Craig-Gordon Evaporation and the Isotopic Composition of Leaf Water
|
|
|
- Marcus O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Craig-Gordon Evaporation and the Isotopic Composition of Leaf Water 1. Definitions All delta s are expressed as: (1) δ = R Multiply this delta by 10 3 to express it in per-mil units. Fractionation factors are expressed in the same way: (2) ε = α In the following equations it is assumed that the isotope ratio, R = N i, can be substituted for the N fractional abundance, F = N i N + N i. This assumption is justified when N i <<N, as is the case for 2 H- 1 H, or isotope differences are small, as is true for 18 O- 16 O (Sessions & Hayes, 2006). 2. Equilibrium Vapor-Liquid Fractionation Equilibrium fractionation is expressed as: (3) α * (T) = R L R V The vapor phase is depleted in heavy isotopes so values for α are greater than 1. Caution is necessary because this fractionation factor is sometimes defined as R V /R L and is thus less than 1. The superscript asterisk to the right of α is used to indicate an equilibrium isotopic fractionation (versus kinetic which gets a subscript K). 1
2 3. Craig-Gordon Evaporation 3.1. Assumptions In the Craig-Gordon evaporation model there is a diffusive sublayer above the water surface, above which is a turbulent sublayer and then the free atmosphere. At the base of the diffusive sublayer the air is saturated (relative humidity equals 1) and the water vapor is in isotopic equilibrium with the underlying liquid. This model is based upon the Langmuir linearresistance model for evaporation. The assumptions are (Gat, 1996): 1. equilibrium conditions at the air/water interface so that relative humidity h=1 and R V =α R L 2. a constant vertical flux, i.e. no divergence or convergence in the air column 3. no isotope fractionation during fully turbulent transport Figure 1 The Craig-Gordon evaporation model (drawn after Gat, 1996). 2
3 3.2. Evaporation Flux The flux equations for the abundant (E) and rare isotopes (E i ) of water are: (4a) (4b) ( E = C S C A ) ( E i = C SR S C A R A ) = C ( 1 h ) S ( ) i = C S R S hr A i where subscripts S and A refer to the saturated layer of water vapor immediately above the air/water surface and the free atmosphere respectively. Equations 4a and 4b describe the evaporation flux of water from the liquid to the atmosphere. The terms and i called resistance terms, and describe the rate that water isotopomers are transported from the saturated layer into the overlying free atmosphere (see section 4 on kinetic effects below). The isotopic ratio of the evaporating moisture, R E, is equal to the ratio the fluxes of the rare and abundant water isotopomers (E i /E). We can also define the isotopic ratio of water vapor in the saturated layer (R S ) in terms of the liquid water R S = R L / α. Dividing 4b by 4a and using this definition yields an equation for the isotopic composition of the evaporating moisture: (5) R E = E i E = i R L 1 h Defining the kinetic isotope effect (see section 4 on kinetic effects below) and solving for / i gives: (6a) = (1 h) i i = (1 h) +1= + (1 h) (1 h) (6b) 1 h = i + (1 h) Substituting Eq. 6b into Eq. 5 gives: 3
4 (7) R E = R L In δ units (δ=r-1), equation (7) becomes: ( ) α * h( δ A +1) δ E = δ L +1 δ E = δ L α * +1 α * hδ A h + h (8) δ E = δ L α * hδ A ε * α * 4. The Kinetic Isotope Factor The resistance terms, and i, are the sum of turbulent (T) and diffusive (M) resistances for the isotopomers of water: (9a) (9b) = M + T i = i,m + i,t These terms describe the rate that isotopomers are transported away from the saturated layer by diffusion and mixed into the free atmosphere by turbulent mixing (turbulent mixing can be described in a similar way to diffusion mixing, but the effective diffusivities are much higher). The term ( i /) 1 in eq. 6a can be evaluated from these equations as (Gat, 1996): i = i,m + i,t M + T = i,m M + T + i,t M + T i = i,m M M + i,t T T i = i,m M M + i,t T + M T T = i,m M M M + i,t T T T 4
5 (10a) i = M i,m M + T i,t T It is assumed that turbulent transport is non-fractionation, therefore i,t = T and Eq. 10a becomes: (10b) i = M i,m M and the kinetic isotope factor (Eq. 6a) becomes: (11) = (1 h) M i,m M For a fully developed diffusion layer, M is proportional to D -1 M, where D M is the molecular diffusivity of water in air. For a rough interface under strong wind conditions, the transient eddy model of Brutsaert (1965) can be applied with M proportional to D -1/2 M. At moderate wind -2/3-1/2 speeds a transition from the proportionality of D M to D M can be expected (Merlivat & Contiac, 1975). The ratio of the diffusivities in air of H 18 2 O/ H 16 2 O and 1 HDO/ 1 H 2 O have been experimentally determined by Merlivat (1978) as and respectively (Merlivat, 1978). (Note that especially for 1 HDO/ 1 H 2 O, this term differs from that calculated by the kinetic theory of gases.) Defining C D as: (12) C D = D M D i,m, re-writing i,m / M 1 from Eq. 11 in terms of diffusivities and substituting Eq. 12 gives: (13a) i,m M = ( D i,m ) q D M ( ) q = D i,m D M q This can be rewritten as: 5
6 (13b) i,m M = nc D with n defined as: (14) n = D i,m D M q D i,m D M Values for n depend upon the diffusion exponent and are ~0.5 for turbulent conditions (q = 1/2), ~0.66 for moderate windspeeds (q = 2/3) and 1 for a fully developed diffusion layer (q = 1). The ratio of diffusive to total transport ( M /) in Eq. 11 can be defined in terms of the relative humidity of the free atmosphere (h) and that of the boundary between the turbulent and diffusive transport layers (h ): (15) θ = M ( 1 h' ) = 1 h For small lakes whose evaporation does not affect the free atmosphere, θ is equal to 1, while for large lakes and the ocean a value 0.5<θ<1 is appropriate. Equations 13b and 15 can be substituted into Eq. 11 to define the kinetic isotope term: (16) = (1 h)θnc D 5. Enrichment of Leaf Water from Transpiration A simple model for the evaporative enrichment of leaf water uses Craig-Gordon evaporation to describe the isotopic composition of liquid water and water vapor at the site of evaporation. At steady state, the isotopic composition of water evaporating from a leaf must equal that of water flowing into the leaf from the xylem. This model calculates an enriched leafwater pool (EL), presumably at the water/vapor boundary. The bulk leaf water (BLW) consists of a mixture of this enriched pool and an unaltered pool of xylem (X) water: (17) R BLW = f l R EL + (1 f l ) 6
7 where f l is the fraction of enriched leaf water. Defining the kinetic fractionation factor (α K ) as: (18) α K = D i,m D M q where q is identical to Eq. 13. From Eq. 11 and 15, and noting that θ=1 for leaf evaporation (Eq. 15), the kinetic enrichment for leaf evaporation (ε K ) can be written in terms of α K as: (19) = (1 h)θ( α K ) = (1 h) ( α K ) Starting from the Craig-Gordon equation for evaporating moisture (Eq. 7), substituting α K for (Eq. 24) and noting that at steady state, the isotopic composition of evaporating water must equal that of the incoming xylem water ( =R E ): = R EL ε K R = EL (1 h) α K ( ) = R EL 1 h ( 1 h)α K = R EL (20) R EL = α * [( 1 h)α K + hr A ] Using rather than α K gives: (20a) R EL = α * [ ( ε K ) + hr A ] In delta notation, this becomes: (20b) δ EL +1= α * ( 1 h)α K δ X +1 ( )α K [ ( ) + h( δ A +1) ] Pratigya Polissar Aug.,
Oxygen and Hydrogen in Plants
 Oxygen and Hydrogen in Plants Outline: Environmental factors Fractionation associated with uptake of water Metabolic Fractionation C3, CAM and C4 plants Environmental factors Regional Precipitation d 18
Oxygen and Hydrogen in Plants Outline: Environmental factors Fractionation associated with uptake of water Metabolic Fractionation C3, CAM and C4 plants Environmental factors Regional Precipitation d 18
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND MODELS
 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
Stable Water Isotopes in the Atmosphere
 Stable Water Isotopes in the Atmosphere Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Overview 1. Stable water isotopes (SWI) illustrate the tightly coupled nature of the earth system, and are useful tools
Stable Water Isotopes in the Atmosphere Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Overview 1. Stable water isotopes (SWI) illustrate the tightly coupled nature of the earth system, and are useful tools
Data Analysis and Modeling with Stable Isotope Ratios. Chun-Ta Lai San Diego State University June 2008
 Data Analysis and Modeling with Stable Isotope Ratios Chun-Ta Lai San Diego State University June 2008 Leaf water is 18 O-enriched via transpiration δ 18 O vapor : -12 H 2 16 O H 2 18 O δ 18 O leaf : +8
Data Analysis and Modeling with Stable Isotope Ratios Chun-Ta Lai San Diego State University June 2008 Leaf water is 18 O-enriched via transpiration δ 18 O vapor : -12 H 2 16 O H 2 18 O δ 18 O leaf : +8
Atm S 547 Boundary Layer Meteorology
 Lecture 5. The logarithmic sublayer and surface roughness In this lecture Similarity theory for the logarithmic sublayer. Characterization of different land and water surfaces for surface flux parameterization
Lecture 5. The logarithmic sublayer and surface roughness In this lecture Similarity theory for the logarithmic sublayer. Characterization of different land and water surfaces for surface flux parameterization
Diffusivity fractionations of H 2 16 O/H 2 17 O and H 2 16 O/ H 2 18 O in air and their implications for isotope hydrology y
 RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007; 21: 2999 3005 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).3180 Diffusivity fractionations of H 2 16
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007; 21: 2999 3005 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).3180 Diffusivity fractionations of H 2 16
Why 17 O-excess? (And, what is it?)
 Why 17 O-excess? (And, what is it?) Advances in cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) have enabled scientists around the world to make quick, easy and highly precise measurements of the stable isotopes
Why 17 O-excess? (And, what is it?) Advances in cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) have enabled scientists around the world to make quick, easy and highly precise measurements of the stable isotopes
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Contents. 1. Evaporation
 Contents 1 Evaporation 1 1a Evaporation from Wet Surfaces................... 1 1b Evaporation from Wet Surfaces in the absence of Advection... 4 1c Bowen Ratio Method........................ 4 1d Potential
Contents 1 Evaporation 1 1a Evaporation from Wet Surfaces................... 1 1b Evaporation from Wet Surfaces in the absence of Advection... 4 1c Bowen Ratio Method........................ 4 1d Potential
EVAPORATION GEOG 405. Tom Giambelluca
 EVAPORATION GEOG 405 Tom Giambelluca 1 Evaporation The change of phase of water from liquid to gas; the net vertical transport of water vapor from the surface to the atmosphere. 2 Definitions Evaporation:
EVAPORATION GEOG 405 Tom Giambelluca 1 Evaporation The change of phase of water from liquid to gas; the net vertical transport of water vapor from the surface to the atmosphere. 2 Definitions Evaporation:
Needs work : define boundary conditions and fluxes before, change slides Useful definitions and conservation equations
 Needs work : define boundary conditions and fluxes before, change slides 1-2-3 Useful definitions and conservation equations Turbulent Kinetic energy The fluxes are crucial to define our boundary conditions,
Needs work : define boundary conditions and fluxes before, change slides 1-2-3 Useful definitions and conservation equations Turbulent Kinetic energy The fluxes are crucial to define our boundary conditions,
Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration
 Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration I. Vegetation canopy interception (I c ): Portion of incident precipitation (P) physically intercepted, stored and ultimately evaporated from vegetation
Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration I. Vegetation canopy interception (I c ): Portion of incident precipitation (P) physically intercepted, stored and ultimately evaporated from vegetation
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
OXYGEN AND HYDROGEN ISOTOPES IN THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996. 24:225 62 Copyright c 1996 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved OXYGEN AND HYDROGEN ISOTOPES IN THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE J. R. Gat Department of Environmental Sciences
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996. 24:225 62 Copyright c 1996 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved OXYGEN AND HYDROGEN ISOTOPES IN THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE J. R. Gat Department of Environmental Sciences
Evapotranspiration. Here, liquid water on surfaces or in the very thin surface layer of the soil that evaporates directly to the atmosphere
 Evapotranspiration Evaporation (E): In general, the change of state from liquid to gas Here, liquid water on surfaces or in the very thin surface layer of the soil that evaporates directly to the atmosphere
Evapotranspiration Evaporation (E): In general, the change of state from liquid to gas Here, liquid water on surfaces or in the very thin surface layer of the soil that evaporates directly to the atmosphere
Mass Transfer Operations-I Prof. Bishnupada Mandal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Mass Transfer Operations-I Prof. Bishnupada Mandal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Mass Transfer Coefficients Lecture - 1 Concept of Mass Transfer
Mass Transfer Operations-I Prof. Bishnupada Mandal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Mass Transfer Coefficients Lecture - 1 Concept of Mass Transfer
Stable Isotopes OUTLINE
 Stable Isotopes OUTLINE Reading: White Ch 9.1 to 9.7.1 (or digital p370-400) Exercise answer? What does the salt do? Today 1. 2 leftovers 2. Stable Isotopes for hydrologic and climate applications 1 CaCO
Stable Isotopes OUTLINE Reading: White Ch 9.1 to 9.7.1 (or digital p370-400) Exercise answer? What does the salt do? Today 1. 2 leftovers 2. Stable Isotopes for hydrologic and climate applications 1 CaCO
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
Evapotranspiration: Theory and Applications
 Evapotranspiration: Theory and Applications Lu Zhang ( 张橹 ) CSIRO Land and Water Evaporation: part of our everyday life Evapotranspiration Global Land: P = 800 mm Q = 315 mm E = 485 mm Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration: Theory and Applications Lu Zhang ( 张橹 ) CSIRO Land and Water Evaporation: part of our everyday life Evapotranspiration Global Land: P = 800 mm Q = 315 mm E = 485 mm Evapotranspiration
2σ e s (r,t) = e s (T)exp( rr v ρ l T ) = exp( ) 2σ R v ρ l Tln(e/e s (T)) e s (f H2 O,r,T) = f H2 O
 Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
 Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Estimating Evaporation : Principles, Assumptions and Myths. Raoul J. Granger, NWRI
 Estimating Evaporation : Principles, Assumptions and Myths Raoul J. Granger, NWRI Evaporation So what is it anyways? Evaporation is the phenomenon by which a substance is converted from the liquid or solid
Estimating Evaporation : Principles, Assumptions and Myths Raoul J. Granger, NWRI Evaporation So what is it anyways? Evaporation is the phenomenon by which a substance is converted from the liquid or solid
Kinetic 17 O effects in the hydrologic cycle: Indirect evidence and implications
 Pergamon doi:10.1016/j.gca.2004.02.010 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 68, No. 17, pp. 3487 3495, 2004 Copyright 2004 Elsevier Ltd Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0016-7037/04 $30.00.00 Kinetic
Pergamon doi:10.1016/j.gca.2004.02.010 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 68, No. 17, pp. 3487 3495, 2004 Copyright 2004 Elsevier Ltd Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0016-7037/04 $30.00.00 Kinetic
1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology... 2
 Contents 1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology............................ 2 2 Equation of State 2 2a Mean and Turbulent Parts...................... 3 2b Reynolds Averaging.........................
Contents 1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology............................ 2 2 Equation of State 2 2a Mean and Turbulent Parts...................... 3 2b Reynolds Averaging.........................
Clumped isotopes of atmospheric trace gases
 Clumped isotopes of atmospheric trace gases Thomas Röckmann Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU) Utrecht University, The Netherlands Thanks to: Magdalena Hofmann, Dipayan Paul,
Clumped isotopes of atmospheric trace gases Thomas Röckmann Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU) Utrecht University, The Netherlands Thanks to: Magdalena Hofmann, Dipayan Paul,
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
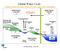 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Modeling the Drying Process of Thin Coatings
 Modeling the Drying Process of Thin Coatings Leonid V. Nikolaychik, TNN Technology, Inc., Milwaukee, WI Abstract There are few computer programs available on the market today for predicting dryer performance
Modeling the Drying Process of Thin Coatings Leonid V. Nikolaychik, TNN Technology, Inc., Milwaukee, WI Abstract There are few computer programs available on the market today for predicting dryer performance
Analysis Methods in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science
 Analysis Methods in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science AOSC 652 Ordinary Differential Equations Week 12, Day 1 1 Differential Equations are central to Atmospheric and Ocean Sciences They provide quantitative
Analysis Methods in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science AOSC 652 Ordinary Differential Equations Week 12, Day 1 1 Differential Equations are central to Atmospheric and Ocean Sciences They provide quantitative
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 104, NO. D15, PAGES 18,619-18,630, AUGUST 20, 1999
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 104, NO. D15, PAGES 18,619-18,630, AUGUST 20, 1999 An advective-diffusive model isotopic evaporation-condensation Hui He I and Ronald B. Smith Department of Geology
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 104, NO. D15, PAGES 18,619-18,630, AUGUST 20, 1999 An advective-diffusive model isotopic evaporation-condensation Hui He I and Ronald B. Smith Department of Geology
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 12
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 12 Next Topic Convective Heat Transfer» Heat and Mass Transfer Analogy» Evaporative Cooling» Types of Flows Heat and Mass Transfer Analogy Equations governing
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 12 Next Topic Convective Heat Transfer» Heat and Mass Transfer Analogy» Evaporative Cooling» Types of Flows Heat and Mass Transfer Analogy Equations governing
Lecture 5. Introduction to Stable Isotopes
 Lecture 5 Introduction to Stable Isotopes Stable Isotope Geochemistry Primarily concerned with the isotope ratios of H, C, N, O, and S Si and B often included and new instrumentation has opened up others
Lecture 5 Introduction to Stable Isotopes Stable Isotope Geochemistry Primarily concerned with the isotope ratios of H, C, N, O, and S Si and B often included and new instrumentation has opened up others
Oxygen & Hydrogen: Ideal, double isotopic tracer system 18
 NATURAL WATERS xygen & ydrogen: Ideal, double isotopic tracer system 18, D, T Conservative tracers Intrinsic to the molecule δd vs. δ 18 plot Utility to ydrology: rigin and Age of Water Tracing of Water,
NATURAL WATERS xygen & ydrogen: Ideal, double isotopic tracer system 18, D, T Conservative tracers Intrinsic to the molecule δd vs. δ 18 plot Utility to ydrology: rigin and Age of Water Tracing of Water,
The use of stable isotopes to study ecosystem gas exchange
 Oecologia (2000) 123: 297 311 Springer-Verlag 2000 Dan Yakir Leonel da Silveira Lobo Sternberg The use of stable isotopes to study ecosystem gas exchange Received: 8 July 1999 / Accepted: 10 January 2000
Oecologia (2000) 123: 297 311 Springer-Verlag 2000 Dan Yakir Leonel da Silveira Lobo Sternberg The use of stable isotopes to study ecosystem gas exchange Received: 8 July 1999 / Accepted: 10 January 2000
Properties of Vapors
 Properties of Vapors Topics for Discussion The Pressure/Temperature Relationship Vaporization Condensation Enthalpy Properties of Vapors Topics for Discussion Entropy Properties of Substances Saturated
Properties of Vapors Topics for Discussion The Pressure/Temperature Relationship Vaporization Condensation Enthalpy Properties of Vapors Topics for Discussion Entropy Properties of Substances Saturated
Introduction to Isotopic Fractionation Reading: Fritz and Clark, Chapter 1, excluding parts on radionuclides
 Introduction to Isotopic Fractionation Reading: Fritz and Clark, Chapter 1, excluding parts on radionuclides Other resources for more information: Tom Johnson s Isotope Geochem Class Notes: http://classes.geology.illinois.edu/12fallclass/geo562/notes.html
Introduction to Isotopic Fractionation Reading: Fritz and Clark, Chapter 1, excluding parts on radionuclides Other resources for more information: Tom Johnson s Isotope Geochem Class Notes: http://classes.geology.illinois.edu/12fallclass/geo562/notes.html
This is the first of several lectures on flux measurements. We will start with the simplest and earliest method, flux gradient or K theory techniques
 This is the first of several lectures on flux measurements. We will start with the simplest and earliest method, flux gradient or K theory techniques 1 Fluxes, or technically flux densities, are the number
This is the first of several lectures on flux measurements. We will start with the simplest and earliest method, flux gradient or K theory techniques 1 Fluxes, or technically flux densities, are the number
Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model
 Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model The energy balance for the greenhouse was obtained by applying energy conservation to the greenhouse system as a control volume and identifying the energy terms.
Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model The energy balance for the greenhouse was obtained by applying energy conservation to the greenhouse system as a control volume and identifying the energy terms.
Atmospheric Processes
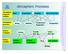 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Stable isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen in the Truckee River-Pyramid Lake surface-water system, 2. A predictive model of a1 *O and cy~h in Pyramid Lake
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(2), 1994, 356-364 0 1994, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Stable isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen in the Truckee River-Pyramid Lake surface-water system,
Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(2), 1994, 356-364 0 1994, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Stable isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen in the Truckee River-Pyramid Lake surface-water system,
Summary of Gas Laws V T. Boyle s Law (T and n constant) Charles Law (p and n constant) Combined Gas Law (n constant) 1 =
 Summary of Gas Laws Boyle s Law (T and n constant) p 1 V 1 = p 2 V 2 Charles Law (p and n constant) V 1 = T 1 V T 2 2 Combined Gas Law (n constant) pv 1 T 1 1 = pv 2 T 2 2 1 Ideal Gas Equation pv = nrt
Summary of Gas Laws Boyle s Law (T and n constant) p 1 V 1 = p 2 V 2 Charles Law (p and n constant) V 1 = T 1 V T 2 2 Combined Gas Law (n constant) pv 1 T 1 1 = pv 2 T 2 2 1 Ideal Gas Equation pv = nrt
2. Irrigation. Key words: right amount at right time What if it s too little too late? Too much too often?
 2. Irrigation Key words: right amount at right time What if it s too little too late? 2-1 Too much too often? To determine the timing and amount of irrigation, we need to calculate soil water balance.
2. Irrigation Key words: right amount at right time What if it s too little too late? 2-1 Too much too often? To determine the timing and amount of irrigation, we need to calculate soil water balance.
( ) = 1005 J kg 1 K 1 ;
 Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Eddy viscosity. AdOc 4060/5060 Spring 2013 Chris Jenkins. Turbulence (video 1hr):
 AdOc 4060/5060 Spring 2013 Chris Jenkins Eddy viscosity Turbulence (video 1hr): http://cosee.umaine.edu/programs/webinars/turbulence/?cfid=8452711&cftoken=36780601 Part B Surface wind stress Wind stress
AdOc 4060/5060 Spring 2013 Chris Jenkins Eddy viscosity Turbulence (video 1hr): http://cosee.umaine.edu/programs/webinars/turbulence/?cfid=8452711&cftoken=36780601 Part B Surface wind stress Wind stress
Influence of condensate evaporation on water vapor and its stable isotopes in a GCM
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12804, doi:10.1029/2009gl038091, 2009 Influence of condensate evaporation on water vapor and its stable isotopes in a GCM Jonathon S.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12804, doi:10.1029/2009gl038091, 2009 Influence of condensate evaporation on water vapor and its stable isotopes in a GCM Jonathon S.
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2)
 Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Part I.
 Part I bblee@unimp . Introduction to Mass Transfer and Diffusion 2. Molecular Diffusion in Gasses 3. Molecular Diffusion in Liquids Part I 4. Molecular Diffusion in Biological Solutions and Gels 5. Molecular
Part I bblee@unimp . Introduction to Mass Transfer and Diffusion 2. Molecular Diffusion in Gasses 3. Molecular Diffusion in Liquids Part I 4. Molecular Diffusion in Biological Solutions and Gels 5. Molecular
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Lecture 6 Asymptotic Structure for Four-Step Premixed Stoichiometric Methane Flames
 Lecture 6 Asymptotic Structure for Four-Step Premixed Stoichiometric Methane Flames 6.-1 Previous lecture: Asymptotic description of premixed flames based on an assumed one-step reaction. basic understanding
Lecture 6 Asymptotic Structure for Four-Step Premixed Stoichiometric Methane Flames 6.-1 Previous lecture: Asymptotic description of premixed flames based on an assumed one-step reaction. basic understanding
A brief summary of isotopes and fractionation
 A brief summary of isotopes and fractionation 1. Isotopes are chemically identical, but mechanically different. 2. Different masses lead to different bond frequencies... ν = 1 2π κ µ Hooke's Law 3....which
A brief summary of isotopes and fractionation 1. Isotopes are chemically identical, but mechanically different. 2. Different masses lead to different bond frequencies... ν = 1 2π κ µ Hooke's Law 3....which
3 ABUNDANCE AND FRACTIONATION OF STABLE ISOTOPES
 3 BUNDNCE ND FRCTIONTION OF STBLE ISOTOPES In classical chemistry isotopes of an element are regarded as having equal chemical properties. In reality variations in isotopic abundances occur far exceeding
3 BUNDNCE ND FRCTIONTION OF STBLE ISOTOPES In classical chemistry isotopes of an element are regarded as having equal chemical properties. In reality variations in isotopic abundances occur far exceeding
More on Diabatic Processes
 More on Diabatic Processes Chapter 3 Write Qtotal = Qrad + Qcond + Qsen total heating radiative heating condensationa l heating sensible heating While diabatic processes drive atmospheric motions, the
More on Diabatic Processes Chapter 3 Write Qtotal = Qrad + Qcond + Qsen total heating radiative heating condensationa l heating sensible heating While diabatic processes drive atmospheric motions, the
PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION
 Tue 8:54:24 AM Slide Nr. 0 of 33 Slides PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION Heat transfer through a fluid is by convection in the presence of bulk fluid motion and by conduction in the absence of it. Chapter
Tue 8:54:24 AM Slide Nr. 0 of 33 Slides PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION Heat transfer through a fluid is by convection in the presence of bulk fluid motion and by conduction in the absence of it. Chapter
Chapter 7. Water and Atmospheric Moisture. Water on Earth Unique Properties of Water Humidity Atmospheric Stability Clouds and Fog
 Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Photosynthesis. Water is one of the raw materials needed for photosynthesis When water is in short supply the rate of photosynthesis is limited
 Photosynthesis Water is one of the raw materials needed for photosynthesis When water is in short supply the rate of photosynthesis is limited Support Water is needed to ensure plant cells remain turgid
Photosynthesis Water is one of the raw materials needed for photosynthesis When water is in short supply the rate of photosynthesis is limited Support Water is needed to ensure plant cells remain turgid
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003
 GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
Mass Transfer Fundamentals. Chapter#3
 Mass Transfer Fundamentals Chapter#3 Mass Transfer Co-efficient Types of Mass Transfer Co-efficient Convective mass transfer can occur in a gas or liquid medium. Different types of mass transfer coefficients
Mass Transfer Fundamentals Chapter#3 Mass Transfer Co-efficient Types of Mass Transfer Co-efficient Convective mass transfer can occur in a gas or liquid medium. Different types of mass transfer coefficients
Theory. Humidity h of an air-vapor mixture is defined as the mass ratio of water vapor and dry air,
 Theory Background In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special
Theory Background In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special
Interphase Mass Transfer see Handout. At equilibrium a species will distribute (or partition ) between two phases.
 Interphase Mass Transfer see Handout At equilibrium a species will distribute (or partition ) between two phases. Examples: 1. oxygen (species) will partition between air (gas phase) and water (liquid
Interphase Mass Transfer see Handout At equilibrium a species will distribute (or partition ) between two phases. Examples: 1. oxygen (species) will partition between air (gas phase) and water (liquid
C ONTENTS CHAPTER TWO HEAT CONDUCTION EQUATION 61 CHAPTER ONE BASICS OF HEAT TRANSFER 1 CHAPTER THREE STEADY HEAT CONDUCTION 127
 C ONTENTS Preface xviii Nomenclature xxvi CHAPTER ONE BASICS OF HEAT TRANSFER 1 1-1 Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer 2 Application Areas of Heat Transfer 3 Historical Background 3 1-2 Engineering Heat
C ONTENTS Preface xviii Nomenclature xxvi CHAPTER ONE BASICS OF HEAT TRANSFER 1 1-1 Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer 2 Application Areas of Heat Transfer 3 Historical Background 3 1-2 Engineering Heat
Mass Transfer Operations
 College of Engineering Tutorial # 1 Chemical Engineering Dept. 14/9/1428 1. Methane and helium gas mixture is contained in a tube at 101.32 k Pa pressure and 298 K. At one point the partial pressure methane
College of Engineering Tutorial # 1 Chemical Engineering Dept. 14/9/1428 1. Methane and helium gas mixture is contained in a tube at 101.32 k Pa pressure and 298 K. At one point the partial pressure methane
Name the surface winds that blow between 0 and 30. GEO 101, February 25, 2014 Monsoon Global circulation aloft El Niño Atmospheric water
 GEO 101, February 25, 2014 Monsoon Global circulation aloft El Niño Atmospheric water Name the surface winds that blow between 0 and 30 What is the atmospheric pressure at 0? What is the atmospheric pressure
GEO 101, February 25, 2014 Monsoon Global circulation aloft El Niño Atmospheric water Name the surface winds that blow between 0 and 30 What is the atmospheric pressure at 0? What is the atmospheric pressure
Develop a lumped parameter model of the following differential equation using Eulers, Huens, and the 4 th order Runga Kutta Method:
 Homework 2 Assigned: 2/1/2012 Due: 3/13/2012 Part 1. Comparison of Euler, Huen, and 4 th Order RK methods Develop a lumped parameter model of the following differential equation using Eulers, Huens, and
Homework 2 Assigned: 2/1/2012 Due: 3/13/2012 Part 1. Comparison of Euler, Huen, and 4 th Order RK methods Develop a lumped parameter model of the following differential equation using Eulers, Huens, and
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting
 Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. A.W. Date Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. A.W. Date Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 32 Stefan Flow Model We are now familiar with
Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. A.W. Date Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 32 Stefan Flow Model We are now familiar with
Stable Water Isotopes in CAM5: Current development and initial results
 Stable Water Isotopes in CAM5: Current development and initial results Jesse Nusbaumer (nusbaume@colorado.edu) David Noone, Mariana Vertenstein, Bette Otto- Bliesner, Esther Brady, Andrew Gettelman, and
Stable Water Isotopes in CAM5: Current development and initial results Jesse Nusbaumer (nusbaume@colorado.edu) David Noone, Mariana Vertenstein, Bette Otto- Bliesner, Esther Brady, Andrew Gettelman, and
Stable Isotope Tracers
 Stable Isotope Tracers OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 5 March 2015 Reading: Emerson and Hedges, Chapter 5, p.134-153 (c) 2015 David Ho and Frank Sansone Outline Stable Isotopes - Introduction & Notation
Stable Isotope Tracers OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 5 March 2015 Reading: Emerson and Hedges, Chapter 5, p.134-153 (c) 2015 David Ho and Frank Sansone Outline Stable Isotopes - Introduction & Notation
Coupled modelling of water isotopes in the GISS GCM
 IAEA: Feb 2004 Coupled modelling of water isotopes in the GISS GCM Gavin Schmidt NASA GISS and Center for Climate Systems Research, Columbia University Focus of GISS water isotope research Forward modelling
IAEA: Feb 2004 Coupled modelling of water isotopes in the GISS GCM Gavin Schmidt NASA GISS and Center for Climate Systems Research, Columbia University Focus of GISS water isotope research Forward modelling
Thermal / Solar. When air is warmed it... Rises. Solar Energy. Evaporation. Condensation Forms Clouds
 Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Multi-scale model for heat and mass transfer during rice drying
 Multi-scale model for heat and mass transfer during rice drying a Ramadan ElGamal a,b, Frederik Ronsse a, Jan G. Pieters a, * Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Department of Biosystems Engineering, Ghent
Multi-scale model for heat and mass transfer during rice drying a Ramadan ElGamal a,b, Frederik Ronsse a, Jan G. Pieters a, * Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Department of Biosystems Engineering, Ghent
Gas transfer rates If either phase concentration can not be predicted by Henry's law then there will be a transfer of mass across the interface until
 Gas transfer rates If either phase concentration can not be predicted by Henry's law then there will be a transfer of mass across the interface until equilibrium is reached. The mechanisms and rate expressions
Gas transfer rates If either phase concentration can not be predicted by Henry's law then there will be a transfer of mass across the interface until equilibrium is reached. The mechanisms and rate expressions
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics.
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
Geol. 656 Isotope Geochemistry
 STABLE ISOTOPE THEORY: KINETIC FRACTIONATION AND THE HYDROLOGIC SYSTEM KINETIC FRACTIONATION Kinetic effects are normally associated with fast, incomplete, or unidirectional processes like evaporation,
STABLE ISOTOPE THEORY: KINETIC FRACTIONATION AND THE HYDROLOGIC SYSTEM KINETIC FRACTIONATION Kinetic effects are normally associated with fast, incomplete, or unidirectional processes like evaporation,
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Weather. Describing Weather
 Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
Introduction Efficiency bounds Source dependence Saturation Shear Flows Conclusions STIRRING UP TROUBLE
 STIRRING UP TROUBLE Multi-scale mixing measures for steady scalar sources Charles Doering 1 Tiffany Shaw 2 Jean-Luc Thiffeault 3 Matthew Finn 3 John D. Gibbon 3 1 University of Michigan 2 University of
STIRRING UP TROUBLE Multi-scale mixing measures for steady scalar sources Charles Doering 1 Tiffany Shaw 2 Jean-Luc Thiffeault 3 Matthew Finn 3 John D. Gibbon 3 1 University of Michigan 2 University of
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Precipitation. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7
 Precipitation GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7 Last lecture! Atmospheric stability! Condensation! Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)! Types of clouds Precipitation! Why clouds don t fall! Terminal
Precipitation GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7 Last lecture! Atmospheric stability! Condensation! Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)! Types of clouds Precipitation! Why clouds don t fall! Terminal
Course , General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget
 Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget Water Vapor Distribution First let us look at the distribution of specific humidity, q. The
Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget Water Vapor Distribution First let us look at the distribution of specific humidity, q. The
WUFI Workshop at NTNU /SINTEF Fundamentals
 WUFI Workshop at NTNU /SINTEF 2008 Fundamentals Contents: From steady-state to transient Heat storage and -transport Moisture storage and -transport Calculation of coupled transport Model limitations 2
WUFI Workshop at NTNU /SINTEF 2008 Fundamentals Contents: From steady-state to transient Heat storage and -transport Moisture storage and -transport Calculation of coupled transport Model limitations 2
Liquid water is one of the
 Formanski 71 1/07/09 8:57 Page 71 V olume 5 - Number 7 - May 2009 (71-75) Abstract Liquid water is one of the agents responsible for damage of building materials. Therefore determination of its content
Formanski 71 1/07/09 8:57 Page 71 V olume 5 - Number 7 - May 2009 (71-75) Abstract Liquid water is one of the agents responsible for damage of building materials. Therefore determination of its content
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Evapotranspiration. Rabi H. Mohtar ABE 325
 Evapotranspiration Rabi H. Mohtar ABE 325 Introduction What is it? Factors affecting it? Why we need to estimate it? Latent heat of vaporization: Liquid gas o Energy needed o Cooling process Saturation
Evapotranspiration Rabi H. Mohtar ABE 325 Introduction What is it? Factors affecting it? Why we need to estimate it? Latent heat of vaporization: Liquid gas o Energy needed o Cooling process Saturation
CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 1 CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The objective of atmospheric chemistry is to understand the factors that control the concentrations of chemical species in the atmosphere. In this book
1 CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The objective of atmospheric chemistry is to understand the factors that control the concentrations of chemical species in the atmosphere. In this book
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Glaciology HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION
 HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS
 Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS Overview Introduction Important Concepts for Understanding water Movement through Vines Osmosis Water Potential Cell Expansion and the Acid Growth
Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS Overview Introduction Important Concepts for Understanding water Movement through Vines Osmosis Water Potential Cell Expansion and the Acid Growth
Phase Change: solid to liquid. Melting
 Phase Change: solid to liquid Melting Most solids shrink in size when frozen. What substance is an exception and actually expands? water Use the phase diagram below to answer the following question. What
Phase Change: solid to liquid Melting Most solids shrink in size when frozen. What substance is an exception and actually expands? water Use the phase diagram below to answer the following question. What
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Air parcel trajectory analysis of stable isotopes in water vapor in the eastern Mediterranean
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd009839, 2008 Air parcel trajectory analysis of stable isotopes in water vapor in the eastern Mediterranean Stephan Pfahl 1 and Heini Wernli
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd009839, 2008 Air parcel trajectory analysis of stable isotopes in water vapor in the eastern Mediterranean Stephan Pfahl 1 and Heini Wernli
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
Effects of Mild Water Stress and Diurnal Changes in Temperature and Humidity on the Stable Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Composition of Leaf Water in
 Plant Physiol. (1991) 97, 298-35 32-889/91 /97/298/8/$1./ Received for publication February 15, 1991 Accepted April 25, 1991 Effects of Mild Water Stress and Diurnal Changes in Temperature and Humidity
Plant Physiol. (1991) 97, 298-35 32-889/91 /97/298/8/$1./ Received for publication February 15, 1991 Accepted April 25, 1991 Effects of Mild Water Stress and Diurnal Changes in Temperature and Humidity
Variability of Evaporation from Lake Taihu and its Response to Climate Change. GAO Yaqi YNCenter Weekly Video Conference
 Variability of Evaporation from Lake Taihu and its Response to Climate Change GAO Yaqi YNCenter Weekly Video Conference 2017.05.05 Outline Background Data and Method Results Conclusion Background The evaporation
Variability of Evaporation from Lake Taihu and its Response to Climate Change GAO Yaqi YNCenter Weekly Video Conference 2017.05.05 Outline Background Data and Method Results Conclusion Background The evaporation
Streams. Water. Hydrologic Cycle. Geol 104: Streams
 Streams Why study streams? Running water is the most important geologic agent in erosion, transportation and deposition of sediments. Water The unique physical and chemical properties of water make it
Streams Why study streams? Running water is the most important geologic agent in erosion, transportation and deposition of sediments. Water The unique physical and chemical properties of water make it
Bulk Boundary-Layer Model
 Bulk Boundary-Layer Model David Randall Ball (1960) was the first to propose a model in which the interior of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) is well-mixed in the conservative variables, while the PBL
Bulk Boundary-Layer Model David Randall Ball (1960) was the first to propose a model in which the interior of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) is well-mixed in the conservative variables, while the PBL
Chapter 2 Mass Transfer Coefficient
 Chapter 2 Mass Transfer Coefficient 2.1 Introduction The analysis reported in the previous chapter allows to describe the concentration profile and the mass fluxes of components in a mixture by solving
Chapter 2 Mass Transfer Coefficient 2.1 Introduction The analysis reported in the previous chapter allows to describe the concentration profile and the mass fluxes of components in a mixture by solving
Modeling Deep-Bed Grain Drying Using COMSOL Multiphysics
 Modeling Deep-Bed Grain Drying Using COMSOL Multiphysics Ramadan ElGamal a,b, Frederik Ronsse a, Jan G. Pieters a, * a Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Department of Biosystems Engineering, Coupure Links
Modeling Deep-Bed Grain Drying Using COMSOL Multiphysics Ramadan ElGamal a,b, Frederik Ronsse a, Jan G. Pieters a, * a Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Department of Biosystems Engineering, Coupure Links
Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
