PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES
|
|
|
- Herbert Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES
2 CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry
3 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application for the detection and quantitative determination of an absorbing species. Spectrophotometry is one such technique noted for its remarkable sensitivity and precision. A change in the intensity of the colour of the system with change in concentration of the system is termed as colorimetry. A substance appears coloured whenever it transmits or absorbs a part of a visible radiation. Absorption spectrum constitutes the optical activity of the substance. When a normal electronic structure of the substance is deformed there is either the production of the colour (or) change of the colour, Thus when molecules containing one or more chromophores and auxochromes, when subjected to irradiation undergo, variation in electronic energy. The presence of chromophores and auxochromes in organic molecules causes deepening of colour by displacing the absorption maximum towards lower wavelengths. This effect is termed as bathochromic shift. The reverse effect is hypsochromic shift. The wavelength range of nm in an electromagnetic spectrum is called the visible region. Beer and Bernard established the general law of absorption of radiation. In spectrophotometric technique an absorbing medium is placed between the source of a radiation and the spectroscope and the light absorbed is measured. The plot of light absorbed on ordinates versus wavelength is characteristic for an absorbing component, and forms the basis for qualitative analysis. The height of the ordinate in the plot due to the component under investigation at any particular
4 124 wavelength is a measure of the concentration of the component and is thus useful for quantitative work. Laws of photometry When a light falls upon a homogeneous medium, a portion of the incident light is reflected, a portion is absorbed within the medium and the remainder is transmitted. Thus the intensity of the incident light IQ is given as Io=I. + I. + Ir... (1) where Ia = intensity of the light absorbed It = intensity of the light transmitted Ir = intensity of the light reflected. Since the measurements are always made with reference to a reference solution in an identical cell, Ir is regarded as constant and hence it can be neglected. The equation (1) becomes lo=i. + It... (2) Fundamental laws of photometry Lambert s law The fraction of radiant energy absorbed increases exponentially with the linear increase in the thickness of the medium, i.e., - = k'.dt... (3) I I = I0e kdt (4)
5 125 k' is proportionality constant. Ie is intensity of incident radiation when V is zero. The ratio of 1/I0 is the fraction of the incident light transmitted by the medium and is termed transmission or transmittance. The reciprocal \J\ is opacity. Beer s law The exponential decrease of the intensity of monochromatic radiation depends upon the arithmetic increase in the absorption of the absorbing species. The law is represented as (5) (6) k" is proportionality constant. The combination of the two laws is known as Lambert-Beer law. The law states that the fraction of radiant energy absorbed increases exponentially with the linear increase in the thickness and concentration of the absorbing species. (7) where k is new proportionality constant. When expressed logarithmically equation (7) becomes log Io/I = a.c.t. (8) where a = k/ Since a.c.t. is a logarithmic quantity, it is a pure number, a in the equation is known as absorptivity. Its units are Litre/gm-cm when the thickness is expressed in centimetre and concentration in gm/litre. When the concentration is expressed in moles/litre the proportionality constant is known as s and is termed molar absorptivity or molar absorption index or molar extinction coefficient. Its units are
6 126 Litre mole'1 cm'1. Emperically molar absorptivities that range from zero upto a maximum of the order of 105 are observed in ultraviolet and visible absorption. For any particular peak the magnitude of e depends on the capture cross section of the species and the probability for any energy absorption transition to occur. The relation between s and these parameters is shown to be s = 3.7 x 1019PA where P = transition probability A = cross section target area in cm2. From electron diffraction studies the cross section target area for a typical organic molecule is estimated to be about 10'15 cm2. Values of P range from for quantum mechanically allowed transition. This value of P leads to strong absorption bands i.e., smax is equal to about 10s. The absorption peaks having e values less than about 103 show low intensity bands. Beer-Lambert law as expressed in equation (8) is also shown as A = log Io/I = set... (9) where A = log Iq/I is referred as absorbance or optical density or extinction. Beer s law - Deviations The absorbances of a series of solutions of known concentration at a fixed wavelength and cell path must bear a linear relationship to the concentration. The deviations from this behaviour is due to so many factors such as interionic forces, complex formation, time and temperature variations, solvent composition in blank and
7 127 test solution and wavelength of radiation etc. The law is obeyed only when the radiation employed is monochromatic. Sensitivity in spectrophotometric method The slope of a calibration plot between concentration and absorbance refer to sensitivity in photometry. Numerically it is expressed as molar absorptivity at wavelength of maximum absorption. s = a/ct... (10) If the value of e given by a method is greater than 104 then the method is said to be sensitive in photometric terms. Specific absorptivity (a) The specific absorptivity (a) is given by equation a = e/atomic weight x (11) The units are ml gm'1 cm'1. This value corresponds to an absorbance of 1 gg/ml solution taken in a cuvette of pathlength 1 cm. Sandell s photometric sensitivity (S) S represents the number of micrograms of determined per ml of solution having an absorption of for a pathlength of 1 cm. S = 10'3/a... (12) Stoichiometry The various spectrophotometric methods employed for establishing the composition of the complex in solution are Job s continuous variation method, Molar ratio method, Slope ratio method, Asmus method and Equilibrium shift method.
8 128 In the present investigations, the author has employed the Job s continuous variation method and molar ratio methods. A brief description of these methods is given. 1. Job s continuous variation method Job1 described a method for determining the stoichiometry of the complex formed between metal ion, M and ligand, L. The formation reaction of the complex is represented as M + nl -» ML... (13) In this method, identical formal concentrations of metal ion and the ligand are used and are mixed in varying volume ratios, keeping the total volume constant. The absorbance of these mixtures is measured at a suitable wavelength against an appropriate blank solution. The absorbance values are then plotted against the volume fraction (same as the mole fraction) Vm/Vm+Vl of one of the reactants. Where Vm and V). represent respectively the volume of the metal ion and the ligand. A curve is obtained which has a maximum (or minimum if the complex absorbs less than the reactants). The composition of the complex is given by the volume fraction ratio. X : [1 - X]...(14) where X V, M... (15) (Vm+Vl) The composition thus corresponding to the point of maximum bears a simple relation to n and is independent of equilibrium constant of the equiformal solutions of M and L\ However the position of the maximum depends on the equilibrium constants
9 129 when the concentrations are not equal. The composition of the several complexes is satisfactorily identified by the Job s method. However, if more than one complex is formed Job s method is generally not applicable. Cooper et al2 reported that the Job s method is still be useful if it is ascertained whether or not one complex is formed in the system under study. In the Job s modified procedure the optical measurements are made at various wavelengths covering the entire range instead of at the wavelength corresponding to the maximum. If all the wavelengths give same conclusion, it can be assumed that a single complex is formed. Thus Job s method is employed for the elucidation of the complex composition. For a system containing only one complex, the value of n is given by n = X (1-X) (16) where X is the volume in litres of L added to the volume in litres of M. Molar ratio method In this method introduced by Yoe and Jones3, a series of solutions are prepared in which the formal concentrations of one of the reactants usually the metal ion is kept constant while that of the other (reagent) is varied. The absorbance values are plotted against mole ratio of the reagent. If the system forms the stable complex, the plot consists of two straight lines of different slopes intercepting at a sharp break. The mole ratio at this break corresponds to the combining ratio in the complex. In the case of weak complexes, the mole ratio plot is a smooth curve and that can be extrapolated to give the combining ratio. A mole ratio plot may reveal stepwise formation of two or more complexes provided the molar absorptivities and formation constants of these complexes are different.
10 130 Methods for evaluating the stability constants of the complexes The available spectrophotometric methods for the determination of stability constant are Job s method, Bent and French method, Edmund and Birn Baum s method and Asmus method. In the present investigations, Job s method is employed for the determination of the stability of the metal complex and is described. Job s method The stability constant, P is obtained by applying the data obtained in Job s method. For 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3 complexes, the stability constant (p) values are calculated using the following equations respectively. 0-q) a2c (17) (1-a) 4a2C2 (18) (1-a) 27a4C3 (19) where Am = absorbance corresponding to the point of intersection of the extrapolated lines A = observed absorbance at concentration C C = concentration corresponding to the point of intersection a = degree of dissociation a Lm J
11 Job, P. Voseburgh, W.C. and Cooper, G.R. REFERENCES Ann. Chim., 9(1928) 113. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 63 (1941)437, 3 Yoe, H.J. and Jones, A.L. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 16 (1944) 111.
(2/uifaiei - *1. Principles of Spectrophotometry
 (2/uifaiei - *1 Principles of Spectrophotometry The methods based on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation are the most important of all the instrumental methods of analysis. Spectrophtometry is
(2/uifaiei - *1 Principles of Spectrophotometry The methods based on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation are the most important of all the instrumental methods of analysis. Spectrophtometry is
UV-Vis Absorption Experiment 5: Beer- Lambert Law and the Temperature Dependence of the Crystal Violet- Sodium Hydroxide Reaction
 1 UV-Vis Absorption Experiment 5: Beer- Lambert Law and the Temperature Dependence of the Crystal Violet- Sodium Hydroxide Reaction Overview In Part A of this experiment, the absorption behaviour of crystal
1 UV-Vis Absorption Experiment 5: Beer- Lambert Law and the Temperature Dependence of the Crystal Violet- Sodium Hydroxide Reaction Overview In Part A of this experiment, the absorption behaviour of crystal
Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13)
 An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
09/05/40 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS
 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
Concepts, Techniques. Concepts, Techniques 9/11/2012. & Beer s Law. For a simple, transparent, COLORED material, e.g. ROYGBV
 9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III
 Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III Syllabus: Principle of spectrophotometry Types of spectrophotometer Applications - Dissociation constants of an indicator simultaneous spectrophotometric
Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III Syllabus: Principle of spectrophotometry Types of spectrophotometer Applications - Dissociation constants of an indicator simultaneous spectrophotometric
Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry Properties of light Electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic spectrum Absorption of light Beer s law Limitation of Beer s
Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry Properties of light Electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic spectrum Absorption of light Beer s law Limitation of Beer s
CHEM 254 EXPERIMENT 9. Chemical Equilibrium-Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constant of a weak acid
 CHEM 254 EXPERIMENT 9 Chemical Equilibrium-Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constant of a weak acid For a weak acid that can only partly dissociate the equilibrium constant is related to activities
CHEM 254 EXPERIMENT 9 Chemical Equilibrium-Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constant of a weak acid For a weak acid that can only partly dissociate the equilibrium constant is related to activities
Spectroscopy Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT Spectroscopy
 Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT.00.009 Spectroscopy 04.09.12 http://tera.chem.ut.ee/~koit/arstpr/spe_en.pdf 1 ntroduction Spectroscopy is a general term for methods that investigate interactions
Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT.00.009 Spectroscopy 04.09.12 http://tera.chem.ut.ee/~koit/arstpr/spe_en.pdf 1 ntroduction Spectroscopy is a general term for methods that investigate interactions
AIM To verify Beer - Lambert s law and to determine the dissociation constant (Ka) of methyl red, Spectrophotometrically.
 C 141(Expt. No. ) NAME : ROLL No. : SIGNATURE : BATCH : DATE : VERIFICATION OF BEER - LAMBERT S LAW & DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANT (Ka) OF METHYLRED, SPECTROPHOTOMETRICALLY AIM To verify Beer
C 141(Expt. No. ) NAME : ROLL No. : SIGNATURE : BATCH : DATE : VERIFICATION OF BEER - LAMBERT S LAW & DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANT (Ka) OF METHYLRED, SPECTROPHOTOMETRICALLY AIM To verify Beer
Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical]
![Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical] Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical]](/thumbs/78/77692425.jpg) Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves BCH 312 [Practical] Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a solution. It consist of two parts:
Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves BCH 312 [Practical] Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a solution. It consist of two parts:
Introduction. The amount of radiation absorbed may be measured in a number of ways: Transmittance, T = P / P 0 % Transmittance, %T = 100 T
 Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
Spectroscopy. Page 1 of 8 L.Pillay (2012)
 Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
COLORIMETER AND LAMBERT S-BEER S LAW. Shingala vaishali Sandha prafulla Tiwari Kuldeep
 COLORIMETER AND LAMBERT S-BEER S LAW Shingala vaishali Sandha prafulla Tiwari Kuldeep TOPIC What is colorimeter? Use of colorimeter. Component & It s function. Function of colorimeter. The principle of
COLORIMETER AND LAMBERT S-BEER S LAW Shingala vaishali Sandha prafulla Tiwari Kuldeep TOPIC What is colorimeter? Use of colorimeter. Component & It s function. Function of colorimeter. The principle of
GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet GPM.1.2.1.1.0003.15 and visible spectral regions Replaces the SPRF X GPM, SPRF XI GPM,
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet GPM.1.2.1.1.0003.15 and visible spectral regions Replaces the SPRF X GPM, SPRF XI GPM,
Spectrophotometry. Introduction
 Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Lambert s law. Beer s law. di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) = - a c dx. I/I 0 = e -kl T = A = - log (T) = - log (I/I 0 )
 di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) Integrating this equation from x=0 ~ l (I x =I 0 ~I) gives ; ln I ln I 0 = -kl ln I/I 0 = -kl Expressing the number of photons absorbed by the slab as di x, and the
di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) Integrating this equation from x=0 ~ l (I x =I 0 ~I) gives ; ln I ln I 0 = -kl ln I/I 0 = -kl Expressing the number of photons absorbed by the slab as di x, and the
R O Y G B V. Spin States. Outer Shell Electrons. Molecular Rotations. Inner Shell Electrons. Molecular Vibrations. Nuclear Transitions
 Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer
 Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
9/28/10. Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Valence Electronic Structure. n σ* transitions
 Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT INTRODUCTION The principle underlying a spectrophotometric method of analysis involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation
Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT INTRODUCTION The principle underlying a spectrophotometric method of analysis involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry
 Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
10/2/2008. hc λ. νλ =c. proportional to frequency. Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength And is directly proportional to wavenumber
 CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry
 1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant
 Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY/BEER S LAW LECTURE HONORS CHEMISTRY NAME
 SPECTROPHOTOMETRY/BEER S LAW LECTURE HONORS CHEMISTRY NAME Overview: Spectroscopy will be a tool that you will use as you continue in your chemistry, biology and physics courses. Background: We will begin
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY/BEER S LAW LECTURE HONORS CHEMISTRY NAME Overview: Spectroscopy will be a tool that you will use as you continue in your chemistry, biology and physics courses. Background: We will begin
CHEMICAL KINETICS E + 2B 2C + D (1)
 CHEMICAL KINETICS Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the study of the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions. The rate of a reaction is a measure of its speed. Consider
CHEMICAL KINETICS Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the study of the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions. The rate of a reaction is a measure of its speed. Consider
EXPERIMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study
 OBJECTVES: EXPERMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study To operate a Spectronic 20 To convert from percent transmission to absorbance units To plot absorbance versus wavelength and find max To plot absorbance versus
OBJECTVES: EXPERMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study To operate a Spectronic 20 To convert from percent transmission to absorbance units To plot absorbance versus wavelength and find max To plot absorbance versus
Paper: 12, Organic Spectroscopy Module: 5, Applications of UV spectroscopy
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 12: Organic Spectroscopy Applications of UV-visible Spectroscopy CHE_P12_M5 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 12: Organic Spectroscopy Applications of UV-visible Spectroscopy CHE_P12_M5 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
CHEM Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy
 CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
Spectroscopy Primer. for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy. by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015
 Spectroscopy Primer for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015 Abstract: An overview of uv vis absorbance spectroscopy including Beer s Law, calibration curves,
Spectroscopy Primer for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015 Abstract: An overview of uv vis absorbance spectroscopy including Beer s Law, calibration curves,
( ) x10 8 m. The energy in a mole of 400 nm photons is calculated by: ' & sec( ) ( & % ) 6.022x10 23 photons' E = h! = hc & 6.
 Introduction to Spectroscopy Spectroscopic techniques are widely used to detect molecules, to measure the concentration of a species in solution, and to determine molecular structure. For proteins, most
Introduction to Spectroscopy Spectroscopic techniques are widely used to detect molecules, to measure the concentration of a species in solution, and to determine molecular structure. For proteins, most
CHEM*3440. Photon Energy Units. Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation. Chemical Instrumentation. Spectroscopic Experimental Concept.
 Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry
 Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry
 Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry 13A Measurement Of Transmittance and Absorbance Absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet and visible radiation
Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry 13A Measurement Of Transmittance and Absorbance Absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet and visible radiation
MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS
 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
Modern Instrumental Methods of Analysis Prof. J. R. Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Modern Instrumental Methods of Analysis Prof J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No # 02 Lecture No # 07 Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometry
Modern Instrumental Methods of Analysis Prof J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No # 02 Lecture No # 07 Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometry
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications
 Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
INTRODUCTION The fundamental law of spectrophotometry is known as the Beer-Lambert Law or Beer s Law. It may be stated as: log(po/p) = A
 S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY AIM 1. To become familiar with the operation of a conventional scanning ultra-violet spectrophotometer 2. To determine suitable cells and solvents
S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY AIM 1. To become familiar with the operation of a conventional scanning ultra-violet spectrophotometer 2. To determine suitable cells and solvents
Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye?
 Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye? USING SPECTROSCOPY TO DETERMINE SOLUTION CON- CENTRATION Guiding Question How could you make more of this dye? INTRODUCTION A solution is a homogeneous
Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye? USING SPECTROSCOPY TO DETERMINE SOLUTION CON- CENTRATION Guiding Question How could you make more of this dye? INTRODUCTION A solution is a homogeneous
Chapter 18. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry. Properties of Light
 Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
DETERMINATION OF K c FOR AN EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEM
 DETERMINATION OF K c FOR AN EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEM 1 Purpose: To determine the equilibrium constant K c for an equilibrium system using spectrophotometry to measure the concentration of a colored complex ion.
DETERMINATION OF K c FOR AN EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEM 1 Purpose: To determine the equilibrium constant K c for an equilibrium system using spectrophotometry to measure the concentration of a colored complex ion.
Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum.
 Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum. a. Is the spectrum above a band spectrum or a line spectrum? This is a band spectra, there are what
Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum. a. Is the spectrum above a band spectrum or a line spectrum? This is a band spectra, there are what
Spectroscopy. a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation.
 Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation. Mass Spectrometry Determines the relative abundance of the different isotopes of an element Used to determine the average
Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation. Mass Spectrometry Determines the relative abundance of the different isotopes of an element Used to determine the average
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Spectroscopy. a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation
 Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Radiation Scale of Absorption involves: Example of spectroscopy Gamma rays pm Nuclear reactions
Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Radiation Scale of Absorption involves: Example of spectroscopy Gamma rays pm Nuclear reactions
Experimental Procedure Overview
 Lab 4: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) Fe(SCN) 2+ (aq)
Lab 4: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) Fe(SCN) 2+ (aq)
A Study of Beer s Law Prelab
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? A Study of Beer s Law Prelab 2. Using the absorbance versus wavelength curve given in Figure I, determine the approximate value of max of the dye used to construct
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? A Study of Beer s Law Prelab 2. Using the absorbance versus wavelength curve given in Figure I, determine the approximate value of max of the dye used to construct
C H E M I S T R Y DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 C H E M I S T R Y 1 5 0 Chemistry for Engineers DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Introduction A system is at
C H E M I S T R Y 1 5 0 Chemistry for Engineers DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Introduction A system is at
CHEMISTRY 135 General Chemistry II. Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 CHEMISTRY 135 General Chemistry II Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Show above is a laboratory sample from chemistry, not phlebotomy. [1] Is the bloody-looking product the main component of this
CHEMISTRY 135 General Chemistry II Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Show above is a laboratory sample from chemistry, not phlebotomy. [1] Is the bloody-looking product the main component of this
Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron
 Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron INTRODUCTION Many investigations of chemical species involve the interaction between light and matter. One class of these investigations, called absorbance spectrophotometry,
Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron INTRODUCTION Many investigations of chemical species involve the interaction between light and matter. One class of these investigations, called absorbance spectrophotometry,
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE. 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation Estimation of Drugs
 CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
Investigating Transition Metal Complexes
 Exercise 4 Investigating Transition Metal Complexes 4 Introduction Colour is a well known property of the transition metals. The colour produced as parts of the visible spectrum are due to electron transitions
Exercise 4 Investigating Transition Metal Complexes 4 Introduction Colour is a well known property of the transition metals. The colour produced as parts of the visible spectrum are due to electron transitions
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
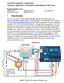 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
Spectrophotometry. Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology
 Spectrophotometry Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology Content Introduction Beer-Lambert law Instrument Applications Introduction 3 Body fluids such as blood, csf and urine contain organic and
Spectrophotometry Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology Content Introduction Beer-Lambert law Instrument Applications Introduction 3 Body fluids such as blood, csf and urine contain organic and
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies. R. Corn - Chem M3LC
 Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies R. Corn - Chem M3LC Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu velocity
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies R. Corn - Chem M3LC Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu velocity
Reference literature. (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters )
 September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant v021214 Objective To determine the equilibrium constant (K c ) for the reaction of iron (III) ion with thiocyanate (SCN - ) to form the thiocyanatoiron(iii)
Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant v021214 Objective To determine the equilibrium constant (K c ) for the reaction of iron (III) ion with thiocyanate (SCN - ) to form the thiocyanatoiron(iii)
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies. Chem M3LC. R. Corn
 Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Chem M3LC. R. Corn Review: Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Chem M3LC. R. Corn Review: Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu
S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY
 S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY PURPOSE 1. To become familiar with the operation of a conventional scanning ultra-violet spectrophotometer 2. To determine suitable cells and solvents
S2. INTRODUCTION TO ULTRA-VIOLET / VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY PURPOSE 1. To become familiar with the operation of a conventional scanning ultra-violet spectrophotometer 2. To determine suitable cells and solvents
two slits and 5 slits
 Electronic Spectroscopy 2015January19 1 1. UV-vis spectrometer 1.1. Grating spectrometer 1.2. Single slit: 1.2.1. I diffracted intensity at relative to un-diffracted beam 1.2.2. I - intensity of light
Electronic Spectroscopy 2015January19 1 1. UV-vis spectrometer 1.1. Grating spectrometer 1.2. Single slit: 1.2.1. I diffracted intensity at relative to un-diffracted beam 1.2.2. I - intensity of light
MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION!
 Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Lecture 3: Light absorbance
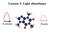 Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
Spectrochemical methods
 Spectrochemical methods G. Galbács The interactions of radiations and matter are the subject of spectroscopy py or spectrochemical methods (also called spectrometry). Spectrochemical methods usually measure
Spectrochemical methods G. Galbács The interactions of radiations and matter are the subject of spectroscopy py or spectrochemical methods (also called spectrometry). Spectrochemical methods usually measure
2-Hydroxy-4-n-propoxy-5-bromoacetophenone (HnPBAO) oxime as a gravimetric reagent for Ni(II) and Cu(II) and spectrophotometric study of the complexes
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Pelagia Research Library Der Chemica Sinica, 2010, 1 (3): 100-106 ISSN: 0976-8505 CODEN (USA) CSHIA5 2-Hydroxy-4-n-propoxy-5-bromoacetophenone (HnPBAO)
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Pelagia Research Library Der Chemica Sinica, 2010, 1 (3): 100-106 ISSN: 0976-8505 CODEN (USA) CSHIA5 2-Hydroxy-4-n-propoxy-5-bromoacetophenone (HnPBAO)
UV / Visible Spectroscopy. Click icon to add picture
 UV / Visible Spectroscopy Click icon to add picture Spectroscopy It is the branch of science that deals with the study of interaction of matter with light. OR It is the branch of science that deals with
UV / Visible Spectroscopy Click icon to add picture Spectroscopy It is the branch of science that deals with the study of interaction of matter with light. OR It is the branch of science that deals with
Experiment#1 Beer s Law: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II)
 : Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
Absorption spectrometry summary
 Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Beer's Law and Data Analysis *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m15131 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis
OpenStax-CNX module: m15131 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis
A very brief history of the study of light
 1. Sir Isaac Newton 1672: A very brief history of the study of light Showed that the component colors of the visible portion of white light can be separated through a prism, which acts to bend the light
1. Sir Isaac Newton 1672: A very brief history of the study of light Showed that the component colors of the visible portion of white light can be separated through a prism, which acts to bend the light
Experiment 2: The Beer-Lambert Law for Thiocyanatoiron (III)
 Chem 1B Dr. White 11 Experiment 2: The Beer-Lambert Law for Thiocyanatoiron (III) Objectives To use spectroscopy to relate the absorbance of a colored solution to its concentration. To prepare a Beer s
Chem 1B Dr. White 11 Experiment 2: The Beer-Lambert Law for Thiocyanatoiron (III) Objectives To use spectroscopy to relate the absorbance of a colored solution to its concentration. To prepare a Beer s
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS
 2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
Beer-Lambert law Decomposition of the manganese oxalate ion
 A34 Beer-Lambert law Decomposition of the manganese oxalate ion Task: 1. Determine the wavelength of maximal absorbance λ max of a hydrated Cu(NH 3 ) 4 2+ complex in the wavelength region of 400 to 800
A34 Beer-Lambert law Decomposition of the manganese oxalate ion Task: 1. Determine the wavelength of maximal absorbance λ max of a hydrated Cu(NH 3 ) 4 2+ complex in the wavelength region of 400 to 800
The mathematics of scattering and absorption and emission
 The mathematics of scattering and absorption and emission The transmittance of an layer depends on its optical depth, which in turn depends on how much of the substance the radiation has to pass through,
The mathematics of scattering and absorption and emission The transmittance of an layer depends on its optical depth, which in turn depends on how much of the substance the radiation has to pass through,
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash
 Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU
 The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
Part I Chapter 1: Introduction to solvent extraction
 1.1 Introduction and historical aspects of solvent Extraction Solvent or liquid-liquid extraction is based on the principle that a solute can distribute itself in a certain ratio between two immiscible
1.1 Introduction and historical aspects of solvent Extraction Solvent or liquid-liquid extraction is based on the principle that a solute can distribute itself in a certain ratio between two immiscible
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample
 Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Concentrations that absorb. Measuring percentage transmittance of solutions at different concentrations
 Measuring percentage transmittance of solutions at different Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 Concentrations that
Measuring percentage transmittance of solutions at different Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 Concentrations that
This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact
 This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact pogil@pogil.org The BEER-LAMBERT LAW Learning Objectives Students
This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact pogil@pogil.org The BEER-LAMBERT LAW Learning Objectives Students
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Prof. Dr. Ashwani K Sharma Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Prof. Dr. Ashwani K Sharma Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 6 Spectroscopic Techniques Lecture - 2 UV-Visible Spectroscopy
Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Prof. Dr. Ashwani K Sharma Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 6 Spectroscopic Techniques Lecture - 2 UV-Visible Spectroscopy
Experiment 2: The Beer-Lambert Law for Thiocyanatoiron (III)
 Chem 1B Saddleback College Dr. White 1 Experiment 2: The Beer-Lambert Law for Thiocyanatoiron (III) Objectives To use spectroscopy to relate the absorbance of a colored solution to its concentration. To
Chem 1B Saddleback College Dr. White 1 Experiment 2: The Beer-Lambert Law for Thiocyanatoiron (III) Objectives To use spectroscopy to relate the absorbance of a colored solution to its concentration. To
Radiant energy is proportional to its frequency (cycles/s = Hz) as a wave (Amplitude is its height) Different types are classified by frequency or
 CHEM 241 UNIT 5: PART B INFRA-RED RED SPECTROSCOPY 1 Spectroscopy of the Electromagnetic Spectrum Radiant energy is proportional to its frequency (cycles/s = Hz) as a wave (Amplitude is its height) Different
CHEM 241 UNIT 5: PART B INFRA-RED RED SPECTROSCOPY 1 Spectroscopy of the Electromagnetic Spectrum Radiant energy is proportional to its frequency (cycles/s = Hz) as a wave (Amplitude is its height) Different
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium
 Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium Introduction The word equilibrium suggests balance or stability. The fact that a chemical reaction
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium Introduction The word equilibrium suggests balance or stability. The fact that a chemical reaction
1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory.
 Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Basic Instrumentation. Learning Objectives:
 Proteomics Basic Instrumentation Basic Instrumentation Handling instruments plays an important role in laboratory working on a daily basis. The use of most instruments is almost inevitable and hence a
Proteomics Basic Instrumentation Basic Instrumentation Handling instruments plays an important role in laboratory working on a daily basis. The use of most instruments is almost inevitable and hence a
A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal
 CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 1.2 A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal In this laboratory exercise, we will determine the amount of Calium in a serving of cereal. We
CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 1.2 A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal In this laboratory exercise, we will determine the amount of Calium in a serving of cereal. We
Experiment 10 Dye Concentration Using a UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
 Experiment 10 Dye Concentration Using a UV-Vis Spectrophotometer version 2 Lynta Thomas, Ph.D. and Laura B. Sessions, Ph.D. In this experiment, you will determine the concentration of Allura Red Dye (FD&C
Experiment 10 Dye Concentration Using a UV-Vis Spectrophotometer version 2 Lynta Thomas, Ph.D. and Laura B. Sessions, Ph.D. In this experiment, you will determine the concentration of Allura Red Dye (FD&C
Fluorescence Workshop UMN Physics June 8-10, 2006 Basic Spectroscopic Principles Joachim Mueller
 Fluorescence Workshop UMN Physics June 8-10, 2006 Basic Spectroscopic Principles Joachim Mueller Fluorescence, Light, Absorption, Jablonski Diagram, and Beer-Law First stab at a definition: What is fluorescence?
Fluorescence Workshop UMN Physics June 8-10, 2006 Basic Spectroscopic Principles Joachim Mueller Fluorescence, Light, Absorption, Jablonski Diagram, and Beer-Law First stab at a definition: What is fluorescence?
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy Types of transitions: 1) Electronic (UV-Vis-Near IR) 2) Vibrational (IR) 3) Rotational (microwave) Electronic Absorption Spectra π π* Gary L. Miessler and Donald A. Tarr, Inorganic
Molecular Spectroscopy Types of transitions: 1) Electronic (UV-Vis-Near IR) 2) Vibrational (IR) 3) Rotational (microwave) Electronic Absorption Spectra π π* Gary L. Miessler and Donald A. Tarr, Inorganic
ULTRAVIOLET SPECTROSCOPY or ELECTRONIC SPECTROSCOPY
 ULTRAVILET SPECTRSCPY or ELECTRNIC SPECTRSCPY S. SANKARARAMAN Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600036, INDIA Sanka@iitm.ac.in Absorption of electromagnetic radiation
ULTRAVILET SPECTRSCPY or ELECTRNIC SPECTRSCPY S. SANKARARAMAN Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600036, INDIA Sanka@iitm.ac.in Absorption of electromagnetic radiation
Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS
 Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS FV 10/21/10 MATERIALS: Spectronic 20 spectrophotometers, 2 cuvettes, brass sample, 7 M HNO 3, 0.100 M CuSO 4, 2 M NH 3, two 50 ml beakers, 100 ml beaker, two 25 ml volumetric
Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS FV 10/21/10 MATERIALS: Spectronic 20 spectrophotometers, 2 cuvettes, brass sample, 7 M HNO 3, 0.100 M CuSO 4, 2 M NH 3, two 50 ml beakers, 100 ml beaker, two 25 ml volumetric
Preparation of Standard Curves. Principle
 Preparation of Standard urves Principle Many laboratory tests require the measurement of concentration be evaluated or read in a photometer (colorimeter or spectrophotometer). Since these instruments are
Preparation of Standard urves Principle Many laboratory tests require the measurement of concentration be evaluated or read in a photometer (colorimeter or spectrophotometer). Since these instruments are
Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry. Flexible. Reliable. Personal.
 L A B O R A T O R Y C O M P E T E N C E Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry Flexible. Reliable. Personal. The interaction of light with molecules is an essential and well accepted technique
L A B O R A T O R Y C O M P E T E N C E Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry Flexible. Reliable. Personal. The interaction of light with molecules is an essential and well accepted technique
