26. LECTURE 26. Objectives
|
|
|
- Dinah Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6. LECTURE 6 Objectives I understand the idea behind the Method of Lagrange Multipliers. I can use the method of Lagrange Multipliers to maximize a multivariate function subject to a constraint. Suppose you have a function f. Back in Lecture, we discussed how to optimize a function like f over a closed region. This required that we found a critical point inside the region and then look at the boundary of that region. When we wanted to find an extreme point on the boundary, we had to define each line on the boundary, plug in that line into our function, and find the extreme points. It was a long process. Today, we learn a different method for finding the critical points of a function on some boundary. This method is called Lagrange Multipliers. It can sometimes be easier to use than the plugging in method we saw before, especially when you are considering more than two independent variables, and the boundary can be described by just one function, g. The concept is a little technical, but is easy to see in a picture. Below, we have a function f(x, y) =z whose level curves are in red. We also have a constraint g(x, y) =k in blue. Notice that f equals a variable z, which g equals a constant k. Restricted to the constraint, what is the largest value f achieves on g? ccording to the picture, the largest value is. g(x, y) =c z =0 z = t that point, something remarkable happens. The gradients of both curves are parallel! That means, an extreme point happens when rf = fair question to ask is, where did come from? Notice that at the maximum point in the picture, we can only say the gradients are parallel. That means they have the same direction but possibly not the same magnitude! For example, the picture below provides gradients that are parallel but have different magnitudes. Including, which may be negative, helps account for this. 4 rg.
2 g(x, y) =k z =0 z = The following steps constitutes the method of Lagrange multipliers: () Find rf and rg in terms of x and y. () Set up the equations rf(x, y) = rg(x, y) g(x, y) =k This will given you a system of equations based on the components of the gradients. () Solve this system of equations to get x, y, and possibly. (There may be multiple solutions.) (4) For each of these solutions, find f(x, y) and compare the values you get. Every solution that gives a maximum value is a maximum point, and every solution that gives a minimum value gives a minimum point. Example 6.: Three alleles (alternative versions of a gene), B, and O determine the four blood types ( or O), B (BB or BO), O (OO), and B. The Hardy-Weinberg Law states that the percentage of the population who carry two different alleles is P =pq +pr +rq where p, q, and r are the proportions of, B, and O in the population. Use the fact that p+q+r = to show that P is at most. Solution 6.: Notice that we have a function of three independent variables and a constraint P (p, q, r) =pq +pr +rq p + q + r =. The method we discussed in Lecture would require that we try to substitute and then find critical points. s you might guess, this would be an exhausting calculation. better approach is to use the Method of Lagrange Multipliers. Let s begin by finding rf and rg. 0 rf q +r p +r p +q 5
3 0 Now, if then we get the following equations: q +r = p +r = p +q = p + q + r = rg = rf We want to solve for p, q, and r using these equations. If it benefits us, we can also solve for. If we take the first two equations, we can combine them: rg q +r =p +r. Once we simplify by canceling out r and dividing by, we get q = p. If we take the second and third equation, we get p +r =p +q Once we simplify by canceling out p and dividing by, we get From these to calculations, we get r = q. p = q = r. If we substitute r for p and q in p + q + r =, we get r =. Therefore p = q = r =. So the extreme point is (/, /, /). ccording to the problem, we want a maximum. How can we know if this is a maximum? We do this by testing a point that satisfies the constraint. Our point: f(/, /, /) = = 6 9 = nother (random, made-up) point on g is (, 0, 0). Notice that g(, 0, 0) =. What s the proportion according to the Hardy-Weinberg Law? f(, 0, 0) = = 0 Since our extreme point (/, /, /) yields a bigger value than our random point (, 0, 0), we know that the point we found was a maximum! Example 6.: package in the shape of a rectangular box can be mailed by the US Postal Service if the sum of its length and girth (the perimeter of a cross-section perpendicular to the length) is at most 08 in. Find the dimensions of the package with largest volume that can be mailed. 6
4 Solution 6.4: Let s begin with a picture. girth z x y The girth of the package is y +z. The length is x. So we have the constraint x +y +z =08 and we d like to maximize volume. That is, we want to maximize. Let s begin by finding the gradients: V (x, y, z) =xyz rv = rg = yz xz xy From rv = rg, we get () yz = () xz = () xy = (4) x +y +z =08 From the second equation, we can solve for x and find x = z. We can substitute this into the third equation to get y = z which can be simplified to y = z. If we substitute this in equation, we get y = which can be simplified to y = ± p. Because y is a measurement, it must be y = p. If y = p, then z = p and x = p. 7
5 . Now, we can substitute this into the fourth equation to get p + p + p =08 If we simplify, we get p =8. Therefore, x =6,y =8, and z =8. The volume is therefore V (6, 8, 8) = (6)(8) =, 664. That is, the maximum volume is, 664 cubic inches, or approximately 6.74 cubic feet. Summary of Ideas Lagrange multipliers allow you to maximize a function f(x, y) subject to a constraint g(x, y) =k. It is a method that can be used to find the extreme points of a function on the boundary of a closed region. The method asks you to solve for x, y, and given the following expressions rf = rg and g(x, y) =k We plug in to determine what points are maximums and what points are minimums. 8
Lagrange Multipliers
 Calculus 3 Lia Vas Lagrange Multipliers Constrained Optimization for functions of two variables. To find the maximum and minimum values of z = f(x, y), objective function, subject to a constraint g(x,
Calculus 3 Lia Vas Lagrange Multipliers Constrained Optimization for functions of two variables. To find the maximum and minimum values of z = f(x, y), objective function, subject to a constraint g(x,
MATH LESSON 24 EXAMPLE SOLUTIONS OCTOBER 27, 2017
 MATH 16020 LESSON 24 EXAMPLE SOLUTIONS OCTOBER 27, 2017 Example 1. We are tasked with constructing a rectangular box with a volume of 64 cubic feet. The material for the top costs 8 dollars per square
MATH 16020 LESSON 24 EXAMPLE SOLUTIONS OCTOBER 27, 2017 Example 1. We are tasked with constructing a rectangular box with a volume of 64 cubic feet. The material for the top costs 8 dollars per square
Absolute Extrema and Constrained Optimization
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Absolute Extrema and Constrained Optimization Recall that a function f (x) is said to have a relative maximum at x = c if f (c) f (x) for all values of x in some open interval containing
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Absolute Extrema and Constrained Optimization Recall that a function f (x) is said to have a relative maximum at x = c if f (c) f (x) for all values of x in some open interval containing
Lagrange Multipliers
 Lagrange Multipliers 3-15-2018 The method of Lagrange multipliers deals with the problem of finding the maxima and minima of a function subject to a side condition, or constraint. Example. Find graphically
Lagrange Multipliers 3-15-2018 The method of Lagrange multipliers deals with the problem of finding the maxima and minima of a function subject to a side condition, or constraint. Example. Find graphically
Method of Lagrange Multipliers
 Method of Lagrange Multipliers A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram September 2013 Lagrange multiplier method is a technique
Method of Lagrange Multipliers A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram September 2013 Lagrange multiplier method is a technique
review To find the coefficient of all the terms in 15ab + 60bc 17ca: Coefficient of ab = 15 Coefficient of bc = 60 Coefficient of ca = -17
 1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
LESSON 25: LAGRANGE MULTIPLIERS OCTOBER 30, 2017
 LESSON 5: LAGRANGE MULTIPLIERS OCTOBER 30, 017 Lagrange multipliers is another method of finding minima and maxima of functions of more than one variable. In fact, many of the problems from the last homework
LESSON 5: LAGRANGE MULTIPLIERS OCTOBER 30, 017 Lagrange multipliers is another method of finding minima and maxima of functions of more than one variable. In fact, many of the problems from the last homework
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I
 IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 12: Nonlinear optimization, continued Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson October 20, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I October 20,
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 12: Nonlinear optimization, continued Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson October 20, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I October 20,
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions
 LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
Math 212-Lecture Interior critical points of functions of two variables
 Math 212-Lecture 24 13.10. Interior critical points of functions of two variables Previously, we have concluded that if f has derivatives, all interior local min or local max should be critical points.
Math 212-Lecture 24 13.10. Interior critical points of functions of two variables Previously, we have concluded that if f has derivatives, all interior local min or local max should be critical points.
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I
 LESSON 6. POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I LESSON 6. POLYNOMIALS OPERATIONS I 63 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Adding and Subtracting a. Definition of polynomial, term, and coefficient b. Evaluating
LESSON 6. POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I LESSON 6. POLYNOMIALS OPERATIONS I 63 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Adding and Subtracting a. Definition of polynomial, term, and coefficient b. Evaluating
Practice problems for Exam 1. a b = (2) 2 + (4) 2 + ( 3) 2 = 29
 Practice problems for Exam.. Given a = and b =. Find the area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides a and b. A = a b a ı j k b = = ı j + k = ı + 4 j 3 k Thus, A = 9. a b = () + (4) + ( 3)
Practice problems for Exam.. Given a = and b =. Find the area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides a and b. A = a b a ı j k b = = ı j + k = ı + 4 j 3 k Thus, A = 9. a b = () + (4) + ( 3)
(Refer Slide Time: 0:35)
 Fluid Dynamics And Turbo Machines. Professor Dr Shamit Bakshi. Department Of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute Of Technology Madras. Part A. Module-1. Lecture-4. Tutorial. (Refer Slide Time: 0:35)
Fluid Dynamics And Turbo Machines. Professor Dr Shamit Bakshi. Department Of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute Of Technology Madras. Part A. Module-1. Lecture-4. Tutorial. (Refer Slide Time: 0:35)
Suggested Approach Pythagorean Theorem The Converse of Pythagorean Theorem Applications of Pythagoras Theorem. Notes on Teaching 3
 hapter 10 Pythagorean Theorem Suggested pproach Students can explore Pythagorean Theorem using the GSP activity in lass ctivity 1. There are over 300 proofs of Pythagorean Theorem. Teachers may illustrate
hapter 10 Pythagorean Theorem Suggested pproach Students can explore Pythagorean Theorem using the GSP activity in lass ctivity 1. There are over 300 proofs of Pythagorean Theorem. Teachers may illustrate
Need help? Try or 4.1 Practice Problems
 Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Friday 9/29/17 (A) Monday 10/9/17 (B) 4.1 Operations with polynomials Tuesday 10/10/17 (A) Wednesday 10/11/17 (B) 4.2 Factoring and solving completely Thursday
Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Friday 9/29/17 (A) Monday 10/9/17 (B) 4.1 Operations with polynomials Tuesday 10/10/17 (A) Wednesday 10/11/17 (B) 4.2 Factoring and solving completely Thursday
Calculus Example Exam Solutions
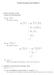 Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
 Twitter: @Owen134866 www.mathsfreeresourcelibrary.com Prior Knowledge Check 1) Simplify: a) 3x 2 5x 5 b) 5x3 y 2 15x 7 2) Factorise: a) x 2 2x 24 b) 3x 2 17x + 20 15x 2 y 3 3) Use long division to calculate:
Twitter: @Owen134866 www.mathsfreeresourcelibrary.com Prior Knowledge Check 1) Simplify: a) 3x 2 5x 5 b) 5x3 y 2 15x 7 2) Factorise: a) x 2 2x 24 b) 3x 2 17x + 20 15x 2 y 3 3) Use long division to calculate:
25. Chain Rule. Now, f is a function of t only. Expand by multiplication:
 25. Chain Rule The Chain Rule is present in all differentiation. If z = f(x, y) represents a two-variable function, then it is plausible to consider the cases when x and y may be functions of other variable(s).
25. Chain Rule The Chain Rule is present in all differentiation. If z = f(x, y) represents a two-variable function, then it is plausible to consider the cases when x and y may be functions of other variable(s).
Constrained Optimization
 Constrained Optimization Joshua Wilde, revised by Isabel Tecu, Takeshi Suzuki and María José Boccardi August 13, 2013 1 General Problem Consider the following general constrained optimization problem:
Constrained Optimization Joshua Wilde, revised by Isabel Tecu, Takeshi Suzuki and María José Boccardi August 13, 2013 1 General Problem Consider the following general constrained optimization problem:
Math Example Set 12A. m10360/homework.html
 Estimating Partial Derivatives. Math 10360 Example Set 12A You should review the estimation for derivative for one variable functions. You can find a pdf pencast that reviews the backward, central, and
Estimating Partial Derivatives. Math 10360 Example Set 12A You should review the estimation for derivative for one variable functions. You can find a pdf pencast that reviews the backward, central, and
D u f f x h f y k. Applying this theorem a second time, we have. f xx h f yx k h f xy h f yy k k. f xx h 2 2 f xy hk f yy k 2
 93 CHAPTER 4 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES We close this section b giving a proof of the first part of the Second Derivatives Test. Part (b) has a similar proof. PROOF OF THEOREM 3, PART (A) We compute the second-order
93 CHAPTER 4 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES We close this section b giving a proof of the first part of the Second Derivatives Test. Part (b) has a similar proof. PROOF OF THEOREM 3, PART (A) We compute the second-order
Practice Midterm 2 Math 2153
 Practice Midterm 2 Math 23. Decide if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE and circle your answer. You do NOT need to justify your answers. (a) ( point) If both partial derivatives f x and f y exist
Practice Midterm 2 Math 23. Decide if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE and circle your answer. You do NOT need to justify your answers. (a) ( point) If both partial derivatives f x and f y exist
$100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500
 Tests for Symmetry Families of Functions Parts of a Function Steps, Pieces & Rates Inverses and f(g(x)) Models of Variation Round 2 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 Final Jeopardy
Tests for Symmetry Families of Functions Parts of a Function Steps, Pieces & Rates Inverses and f(g(x)) Models of Variation Round 2 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 Final Jeopardy
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations
 Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
13. LECTURE 13. Objectives
 13. LECTURE 13 Objectives I can use Clairaut s Theorem to make my calculations easier. I can take higher derivatives. I can check if a function is a solution to a partial differential equation. Higher
13. LECTURE 13 Objectives I can use Clairaut s Theorem to make my calculations easier. I can take higher derivatives. I can check if a function is a solution to a partial differential equation. Higher
Optimization. Numerical Optimization. Linear Programming
 Mathematical Modeling Lia Vas Optimization. Numerical Optimization. Linear Programming Problems asking for a set of optimal conditions (maxima or minima) in relation to a certain situation appear very
Mathematical Modeling Lia Vas Optimization. Numerical Optimization. Linear Programming Problems asking for a set of optimal conditions (maxima or minima) in relation to a certain situation appear very
Chapter 5 Simplifying Formulas and Solving Equations
 Chapter 5 Simplifying Formulas and Solving Equations Look at the geometry formula for Perimeter of a rectangle P = L W L W. Can this formula be written in a simpler way? If it is true, that we can simplify
Chapter 5 Simplifying Formulas and Solving Equations Look at the geometry formula for Perimeter of a rectangle P = L W L W. Can this formula be written in a simpler way? If it is true, that we can simplify
Solutions to Homework 5
 Solutions to Homework 5 1.7 Problem. f = x 2 y, y 2 x. If we solve f = 0, we can find two solutions (0, 0) and (1, 1). At (0, 0), f xx = 0, f yy = 0, f xy = and D = f xx f yy fxy 2 < 0, therefore (0, 0)
Solutions to Homework 5 1.7 Problem. f = x 2 y, y 2 x. If we solve f = 0, we can find two solutions (0, 0) and (1, 1). At (0, 0), f xx = 0, f yy = 0, f xy = and D = f xx f yy fxy 2 < 0, therefore (0, 0)
26. Directional Derivatives & The Gradient
 26. Directional Derivatives & The Gradient Given a multivariable function z = f(x, y) and a point on the xy-plane P 0 = (x 0, y 0 ) at which f is differentiable (i.e. it is smooth with no discontinuities,
26. Directional Derivatives & The Gradient Given a multivariable function z = f(x, y) and a point on the xy-plane P 0 = (x 0, y 0 ) at which f is differentiable (i.e. it is smooth with no discontinuities,
UNC Charlotte 2004 Algebra with solutions
 with solutions March 8, 2004 1. Let z denote the real number solution to of the digits of z? (A) 13 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 (E) 17 3 + x 1 = 5. What is the sum Solution: E. Square both sides twice to get
with solutions March 8, 2004 1. Let z denote the real number solution to of the digits of z? (A) 13 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 (E) 17 3 + x 1 = 5. What is the sum Solution: E. Square both sides twice to get
Which one of the following is the solution to the equation? 1) 4(x - 2) + 6 = 2x ) A) x = 5 B) x = -6 C) x = -5 D) x = 6
 Review for Final Exam Math 124A (Flatley) Name Which one of the following is the solution to the equation? 1) 4(x - 2) + 6 = 2x - 14 1) A) x = 5 B) x = -6 C) x = -5 D) x = 6 Solve the linear equation.
Review for Final Exam Math 124A (Flatley) Name Which one of the following is the solution to the equation? 1) 4(x - 2) + 6 = 2x - 14 1) A) x = 5 B) x = -6 C) x = -5 D) x = 6 Solve the linear equation.
MATH The Chain Rule Fall 2016 A vector function of a vector variable is a function F: R n R m. In practice, if x 1, x n is the input,
 MATH 20550 The Chain Rule Fall 2016 A vector function of a vector variable is a function F: R n R m. In practice, if x 1, x n is the input, F(x 1,, x n ) F 1 (x 1,, x n ),, F m (x 1,, x n ) where each
MATH 20550 The Chain Rule Fall 2016 A vector function of a vector variable is a function F: R n R m. In practice, if x 1, x n is the input, F(x 1,, x n ) F 1 (x 1,, x n ),, F m (x 1,, x n ) where each
Math 2163, Practice Exam II, Solution
 Math 63, Practice Exam II, Solution. (a) f =< f s, f t >=< s e t, s e t >, an v v = , so D v f(, ) =< ()e, e > =< 4, 4 > = 4. (b) f =< xy 3, 3x y 4y 3 > an v =< cos π, sin π >=, so
Math 63, Practice Exam II, Solution. (a) f =< f s, f t >=< s e t, s e t >, an v v = , so D v f(, ) =< ()e, e > =< 4, 4 > = 4. (b) f =< xy 3, 3x y 4y 3 > an v =< cos π, sin π >=, so
2015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution
 015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities
 Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Factorisation CHAPTER Introduction
 FACTORISATION 217 Factorisation CHAPTER 14 14.1 Introduction 14.1.1 Factors of natural numbers You will remember what you learnt about factors in Class VI. Let us take a natural number, say 30, and write
FACTORISATION 217 Factorisation CHAPTER 14 14.1 Introduction 14.1.1 Factors of natural numbers You will remember what you learnt about factors in Class VI. Let us take a natural number, say 30, and write
f x, y x 2 y 2 2x 6y 14. Then
 SECTION 11.7 MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM VALUES 645 absolute minimum FIGURE 1 local maimum local minimum absolute maimum Look at the hills and valles in the graph of f shown in Figure 1. There are two points a,
SECTION 11.7 MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM VALUES 645 absolute minimum FIGURE 1 local maimum local minimum absolute maimum Look at the hills and valles in the graph of f shown in Figure 1. There are two points a,
Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7)
 Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7) 1 Graph f(x) = x and g(x) = 1 x 4. Then describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = x to the graph 2 of g(x) = 1 2 x 4. The transformations are
Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7) 1 Graph f(x) = x and g(x) = 1 x 4. Then describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = x to the graph 2 of g(x) = 1 2 x 4. The transformations are
LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS 253
 LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS 5 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Properties of Exponents Definition of exponent, power, and base b. Multiplication Property c. Division Property
LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS 5 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Properties of Exponents Definition of exponent, power, and base b. Multiplication Property c. Division Property
Writing and Graphing Inequalities
 4.1 Writing and Graphing Inequalities solutions of an inequality? How can you use a number line to represent 1 ACTIVITY: Understanding Inequality Statements Work with a partner. Read the statement. Circle
4.1 Writing and Graphing Inequalities solutions of an inequality? How can you use a number line to represent 1 ACTIVITY: Understanding Inequality Statements Work with a partner. Read the statement. Circle
1. For each function, find all of its critical points and then classify each point as a local extremum or saddle point.
 Solutions Review for Exam # Math 6. For each function, find all of its critical points and then classify each point as a local extremum or saddle point. a fx, y x + 6xy + y Solution.The gradient of f is
Solutions Review for Exam # Math 6. For each function, find all of its critical points and then classify each point as a local extremum or saddle point. a fx, y x + 6xy + y Solution.The gradient of f is
Review Sheet for the Final
 Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Name: Instructor: Lecture time: TA: Section time:
 Math 2220 Prelim 1 February 17, 2009 Name: Instructor: Lecture time: TA: Section time: INSTRUCTIONS READ THIS NOW This test has 6 problems on 7 pages worth a total of 100 points. Look over your test package
Math 2220 Prelim 1 February 17, 2009 Name: Instructor: Lecture time: TA: Section time: INSTRUCTIONS READ THIS NOW This test has 6 problems on 7 pages worth a total of 100 points. Look over your test package
CALCULUS III. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS III Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iv Three Dimensional Space... Introduction... The -D Coordinate System... Equations of Lines... 9 Equations of Planes... 5 Quadric
CALCULUS III Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iv Three Dimensional Space... Introduction... The -D Coordinate System... Equations of Lines... 9 Equations of Planes... 5 Quadric
Linear Algebra Review
 Linear Algebra Review ORIE 4741 September 1, 2017 Linear Algebra Review September 1, 2017 1 / 33 Outline 1 Linear Independence and Dependence 2 Matrix Rank 3 Invertible Matrices 4 Norms 5 Projection Matrix
Linear Algebra Review ORIE 4741 September 1, 2017 Linear Algebra Review September 1, 2017 1 / 33 Outline 1 Linear Independence and Dependence 2 Matrix Rank 3 Invertible Matrices 4 Norms 5 Projection Matrix
Preface.
 This document was written and copyrighted by Paul Dawkins. Use of this document and its online version is governed by the Terms and Conditions of Use located at. The online version of this document is
This document was written and copyrighted by Paul Dawkins. Use of this document and its online version is governed by the Terms and Conditions of Use located at. The online version of this document is
Find the absolute maximum and the absolute minimum of the function. f(x, y) = 3x + 4y. g(x, y) = x 2 + y 2 = 25.
 MATLAB assignment Math 222, Fall 2011 ROOT FINDING AND OPTIMIZATION!!! Part I: The Mathematical Prelude So the goal of this part of the assignment is to approximate solutions to nonlinear systems of equations
MATLAB assignment Math 222, Fall 2011 ROOT FINDING AND OPTIMIZATION!!! Part I: The Mathematical Prelude So the goal of this part of the assignment is to approximate solutions to nonlinear systems of equations
Algebraic Expressions
 Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
Math 212-Lecture 8. The chain rule with one independent variable
 Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities
 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Tangent Plane. Linear Approximation. The Gradient
 Calculus 3 Lia Vas Tangent Plane. Linear Approximation. The Gradient The tangent plane. Let z = f(x, y) be a function of two variables with continuous partial derivatives. Recall that the vectors 1, 0,
Calculus 3 Lia Vas Tangent Plane. Linear Approximation. The Gradient The tangent plane. Let z = f(x, y) be a function of two variables with continuous partial derivatives. Recall that the vectors 1, 0,
Polynomials. In many problems, it is useful to write polynomials as products. For example, when solving equations: Example:
 Polynomials Monomials: 10, 5x, 3x 2, x 3, 4x 2 y 6, or 5xyz 2. A monomial is a product of quantities some of which are unknown. Polynomials: 10 + 5x 3x 2 + x 3, or 4x 2 y 6 + 5xyz 2. A polynomial is a
Polynomials Monomials: 10, 5x, 3x 2, x 3, 4x 2 y 6, or 5xyz 2. A monomial is a product of quantities some of which are unknown. Polynomials: 10 + 5x 3x 2 + x 3, or 4x 2 y 6 + 5xyz 2. A polynomial is a
MATH2070 Optimisation
 MATH2070 Optimisation Nonlinear optimisation with constraints Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The full nonlinear optimisation problem with equality constraints
MATH2070 Optimisation Nonlinear optimisation with constraints Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The full nonlinear optimisation problem with equality constraints
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations
 1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
(x + 3)(x 1) lim(x + 3) = 4. lim. (x 2)( x ) = (x 2)(x + 2) x + 2 x = 4. dt (t2 + 1) = 1 2 (t2 + 1) 1 t. f(x) = lim 3x = 6,
 Math 140 MT1 Sample C Solutions Tyrone Crisp 1 (B): First try direct substitution: you get 0. So try to cancel common factors. We have 0 x 2 + 2x 3 = x 1 and so the it as x 1 is equal to (x + 3)(x 1),
Math 140 MT1 Sample C Solutions Tyrone Crisp 1 (B): First try direct substitution: you get 0. So try to cancel common factors. We have 0 x 2 + 2x 3 = x 1 and so the it as x 1 is equal to (x + 3)(x 1),
IES Parque Lineal - 2º ESO
 UNIT5. ALGEBRA Contenido 1. Algebraic expressions.... 1 Worksheet: algebraic expressions.... 2 2. Monomials.... 3 Worksheet: monomials.... 5 3. Polynomials... 6 Worksheet: polynomials... 9 4. Factorising....
UNIT5. ALGEBRA Contenido 1. Algebraic expressions.... 1 Worksheet: algebraic expressions.... 2 2. Monomials.... 3 Worksheet: monomials.... 5 3. Polynomials... 6 Worksheet: polynomials... 9 4. Factorising....
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide
 The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
Collecting Like Terms
 MPM1D Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 5 Learning goal: how to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Date: Collecting Like Terms WARM-UP Example 1: Simplify each expression using exponent laws.
MPM1D Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 5 Learning goal: how to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Date: Collecting Like Terms WARM-UP Example 1: Simplify each expression using exponent laws.
********************************************************** 1. Evaluate the double or iterated integrals:
 Practice problems 1. (a). Let f = 3x 2 + 4y 2 + z 2 and g = 2x + 3y + z = 1. Use Lagrange multiplier to find the extrema of f on g = 1. Is this a max or a min? No max, but there is min. Hence, among the
Practice problems 1. (a). Let f = 3x 2 + 4y 2 + z 2 and g = 2x + 3y + z = 1. Use Lagrange multiplier to find the extrema of f on g = 1. Is this a max or a min? No max, but there is min. Hence, among the
Major Ideas in Calc 3 / Exam Review Topics
 Major Ideas in Calc 3 / Exam Review Topics Here are some highlights of the things you should know to succeed in this class. I can not guarantee that this list is exhaustive!!!! Please be sure you are able
Major Ideas in Calc 3 / Exam Review Topics Here are some highlights of the things you should know to succeed in this class. I can not guarantee that this list is exhaustive!!!! Please be sure you are able
Partial Derivatives. w = f(x, y, z).
 Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of Several Variables So far we have focused our attention of functions of one variable. These functions model situations in which a variable depends on another independent
Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of Several Variables So far we have focused our attention of functions of one variable. These functions model situations in which a variable depends on another independent
- parametric equations for the line, z z 0 td 3 or if d 1 0, d 2 0andd 3 0, - symmetric equations of the line.
 Lines and Planes in Space -(105) Questions: What do we need to know to determine a line in space? What are the fms of a line? If two lines are not parallel in space, must they be intersect as two lines
Lines and Planes in Space -(105) Questions: What do we need to know to determine a line in space? What are the fms of a line? If two lines are not parallel in space, must they be intersect as two lines
HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, find the largest and smallest values of the function f(x, y) xy on the ellipse x + y 1. Solution: The
HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, find the largest and smallest values of the function f(x, y) xy on the ellipse x + y 1. Solution: The
O.K. But what if the chicken didn t have access to a teleporter.
 The intermediate value theorem, and performing algebra on its. This is a dual topic lecture. : The Intermediate value theorem First we should remember what it means to be a continuous function: A function
The intermediate value theorem, and performing algebra on its. This is a dual topic lecture. : The Intermediate value theorem First we should remember what it means to be a continuous function: A function
Chapter 7: Exponents
 Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Algebra Homework: Chapter (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) HW# Date In-Class Homework M / Review of Sections.-.
Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Algebra Homework: Chapter (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) HW# Date In-Class Homework M / Review of Sections.-.
MATH 3B (Butler) Practice for Final (I, Solutions)
 MATH 3B (Butler) Practice for Final (I, Solutions). Gabriel s horn is a mathematical object taken by rotating the curve y = x around the x-axis for x
MATH 3B (Butler) Practice for Final (I, Solutions). Gabriel s horn is a mathematical object taken by rotating the curve y = x around the x-axis for x
Multivariable Calculus and Matrix Algebra-Summer 2017
 Multivariable Calculus and Matrix Algebra-Summer 017 Homework 4 Solutions Note that the solutions below are for the latest version of the problems posted. For those of you who worked on an earlier version
Multivariable Calculus and Matrix Algebra-Summer 017 Homework 4 Solutions Note that the solutions below are for the latest version of the problems posted. For those of you who worked on an earlier version
15. LECTURE 15. I can calculate the dot product of two vectors and interpret its meaning. I can find the projection of one vector onto another one.
 5. LECTURE 5 Objectives I can calculate the dot product of two vectors and interpret its meaning. I can find the projection of one vector onto another one. In the last few lectures, we ve learned that
5. LECTURE 5 Objectives I can calculate the dot product of two vectors and interpret its meaning. I can find the projection of one vector onto another one. In the last few lectures, we ve learned that
Permutations and Polynomials Sarah Kitchen February 7, 2006
 Permutations and Polynomials Sarah Kitchen February 7, 2006 Suppose you are given the equations x + y + z = a and 1 x + 1 y + 1 z = 1 a, and are asked to prove that one of x,y, and z is equal to a. We
Permutations and Polynomials Sarah Kitchen February 7, 2006 Suppose you are given the equations x + y + z = a and 1 x + 1 y + 1 z = 1 a, and are asked to prove that one of x,y, and z is equal to a. We
Algebra Review. Finding Zeros (Roots) of Quadratics, Cubics, and Quartics. Kasten, Algebra 2. Algebra Review
 Kasten, Algebra 2 Finding Zeros (Roots) of Quadratics, Cubics, and Quartics A zero of a polynomial equation is the value of the independent variable (typically x) that, when plugged-in to the equation,
Kasten, Algebra 2 Finding Zeros (Roots) of Quadratics, Cubics, and Quartics A zero of a polynomial equation is the value of the independent variable (typically x) that, when plugged-in to the equation,
Christmas Calculated Colouring - C1
 Christmas Calculated Colouring - C Tom Bennison December 20, 205 Introduction Each question identifies a region or regions on the picture Work out the answer and use the key to work out which colour to
Christmas Calculated Colouring - C Tom Bennison December 20, 205 Introduction Each question identifies a region or regions on the picture Work out the answer and use the key to work out which colour to
Lesson 26 MA Nick Egbert
 Overview There is no new material for this lesson. Here, we explore a multitude of fun word problems that we can now do using the method of Lagrange multipliers from the previous lesson. Examples Example
Overview There is no new material for this lesson. Here, we explore a multitude of fun word problems that we can now do using the method of Lagrange multipliers from the previous lesson. Examples Example
Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? A. (1,10) B. (2,7) C. (3,5) D. (4,3) E.
 April 9, 01 Standards: MM1Ga, MM1G1b Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? (1,10) B. (,7) C. (,) (,) (,1). Points P, Q, R, and S lie on a line
April 9, 01 Standards: MM1Ga, MM1G1b Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? (1,10) B. (,7) C. (,) (,) (,1). Points P, Q, R, and S lie on a line
Using the binomial square thm. rewrite the following trinomial into an equivalent expression (The square of a binomial) 25c 2 70cd + 49d 2
 Using the binomial square thm. rewrite the following trinomial into an equivalent expression (The square of a binomial) 25c 2 70cd + 49d 2 Dec 6 7:24 AM 1 Notes 6 1 Quadratic Expressions, Rectangles &
Using the binomial square thm. rewrite the following trinomial into an equivalent expression (The square of a binomial) 25c 2 70cd + 49d 2 Dec 6 7:24 AM 1 Notes 6 1 Quadratic Expressions, Rectangles &
Name: Class: IM8 Block:
 Name: Block: Class: IM8 Investigation 1: Mathematical Properties and Order of Operations Mathematical Properties 2 Practice Level 1: Write the name of the property shown in the examples below. 1. 4 + 5
Name: Block: Class: IM8 Investigation 1: Mathematical Properties and Order of Operations Mathematical Properties 2 Practice Level 1: Write the name of the property shown in the examples below. 1. 4 + 5
Chapter 7. Extremal Problems. 7.1 Extrema and Local Extrema
 Chapter 7 Extremal Problems No matter in theoretical context or in applications many problems can be formulated as problems of finding the maximum or minimum of a function. Whenever this is the case, advanced
Chapter 7 Extremal Problems No matter in theoretical context or in applications many problems can be formulated as problems of finding the maximum or minimum of a function. Whenever this is the case, advanced
Note: An algebraic expression is made of one or more terms. The terms in an algebraic expression are connected with either addition or subtraction.
 .4 Combining Like Terms Term A term is a single number or variable, or it can be a product of a number (called its coefficient) and one or more variables. Examples of terms:, x, a, xy, 4 a bc, 5, xyz coefficient
.4 Combining Like Terms Term A term is a single number or variable, or it can be a product of a number (called its coefficient) and one or more variables. Examples of terms:, x, a, xy, 4 a bc, 5, xyz coefficient
Geometry of Vector Spaces
 Geometry of Vector Spaces Fall 14 MATH43 In these notes we show that it is possible to do geometry in vector spaces as well, that is similar to plane geometry. We start by giving the definition of an abstract
Geometry of Vector Spaces Fall 14 MATH43 In these notes we show that it is possible to do geometry in vector spaces as well, that is similar to plane geometry. We start by giving the definition of an abstract
3.3 Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 71_00.qxp 12/27/06 1:25 PM Page 276 276 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions. Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions Long Division of Polynomials Consider the graph of f x 6x 19x 2 16x 4. Notice in Figure.2
71_00.qxp 12/27/06 1:25 PM Page 276 276 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions. Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions Long Division of Polynomials Consider the graph of f x 6x 19x 2 16x 4. Notice in Figure.2
MEI Core 1. Basic Algebra. Section 1: Basic algebraic manipulation and solving simple equations. Manipulating algebraic expressions
 MEI Core Basic Algebra Section : Basic algebraic manipulation and solving simple equations Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Manipulating algebraic expressions Collecting like terms
MEI Core Basic Algebra Section : Basic algebraic manipulation and solving simple equations Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Manipulating algebraic expressions Collecting like terms
V. Graph Sketching and Max-Min Problems
 V. Graph Sketching and Max-Min Problems The signs of the first and second derivatives of a function tell us something about the shape of its graph. In this chapter we learn how to find that information.
V. Graph Sketching and Max-Min Problems The signs of the first and second derivatives of a function tell us something about the shape of its graph. In this chapter we learn how to find that information.
5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 6/7/2014. c = Properites of Exponents. *Simplify each of the following:
 48 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 6/7/2014 Properites of Exponents 1. x a x b = x a+b *Simplify each of the following: a. x 4 x 8 = b. x 5 x 7 x = 2. xa xb = xa b c. 5 6 5 11 = d. x14
48 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 6/7/2014 Properites of Exponents 1. x a x b = x a+b *Simplify each of the following: a. x 4 x 8 = b. x 5 x 7 x = 2. xa xb = xa b c. 5 6 5 11 = d. x14
Midterm Review Packet
 Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I
 LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I Overview In business, people use algebra everyday to find unknown quantities. For example, a manufacturer may use algebra to determine a product s selling price in order
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I Overview In business, people use algebra everyday to find unknown quantities. For example, a manufacturer may use algebra to determine a product s selling price in order
= = =
 . D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
. D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
LECTURE 5, FRIDAY
 LECTURE 5, FRIDAY 20.02.04 FRANZ LEMMERMEYER Before we start with the arithmetic of elliptic curves, let us talk a little bit about multiplicities, tangents, and singular points. 1. Tangents How do we
LECTURE 5, FRIDAY 20.02.04 FRANZ LEMMERMEYER Before we start with the arithmetic of elliptic curves, let us talk a little bit about multiplicities, tangents, and singular points. 1. Tangents How do we
1 a 2 b 10 c 4 d 12. e 7 f 11 g 12 h 30. i 8 j 7 k 5 l a 9 b 14 c 3 d 10. e 11 f 5 g 15 h 1. i 12 j 2 k 35 l 49.
 Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Core 7 A1.1 Answers A1.1 Answers 1 a 2 b 10 c 4 d 12 e 7 f 11 g 12 h 30 i 8 j 7 k 5 l 20 2 a 9 b 14 c 3 d 10 e 11 f 5 g 15 h 1 i 12 j 2 k 35 l 49 m 25 n 1 o 1 p 18 3 a
Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Core 7 A1.1 Answers A1.1 Answers 1 a 2 b 10 c 4 d 12 e 7 f 11 g 12 h 30 i 8 j 7 k 5 l 20 2 a 9 b 14 c 3 d 10 e 11 f 5 g 15 h 1 i 12 j 2 k 35 l 49 m 25 n 1 o 1 p 18 3 a
- parametric equations for the line, z z 0 td 3 or if d 1 0, d 2 0andd 3 0, - symmetric equations of the line.
 Lines and Planes in Space -(105) Questions: 1 What is the equation of a line if we know (1) two points P x 1,y 1,z 1 and Q x 2,y 2,z 2 on the line; (2) a point P x 1,y 1,z 1 on the line and the line is
Lines and Planes in Space -(105) Questions: 1 What is the equation of a line if we know (1) two points P x 1,y 1,z 1 and Q x 2,y 2,z 2 on the line; (2) a point P x 1,y 1,z 1 on the line and the line is
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Homework 5 Solutions
 MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2011 Homework 5 Solutions Note: In what follows, numbers in parentheses indicate the problem numbers for users of the sixth edition. A * indicates that this
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2011 Homework 5 Solutions Note: In what follows, numbers in parentheses indicate the problem numbers for users of the sixth edition. A * indicates that this
Problem 1. Answer: 95
 Talent Search Test Solutions January 2014 Problem 1. The unit squares in a x grid are colored blue and gray at random, and each color is equally likely. What is the probability that a 2 x 2 square will
Talent Search Test Solutions January 2014 Problem 1. The unit squares in a x grid are colored blue and gray at random, and each color is equally likely. What is the probability that a 2 x 2 square will
Lecture 13 - Wednesday April 29th
 Lecture 13 - Wednesday April 29th jacques@ucsdedu Key words: Systems of equations, Implicit differentiation Know how to do implicit differentiation, how to use implicit and inverse function theorems 131
Lecture 13 - Wednesday April 29th jacques@ucsdedu Key words: Systems of equations, Implicit differentiation Know how to do implicit differentiation, how to use implicit and inverse function theorems 131
Midterm 1 Review. Distance = (x 1 x 0 ) 2 + (y 1 y 0 ) 2.
 Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Final Review Worksheet
 Score: Name: Final Review Worksheet Math 2110Q Fall 2014 Professor Hohn Answers (in no particular order): f(x, y) = e y + xe xy + C; 2; 3; e y cos z, e z cos x, e x cos y, e x sin y e y sin z e z sin x;
Score: Name: Final Review Worksheet Math 2110Q Fall 2014 Professor Hohn Answers (in no particular order): f(x, y) = e y + xe xy + C; 2; 3; e y cos z, e z cos x, e x cos y, e x sin y e y sin z e z sin x;
264 CHAPTER 4. FRACTIONS cm in cm cm ft pounds
 6 CHAPTER. FRACTIONS 9. 7cm 61. cm 6. 6ft 6. 0in 67. 10cm 69. pounds .. DIVIDING FRACTIONS 6. Dividing Fractions Suppose that you have four pizzas and each of the pizzas has been sliced into eight equal
6 CHAPTER. FRACTIONS 9. 7cm 61. cm 6. 6ft 6. 0in 67. 10cm 69. pounds .. DIVIDING FRACTIONS 6. Dividing Fractions Suppose that you have four pizzas and each of the pizzas has been sliced into eight equal
CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms Term 2. Lecture 9
 CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms 2011-12 Term 2 Prof. Nick Harvey Lecture 9 University of British Columbia 1 Polynomial Identity Testing In the first lecture we discussed the problem of testing equality
CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms 2011-12 Term 2 Prof. Nick Harvey Lecture 9 University of British Columbia 1 Polynomial Identity Testing In the first lecture we discussed the problem of testing equality
( ) 0. Section 3.3 Graphs of Polynomial Functions. Chapter 3
 76 Chapter 3 Section 3.3 Graphs of Polynomial Functions In the previous section we explored the short run behavior of quadratics, a special case of polynomials. In this section we will explore the short
76 Chapter 3 Section 3.3 Graphs of Polynomial Functions In the previous section we explored the short run behavior of quadratics, a special case of polynomials. In this section we will explore the short
Supplementary Questions for HP Chapter Sketch graphs of the following functions: (a) z = y x. (b) z = ye x. (c) z = x 2 y 2
 Supplementary Questions for HP Chapter 17 1. Sketch graphs of the following functions: (a) z = y x (b) z = ye x (c) z = x y. Find the domain and range of the given functions: (a) f(x, y) = 36 9x 4y (b)
Supplementary Questions for HP Chapter 17 1. Sketch graphs of the following functions: (a) z = y x (b) z = ye x (c) z = x y. Find the domain and range of the given functions: (a) f(x, y) = 36 9x 4y (b)
MATH 1910 Limits Numerically and Graphically Introduction to Limits does not exist DNE DOES does not Finding Limits Numerically
 MATH 90 - Limits Numerically and Graphically Introduction to Limits The concept of a limit is our doorway to calculus. This lecture will explain what the limit of a function is and how we can find such
MATH 90 - Limits Numerically and Graphically Introduction to Limits The concept of a limit is our doorway to calculus. This lecture will explain what the limit of a function is and how we can find such
WOCOMAL. Varsity Meet #1. October 9, 2002
 WOCOMAL Varsity Meet #1 October 9, 2002 October 9, 2002 Varsity Meet#1 ROUND#1: Arithmetic - No Calculators Allowed 1. The formula W = 5.5( d + 8) gives the normal weight W in pounds of a person who is
WOCOMAL Varsity Meet #1 October 9, 2002 October 9, 2002 Varsity Meet#1 ROUND#1: Arithmetic - No Calculators Allowed 1. The formula W = 5.5( d + 8) gives the normal weight W in pounds of a person who is
CHAPTER 12 Boolean Algebra
 318 Chapter 12 Boolean Algebra CHAPTER 12 Boolean Algebra SECTION 12.1 Boolean Functions 2. a) Since x 1 = x, the only solution is x = 0. b) Since 0 + 0 = 0 and 1 + 1 = 1, the only solution is x = 0. c)
318 Chapter 12 Boolean Algebra CHAPTER 12 Boolean Algebra SECTION 12.1 Boolean Functions 2. a) Since x 1 = x, the only solution is x = 0. b) Since 0 + 0 = 0 and 1 + 1 = 1, the only solution is x = 0. c)
