6. Tolerances are specified (a) to obtain desired fits (b) because it is not possible to manufac ture a size exactly (c) to obtain high accuracy
|
|
|
- Cory Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Who made the following classic statement. "When you can measure what you are speaking about and express it in numbers, you know something about it, and when you can't express it in numbers, your knowledge, is of a meagre and unsatisfactory kind. It may be the beginning of knowledge, but you have scarcely in your thought advanced to the stage of science." (a) Arnold Young (b) Taylorson (c) Johanson (d) Lord Kelvin (e) Taylor. 2. The ease with which observations can be made accurately is referred to as (a) readability (b) sensitivity (c) accuracy (d) precision (e) repeatability. 3. Accuracy of measuring equipment is (a) the closeness with which a measure-ment can be read directly from a measuring instrument. (b) a measure of how close the reading is to the true size. (c) the difference between measured value and actual value (d) the smallest change in measurand that can be measured (e) the capability to indicate the same reading again and again for a given measurand. 4. Which of the following error's are generally distributed in accordance "with the Gaussian distribution (a) controllable errors (b) calibration errors (c) avoidable errors (d) random errors (e) error due to ambient conditions. 6. Tolerances are specified (a) to obtain desired fits (b) because it is not possible to manufac ture a size exactly (c) to obtain high accuracy
2 (d) to have proper allowance (e) to have proper inspection. 7. Which of the following is the most important characteristic of a measuring instrument in general (a) precision (b) accuracy (c) repeatability (d) sensitivity (e) readability. 8. Sensitivity and range of measuring instrument have (a) direct relationship (b) linear relationship (c) inverse relationship (d) unpredictable relationship (e) no relationship. 9. Systematic errors are (a) randomly distributed (b) regularly repetitive in nature (c) distributed on both + ve and - ve sides of mean value (d) unknown errors (e) of unpredictable nature. 10. Precision of measuring equipment is (a) the closeness with which a measure ment can be read directly from a measuring instrument (b) a measure of how close the reading is to the true size (c) the difference between measured value and actual value (d) the smallest change in measurand that can be measured (e) the capability to indicate the same reading again and again for a given measurand. 11. The maximum amount by which the result differs from the true value is called (a) correction (b) discrepancy (c) error (d) accuracy (e) uncertainty.
3 12. Response is defined as the measure of a system's fidelity to purpose. The response of measuring instruments may be considered to the following cases (a) amplitude response (b) frequency response (c) phase response (d) delay or rise time (e) all of the above. 13. Which of the following can be used to scribe lines parallel to the edges of a part (a) vernier calipers (b) screw gauge (c) divider (d) hermaphrodite caliper (e) combination set. 14. Which of the following can't fall under the head controllable errors (a) calibration errors (b) environmental errors (c) avoidable errors (d) random errors (e) non-similarity of conditions while calibrating and measuring. 15. Which of the following errors are regularly repetitive in nature (a) systematic errors (b) random errors (c) illegitimate errors (d) controllable errors (e) avoidable errors. 16. Which of the following errors are inevitable in the measuring system and it would be vainflul exercise to avoid them (a) systematic errors (b) random errors (c) calibration errors (d) environmental errors (e) deformation errors.
4 18. Which of the following instruments is most accurate (a) vertical caliper (b) manometric screw gauge (c) optical projector (d) mechanical comparator (e) slip gauges. 19. Which of the following refers to parasitic error. (a) Error, often gross, which results from incorrect execution of measurement (b) algebraic difference between the results of measurement and the value of comparison (c) error which varies in an unpredictable manner in absolute value and in sign when a large number of measurements of the same value of a quantity are made under practically identical conditions. (d) disagreement between the result of measurement and the value of the quantity measured (e) error which during several measure-ments, under the same conditions of the same value of a certain quantity, remains constant in absolute value and sign or varies in accordance with a specified law when the conditions change. 20. Which of the following characterises the dispersion of the results obtained in a & ries of measurements of the same value of a quantity measured (a) absolute error (b) relative error (c) root mean square deviation (d) uncertainty of measurement (e) variation of indication. 21. A surface gauge is used for (a) levelling the surface plate (b) checking the surface finish (c) laying out the work accurately (d) finding the depth of the surface (e) finding flatness of surfaces. 22. Parasitic error is caused due to (a) improper use of measuring instrument (b) wrong design of instrument
5 (c) changes in ambient conditions (d) errors in computation (e) deflection of stylus. 24. A feeler gauge is used to check (a) radius (b) screw pitch (c) surface roughness (d) unsymmetrical shape (e) thickness of clearance. 25. Measuring mechanism whose mobile component attains its equilibrium position without oscillations round new position is called (a) damped measuring mechanism (b) aperiodic measuring mechanism (c) stable measuring mechanism (d) precise measuring mechanism (e) analogue measuring mechanism. 26. Measuring instrument which conforms to all the specified statutory provisions is called (a) ordinary measuring instrument (b) measuring' instrument acceptable for verification (c) auxiliary measuring instrument (d) legal measuring instrument (e) statutory measuring instrument. 27. Measuring instrument intended to define or present physically, conserve or reproduce the unit of measurement of a quantity (or a multiple or sub-multiple of that unit) and to transfer it to other measuring instruments by comparison is known as (a) legal measuring standard (b) secondary standard (c) working standard (d) primary standard (e) standard. 28. Work is usually required to be held in a vertical position for laying out. For this purpose, it is
6 clamped to (a) surface plate (b) an angle plate (c) a V-block (d) a machine bed (e) enginee's square. 29. The phenomenon shown by a measuring instrument which gives different indications in a series of measurements of the same value of the quantity measured is called (a) repeatability of measuring instrument (b) error of repeatability (c) dispersion of indications (d) error of trueness (e) discrimination of measuring instrument. 30. The quality of a measuring instrument which characterises the ability to respond to small changes of the quantity measured is called (a) discrimination of a measuring instru-ment (b) response of a measuring instrument (c) accuracy (d) precision (e) repeatability. 31. Instrument which is designed to eliminate the personal element of feel when setting a measuring instrument is called (a) fiducial indicator (b) zero setting device (c) auxiliary measuring instruments (d) measuring standard (e) indicating element. 32. The thickness of light gauge sheet steel can be best checked with a (a) finely divided steel scale (b) depth gauge (c) hermaphrodite caliper (d) micrometer (e) thickness measuring machine fitted with dial gauge.
7 33. Which of the following gives an idea about the ability of the equipment to detect small vartiation in the input signal (quantity being measured) (a) readability (b) accuracy (c) sensivity (d) precision (e) repeatability. 34. If attempts are made to make an instrument very sensitive, which of the following qualities is likely to be impaired (a) precision (b) accuracy (c) readability (d) rangeability (e) all of the above. 35. Optical flats are made of (a) quartz (b) glass (c) plastic (d) steel (e) silicon. 36. The axis of measurement of the scale or other dimensional reference should coincide. This principle is called the (a) principle of kinematic design (b) principle of alignment (c) principle of linear measuring instru-ments (d) principle of collinearity (e) principle of location and movement. 37. Pick out the wrong statement about flexible strips. (a) These are used in instruments where small movements are required between component parts (b) no force or torque is required to dis-place a member located on flexible strip from its mid position (c) it has no friction or backlash
8 (d) it is not subjected to wear (e) it has negligible hysterisis. 38. The least count of a metric vernier caliper having 25 divisions on vernier scale, matching with 24 divisions of main scale (1 main scale division = 0.5 mm) is (a) 0.05 mm (b) 0.01 mm (c) 0.02 mm (d) mm (e) mm. 39. A scale in which the distance between graduations if proportional to the value of that graduation is called (a) regular scale (b) equidistant scale (c) linear scale (d) line scale (e) continuous scale. 40. A scale whose graduation marks are in a discontinuous manner and are composed of aligned numbers indicating directly the numerical value of the quantity measured is called (a) linear scale (b) base of a linear scale (c) equidistant scale (d) regular scale (e) digital scale. 41. Element of the indicating device carrying the scale is called (a) dial (b) housing (c) transducer (d) index (e) frame. 42. The thread micrometer measures (a) the major diameter of the thread (b) the minor diameter of the thread
9 (c) the effective diameter of the thread (d) the root diameter of the thread (e) all the diameters of the thread. 43. V-block is used in the workshop to check (a) roundness of a cylindrical work (b) surface roughness (c) dimensions of oval job (d) taper on a job (e) none of the above. 44. Repeatability of measuring equipment is (a) the closeness with which a measurement can be read directly from a measuring instrument (b) a measure of how close the reading is to the true size (c) difference between measured value and actual valve (d) the smallest change in measurand that can be measured (e) the capability of indicate the same reading again and again for a given measurand. 45. The purpose of ratchet screw in micrometer screw gauge is (a) to lock a dimension (b) to impart blow motion (c) to maintain sufficient and uniform measuring pressure (d) to take care of wear of screw threads (e) to allow zero adjustment. 46. The purpose of adjusting nut in a micrometer screw gauge is to (a) take care of zero error (b) impart slow motion (c) compensate for wear between screw and nut (d) take care of backlash (e) ensure uniform measuring pressure. 47. The taper of internal dovetail can be measured with the help of (a) sine bar (b) combination set (c) balls of standard dimensions and slip gauges (d) clinometer
10 (e) dial gauges. 48. External taper can be accurately measured with the help of (a) sine bar and slip gauges (b) dividing head (c) precision balls and height gauge (d) combination set (e) clinometer. 49. Stick micrometers are designed for measuring (a) bore of cylinders (b) longer external lengths (c) cylindricity (d) longer internal lengths (e) diameters which can't be easily accessed. 50. Differential screw micrometer is used (a) to give direct indication of difference between two readings (b) to measure gap between grooves (c) for digital readout (d) to_ measure diameter of inaccessible holes (e) for very high degree of accuracy. 51. A sine bar is specified by (a) its total length (b) the centre distance between the two rollers (c) the size of the rollers (d) the distance between rollers and upper surface (e) weight of sine bar. 52. The diameter of very large bores can be, measured accurately by (a) flexibile graduated tape (b) cylindrical gauge (c) keilpart gauge (d) four balls method (e) swinging a pin gauge in the bore.
11 53. The number of slip gauges in a set are (a) 87 (b) 45 (c) 103 (d) 31 (e) all of the above sets are available. 54. Profile of a gear tooth can be checked by (a) sine bar (b) bench micrometer (c) optical pyrometer (d) optical projector (e) slip gauges. 55. Gear tooth caliper is used to find the chordal thickness of the following type of gear tooth (a) spur gears (b) helical gears (c) worm gears (d) bevel gears (e) any type of gear. 57. The M-and E-system in metrology are related with measurement of (a) gears (b) screw threads (c) flatness (d) angularity (e) surface finish. 58. All the thread characteristics can be measured precisely with (a) screw pitch gauge (b) micrometer with V-anvil (c) tool room microscope (d) thread gauge (e) thread measuring machine. 59. The advantage of vernier calpier over micrometer is that it (a) is easier and quicker to use
12 (b) is more accurate (c) can be used to make both inside and outside measurments over a range of sizes (d) all of the above (e) none of the above. 60. Standards to be used for reference purposes in laboratories and workshops are referred to as (a) primary standards (b) secondary standards (c) tertiary standards (d) working standards (e) none of the above. 62. The combination set can be used to (a) check angular surfaces (b) draw circles and arcs (c) scribe lines (d) all of the above (e) none of the above. 63. In layout work, a pencil should not be used to draw lines on metal because (a) it will wipe off easily (b) the line will be too wide for accurate work (c) the lines will smudge and be difficult to see (d) the lines do remain on metal even after good rubbing (e) all of the above. 64. Surface plate is usually made of grey cast iron because it provides (a) non wearing plate (b) very hard plate (c) easy to cast plate (d) lubrication due to graphite flakes (g) stable plate. 65. The term traceability in Engineering Metrology is concerned with (a) measuring machines (b) optical instruments (c) pneumatic comparator
13 (d) standards (e) limits and fits. 66. In selective assembly (a) parts in an assembly can be replaced by a similar part without any further alteration (b) parts are produced on hole basis sys tem (c) all the parts are always interchange able (d) the size of one of the components is measured accurately and then mating component is made to match with this (e) the parts of any one type are classified into several groups according to size. 67. Constant measuring pressure in micrometer screw gauges is ensured by (a) locknut (b) barrel and thimble (c) spindle (d) spanner (e) ratchet. 69. The basic unit in angular measurements is (a) degree (b) minute (c) second (d) right angle (e) Optical gauge works on the principle of (a) refraction (b) reflection (c) dispersion (d) polarisation (e) interference of light rays. 74. Circular scale of the micrometer is marked on (a) anvil (b) barrel (c) ratchet (d) thimble
14 (e) spindle. 75. According to well accepted practice, slip gauges which have been handled for a few minutes should be left for sometime. The reason for this could be (a) the moisture transferred from hand would evaporate (b) the structure of gauges, if disturbed would stabilise (c) gauges attain the room temperature again (d) with continuous use, gauges may wear quickly (e) there is no such practice. 76. Which of the following is not the essential requirement for accuracy of measurement with a sine bar (a) flatness of upper surface (b) equality of size and roundness of rollers (c) exact distance between roller axes and mutual parallelism (d) parallelism between top and bottom surfaces (e) parallelism of rollers to upper surface and equality of axis distance as from, surface. 18,77. The following type of gauges has gauging sections combined on one end (a) combination gauge (b) limit gauge (c) Go and No Go gauge (d) fixed gauge (e) progressive gauge. 78. The vernier reading should not be taken at its face value before an actual check has been taken for (a) zero error (b) its calibration (c) flatness of measuring jaws (d) temperature equalisation (e) all of the above. 79. Which comparator utilises the principle of a button spinning on a loop of string (a) Sigma comparator (b) Aramson comparator (c) Optical comparator
15 (d) Zeiss interferometer (e) Eden-Rolt comparator. 80. Gear tooth vernier is used to measure (a) circular pitch (b) depth of tooth (c) tooth thickness (d) addendum and dedendum (e) pitch line thickness of tooth. 81. Error of measuring equipment is (a) the closeness with which a measure-ment can be read directly from a measuring instrument. (b) a measure of how close the reading is to the true size (c) the difference between measured value and actual value (d) the smallest change in measureand that can be measured (e) the capability to indicate the same reading again and again for a given measureand. 82. Which of the following is not provided on combination set (a) centre head (b) protractor head (c) vernier scale (d) spirit level (e) squaring head. 83. Universal surface gauge is used (a) for flatness testing (b) for layout work and inspection (c) for measuring profile of complex sur-face (d) for measuring surface roughness (e) for measuring concavity of surface. 84. Accuracy is (a) the repeatability of a measuring process (b) error of judgement in recording an ob-servation (c) the ability of instrument to reproduce same reading under identical situations (d) agreement of the result of a measure-ment with the true value of the measured quantity (e) the least resolution of an instrument.
16 85. Random errors follow the following distribution (a) claussian (b) hyperbolic (c) parabolic (d) t- student (e) p-distribution. 86. Which one of the following is the least accurate measuring device (a) air gauge (b) micrometer screw gauge (c) optical projector (d) vernier micrometer (e) steel scale. 87. Pick up the wrong statement: (a) Accuracy of an instrument is closeness to the true dimension (b) Precision represents the degree of repetitiveness. (c) Sensitivity refers to minimum change in value that the instrument can reliab ly indicate. (d) As the sensitivity of an instrument in-crease, its range of measurement also increases. (e) If an instrument is not precise it will give different results for same dimen sion when measured again and again. 88. Fiducial indicators contain (a) calibrated scale (b) a single index mark (c) micrometer screw movement (d) optical head (e) interferometric devices. 89. A comparator for its working depends on (a) accurately calibrated scale (b) comparison with standard such as slip gauges (c) accurate micrometer gauge (d) optical devices (e) determining zero error of scale correct-
17 90. Precision is (a) the repeatability of a measuring process (b) agreement of the result of a measure-ment with the true value of the measured quantity (c) the ability of a measuring device to detect small differences in a quantity being measured (d) the ability of.an instrument to reproduce same reading under identi cal conditions (e) error of judgment in reading an obser-vation. 91. The thickness of oil film at the surface of slip gauges is of the order of (a).005 micron (b).1 micron (c) 1 micron (d) 10 microns (e) 100 microns. 92. Pick up the wrong statement. Surface plates are usually made of granite because of following advantages (a) because of long period of time for relaxing, it is free from built in residual stresses. There is no corrosion effect also. (b) there is less tendency for it to warp (c) if a tool or workpiece drops accidently over its surface, residual stresses are not induced (d) it simply powders somewhat at the point of impact by falling object (e) it enables the phenomenon of wringing flat surfaces over it. 93. Pick up the wrong statement. (a) Error is the disagreement between the result of measurement and actual value. (b) Random error are regularly repetitive in nature and result from improper conditions or procedures that are con-sistant in action (c) Parasitic error results from incorrect execution of measurement. (d) Uncertainty of measurement repre-sents the dispersion of the result of measurement defined by the limits of. the error. (e) Absolute error is the algebraic dif-ference between the result of measure-ment and the value of comparison. 96. Which one of the following instruments is the most accurate (a) steel scale (b) micrometer screw gauge (c) vernier caliper
18 (d) vernier dial gauge (e) optical projector. 98. In the case of high precision surface plates of diameter upto 200 mm, the working surface should lie between two parallel planes, whose maximum distance apart is (a) mm (b) mm (c) 0.05 mm (d) 0.5 mm (e) mm The lateral faces of slip gauges are at right angles correct to within (a) ± 1 degree (b) ± 30 minutes (c) ± 10 minutes (d) ± 1 minute (e) ± 10 seconds Protector gauge blocks in slip gauges are (a) used as reference blocks (b) mounted in the centre of pile (c) never touched (d) wrung on the end of combinations (e) made of same material as the slip gauges According to accuracy, slip gauges are classed under following number of accuracy classes (a) two (b) three (c) five (d) seven (e) ten A protector in slip gauges is provided to (a) protect slip gauges when not is use (b) take up all the wear when in use (c) clean the slip gauges
19 (d) facilitate wringing of slip gauges (e) assemble the slip gauges properly Pick out the wrong statement about Taylor's principle of gauging. (a) Go gauges should be full form gauges (b) Go gauges should check all the related dimensions simultaneously (c) It is sufficient to use Go gauges on the width and length of the com ponent (d) Not Go gauges should check only one dimension at a time (e) It is useless to have the Not Go gauges of the full form The term "Allowance" in limits and fits is usually referred to (a) minimum clearance between shaft and hole (b) maximum clearance between shaft and hole (c) difference of tolerances of hole and shaft (d) difference between maximum size and minimum size of the hole (e) difference between maximum size and minimum size of the shaft Which of the following is the correct way of designating fit (a) Hs/g7 (b) g7/hs (c) 50H8/ 7 (d) H8/g7-50 (e) 50H8/50/j The standard tolerance unit / in the case of limits and fits for sizes above 500 mm and upto 3150 mm is (a) 0.45 (W) ID (b) 0.52 (W) ID (c) 0.30(W) D (d) (W) (e) 0.004O (D is in mm) Sensitivity of measuring equipment is (a) the closeness with which a measure-ment can be read directly from a measuring instrument (b) a measure of how close the reading is to the true size (c) the difference between measured value and actual value (d) the smallest change in measurand that can be measured
20 (e) the capability to indicate the same reading again and again for a given measurand Newall system of limits and fits is the oldest system working on hole basis system. The grades of holes and shafts specified respectively are (a) 2, 6 (b) 1, 8 (c) 4, 12 (d) 6, 20 (e) 8, ISA tolerance system consists of following numbers of qualities of tolerance, and grades of fit respectively (a) 6, 15 (b) 8, 20 (c) 12, 21 (d) 16, 21 (e) 21, Expressing a dimension as 25.3* 05 mm is the case of (a) unilateral tolerance (b) bilateral tolerance (c) limiting dimensions (d) all of the above (e) none of the above Surface roughness on a drawing is represented by (a) triangles (b) circles (c) squares (d) rectangles (e) none of the above Expressing a dimension as 32.5/32.3 mm is the case of (a) unilateral tolerance (b) bilateral tolerance (c) limiting dimension
21 (d) all of the above (e) none of the above A bore of mm in a workpiece can be measured by (a) steel rule (b) vernier caliper (c) pneumatic gauge (d) micrometer (e) plug gauge The diameter of finish turned shaft can best be checked with a (a) combination set (b) slip gauge (c) height gauge (d) micrometer screw gauge (e) dial indicator Accurate centring of work mounted in an independent chuck can be determined by using a (a) centre gauge (b) height gauge (c) dial indicator (d) surface gauge (e) micrometer In limits and fits system, basic shaft system is one whose (a) lower deviation is zero (b) upper deviation is zero (c) minimum clearance is zero (d) maximum clearance is zero (e) standard tolerance is zero Which of the following is not the angle measuring device (a) angle plate (b) sine bar (c) bevel protector (d) angle gauge (e) combination square.
22 137. To check the diameter of a twist drill with a micrometer, the measurement must be taken across the (a) margins of the drill (b) flutes of the drill (c) cutting edges of the drill (d) lips of the drill (e) web of the drill Pick out the wrong statement about gauges for internal threads. (a) The Go screw plug gauge is made to the minimum metal limit and of full form and checks the virtual effective diameter. Any error in the pitch or flank angle of screw affects the effec-tive diameter (b) The minimum limit of the major diameter and maximum size of the effective diameter are also checked. (c) Not Go screw plug gauge is made to the maximum effective diameter of the screw thread cleared at the root and crest. (d) The plain Go and Not Go gauges are used for checking the limits of the size of minor diameter. (e) The dimensions of Go and Not Go gauges correspond to maximum and minimum minor diameters Expressing a dimension as 3^ o!o2 mm is the case of (a) unilateral tolerance (b) bilateral tolerance (c) limiting dimensions (d) all of the above (e) none of the above In instrumentation a correction is (a) an error (b) the revision applied to the indicated value so that the final result obtained improves the worth of the result (c) reading-error (d) range of error-degree of correctness (e) lowest value of input which does not indicate the result Many external comparators have anvils or work tables which are grooved. The purpose of this
23 is to (a) facilitate supporting of work. (b) provide three point support to the work (c) not to pass on inaccuracy of surface to the measurement (d) trap any dirt on the table so that it does not interfere with the measure ment (e) avoid sticking of standards on the table Straight edges are used to measure (a) straight length of parts (b) flatness (c) parallelism (d) perpendicularity (e) circularity IS : 919 on limits and fits specifies following numbers of grades of fundamental tolerances, and fundamental deviations respectively (a) 25, 18 (b) 25, 16 (c) 18, 22 (d) 18, 25 (e) 18, For general use the measuring tip of a comparator should be (a) flat (b) spherical (c) conical (d) concave (e) grooved Basic shaft and basic hole are those whose upper deviations and lower- deviation respectively are (a) + ve, - ve (b) - ve, 4- ve (c) minimum, minimum (d) minimum, maximum (e) zero, zero.
24 146. The standard tolerance unit is equal to (a) 0.45 (W) ID (b) 0.45 (W) ID (c) 0.45 (W) D (d) 0.45 (<D) + 0.0W (e) 0.45 (W). where D = geometric means of the lower and upper diameters of a particular diameter step Eden-Rolt comparator is a popular instrument for the (a) calibration of slip gauges (b) absolute measurement of length of slip gauges (c) measurement of flatness (d) measurement of angles (e) measurement of linear movement It is desirable to handle the slip gauges with a cloth or chamois leather in order to (a) avoid injury to hands (b) protect the surfaces of slip gauges (c) insulate them from the heat of die hand (d) ensure that the varnish applied on gauges does not come out (e) none of the above For grade IT 7, value of tolerance is equal to (a) 7 i (b) 10 i (c) 16 i (d) 25 i (e) 40 i For defining lengui die standard generally followed is (a) bar standard (b) end standard (c) light wave standard (d) any of the above (e) none of the above.
25 151. Planer gauge is used for (a) testing flatness of surface (b) adding to utility of measurements on surface plate (c) angular measurement (d) testing radius of corners (e) testing thickness of small gaps IS specifications specify vernier calipers as type A, B and C. This classification is based on (a) accuracy (b) least count (c) range (d) internal or external measurement and for marking purpose (e) type of graduations The cross-section of straight edges upto 180 mm lengui is (a) rectangular (b) circular (c) I-section (d) elliptical (e) L-shape Optical micrometer is used to (a) measure small linear displacements (b) measure surface profiles (c) measure surface roughness (d) set very small displacement by rotat-ing the glass block through relatively large angles (e) check parallelism Airy points of support are (a) L apart (b) L apart (c) 0.5 L apart (d) 0.58 L apart (e) L apart Where L = lengui of bar The maximum nurnber of faces in precision polygons can be
26 (a) 6 (b) 8 (c) 12 (d) 20 (e) In precision polygon, a central hole and small holes are drilled uirough die mickness (a) for mounting purposes (b) to achieve high accuracy (c) for ease of manufacture (d) to make them light (e) for decoration Precision polygons are calibrated from first principles using (a) one autocollimator (b) two autocollimators (c) uiree autocollimators (d) two precision spirit levels (e) angle gauges The fact mat how closely the instrument reading follows the measured variables is termed as (a) fidelity (b) accuracy (c) direshold sensitivity (d) precision (e) hysteresis Which of die following methods is not used for testing straightness (a) spirit level metiiod (b) autocollimator (c) interference method (d) beam comparator (e) laser beam Optical square is (a) Engineer's square having stock and blade set at 90 (b) a constant deviation prism having the angle of deviation between the inci-dent ray and reflected
27 ray, equal to 90 (c) a constant deviation prism having the angle of deviation between the inci-dent ray and reflected ray, equal to 45 (d) used to produce interference fringes (e) used for angular measurement In a sine bar the standard lengm is measured from (a) edge to edge (b) between inner circumference of two rollers (c) between outer circumference of two rollers (d) between the centres of two rollers (e) none of the above Electronic level instrument is a replacement for (a) vernier depth gauge (b) microscope (c) auto-collimator (d) angle dekkor (e) spirit level Polygons in metrology are concerned with (a) method of circular dividing (b) testing of parallelism (c) testing of circularity (d) interferrometry measurements (e) linear measurements The long straight edges are supported at two points for minimum deflection at centre. The distance between supports compared to the length of straight edge should be (a) 0.5 (b) (c) (d) 0.6 (e) Bevel protractor is used for (a) angular measurements
28 (b) linear measurements (c) height measurements (d) flatness measurement (e) parallelism measurement Clinometer is related with (a) Engineer's parallels (b) angle gauges (c) spirit level (d) bevel protractor (e) tolerance measurement Pick up the correct statement. A comparator (a) needs to be calibrated (b) need not be calibrated (c) contains a calibrated scale (d) is highly accurate over its complete measuring range (e) is best suited for measurement of ab-solute dimensions Which of the following is the essential condition for interferometry measurement (a) an air gap (a wedge) of varying thick-ness must exist between the two sur-faces (b) an optical flat is required (c) the work surface must be reflective (d) monochromatic source of light is re-quired (e) all of the above Autocollimator is used for (a) parallelism measurement (b) straightness measurement (c) flatness measurement (d) angular measurement (e) linear movement measurement Which one of the following is an angle measuring device (a) trammel (b) hermaphrodite caliper (c) divider
29 (d) (e) angle iron sine bar Filar microscopes (a) have no reticles (b) have fixed reticles (c) have moving reticles (d) can be.moved relative to the work by means of a fine-pitch lead screw (e) use a scale on the side of the optical tube to give a measure of the focusing position A collimator is simply a (a) source of a bundle of parallel light rays (b) source of point light (c) sort of alignment telescope (d) standard for flatness (e) device used in interferometric meas-urements If x be half the included angle of thread and p its pitch, then best size wire's diameter for measurement of effective diameter of thread is (a) p/2 sec x (b) p sec x/2 (c) p cos x/2 (d) p/2 cos x/2 (e) p/2 sec x/ Angle Dekkor is another type of (a) auto-collimator (b) optical square (c) clinometer (d) angle gauge (e) electronic level The angles of angle gauges in the degrees series are (a) 1, 3, 9, 25, 42 (b) 1, 3, 9, 27, 81 (c) 1, 3, 9, 27, 41
30 (d) 1, 5, 10, 25, 45 (e) 2, 3, 5, 27, Wickman gauge is used for inspection of (a) holes (b) shafts (c) gears (d) tapers (e) screw threads Which one of the following is not an angle measuring device (a) bevel protector (b) sine bar (c) combination square (d) angle iron (e) angle gauge blocks The reflector combined with autocollimator can be used for checking (a) alignment (b) parallelism (c) circularity (d) distance between two far off points (e) surface finish Some substances generate voltage when they are subjected to mechanical forces or stresses along specific planes. Such substances are known as (a) thermo-electric (b) magneto-electric (c) piezo-electric (d) photo-electric (e) radio-active Tomlinson recorder is associated with measurement of (a) surface flaws (b) surface perpendicularity (c) surface finish (d) surface curvature
31 (e) surface flatness Which of the following methods is not concerned with surface finish measurement (a) spectrophotometry method (b) ultrasonic method (c) field emission method (d) critical angle of attack method (e) Talysurf principle The only natural material producing a spectral line (6440 A red) almost completely symmetrical is (a) Cadmium (b) Mercury (c) Krypton (d) Helium (e) Neon A photo-electric device in which the resistance of the metal changes directly proportional to the light striking on it, is known as (a) photo-cell (b) photo-emission cell (c) photo-voltaic cell (d) photo conductive cell (e) none of the above Universal surface gauge is used for (a) checking straightness (b) checking flatness (c) checking parallelism (d) layout work and inspection (e) checking the surface finish According to Taylor's Principle, No Gog auge checks (a) only one feature at a time (b) only important dimensions at a time (c) all the dimensions at a time (d) only the related dimensions at a time
32 (e) as many dimensions as possible at a time The primary texture or roughness or micro-errors on surface results due to (a) normal action of the tool in produc tion process (b) vibrations and non-uniformity of cut-ting process (c) flaws in material (d) dominant direction of tool marks (lay) (e) all of the above* 196. The secondary texture or waviness, or macro-error on surface results due to (a) normal action of the tool in produc tion process (b) vibrations and non-uniformity of cut-ting process (c) flaws in material (d) dominant direction of tool marks (lay) (e) all of the above The function of a transducer is (a) to amplify the input signal (b) to modify the input signal (c) to convert the primary signal into a more useful quantity usually an electrical impulse (d) to codify the input signal (e) to decodify the input signal Pick up the correct statement in connection with surface finish. (a) Pitch of secondary texture is same as pitch of primary texture (b) Pitch of secondary texture is more than pitch of primary texture (c) Pitch of secondary texture is less than pitch of primary texture (d) Pitch of primary and secondary tex-ture can't have any relationship (e) Pitch of primary and secondary tex-tures is related mathematically If graduations on beam of a vernier gauge are marked at every 1/2 mm and 10 divisions on vernier scale are on a distance of 9.5 mm, then least count is (a) 0.1 mm (b) 0.05 mm (c) 0.01 mm (d) 0.02 mm (e) mm.
33 200. Scale sensitivity is defined as (a) Ratio of a change in scale reading to corresponding change in pointer deflection (b) Least reading of scale/range of scale (c) Least reading of scale/unit measurable quantity (d) Least count of scale/range of scale (e) none of the above A three-lobed part if checked on 60 V block would provide following magnification of the radial out-of-round characteristics (a) 1 time (b) 2 time (c) 3 time (d) 4 time (e) 5 time A five-lobed part, if gauged in the 60 V-block would produce the following magnification of the radial out-of-round characteristics (a) 0 time (b) 1 time (c) 2 times (d) 3 times (e) 5 times Diametral gauging for out-of-roundness measurement is not sufficient because (a) it can't sense even lobed parts (b) radial changes always occur which can't be sensed by it (c) it is difficult to find true centre (d) its readings can't be fed to computer (e) it provides measurement at 2 points only A plug gauge is used for measuring (a) cylinders (b) cylindrical bores (c) spherical holes (d) screw threads
34 (e) angles.
Unit III Introduction sine bar Sine bar Working principle of sine bar
 Unit III Introduction Angular measurement is an important element in measuring. It involves the measurement of angles of tapers and similar surfaces. In angular measurements, two types of angle measuring
Unit III Introduction Angular measurement is an important element in measuring. It involves the measurement of angles of tapers and similar surfaces. In angular measurements, two types of angle measuring
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
SIR C.R.REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ELURU
 SIR C.R.REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ELURU-534007 METROLOGY LABORATORY MANUAL III/IV B.TECH (Mechanical): II SEMESTER DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING METROLOGY
SIR C.R.REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ELURU-534007 METROLOGY LABORATORY MANUAL III/IV B.TECH (Mechanical): II SEMESTER DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING METROLOGY
LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS
 UNIT II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS UNIT-II 2. 1 CONTENTS 2.1 LINEAR MEASURING INSTRUMENTS 2.1.1 SCALES 2.1.2 CALIPERS 2.1.3 VERNIER CALIPERS 2.1.4 MICROMETERS 2.1.5 SLIP GAUGES 2.2 INTERFEROMETERS
UNIT II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS UNIT-II 2. 1 CONTENTS 2.1 LINEAR MEASURING INSTRUMENTS 2.1.1 SCALES 2.1.2 CALIPERS 2.1.3 VERNIER CALIPERS 2.1.4 MICROMETERS 2.1.5 SLIP GAUGES 2.2 INTERFEROMETERS
Introduction To Metrology
 Introduction To Metrology Meaning of Metrology Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology may be divided depending upon the quantity to be measured like metrology of length, metrology of time.
Introduction To Metrology Meaning of Metrology Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology may be divided depending upon the quantity to be measured like metrology of length, metrology of time.
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING. (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING III YEAR V SEMESTER ME6504 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING III YEAR V SEMESTER ME6504 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Sub Code/Name: ME 1304/Engineering Metrology & Measurements Year/Sem :III/ V UNIT-I
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1304/Engineering Metrology & Measurements Year/Sem :III/ V UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT Part- A (2 Marks) 1. Differentiate between
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1304/Engineering Metrology & Measurements Year/Sem :III/ V UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT Part- A (2 Marks) 1. Differentiate between
UNIT-II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS
 UNIT-II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS MEASUREMENT OF ENGINEERING COMPONENTS: v Measurement systems are mainly used in industries for quality control management. v Often quality control engineers are
UNIT-II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS MEASUREMENT OF ENGINEERING COMPONENTS: v Measurement systems are mainly used in industries for quality control management. v Often quality control engineers are
Read the following BEFORE getting started:
 BASIC MEASUREMENTS Read the following BEFORE getting started: Ruler: A ruler, or rule, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing and engineering/ building to measure distances and/or to rule
BASIC MEASUREMENTS Read the following BEFORE getting started: Ruler: A ruler, or rule, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing and engineering/ building to measure distances and/or to rule
Engineering Metrology and Instrumentation
 3 types Mechanical Cleaning Physically disturb contaminants Electrolytic Cleaning Abrasive bubbles aid in contaminant removal Chemical Cleaning Solution Saponification Emulsification Dispersion Aggregation
3 types Mechanical Cleaning Physically disturb contaminants Electrolytic Cleaning Abrasive bubbles aid in contaminant removal Chemical Cleaning Solution Saponification Emulsification Dispersion Aggregation
DISCONTINUED PRECISION MEASURING FOWLER CALIPERS 1 - VERNIER CALIPERS 4 - ELECTRONIC CALIPERS
 FOWLER CALIPERS 1 - VERNIER CALIPERS 4 - ELECTRONIC CALIPERS 52-058-016 Fine quality vernier calipers are constructed of stainless steel. 52-057-004 offers 3-way measurement to accuracy. 52-058-XXX series
FOWLER CALIPERS 1 - VERNIER CALIPERS 4 - ELECTRONIC CALIPERS 52-058-016 Fine quality vernier calipers are constructed of stainless steel. 52-057-004 offers 3-way measurement to accuracy. 52-058-XXX series
E.G.S. PILLAY ENGINEERING COLLEGE Nagapattinam DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING V SEMESTER REGULATION 2013 CHENNAI
 E.G.S. PILLAY ENGINEERING COLLEGE Nagapattinam 611002. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING V SEMESTER REGULATION 2013 CHENNAI ME 6513- METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS LAB LAB MANUAL Prepared & Compiled by
E.G.S. PILLAY ENGINEERING COLLEGE Nagapattinam 611002. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING V SEMESTER REGULATION 2013 CHENNAI ME 6513- METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS LAB LAB MANUAL Prepared & Compiled by
2 - Machining Fundamentals Measurement. Manufacturing Processes - 2, IE-352 Ahmed M El-Sherbeeny, PhD Spring-2015
 2 - Machining Fundamentals Measurement Manufacturing Processes - 2, IE-352 Ahmed M El-Sherbeeny, PhD Spring-2015 Learning Objectives Measure to 1/64 (.5 mm) with a steel rule Reading an Inch-based Vernier
2 - Machining Fundamentals Measurement Manufacturing Processes - 2, IE-352 Ahmed M El-Sherbeeny, PhD Spring-2015 Learning Objectives Measure to 1/64 (.5 mm) with a steel rule Reading an Inch-based Vernier
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere
 Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 32 Introduction To Comparators, Mechanical Comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:15) I welcome you
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 32 Introduction To Comparators, Mechanical Comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:15) I welcome you
TR CRITERIA FOR LABORATORY ACCREDITATION IN THE FIELD OF DIMENSIONAL METROLOGY
 CRITERIA FOR LABORATORY ACCREDITATION IN THE FIELD OF DIMENSIONAL METROLOGY Approved By: Chief Executive Officer: Ron Josias Executive: Accreditation: Mpho Phaloane Revised By: Specialist Technical Committee
CRITERIA FOR LABORATORY ACCREDITATION IN THE FIELD OF DIMENSIONAL METROLOGY Approved By: Chief Executive Officer: Ron Josias Executive: Accreditation: Mpho Phaloane Revised By: Specialist Technical Committee
Course: Technology II Training course topic: Metrology
 Department of machining, process planning and metrology ver.2017-01 Following problems and tasks will be solved during the first two weeks of the training courses of Technology II. Detailed information
Department of machining, process planning and metrology ver.2017-01 Following problems and tasks will be solved during the first two weeks of the training courses of Technology II. Detailed information
USS ProCoil Company. WELCOME To Micrometer Training. Introduction and Lecture Phase I 6/18/2010
 1 WELCOME To Micrometer Training Introduction and Lecture Phase I 2 Primary Instructor Charles J. Barger Secondary Instructor Fred Davis Today's training will be conducted in a four hour block of instruction,
1 WELCOME To Micrometer Training Introduction and Lecture Phase I 2 Primary Instructor Charles J. Barger Secondary Instructor Fred Davis Today's training will be conducted in a four hour block of instruction,
Physical Measurements
 PC1141 Physics I Physical Measurements 1 Objectives Demonstrate the specific knowledge gained by repeated physical measurements for the mass, length, inner and outer diameters of a hollow cylinder. Apply
PC1141 Physics I Physical Measurements 1 Objectives Demonstrate the specific knowledge gained by repeated physical measurements for the mass, length, inner and outer diameters of a hollow cylinder. Apply
Uncertainty Analysis of Experimental Data and Dimensional Measurements
 Uncertainty Analysis of Experimental Data and Dimensional Measurements Introduction The primary objective of this experiment is to introduce analysis of measurement uncertainty and experimental error.
Uncertainty Analysis of Experimental Data and Dimensional Measurements Introduction The primary objective of this experiment is to introduce analysis of measurement uncertainty and experimental error.
Wenzhou Tripod Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
 Wenzhou Tripod Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd. Website: http://aliyiqi.en.alibaba.com http://www.wzydyq.com/english/ Phone: 86-577-57572515 57572515 Fax: 86-577-57572516 57572516 E-mail: aliyiqi@gmail.com
Wenzhou Tripod Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd. Website: http://aliyiqi.en.alibaba.com http://www.wzydyq.com/english/ Phone: 86-577-57572515 57572515 Fax: 86-577-57572516 57572516 E-mail: aliyiqi@gmail.com
1 Measure various dimensions of component using Vernier caliper and dial type vernier caliper. d 3 d 1
 1 Measure various dimensions of component using Vernier caliper and dial type vernier caliper. 1. Note down the apparatus needed and draw component drawing and label parameters to measure. Vernier Caliper
1 Measure various dimensions of component using Vernier caliper and dial type vernier caliper. 1. Note down the apparatus needed and draw component drawing and label parameters to measure. Vernier Caliper
Tutorials. 1. Autocollimator. Angle Dekkor. General
 Tutorials 1. Autocollimator General An autocollimator is a Precise Optical Instrument for measurement of small angle deviations with very high sensitivity. Autocollimator is essentially an infinity telescope
Tutorials 1. Autocollimator General An autocollimator is a Precise Optical Instrument for measurement of small angle deviations with very high sensitivity. Autocollimator is essentially an infinity telescope
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Subject Title: MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17530 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Subject Title: MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17530 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Engineering Metrology
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Engineering Metrology Lecture 04: Angular Measurements Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Engineering Metrology Lecture 04: Angular Measurements Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department
TESA MICROMASTER Electronic Micrometers with Digital Display
 TESA MICROMASTER Electronic Micrometers with Digital Display DIN 86 T1 0,001 0.00005 in Metric/Inch conversion 100 : Ø 6,5 > 100 : Ø 8 With patented TESA capa µ system Measuring span of 0 or 25. Large
TESA MICROMASTER Electronic Micrometers with Digital Display DIN 86 T1 0,001 0.00005 in Metric/Inch conversion 100 : Ø 6,5 > 100 : Ø 8 With patented TESA capa µ system Measuring span of 0 or 25. Large
Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering
 Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6513 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS LABORATORY V SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6513 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS LABORATORY V SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering
 Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6513 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS LABORATORY V SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6513 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS LABORATORY V SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
Auto collimator. Introduction. Objectives: Apparatus: Theory:
 Auto collimator Introduction An autocollimator is an optical instrument that is used to measure small angles with very high sensitivity. As such, the autocollimator has a wide variety of applications including
Auto collimator Introduction An autocollimator is an optical instrument that is used to measure small angles with very high sensitivity. As such, the autocollimator has a wide variety of applications including
Metrology is science considering measurement
 Metrology is science considering measurement Categories: Scientific deals with organization and development of etalons and their conservation(highest level) Industrial deals with function of measuring
Metrology is science considering measurement Categories: Scientific deals with organization and development of etalons and their conservation(highest level) Industrial deals with function of measuring
ME6504 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS
 ME6504 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS Lecture by, M.E., Ph.D. Associate Professor/ Mechanical E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College, Nagapattinam SYLLABUS 06-Jul-18 2 UNIT I BASICS OF METROLOGY Introduction to
ME6504 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS Lecture by, M.E., Ph.D. Associate Professor/ Mechanical E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College, Nagapattinam SYLLABUS 06-Jul-18 2 UNIT I BASICS OF METROLOGY Introduction to
Measurement of basic constants: length, weight and time
 Measurement of basic constants: length, weight and time TEP Related topics Length, diameter, inside diameter thickness, curvature, vernier, weight resolution, time measurement. Principle Caliper gauges,
Measurement of basic constants: length, weight and time TEP Related topics Length, diameter, inside diameter thickness, curvature, vernier, weight resolution, time measurement. Principle Caliper gauges,
Mechanical Measurement & Metrology
 1 Mechanical Measurement & Metrology Course Contents 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Need Of Inspection 1.3 Objectives of Metrology 1.4 Precision And Accuracy 1.5 Errors in Measurement 1.6 General Care Of Metrological
1 Mechanical Measurement & Metrology Course Contents 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Need Of Inspection 1.3 Objectives of Metrology 1.4 Precision And Accuracy 1.5 Errors in Measurement 1.6 General Care Of Metrological
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere. Lecture 26 Measurement of Gear Elements
 Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 26 Measurement of Gear Elements (Refer Slide Time: 00:19) (Refer Slide Time: 00:28) I welcome
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 26 Measurement of Gear Elements (Refer Slide Time: 00:19) (Refer Slide Time: 00:28) I welcome
External Micrometers. C-1
 External Micrometers C-1 E X T E R N A L M I C R O M E T E R S PRECISION MEASUREMENT Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. In 1848, the first measuring tool of this type was patented by
External Micrometers C-1 E X T E R N A L M I C R O M E T E R S PRECISION MEASUREMENT Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. In 1848, the first measuring tool of this type was patented by
External Micrometers. C-1
 External Micrometers www.tesatechnology.com C-1 External Micrometers Precision Measurement Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. In 1848, the first measuring tool of this type was patented
External Micrometers www.tesatechnology.com C-1 External Micrometers Precision Measurement Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. In 1848, the first measuring tool of this type was patented
LAB 1 PRE-LAB. residuals (cm)
 LAB 1 PRE-LAB 1. The table below records measurements of the lengths l of five goldfish. Calculate the average length l avg of this population of goldfish, and the residual, or deviation from average length
LAB 1 PRE-LAB 1. The table below records measurements of the lengths l of five goldfish. Calculate the average length l avg of this population of goldfish, and the residual, or deviation from average length
ME3192 METROLOGY AND INSTRUMENTATION LABORATORY
 ME19 METROLOGY AND INSTRUMENTATION LABORATORY FORMAT FOR TABULAR COLUMNS - CYCLE 1 Batch 1 Expt 1 FIT BETWEEN NUT AND BOLTS Table 1: Order of specimens for different parameters Sl No Parameters Order 1
ME19 METROLOGY AND INSTRUMENTATION LABORATORY FORMAT FOR TABULAR COLUMNS - CYCLE 1 Batch 1 Expt 1 FIT BETWEEN NUT AND BOLTS Table 1: Order of specimens for different parameters Sl No Parameters Order 1
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Seminar report Autocollimator Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical
 A Seminar report On Autocollimator Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org Preface I
A Seminar report On Autocollimator Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org Preface I
Lesson of Mechanics and Machines done in the 5th A-M, by the teacher Pietro Calicchio. THE GEARS CYLINDRICAL STRAIGHT TEETH GEARS
 MESA PROJECT Lesson of Mechanics and Machines done in the 5th A-M, 2012-2013 by the teacher Pietro Calicchio. THE GEARS To transmit high power are usually used gear wheels. In this case, the transmission
MESA PROJECT Lesson of Mechanics and Machines done in the 5th A-M, 2012-2013 by the teacher Pietro Calicchio. THE GEARS To transmit high power are usually used gear wheels. In this case, the transmission
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 & ANSI/NCSL Z
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 & ANSI/NCSL Z540-1-1994 A.A. JANSSON Inc. 2070 Airport Road Waterford, MI 48327-1204 Justin Frazzini Phone: 248 674 4811 CALIBRATION Valid To: August 31, 2016
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 & ANSI/NCSL Z540-1-1994 A.A. JANSSON Inc. 2070 Airport Road Waterford, MI 48327-1204 Justin Frazzini Phone: 248 674 4811 CALIBRATION Valid To: August 31, 2016
External Micrometers. C-1
 External Micrometers C-1 E X T E R N A L M I C R O M E T E R S PRECISION MEASUREMENT Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. In 1848, the first measuring tool of this type was patented by
External Micrometers C-1 E X T E R N A L M I C R O M E T E R S PRECISION MEASUREMENT Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. In 1848, the first measuring tool of this type was patented by
Height Master Page 343. Check Master Page 347. Calibration Tools Page 352
 Calibration Instruments Height Master Page 343 Check Master Page 347 Calibration Tools Page 352 342 Digital Height Master Functions ZERO/ABS DATA/HOLD Auto Power OFF after 20 min. non use Low voltage alarm
Calibration Instruments Height Master Page 343 Check Master Page 347 Calibration Tools Page 352 342 Digital Height Master Functions ZERO/ABS DATA/HOLD Auto Power OFF after 20 min. non use Low voltage alarm
+ + = integer (13-15) πm. z 2 z 2 θ 1. Fig Constrained Gear System Fig Constrained Gear System Containing a Rack
 Figure 13-8 shows a constrained gear system in which a rack is meshed. The heavy line in Figure 13-8 corresponds to the belt in Figure 13-7. If the length of the belt cannot be evenly divided by circular
Figure 13-8 shows a constrained gear system in which a rack is meshed. The heavy line in Figure 13-8 corresponds to the belt in Figure 13-7. If the length of the belt cannot be evenly divided by circular
FLENDER drives Fundamental Principles of Mechanical Engineering
 FLENDER drives Fundamental Principles of Mechanical Engineering Technical Handbook Technical Drawings Standardization 2 Physics 3 Mathematics / Geometry 4 Mechanics / Strength of Materials 5 Hydraulics
FLENDER drives Fundamental Principles of Mechanical Engineering Technical Handbook Technical Drawings Standardization 2 Physics 3 Mathematics / Geometry 4 Mechanics / Strength of Materials 5 Hydraulics
FUNDAMENTALS OF DIMENSIONAL METROLOGY
 FUNDAMENTALS OF DIMENSIONAL METROLOGY CEJohansson Irvine, California SUB Gfittingen 7 215 940 806 Mesa Community College Mesa, Arizona CONTENTS ASUREMENT AND METROLOGY 1 1-1 Measurement as the Language
FUNDAMENTALS OF DIMENSIONAL METROLOGY CEJohansson Irvine, California SUB Gfittingen 7 215 940 806 Mesa Community College Mesa, Arizona CONTENTS ASUREMENT AND METROLOGY 1 1-1 Measurement as the Language
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
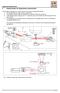 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
ACCREDITED CALIBRATION AND MEASUREMENT CAPABILITY SCOPE. Ring gaugeф(50~100)mm U=1.1 μm
 Name: Shanghai Institute of Quality Inspection and Technical Research Address: No.627, Yongjia Road, Shanghai, China Registration Accreditation Criteria: ISO/IEC 17025 and relevant requirements of CNAS
Name: Shanghai Institute of Quality Inspection and Technical Research Address: No.627, Yongjia Road, Shanghai, China Registration Accreditation Criteria: ISO/IEC 17025 and relevant requirements of CNAS
Inclined plane with protractor and pulley, roller, weight box, spring balance, spirit level, pan and thread.
 To find the downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a roller due to gravity and study its relationship with the angle of inclination by plotting graph between force and sin θ. Inclined plane
To find the downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a roller due to gravity and study its relationship with the angle of inclination by plotting graph between force and sin θ. Inclined plane
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
Introduction. Earlier. To Scales. We talked about. L Dimensions
 1 Introduction To Scales Introduction 2 Earlier We talked about Dimensions T Parts of the dimension object OExtension lines ODimension line OArrowheads ONumeric value T ocation of the numeric value Earlier
1 Introduction To Scales Introduction 2 Earlier We talked about Dimensions T Parts of the dimension object OExtension lines ODimension line OArrowheads ONumeric value T ocation of the numeric value Earlier
Measurement devices. Kalevi Aaltonen, Aalto University
 Measurement devices Kalevi Aaltonen, Aalto University Production engineering measurements, measuring uncertainty, measurement accuracy = statistical mathematical methods The pyramid of accuracy Material
Measurement devices Kalevi Aaltonen, Aalto University Production engineering measurements, measuring uncertainty, measurement accuracy = statistical mathematical methods The pyramid of accuracy Material
E x t e r n a l M i c r o m e t e r s
 External Micrometers B-1 Precision Measurement Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. The first measuring tool of this type was patented by the French inventor Jean Laurent Palmer in 1848
External Micrometers B-1 Precision Measurement Precision measurement requires the use of micrometers. The first measuring tool of this type was patented by the French inventor Jean Laurent Palmer in 1848
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 Table of Contents Page 1. Scope 2 2. Objective 2 3. Definitions 2 4. Responsibility 3 5. Procedure 4 6. Precautions 12 7. References 12 8. Appendices 13 9. Revision History 13 Original Authorised Copy
Table of Contents Page 1. Scope 2 2. Objective 2 3. Definitions 2 4. Responsibility 3 5. Procedure 4 6. Precautions 12 7. References 12 8. Appendices 13 9. Revision History 13 Original Authorised Copy
Lever-type Dial Test Indicators
 Lever-type Dial Test Indicators www.tesatechnology.com G-1 Lever-type Dial Test Indicators TESA IP65 Electronic Dial Test Indicators Provides the advantages of a mechanical test indicator with a digital
Lever-type Dial Test Indicators www.tesatechnology.com G-1 Lever-type Dial Test Indicators TESA IP65 Electronic Dial Test Indicators Provides the advantages of a mechanical test indicator with a digital
Lever-type Dial Test Indicators
 Lever-type Dial Test Indicators G-1 Lever-type Dial Test Indicators TESA IP65 Electronic Dial Test Indicators Provides the advantages of a mechanical test indicator with a digital reading. Inductive patented
Lever-type Dial Test Indicators G-1 Lever-type Dial Test Indicators TESA IP65 Electronic Dial Test Indicators Provides the advantages of a mechanical test indicator with a digital reading. Inductive patented
Using a Simple Pendulum plot L T and L T 2 graphs, hence find the effective length of second's pendulum using appropriate graph.
 LABORATORY MANUAL LABORATORY MANUAL Using a Simple Pendulum plot L T and L T 2 graphs, hence find the effective length of second's pendulum using appropriate graph. Clamp stand; a split cork; a heavy metallic
LABORATORY MANUAL LABORATORY MANUAL Using a Simple Pendulum plot L T and L T 2 graphs, hence find the effective length of second's pendulum using appropriate graph. Clamp stand; a split cork; a heavy metallic
NCERT. To make a paper scale of given least count: (a) 0.2 cm and (b) 0.5 cm
 ACTIVITIES 1 ACTIVITY AIM To make a paper scale of given least count: (a) 0.2 cm and (b) 0.5 cm APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Thick ivory/drawing sheet; white paper sheet; pencil; sharpener; eraser;
ACTIVITIES 1 ACTIVITY AIM To make a paper scale of given least count: (a) 0.2 cm and (b) 0.5 cm APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Thick ivory/drawing sheet; white paper sheet; pencil; sharpener; eraser;
Laboratory Manual Physics_1. Index of refraction for solids
 AGH University of Science and Technology in Cracow Department of Electronics Laboratory Manual Physics_ Title: 009 r. Index of refraction for solids Experiment No. 9 . Goal To determine the index of refraction
AGH University of Science and Technology in Cracow Department of Electronics Laboratory Manual Physics_ Title: 009 r. Index of refraction for solids Experiment No. 9 . Goal To determine the index of refraction
Refer to page E-6 for details. Refer to page E-31 for details. Digital Height Master. Refer to page E-35 for details. High Precision Square
 NewProducts Ultra Low xpansion Ceramic Gauge (ZRO CRA Block) Refer to page -6 for details. Gauge Block Comparator GBCD-00A Refer to page -3 for details. Digital Height Master Refer to page -35 for details.
NewProducts Ultra Low xpansion Ceramic Gauge (ZRO CRA Block) Refer to page -6 for details. Gauge Block Comparator GBCD-00A Refer to page -3 for details. Digital Height Master Refer to page -35 for details.
Errors in Measurement. ME 338: Manufacturing Processes II Instructor: Ramesh Singh; Notes: Profs. Singh/Melkote/Colton
 Errors in Measurement 1 Errors in Measurement Controllable Errors Environmental Conditions Elastic Deformation Due to Loading Alignment Errors Parallax Errors Non-Controllable Errors Scale Errors Reading
Errors in Measurement 1 Errors in Measurement Controllable Errors Environmental Conditions Elastic Deformation Due to Loading Alignment Errors Parallax Errors Non-Controllable Errors Scale Errors Reading
Automatic Level Maintenance Manual SAL-XX W/ AIR DAMPENED COMPENSATOR
 Automatic Level Maintenance Manual SAL-XX W/ AIR DAMPENED COMPENSATOR CST/Berger 2001 SAL 20/24/28/32 PAGE 1 REV. C 071803 Automatic Level Maintenance Manual User Calibration and Testing... 3 Circular
Automatic Level Maintenance Manual SAL-XX W/ AIR DAMPENED COMPENSATOR CST/Berger 2001 SAL 20/24/28/32 PAGE 1 REV. C 071803 Automatic Level Maintenance Manual User Calibration and Testing... 3 Circular
Journal bearing performance and metrology issues
 of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering VOLUME 3 ISSUE 1 January 009 Journal bearing performance and metrology issues S. Sharma a, *, D. Hargreaves b, W. Scott b a School of Engineering
of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering VOLUME 3 ISSUE 1 January 009 Journal bearing performance and metrology issues S. Sharma a, *, D. Hargreaves b, W. Scott b a School of Engineering
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14
 AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 and Guidelines Page 1 of 12 22 Table of Contents TUPURPOSE...UT2 TUWORK INSTRUCTION UT2 TU1 TU2 TU3 Introduction.2 Subject and Condition of Calibration...2 TU2.1UT TUSubject and Main Tools of Calibration...UT2
and Guidelines Page 1 of 12 22 Table of Contents TUPURPOSE...UT2 TUWORK INSTRUCTION UT2 TU1 TU2 TU3 Introduction.2 Subject and Condition of Calibration...2 TU2.1UT TUSubject and Main Tools of Calibration...UT2
ACCREDITED LABORATORY. INSPECTION MEASUREMENT COMPANY Wyoming, MI
 THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR LABORATORY ACCREDITATION ACCREDITED LABORATORY A2LA has accredited INSPECTION MEASUREMENT COMPANY Wyoming, MI for technical competence in the field of Calibration The accreditation
THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR LABORATORY ACCREDITATION ACCREDITED LABORATORY A2LA has accredited INSPECTION MEASUREMENT COMPANY Wyoming, MI for technical competence in the field of Calibration The accreditation
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING SURVEYING (CE 1305)
 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING SURVEYING (CE 1305) Linear Measurements Sr Dr. Tan Liat Choon Email: tanliatchoon@gmail.com Mobile: 016-4975551 1 EDM, TOTAL STATION, PRISM AND POLE 2 ELECTROMAGNETIC DISTANCE
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING SURVEYING (CE 1305) Linear Measurements Sr Dr. Tan Liat Choon Email: tanliatchoon@gmail.com Mobile: 016-4975551 1 EDM, TOTAL STATION, PRISM AND POLE 2 ELECTROMAGNETIC DISTANCE
PHYS 281 General Physics Laboratory
 King Abdul-Aziz University Faculty of Science Physics Department PHYS 281 General Physics Laboratory Student Name: ID Number: Introduction Advancement in science and engineering has emphasized the microscopic
King Abdul-Aziz University Faculty of Science Physics Department PHYS 281 General Physics Laboratory Student Name: ID Number: Introduction Advancement in science and engineering has emphasized the microscopic
For use with Comprehensive Secondary Physics
 For use with 139 For use with Physics Secondary Form Two Physics : Term One WEEK 1 Magnetic and nonmagnetic materials identify magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Observing attraction and repulsion of
For use with 139 For use with Physics Secondary Form Two Physics : Term One WEEK 1 Magnetic and nonmagnetic materials identify magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Observing attraction and repulsion of
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Hot objects should not be touched with bare hands - gloves should be used
 Live wires should not be touched. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Page 2 Hot objects should not be touched with bare hands - gloves should be used Circuit connections should be checked and approved by the teacher and
Live wires should not be touched. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Page 2 Hot objects should not be touched with bare hands - gloves should be used Circuit connections should be checked and approved by the teacher and
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra
 Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
Control Engineering BDA30703
 Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2017
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2017 FRANK COX METROLOGY (Formerly CANADIAN CENTRAL GAUGE LABORATORY) 40 West Drive Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T 3T6 Hilliard Cox Phone: 905 457 9190 CALIBRATION
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2017 FRANK COX METROLOGY (Formerly CANADIAN CENTRAL GAUGE LABORATORY) 40 West Drive Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T 3T6 Hilliard Cox Phone: 905 457 9190 CALIBRATION
Atomic emission spectra experiment
 Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
ROTARY CONTROLS. Rotary controls 1. GENERAL FEATURES 2. POSITION INDICATORS
 ROTARY CONTROLS 1. GENERAL FEATURES ELESA-CLAYTON rotary controls are used to set and regulating a wide variety of machine functions. The device consists of: - a handwheel/knob, to manoeuvre the control
ROTARY CONTROLS 1. GENERAL FEATURES ELESA-CLAYTON rotary controls are used to set and regulating a wide variety of machine functions. The device consists of: - a handwheel/knob, to manoeuvre the control
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 & ANSI/NCSL Z
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 & ANSI/NCSL Z540-1-1994 TRI-STATE INSTRUMENT SERVICE, INC. 3024 Wayne Trace Ft. Wayne, IN 46806 Lynn A. Stroble Phone: 260 456 4545 CALIBRATION Valid To: September
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 & ANSI/NCSL Z540-1-1994 TRI-STATE INSTRUMENT SERVICE, INC. 3024 Wayne Trace Ft. Wayne, IN 46806 Lynn A. Stroble Phone: 260 456 4545 CALIBRATION Valid To: September
Sliding Contact Bearings
 Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
THE SCREW GAUGE. AIM: To learn to use a Screw Gauge and hence use it to find the dimensions of various regular materials given.
 EXPERIMENT NO: DATE: / / 0 THE SCREW GAUGE AIM: To learn to use a Screw Gauge and hence use it to find the dimensions of various regular materials given. APPARUTUS: Given a Screw Gauge, cylindrical glass
EXPERIMENT NO: DATE: / / 0 THE SCREW GAUGE AIM: To learn to use a Screw Gauge and hence use it to find the dimensions of various regular materials given. APPARUTUS: Given a Screw Gauge, cylindrical glass
NEW STANDARD SEXTANT OF THE U. S. NAVY
 NEW STANDARD SEXTANT OF THE U. S. NAVY Director of the United States of America Hydrographic Office has sent to the International Hydrographic Bureau the following data relating to the new Standard Sextant
NEW STANDARD SEXTANT OF THE U. S. NAVY Director of the United States of America Hydrographic Office has sent to the International Hydrographic Bureau the following data relating to the new Standard Sextant
VERIFICATION OF TAPPING MACHINES. Håkan Andersson
 VERIFICATION OF TAPPING MACHINES Håkan Andersson SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute Acoustics Laboratory Box 57, SE-51 15 Borås, Sweden hakan.andersson@sp.se ABSTRACT Six tapping machines
VERIFICATION OF TAPPING MACHINES Håkan Andersson SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute Acoustics Laboratory Box 57, SE-51 15 Borås, Sweden hakan.andersson@sp.se ABSTRACT Six tapping machines
Introduction. Procedure. In this experiment, you'll use the interferometer to EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Lens 18mm FL. Component holder.
 12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating.
 12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
Leveling. 3.1 Definitions
 Leveling 3.1 Definitions Leveling is the procedure used to determine differences in elevation between points that are remote from each other. Elevation is a vertical distance above or below a reference
Leveling 3.1 Definitions Leveling is the procedure used to determine differences in elevation between points that are remote from each other. Elevation is a vertical distance above or below a reference
Classical Dynamics: Question Sheet
 Pt 1B Advanced Physics Lent 5 Classical Dynamics: Question Sheet J. Ellis Questions are graded A to C in increasing order of difficulty. Energy Method 1(B) A ladder of length l rests against a wall at
Pt 1B Advanced Physics Lent 5 Classical Dynamics: Question Sheet J. Ellis Questions are graded A to C in increasing order of difficulty. Energy Method 1(B) A ladder of length l rests against a wall at
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? 20cm T =? 20kg
 1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING
 CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
Volkswagen of America, Inc. Service Training Printed in U.S.A. Printed in 4/2001 Course Number Volkswagen of America, Inc.
 Volkswagen of America, Inc. Service Training Printed in U.S.A. Printed in 4/2001 Course Number 821003 2001 Volkswagen of America, Inc. All rights reserved. All information contained in this manual is based
Volkswagen of America, Inc. Service Training Printed in U.S.A. Printed in 4/2001 Course Number 821003 2001 Volkswagen of America, Inc. All rights reserved. All information contained in this manual is based
PH2200 Practice Final Exam Summer 2003
 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
Standard Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insulation 1
 Designation: D 374 99 An American National Standard Standard Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insulation 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 374; the number immediately
Designation: D 374 99 An American National Standard Standard Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insulation 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 374; the number immediately
UNIT 1 - STANDARDS AND THEIR MEASUREMENT: Units of Measurement: Base and derived units: Multiple and submultiples of the units: 1
 AS Physics 9702 unit 1: Standards and their Measurements 1 UNIT 1 - STANDARDS AND THEIR MEASUREMENT: This unit includes topic 1 and 2 from the CIE syllabus for AS course. Units of Measurement: Measuring
AS Physics 9702 unit 1: Standards and their Measurements 1 UNIT 1 - STANDARDS AND THEIR MEASUREMENT: This unit includes topic 1 and 2 from the CIE syllabus for AS course. Units of Measurement: Measuring
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 FRANK COX METROLOGY (Formerly CANADIAN CENTRAL GAUGE LABORATORY) 40 West Drive Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T 3T6 Hilliard Cox Phone: 905 457 9190 CALIBRATION
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 FRANK COX METROLOGY (Formerly CANADIAN CENTRAL GAUGE LABORATORY) 40 West Drive Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T 3T6 Hilliard Cox Phone: 905 457 9190 CALIBRATION
[ Extract from Astronomical Spectroscopy for Amateurs ] 18.0 Guiding, OAG and Beam splitters/ Flip mirrors Off Axis Guiders
![[ Extract from Astronomical Spectroscopy for Amateurs ] 18.0 Guiding, OAG and Beam splitters/ Flip mirrors Off Axis Guiders [ Extract from Astronomical Spectroscopy for Amateurs ] 18.0 Guiding, OAG and Beam splitters/ Flip mirrors Off Axis Guiders](/thumbs/82/85289082.jpg) [ Extract from Astronomical Spectroscopy for Amateurs ] 18.0 Guiding, OAG and Beam splitters/ Flip mirrors You ll quickly find it s a challenge to get a star focused on the spectroscope slit and hold it
[ Extract from Astronomical Spectroscopy for Amateurs ] 18.0 Guiding, OAG and Beam splitters/ Flip mirrors You ll quickly find it s a challenge to get a star focused on the spectroscope slit and hold it
No. Experiments Page No. 1 Use of Vernier Callipers 1. 2 Use of Micrometer screw gauge 5. 3 Use of Spherometer 9. 4 Parallelogram law of forces 12
 No. Experiments Page No. 1 Use of Vernier Callipers 1 2 Use of Micrometer screw gauge 5 3 Use of Spherometer 9 4 Parallelogram law of forces 12 5 Coefficient of static friction 15 6 Determination of Resistance
No. Experiments Page No. 1 Use of Vernier Callipers 1 2 Use of Micrometer screw gauge 5 3 Use of Spherometer 9 4 Parallelogram law of forces 12 5 Coefficient of static friction 15 6 Determination of Resistance
Q11: WHAT IS A MEANT GOOD ELECTRICAL CONNECTION?
 Q1. How to check for zero error in a: (i) Vernier caliper (ii) Micrometer screw gauge (iii) Meter rule (iv) Stopwatch Ans: (i) Close the jaws of the vernier caliper fully. When the zeros of both MAIN SCALE
Q1. How to check for zero error in a: (i) Vernier caliper (ii) Micrometer screw gauge (iii) Meter rule (iv) Stopwatch Ans: (i) Close the jaws of the vernier caliper fully. When the zeros of both MAIN SCALE
Service Information Letter SIL # 017
 Service Information Letter SIL # 017 Trunnion Adjustment - Double Barrels Only Equipment: Double Barrels With Sloped Trunnions Date Issued: 9-24-03 Additional Reference: SIL # 016 Revised: Revision #:
Service Information Letter SIL # 017 Trunnion Adjustment - Double Barrels Only Equipment: Double Barrels With Sloped Trunnions Date Issued: 9-24-03 Additional Reference: SIL # 016 Revised: Revision #:
Metal core drills the most cost-effective drilling experience.
 Metal core drilling Metal core drills the most cost-effective drilling experience. Core drilling is an extremely efficient process: faster, quieter and more accurate than twist drilling. And since core
Metal core drilling Metal core drills the most cost-effective drilling experience. Core drilling is an extremely efficient process: faster, quieter and more accurate than twist drilling. And since core
Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P )
 Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P2210300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Light and Optics Subtopic: Diffraction
Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P2210300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Light and Optics Subtopic: Diffraction
Operating Instructions Spectro-Goniometer Student. 1 Functional Elements. 2 Safety Precautions. Figure 1: Spectro-Goniometer Student
 Operating Instructions Spectro-Goniometer Student 1 Functional Elements Figure 1: Spectro-Goniometer Student 1. Adjustable entrance slit, holding screw for slit cover 2. Lock ring fixing entrance slit
Operating Instructions Spectro-Goniometer Student 1 Functional Elements Figure 1: Spectro-Goniometer Student 1. Adjustable entrance slit, holding screw for slit cover 2. Lock ring fixing entrance slit
Dr. Radhakrishnan A N Assistant Professor of Physics GPTC, Vechoochira
 CONTENTS. Vernier Calipers. Screw Gauge. Simple Pendulum 7. Moment Bar 9. Convex Lens Appendix Vernier Calipers Exp. No: Date: Aim (i) To nd the volume of the given cylinder by measuring its length and
CONTENTS. Vernier Calipers. Screw Gauge. Simple Pendulum 7. Moment Bar 9. Convex Lens Appendix Vernier Calipers Exp. No: Date: Aim (i) To nd the volume of the given cylinder by measuring its length and
