J. Phys. B 39 (2006) R325
42 Photoionization of ions Photoionization of O + as a function of photon energy for an admixture of 57% metastable and 43% ground-state O + ions Single and double ionization of Xe 4+. Discrete lines result from autoionization of Xe 4+ excited states, continuous lines from single 4d photoionization of part of the Xe 4+ and from the Auger decay of coreionized Xe 5+. (Bizeau et al.)
43 Measured and calculated cross sections for PI of C 2+ ions The solid curve represents the weighted sum of the R-matrix results assuming 60% of ground state (gs) ions in the primary beam, 30% in the 3 P 0 and 5% each in the 3 P 1 and 3 P 2 metastable (ms) states. The theoretical result is almost indistinguishable from the measurements below 51 ev... Photoionization of C 2+ ions: time-reversed recombination of C 3+ with electrons, A. Müller et al., J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 35, L137 (2002)
44
45 Photoionization of ions Photoionization theory has few experimental benchmarks for HCI HCI photon opacity data are based completely on untested theory EBIT allows for systematic studies with HCI along: isoelectronic sequences, isonuclear sequences, isotopic shifts
46
47 Photoionization of HCI in the EBIT - Photoionizing trapped HCI Velocity filter Soft x-ray photon beam - Extracting photoions Position-sensitive ion detector (TOF) Ion deflector BESSY 2008/09 Ion optics EBIT Electron collector Fluorescence diagnostics Trap electrodes Magnet coils Electron gun
48 Photoionization of trapped HCI
49 Photoion extraction and analysis mirror z-manipulation Wien filter & PSD electrostatic ion deflector FLASH steering lens FLASH trap trap YAG fluorescence light CCD HCIs ion optic positive ground negative voltage
50 Photoion extraction and charge analysis Fe 14+ Wien filter monochromator position sensitive detector Fe 15+ B E extracted ions photon beam: photons/s electrostatic deflector collector trap gun
51 Overlap monitoring Mirror with hole allows imaging of screen N 2 injection collector electron beam: ~3mA, 60eV trap electron beam photon beam trap 4 mm gun overlap of ions and photons: fluorescent screen 120 µm
52 Overlap monitoring horizontal beam extension: 240 μm 50 vertical beam extension (pixel) ~22.5 μm/pixel electron beam d ~ 180 μm slit width (μm)
53 Calibration runs: Photoionization Ne (He ) Intensity (counts) Data: TMETM5_F Model: Fano Weighting: y Statistical Chi^2/DoF = R^2 = q ± gammares ± Eres ± y ± A ± Data: TMETM5_F Model: Fano Weighting: y Statistical Chi^2/DoF = R^2 = q ± gammares ± Eres ± y ± A ± The use of narrow photoionization resonances of He etc. can provide calculable standards in the region up to 80 ev F J Fano fit of TMETM5_F Energy (ev) Intensity (counts) 700 Model: Fano Weighting: Statistical Chi^2/DoF = R^2 = q ± 0.04 res ± Eres ± y0 161 ± 4 A 107 ± 5 L Fano simulation residue Photon energy (ev)
54 600 Photoionizing trapped N 3+ at BESSY Ration N 4+ /N Ionisation edge N 3+ 1s 2 2s 2p 3 P Ionisation edge N 3+ 1s 2 2s 2 1 S Photon energy (ev)
55 Photoionizing trapped N 3+ at BESSY
56 N 3+ in comparison with earlier work
57 Photoionized Fe 14+ : highest charge state reported Ar 8+,10+,12+, Fe 12+,14+ also studied 34 Photoionization signal (arb. u.) Ar 8+ to Ar 9+ threshold 2s7p 2s8p 2s9p 2s10p 2s11p Photon energy (ev) ,4 447,6 447,8
58 Ar 12+ has an IP of 684 ev
59
60 Fe 14+ photoionization
61 Fe 14+ photoionization Current sensitivity 20 kbarn
62 Autoionizing resonances natural linewidth 40 mev Photoion signal (counts) Lorentz fit /DoF = R 2 = 0.94 y 0 =167 ± 3 x c = ± w = ± A = 106 ± Photon energy (ev) Current resolution E/ E=6500, but monochromators reach >50000, very interesting for precision studies!
63 Agreement with RMBPT at 0.2 ev for strongest lines
64 Population of Fe 15+ in trap depends on time with photons without photons Rate: probability for photoionization per unit time per unit of photon flux: absolute cross section for photoionization! Resonance at 807 ev res = (430±260) Mbarn
65 Calculations available for Fe 14+ Magenta dots: our data Red curve: HULLAC Black curve: RMBPT Doppler shift depends on prediction (M. Gu, E. Behar) Hypothetical two-phase outflows? Our results confirm RMBPT calculations; therefore, no two-phase outflows occur in NGC 3783
66 Doppler shift corrected based on experiment Laboratory measurements of HCI absorption line positions and cross sections are possible with EBITs
67 Photon energy ranges accessed BESSY 2009: resonant photoionization approved proposal for PRL 98, (2007) FLASH EBIT proposal (2001) Bi 82+ I. Klaft et al. 5.1 ev 2. S 15+ H. Sträter et al. 2.9 ev 3. F 7+ E. Myers et al ev
68 PI range extended
69 Summary Photoionization of Fe 14+ in the X-ray region, soft X-ray laser spectroscopy (Fe 23+ ) demonstated Energies at 1 kev better than 0.1 ev (calibration limited), statistical uncertainties of 10 mev Absolute PI cross sections with less systematic error sources EBITs allow study of HCI photonic interactions in an experimentally unexplored regime
70 A brilliant outlook Higher photon energies at X-ray FELs: LCLS, X-FEL Photoionization of HCI at kev energies: Fe K shell Multiphoton processes, multiply excitations Lifetime measurements in the fs range: pump-probe HCI as atomic X-ray frequency standards
71 People involved MPIK T. Baumann, C. Beilmann, S. Bernitt, G. Brenner, F. Brunner, S. W. Epp, R. Ginzel, M. C. Simon, M. Schwarz, R. Klawitter, K. Kubicek, V. Mäckel, P. Mokler, B. L. Schmitt, JRCLU, J. Ullrich HI-LIGHT Collab. E. Behar, Technion P. Beiersdorfer, LLNL A. Rassmussen, SLAC G. Brown, LLNL DESY R. Treusch M. Kuhlmann N. Guerassimova M.V. Yurkov E. Schneidmiller J. Feldhaus J. R. Schneider Univ. Hamburg M. Wellhöfer M. Martins W. Wurth BESSY G. Reichardt O. Schwarzkopf R. Follath R. Püttner Support by Max-Planck Gesellschaft: Advanced Study Group ASG at the Center for Free Electron Lasers Physics CFEL
72
73 LCLS and XFEL experiments Inner-shell photoionization of HCI can produce multiply excited states decaying through a cascade channels resonantly coupled to the nucleus Direct photoexcitation can be achieved, even multiphoton processes may be accessible Collaboration HI-LIGHT: Highly Charged Ions in the Ultrabrilliant Light of the LCLS P. Beiersdorfer et al.(llnl), J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, J. Ullrich, et al. (MPI-K Heidelberg), S. W. Epp (MPG Advanced Study Group/CFEL), A. Müller, S. Schippers (Giessen University), R. Schuch, E. Lindroth (Stockholm University), D. W. Savin (Columbia University), S. M. Kahn (SLAC), F. Schlachter (LBNL), J. Burke, N. Scielzo (LLNL), S. Manson (University of Georgia), F. S. Porter (NASA Goddard), J. Sapirstein (Notre Dame University), L. Schweikhard (Greifswald University)
74
Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions with Free Electron Lasers. Sascha Epp MPI-K Heidelberg & ASG within CFEL PSAS 2008
 Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions with Free Electron Lasers Sascha Epp MPI-K Heidelberg & ASG within CFEL Hamburg @ PSAS 2008 People involved in this work MPI-K S. W. E. (ASG) J. R. Crespo L. U. G. Brenner
Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions with Free Electron Lasers Sascha Epp MPI-K Heidelberg & ASG within CFEL Hamburg @ PSAS 2008 People involved in this work MPI-K S. W. E. (ASG) J. R. Crespo L. U. G. Brenner
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
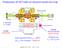 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
AMO at FLASH. FELs provide unique opportunities and challenges for AMO physics. due to essentially three reasons:
 Experience at FLASH AMO at FLASH FELs provide unique opportunities and challenges for AMO physics due to essentially three reasons: AMO at FLASH 1. huge integrated flux dilute samples Highly charged ions
Experience at FLASH AMO at FLASH FELs provide unique opportunities and challenges for AMO physics due to essentially three reasons: AMO at FLASH 1. huge integrated flux dilute samples Highly charged ions
Introduction to the physics of highly charged ions. Lecture 7: Direct and resonant photoionization of HCI
 Introduction to the physics of highly charged ions Lecture 7: Direct and resonant photoionization of HCI Zoltán Harman harman@mpi-hd.mpg.de Universität Heidelberg, 02.12.2013 So far: radiative decay and
Introduction to the physics of highly charged ions Lecture 7: Direct and resonant photoionization of HCI Zoltán Harman harman@mpi-hd.mpg.de Universität Heidelberg, 02.12.2013 So far: radiative decay and
Atomic structure and dynamics
 Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
Progress at the Heidelberg EBIT
 Progress at the Heidelberg EBIT J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, J. Braun, G. Brenner, H. Bruhns, C. Dimopoulou, I. N. Draganić, D. Fischer, A. J. González Martínez, A. Lapierre, V. Mironov, R. Moshammer, R.
Progress at the Heidelberg EBIT J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, J. Braun, G. Brenner, H. Bruhns, C. Dimopoulou, I. N. Draganić, D. Fischer, A. J. González Martínez, A. Lapierre, V. Mironov, R. Moshammer, R.
Excitation and cooling of large molecular and cluster ions
 Excitation and cooling of large molecular and cluster ions Andreas Wolf Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany Laboratory Astrophysics Workshop, Tabarz, 16-18 October 2014 Decay mechanisms
Excitation and cooling of large molecular and cluster ions Andreas Wolf Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany Laboratory Astrophysics Workshop, Tabarz, 16-18 October 2014 Decay mechanisms
The World s Smallest Extreme Laboratories:
 The World s Smallest Extreme Laboratories: Probing QED with Highly Charged Ions. Joan Marler Clemson University Outline About HCIs About Ion trapping Precision spectroscopy with HCIs Highly Charged Ions
The World s Smallest Extreme Laboratories: Probing QED with Highly Charged Ions. Joan Marler Clemson University Outline About HCIs About Ion trapping Precision spectroscopy with HCIs Highly Charged Ions
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics
 Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects
 AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
Extreme ultraviolet spectroscopy of highly charged argon ions at the Berlin EBIT
 Extreme ultraviolet spectroscopy of highly charged argon ions at the Berlin EBIT C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, G. Fussmann, F.I. Allen Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Lehrstuhl Plasmaphysik,
Extreme ultraviolet spectroscopy of highly charged argon ions at the Berlin EBIT C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, G. Fussmann, F.I. Allen Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Lehrstuhl Plasmaphysik,
free electron plus He-like ion
 free electron plus He-like ion E e I p,n E 2 E 1 ΔE=E e +I p,n aber: ΔE=E 2 -E 1 n n n n n n=1 n=2 n=3 AAMOP 2011-2012 2011-11-16 1 dielectronic recombination E 2 E 1 n n n n n n=1 n=2 n=3 AAMOP 2011-2012
free electron plus He-like ion E e I p,n E 2 E 1 ΔE=E e +I p,n aber: ΔE=E 2 -E 1 n n n n n n=1 n=2 n=3 AAMOP 2011-2012 2011-11-16 1 dielectronic recombination E 2 E 1 n n n n n n=1 n=2 n=3 AAMOP 2011-2012
EUV spectra from the NIST EBIT
 EUV spectra from the NIST EBIT D. Kilbane and G. O Sullivan Atomic and Molecular Plasma Physics group, UCD, Ireland J. D. Gillaspy, Yu. Ralchenko and J. Reader National Institute of Standards and Technology,
EUV spectra from the NIST EBIT D. Kilbane and G. O Sullivan Atomic and Molecular Plasma Physics group, UCD, Ireland J. D. Gillaspy, Yu. Ralchenko and J. Reader National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Upgrade of the FLASH beamlines New diagnostic and beam transport tools
 Upgrade of the FLASH beamlines New diagnostic and beam transport tools Kai Tiedtke FLASH Seminar 16.3.2010 Installation in the tunnel and experimental hall -Install a focusing mirror at BL3 Experimental
Upgrade of the FLASH beamlines New diagnostic and beam transport tools Kai Tiedtke FLASH Seminar 16.3.2010 Installation in the tunnel and experimental hall -Install a focusing mirror at BL3 Experimental
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008
 Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Research with Synchrotron Radiation. Part I
 Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
X-ray production from resonant coherent excitation of relativistic HCIs in crystals as a model for polarization XFEL studies in the kev range
 X-ray production from resonant coherent excitation of relativistic HCIs in crystals as a model for polarization XFEL studies in the kev range V.V.Balashov, A.A.Sokolik, A.V.Stysin D.V.Skobeltsyn Institute
X-ray production from resonant coherent excitation of relativistic HCIs in crystals as a model for polarization XFEL studies in the kev range V.V.Balashov, A.A.Sokolik, A.V.Stysin D.V.Skobeltsyn Institute
Clusters in intense x-ray pulses from 100 nm to.7 nm
 Clusters in intense x-ray pulses from 100 nm to.7 nm Linac Coherent Light Source, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Outline: Introduction and motivation Spectroscopy of clusters Single shot imaging
Clusters in intense x-ray pulses from 100 nm to.7 nm Linac Coherent Light Source, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Outline: Introduction and motivation Spectroscopy of clusters Single shot imaging
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10721 Experimental Methods The experiment was performed at the AMO scientific instrument 31 at the LCLS XFEL at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The nominal electron bunch charge
doi:10.1038/nature10721 Experimental Methods The experiment was performed at the AMO scientific instrument 31 at the LCLS XFEL at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The nominal electron bunch charge
Lecture on: Multiphoton Physics. Carsten Müller
 Lecture on: Multiphoton Physics Carsten Müller Institut für Theoretische Physik I, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg IMPRS-QD Annual Event, MPIK, Heidelberg,
Lecture on: Multiphoton Physics Carsten Müller Institut für Theoretische Physik I, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg IMPRS-QD Annual Event, MPIK, Heidelberg,
Cold Metastable Neon Atoms Towards Degenerated Ne*- Ensembles
 Cold Metastable Neon Atoms Towards Degenerated Ne*- Ensembles Supported by the DFG Schwerpunktprogramm SPP 1116 and the European Research Training Network Cold Quantum Gases Peter Spoden, Martin Zinner,
Cold Metastable Neon Atoms Towards Degenerated Ne*- Ensembles Supported by the DFG Schwerpunktprogramm SPP 1116 and the European Research Training Network Cold Quantum Gases Peter Spoden, Martin Zinner,
Study of matter in extreme conditions using 4th generation FEL light sources
 Study of matter in extreme conditions using 4th generation FEL light sources Sam Vinko Department of Physics Clarendon Laboratory University of Oxford Workshop on Science with Free Electron Lasers Shanghai,
Study of matter in extreme conditions using 4th generation FEL light sources Sam Vinko Department of Physics Clarendon Laboratory University of Oxford Workshop on Science with Free Electron Lasers Shanghai,
Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source
 3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
3. Synchrotrons. Synchrotron Basics
 1 3. Synchrotrons Synchrotron Basics What you will learn about 2 Overview of a Synchrotron Source Losing & Replenishing Electrons Storage Ring and Magnetic Lattice Synchrotron Radiation Flux, Brilliance
1 3. Synchrotrons Synchrotron Basics What you will learn about 2 Overview of a Synchrotron Source Losing & Replenishing Electrons Storage Ring and Magnetic Lattice Synchrotron Radiation Flux, Brilliance
The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science
 The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science Singapore, fttp-5, April 20th, 2011 Bob Nagler BNagler@slac.stanford.edu SLAC national accelerator laboratory 1 Overview Motivation
The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science Singapore, fttp-5, April 20th, 2011 Bob Nagler BNagler@slac.stanford.edu SLAC national accelerator laboratory 1 Overview Motivation
Opportunities with collinear laser spectroscopy at DESIR:
 Opportunities with collinear laser spectroscopy at DESIR: the LUMIERE facility GOALS of LUMIERE experiments: Gerda Neyens, K.U. Leuven, Belgium (1) measure ground state properties of exotic isotopes: (see
Opportunities with collinear laser spectroscopy at DESIR: the LUMIERE facility GOALS of LUMIERE experiments: Gerda Neyens, K.U. Leuven, Belgium (1) measure ground state properties of exotic isotopes: (see
This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract
 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-7NA27344. Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC The ITER tokamak Tungsten (W) is attractive as
This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-7NA27344. Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC The ITER tokamak Tungsten (W) is attractive as
Auger electron and x-ray emission from high-z few-electron ions
 Auger electron and x-ray emission from high-z few-electron ions S. Fritzsche MPI für Kernphysik Heidelberg and GSI Darmstadt 4th August 2007 Main goal for studying high-z ions is the better understanding
Auger electron and x-ray emission from high-z few-electron ions S. Fritzsche MPI für Kernphysik Heidelberg and GSI Darmstadt 4th August 2007 Main goal for studying high-z ions is the better understanding
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2
 CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
The MID instrument.
 The MID instrument International Workshop on the Materials Imaging and Dynamics Instrument at the European XFEL Grenoble, Oct 28/29, 2009 Thomas Tschentscher thomas.tschentscher@xfel.eu Outline 2 History
The MID instrument International Workshop on the Materials Imaging and Dynamics Instrument at the European XFEL Grenoble, Oct 28/29, 2009 Thomas Tschentscher thomas.tschentscher@xfel.eu Outline 2 History
High-energy collision processes involving intense laser fields
 High-energy collision processes involving intense laser fields Carsten Müller Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Theory Division (Christoph H. Keitel), Heidelberg, Germany EMMI Workshop: Particle
High-energy collision processes involving intense laser fields Carsten Müller Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Theory Division (Christoph H. Keitel), Heidelberg, Germany EMMI Workshop: Particle
FLASH overview. Nikola Stojanovic. PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg,
 FLASH overview Nikola Stojanovic PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg, 16.12.2011 Outline Overview of the FLASH facility Examples of research at FLASH Nikola Stojanovic PIDID: FLASH overview Hamburg, December
FLASH overview Nikola Stojanovic PIDID collaboration meeting, Hamburg, 16.12.2011 Outline Overview of the FLASH facility Examples of research at FLASH Nikola Stojanovic PIDID: FLASH overview Hamburg, December
AMO physics with LCLS
 AMO physics with LCLS Phil Bucksbaum Director, Stanford PULSE Center SLAC Strong fields for x-rays LCLS experimental program Experimental capabilities End-station layout PULSE Ultrafast X-ray Summer June
AMO physics with LCLS Phil Bucksbaum Director, Stanford PULSE Center SLAC Strong fields for x-rays LCLS experimental program Experimental capabilities End-station layout PULSE Ultrafast X-ray Summer June
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 12: January 15, 2016
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 12: January 15, 2016 12 High Harmonic Generation 12.1 Atomic units 12.2 The three step model 12.2.1 Ionization 12.2.2 Propagation 12.2.3 Recombination 12.3 Attosecond
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 12: January 15, 2016 12 High Harmonic Generation 12.1 Atomic units 12.2 The three step model 12.2.1 Ionization 12.2.2 Propagation 12.2.3 Recombination 12.3 Attosecond
Plasma EUV source has been studied to achieve 180W of power at λ=13.5nm, which is required for the next generation microlithography
 Acknowledgement K. Nishihara, H. Nishimura, S. Fujioka Institute for Laser Engineering, Osaka University A. Sunahara, H. Furukawa Institute for Laser Technology T. Nishikawa, Okayama University F. Koike,
Acknowledgement K. Nishihara, H. Nishimura, S. Fujioka Institute for Laser Engineering, Osaka University A. Sunahara, H. Furukawa Institute for Laser Technology T. Nishikawa, Okayama University F. Koike,
Lecture 11, May 11, 2017
 Lecture 11, May 11, 2017 This week: Atomic Ions for QIP Ion Traps Vibrational modes Preparation of initial states Read-Out Single-Ion Gates Two-Ion Gates Introductory Review Articles: D. Leibfried, R.
Lecture 11, May 11, 2017 This week: Atomic Ions for QIP Ion Traps Vibrational modes Preparation of initial states Read-Out Single-Ion Gates Two-Ion Gates Introductory Review Articles: D. Leibfried, R.
Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL
 Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov FEL seminar, DESY Hamburg June 21, 2016 In a planar undulator (K ~ 1 or K >1) the odd harmonics can be radiated on-axis (widely used in SR
Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded FEL E. Schneidmiller and M. Yurkov FEL seminar, DESY Hamburg June 21, 2016 In a planar undulator (K ~ 1 or K >1) the odd harmonics can be radiated on-axis (widely used in SR
Ultra-Pure 163 Ho Samples for Neutrino Mass Measurements
 Ultra-Pure 163 Ho Samples for Neutrino Mass Measurements T. Kieck 1, H. Dorrer 1, Ch. E. Düllmann 1,2, K. Eberhardt 1, L. Gamer 3, L. Gastaldo 3, C. Hassel 3, U. Köster 4, B. Marsh 5, Ch. Mokry 1, S. Rothe
Ultra-Pure 163 Ho Samples for Neutrino Mass Measurements T. Kieck 1, H. Dorrer 1, Ch. E. Düllmann 1,2, K. Eberhardt 1, L. Gamer 3, L. Gastaldo 3, C. Hassel 3, U. Köster 4, B. Marsh 5, Ch. Mokry 1, S. Rothe
PB I FEL Gas-Monitor Detectors for FEL Online Photon Beam Diagnostics BESSY
 FEL 2004 Gas-Monitor Detectors for FEL Online Photon Beam Diagnostics M. Richter S.V. Bobashev, J. Feldhaus A. Gottwald, U. Hahn A.A. Sorokin, K. Tiedtke BESSY PTB s Radiometry Laboratory at BESSY II 1
FEL 2004 Gas-Monitor Detectors for FEL Online Photon Beam Diagnostics M. Richter S.V. Bobashev, J. Feldhaus A. Gottwald, U. Hahn A.A. Sorokin, K. Tiedtke BESSY PTB s Radiometry Laboratory at BESSY II 1
High Resolution Electron Spectrometry at the NESR. Ajay Kumar
 High Resolution Electron Spectrometry at the NESR Collaboration Ajay Kumar GSI, Darmstadt Stored Particles Atomic Physics Research Collaboration R. Mann G. Garcia X. Ma B. Sulik J. Ullrich L.C. Tribedi
High Resolution Electron Spectrometry at the NESR Collaboration Ajay Kumar GSI, Darmstadt Stored Particles Atomic Physics Research Collaboration R. Mann G. Garcia X. Ma B. Sulik J. Ullrich L.C. Tribedi
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions
 New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: FROM THE CENTRAL BLACK HOLE TO THE GALACTIC ENVIRONMENT
 Julian H. Krolik ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: FROM THE CENTRAL BLACK HOLE TO THE GALACTIC ENVIRONMENT PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS Princeton, New Jersey Preface Guide for Readers xv xix 1. What Are Active Galactic
Julian H. Krolik ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: FROM THE CENTRAL BLACK HOLE TO THE GALACTIC ENVIRONMENT PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS Princeton, New Jersey Preface Guide for Readers xv xix 1. What Are Active Galactic
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering
 X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
Proportional Counters
 Proportional Counters 3 1 Introduction 3 2 Before we can look at individual radiation processes, we need to understand how the radiation is detected: Non-imaging detectors Detectors capable of detecting
Proportional Counters 3 1 Introduction 3 2 Before we can look at individual radiation processes, we need to understand how the radiation is detected: Non-imaging detectors Detectors capable of detecting
LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES
 LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES A.E. Barzakh, D.V. Fedorov, A.M. Ionan, V.S. Ivanov, F.V. Moroz, K.A. Mezilev, S.Yu. Orlov, V.N. Panteleev, Yu.M. Volkov
LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES A.E. Barzakh, D.V. Fedorov, A.M. Ionan, V.S. Ivanov, F.V. Moroz, K.A. Mezilev, S.Yu. Orlov, V.N. Panteleev, Yu.M. Volkov
Theory of optically thin emission line spectroscopy
 Theory of optically thin emission line spectroscopy 1 Important definitions In general the spectrum of a source consists of a continuum and several line components. Processes which give raise to the continuous
Theory of optically thin emission line spectroscopy 1 Important definitions In general the spectrum of a source consists of a continuum and several line components. Processes which give raise to the continuous
Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Fusion Plasma Modelling using Atomic and Molecular Data January 2012
 2327-4 Joint ICTP- Workshop on Fusion Plasma Modelling using Atomic and Molecular Data 23-27 January 2012 Atomic Processes Modeling in Plasmas Modeling Spectroscopic Observables from Plasmas Hyun-Kyung
2327-4 Joint ICTP- Workshop on Fusion Plasma Modelling using Atomic and Molecular Data 23-27 January 2012 Atomic Processes Modeling in Plasmas Modeling Spectroscopic Observables from Plasmas Hyun-Kyung
Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions
 Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions W. Scheid 1,A.Pálffy 2,Z.Harman 2, C. Kozhuharov 3, and C. Brandau 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik der Justus-Liebig-Universität
Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions W. Scheid 1,A.Pálffy 2,Z.Harman 2, C. Kozhuharov 3, and C. Brandau 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik der Justus-Liebig-Universität
1.4 The Tools of the Trade!
 1.4 The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
1.4 The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
PHYSICS 359E: EXPERIMENT 2.2 THE MOSSBAUER EFFECT: RESONANT ABSORPTION OF (-RAYS
 PHYSICS 359E: EXPERIMENT 2.2 THE MOSSBAUER EFFECT: RESONANT ABSORPTION OF (-RAYS INTRODUCTION: In classical physics resonant phenomena are expected whenever a system can undergo free oscillations. These
PHYSICS 359E: EXPERIMENT 2.2 THE MOSSBAUER EFFECT: RESONANT ABSORPTION OF (-RAYS INTRODUCTION: In classical physics resonant phenomena are expected whenever a system can undergo free oscillations. These
1.5. The Tools of the Trade!
 1.5. The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
1.5. The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
First Technical Meeting on Spectroscopic and Collisional Data for W from 1 ev to 20 kev IAEA, Vienna, December 13 15, 2010
 Exploratory studies towards experimental data for electron-impact ionization, electron-ion recombination and photoionization i ti of tungsten t ions Alfred Müller Institut für Atom- und Molekülphysik JUSTUS-LIEBIG-
Exploratory studies towards experimental data for electron-impact ionization, electron-ion recombination and photoionization i ti of tungsten t ions Alfred Müller Institut für Atom- und Molekülphysik JUSTUS-LIEBIG-
X-ray Spectroscopy on Fusion Plasmas
 X-ray Spectroscopy on s An ongoing discussion between the two Manfreds Manfred von Hellermann for CXRS Manfred Bitter for x-ray spectroscopy G. Bertschinger for many contributers (Bitter, Kunze, Weinheimer,
X-ray Spectroscopy on s An ongoing discussion between the two Manfreds Manfred von Hellermann for CXRS Manfred Bitter for x-ray spectroscopy G. Bertschinger for many contributers (Bitter, Kunze, Weinheimer,
AG Draconis. A high density plasma laboratory. Dr Peter Young Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B.
 AG Draconis A high density plasma laboratory Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B. Ake p.r.young@rl.ac.uk Overview CHIANTI database Symbiotic Stars AG Draconis FUSE FUSE observations of AG
AG Draconis A high density plasma laboratory Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B. Ake p.r.young@rl.ac.uk Overview CHIANTI database Symbiotic Stars AG Draconis FUSE FUSE observations of AG
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy. HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric
 Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom
 Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom Jayash Panigrahi August 17, 2013 Abstract Saturated absorption spectroscopy has various application in laser cooling which have many relevant uses in
Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom Jayash Panigrahi August 17, 2013 Abstract Saturated absorption spectroscopy has various application in laser cooling which have many relevant uses in
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
 X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Louis Scudiero http://www.wsu.edu/~scudiero; 5-2669 Fulmer 261A Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) The basic principle of the photoelectric effect
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Louis Scudiero http://www.wsu.edu/~scudiero; 5-2669 Fulmer 261A Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) The basic principle of the photoelectric effect
RELATIVISTIC SPECTROSCOPY OF BLACK HOLES
 RELATIVISTIC SPECTROSCOPY OF BLACK HOLES Michael Parker ESAC science seminar 24/5/18 BLACK HOLES 101 For an object to just escape a massive body, it needs the sum: Kinetic energy + gravitational binding
RELATIVISTIC SPECTROSCOPY OF BLACK HOLES Michael Parker ESAC science seminar 24/5/18 BLACK HOLES 101 For an object to just escape a massive body, it needs the sum: Kinetic energy + gravitational binding
Extreme Light Infrastructure - Nuclear Physics ELI - NP
 Extreme Light Infrastructure - Nuclear Physics ELI - NP Nicolae-Victor Zamfir National Institute for Physics and Nuclear Engineering (IFIN-HH) Bucharest-Magurele, Romania www.eli-np.ro Bucharest-Magurele
Extreme Light Infrastructure - Nuclear Physics ELI - NP Nicolae-Victor Zamfir National Institute for Physics and Nuclear Engineering (IFIN-HH) Bucharest-Magurele, Romania www.eli-np.ro Bucharest-Magurele
Atomic Spectra in Astrophysics
 Atomic Spectra in Astrophysics Potsdam University : Wi 2016-17 : Dr. Lidia Oskinova lida@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de Helium Spectra 01 He is the second-most abundant element: 25% by mass of the Universe
Atomic Spectra in Astrophysics Potsdam University : Wi 2016-17 : Dr. Lidia Oskinova lida@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de Helium Spectra 01 He is the second-most abundant element: 25% by mass of the Universe
Femtosecond time-delay holography Henry Chapman Centre for Free-Electron Laser Science - DESY Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 Femtosecond time-delay holography Henry Chapman Centre for Free-Electron Laser Science - DESY Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Henry.Chapman@desy.de Isaac Newton Opticks 1704 Newton was the first
Femtosecond time-delay holography Henry Chapman Centre for Free-Electron Laser Science - DESY Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Henry.Chapman@desy.de Isaac Newton Opticks 1704 Newton was the first
Innovative XUV- und X-ray-Spectroscopy to explore Warm Dense Matter
 3rd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with intense Lasers and Heavy Ion Beams Innovative XUV- und X-ray-Spectroscopy to explore Warm Dense Matter Eckhart Förster X-ray Optics Group - IOQ - Friedrich-Schiller-University
3rd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with intense Lasers and Heavy Ion Beams Innovative XUV- und X-ray-Spectroscopy to explore Warm Dense Matter Eckhart Förster X-ray Optics Group - IOQ - Friedrich-Schiller-University
EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS
 Chapter 7 EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS Hot dense plasma lasing medium d θ λ λ Visible laser pump Ch07_00VG.ai The Processes of Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission Absorption
Chapter 7 EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS Hot dense plasma lasing medium d θ λ λ Visible laser pump Ch07_00VG.ai The Processes of Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission Absorption
Developments for the FEL user facility
 Developments for the FEL user facility J. Feldhaus HASYLAB at DESY, Hamburg, Germany Design and construction has started for the FEL user facility including the radiation transport to the experimental
Developments for the FEL user facility J. Feldhaus HASYLAB at DESY, Hamburg, Germany Design and construction has started for the FEL user facility including the radiation transport to the experimental
Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs
 100 Chapter 5 Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs 5.1 Experiments The photodissociation experiments were performed with protonated PAHs using different laser sources. The calculations from Chapter 3
100 Chapter 5 Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs 5.1 Experiments The photodissociation experiments were performed with protonated PAHs using different laser sources. The calculations from Chapter 3
TAMU-TRAP facility for Weak Interaction Physics. P.D. Shidling Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University
 TAMU-TRAP facility for Weak Interaction Physics P.D. Shidling Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University Outline of the talk Low energy test of Standard Model T =2 Superallowed transition Facility T-REX
TAMU-TRAP facility for Weak Interaction Physics P.D. Shidling Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University Outline of the talk Low energy test of Standard Model T =2 Superallowed transition Facility T-REX
The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design
 UVX 2010 (2011) 63 67 DOI: 10.1051/uvx/2011009 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2011 The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design J. Gaudin, H. Sinn and Th. Tschentscher
UVX 2010 (2011) 63 67 DOI: 10.1051/uvx/2011009 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2011 The European XFEL in Hamburg: Status and beamlines design J. Gaudin, H. Sinn and Th. Tschentscher
Photoionized Gas Ionization Equilibrium
 Photoionized Gas Ionization Equilibrium Ionization Recombination H nebulae - case A and B Strömgren spheres H + He nebulae Heavy elements, dielectronic recombination Ionization structure 1 Ionization Equilibrium
Photoionized Gas Ionization Equilibrium Ionization Recombination H nebulae - case A and B Strömgren spheres H + He nebulae Heavy elements, dielectronic recombination Ionization structure 1 Ionization Equilibrium
SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Principles and Applications DAVID ATTWOOD UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Principles and Applications DAVID ATTWOOD UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
SPARCLAB. Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam
 SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X Introduction to SPARC_LAB 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current can be
SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X Introduction to SPARC_LAB 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current can be
Monte Carlo Simulator to Study High Mass X-ray Binary System
 SLAC-PUB-11350 Monte Carlo Simulator to Study High Mass X-ray Binary System S. Watanabe, F. Nagase, T. Takahashi ISAS/JAXA, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan M. Sako, S.M. Kahn KIPAC/Stanford, Stanford,
SLAC-PUB-11350 Monte Carlo Simulator to Study High Mass X-ray Binary System S. Watanabe, F. Nagase, T. Takahashi ISAS/JAXA, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan M. Sako, S.M. Kahn KIPAC/Stanford, Stanford,
SPARCLAB. Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton. On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration
 SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current
SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current
high temp ( K) Chapter 20: Atomic Spectroscopy
 high temp (2000-6000K) Chapter 20: Atomic Spectroscopy 20-1. An Overview Most compounds Atoms in gas phase high temp (2000-6000K) (AES) (AAS) (AFS) sample Mass-to-charge (ICP-MS) Atomic Absorption experiment
high temp (2000-6000K) Chapter 20: Atomic Spectroscopy 20-1. An Overview Most compounds Atoms in gas phase high temp (2000-6000K) (AES) (AAS) (AFS) sample Mass-to-charge (ICP-MS) Atomic Absorption experiment
Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility
 2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
Small Quantum Systems Scientific Instrument
 Small Quantum Systems Scientific Instrument WP-85 A. De Fanis, T. Mazza, H. Zhang, M. Meyer European XFEL GmbH TDR_2012: http://www.xfel.eu/documents/technical_documents XFEL Users Meeting 2014, January
Small Quantum Systems Scientific Instrument WP-85 A. De Fanis, T. Mazza, H. Zhang, M. Meyer European XFEL GmbH TDR_2012: http://www.xfel.eu/documents/technical_documents XFEL Users Meeting 2014, January
Mossbauer Effect and Spectroscopy. Kishan Sinha Xu Group Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln
 Mossbauer Effect and Spectroscopy Kishan Sinha Xu Group Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln Emission E R γ-photon E transition hν = E transition - E R Photon does not carry
Mossbauer Effect and Spectroscopy Kishan Sinha Xu Group Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln Emission E R γ-photon E transition hν = E transition - E R Photon does not carry
Photoelectron Spectroscopy using High Order Harmonic Generation
 Photoelectron Spectroscopy using High Order Harmonic Generation Alana Ogata Yamanouchi Lab, University of Tokyo ABSTRACT The analysis of photochemical processes has been previously limited by the short
Photoelectron Spectroscopy using High Order Harmonic Generation Alana Ogata Yamanouchi Lab, University of Tokyo ABSTRACT The analysis of photochemical processes has been previously limited by the short
Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1
 J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
Formation of excited states in high-z helium-like systems
 Hyperfine Interactions 127 (2000) 257 262 257 Formation of excited states in high-z helium-like systems S. Fritzsche a,th.stöhlker b,c, O. Brinzanescu c,d and B. Fricke a a Fachbereich Physik, Universität
Hyperfine Interactions 127 (2000) 257 262 257 Formation of excited states in high-z helium-like systems S. Fritzsche a,th.stöhlker b,c, O. Brinzanescu c,d and B. Fricke a a Fachbereich Physik, Universität
Short Wavelength SASE FELs: Experiments vs. Theory. Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY
 Short Wavelength SASE FELs: Experiments vs. Theory Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY Contents INPUT (electrons) OUTPUT (photons) Momentum Momentum spread/chirp Slice emittance/ phase space distribution
Short Wavelength SASE FELs: Experiments vs. Theory Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY Contents INPUT (electrons) OUTPUT (photons) Momentum Momentum spread/chirp Slice emittance/ phase space distribution
Rb, which had been compressed to a density of 1013
 Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Construction of a 100-TW laser and its applications in EUV laser, wakefield accelerator, and nonlinear optics
 Construction of a 100-TW laser and its applications in EUV laser, wakefield accelerator, and nonlinear optics Jyhpyng Wang ( ) Institute of Atomic and Molecular Sciences Academia Sinica, Taiwan National
Construction of a 100-TW laser and its applications in EUV laser, wakefield accelerator, and nonlinear optics Jyhpyng Wang ( ) Institute of Atomic and Molecular Sciences Academia Sinica, Taiwan National
Ion trap quantum processor
 Ion trap quantum processor Laser pulses manipulate individual ions row of qubits in a linear Paul trap forms a quantum register Effective ion-ion interaction induced by laser pulses that excite the ion`s
Ion trap quantum processor Laser pulses manipulate individual ions row of qubits in a linear Paul trap forms a quantum register Effective ion-ion interaction induced by laser pulses that excite the ion`s
Sub-Doppler two-photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton-toelectron
 Sub-Doppler two-photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton-toelectron mass ratio Fukuoka, August 2012 Masaki Hori Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics A. Sótér, D. Barna, A.
Sub-Doppler two-photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton-toelectron mass ratio Fukuoka, August 2012 Masaki Hori Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics A. Sótér, D. Barna, A.
FLASH/DESY, Hamburg. Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team -
 First Lasing below 7nm Wavelength at FLASH/DESY, Hamburg Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team - email: joerg.rossbach@desy.de FLASH: The first FEL user facility for
First Lasing below 7nm Wavelength at FLASH/DESY, Hamburg Jörg Rossbach University of Hamburg & DESY, Germany - For the FLASH Team - email: joerg.rossbach@desy.de FLASH: The first FEL user facility for
Detecting high energy photons. Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples)
 Detecting high energy photons Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples) Interactions of high energy photons with matter Cross section/attenution length/optical depth Photoelectric
Detecting high energy photons Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples) Interactions of high energy photons with matter Cross section/attenution length/optical depth Photoelectric
Theoretical approach to estimate radiation damage within FEL irradiated samples. Beata Ziaja
 Theoretical approach to estimate radiation damage within FEL irradiated samples Beata Ziaja Hasylab, DESY Hamburg and INP, Krakow Prague, 23-24 November 2006 I. Mechanisms 2 Radiation damage Contribution
Theoretical approach to estimate radiation damage within FEL irradiated samples Beata Ziaja Hasylab, DESY Hamburg and INP, Krakow Prague, 23-24 November 2006 I. Mechanisms 2 Radiation damage Contribution
ECT* Trento The Lead Radius. Precision measurements of nuclear ground state properties for nuclear structure studies. Klaus Blaum
 ECT* Trento The Lead Radius Precision measurements of nuclear ground state properties for nuclear structure studies Klaus Blaum 04.08.2009 Outline Introduction, history and methods Principle of laser spectroscopy
ECT* Trento The Lead Radius Precision measurements of nuclear ground state properties for nuclear structure studies Klaus Blaum 04.08.2009 Outline Introduction, history and methods Principle of laser spectroscopy
Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS. Coherence Properties. J. B. Hastings. Stanford Linear Accelerator Center
 Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS Coherence Properties J. B. Hastings Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Coherent Synchrotron Radiation Coherent Synchrotron Radiation coherent power N 6 10 9 incoherent
Linac Based Photon Sources: XFELS Coherence Properties J. B. Hastings Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Coherent Synchrotron Radiation Coherent Synchrotron Radiation coherent power N 6 10 9 incoherent
A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu February 11, 2016 Read: Chap 5 02/11/16 slide 1 Exam #1: Thu 18 Feb
A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu February 11, 2016 Read: Chap 5 02/11/16 slide 1 Exam #1: Thu 18 Feb
An import year!
 1759.. An import year! Some Historic and Current Aspects of Plasma Diagnostics Using Atomic Spectroscopy Roger Hutton and Yaming Zou Shanghai Electron Beam Ion Trap Laboratory Modern Physics Institute,
1759.. An import year! Some Historic and Current Aspects of Plasma Diagnostics Using Atomic Spectroscopy Roger Hutton and Yaming Zou Shanghai Electron Beam Ion Trap Laboratory Modern Physics Institute,
TRIUMF The TITAN EBIT: Status & Research Plans
 The TITAN EBIT: Status & Research Plans A. Lapierre, T. Brunner, C. Champagne, P. Delheij, and J. Dilling for the TITAN collaboration Canada s National Laboratory for Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vancouver,
The TITAN EBIT: Status & Research Plans A. Lapierre, T. Brunner, C. Champagne, P. Delheij, and J. Dilling for the TITAN collaboration Canada s National Laboratory for Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vancouver,
Experimental Initiatives in Nuclear Astrophysics
 Experimental Initiatives in Nuclear Astrophysics Carl Brune Astrophysics: H and He burning, S process Facilities: neutron and gamma beams, underground accelerators, ICF plasmas Joint DNP Town Meetings
Experimental Initiatives in Nuclear Astrophysics Carl Brune Astrophysics: H and He burning, S process Facilities: neutron and gamma beams, underground accelerators, ICF plasmas Joint DNP Town Meetings
Jitter measurement by electro-optical sampling
 Jitter measurement by electro-optical sampling VUV-FEL at DESY - Armin Azima S. Duesterer, J. Feldhaus, H. Schlarb, H. Redlin, B. Steffen, DESY Hamburg K. Sengstock, Uni Hamburg Adrian Cavalieri, David
Jitter measurement by electro-optical sampling VUV-FEL at DESY - Armin Azima S. Duesterer, J. Feldhaus, H. Schlarb, H. Redlin, B. Steffen, DESY Hamburg K. Sengstock, Uni Hamburg Adrian Cavalieri, David
First Experiments with the Greifswald EBIT
 First Experiments with the Greifswald EBIT B Schabinger 1, C Biedermann 2, S Gierke 1, G Marx 1, R Radtke 1,2 and L Schweikhard 1 1 Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald, Institute of Physics, Felix-Hausdorff-Str.
First Experiments with the Greifswald EBIT B Schabinger 1, C Biedermann 2, S Gierke 1, G Marx 1, R Radtke 1,2 and L Schweikhard 1 1 Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald, Institute of Physics, Felix-Hausdorff-Str.
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-30 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 4 - Detectors Binding Energy Nuclear mass MN less than sum of nucleon masses Shows nucleus is a bound (lower energy) state for this configuration
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-30 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 4 - Detectors Binding Energy Nuclear mass MN less than sum of nucleon masses Shows nucleus is a bound (lower energy) state for this configuration
Plasma spectroscopy when there is magnetic reconnection associated with Rayleigh-Taylor instability in the Caltech spheromak jet experiment
 Plasma spectroscopy when there is magnetic reconnection associated with Rayleigh-Taylor instability in the Caltech spheromak jet experiment KB Chai Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute/Caltech Paul M.
Plasma spectroscopy when there is magnetic reconnection associated with Rayleigh-Taylor instability in the Caltech spheromak jet experiment KB Chai Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute/Caltech Paul M.
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering
 X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
Main Magnetic Focus Ion Trap, new tool for trapping of highly charged ions
 V. P. Ovsyannikov a Main Magnetic Focus Ion Trap, new tool for trapping of highly charged ions Hochschulstr. 13, 01069, Dresden, Germany It is proposed to produce the highly charged ions in the local ion
V. P. Ovsyannikov a Main Magnetic Focus Ion Trap, new tool for trapping of highly charged ions Hochschulstr. 13, 01069, Dresden, Germany It is proposed to produce the highly charged ions in the local ion
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 21 Jun 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 21 Jun 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 21 Jun 2011](/thumbs/80/80601513.jpg) arxiv:1106.4155v1 [physics.atom-ph] 21 Jun 2011 Differential energy measurement between He- and Li-like uranium intra-shell transitions M. Trassinelli 1, A. Kumar 2, H.F. Beyer 3, P. Indelicato 4, R. Märtin
arxiv:1106.4155v1 [physics.atom-ph] 21 Jun 2011 Differential energy measurement between He- and Li-like uranium intra-shell transitions M. Trassinelli 1, A. Kumar 2, H.F. Beyer 3, P. Indelicato 4, R. Märtin
