Errors in Nobel Prize for Physics (3) Conservation of Energy Leads to Probability Conservation of Parity, Momentum and so on
|
|
|
- Lawrence Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eos in Nobel ize fo hysics (3) Conseation of Enegy Leads to obability Conseation of aity, Momentum and so on Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, Abstact: One of the easons fo 957 Nobel ize fo physics is fo thei penetating inestigation of the so-called paity laws which has led to impotant discoeies egading the elementay paticles. While the concepts of paity laws (law of conseation of paity and law of nonconseation of paity) ae questionable. Fo the expeiment of Chien-Shiung Wu et al in 957, the coect way of saying should be that the pobability of conseation of paity is 7% and the pobability of nonconseation of paity is only 9%. The essential eason fo the phenomena of nonconseation (including nonconseation of paity, momentum, angula momentum and the like) is that so fa only the law of conseation of enegy can be consideed as the unique tuth in physics. As fo othe laws, they ae coect only in the cases that they ae not contadicted with law of conseation of enegy o they can be deied by law of conseation of enegy; othewise thei pobability of coectness should be detemined by law of conseation of enegy o expeiment (cuently fo the most cases the coectness can only be detemined by expeiment). Conclusion: besides law of conseation of enegy, all othe laws of conseation in physics may not be coect (o thei pobabilities of coectness ae all less than %). Discussing the examples that law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae not coect (thei esults ae contadicted with law of conseation of enegy). In addition, the essential shotcomings of special elatiity and geneal elatiity ae caused fom the eason that law of conseation of enegy was not consideed at the established time of these two theoies; theefoe thei esults will appea the examples contadicted with law of conseation of enegy, and in the aea of geneal elatiity the attempt to deie the coect expession of enegy will nee be success. Finally the examples deiing the impoed Newton's second law and impoed law of gaity accoding to law of conseation of enegy ae discussed, which show the geat potentiality of law of conseation of enegy, and giing full play to the ole of law of conseation of enegy will completely change the situation of physics. Key wods: Weak inteaction, conseation of paity, nonconseation of paity, nonconseation of momentum, nonconseation of angula momentum, pobability, law of conseation of enegy, unique tuth, expession of enegy, impoed Newton's second law, impoed law of gaity Intoduction The impotance of law of conseation of enegy is fa fom being fully undestood, and its geat potentiality is fa fom being fully ealized.
2 One of the easons fo 957 Nobel ize fo physics is fo thei penetating inestigation of the so-called paity laws which has led to impotant discoeies egading the elementay paticles. Why is the paity nonconseation? The essential eason fo this is that so fa only the "law of conseation of enegy" will be qualified to become the unique tuth in physics. Not only we cannot poe that "law of conseation of paity" is not contadicted with law of conseation of enegy, but also cannot poe that "law of conseation of paity" can be deied fom law of conseation of enegy, so the so-called "law of conseation of paity" is not coect. Similaly, the so-called law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae not coect (o thei pobabilities of coectness ae less than %). By extension, all the physical laws that cannot be deied fom law of conseation of enegy ae pobably not coect (o thei pobabilities of coectness ae less than %). Fo example, the special elatiity and geneal elatiity ae not coect (o thei pobabilities of coectness ae less than %) fo the eason that law of conseation of enegy was not consideed at the established time of these two theoies. Othewise, all laws that can be deied fom law of conseation of enegy ae coect. Fo example, the impoed Newton's second law and impoed law of gaity can be deied fom law of conseation of enegy. Detemine the pobabilities of conseation of paity and nonconseation of paity accoding to the expeiment of Chien-Shiung Wu et al in 957 In the expeiment of Chien-Shiung Wu et al in 957, they found that the numbe of the electons that exiting angle θ>9 is 4% moe than that of θ<9. Fo this esult, we cannot simply say that paity is conseation o nonconseation. The coect way of saying should be that the pobability of conseation of paity is 7% and the pobability of nonconseation of paity is only 9%. Similaly, the pobabilities of coectness fo othe laws of conseation should be detemined by law of conseation of enegy o expeiment (cuently fo the most cases the coectness can only be detemined by expeiment). Examples that the law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae not coect In efeence [], an example is pesented in which the law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae not coect (the esults ae diectly contadicted with law of conseation of enegy). Hee we pesent the eason that the law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae not coect in anothe way. As well-known, in many cases, the law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum can be deied accoding to the oiginal Newton's second law. Howee, in efeences [] and [3], we hae pointed out that in some cases the oiginal Newton's second law is not coect, and the impoed Newton's second law F ma is needed to be applied. In this case, the law of
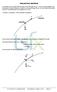
3 conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae no longe coect. Hee, because the impoed Newton's second law is deied accoding to the law of conseation of enegy expot, so we can say that based on the impoed Newton's second law, the esults of law of conseation of momentum and law of conseation of angula momentum ae indiectly contadicted with the law of conseation of enegy. 3 Example that elatiity theoy is contadicted with law of conseation of enegy The essential shotcomings of special elatiity and geneal elatiity ae caused fom the eason that law of conseation of enegy was not consideed at the established time of these two theoies; theefoe thei esults will appea the examples contadicted with law of conseation of enegy. Fo example, accoding to elatiity theoy, an object s speed cannot each the speed of light. Howee, based on law of conseation of enegy, when the speed of an object is close o equal to the speed of light, fo beaking the light baie, the speed of this object could be faste than light as it passes though the Sun s gaitational field. Figue. An object passes though the Sun's gaitational field at the speed of light As shown in Figue, an object passes though the Sun's gaitational field at the speed of light fom the infinite distance, assuming that its closest distance to the Sun is equal to, if the obit of this object will be tangent to the Sun, then is equal to the adius of the Sun. Ty to decide this object s maximum speed max as its distance to the Sun is equal to. Fo this poblem, in efeence [3], the impoed law of gaity eads.5 F () 4 Fo the eason that, as the object is located at the infinite distance, and the closest distance to the Sun, the enegies should be equal, so we hae
4 It gies mc. 5 mmax max c GM / 3 () Obiously this speed is faste than the speed of light, if the obit of this object will be tangent to the Sun, afte calculating it gies 6 ( 3.8 )c (A) max In addition, in the aea of geneal elatiity the attempt to deie the coect expession of enegy will nee be success. Einstein could not deie this expession of enegy, othe people also cannot deie it. 4 Deiing the impoed Newton's second law and impoed law of gaity accoding to law of conseation of enegy Now fo an example, we simultaneously deie the impoed Newton's second law and impoed law of gaity accoding to law of conseation of enegy, and it should be noted that they ae suitable fo this example only. Fistly, the aiational pinciples established by the law of conseation of enegy can be gien with least squaes method (LSM). Supposing that the initial total enegy of a closed system equals W (), and fo time t the total enegy equals W (t), then accoding to the law of conseation of enegy: W () = W (t) (3) This can be witten as: W( t) R W= W() (4) Accoding to LSM, fo the inteal [ t,t aiational pinciple: t ], we can wite the following R Wdt min (5) t whee: min denotes the minimum alue of functional Π and it should be equal to zeo. It should be noted that, in many cases W (t) is appoximate, and R W is not identically equal to zeo, theefoe Eq.(5) can be used to sole the poblem.
5 Besides the time coodinate, anothe one can also be used. Fo example, fo inteal [ x, x ], the following aiational pinciple can be gien accoding to the law of conseation of enegy: x x R W dx min (6) The aboe-mentioned pinciples ae established by using the law of conseation of enegy diectly. Sometimes, a cetain pinciple should be established by using the law of conseation of enegy indiectly. Fo example, a special physical quantity Q may be inteested,not only it can be calculated by using the law of conseation of enegy, but also can be calculated by using othe laws (fo this pape they ae the law of gaity, and Newton s second law). Fo distinguishing the alues, let s denote the alue gien by othe laws as Q,while denote the alue gien by the law of conseation of enegy as Q ',then the alue of R W can be edefined as follows: Q R W = Q' (7) Substituting Eq.(7)into Eqs.(5)and(6),as Q ' is the esult calculated with the law of conseation of enegy, it gies the aiational pinciple established by using the law of conseation of enegy indiectly. Othewise, it is clea that the extent of the alue of Q accods with Q '. Substituting the elated quantities into Eq.(5)o Eq.(6),the equations deied by the condition of an extemum can be witten as follows: a i k i (8) Afte soling these equations, the impoed law of gaity, and Newton s second law can be eached at once. Accoding to the alue of Π, the effect of the solution can be judged. The neae the alue of Π is to zeo, the bette the effect of the solution. It should be noted that besides of soling equations, optimum-seeking methods could also be used fo finding the minimum and the constants to be detemined. In fact, the optimum seeking method will be used in this pape. Now we sole an example. As shown in Fig., supposing that the small ball olls along a long incline fom A to B. Its initial elocity is zeo and the fiction and the otational enegy of small ball ae neglected. Fig. A small ball olls fom A to B Supposing that cicle O ' denotes the Eath, M denotes its mass; m denotes the mass of the small ball (teated as a mass point ), O A is a plumb
6 line, coodinate x is othogonal to O A, coodinate y is othogonal to coodinate x (paallel to O A), BC is othogonal to O A. The lengths of OA, OB, BC, and AC ae all equal to H, and O C equals the adius R of the Eath. In this example, the alue of which is the squae of the elocity fo the ball located at point is inestigated. To distinguish the quantities, denote the alue gien by the impoed law of gaity and impoed Newton s second law as,while denotes the alue gien by the law of conseation of enegy,then ' Eq.(6)can be witten as H ( ' ) dx min (9) Supposing that the impoed law of gaity and impoed Newton s second law can be witten as the following constant dimension factal foms F () D F ma () whee: D and ae constants. Now we calculate the elated quantities accoding to the law of conseation of enegy. Fom Eq.(), the potential enegy of the small ball located at point is V () ( D) D O ' Accoding to the law of conseation of enegy, we can get ( D ) D O' A m' ( D ) D O ' (3) And theefoe GM ' [ ] (4) D D D ( R H) O' Now we calculate the elated quantities accoding to the impoed law of gaity and impoed Newton s second law. Supposing that the equation of olling line is y x H (5) Fo the ball located at point, d/ dt a (6) because dt ds dx theefoe d a dx (7)
7 Accoding to the impoed law of gaity, the foce along to the tangent is Fa (8) D O ' Accoding to the impoed Newton s second law, fo point, the acceleation along to the tangent is Fa GM a ( ) ( ) (9) m Fom Eq.(7), it gies / / D O ' GM / d { } dx () D/ [( H x) ( R H y) ] Substituting Eq.(5) into Eq.(), and fo the two sides, we un the integal opeation fom A to, it gies x GM / / { } ( ) dx D / [( H x) ( R x) ] () H then the alue can be calculated by a method of numeical integal. The gien data ae assumed to be: fo Eath, GM= m 3 /s ; the adius of the Eath R= m, H=R/, ty to sole the poblem shown in Fig., find the solution fo the alue of B,and deie the impoed law of gaity and the impoed Newton s second law. Fistly, accoding to the oiginal law of gaity, the oiginal Newton s second law (i.e., let D = in Eq.(), = in Eq.()) and the law of conseation of enegy, all the elated quantities can be calculated, then substitute them into Eq.(9), it gies =57.45 Hee, accoding to the law of conseation of enegy, it gies ' B =.767 7, while accoding to the oiginal law of gaity, and the oiginal Newton s second law, it gies B =.35 7,the diffeence is about 5.4 %. Fo the eason that the alue of Π is not equal to zeo, then the alues of D and can be decided by the optimum seeking method. At pesent all the optimum seeking methods can be diided into two types, one type may not depend on the initial alues which pogam may be complicated, and anothe type equies the bette initial alues which pogam is simple. One method of the second type, namely the seaching method will be used in this pape. Fistly, the alue of D is fixed so let D =,then seach the alue of,as =.46, the alue of Π eaches the minimum ;then the alue of is fixed,and seach the alue of D,as D =.99989, the alue of Π eaches the minimum ;then the alue of D is fixed,and seach the alue of,as =.458, the alue of Π eaches minimum Because the last two esults ae highly close, the seaching can be stopped, and the final esults ae as follows D=.99989,ε=.458, =37.33 Hee the alue of Π is only 4% of Π. While accoding to the law of conseation of enegy, it gies ' B =.785 7,accoding to the impoed law of
8 gaity and the impoed Newton s second law, it gies B =.73 7, the diffeence is about.7 % only. The esults suitable fo this example with the constant dimension factal fom ae as follows The impoed law of gaity eads F () The impoed Newton s second law eads.458 F ma (3) The aboe mentioned esults hae been published on efeence []. Accoding to the esults fo the example shown in Fig., it can be said that we could not ely on any expeimental data, only apply the law of conseation of enegy to deie the impoed law of gaity, and impoed Newton's second law; and demonstate that the oiginal Newton s law of gaity and Newton's second law ae all tenable appoximately fo this example. So, can only apply the law of conseation of enegy to deie that these two oiginal laws o demonstate they ae tenable accuately in some cases? The answe is that in some cases we can indeed deie the oiginal Newton's second law and poe the oiginal Newton s law of gaity is tenable accuately. Now, in the case that a small ball fee falls (equialent to fee fall fom A to C in Fig. ), we deie the oiginal Newton's second law and poe the oiginal Newton s law of gaity is tenable accuately. Assuming that fo the oiginal law of gaity and Newton's second law, the elated exponents ae unknown, only know the foms of these two fomulas ae as D' follows: F, F ma ; whee: D and D ae undetemined constants. D As shown in Fig., supposing that a small ball fee falls fom point A to point C. Simila to the aboe deiation, when the small ball falls to point (point is not shown in Fig.), the alue of calculated by the undetemined Newton's second law and the law of gaity, as well as the alue of ' calculated by the law of conseation of enegy ae as follows: GM [ D D ( R H) ' D O' ] y p / D' ( GM ) ( R H y) D / D' dy ( GM ) / D ' { [( R H y) D / D' D / D' ] y p }
9 / D' ( GM ) [ ( D / D' ) ( D / D') O' ( R H) ( D / D') ] Let, then we should hae: / D', and D ( D / D') ; these ' two equations all gie: D ', this means that fo fee fall poblem, by using the law of conseation of enegy, we stictly deie the oiginal Newton's second law F ma. Hee, although the oiginal law of gaity cannot be deied (the alue of D may be any constant, cetainly including the case that D=), we aleady poe that the oiginal law of gaity is not contadicted to the law of conseation of enegy, o the oiginal law of gaity is tenable accuately. Fo the example shown in Fig. that a small ball olls along the inclined plane, in ode to obtain the bette esults, we discuss the aiable dimension factal solution with Eq.(4) that is established by the law of conseation of enegy diectly. Supposing that the impoed Newton s second law and the impoed law of gaity with the fom of aiable dimension factal can be witten as follows: F ma, k u ; F /, k u ; whee: u is the hoizon distance that the small ball olls ( u x H ). With the simila seaching method, the alues of k, k can be detemined, and the esults ae as follows u,.7 u The esults of aiable dimension factal ae much bette than that of constant 4 dimension factal. Fo example, the final Π 5.866, it is only.9% of Π (3.7). While accoding to the law of conseation of enegy, it gies ' B =.767 7, accoding to the impoed law of gaity and the impoed Newton s second law, it gies B =.777 7, the diffeence is about.93 % only. The esults suitable fo this example with the aiable dimension factal fom ae as follows The impoed law of gaity eads (4) F 3.7 u The impoed Newton s second law eads u F ma (5) whee: u is the hoizon distance that the small ball olls ( u x H ) Thee is anothe poblem should also be discussed. That is the impoed kinetic enegy fomula. As well-known, the kinetic enegy fomula has been modified in the theoy of elatiity, now we impoe the kinetic enegy fomula with the law of conseation of enegy. Supposing that the impoed kinetic enegy fomula is m Ed,
10 k 3 u ;whee: u is the hoizon distance that the small ball olls ( u x H ). 3 With the simila seaching method, we can get: k , then the impoed kinetic enegy fomula with aiable dimension factal fom eads u E d m Because the effect of impoement is ey small (the alue of Π is only impoed fom into ), theefoe these esults should be fo efeence only. 5 Conclusions In this pape, we econside the poblems about conseation of paity and nonconseation of paity with a new iewpoint. Fo the expeiment of Chien-Shiung Wu et al in 957, the new conclusion is that the pobability of conseation of paity is 7% and the pobability of nonconseation of paity is only 9%. We point out that, besides law of conseation of enegy, all othe laws of conseation in physics may not be coect (o thei pobabilities of coectness ae all less than %). So fa, because only the law of conseation of enegy can be qualified to become the unique tuth in physics, theefoe fo all the theoies and laws in physics (including the elatiity theoy, law of gaity, Newton's second law, law of conseation of momentum, law of conseation angula momentum, so-called paity laws, and so on), we should e-examine thei elations with law of conseation of enegy. In fact, many theoies and laws (such as impoed Newton's second law and impoed law of gaity) can be deied accoding to law of conseation of enegy, which show the geat potentiality of law of conseation of enegy, and giing full play to the ole of law of conseation of enegy will completely change the situation of physics. In addition, in a moe wide ange, the law of conseation of enegy can be used to deal with all the poblems elated to enegy in physics, astonomy, mechanics, engineeing, chemisty, biology, and the like with a unified way. Refeences Fu Yuhua, Science of Conseation of Enegy. Jounal of Dezhou Uniesity. 4(6):-4 Fu Yuhua, Deiing Impoed Newton s Second Law and the Law of Gaity at One Time with Fom of Factal Fomula, Engineeing Science. 3,Vol.5,No.6, Fu Yuhua. Shotcomings and Applicable Scopes of Special and Geneal Relatiity. See: Unsoled oblems in Special and Geneal Relatiity. Edited by: Floentin Smaandache, Fu Yuhua and Zhao Fengjuan. Education ublishing,
Expanding Newton Mechanics with Neutrosophy and Quadstage Method New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of. Conservation of Energy as Unique Source Law
 Neutosophic Sets and Systems, Vol. 3, 4 3 Epanding Newton Mechanics with Neutosophy and Quadstage Method New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conseation of Enegy as Unique Souce Law Fu Yuhua CNOOC Reseach
Neutosophic Sets and Systems, Vol. 3, 4 3 Epanding Newton Mechanics with Neutosophy and Quadstage Method New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conseation of Enegy as Unique Souce Law Fu Yuhua CNOOC Reseach
New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conservation of Energy as Unique Source Law (Revised Version 3)
 New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conseation of Enegy as Unique Souce Law eised Vesion 3 u Yuhua CNOOC eseach Institute E-mail: fuyh945@sina.com Abstact: Accoding to the pinciple of the uniqueness of
New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conseation of Enegy as Unique Souce Law eised Vesion 3 u Yuhua CNOOC eseach Institute E-mail: fuyh945@sina.com Abstact: Accoding to the pinciple of the uniqueness of
New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conservation of Energy as Unique Source Law (Revised Version)
 New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conseation of Enegy as Unique Souce Law (Reised Vesion) Fu Yuhua CNOOC Reseach Institute E-mail: fuyh945@sina.com Abstact: Accoding to the pinciple of the uniqueness
New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conseation of Enegy as Unique Souce Law (Reised Vesion) Fu Yuhua CNOOC Reseach Institute E-mail: fuyh945@sina.com Abstact: Accoding to the pinciple of the uniqueness
New Newton Mechanics Taking Law of Conservation of Energy as Unique Source Law
 Science Jonal of hysics ISSN: 76-6367 http://www.sjpb.og Atho(s 5. CC Attibtion 3. License. Reseach Aticle blished By Science Jonal blication Intenational Open Access blishe New Newton Mechanics Taking
Science Jonal of hysics ISSN: 76-6367 http://www.sjpb.og Atho(s 5. CC Attibtion 3. License. Reseach Aticle blished By Science Jonal blication Intenational Open Access blishe New Newton Mechanics Taking
Solving Problems of Advance of Mercury s Perihelion and Deflection of. Photon Around the Sun with New Newton s Formula of Gravity
 Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Chap13. Universal Gravitation
 Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
rt () is constant. We know how to find the length of the radius vector by r( t) r( t) r( t)
 Cicula Motion Fom ancient times cicula tajectoies hae occupied a special place in ou model of the Uniese. Although these obits hae been eplaced by the moe geneal elliptical geomety, cicula motion is still
Cicula Motion Fom ancient times cicula tajectoies hae occupied a special place in ou model of the Uniese. Although these obits hae been eplaced by the moe geneal elliptical geomety, cicula motion is still
r cos, and y r sin with the origin of coordinate system located at
 Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
ESTIMATION MODELS USING MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS AND NEWTON S LAWS FOR CONIC SECTION TRAJECTORIES ON EARTH S SURFACE
 Fundamental Jounal of Mathematical Physics Vol. 3 Issue 1 13 Pages 33-44 Published online at http://www.fdint.com/ ESTIMATION MODELS USING MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS AND NEWTON S LAWS FOR CONIC SECTION TRAJECTORIES
Fundamental Jounal of Mathematical Physics Vol. 3 Issue 1 13 Pages 33-44 Published online at http://www.fdint.com/ ESTIMATION MODELS USING MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS AND NEWTON S LAWS FOR CONIC SECTION TRAJECTORIES
ENGI 4430 Non-Cartesian Coordinates Page xi Fy j Fzk from Cartesian coordinates z to another orthonormal coordinate system u, v, ˆ i ˆ ˆi
 ENGI 44 Non-Catesian Coodinates Page 7-7. Conesions between Coodinate Systems In geneal, the conesion of a ecto F F xi Fy j Fzk fom Catesian coodinates x, y, z to anothe othonomal coodinate system u,,
ENGI 44 Non-Catesian Coodinates Page 7-7. Conesions between Coodinate Systems In geneal, the conesion of a ecto F F xi Fy j Fzk fom Catesian coodinates x, y, z to anothe othonomal coodinate system u,,
Circular Motion. x-y coordinate systems. Other coordinates... PHY circular-motion - J. Hedberg
 Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Newton s Laws, Kepler s Laws, and Planetary Orbits
 Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Determining solar characteristics using planetary data
 Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G-type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this investigation
Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G-type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this investigation
AP Physics 1 - Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test (Multiple Choice Section) Answer Section
 AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Universal Gravitation
 Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
A New Approach to General Relativity
 Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
ASTR415: Problem Set #6
 ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
Projection Gravitation, a Projection Force from 5-dimensional Space-time into 4-dimensional Space-time
 Intenational Jounal of Physics, 17, Vol. 5, No. 5, 181-196 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/5/6 Science and ducation Publishing DOI:1.1691/ijp-5-5-6 Pojection Gavitation, a Pojection Foce
Intenational Jounal of Physics, 17, Vol. 5, No. 5, 181-196 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/5/6 Science and ducation Publishing DOI:1.1691/ijp-5-5-6 Pojection Gavitation, a Pojection Foce
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Midterm Examination Thursday March
 EN40: Dynamics and Vibations Midtem Examination Thusday Mach 9 2017 School of Engineeing Bown Univesity NAME: Geneal Instuctions No collaboation of any kind is pemitted on this examination. You may bing
EN40: Dynamics and Vibations Midtem Examination Thusday Mach 9 2017 School of Engineeing Bown Univesity NAME: Geneal Instuctions No collaboation of any kind is pemitted on this examination. You may bing
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
PROJECTILE MOTION. At any given point in the motion, the velocity vector is always a tangent to the path.
 PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
Version 1.0. klm. General Certificate of Education June Mathematics. Mechanics 2B. Mark Scheme
 Vesion.0 klm Geneal Cetificate of Education June 00 Mathematics MMB Mechanics B Mak Scheme Mak schemes ae pepaed by the Pincipal Examine and consideed, togethe with the eleant questions, by a panel of
Vesion.0 klm Geneal Cetificate of Education June 00 Mathematics MMB Mechanics B Mak Scheme Mak schemes ae pepaed by the Pincipal Examine and consideed, togethe with the eleant questions, by a panel of
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Class #16 Monday, March 20, 2017
 D. Pogo Class #16 Monday, Mach 0, 017 D Non-Catesian Coodinate Systems A point in space can be specified by thee numbes:, y, and z. O, it can be specified by 3 diffeent numbes:,, and z, whee = cos, y =
D. Pogo Class #16 Monday, Mach 0, 017 D Non-Catesian Coodinate Systems A point in space can be specified by thee numbes:, y, and z. O, it can be specified by 3 diffeent numbes:,, and z, whee = cos, y =
Theoretical Competition:Solution Question 1 Page 1 of 8. I. Solution Q1_THEORY_SOLUTION_1700_SENT_TO_LEADER.DOCX. r 2. r 1
 Q_THEOY_SOLUTION_7_SENT_TO_LEADE.DOCX Theoetical Competition:Solution Question Page of 8 I. Solution M O m. Let O be thei cente of mass. Hence M m () m M GMm GMm () G M m Fom Eq. (), o using educed mass,
Q_THEOY_SOLUTION_7_SENT_TO_LEADE.DOCX Theoetical Competition:Solution Question Page of 8 I. Solution M O m. Let O be thei cente of mass. Hence M m () m M GMm GMm () G M m Fom Eq. (), o using educed mass,
2018 Physics. Advanced Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 National Qualifications 018 018 Physics Advanced Highe Finalised Making Instuctions Scottish Qualifications Authoity 018 The infomation in this publication may be epoduced to suppot SQA qualifications
National Qualifications 018 018 Physics Advanced Highe Finalised Making Instuctions Scottish Qualifications Authoity 018 The infomation in this publication may be epoduced to suppot SQA qualifications
Physics 181. Assignment 4
 Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
arxiv: v1 [physics.gen-ph] 18 Aug 2018
![arxiv: v1 [physics.gen-ph] 18 Aug 2018 arxiv: v1 [physics.gen-ph] 18 Aug 2018](/thumbs/86/94149469.jpg) Path integal and Sommefeld quantization axiv:1809.04416v1 [physics.gen-ph] 18 Aug 018 Mikoto Matsuda 1, and Takehisa Fujita, 1 Japan Health and Medical technological college, Tokyo, Japan College of Science
Path integal and Sommefeld quantization axiv:1809.04416v1 [physics.gen-ph] 18 Aug 018 Mikoto Matsuda 1, and Takehisa Fujita, 1 Japan Health and Medical technological college, Tokyo, Japan College of Science
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
1 Dark Cloud Hanging over Twentieth Century Physics
 We ae Looking fo Moden Newton by Caol He, Bo He, and Jin He http://www.galaxyanatomy.com/ Wuhan FutueSpace Scientific Copoation Limited, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China E-mail: mathnob@yahoo.com Abstact Newton
We ae Looking fo Moden Newton by Caol He, Bo He, and Jin He http://www.galaxyanatomy.com/ Wuhan FutueSpace Scientific Copoation Limited, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China E-mail: mathnob@yahoo.com Abstact Newton
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Chapters 5-8. Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws
 Chaptes 5-8 Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws Systems of Inteacting Objects The Fee Body Diagam Technique Examples: Masses Inteacting ia Nomal Foces Masses Inteacting ia Tensions in Ropes. Ideal Pulleys
Chaptes 5-8 Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws Systems of Inteacting Objects The Fee Body Diagam Technique Examples: Masses Inteacting ia Nomal Foces Masses Inteacting ia Tensions in Ropes. Ideal Pulleys
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department. Problem Set 10 Solutions. r s
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Nuclear and Particle Physics - Lecture 20 The shell model
 1 Intoduction Nuclea and Paticle Physics - Lectue 0 The shell model It is appaent that the semi-empiical mass fomula does a good job of descibing tends but not the non-smooth behaviou of the binding enegy.
1 Intoduction Nuclea and Paticle Physics - Lectue 0 The shell model It is appaent that the semi-empiical mass fomula does a good job of descibing tends but not the non-smooth behaviou of the binding enegy.
The study of the motion of a body along a general curve. the unit vector normal to the curve. Clearly, these unit vectors change with time, u ˆ
 Section. Cuilinea Motion he study of the motion of a body along a geneal cue. We define u ˆ û the unit ecto at the body, tangential to the cue the unit ecto nomal to the cue Clealy, these unit ectos change
Section. Cuilinea Motion he study of the motion of a body along a geneal cue. We define u ˆ û the unit ecto at the body, tangential to the cue the unit ecto nomal to the cue Clealy, these unit ectos change
Duality between Statical and Kinematical Engineering Systems
 Pape 00, Civil-Comp Ltd., Stiling, Scotland Poceedings of the Sixth Intenational Confeence on Computational Stuctues Technology, B.H.V. Topping and Z. Bittna (Editos), Civil-Comp Pess, Stiling, Scotland.
Pape 00, Civil-Comp Ltd., Stiling, Scotland Poceedings of the Sixth Intenational Confeence on Computational Stuctues Technology, B.H.V. Topping and Z. Bittna (Editos), Civil-Comp Pess, Stiling, Scotland.
Auchmuty High School Mathematics Department Advanced Higher Notes Teacher Version
 The Binomial Theoem Factoials Auchmuty High School Mathematics Depatment The calculations,, 6 etc. often appea in mathematics. They ae called factoials and have been given the notation n!. e.g. 6! 6!!!!!
The Binomial Theoem Factoials Auchmuty High School Mathematics Depatment The calculations,, 6 etc. often appea in mathematics. They ae called factoials and have been given the notation n!. e.g. 6! 6!!!!!
A thermodynamic degree of freedom solution to the galaxy cluster problem of MOND. Abstract
 A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
1131 T Question 1
 1131 T1 2008 Question 1 ( aks) You ae cycling, on a long staight path, at a constant speed of 6.0.s 1. Anothe cyclist passes you, taelling on the sae path in the sae diection as you, at a constant speed
1131 T1 2008 Question 1 ( aks) You ae cycling, on a long staight path, at a constant speed of 6.0.s 1. Anothe cyclist passes you, taelling on the sae path in the sae diection as you, at a constant speed
Kepler s problem gravitational attraction
 Kele s oblem gavitational attaction Summay of fomulas deived fo two-body motion Let the two masses be m and m. The total mass is M = m + m, the educed mass is µ = m m /(m + m ). The gavitational otential
Kele s oblem gavitational attaction Summay of fomulas deived fo two-body motion Let the two masses be m and m. The total mass is M = m + m, the educed mass is µ = m m /(m + m ). The gavitational otential
Physics 161 Fall 2011 Extra Credit 2 Investigating Black Holes - Solutions The Following is Worth 50 Points!!!
 Physics 161 Fall 011 Exta Cedit Investigating Black Holes - olutions The Following is Woth 50 Points!!! This exta cedit assignment will investigate vaious popeties of black holes that we didn t have time
Physics 161 Fall 011 Exta Cedit Investigating Black Holes - olutions The Following is Woth 50 Points!!! This exta cedit assignment will investigate vaious popeties of black holes that we didn t have time
Gravitation. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
- 5 - TEST 1R. This is the repeat version of TEST 1, which was held during Session.
 - 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
- 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
7.2. Coulomb s Law. The Electric Force
 Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
= e2. = 2e2. = 3e2. V = Ze2. where Z is the atomic numnber. Thus, we take as the Hamiltonian for a hydrogenic. H = p2 r. (19.4)
 Chapte 9 Hydogen Atom I What is H int? That depends on the physical system and the accuacy with which it is descibed. A natual stating point is the fom H int = p + V, (9.) µ which descibes a two-paticle
Chapte 9 Hydogen Atom I What is H int? That depends on the physical system and the accuacy with which it is descibed. A natual stating point is the fom H int = p + V, (9.) µ which descibes a two-paticle
is the instantaneous position vector of any grid point or fluid
 Absolute inetial, elative inetial and non-inetial coodinates fo a moving but non-defoming contol volume Tao Xing, Pablo Caica, and Fed Sten bjective Deive and coelate the govening equations of motion in
Absolute inetial, elative inetial and non-inetial coodinates fo a moving but non-defoming contol volume Tao Xing, Pablo Caica, and Fed Sten bjective Deive and coelate the govening equations of motion in
Physics 506 Winter 2006 Homework Assignment #9 Solutions
 Physics 506 Winte 2006 Homewok Assignment #9 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.2, 12.9, 12.13, 12.14 12.2 a) Show fom Hamilton s pinciple that Lagangians that diffe only by a total time deivative
Physics 506 Winte 2006 Homewok Assignment #9 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.2, 12.9, 12.13, 12.14 12.2 a) Show fom Hamilton s pinciple that Lagangians that diffe only by a total time deivative
Scattering in Three Dimensions
 Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
arxiv:hep-th/ v11 4 Feb 2016
 A Fundamental Modification of Standad Cosmological Metic ChiYi Chen a a chenchiyi@hznu.edu.cn Hangzhou Nomal Univesity, Hangzhou 310036, China axiv:hep-th/0411047v11 4 Feb 016 In this pape a novel physical
A Fundamental Modification of Standad Cosmological Metic ChiYi Chen a a chenchiyi@hznu.edu.cn Hangzhou Nomal Univesity, Hangzhou 310036, China axiv:hep-th/0411047v11 4 Feb 016 In this pape a novel physical
Qualifying Examination Electricity and Magnetism Solutions January 12, 2006
 1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
FARADAY'S LAW dt
 FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
Chapter 7 Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
 Chapte 7 Rotational Motion and the Law of Gaity What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and
Chapte 7 Rotational Motion and the Law of Gaity What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and
Δt The textbook chooses to say that the average velocity is
 1-D Motion Basic I Definitions: One dimensional motion (staight line) is a special case of motion whee all but one vecto component is zeo We will aange ou coodinate axis so that the x-axis lies along the
1-D Motion Basic I Definitions: One dimensional motion (staight line) is a special case of motion whee all but one vecto component is zeo We will aange ou coodinate axis so that the x-axis lies along the
Related Rates - the Basics
 Related Rates - the Basics In this section we exploe the way we can use deivatives to find the velocity at which things ae changing ove time. Up to now we have been finding the deivative to compae the
Related Rates - the Basics In this section we exploe the way we can use deivatives to find the velocity at which things ae changing ove time. Up to now we have been finding the deivative to compae the
Shree Datta Coaching Classes, Contact No Circular Motion
 Shee Datta Coaching Classes, Contact No. 93698036 Pof. Deepak Jawale Cicula Motion Definition : The motion of the paticle along the cicumfeence of a cicle is called as cicula motion. Eg. i) Motion of eath
Shee Datta Coaching Classes, Contact No. 93698036 Pof. Deepak Jawale Cicula Motion Definition : The motion of the paticle along the cicumfeence of a cicle is called as cicula motion. Eg. i) Motion of eath
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
An Overview of Particle Sampling Bias
 An Oeiew of Paticle Sampling Bias Robet V. Edwads Case Westen Resee Uniesity Case Cente fo Complex Flow easuements Cleeland, Ohio 44106 and James F. eyes NASA - Langley Reseach Cente Hampton, Viginia 3665
An Oeiew of Paticle Sampling Bias Robet V. Edwads Case Westen Resee Uniesity Case Cente fo Complex Flow easuements Cleeland, Ohio 44106 and James F. eyes NASA - Langley Reseach Cente Hampton, Viginia 3665
Thomas Whitham Sixth Form Mechanics in Mathematics. Rectilinear Motion Dynamics of a particle Projectiles Vectors Circular motion
 Thomas Whitham Sith om Mechanics in Mathematics Unit M Rectilinea Motion Dynamics of a paticle Pojectiles Vectos Cicula motion . Rectilinea Motion omation and solution of simple diffeential equations in
Thomas Whitham Sith om Mechanics in Mathematics Unit M Rectilinea Motion Dynamics of a paticle Pojectiles Vectos Cicula motion . Rectilinea Motion omation and solution of simple diffeential equations in
Surveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces
 Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
5.61 Physical Chemistry Lecture #23 page 1 MANY ELECTRON ATOMS
 5.6 Physical Chemisty Lectue #3 page MAY ELECTRO ATOMS At this point, we see that quantum mechanics allows us to undestand the helium atom, at least qualitatively. What about atoms with moe than two electons,
5.6 Physical Chemisty Lectue #3 page MAY ELECTRO ATOMS At this point, we see that quantum mechanics allows us to undestand the helium atom, at least qualitatively. What about atoms with moe than two electons,
Lab #4: Newton s Second Law
 Lab #4: Newton s Second Law Si Isaac Newton Reading Assignment: bon: Januay 4, 1643 Chapte 5 died: Mach 31, 1727 Chapte 9, Section 9-7 Intoduction: Potait of Isaac Newton by Si Godfey Knelle http://www.newton.cam.ac.uk/at/potait.html
Lab #4: Newton s Second Law Si Isaac Newton Reading Assignment: bon: Januay 4, 1643 Chapte 5 died: Mach 31, 1727 Chapte 9, Section 9-7 Intoduction: Potait of Isaac Newton by Si Godfey Knelle http://www.newton.cam.ac.uk/at/potait.html
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 10-: MOTION IN A GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Questions Fom Reading Activity? Gavity Waves? Essential Idea: Simila appoaches can be taken in analyzing electical
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 10-: MOTION IN A GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Questions Fom Reading Activity? Gavity Waves? Essential Idea: Simila appoaches can be taken in analyzing electical
Physics 201, Lecture 6
 Physics 201, Lectue 6 Today s Topics q Unifom Cicula Motion (Section 4.4, 4.5) n Cicula Motion n Centipetal Acceleation n Tangential and Centipetal Acceleation q Relatie Motion and Refeence Fame (Sec.
Physics 201, Lectue 6 Today s Topics q Unifom Cicula Motion (Section 4.4, 4.5) n Cicula Motion n Centipetal Acceleation n Tangential and Centipetal Acceleation q Relatie Motion and Refeence Fame (Sec.
The Substring Search Problem
 The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
PHYS-3301 Lecture 2. Aug. 31, How Small. is Small? How Fast is Fast? Structure of the course Modern Physics. Relativistic
 Quantum (1920 s-) quantum (1927-) PHYS-3301 Lectue 2 Classical phsics Newtonian Mechanics, Themodnamics Statistical Mechanics, El.-Mag. (1905) Mawell s Equations of electomagnetism (1873) Aug. 31, 2017
Quantum (1920 s-) quantum (1927-) PHYS-3301 Lectue 2 Classical phsics Newtonian Mechanics, Themodnamics Statistical Mechanics, El.-Mag. (1905) Mawell s Equations of electomagnetism (1873) Aug. 31, 2017
AST 121S: The origin and evolution of the Universe. Introduction to Mathematical Handout 1
 Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Between any two masses, there exists a mutual attractive force.
 YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
A Level Exam-style Practice Paper
 A Leel Exam-style Pactice Pape a i The peiod is gien by the time lapse between high tide and low tide which is.5 hous. ii The amplitude is gien by half the total displacement and so is 5 m. b The safe
A Leel Exam-style Pactice Pape a i The peiod is gien by the time lapse between high tide and low tide which is.5 hous. ii The amplitude is gien by half the total displacement and so is 5 m. b The safe
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Ch04: Motion in two and three dimensions (2D and 3D)
 Ch4: Motion in two and thee dimensions (D and 3D) Displacement, elocity and acceleation ectos Pojectile motion Cicula motion Relatie motion 4.: Position and displacement Position of an object in D o 3D
Ch4: Motion in two and thee dimensions (D and 3D) Displacement, elocity and acceleation ectos Pojectile motion Cicula motion Relatie motion 4.: Position and displacement Position of an object in D o 3D
Vectors, Vector Calculus, and Coordinate Systems
 Apil 5, 997 A Quick Intoduction to Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David A. Randall Depatment of Atmospheic Science Coloado State Univesity Fot Collins, Coloado 80523. Scalas and vectos Any
Apil 5, 997 A Quick Intoduction to Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David A. Randall Depatment of Atmospheic Science Coloado State Univesity Fot Collins, Coloado 80523. Scalas and vectos Any
New problems in universal algebraic geometry illustrated by boolean equations
 New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Circular Orbits. and g =
 using analyse planetay and satellite motion modelled as unifom cicula motion in a univesal gavitation field, a = v = 4π and g = T GM1 GM and F = 1M SATELLITES IN OBIT A satellite is any object that is
using analyse planetay and satellite motion modelled as unifom cicula motion in a univesal gavitation field, a = v = 4π and g = T GM1 GM and F = 1M SATELLITES IN OBIT A satellite is any object that is
c n ψ n (r)e ient/ h (2) where E n = 1 mc 2 α 2 Z 2 ψ(r) = c n ψ n (r) = c n = ψn(r)ψ(r)d 3 x e 2r/a0 1 πa e 3r/a0 r 2 dr c 1 2 = 2 9 /3 6 = 0.
 Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Chapter 6 Balanced Incomplete Block Design (BIBD)
 Chapte 6 Balanced Incomplete Bloc Design (BIBD) The designs lie CRD and RBD ae the complete bloc designs We now discuss the balanced incomplete bloc design (BIBD) and the patially balanced incomplete bloc
Chapte 6 Balanced Incomplete Bloc Design (BIBD) The designs lie CRD and RBD ae the complete bloc designs We now discuss the balanced incomplete bloc design (BIBD) and the patially balanced incomplete bloc
Physics 211: Newton s Second Law
 Physics 211: Newton s Second Law Reading Assignment: Chapte 5, Sections 5-9 Chapte 6, Section 2-3 Si Isaac Newton Bon: Januay 4, 1643 Died: Mach 31, 1727 Intoduction: Kinematics is the study of how objects
Physics 211: Newton s Second Law Reading Assignment: Chapte 5, Sections 5-9 Chapte 6, Section 2-3 Si Isaac Newton Bon: Januay 4, 1643 Died: Mach 31, 1727 Intoduction: Kinematics is the study of how objects
TAMPINES JUNIOR COLLEGE 2009 JC1 H2 PHYSICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD
 TAMPINES JUNIOR COLLEGE 009 JC1 H PHYSICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD OBJECTIVES Candidates should be able to: (a) show an undestanding of the concept of a gavitational field as an example of field of foce and
TAMPINES JUNIOR COLLEGE 009 JC1 H PHYSICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD OBJECTIVES Candidates should be able to: (a) show an undestanding of the concept of a gavitational field as an example of field of foce and
Escape Velocity. GMm ] B
![Escape Velocity. GMm ] B Escape Velocity. GMm ] B](/thumbs/84/90630003.jpg) 1 PHY2048 Mach 31, 2006 Escape Velocity Newton s law of gavity: F G = Gm 1m 2 2, whee G = 667 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 2 3 10 10 N m 2 /kg 2 is Newton s Gavitational Constant Useful facts: R E = 6 10 6 m M E
1 PHY2048 Mach 31, 2006 Escape Velocity Newton s law of gavity: F G = Gm 1m 2 2, whee G = 667 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 2 3 10 10 N m 2 /kg 2 is Newton s Gavitational Constant Useful facts: R E = 6 10 6 m M E
Torque, Angular Momentum and Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Toque, Angula Moentu and Rotational Kinetic Enegy In ou peious exaples that inoled a wheel, like fo exaple a pulley we wee always caeful to specify that fo the puposes of the poble it would be teated as
Toque, Angula Moentu and Rotational Kinetic Enegy In ou peious exaples that inoled a wheel, like fo exaple a pulley we wee always caeful to specify that fo the puposes of the poble it would be teated as
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
you of a spring. The potential energy for a spring is given by the parabola U( x)
 Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
d 2 x 0a d d =0. Relative to an arbitrary (accelerating frame) specified by x a = x a (x 0b ), the latter becomes: d 2 x a d 2 + a dx b dx c
 Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Physics 121 Hour Exam #5 Solution
 Physics 2 Hou xam # Solution This exam consists of a five poblems on five pages. Point values ae given with each poblem. They add up to 99 points; you will get fee point to make a total of. In any given
Physics 2 Hou xam # Solution This exam consists of a five poblems on five pages. Point values ae given with each poblem. They add up to 99 points; you will get fee point to make a total of. In any given
Newton s E = mc 2 Two Hundred Years Before Einstein? Newton = Einstein at the Quantum Scale
 Newton s E = Two Hunded Yeas Befoe Einstein? Newton = Einstein at the Quantu Scale Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Uniesity of Life Sciences August 7, 07 Abstact The ost faous Einstein foula is E =, while Newton
Newton s E = Two Hunded Yeas Befoe Einstein? Newton = Einstein at the Quantu Scale Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Uniesity of Life Sciences August 7, 07 Abstact The ost faous Einstein foula is E =, while Newton
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Midterm Examination Tuesday March
 EN4: Dynaics and Vibations Midte Exaination Tuesday Mach 8 16 School of Engineeing Bown Univesity NME: Geneal Instuctions No collaboation of any kind is peitted on this exaination. You ay bing double sided
EN4: Dynaics and Vibations Midte Exaination Tuesday Mach 8 16 School of Engineeing Bown Univesity NME: Geneal Instuctions No collaboation of any kind is peitted on this exaination. You ay bing double sided
Lecture 7: Angular Momentum, Hydrogen Atom
 Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
4. Two and Three Dimensional Motion
 4. Two and Thee Dimensional Motion 1 Descibe motion using position, displacement, elocity, and acceleation ectos Position ecto: ecto fom oigin to location of the object. = x i ˆ + y ˆ j + z k ˆ Displacement:
4. Two and Thee Dimensional Motion 1 Descibe motion using position, displacement, elocity, and acceleation ectos Position ecto: ecto fom oigin to location of the object. = x i ˆ + y ˆ j + z k ˆ Displacement:
An Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation
 An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
Answers to test yourself questions
 Answes to test youself questions opic. Cicula motion π π a he angula speed is just ω 5. 7 ad s. he linea speed is ω 5. 7 3. 5 7. 7 m s.. 4 b he fequency is f. 8 s.. 4 3 a f. 45 ( 3. 5). m s. 3 a he aeage
Answes to test youself questions opic. Cicula motion π π a he angula speed is just ω 5. 7 ad s. he linea speed is ω 5. 7 3. 5 7. 7 m s.. 4 b he fequency is f. 8 s.. 4 3 a f. 45 ( 3. 5). m s. 3 a he aeage
