Light scattering in Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion
|
|
|
- Aleesha Hubbard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Light scattering in Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion OCEANOLOGIA, 51 (3), 29. pp C 29, by Institute of Oceanology PAS. KEYWORDS Emulsion Light scattering Petroleum Seawater Adam Stelmaszewski Tadeusz Król Henryk Toczek Physics Department, Gdynia Maritime University, Morska 81 87, PL Gdynia, Poland; stel@am.gdynia.pl corresponding author Received 18 March 29, revised 14 July 29, accepted 31 July 29. Abstract The paper discusses the scattering of radiation by a Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion. The scattering spectrum calculated using the Mie solution in the spectral range from 38 nm to 73 nm is compared with the measured spectrum of light scattered through a right angle. Spectra in the wavelength range from 21 nm to 73 nm were measured using a spectrofluorimeter for fresh and stored samples of the Baltic crude oil emulsion. Scattering increases with wavelength in the UV range and then decreases slightly with the wavelength of visible light. The result of the calculation is similar to the measured spectra. Both the calculated and measured spectra display numerous relative extremes throughout the spectral area. Light scattering in the emulsion decreases during storage as the oil concentration in the medium diminishes. The results also demonstrate that the single scattering model describes the phenomenon correctly. 1. Introduction Petroleum is a very common pollutant of the marine environment and occurs in various forms. Each of these forms exerts its own individual The complete text of the paper is available at
2 46 A. Stelmaszewski, T. Król, H. Toczek influence on the environment, thereby changing the latter s physical and chemical properties. One of these forms is an oil-water emulsion. Apart from increasing light attenuation, scattering is the optical phenomenon through which such an emulsion makes its presence felt in deep water. An emulsion a suspension of oil droplets in water is a turbid medium. The droplets are spherical particles with a radius of several micrometers, so the Mie solution is suitable for describing the scattering of light by them (van de Hulst 1957). The scattering function characterising an emulsion is an averaged function that takes into consideration the size distribution of the droplets and their concentration. The aim of this work was to corroborate the scattering model. The research questions were two: 1) Can the single scattering model be used to describe the phenomenon? 2) Does the scattering function obtained from calculations correspond to the real scattering spectrum? This paper reports on preliminary studies of this subject carried out for a Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion. 2. Material and methods The object of study was Baltic crude oil emulsified in seawater. The seawater was prepared by dissolving the principal sea salts in demineralised water to achieve an ionic composition similar to that of natural water of salinity 7.5 PSU. The emulsion was prepared as follows. Portions of Baltic crude oil dissolved in n-hexane (3 cm 3 of oil and 2 cm 3 of solvent) were poured into a stainless steel vessel containing 1 dm 3 of water. After being stirred with a propeller at 6 rpm (1 s 1 ) for 3 hours the emulsion was allowed to stabilise for half an hour. Then, a small amount of the emulsion was sampled for the test. The vessel was equipped with a drain valve in the sidewall so that samples could be drawn from the middle of the emulsion bulk. During preparation and storage the emulsion remained in darkness and at constant temperature (2 C). The intensity of the scattered radiation was measured in the spectral range from 21 nm to 73 nm using a Fluorat-2 Panorama spectrofluorimeter. In this set, the monochromatic illuminating beam passes through the centre of a square, 1 cm long quartz-glass cuvette. The beam is about 1 mm in diameter and has a half-intensity width of 4 nm. The radiation scattered by the emulsion filling the cell was restricted by a diaphragm with a circular hole.8 mm in diameter. The measured radiation came from the centre of the cuvette at right angles to the illuminating flux. The solid angle of the scattered beam did not exceed.2 sr and was much less than the dilation angle of the receiver. The fluorimeter measures two non-dimensional values: F and T. F is the intensity of the radiation J r
3 Light scattering in Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion 47 reaching the receiver (fluorescence channel) in relation to the intensity of the illuminating flux J o : F = J r. J o T (transmission 1 ) is the intensity of the light after having passed through the sample J ex in relation to the intensity of radiation reaching the cell J o : T = J ex. J o The parameter S is given by the following equation: S = F T o T F o (1) and describes the scattering at the point where this occurs. F and T denote the results of measurements carried out on the tested emulsion, while F o and T o are the background parameters (results of measurements performed on the pure medium). S is proportional to the volume scattering function β 9 characterising the emulsion. Equation (1) allows for molecular scattering in the medium F o and light attenuation by the emulsion. Equation (1) is derived from the Lambert-Beer law; its correctness is governed by the correctness of the single scattering model used to describe the phenomenon. This has been confirmed by measurements of emulsions diluted to different degrees. Light scattering can be expressed as follows: J(λ) J o (λ) = 1 k 2 R 2 g(r)i(λ, r)dr, (2) where J and J o respectively denote the intensities of scattered and illuminating radiation, k (the imaginary part of the complex refractive index) depends on the absorption coefficient a and the light wavelength λ: k = aλ/4π, R denotes distance from the scattering centre and r is the droplet radius (van de Hulst 1957, Bohren & Huffman 1983). The intensity of scattered radiation was calculated using the Mie solution (Król 1984, 1985). The intensity function I(λ, r) for the perpendicular direction was calculated for an emulsion droplet of any radius r from.5 µm upto1µm with a.5 µm step. The intensity functions were then averaged with the size distribution g according to the expression J(λ) λ 2 g(r i )I(λ, r i ). (3) J o (λ) i 1 Sometimes this quantity is called the transmittance, whereas the term transmission refers to the physical process of light passing through a sample.
4 48 A. Stelmaszewski, T. Król, H. Toczek The light refractivity and the absorption coefficient characterising both oil and water and the size distribution of the droplets are the background parameters for the calculations. The size distribution of the emulsion droplets was determined from microscopic measurements using a Burker plate. The optical properties of the oil are known (Kaniewski et al. 23). Table 1 lists parameters n and k (the real and imaginary parts of the Table 1. Optical parameters n and k (the real and imaginary parts of the complex refractive index) characterising fresh Baltic crude oil with respect to radiation of wavelength λ λ n k λ n k [nm] [ 1 5 ] [nm] [ 1 5 ] complex refractive index) characterising the petroleum, which were used in the calculations. The water was assumed to be a fully transparent medium. Its refractivity was measured using an Abbe refractometer in the wavelength range nm, which enabled the refraction coefficient n to be expressed as the following dependence on the radiation wavelength λ (in µm) n = A 1 + B, (4) λ2 where A = µm 2 and B = Relation (4) tallies very well with the standard relationship (Quan & Fry 1995, IAPWS 1997) throughout the range from 3 nm to 75 nm.
5 Light scattering in Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion Results The majority of Baltic crude oil droplets emulsified in water had adiameter 2.5 µm.atthesametimeonlyafewdropletswere> 5 µm in radius. The emulsion particle radii form a size distribution that appears to be best described by a log-normal function. Figure 1 presents the distribution function g and the results of the microscopic measurement. The number of particles of diameter 2.5 µm ranged from 37 to 48 in a cell of volume.4 mm 3. Taking into consideration the size distribution, the relative volume concentration of oil in the emulsion was estimated to be The oil concentration and fragmentation of the particles reach a certain level during emulsification. Prolonging the stirring time or increasing of the speed of propeller rotation do not cause meaningful changes (Mikłaszewicz 26). Thus, the oil concentration in a fresh emulsion can be considered to be close to the maximum..8.7 fraction of results [-] the measurement results the log-normal function droplet radius r [µm] Figure 1. Size distribution of particles in a Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion The possible application of the single scattering model is a precondition for the correct calculation of the scattering function as well as of the suitability of equation (1). This was confirmed by the following test. The emulsion was diluted with water, the diluted samples being emulsions with the same composition but different concentrations. Then, scattering and light attenuation were measured for these samples. In the case of the single scattering model, the intensity of scattered radiation S should be proportional to the oil concentration C, while transmission T through a cell
6 41 A. Stelmaszewski, T. Król, H. Toczek filled with emulsion should satisfy the following relation: T = T o exp( γc). (5) T o denotes the transmission through pure water and γ is a constant (proportional to the light attenuation coefficient). Figures 2 and 3 present.6.6 scattering intensity S [-] = 3 nm scattering intensity S [-] = 6 nm relative concentration C [-] relative concentration C [-] Figure 2. Scattering intensity of Baltic crude oil in a seawater emulsion relative to the oil concentration C for radiation of wavelength λ = 3 nm (a) and λ = 6 nm (b) = 3 nm 1. ln( T / T).5 = 5 nm = 71 nm relative oil concentration C [-] Figure 3. Logarithm of the reciprocal of the relative transmission ln(t o /T ) with respect to the relative oil concentration C in the Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion for radiation of a number of wavelengths
7 Light scattering in Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion 411 the results of the test. Both the scattering intensity S and the expression ln(t o /T ) are almost linearly dependent on the concentration. Thus, it can be assumed that the single scattering model describes this phenomenon satisfactorily even when the concentration of the emulsion is relatively high Results of scattering measurements Figure 4 presents a number of the scattering spectra measured on fresh and stored emulsions. The scattering in any sample increases with the radiation wavelength in the UV range and each spectrum has numerous relative extremes in the whole spectral area. The turbidity of the emulsion decreases during its storage. The scattering intensity decreases but the spectrum itself retains its shape. This indicates that the oil concentration falls in an emulsion although its composition is stable. scattering intensity S [-] fresh 2.5 hrs 25 hrs radiation wavelength [nm] Figure 4. Measured scattering spectra S of Baltic crude oil water emulsions: fresh (black line), after storage for 2.5 hrs (blue line) and after storage for 25 hrs (red line) 3.2. Results of calculations The intensity function is a parameter describing scattering at individual particles. The function depends on droplet size, radiation wavelength and the scattering angle. Figure 5 presents spectra of the intensity function of scattering at right angles for wavelengths from 38 nm to 73 nm calculated for Baltic crude oil particles of different radii r.
8 412 A. Stelmaszewski, T. Król, H. Toczek 1 intensity function [-] m 4m 2m 1m radiation wavelength [nm] Figure 5. Spectra of the intensity function of scattering at right angles calculated for Baltic crude oil particles of various radii Taking into consideration the distribution of the particles and the oil concentration one can obtain the volume scattering function β, which describes scattering by an emulsion. The spectrum of the function β 9 = β 9 (λ) was compared with the measured spectrum of the fresh emulsion (see Figure 6). It is essential to compare the course of function β with the shape of the 1. relative scattering [-] radiation wavelength [nm] Figure 6. Calculated scattering function of the Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion (red line) in comparison with the measured spectrum (blue line). The function and spectrum have been normalised to their maximum values
9 Light scattering in Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion 413 measured spectrum. As a result, the calculated function and the measured spectrum were normalised to their maximum values. The similarity between the spectra is apparent, although they do not coincide. The various maxima of the theoretical function are shifted by several nanometers in relation to the corresponding extremes of the measured spectrum. The following reasons may explain this difference: fresh crude oil is not a stable substance and its properties change during emulsification (Kaniewski et al. 23, Król et al. 26), and the optical properties of emulsion droplets are not exactly the same as the properties of the original oil (Stelmaszewski & Toczek 27). 4. Summary A Baltic crude oil seawater emulsion scatters visible light more effectively than UV radiation the scattering increases with UV wavelength up to about 4 nm. The scattering spectrum has many local extremes throughout the spectral area. The similarities between the scattering spectra of the stored emulsion and the fresh one indicate that the emulsion retains its optical properties. This test has shown that the volume scattering function based on the Mie solution corresponds with experimental results and that the single scattering model provides an adequate description of the phenomenon. The above conclusions have been drawn from preliminary experimental studies of only one crude oil emulsion. They will require confirmation by tests carried out on other species, especially oils with stable properties. References Bohren C. F., Huffman D. R., 1983, Absorption and scattering of light by small particles, Wiley, New York, 53 pp. IAPWS (The International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam), 1997, Release on the refractive index of ordinary water substance as a function of wavelength, temperature and pressure, rindex.pdf. Kaniewski E., Otremba Z., Stelmaszewski A., Toczek H., 23, Optical properties of the Baltic crude oil, Gd. Maritime Univ. Trans., 49, , (in Polish). Król T., 1984, A simple computational model of light scattering function for spherical particles, Stud. Mater. Oceanol., 45, , (in Polish). Król T., 1985, Computational model of Mie coefficients for spherical absorbing scattering particles, Stud. Mater. Oceanol., 49, 43 62, (in Polish). Król T., Stelmaszewski A., Freda W., 26, Variability in the optical properties of a crude oil seawater emulsion, Oceanologia, 48 (S),
10 414 A. Stelmaszewski, T. Król, H. Toczek Mikłaszewicz B., 26, Self-purification of Odra estuary and Pomeranian Bay waters polluted with crude oil derivative emulsions, Ph.D. thesis, Inst. Oceanol. PAS, Sopot, 118 pp., (in Polish). Quan X., Fry E. S., 1995, Empirical equation for the index of refraction of seawater, App. Optics, 34 (18), Stelmaszewski A., Toczek H., 27, Preliminary studies of optical properties of oil-water emulsion particles, [in:] Physicochemical problems of natural waters ecology, Vol. 5, Gd. Maritime Univ. Publ., Gdynia, Van de Hulst H. C., 1957, Light scattering by small particles, Wiley, New York, 47 pp.
GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet GPM.1.2.1.1.0003.15 and visible spectral regions Replaces the SPRF X GPM, SPRF XI GPM,
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet GPM.1.2.1.1.0003.15 and visible spectral regions Replaces the SPRF X GPM, SPRF XI GPM,
The mathematics of scattering and absorption and emission
 The mathematics of scattering and absorption and emission The transmittance of an layer depends on its optical depth, which in turn depends on how much of the substance the radiation has to pass through,
The mathematics of scattering and absorption and emission The transmittance of an layer depends on its optical depth, which in turn depends on how much of the substance the radiation has to pass through,
Spectroscopy. Page 1 of 8 L.Pillay (2012)
 Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Hands-on Mie lab. Emmanuel Boss, U. of Maine, Radiation transfer in the environment, 2008.
 Hands-on Mie lab. Emmanuel Boss, U. of Maine, Radiation transfer in the environment, 2008. Introduction: Mie theory provides the solution for a plane-parallel EM energy interacting with a homogeneous sphere.
Hands-on Mie lab. Emmanuel Boss, U. of Maine, Radiation transfer in the environment, 2008. Introduction: Mie theory provides the solution for a plane-parallel EM energy interacting with a homogeneous sphere.
The Physical Properties of Sea Water OCEA 101
 The Physical Properties of Sea Water OCEA 101 Why should you care? - water provides the primary environment for marine organisms - properties of water significantly influence the evolution of marine organisms
The Physical Properties of Sea Water OCEA 101 Why should you care? - water provides the primary environment for marine organisms - properties of water significantly influence the evolution of marine organisms
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics GOALS After you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics GOALS After you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Lecture 26. Regional radiative effects due to anthropogenic aerosols. Part 2. Haze and visibility.
 Lecture 26. Regional radiative effects due to anthropogenic aerosols. Part 2. Haze and visibility. Objectives: 1. Attenuation of atmospheric radiation by particulates. 2. Haze and Visibility. Readings:
Lecture 26. Regional radiative effects due to anthropogenic aerosols. Part 2. Haze and visibility. Objectives: 1. Attenuation of atmospheric radiation by particulates. 2. Haze and Visibility. Readings:
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Temperature ( o C)
 Viscosity (Pa sec) Supplementary Information 10 8 10 6 10 4 10 2 150 200 250 300 Temperature ( o C) Supplementary Figure 1 Viscosity of fibre components (PC cladding blue; As 2 Se 5 red; CPE black) as
Viscosity (Pa sec) Supplementary Information 10 8 10 6 10 4 10 2 150 200 250 300 Temperature ( o C) Supplementary Figure 1 Viscosity of fibre components (PC cladding blue; As 2 Se 5 red; CPE black) as
Radiation in the atmosphere
 Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Lambert s law. Beer s law. di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) = - a c dx. I/I 0 = e -kl T = A = - log (T) = - log (I/I 0 )
 di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) Integrating this equation from x=0 ~ l (I x =I 0 ~I) gives ; ln I ln I 0 = -kl ln I/I 0 = -kl Expressing the number of photons absorbed by the slab as di x, and the
di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) Integrating this equation from x=0 ~ l (I x =I 0 ~I) gives ; ln I ln I 0 = -kl ln I/I 0 = -kl Expressing the number of photons absorbed by the slab as di x, and the
Received 27 October 2008, revised 9 February 2009, accepted 18 February 2009.
 Papers Ångström coefficient as an indicator of the atmospheric aerosol type for a well-mixed atmospheric boundary layer: Part 1: Model development OCEANOLOGIA, 51 (1), 2009. pp. 5 39. C 2009, by Institute
Papers Ångström coefficient as an indicator of the atmospheric aerosol type for a well-mixed atmospheric boundary layer: Part 1: Model development OCEANOLOGIA, 51 (1), 2009. pp. 5 39. C 2009, by Institute
Absorption properties. Scattering properties
 Absorption properties Scattering properties ocean (water) color light within water medium Lu(ϴ,ϕ) (Voss et al 2007) (Kirk 1994) They are modulated by water constituents! Sensor measures E d L w [Chl] [CDOM]
Absorption properties Scattering properties ocean (water) color light within water medium Lu(ϴ,ϕ) (Voss et al 2007) (Kirk 1994) They are modulated by water constituents! Sensor measures E d L w [Chl] [CDOM]
UV-Vis optical fiber assisted spectroscopy in thin films and solutions
 UV-Vis optical fiber assisted spectroscopy in thin films and solutions Description UV-Visible absorption and transmission spectra provide fundamental information for all experiments related to the attenuation
UV-Vis optical fiber assisted spectroscopy in thin films and solutions Description UV-Visible absorption and transmission spectra provide fundamental information for all experiments related to the attenuation
Characterization of the Initial Conditions in Emulsion Polymerization: Loci for Particle Nucleation
 Characterization of the Initial Conditions in Emulsion Polymerization: Loci for Particle Nucleation Vineet Shastry, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of South Florida, Tampa USA. Luis H Garcia-Rubio,
Characterization of the Initial Conditions in Emulsion Polymerization: Loci for Particle Nucleation Vineet Shastry, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of South Florida, Tampa USA. Luis H Garcia-Rubio,
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
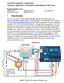 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13)
 An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
Lecture 4* Inherent optical properties, IOP Theory. Loss due to absorption. IOP Theory 12/2/2008
 Lecture 4* Inherent optical properties, part I IOP Theory What properties of a medium affect the radiance field as it propagate through it? 1. Sinks of photons (absorbers) 2. Sources of photons (internal
Lecture 4* Inherent optical properties, part I IOP Theory What properties of a medium affect the radiance field as it propagate through it? 1. Sinks of photons (absorbers) 2. Sources of photons (internal
Aerosol Optical Properties
 ATM 507 Lecture 25 Text reading Chapter 15 Paper Due Dec. 9 Review Session Dec. 9 Final Dec. 12 (10:30 AM-12:30 PM) Today s topic Aerosol Optical Properties 1 Aerosol Optical Properties There are a number
ATM 507 Lecture 25 Text reading Chapter 15 Paper Due Dec. 9 Review Session Dec. 9 Final Dec. 12 (10:30 AM-12:30 PM) Today s topic Aerosol Optical Properties 1 Aerosol Optical Properties There are a number
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications
 Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Basics of UV-Visible Spectroscopy *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m34525 1 Basics of UV-Visible Spectroscopy * Brittany L. Oliva-Chatelain Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m34525 1 Basics of UV-Visible Spectroscopy * Brittany L. Oliva-Chatelain Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Millikan determined the charge on individual oil droplets using an arrangement as represented in the diagram. The plate voltage necessary to hold a charged droplet stationary
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Millikan determined the charge on individual oil droplets using an arrangement as represented in the diagram. The plate voltage necessary to hold a charged droplet stationary
Mie theory for light scattering by a spherical particle in an absorbing medium
 Mie theory for light scattering by a spherical particle in an absorbing medium Qiang Fu and Wenbo Sun Analytic equations are developed for the single-scattering properties of a spherical particle embedded
Mie theory for light scattering by a spherical particle in an absorbing medium Qiang Fu and Wenbo Sun Analytic equations are developed for the single-scattering properties of a spherical particle embedded
GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Colour intensity of liquids GPM.1.2.1.0006.15 Replaces the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XII, Part 1 Monograph,
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Colour intensity of liquids GPM.1.2.1.0006.15 Replaces the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XII, Part 1 Monograph,
4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy
 4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy The optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and the circular dichroism (CD) are special variations of absorption spectroscopy in the UV and VIS region of the spectrum. The
4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy The optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and the circular dichroism (CD) are special variations of absorption spectroscopy in the UV and VIS region of the spectrum. The
OPTIMAL WAVELENGTH SELECTION ALGORITHM OF NON-SPHERICAL PARTICLE SIZE DISTRIBUTION BASED ON THE LIGHT EXTINCTION DATA
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2012, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 1353-1357 1353 OPTIMAL WAVELENGTH SELECTION ALGORITHM OF NON-SPHERICAL PARTICLE SIZE ISTRIBUTION BASE ON THE LIGHT EXTINCTION ATA by Hong TANG * College
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2012, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 1353-1357 1353 OPTIMAL WAVELENGTH SELECTION ALGORITHM OF NON-SPHERICAL PARTICLE SIZE ISTRIBUTION BASE ON THE LIGHT EXTINCTION ATA by Hong TANG * College
MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
THE EXOSPHERIC HEAT BUDGET
 E&ES 359, 2008, p.1 THE EXOSPHERIC HEAT BUDGET What determines the temperature on earth? In this course we are interested in quantitative aspects of the fundamental processes that drive the earth machine.
E&ES 359, 2008, p.1 THE EXOSPHERIC HEAT BUDGET What determines the temperature on earth? In this course we are interested in quantitative aspects of the fundamental processes that drive the earth machine.
METHOD FOR THE IN VITRO DETERMINATION OF UVA PROTECTION PROVIDED BY SUNSCREEN PRODUCTS. Edition of 2007a
 METHOD FOR THE IN VITRO DETERMINATION OF UVA PROTECTION PROVIDED BY SUNSCREEN PRODUCTS Edition of 2007a METHOD FOR THE IN VITRO DETERMINATION OF UVA PROTECTION PROVIDED BY SUNSCREEN PRODUCTS Guideline
METHOD FOR THE IN VITRO DETERMINATION OF UVA PROTECTION PROVIDED BY SUNSCREEN PRODUCTS Edition of 2007a METHOD FOR THE IN VITRO DETERMINATION OF UVA PROTECTION PROVIDED BY SUNSCREEN PRODUCTS Guideline
Analysis of the particle size distribution and optical properties in the Korean seas
 Analysis of the particle size distribution and optical properties in the Korean seas Boram Lee 1,2, Young-Je Park 1, Wonkook Kim 1, Jae-Hyun Ahn 1, Kwangseok Kim 1, Jeong-Eon Moon 1 and Sang-Wan Kim 2
Analysis of the particle size distribution and optical properties in the Korean seas Boram Lee 1,2, Young-Je Park 1, Wonkook Kim 1, Jae-Hyun Ahn 1, Kwangseok Kim 1, Jeong-Eon Moon 1 and Sang-Wan Kim 2
9/28/10. Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Valence Electronic Structure. n σ* transitions
 Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Lecture 05. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (3)
 Lecture 05. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (3) Physical Processes in Lidar Overview of physical processes in lidar Light transmission through the atmosphere Light interaction with objects Elastic
Lecture 05. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (3) Physical Processes in Lidar Overview of physical processes in lidar Light transmission through the atmosphere Light interaction with objects Elastic
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
 HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
Chapter 18. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry. Properties of Light
 Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1. Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry. Accuracy vs Precision
 Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
R O Y G B V. Spin States. Outer Shell Electrons. Molecular Rotations. Inner Shell Electrons. Molecular Vibrations. Nuclear Transitions
 Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Fresnel Equations cont.
 Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
The Scattering of Light by Small Particles. Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706
 (4/6/10) The Scattering of Light by Small Particles Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract In this experiment we study the scattering of light from various
(4/6/10) The Scattering of Light by Small Particles Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract In this experiment we study the scattering of light from various
Papers. Sea salt emission from the coastal zone. 1. Introduction
 Papers Sea salt emission from the coastal zone OCEANOLOGIA, 42 (4), 2000. pp. 399 4. 2000, by Institute of Oceanology PAS. KEYWORDS Aerosol Sea salt Fluxes Emission Coastal zone Tomasz Petelski Maria Chomka
Papers Sea salt emission from the coastal zone OCEANOLOGIA, 42 (4), 2000. pp. 399 4. 2000, by Institute of Oceanology PAS. KEYWORDS Aerosol Sea salt Fluxes Emission Coastal zone Tomasz Petelski Maria Chomka
Radiative Transfer Multiple scattering: two stream approach 2
 Radiative Transfer Multiple scattering: two stream approach 2 N. Kämpfer non Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern 28. Oct. 24 Outline non non Interpretation of some specific cases Semi-infinite
Radiative Transfer Multiple scattering: two stream approach 2 N. Kämpfer non Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern 28. Oct. 24 Outline non non Interpretation of some specific cases Semi-infinite
Lecture # 04 January 27, 2010, Wednesday Energy & Radiation
 Lecture # 04 January 27, 2010, Wednesday Energy & Radiation Kinds of energy Energy transfer mechanisms Radiation: electromagnetic spectrum, properties & principles Solar constant Atmospheric influence
Lecture # 04 January 27, 2010, Wednesday Energy & Radiation Kinds of energy Energy transfer mechanisms Radiation: electromagnetic spectrum, properties & principles Solar constant Atmospheric influence
Improved Process Measurement & Control. OD 600 vs. AU Measurements in Fermentation Cell Density
 Finesse, LLC 3350 Scott Boulevard #1 Santa Clara, CA 95054 9351 Irvine Boulevard Irvine, CA 92618 800-598-9515 www.finesse-inc.com P01 OD 600 vs. AU Measurements in Fermentation Cell Density This technical
Finesse, LLC 3350 Scott Boulevard #1 Santa Clara, CA 95054 9351 Irvine Boulevard Irvine, CA 92618 800-598-9515 www.finesse-inc.com P01 OD 600 vs. AU Measurements in Fermentation Cell Density This technical
What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to
 What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to 10µm Concentrations decrease exponentially with height N(z) = N(0)exp(-z/H) Long-lived
What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to 10µm Concentrations decrease exponentially with height N(z) = N(0)exp(-z/H) Long-lived
3. Anaemia can be diagnosed by (a) 15 P 31 (b) 15 P 32 (c) 26 Fe 59 (d) 11 Na 24. (b) α particle (Alpha particle)
 MARCH 2010 PHYSICS Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 150 PART - I 30 x 1 = 30 Note: i) Answer all the questions. ii) Choose and write the correct answer. 1. Electron microscope works on the principle
MARCH 2010 PHYSICS Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 150 PART - I 30 x 1 = 30 Note: i) Answer all the questions. ii) Choose and write the correct answer. 1. Electron microscope works on the principle
Polarized light propagation and scattering in random media
 Polarized light propagation and scattering in random media Arnold D. Kim a, Sermsak Jaruwatanadilok b, Akira Ishimaru b, and Yasuo Kuga b a Department of Mathematics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Polarized light propagation and scattering in random media Arnold D. Kim a, Sermsak Jaruwatanadilok b, Akira Ishimaru b, and Yasuo Kuga b a Department of Mathematics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon
 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Absorption and scattering
 Absorption and scattering When a beam of radiation goes through the atmosphere, it encounters gas molecules, aerosols, cloud droplets, and ice crystals. These objects perturb the radiation field. Part
Absorption and scattering When a beam of radiation goes through the atmosphere, it encounters gas molecules, aerosols, cloud droplets, and ice crystals. These objects perturb the radiation field. Part
429 LIGHT DIFFRACTION MEASUREMENT OF PARTICLE SIZE
 Search USP29 429 LIGHT DIFFRACTION MEASUREMENT OF PARTICLE SIZE Light diffraction is one of the most widely used techniques for measuring the size of a wide range of particles from very fine to very coarse.
Search USP29 429 LIGHT DIFFRACTION MEASUREMENT OF PARTICLE SIZE Light diffraction is one of the most widely used techniques for measuring the size of a wide range of particles from very fine to very coarse.
CHEM*3440. Photon Energy Units. Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation. Chemical Instrumentation. Spectroscopic Experimental Concept.
 Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Analysis on the birefringence property of lyotropic liquid crystals below Krafft temperature
 Analysis on the birefringence property of lyotropic liquid crystals below Krafft temperature Radhakrishnan Ranjini, Murukeshan Vadakke Matham *, Nam-Trung Nguyen Department of Mechanical and Aerospace
Analysis on the birefringence property of lyotropic liquid crystals below Krafft temperature Radhakrishnan Ranjini, Murukeshan Vadakke Matham *, Nam-Trung Nguyen Department of Mechanical and Aerospace
Chapter 6. Fiber Optic Thermometer. Ho Suk Ryou
 Chapter 6. Fiber Optic Thermometer Ho Suk Ryou Properties of Optical Fiber Optical Fiber Composed of rod core surrounded by sheath Core: conducts electromagnetic wave Sheath: contains wave within the core
Chapter 6. Fiber Optic Thermometer Ho Suk Ryou Properties of Optical Fiber Optical Fiber Composed of rod core surrounded by sheath Core: conducts electromagnetic wave Sheath: contains wave within the core
Langmuir-Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers. Supporting Information
 Langmuir-Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers Supporting Information I. AFM, UV-VIS and TEM characterization of LS layers S1 Low-magnification TEM images of Q-CdSe layers, deposited on a carbon-coated
Langmuir-Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers Supporting Information I. AFM, UV-VIS and TEM characterization of LS layers S1 Low-magnification TEM images of Q-CdSe layers, deposited on a carbon-coated
often display a deep green color due to where the SPR occurs (i.e., the wavelength of light that interacts with this specific morphology).
 Synthesis-Dependent Catalytic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Nanoscience is the study of materials that have dimensions, intuitively, on the nanoscale, typically between 1 100 nm. This field has received
Synthesis-Dependent Catalytic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Nanoscience is the study of materials that have dimensions, intuitively, on the nanoscale, typically between 1 100 nm. This field has received
Illuminated Reticle Technologies for Rifle Scopes. Illuminated Reticle Technologies for Riflescopes
 Illuminated Reticle Technologies for Rifle Scopes A comparison of the diffraction grating technology with etch-and-fill Illuminated Reticle Technologies for Riflescopes A comparison of the diffraction
Illuminated Reticle Technologies for Rifle Scopes A comparison of the diffraction grating technology with etch-and-fill Illuminated Reticle Technologies for Riflescopes A comparison of the diffraction
Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2
 Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2 Schroder: Chapters 2, 7, 10 1/68 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June).
Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2 Schroder: Chapters 2, 7, 10 1/68 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June).
Mie Theory, Cross-Sections, Efficiency Factors and Phase Function
 Appendix C Mie Theory, Cross-Sections, Efficiency Factors and Phase Function C.1 Mie Theory The concept behind the Mie Theory is explained in section.6.1. However, the mathematical derivation of the theory
Appendix C Mie Theory, Cross-Sections, Efficiency Factors and Phase Function C.1 Mie Theory The concept behind the Mie Theory is explained in section.6.1. However, the mathematical derivation of the theory
Particle Size Determination with Dynamic Light Scattering DLS
 Particle Size Determination with Dynamic Light Scattering DLS Applications with the Nano Particle Sizer ANALYSETTE 12 DynaSizer The new ANALYSETTE 12 DynaSizer uses the dynamic light scattering as a measuring
Particle Size Determination with Dynamic Light Scattering DLS Applications with the Nano Particle Sizer ANALYSETTE 12 DynaSizer The new ANALYSETTE 12 DynaSizer uses the dynamic light scattering as a measuring
UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs. Eman Mousa Alhajji
 UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Effect of Addition Au Nanoparticles on Emission Spectra of Laser Dye
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 973-462 Volume 2, Number 24 (27) pp. 4833-484 Effect of Addition Au Nanoparticles on Emission Spectra of Laser Dye Sara Ali Razzak, Lazem Hassan
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 973-462 Volume 2, Number 24 (27) pp. 4833-484 Effect of Addition Au Nanoparticles on Emission Spectra of Laser Dye Sara Ali Razzak, Lazem Hassan
Influence of microphytobenthos photosynthesis on the spectral characteristics of the signal reflected from Baltic sandy sediments
 Influence of microphytobenthos photosynthesis on the spectral characteristics of the signal reflected from Baltic sandy sediments Damian JAŚNIEWICZ 1, Natalia GORSKA 2 1 Institute of Oceanology, PAS Powstańców
Influence of microphytobenthos photosynthesis on the spectral characteristics of the signal reflected from Baltic sandy sediments Damian JAŚNIEWICZ 1, Natalia GORSKA 2 1 Institute of Oceanology, PAS Powstańców
ZhongPing Lee, University of Massachusetts Boston
 ZhongPing Lee, University of Massachusetts Boston Absorption properties Scattering properties ocean (water) color light within water medium Lu(ϴ,ϕ) (Voss et al 2007) (Kirk 1994) They are modulated by water
ZhongPing Lee, University of Massachusetts Boston Absorption properties Scattering properties ocean (water) color light within water medium Lu(ϴ,ϕ) (Voss et al 2007) (Kirk 1994) They are modulated by water
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven
 Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals in air radition properties Lecture 8 Lessons 22-24
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals in air radition properties Lecture 8 Lessons 22-24
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
ElectroMagnetic Radiation (EMR) Lecture 2-3 August 29 and 31, 2005
 ElectroMagnetic Radiation (EMR) Lecture 2-3 August 29 and 31, 2005 Jensen, Jensen, Ways of of Energy Transfer Energy is is the the ability to to do do work. In In the the process of of doing work, energy
ElectroMagnetic Radiation (EMR) Lecture 2-3 August 29 and 31, 2005 Jensen, Jensen, Ways of of Energy Transfer Energy is is the the ability to to do do work. In In the the process of of doing work, energy
Distribution equilibrium
 Distribution equilibrium TEC Related concepts Principles of thermodynamics; partial molar free enthalpy (chemical potential); equilibrium between phases; distribution and extraction; Nernst distribution
Distribution equilibrium TEC Related concepts Principles of thermodynamics; partial molar free enthalpy (chemical potential); equilibrium between phases; distribution and extraction; Nernst distribution
Application of IR Raman Spectroscopy
 Application of IR Raman Spectroscopy 3 IR regions Structure and Functional Group Absorption IR Reflection IR Photoacoustic IR IR Emission Micro 10-1 Mid-IR Mid-IR absorption Samples Placed in cell (salt)
Application of IR Raman Spectroscopy 3 IR regions Structure and Functional Group Absorption IR Reflection IR Photoacoustic IR IR Emission Micro 10-1 Mid-IR Mid-IR absorption Samples Placed in cell (salt)
Discussion Review Test #2. Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
 Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
Small-scale effects of underwater bubble clouds on ocean reflectance: 3-D modeling results
 Small-scale effects of underwater bubble clouds on ocean reflectance: 3-D modeling results Jacek Piskozub, 1,* Dariusz Stramski, 2 Eric Terrill, 2 and W. Kendall Melville 2 1 Institute of Oceanology, Polish
Small-scale effects of underwater bubble clouds on ocean reflectance: 3-D modeling results Jacek Piskozub, 1,* Dariusz Stramski, 2 Eric Terrill, 2 and W. Kendall Melville 2 1 Institute of Oceanology, Polish
Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time.
 L e c t u r e 8 1 Polarization Polarized light Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time. Imagine two harmonic, linearly polarized light
L e c t u r e 8 1 Polarization Polarized light Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time. Imagine two harmonic, linearly polarized light
1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory.
 Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
10/2/2008. hc λ. νλ =c. proportional to frequency. Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength And is directly proportional to wavenumber
 CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
INTERFEROMETERS. There are 4 principal types of measurements that can be made with this type of interferometer.
 INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
Optical properties of spherical and anisotropic gold shell colloids
 8 Optical properties of spherical and anisotropic gold shell colloids Core/shell colloids consisting of a metal shell and a dielectric core are known for their special optical properties. The surface plasmon
8 Optical properties of spherical and anisotropic gold shell colloids Core/shell colloids consisting of a metal shell and a dielectric core are known for their special optical properties. The surface plasmon
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry
 1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
Optical Properties of Metals. Institute of Solid State Physics. Advanced Materials - Lab Intermediate Physics. Ulm University.
 Advanced Materials - Lab Intermediate Physics Ulm University Institute of Solid State Physics Optical Properties of Metals Burcin Özdemir Luyang Han April 28, 2014 Safety Precations MAKE SURE THAT YOU
Advanced Materials - Lab Intermediate Physics Ulm University Institute of Solid State Physics Optical Properties of Metals Burcin Özdemir Luyang Han April 28, 2014 Safety Precations MAKE SURE THAT YOU
The new physiology of vision-chapter The colours of interference. SIR C V RAMAN Received October 14, 1965
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A62 243-248 (1965) The new physiology of vision-chapter The colours of interference XXVII. SIR C V RAMAN Received October 14, 1965 The characteristic features and properties of
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A62 243-248 (1965) The new physiology of vision-chapter The colours of interference XXVII. SIR C V RAMAN Received October 14, 1965 The characteristic features and properties of
Particle Size and Rapid Stability Analyses of Concentrated Dispersions
 RESERVE THIS SPACE Particle Size and Rapid Stability Analyses of Concentrated Dispersions Use of Multiple Light Scattering Technique P. Bru 1, L. Brunel 1, H. Buron 1*, I. Cayré 1, X. Ducarre 1, A. Fraux
RESERVE THIS SPACE Particle Size and Rapid Stability Analyses of Concentrated Dispersions Use of Multiple Light Scattering Technique P. Bru 1, L. Brunel 1, H. Buron 1*, I. Cayré 1, X. Ducarre 1, A. Fraux
Light Scattering from Silica-Iron Oxide Core-Shell Colloids
 7 Light Scattering from Silica-Iron Oxide Core-Shell Colloids Abstract Static light scattering measurements have been performed on colloidal dispersions of silica particles with two concentric shells one
7 Light Scattering from Silica-Iron Oxide Core-Shell Colloids Abstract Static light scattering measurements have been performed on colloidal dispersions of silica particles with two concentric shells one
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Transformations of Oxidized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Exposed to UVC (254nm) Irradiation. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Transformations of Oxidized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Exposed to UVC (254nm)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Transformations of Oxidized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Exposed to UVC (254nm)
Introduction. The amount of radiation absorbed may be measured in a number of ways: Transmittance, T = P / P 0 % Transmittance, %T = 100 T
 Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
Studies to develop certified reference material to calibrate spectrophotometer in ultraviolet region
 Studies to develop certified reference material to calibrate spectrophotometer in ultraviolet region Felipe Carvalho da Conceição, Paulo Paschoal Borges and Juliana Freitas Santos Gomes 2 National Institute
Studies to develop certified reference material to calibrate spectrophotometer in ultraviolet region Felipe Carvalho da Conceição, Paulo Paschoal Borges and Juliana Freitas Santos Gomes 2 National Institute
Applied Spectroscopy Spectroscopic Nomenclature
 Applied Spectroscopy Spectroscopic Nomenclature Absorbance, A Negative logarithm to the base 10 of the transmittance: A = log 10 (T). (Not used: absorbancy, extinction, or optical density). (See Note 3).
Applied Spectroscopy Spectroscopic Nomenclature Absorbance, A Negative logarithm to the base 10 of the transmittance: A = log 10 (T). (Not used: absorbancy, extinction, or optical density). (See Note 3).
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Analytical Chemistry II
 Analytical Chemistry II L4: Signal processing (selected slides) Computers in analytical chemistry Data acquisition Printing final results Data processing Data storage Graphical display https://www.creativecontrast.com/formal-revolution-of-computer.html
Analytical Chemistry II L4: Signal processing (selected slides) Computers in analytical chemistry Data acquisition Printing final results Data processing Data storage Graphical display https://www.creativecontrast.com/formal-revolution-of-computer.html
Optical & Spectroscopic Insight into Rheology. SR Kim
 Optical & Spectroscopic Insight into Rheology SR Kim 14.11.2014 Contents Rheology and Microscopy Rheology and Simultaneous FT-IR Analysis 2 3 RHEOLOGY AND MICROSCOPY What does Rheology Do? Put a defined
Optical & Spectroscopic Insight into Rheology SR Kim 14.11.2014 Contents Rheology and Microscopy Rheology and Simultaneous FT-IR Analysis 2 3 RHEOLOGY AND MICROSCOPY What does Rheology Do? Put a defined
PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES
 PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application
PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application
Measurement of the effective refractive index of a turbid colloidal suspension using light refraction
 Measurement of the effective refractive index of a turbid colloidal suspension using light refraction A Reyes-Coronado 1,, A García-Valenzuela,4, C Sánchez-Pérez and R G Barrera 1,3 1 Instituto de Física,
Measurement of the effective refractive index of a turbid colloidal suspension using light refraction A Reyes-Coronado 1,, A García-Valenzuela,4, C Sánchez-Pérez and R G Barrera 1,3 1 Instituto de Física,
Interaction X-rays - Matter
 Interaction X-rays - Matter Pair production hν > M ev Photoelectric absorption hν MATTER hν Transmission X-rays hν' < hν Scattering hν Decay processes hν f Compton Thomson Fluorescence Auger electrons
Interaction X-rays - Matter Pair production hν > M ev Photoelectric absorption hν MATTER hν Transmission X-rays hν' < hν Scattering hν Decay processes hν f Compton Thomson Fluorescence Auger electrons
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
emulsions, and foams March 21 22, 2009
 Wetting and adhesion Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecure 2 - Wetting and adhesion
Wetting and adhesion Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecure 2 - Wetting and adhesion
Efficient charge storage in photoexcited TiO 2 nanorod-noble metal nanoparticle composite systems
 Electronic Supplementary Information Efficient charge storage in photoexcited TiO 2 nanorod-noble metal nanoparticle composite systems P. D. Cozzoli, M. L. Curri, and A. Agostiano 1. Synthesis of TiO 2
Electronic Supplementary Information Efficient charge storage in photoexcited TiO 2 nanorod-noble metal nanoparticle composite systems P. D. Cozzoli, M. L. Curri, and A. Agostiano 1. Synthesis of TiO 2
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
Radiation in the Earth's Atmosphere. Part 1: Absorption and Emission by Atmospheric Gases
 Radiation in the Earth's Atmosphere Part 1: Absorption and Emission by Atmospheric Gases Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves are transversal. Electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular. In
Radiation in the Earth's Atmosphere Part 1: Absorption and Emission by Atmospheric Gases Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves are transversal. Electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular. In
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Scattering of EM waves by spherical particles: Overview of Mie Scattering
 ATMO 551a Fall 2010 Scattering of EM waves by spherical particles: Overview of Mie Scattering Mie scattering refers to scattering of electromagnetic radiation by spherical particles. Under these conditions
ATMO 551a Fall 2010 Scattering of EM waves by spherical particles: Overview of Mie Scattering Mie scattering refers to scattering of electromagnetic radiation by spherical particles. Under these conditions
INTRODUCTION The fundamental law of spectrophotometry is known as the Beer-Lambert Law or Beer s Law. It may be stated as: log(po/p) = A
 S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY AIM 1. To become familiar with the operation of a conventional scanning ultra-violet spectrophotometer 2. To determine suitable cells and solvents
S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY AIM 1. To become familiar with the operation of a conventional scanning ultra-violet spectrophotometer 2. To determine suitable cells and solvents
CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK AND SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK
 161 CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK AND SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK 7.1 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK Nonlinear optical materials are required in a wide range of important applications, such as optical
161 CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK AND SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK 7.1 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK Nonlinear optical materials are required in a wide range of important applications, such as optical
