GATEFORUM- India s No.1 institute for GATE training
|
|
|
- Lenard Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. The partial differential equation + u = t x x u u u (A) Linear equation of order (B) Non-linear equation of order (C) Linear equation of order (D) Non-linear equation of order is a. The eigen values of symmetric matrix are all (A) Complex with non-zero positive imaginary part (B) Complex with non-zero negative imaginary part (C) Real (D) Pure imaginary 3. Match the CORRECT pairs: Numerical Integration Scheme Order of Fitting Polynomial P. Simpson s 3/8 Rule. First Q. Trapezoidal Rule. Second R. Simpson s /3 Rule 3. Third (A) P-; Q-; R-3 (B) P-3; Q-; R- (C) P-; Q-; R-3 (D) P-3; Q-; R-. A rod of length L having uniform cross-sectional area A is subjected to a tensile force P as shown in the figure below. If the Young s modulus of the material varies linearly from E to E along the length of the rod, the normal stress developed at the section-ss is E S E P P L / S L (A) P A (B) ( E ) ( + E ) P E A E (C) PE AE PE (D) AE Answer: (A) Stress depends on area. 5. The threaded bolts A and B of same material and length are subjected to identical tensile load. If the elastic strain energy stored in bolt A is times that of the bolt B and the mean diameter of bolt A is mm, the mean diameter of bolt B in mm is (A) 6 (B) (C) 36 (D) 8 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training
2 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Explanation: E E P l AE = = P l A AE d = d A d = d = 6. A link OB is rotating with a constant angular velocity of rad/s in counter clockwise direction and a block is sliding radially outward on it with an uniform velocity of 0.75 m/s with respect to the rod, as shown in the figure below. If OA = m, the magnitude of the absolute acceleration of the block at location A in m / s is B A O (A) 3 (B) (C) 5 (D) 6 Explanation: α = vω = 0.75 = 3 t v α r = = r Resultant α = 3 + = 5 7. For steady, fully developed flow inside a straight pipe of diameter D, neglecting gravity effects, the pressure drop p over a length L and the wall shear stress τ w are related by pd pd pd pl (A) τ w = (B) τ w = (C) τ w = (D) τ w = L L L D Answer: (A) Explanation: π pd ( DL) D p τω π = τ ω = L GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training
3 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 8. The pressure, dry bulb temperature, and relative humidity of air in a room are bar, 30ºC and 70% respectively. If the saturated steam pressure at 30ºC is.5kpa, the specific humidity of the room air in kg water vapour / kg dry air is Explanation: (A) (B) 0.00 (C) 0.09 (D) P = bar = 0 Pa = 00 KPa Psat =.5KPa S.humidity = = 0.09 p ( 00.5) 9. Consider one-dimensional steady state heat conduction, without heat generation, in a plane wall; with boundary conditions as shown in the figure below. The conductivity of the wall is given by k = k0 + bt ; where k 0 and b are positive constants and T is temperature. T where T > T T As x increases, the temperature gradient ( dt / dx ) will x (A) Remain constant (B) Be zero (C) Increase (D) Decrease 0. In a rolling process, the state of stress of the material undergoing deformation is (A) Pure compression (B) Pure shear (C) Compression and shear (D) Tension and shear. Match the CORRECT pairs. Processes Characteristics / Application P. Friction Welding. Non-consumable electrode Q. Gas Metal Arc Welding. Joining of thick plates R. Tungsten Inert Gas Welding 3. Consumable electrode wire S. Electroslag Welding. Joining of cylindrical dissimilar materials Answer: (A) (A) P-;Q-3;R-;S- (C) P-;Q-3;R-;S- (B) P-;Q-;R-3;S- (D) P-;Q-;R-;S-3 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 3
4 ME-GATE-03 PAPER. A metric thread of pitch mm and thread angle 60º is inspected for its pitch diameter using 3-wire method. The diameter of the best size wire in mm is (A) (B).000 (C).5 (D).000 For 60 o thread angle, best wire size =0.5735xP=.5 3. Customers arrive at a ticket counter at a rate of 50 per hour and tickets are issued in the order of their arrival. The average time taken for issuing a ticket is min. Assuming that customer arrivals form a Poisson process and service times are exponentially distributed, the average waiting time in queue in minutes is: Explanation: (A) 3 (B) (C) 5 (D) 6 λ λ = 50 / hr µ = 60 / hr W.T = = 0.083hr = 5min µ µ λ ( ). In simple exponential smoothing forecasting, to give higher weightage to recent demand information, the smoothing constant must be close to (A) - (B) zero (C) 0.5 (D) Value of α close to one have less of a smoothing effect and give greater weight to recent changes in the data. 5. A steel bar 00 mm in diameter is turned at a feed of 0.5 mm/rev with a depth of cut of mm. The rotational speed of the workpiece is 60 rpm. The material 3 removal rate in mm / s is (A) 60 (B) 67.6 (C) 600 (D) f d v π = ( 0.5) ( ) = A cube shaped casting solidifies in 5 minutes. The solidification time in minutes for a cube of the same material, which is 8 times heavier than the original casting will be (A) 0 (B) 0 (C) (D) 0 Now V V V = A = = A t C ; t 5 C = 8V Which implies each ride is getting doubled. So A = A V V t = c = c = t = 5 = 0 min A A GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training
5 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 7. For a ductile material, toughness is a measure of (A) Resistance to scratching (B) Ability to absorb energy up to fracture (C) Ability to absorb energy till elastic limit (D) Resistance to indentation Since, toughness has ability to absorb energy up to fracture. 8. In order to have maximum power from a Pelton turbine, the bucket speed must be (A) Equal to the jet speed (C) Equal to twice the jet speed (B) Equal to half the jet speed Explanation: Since, velocity of bucket = ½ times the velocity of jet. (D) Independent of the jet speed 9. Consider one-dimensional steady state heat conduction along x-axis ( 0 x L), through a plane wall with the boundary surfaces ( x = 0 and x = L) maintained at temperatures 0ºC and 00ºC. Heat is generated uniformly throughout the wall. Choose the CORRECT statement. (A) The direction of heat transfer will be from the surface at 00ºC to surface at 0ºC. (B) The maximum temperature inside the wall must be greater than 00ºC (C) The temperature distribution is linear within the wall (D) The temperature distribution is symmetric about the mid-plane of the wall 3 0. A cylinder contains 5m of ideal gas at a pressure of bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process till its pressure increases to 5 bar. The work in kj required for this process is Answer: (A) (A) 80.7 (B) 953. (C) 98.7 (D) 0. P P V ln P = 5 5 wd wd = 0 5 ln = = 80.7 kj. A long thin walled cylindrical shell, closed at both ends, is subjected to an internal pressure. The ratio of the hoop stress (circumferential stress) to longitudinal stress developed in the shell is (A) 0.5 (B).0 (C).0 (D).0 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 5
6 ME-GATE-03 PAPER σ hoop = σ = σ σ ong hoop long Pd t = Pd t. If two nodes are observed at a frequency of 800 rpm during whirling of a simply supported long slender rotating shaft, the first critical speed of the shaft in rpm is (A) 00 (B) 50 (C) 600 (D) 900 Since it is simply supported critical speed will be half 3. A planar closed kinematic chain is formed with rigid links PQ =.0m, QR = 3.0m, RS =.5m and SP =.7m with all revolute joints. The link to be fixed to obtain a double rocker (rocker-rocker) mechanism is (A) PQ (B) QR (C) RS (D) SP Since for Rocker Rocker mechanism the link opposite to smaller link must be fixed. Let X be a nominal variable with mean and variance. The probability P ( X < 0) is (A) 0.5 (B) Greater than zero and less than 0.5 (C) Greater than 0.5 and less than (D).0 x µ 0 µ σ σ P ( x < 0) = P < P ( Z < 0.5) ( ) ( ) = P Z > 0.5 = 0.5 P 0 < Z < 0.5, which is greater than zero and less than Choose the CORRECT set of functions, which are linearly dependent. (A) (C) sinx, sin x and cos x cosx, sin x and cos x (B) cosx, sinx and tan x (D) cosx, sinx and cosx (C) cos x = cos x sin x cos x is the linear combination of the functions cos x,sin x The functions cos x,sin x and cos x are linearly dependent GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 6
7 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No Carry Two Marks Each 6. The following surface integral is to be evaluated over a sphere for the given steady velocity vector field, F = xi + yj + zk defined with respect to a Cartesian coordinate system having i, j, and k as unit base vectors. s (F.n)dA Where S is the sphere, the sphere. The value of the surface integral is x + y + z = and n is the outward unit normal vector to (A) π (B) π (C) 3 π (D) π Answer: (A) divf dv (Using divergence theorem) 3 = 3dv volume of the sphere = 3 () 3 as radius = = π = 3 7. The function f(t) satisfies the differential equation + f = 0 and the auxiliary dt df conditions, f(0) = 0, (0) =. The Laplace transform of f(t) is given by dt (A) s + (B) Given Eqisf"(t) + f(t) = 0 L f"(t) + L f(t) = L(0) ' s F(s) sf(0) f (0) + F(s) = 0 ( ) s + F(s) = f(s) = s + s + (C) s + d f (D) s + 8. Specific enthalpy and velocity of steam at inlet and exit of a steam turbine, running under steady state, are as given below: Specific enthalpy (kj/kg) Velocity(m/s) Inlet steam condition Exit steam condition The rate of heat loss from the turbine per kg of steam flow rate is 5 kw. Neglecting changes in potential energy of steam, the power developed in kw by the steam turbine per kg of steam flow rate, is (A) 90. (B) 9. (C) (D) GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 7
8 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Explanation: V V h + + dq = h + + dw ( ) ( 80 5 ) dw = = kw 9. Water is coming out from a tap and falls vertically downwards. At the tap opening, the stream diameter is 0mm with uniform velocity of m/s. Acceleration due to gravity is 9.8m / s. Assuming steady, inviscid flow, constant atmospheric pressure everywhere and neglecting curvature and surface tension effects, the diameter is mm of the stream 0.5m below the tap is approximately (A) 0 (B) 5 (C) 0 (D) A steel ball of diameter 60 mm is initially in thermal equilibrium at 030 C in a furnace. It is suddenly removed from the furnace and cooled in ambient air at 30 C, with convective heat transfer coefficient h=0 W / m K. The thermophysical properties of steel are: density 3 ρ = 7800 kg / m, conductivity W k = 0 and specific heat c=600 J/kgK. The time required in seconds to cool mk the steel ball in air from 030 C to 30 C is (A) 59 (B) 93 (C) 95 (D) i co LAt SCpV T Tco V = e 0.0 = T T A t = = e 0 L A flywheel connected to a punching machine has to supply energy of 00 Nm while running at a mean angular speed of 0 radians/s. If the total fluctuation of speed is not to exceed ± %, the mass moment of inertia of the flywheel in kg m is (A) 5 (B) 50 (C) 00 (D) 5 Answer: (A) E = Iw CS 00 I = = 5kg m GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 8
9 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 3. A compound gear train with gears P, Q, R and S has number of teeth 0, 0, 5 and 0, respectively. Gears Q and R are mounted on the same shaft as shown in the figure below. The diameter of the gear Q is twice that of the gear R. If the module of the gear R is mm, the center distance in mm between gears P and S is Q (A) 0 (B) 80 (C) 0 P + + S + (D) 60 d = m t = 5 = 30 R Q Q R dq = dr = 60 dp tp 0 = dp = 60 = 30 d t 0 d t t 30 0 = d = dr = = 0 d t t 5 R R S s S S R d d P Q dr ds centre dis tance = = = 80 R 33. A pin jointed uniform rigid rod of weight W and Length L is supported horizontally by an external force F as shown in the figure below. The force F is suddenly removed. At the instant of force removal, the magnitude of vertical reaction developed at the support is L F (A) zero (B) W (C) W (D) W R W L = = α 3 g I L ; W I 3g α = L w GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 9
10 ME-GATE-03 PAPER L 3g Linear accleration at centre = α = 3 Inertial force at centre = W 3W W Re action at sup port = W = 3. Two cutting tools are being compared for a machining operation. The tool life equations are: Carbide tool: HSS tool:.6 VT = VT = 00 Where V is the cutting speed in m/min and T is the tool life in min. The carbide toll will provide higher tool life if the cutting speed in m/min exceeds (A) 5.0 (B) 39. (C) 9.3 (D)60.0 VT VT = 5 T = 5 ( ).6 V 5 = 3000 V = In a CAD package, mirror image of a D point P(5, 0) is to be obtained about a line which passes through the origin and makes an angle of 5 counterlockwise with the X-axis. The coordinates of the transformed point will be (A) (7.5, 5) (B) (0, 5) (C) (7.5, -5) (D) (0, -5) 36. A linear programming problem is shown below: Maximize 3x + 7y Subject to 3x + 7y 0 x + 6y 8 x, y 0 It has (A) an unbounded objective function (C) exactly two optimal solutions (B) exactly one optimal solution (D) infinitely many optimal solutions GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 0
11 ME-GATE-03 PAPER y (0,.) (0,.33) 3x + 7y 0 x + 6y 8 (,0) (3.33,0) x 37. Cylindrical pins of mm diameter are electroplated in a shop. Thickness of +.0 the plating is 30 micron. Neglecting gage tolerances, the size of the GO gage in mm to inspect the plated components is (A) 5.0 (B) 5.05 (C) 5.07 (D) Go gauge = max. Limit = 5.05 ± During the electrochemical machining (ECM) of iron (atomic weight=56, valency=) at current of 000 A with 90% current efficiency, the material removal rate was observed to be 0.6 gm/s. If Titanium (atomic weight = 8, valency=3) is machined by the ECM process at the current of 000 A with 90% current efficiency, the expected material removal rate in gm/s will be Explanation: (A) 0. (B) 0.3 (C) 0.30 (D)0.5 AI Q = = F Q = A single degree of freedom system having mass kg and stiffness 0kN/m initially at rest is subjected to an impulse force of magnitude 5 kn for 0 seconds. The amplitude in mm of the resulting free vibration is (A) 0.5 (B).0 (C) 5.0 (D) A bar is subjected to fluctuating tensile load from 0 kn to 00 kn. The material has yield strength of 0 MPa and endurance limit in reversed bending is 60 MPa. According to the Soderberg principle, the area of cross-section in mm of the bar for a factor of safety of is (A) 00 (B) 600 (C) 750 (D)000 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training
12 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Answer: σ σ m y (D) σv + = σ F.S e = A 0 A 60 A = 000. A simply supported beam of length L is subjected to a varying distributed load x sin 3π Nm L, where the distance x is measured from the left support. The magnitude of the vertical force in N at the left support is Answer: (A) zero (B) (B) 3πx N Load = sin L m L 3π (C) L π (D) L π L 3πx TotalLoad = sin dx L 0 L 3πL L = cos cos0 = + 3π L 3π Since the load is distributed equally on both supports R A Total Load L = RB = = 3 π x L. Two large diffuse gray parallel plates, separated by a small distance, have surface temperatures of 00 K and 300 K. If the emissivities of the surfaces are and the Stefan-Boltzmann constant is W / m K, the net radiation Answer: heat exchange rate in kw / m between the two plates is (A) 0.66 (B) 0.79 (C) 0.99 (D) 3.96 (A) ( T ) σa T dq = ; ε = ε = ε ε dq = 0.66 kw / h 3. A hinged gate of length 5 m, inclined at 30 with the horizontal and with water mass on its left, is shown in figure below. Density of water is 000 kg / m. The minimum mass of the gate in kg per unit width (perpendicular to the plane of paper), required to keep it closed is GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training
13 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 5m (A) 5000 (B) 6600 (C) 756 (D) 963 Explanation: An equilibrium moment of weight at 0 = Moment of pressure force at O Moment at O, w x = F y F = pgax; A = Area of gate = 5 p x = distance of C.G of Gate from free surface x θ = 30 ; sin30 = x =.5.5 Ig8m θ h = centre of pressure= x+ Ax 3 3 bd 5 (Ia) = = = 0. xx 0. h =.5 + = ( ) p x cos θ = x =.65.5 h.666 sin θ = y = = 3.3 y sin 30 w.65 = p g Ax y = w = 90.9 w = mg The pressure, temperature and velocity of air flowing in a pipe are 5 bar, 500 K and 50 m/s, respectively. The specific heats of air at constant pressure and at constant volume are.005 kj/kgk and 0.78 kj/kgk, respectively. Neglect potential energy. If the pressure and temperature of the surroundings are bar and 300 K, respectively, the available energy in kj/kg of the air stream is (A) 70 (B) 87 (C) 9 (D) 3 5. The probability that a student knows the correct answer to a multiple choice question is. If the student does not know the answer, then the student 3 guesses the answer. The probability of the guessed answer being correct is. Given that the student has answered the question correctly, the conditional probability that the student known the correct answer is h x x.5 F p y 5m.5 (A) 3 (B) 3 (C) 5 6 (D) 8 9 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 3
14 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Answer: (D) A = The student answer the question correctly E = Student knows the correct answer E = Student guesses the correct answer p(e ) =, p(e ) = 3 3 A A p(a) = p(e ) p + p(e ) p E E 3 = + = 3 3 Using Bayes theorem, E p A ( ) A E 3 8 = = p(a) 3 9 p E p d u du 6. The solution to the differential equation k = 0 where k is a constant, dx dx subjected to the boundary conditions u(0)=0 and u(l)=u, is kx x e (A) u = U (B) u = U L e kl Answer: (C) kx e u = U e kl (B) d u du dx = K 0 dx = = D kd 0 D(D K) 0 D = 0, D = K u = C e + C e 0 kx u = C + C e u(0) = 0 kx C + C = 0...() u(l) = u = + = kl u C Ce U...() solving () and () U kx U C =, C e kl e e kl e u = U e kx kl (D) kx + e u = U e kl + GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training
15 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 7. The value of the definite integral e x ln(x)dx is (A) e + (B) e (C) e + (D) e x ln(x)dx e 3 3 x x = ln(x) dx 3 x 3 = ln(x) x x = e e 3 e 9 9 Common Data Questions: 8 & 9 A single riveted lap joint of two similar plates as shown in the figure below has the following geometrical and material details: P w w P t t Width of the plate w=00 mm, thickness of the plate t=5 mm, number of rivets n=3, diameter of the rivet dr = 0 mm, diameter of the rivet hole dh = mm, allowable tensile stress of the plate σ p = 00 MPa, allowable shear stress of the rivet σ s = 00 MPa and allowable bearing stress of the σ c = 50 MPa 8. If the rivets are to be designed to avoid crushing failure, the maximum permissible load P in kn is Answer: (A) 7.50 (B) 5.00 (C).50 (D) (C) p = σ n d t = =.5kN c 9. If the plates are to be designed to avoid tearing failure, the maximum permissible load P in kn is Answer: (A) 83 (B) 5 (C) 67 (D) 50 (C) t ( ) ( ) p = σ w 3d t = = 67kN GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 5
16 ME-GATE-03 PAPER Common Data Questions: 50 & 5 Water (specific heat, cp =.8 kj /kgk ) enters a pipe at a rate of 0.0 kg/s and a temperature of 0 C. The pipe, of diameter 50 mm and length 3m, is " W subjected to a wall heat flux q in. m w " 50. If qw = 500x, where x is in m and in the direction of flow (x=0 at the inlet), the bulk mean temperature of the water leaving the pipe in C is (A) (B) 6 (C) 7 (D) 0 Explanation: " q w " wi = 500x x = 0 q = 0 " wi x = 3 q = = qavg = = 3750 q Area = mcp T avg π = (T 0) T =. + 0 = 6. C 5. If Explanation: " qw = 5000, and the convection heat transfer coefficient at the pipe outlet is 000 W / m K, the temperature in C at the inner surface of the pipe at the outlet is (A) 7 (B) 76 (C) 79 (D) 8 " w " q w = 5000 consant q A = MCP T 3 Q = 5000 π = (To 0) T0 0 = 56.3 = To = 76.3 C Heat flux between any two sections is same Q = ha(t T ) p p o Q " But = q w = 5000 = h(tp T o) A 5000 = 000(T 76.3) T = = 8.3 p Linked Answer Questions: Q.5 to Q.55 Carry Two Marks Each Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 5 & 53 In orthogonal turning of a bar of 00 mm diameter with a feed of 0.5 mm/rev, depth of cut of mm and cutting velocity of 90 m/min, it is observed that the main (tangential) cutting force is perpendicular to the friction force acting at the chip-tool interface. The main (tangential) cutting force is 500 N. GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 6
17 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 5. The orthogonal rake angle of the cutting tool in degree is (A) Zero (B) 3.58 (C) 5 (D) 7.6 Answer: (A) As cutting Rake angle α = 0 ar f is f to F F 53. The normal force acting at the chip-tool interface in N is Answer: (A) 000 (B) 500 (C) 000 (D) 500 (B) Normal force N = FH cos α FV sin α = 500 cos0 F sin0 = 500 v Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 5 & 55 In a simple Brayton cycle, the pressure ration is 8 and temperatures at the entrance of compressor and turbine are 300 K and 00 K, respectively. Both compressor and gas turbine have isentropic efficiencies equal to 0.8. For the gas, assume a constant value of c (specific heat at constant pressure) equal to p kj/kgk and ratio of specific heats as.. Neglect changes in kinetic and potential energies. 5. The power required by the compressor in kw/kg of gas flow rate is Answer: (A) 9.7 (B) 3. (C) 30.3 (D) (C) r = 8; T = 300K; T = 00K D 3 γ =. 0. T γ = ( r ) ( ). P = r T = 53.3K T γ T T w η = = T T T 300 C 0.8 γ 0. γ. T T = 60.9k; = = T 3 r P 8 T = 77.86k 3 T T w T η T = 0.8 = T T T = ( ) ( ) w = C T T = = 30.3 C P ' 3 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 7
18 ME-GATE-03 PAPER 55. The thermal efficiency of the cycle in percentage (%) is (A).8 (B) 38.6 (C).8 (D) 53. Answer: (A) ( ) ( ) w = C T T = w = 50.7 T P 3 wt wc Thermal efficiency = θ = = = C T T ( ) ( ) P 3.8% Q. No Carry One Mark Each 56. Complete the sentence: Universalism is to particularism as diffuseness is to (A) specificity (B) neutrality (C) generality (D) adaptation Answer: (A) The relation is that of antonyms 57. Were you a bird, you in the sky. (A) would fly (B) shall fly (C) should fly (D) shall have flown Answer: (A) 58. Which one of the following options is the closest in meaning to the word given below? Nadir (A) Highest (B) Lowest (C) Medium (D) Integration Nadir in the lowest point on a curve 59. Choose the grammatically INCORRECT sentence: (A) He is of Asian origin (B) They belonged to Africa (C) She is an European (D) They migrated from India to Australia 60. What will be the maximum sum of,, 0,...? (A) 50 (B) 50 (C) 506 (D) 500 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 8
19 ME-GATE-03 PAPER The maximum sum is the sum of,, The sum of n terms of an AP = n a ( n ) d + In this case, n =, a = and d = Sum = + = 6 = 506 Q. No Carry Two Marks Each 6. Out of all the -digit integers between and 00, a -digit number has to be selected at random. What is the probability that the selected number is not divisible by 7? (A) 3/90 (B) /90 (C) 78/90 (D) 77/90 The number of digit multiples of 7 = 3 Probability of choosing a number Not divisible by = = A tourist covers half of his journey by train at 60 km/h, half of the remainder by bus at 30 km/h and the rest by cycle at 0 km/h. The average of the tourist in km/h during his entire journey is (A) 36 (B) 30 (C) (D) 8 Let the total distance covered be D Now, average speed = D Total time taken D 0 = = = = km / hr D D D Find the sum of the expression (A) 7 (B) 8 (C) 9 (D) 0 GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 9
20 ME-GATE-03 PAPER The expression can be written as ( ) ( ) ( 3) ( ) ( 8) ( 80 ) ( ) ( ) ( + ) ( ) ( ) = The current erection cost of a structure is Rs. 3,00. If the labour wages per day increase by /5 of the current wages and the working hours decrease by / of the current period, then the new cost of erection in Rs. is (A) 6,500 (B) 5,80 (C),000 (D) 0,0 Let W be the labour wages, and T be the working hours. Now, total cost is a function of W T Increase in wages = 0% Revised wages =. W Decrease in labour time = 00 % 3 Re vised time = T T = 3 Re vised Total cos t =. WT =.5 WT = = After several defeats in wars, Robert Bruce went in exile and wanted to commit suicide. Just before committing suicide, he came across a spider attempting tirelessly to have its net. Time and again the spider failed but that did not deter it to refrain from making attempts. Such attempts by the spider made Bruce curious. Thus, Bruce started observing the near-impossible goal of the spider to have the net. Ultimately, the spider succeeded in having its net despite several failures. Such act of the spider encouraged Bruce not to commit suicide. And then, Bruce went back again and won many a battle, and the rest is history. Which one of the following assertions is best supported by the above information? (A) Failure is the pillar of success (B) Honesty is the best policy (C) Life begins and ends with adventures (D) No adversity justifies giving up hope GATEFORUM- India s No. institute for GATE training 0
ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 013 Question Booklet Code C ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are
013 Question Booklet Code C ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are
SESSION - 1. Auhippo.com
 SESSION - 1 Auhippo.com 013 Question Booklet Code A ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
SESSION - 1 Auhippo.com 013 Question Booklet Code A ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
SESSION - 1. Auhippo.com
 SESSION - 1 013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
SESSION - 1 013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING
 013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Sub. Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
General Aptitude (GA) Set-1. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
2014 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? 20cm T =? 20kg
 1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SECTION A. 8 kn/m. C 3 m 3m
 SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
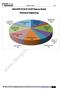 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS. Level 3 Unit 5
 BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS Level 3 Unit 5 FORCES AS VECTORS Vectors have a magnitude (amount) and a direction. Forces are vectors FORCES AS VECTORS (2 FORCES) Forces F1 and F2 are in
BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS Level 3 Unit 5 FORCES AS VECTORS Vectors have a magnitude (amount) and a direction. Forces are vectors FORCES AS VECTORS (2 FORCES) Forces F1 and F2 are in
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
3 Shearing stress. 3.1 Introduction
 3 Shearing stress 3.1 Introduction In Chapter 1 we made a study of tensile and compressive stresses, which we called direct stresses. There is another type of stress which plays a vital role in the behaviour
3 Shearing stress 3.1 Introduction In Chapter 1 we made a study of tensile and compressive stresses, which we called direct stresses. There is another type of stress which plays a vital role in the behaviour
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS ACADEMIC YEAR
 CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS ACADEMIC YEAR 2014-2015 UNIT - 1 STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART- A 1. Define tensile stress and tensile strain. The stress induced
CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS ACADEMIC YEAR 2014-2015 UNIT - 1 STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART- A 1. Define tensile stress and tensile strain. The stress induced
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at C of the beam shown in Fig. 1 4a.
 E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
ROTATING RING. Volume of small element = Rdθbt if weight density of ring = ρ weight of small element = ρrbtdθ. Figure 1 Rotating ring
 ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 2018
 TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
10 minutes reading time is allowed for this paper.
 EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5/2/2015 7:42 AM. Chapter 17. Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE
 5//05 7:4 AM Chapter 7 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods 5//05 7:4 AM Chapter Outline Principle of Work and Energy for a Rigid Body Work of Forces Acting on a Rigid Body Kinetic
5//05 7:4 AM Chapter 7 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods 5//05 7:4 AM Chapter Outline Principle of Work and Energy for a Rigid Body Work of Forces Acting on a Rigid Body Kinetic
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
STRESS. Bar. ! Stress. ! Average Normal Stress in an Axially Loaded. ! Average Shear Stress. ! Allowable Stress. ! Design of Simple Connections
 STRESS! Stress Evisdom! verage Normal Stress in an xially Loaded ar! verage Shear Stress! llowable Stress! Design of Simple onnections 1 Equilibrium of a Deformable ody ody Force w F R x w(s). D s y Support
STRESS! Stress Evisdom! verage Normal Stress in an xially Loaded ar! verage Shear Stress! llowable Stress! Design of Simple onnections 1 Equilibrium of a Deformable ody ody Force w F R x w(s). D s y Support
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3
 MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3 Samantha Ramirez TENSION AND COMPRESSION TESTS Tension and compression tests are used primarily to determine the relationship between σ avg and ε avg in any material.
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3 Samantha Ramirez TENSION AND COMPRESSION TESTS Tension and compression tests are used primarily to determine the relationship between σ avg and ε avg in any material.
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts
 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 87 C H A P T E R 4 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 1. Introduction.. Load. 3. Stress. 4. Strain. 5. Tensile Stress and Strain. 6. Compressive Stress and Strain. 7. Young's
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 87 C H A P T E R 4 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 1. Introduction.. Load. 3. Stress. 4. Strain. 5. Tensile Stress and Strain. 6. Compressive Stress and Strain. 7. Young's
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory
 7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 3013 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6
 COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
18.Define the term modulus of resilience. May/June Define Principal Stress. 20. Define Hydrostatic Pressure.
 CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
Unit I Stress and Strain
 Unit I Stress and Strain Stress and strain at a point Tension, Compression, Shear Stress Hooke s Law Relationship among elastic constants Stress Strain Diagram for Mild Steel, TOR steel, Concrete Ultimate
Unit I Stress and Strain Stress and strain at a point Tension, Compression, Shear Stress Hooke s Law Relationship among elastic constants Stress Strain Diagram for Mild Steel, TOR steel, Concrete Ultimate
GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper
 GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
Direct and Shear Stress
 Direct and Shear Stress 1 Direct & Shear Stress When a body is pulled by a tensile force or crushed by a compressive force, the loading is said to be direct. Direct stresses are also found to arise when
Direct and Shear Stress 1 Direct & Shear Stress When a body is pulled by a tensile force or crushed by a compressive force, the loading is said to be direct. Direct stresses are also found to arise when
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion
 EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel.
 TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The volume of a sphere of diameter 1 unit is than the volume of a cube of side 1 unit. (A) least (B) less (C) lesser (D) low Q.2
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The volume of a sphere of diameter 1 unit is than the volume of a cube of side 1 unit. (A) least (B) less (C) lesser (D) low Q.2
Chapter 8 Structural Design and Analysis. Strength and stiffness 5 types of load: Tension Compression Shear Bending Torsion
 Chapter 8 Structural Design and Analysis 1 Strength and stiffness 5 types of load: Tension Compression Shear Bending Torsion Normal Stress Stress is a state when a material is loaded. For normal forces
Chapter 8 Structural Design and Analysis 1 Strength and stiffness 5 types of load: Tension Compression Shear Bending Torsion Normal Stress Stress is a state when a material is loaded. For normal forces
[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams
![[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams](/thumbs/92/110949676.jpg) [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams Page 1 of 28 [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8.1] Bending of Beams (will not be covered in class) [8.2] Bending Strain and Stress [8.3] Shear in Straight
[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams Page 1 of 28 [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8.1] Bending of Beams (will not be covered in class) [8.2] Bending Strain and Stress [8.3] Shear in Straight
A Notes Formulas. This chapter is composed of 15 double pages which list, with commentaries, the results for:
 The modeling process is a key step of conception. First, a crude modeling allows to validate (or not) the concept and identify the best combination of properties that maximize the performances. Then, a
The modeling process is a key step of conception. First, a crude modeling allows to validate (or not) the concept and identify the best combination of properties that maximize the performances. Then, a
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Inertia Forces in Reciprocating. Parts. 514 l Theory of Machines
 514 l Theory of Machines 15 Features 1. Introduction.. Resultant Effect of a System of Forces Acting on a Rigid Body. 3. D-Alembert s Principle. 4. Velocity and Acceleration of the Reciprocating Parts
514 l Theory of Machines 15 Features 1. Introduction.. Resultant Effect of a System of Forces Acting on a Rigid Body. 3. D-Alembert s Principle. 4. Velocity and Acceleration of the Reciprocating Parts
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The volume of a sphere of diameter 1 unit is than the volume of a cube of side 1 unit. (A) least (B) less (C) lesser (D) low Q.2
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The volume of a sphere of diameter 1 unit is than the volume of a cube of side 1 unit. (A) least (B) less (C) lesser (D) low Q.2
A concrete cylinder having a a diameter of of in. mm and elasticity. Stress and Strain: Stress and Strain: 0.
 2011 earson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. ll rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently 8 1. 3 1. concrete cylinder having a a diameter of of 6.00
2011 earson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. ll rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently 8 1. 3 1. concrete cylinder having a a diameter of of 6.00
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
 5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
Strain Gages. Approximate Elastic Constants (from University Physics, Sears Zemansky, and Young, Reading, MA, Shear Modulus, (S) N/m 2
 When you bend a piece of metal, the Strain Gages Approximate Elastic Constants (from University Physics, Sears Zemansky, and Young, Reading, MA, 1979 Material Young's Modulus, (E) 10 11 N/m 2 Shear Modulus,
When you bend a piece of metal, the Strain Gages Approximate Elastic Constants (from University Physics, Sears Zemansky, and Young, Reading, MA, 1979 Material Young's Modulus, (E) 10 11 N/m 2 Shear Modulus,
2. Rigid bar ABC supports a weight of W = 50 kn. Bar ABC is pinned at A and supported at B by rod (1). What is the axial force in rod (1)?
 IDE 110 S08 Test 1 Name: 1. Determine the internal axial forces in segments (1), (2) and (3). (a) N 1 = kn (b) N 2 = kn (c) N 3 = kn 2. Rigid bar ABC supports a weight of W = 50 kn. Bar ABC is pinned at
IDE 110 S08 Test 1 Name: 1. Determine the internal axial forces in segments (1), (2) and (3). (a) N 1 = kn (b) N 2 = kn (c) N 3 = kn 2. Rigid bar ABC supports a weight of W = 50 kn. Bar ABC is pinned at
Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Bhattacharya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 Torsion - I
 Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Bhattacharya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 Torsion - I Welcome to the first lesson of Module 4 which is on Torsion
Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Bhattacharya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 Torsion - I Welcome to the first lesson of Module 4 which is on Torsion
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
Entrance exam Master Course
 - 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
- 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALYSIS OF GATE 2012 Mechanical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALYSIS OF GATE 2012 Mechanical
ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Chapter III. Mechanical Properties of Materials 1 Tension and Compression Test The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation
ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Chapter III. Mechanical Properties of Materials 1 Tension and Compression Test The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation
GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering
 GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (P) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-Kutta method (S)
GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (P) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-Kutta method (S)
1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor.
 Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER I
 C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER I FROM 1995-018 UPSC Engineering Services Eamination, State Engineering Service Eamination & Public Sector Eamination. Regd. office
C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER I FROM 1995-018 UPSC Engineering Services Eamination, State Engineering Service Eamination & Public Sector Eamination. Regd. office
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
3. Kinetics of Particles
 3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
2. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, J is defined as. Sample copy
 GATE PATHSHALA - 91. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, is defined as z π r dr 0 R r π R π D For a solid shaft π (6) QP 0 π d Solid shaft π d Hollow shaft, " ( do
GATE PATHSHALA - 91. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, is defined as z π r dr 0 R r π R π D For a solid shaft π (6) QP 0 π d Solid shaft π d Hollow shaft, " ( do
Physics in Faculty of
 Why we study Physics in Faculty of Engineering? Dimensional analysis Scalars and vector analysis Rotational of a rigid body about a fixed axis Rotational kinematics 1. Dimensional analysis The ward dimension
Why we study Physics in Faculty of Engineering? Dimensional analysis Scalars and vector analysis Rotational of a rigid body about a fixed axis Rotational kinematics 1. Dimensional analysis The ward dimension
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose the correct verb to fill in the blank below: Let us. (a) introvert (b) alternate (c) atheist (d) altruist Q. Choose the most appropriate word from the options
1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose the correct verb to fill in the blank below: Let us. (a) introvert (b) alternate (c) atheist (d) altruist Q. Choose the most appropriate word from the options
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
DYNAMICS VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods. Seventh Edition CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 7 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: DYNAMICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods
CHAPTER 7 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: DYNAMICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s
 D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
