Construction of a Low Temperature Scanning. Tunneling Microscope
|
|
|
- Bernice York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Construction of a Low Temperature Scanning Tunneling Microscope JacobTosado July 22, 2004 This paper discusses work I have done with the construction of a low temperature scanning tunneling microscope (LTSTM) and the operation of a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). A brief description to why a LTSTM is used and the background concerning that description, is covered. Mainly methods in STM imaging are described giving insight into two possible sources of imaging deformation. I. Introduction The variation of the density of states of ferromagnetic manganite thin films as a function of temperature and its spatial variation is currently a topic of great interest. Tunneling spectroscopy and surface imaging via scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) is an excellent technique for studying such properties and has promoted the use of low temperature scanning tunneling microscopy (LTSTM). In this field it has been observed that at the curie temperature manganites such as LaPrCaMnO 3 exhibit steep drops in resistivity (also the metal insulator transition point) where the isolated creation of ferromagnetic domains begin to merge. Our plan is to study the behavior of these domains as a function of temperature using LTSTM.
2 A manganite is an insulating solid at room temperature. As temperature is decreased to its curie temperature the materials resistivity peaks after which there occurs a steep decrease of resistivity into a metallic state. The transition from insulating to metallic states is characterized by the behavior of magnetic domains throughout the manganite. A large drop in resistivity also occurs when a magnetic field ~10 Tesla is applied and this phenomenon is called colossal magnetoresistance (CMR). These domains will initially occur in isolated areas then spread until the manganite reaches saturation magnetization. Depending on the composition of the manganite, the nature of magnetic field saturation can be changed. Utilizing the angstrom scale resolving power of a LTSTM, it is possible to make real time analysis of these phase transitions. Our goal is to image these transitions at temperatures of around 10 Kelvin in fields of nine Tesla. Theories concerning charge ordering, the "Hunds coupling" energy, and the Jahn-Teller effect go very far in explaining the mechanics behind manganite behavior [7]. Any measurements that may confirm or disprove these theories could make a profound impact in understanding the behavior of manganites. An LTSTM provides an experimental way to make these measurements. In this paper I will describe our progress towards the construction of a LTSTM over the course of this REU project. II. Background Several concepts concerning STM should be clarified. STM technology was initiated by G. Binnig and H. Rorher in 1981 culminating over a decade of technology and
3 humanity's desire to see the atom [1]. Seven years later perovskite type crystals became noted for their CMR properties, namely manganites. Extensive LTSTM research of managanites finally culminated in the mid to late 90 s revealing the effectiveness of LTSTM in imaging CMR effects [5]. Atomically resolved imaging with an STM involves positioning a tip of some material at a distance of about five angstroms from another material which is the sample. At this separation the electrons are able to tunnel across the potential barrier created by the gap. A tunnel current is produced and can be measured to create an image. Often images will be displayed showing neat rows and columns of atoms. However, STM images are actually a measure of the electron density over the surface. Bright colors illustrate the maxima and dark the minima. The atomic structure can be studied in detail though Fourier transform. Our scan area ranges from two to ten nanometers square at a frequency range of 20 to 40 hertz. Maintaining the five-angstrom tunnel gap while in scan is achieved with a piezoelectric control system. This system utilizes piezo-electric material, which deforms by only a few angstroms on application of a few volts (10-100Å/V). Movement in the direction normal to a sample's surface is required for coarse approach of the tip towards the sample. Hence, the tip is not rigidly connected to the sample. Instead friction of the piezo material along an adjacent surface holds the tip in place where
4 periodic voltage jerks to the piezos move the tip towards the sample. Our current system operates at one kilohertz where previous systems work at 60 hertz [6]. The higher frequency is an advantage since the coarse approach is done manually and can take up a lot of time. While in tunneling range (fine approach) the STM is subjected to inertial vibrations, which could potentially destroy imaging and image quality. Various types of vibration isolation systems are employed. Our systems use a tripedal air spring system, similar to those in optical research. III. STM The most delicate part of the STM is the STM tip. Many advances in this area have been made. In principal the sharper a tip the better; however, for our purposes, a simple platinum rhodium wire is used which produces good atomically resolved images. We use a 0.25mm diameter platinum-rhodium wire cut to about one tenth of an inch. The platinum-rhodium alloy is used for its brittle structure. Since the cutting tool can be a pair of sheers or wire snips, the actual cut, if looked at up close, can be quite jagged and rough. For platinum-rhodium, a cut will tend to be a fracture leaving exposed atomic sized sharp edges, all potentially tips where ideally only a single maximum tip will participate in tunneling.
5 The ideal case of a single tip being the sole producer of the tunneling current is not always true. Quite often there occurs multi-tip phenomenon as described by Mizes et al., [2] which will cause the image to look foggy creating an ambiguity between one maxima and the next. For instance, a normal graphite image of singly spaced maxima is constructed with three sine waves of different phases and equal amplitudes as shown in Fig.1. If the value of one of these amplitudes dominates the other two, rows of maxima occur (Fig. 2). If two amplitudes dominate the third, a triangular array of ellipses occur [2]. FIGURE 1. (left) Single-spaced maxima. (right) Fourier transform revealing the triangular symmetry of graphite. Aside from the multi-tip phenomenon there is also the explanation given by Kobayashi and Tsukada [3] for a particular image deformation resulting in linear chains or rows of maxima. This phenomenon calls to the existence of the tip possessing different electronic levels [4]. One of the defining characteristics in constructing the anomalous rows of maxima required that the three-fold-symmetry axis of the tip be tilted by 7.5 degrees.
6 FIGURE 2. (left) Rows of maxima. (right) Fourier transform where the amplitudes of one axis dominates the other two. Images as in Fig. 2 depicting linear chains of maxima are a common recording on our systems. These images usually occur just before acquiring individual atomic resolution. In some instances these images are the only ones recorded. On analysis I made a rough comparison of the electron density surface to a corrugated surface whose maxima correspond to the maxima of the electron density. I noticed that if one looks directly at the corrugated surface, with the general plane of the surface perpendicular to the line of site, then rotates this plane slightly, so that one edge is further away and the other edge is closer, one sees a silhouette of rows. Each of these silhouettes designate rows of maxima equidistance from the observer. If I now rotated this corrugated surface about an axis parallel to the line of sight, the appearance of continuous silhouettes become periodic. This allows the observer at certain angles to view silhouettes of single maxima.
7 Drawing the analogy of the corrugated surface to the surface of electron density I took note of three ideas. Primarily, the spatial configuration of the corrugated surface and the electron surface has little correlation. Second, the appearance of rows can be characterized as maxima of equal denomination. Third, rotation of the surface along an axis parallel to the line of sight can be analogous to the rotation in the direction of scan across the surface electron density. From these three ideas I predicted that a scan depicting rows of maxima might be rotated a certain number of degrees to where it gives single maxima and that this effect is periodic. The scans shown in Fig. 3 demonstrate this phenomenon. FIGURE 3. Various graphite scans where the approximate scan direction is labeled. Mizes et al. and Kobayashi and Tsukada [2][3] explain the appearance of rows of maxima each giving defining characteristics to its cause. A Fourier transform of an image with maxima rows shows that one of the three amplitudes dominate (Fig. 2, right). This dominance is consistent with multi-tip phenomenon. However, if the periodicity of rows when the scan direction is rotated correlates to the spatial configuration of the surface of electron density, then it is possible that the rows are due to a slight tilt between the axis of
8 the electron surface and the three-fold-symmetry of the tip resulting in maxima of equal denomination which is consistent with the tip possessing various electronic levels. IV. LTSTM Our LTSTM in contrast to our STM will be subject to extreme low temperatures and high magnetic fields. These conditions necessitate the use of appropriate materials for its construction. Macor, a white machinable glass ceramic with a coefficient of expansion of 93 x 10-7 / o C, is suitable since it does not deform greatly at low temperatures. The LTSTM, as shown in Fig. 4, uses Macor as the main structure. Other materials include copper and stainless steel for conductivity and strength respectively. The LTSTM probe, made from stainless steel is attached to the LTSTM allowing is to be placed in and removed from the Dewar (Fig. 5). FIGURE 4. White structure is made form Macor The vibration isolation system required for the operation of the LTSTM are a set of three nitrogen filled air springs on a tripedal base. The Dewar in which the LTSTM will be cooled and subjected to high magnetic fields is suspended form an aluminum platform
9 resting on the air springs, as shown in Fig. 5. Lead is added to the platform to increase its mass dampening any inertial oscillations in the structure. Figure 5. Vibration isolation system V. Summary As of now the LTSTM, LTSTM probe, Dewar and vibration isolation system have been completed. Plans are under way to have the LTSTM operating by the end of August Preliminary calibrations of the LTSTM have been successful. Final scan calibrations of the LTSTM will be done using a graphite sample. Further tests will involve gold thin films. Once operational, tests of various manganites will commence.
10 Thanks to: Dr. Amlan Biswas Tara Dhakal Yun Sunghee [1] G. Binnig and H. Rohrer, Nobel lecture, December 8, [2] H.A. Mizes, Sang-il Park, W.A. Harrison: Phys.Rev. B36, 4491 (1987). [3] K. Kobayashi, and M. Tsukada: J. Vac Sci. Thecnol. A8, 300 (1988). [4] H.-J. Guntherodt, R.Wiesendanger Scanning Tunneling Microscopy I, edited by G. Ertl, R. Gomer, and D.L.Mills (Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 1992), Vol.20, Chap. 6.1, pp [5] A. Biswas et al., Phys. Rev. B59, 5368 (1999). [6] S.H. Pan, E.W. Hudson, and J.C. Davis, Rev. Sci. Instrum.70, 1459 (1999). [7] A.J. Millis Colossal Magnetoresistive Oxides, edited by D.D. Sarma, G. Kotliar and Y. Tokura (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000), Vol 2, Chap. 2, pp
Tunneling Spectroscopy of PCCO
 Tunneling Spectroscopy of PCCO Neesha Anderson and Amlan Biswas Department of Physics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Abstract A point-contact probe capable of operating down to temperatures
Tunneling Spectroscopy of PCCO Neesha Anderson and Amlan Biswas Department of Physics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Abstract A point-contact probe capable of operating down to temperatures
INTRODUCTION TO SCA\ \I\G TUNNELING MICROSCOPY
 INTRODUCTION TO SCA\ \I\G TUNNELING MICROSCOPY SECOND EDITION C. JULIAN CHEN Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia University, New York OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface
INTRODUCTION TO SCA\ \I\G TUNNELING MICROSCOPY SECOND EDITION C. JULIAN CHEN Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia University, New York OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface
Chapter 10. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
3.1 Electron tunneling theory
 Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) was invented in the 80s by two physicists: G. Binnig and H. Rorher. They got the Nobel Prize a few years later. This invention paved the way for new possibilities in
Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) was invented in the 80s by two physicists: G. Binnig and H. Rorher. They got the Nobel Prize a few years later. This invention paved the way for new possibilities in
Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)
 Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) General components of SPM; Tip --- the probe; Cantilever --- the indicator of the tip; Tip-sample interaction --- the feedback system; Scanner --- piezoelectric
Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) General components of SPM; Tip --- the probe; Cantilever --- the indicator of the tip; Tip-sample interaction --- the feedback system; Scanner --- piezoelectric
Scanning tunneling microscopy
 IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology Lab 72 in TFFM08 Scanning tunneling microscopy NAME PERS. - NUMBER DATE APPROVED Rev. Dec 2006 Ivy Razado Aug 2014 Tuomas Hänninen Contents 1 Introduction
IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology Lab 72 in TFFM08 Scanning tunneling microscopy NAME PERS. - NUMBER DATE APPROVED Rev. Dec 2006 Ivy Razado Aug 2014 Tuomas Hänninen Contents 1 Introduction
672 Advanced Solid State Physics. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 672 Advanced Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Biao Hu Outline: 1. Introduction to STM 2. STM principle & working modes 3. STM application & extension 4. STM in our group 1. Introduction
672 Advanced Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Biao Hu Outline: 1. Introduction to STM 2. STM principle & working modes 3. STM application & extension 4. STM in our group 1. Introduction
Citation for published version (APA): Mendoza, S. M. (2007). Exploiting molecular machines on surfaces s.n.
 University of Groningen Exploiting molecular machines on surfaces Mendoza, Sandra M IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Exploiting molecular machines on surfaces Mendoza, Sandra M IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM)
 Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM) The atomic force microscope (AFM) probes the surface of a sample with a sharp tip, a couple of microns long and often less than 100 Å in diameter.
Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM) The atomic force microscope (AFM) probes the surface of a sample with a sharp tip, a couple of microns long and often less than 100 Å in diameter.
MATERIAL SCIENCE AND TECHONOLOGY-1. Scanning Tunneling Microscope, STM Tunneling Electron Microscope, TEM HATİCE DOĞRUOĞLU
 MATERIAL SCIENCE AND TECHONOLOGY-1 Scanning Tunneling Microscope, STM Tunneling Electron Microscope, TEM HATİCE DOĞRUOĞLU Scanning Tunelling Microscope (STM) In 1981,Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer and
MATERIAL SCIENCE AND TECHONOLOGY-1 Scanning Tunneling Microscope, STM Tunneling Electron Microscope, TEM HATİCE DOĞRUOĞLU Scanning Tunelling Microscope (STM) In 1981,Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer and
Design of a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope head with a lowfriction, piezoelectric coarse approach mechanism
 Design of a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope head with a lowfriction, piezoelectric coarse approach mechanism T. A. Smith 1 and A. Biswas 2 1 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University
Design of a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope head with a lowfriction, piezoelectric coarse approach mechanism T. A. Smith 1 and A. Biswas 2 1 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Studies of the Ge(111) Surface
 VC Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Studies of the Ge(111) Surface Anna Rosen University of California, Berkeley Advisor: Dr. Shirley Chiang University of California, Davis August 24, 2007 Abstract: This
VC Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Studies of the Ge(111) Surface Anna Rosen University of California, Berkeley Advisor: Dr. Shirley Chiang University of California, Davis August 24, 2007 Abstract: This
Introduction to the Scanning Tunneling Microscope
 Introduction to the Scanning Tunneling Microscope A.C. Perrella M.J. Plisch Center for Nanoscale Systems Cornell University, Ithaca NY Measurement I. Theory of Operation The scanning tunneling microscope
Introduction to the Scanning Tunneling Microscope A.C. Perrella M.J. Plisch Center for Nanoscale Systems Cornell University, Ithaca NY Measurement I. Theory of Operation The scanning tunneling microscope
tip of a current tip and the sample. Components: 3. Coarse sample-to-tip isolation system, and
 SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPE Brief history: Heinrich Rohrer and Gerd K. Binnig, scientists at IBM's Zurich Research Laboratory in Switzerland, are awarded the 1986 Nobel Prize in physicss for their work
SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPE Brief history: Heinrich Rohrer and Gerd K. Binnig, scientists at IBM's Zurich Research Laboratory in Switzerland, are awarded the 1986 Nobel Prize in physicss for their work
Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy C. JULIAN CHEN IBM Research Division Thomas J. Watson Research Center Yorktown Heights, New York New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS List
Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy C. JULIAN CHEN IBM Research Division Thomas J. Watson Research Center Yorktown Heights, New York New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS List
Coulomb Blockade IV characteristics in. (La,Pr,Ca)MnO3
 Coulomb Blockade IV characteristics in (La,Pr,Ca)MnO3 Sarah Joy Advisor: Dr. Selman Hershfield 2008 REU University of Florida July 29, 2008 Abstract In a sample of manganite at 70K, ferromagnetic islands
Coulomb Blockade IV characteristics in (La,Pr,Ca)MnO3 Sarah Joy Advisor: Dr. Selman Hershfield 2008 REU University of Florida July 29, 2008 Abstract In a sample of manganite at 70K, ferromagnetic islands
Instrumentation and Operation
 Instrumentation and Operation 1 STM Instrumentation COMPONENTS sharp metal tip scanning system and control electronics feedback electronics (keeps tunneling current constant) image processing system data
Instrumentation and Operation 1 STM Instrumentation COMPONENTS sharp metal tip scanning system and control electronics feedback electronics (keeps tunneling current constant) image processing system data
Chapter 12. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Transmission Electron Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Transmission Electron Microscopy Speakers Burcu Başar Semih Gezgin Yavuz Selim Telis Place Hacettepe University Department of Chemical Engineering It s a small world after
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Transmission Electron Microscopy Speakers Burcu Başar Semih Gezgin Yavuz Selim Telis Place Hacettepe University Department of Chemical Engineering It s a small world after
Scanning Probe Microscopy. Amanda MacMillan, Emmy Gebremichael, & John Shamblin Chem 243: Instrumental Analysis Dr. Robert Corn March 10, 2010
 Scanning Probe Microscopy Amanda MacMillan, Emmy Gebremichael, & John Shamblin Chem 243: Instrumental Analysis Dr. Robert Corn March 10, 2010 Scanning Probe Microscopy High-Resolution Surface Analysis
Scanning Probe Microscopy Amanda MacMillan, Emmy Gebremichael, & John Shamblin Chem 243: Instrumental Analysis Dr. Robert Corn March 10, 2010 Scanning Probe Microscopy High-Resolution Surface Analysis
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
STM spectroscopy (STS)
 STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
MEMS Metrology. Prof. Tianhong Cui ME 8254
 MEMS Metrology Prof. Tianhong Cui ME 8254 What is metrology? Metrology It is the science of weights and measures Refers primarily to the measurements of length, weight, time, etc. Mensuration- A branch
MEMS Metrology Prof. Tianhong Cui ME 8254 What is metrology? Metrology It is the science of weights and measures Refers primarily to the measurements of length, weight, time, etc. Mensuration- A branch
And Manipulation by Scanning Probe Microscope
 Basic 15 Nanometer Scale Measurement And Manipulation by Scanning Probe Microscope Prof. K. Fukuzawa Dept. of Micro/Nano Systems Engineering Nagoya University I. Basics of scanning probe microscope Basic
Basic 15 Nanometer Scale Measurement And Manipulation by Scanning Probe Microscope Prof. K. Fukuzawa Dept. of Micro/Nano Systems Engineering Nagoya University I. Basics of scanning probe microscope Basic
Basic Laboratory. Materials Science and Engineering. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
 Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
REPORT ON SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPE. Course ME-228 Materials and Structural Property Correlations Course Instructor Prof. M. S.
 REPORT ON SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPE Course ME-228 Materials and Structural Property Correlations Course Instructor Prof. M. S. Bobji Submitted by Ankush Kumar Jaiswal (09371) Abhay Nandan (09301) Sunil
REPORT ON SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPE Course ME-228 Materials and Structural Property Correlations Course Instructor Prof. M. S. Bobji Submitted by Ankush Kumar Jaiswal (09371) Abhay Nandan (09301) Sunil
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Part I
 Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Part I CHEM-L2000 Eero Kontturi 6 th March 2018 Lectures on AFM Part I Principles and practice Imaging of native materials, including nanocellulose Part II Surface force measurements
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Part I CHEM-L2000 Eero Kontturi 6 th March 2018 Lectures on AFM Part I Principles and practice Imaging of native materials, including nanocellulose Part II Surface force measurements
Scanning Probe Microscopy. EMSE-515 F. Ernst
 Scanning Probe Microscopy EMSE-515 F. Ernst 1 Literature 2 3 Scanning Probe Microscopy: The Lab on a Tip by Ernst Meyer,Ans Josef Hug,Roland Bennewitz 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy and Spectroscopy : Theory,
Scanning Probe Microscopy EMSE-515 F. Ernst 1 Literature 2 3 Scanning Probe Microscopy: The Lab on a Tip by Ernst Meyer,Ans Josef Hug,Roland Bennewitz 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy and Spectroscopy : Theory,
Study of the Potential Dirac Material Pb 0.9 Sn 0.1 Se by Soft Point-Contact Spectroscopy
 Study of the Potential Dirac Material Pb 0.9 Sn 0.1 Se by Soft Point-Contact Spectroscopy Tiffany Paul University of Florida, Dept. of Physics, Gainesville, Florida 32612, USA The method of soft point-contact
Study of the Potential Dirac Material Pb 0.9 Sn 0.1 Se by Soft Point-Contact Spectroscopy Tiffany Paul University of Florida, Dept. of Physics, Gainesville, Florida 32612, USA The method of soft point-contact
Atomic Force Microscopy and Real Atomic Resolution. Simple Computer Simulations.
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 26 (2), pp. 103-107 (1994) 10 April 1994 Atomic Force Microscopy and Real Atomic Resolution. Simple Computer Simulations. V. KOUTSOS, E. MANIAS, G. TEN BRINKE and G.
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 26 (2), pp. 103-107 (1994) 10 April 1994 Atomic Force Microscopy and Real Atomic Resolution. Simple Computer Simulations. V. KOUTSOS, E. MANIAS, G. TEN BRINKE and G.
General concept and defining characteristics of AFM. Dina Kudasheva Advisor: Prof. Mary K. Cowman
 General concept and defining characteristics of AFM Dina Kudasheva Advisor: Prof. Mary K. Cowman Overview Introduction History of the SPM invention Technical Capabilities Principles of operation Examples
General concept and defining characteristics of AFM Dina Kudasheva Advisor: Prof. Mary K. Cowman Overview Introduction History of the SPM invention Technical Capabilities Principles of operation Examples
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is an instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is an instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 12
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 12 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2016 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 12.1 QCMP Course Contents 1. Classical models for electrons in solids 2. Sommerfeld
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 12 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2016 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 12.1 QCMP Course Contents 1. Classical models for electrons in solids 2. Sommerfeld
Imaging of Quantum Confinement and Electron Wave Interference
 : Forefront of Basic Research at NTT Imaging of Quantum Confinement and lectron Wave Interference Kyoichi Suzuki and Kiyoshi Kanisawa Abstract We investigated the spatial distribution of the local density
: Forefront of Basic Research at NTT Imaging of Quantum Confinement and lectron Wave Interference Kyoichi Suzuki and Kiyoshi Kanisawa Abstract We investigated the spatial distribution of the local density
Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy
 Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy Second Edition E. L. Wolf Polytechnic Institute of New York University, USA OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Concepts of quantum mechanical
Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy Second Edition E. L. Wolf Polytechnic Institute of New York University, USA OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Concepts of quantum mechanical
SEEING Phase Transitions with. Magnetic Force Microscopy. Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin. Alex de Lozanne
 SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
Bonds and Wavefunctions. Module α-1: Visualizing Electron Wavefunctions Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Instructor: Silvija Gradečak
 3.014 Materials Laboratory December 8 th 13 th, 2006 Lab week 4 Bonds and Wavefunctions Module α-1: Visualizing Electron Wavefunctions Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Instructor: Silvija Gradečak OBJECTIVES
3.014 Materials Laboratory December 8 th 13 th, 2006 Lab week 4 Bonds and Wavefunctions Module α-1: Visualizing Electron Wavefunctions Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Instructor: Silvija Gradečak OBJECTIVES
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Scanning Direction References: Classical Tunneling Quantum Mechanics Tunneling current Tunneling current I t I t (V/d)exp(-Aφ 1/2 d) A = 1.025 (ev) -1/2 Å -1 I t = 10 pa~10na
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Scanning Direction References: Classical Tunneling Quantum Mechanics Tunneling current Tunneling current I t I t (V/d)exp(-Aφ 1/2 d) A = 1.025 (ev) -1/2 Å -1 I t = 10 pa~10na
Nanoscale work function measurements by Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy
 Related Topics Tunneling effect, Defects, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), (STS), Local Density of States (LDOS), Work function, Surface activation, Catalysis Principle Scanning tunneling microscopy
Related Topics Tunneling effect, Defects, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), (STS), Local Density of States (LDOS), Work function, Surface activation, Catalysis Principle Scanning tunneling microscopy
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy References: 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982); and ibid 50, 120 (1983). 2. J. Chen, Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy,
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy References: 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982); and ibid 50, 120 (1983). 2. J. Chen, Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy,
Table of Content. Mechanical Removing Techniques. Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB)
 Table of Content Mechanical Removing Techniques Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB) Ultrasonic Machining In ultrasonic machining (USM), also called ultrasonic grinding,
Table of Content Mechanical Removing Techniques Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB) Ultrasonic Machining In ultrasonic machining (USM), also called ultrasonic grinding,
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy References: 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982); and ibid 50, 120 (1983). 2. J. Chen, Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy,
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy References: 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982); and ibid 50, 120 (1983). 2. J. Chen, Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy,
1986 s Nobel Prize in Physics
 Revised version: 2017.12.19 1986 s Nobel Prize in Physics (Electron Microscope & STM) Huiwon Ahn Seoul National University Department of Physics & Astronomy, Korea Abstract The structure of matter or organisms
Revised version: 2017.12.19 1986 s Nobel Prize in Physics (Electron Microscope & STM) Huiwon Ahn Seoul National University Department of Physics & Astronomy, Korea Abstract The structure of matter or organisms
Experimental methods in physics. Local probe microscopies I
 Experimental methods in physics Local probe microscopies I Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) Jean-Marc Bonard Academic year 09-10 1. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy 1.1. Introduction Image of surface
Experimental methods in physics Local probe microscopies I Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) Jean-Marc Bonard Academic year 09-10 1. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy 1.1. Introduction Image of surface
Integrating MEMS Electro-Static Driven Micro-Probe and Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Mode SPM System Design
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 399 407 (2009) 399 Integrating MEMS Electro-Static Driven Micro-Probe and Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Mode SPM System
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 399 407 (2009) 399 Integrating MEMS Electro-Static Driven Micro-Probe and Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Mode SPM System
Electron Transport Properties of High Temperature Superconductors. Heather Stephenson East Orange Campus High School
 Electron Transport Properties of High Temperature Superconductors Heather Stephenson East Orange Campus High School Introduction (Part 1) History of Superconductors Superconductors are materials in which
Electron Transport Properties of High Temperature Superconductors Heather Stephenson East Orange Campus High School Introduction (Part 1) History of Superconductors Superconductors are materials in which
Understanding the properties and behavior of groups of interacting atoms more than simple molecules
 Condensed Matter Physics Scratching the Surface Understanding the properties and behavior of groups of interacting atoms more than simple molecules Solids and fluids in ordinary and exotic states low energy
Condensed Matter Physics Scratching the Surface Understanding the properties and behavior of groups of interacting atoms more than simple molecules Solids and fluids in ordinary and exotic states low energy
Scanning Force Microscopy
 Scanning Force Microscopy Roland Bennewitz Rutherford Physics Building 405 Phone 398-3058 roland.bennewitz@mcgill.ca Scanning Probe is moved along scan lines over a sample surface 1 Force Microscopy Data
Scanning Force Microscopy Roland Bennewitz Rutherford Physics Building 405 Phone 398-3058 roland.bennewitz@mcgill.ca Scanning Probe is moved along scan lines over a sample surface 1 Force Microscopy Data
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Santosh Devasia Mechanical Eng. Dept., UW
 Nano-positioning Santosh Devasia Mechanical Eng. Dept., UW http://faculty.washington.edu/devasia/ Outline of Talk 1. Why Nano-positioning 2. Sensors for Nano-positioning 3. Actuators for Nano-positioning
Nano-positioning Santosh Devasia Mechanical Eng. Dept., UW http://faculty.washington.edu/devasia/ Outline of Talk 1. Why Nano-positioning 2. Sensors for Nano-positioning 3. Actuators for Nano-positioning
Introduction to Scanning Probe Microscopy Zhe Fei
 Introduction to Scanning Probe Microscopy Zhe Fei Phys 590B, Apr. 2019 1 Outline Part 1 SPM Overview Part 2 Scanning tunneling microscopy Part 3 Atomic force microscopy Part 4 Electric & Magnetic force
Introduction to Scanning Probe Microscopy Zhe Fei Phys 590B, Apr. 2019 1 Outline Part 1 SPM Overview Part 2 Scanning tunneling microscopy Part 3 Atomic force microscopy Part 4 Electric & Magnetic force
Quantum Mechanics A PHY-319 Note Set No.9 Quantum Tunnelling: The Scanning Tunnelling Microscope (STM)
 Quantum Mechanics A PHY-319 Note Set No.9 Quantum Tunnelling: The Scanning Tunnelling Microscope (STM) The STM was developed by Binnig and Rohrer (Nobel prize, 1986 - their breakthrough was in achieving
Quantum Mechanics A PHY-319 Note Set No.9 Quantum Tunnelling: The Scanning Tunnelling Microscope (STM) The STM was developed by Binnig and Rohrer (Nobel prize, 1986 - their breakthrough was in achieving
Program Operacyjny Kapitał Ludzki SCANNING PROBE TECHNIQUES - INTRODUCTION
 Program Operacyjny Kapitał Ludzki SCANNING PROBE TECHNIQUES - INTRODUCTION Peter Liljeroth Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University School of Science peter.liljeroth@aalto.fi Projekt współfinansowany
Program Operacyjny Kapitał Ludzki SCANNING PROBE TECHNIQUES - INTRODUCTION Peter Liljeroth Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University School of Science peter.liljeroth@aalto.fi Projekt współfinansowany
tip conducting surface
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. The diagram shows the tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) above a conducting surface. The tip is at a potential of 1.0 V relative to the surface. If the tip is sufficiently
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. The diagram shows the tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) above a conducting surface. The tip is at a potential of 1.0 V relative to the surface. If the tip is sufficiently
Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)
 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) --- G. Binnig, H. Rohrer et al, (1982) Near-Field Scanning Optical Microscopy (NSOM) --- D. W. Pohl (1982) Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) --- G. Binnig, H. Rohrer et al, (1982) Near-Field Scanning Optical Microscopy (NSOM) --- D. W. Pohl (1982) Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Atomic emission spectra experiment
 Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Surface Studies by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Surface Studies by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, Ch. Gerber, and E. Weibel IBM Zurich Research Laboratory, 8803 Ruschlikon-ZH, Switzerland (Received by Phys. Rev. Lett. on 30th April,
Surface Studies by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, Ch. Gerber, and E. Weibel IBM Zurich Research Laboratory, 8803 Ruschlikon-ZH, Switzerland (Received by Phys. Rev. Lett. on 30th April,
MS482 Materials Characterization ( 재료분석 ) Lecture Note 11: Scanning Probe Microscopy. Byungha Shin Dept. of MSE, KAIST
 2015 Fall Semester MS482 Materials Characterization ( 재료분석 ) Lecture Note 11: Scanning Probe Microscopy Byungha Shin Dept. of MSE, KAIST 1 Course Information Syllabus 1. Overview of various characterization
2015 Fall Semester MS482 Materials Characterization ( 재료분석 ) Lecture Note 11: Scanning Probe Microscopy Byungha Shin Dept. of MSE, KAIST 1 Course Information Syllabus 1. Overview of various characterization
Contents. What is AFM? History Basic principles and devices Operating modes Application areas Advantages and disadvantages
 Contents What is AFM? History Basic principles and devices Operating modes Application areas Advantages and disadvantages Figure1: 2004 Seth Copen Goldstein What is AFM? A type of Scanning Probe Microscopy
Contents What is AFM? History Basic principles and devices Operating modes Application areas Advantages and disadvantages Figure1: 2004 Seth Copen Goldstein What is AFM? A type of Scanning Probe Microscopy
Final exam: take-home part
 Final exam: take-home part! List five things that can be done to improve this class. Be specific; give much detail.! (You will be penalized only for insulting comments made for no benefit; you will not
Final exam: take-home part! List five things that can be done to improve this class. Be specific; give much detail.! (You will be penalized only for insulting comments made for no benefit; you will not
EFFECT OF TIP-SIZE ON STM IMAGES OF GRAPHITE
 EFFECT OF TIP-SIZE ON STM IMAGES OF GRAPHITE C. Horie, H. Miyazaki To cite this version: C. Horie, H. Miyazaki. EFFECT OF TIP-SIZE ON STM IMAGES OF GRAPHITE. Journal de Physique Colloques, 1987, 48 (C6),
EFFECT OF TIP-SIZE ON STM IMAGES OF GRAPHITE C. Horie, H. Miyazaki To cite this version: C. Horie, H. Miyazaki. EFFECT OF TIP-SIZE ON STM IMAGES OF GRAPHITE. Journal de Physique Colloques, 1987, 48 (C6),
Control of Dynamics of SPM Probes for Non-destructive Defectoscopy
 XXX. ASR '2005 Seminar, Instruments and Control, Ostrava, April 29, 2005 209 Control of Dynamics of SPM Probes for Non-destructive Defectoscopy KALA, Jaroslav Ing., Physics Department, FEEC, BUT, Technická
XXX. ASR '2005 Seminar, Instruments and Control, Ostrava, April 29, 2005 209 Control of Dynamics of SPM Probes for Non-destructive Defectoscopy KALA, Jaroslav Ing., Physics Department, FEEC, BUT, Technická
SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES OR APPARATUS; APPLICATIONS OF SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES, e.g. SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY [SPM]
![SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES OR APPARATUS; APPLICATIONS OF SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES, e.g. SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY [SPM] SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES OR APPARATUS; APPLICATIONS OF SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES, e.g. SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY [SPM]](/thumbs/81/83165631.jpg) G01Q SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES OR APPARATUS; APPLICATIONS OF SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES, e.g. SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY [SPM] Scanning probes, i.e. devices having at least a tip of nanometre sized dimensions
G01Q SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES OR APPARATUS; APPLICATIONS OF SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES, e.g. SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY [SPM] Scanning probes, i.e. devices having at least a tip of nanometre sized dimensions
MRSEC. Refrigerator Magnet Activity Guide. Quick Reference Activity Guide. a) b) c) = north = south. Activity Materials
 MRSEC Refrigerator Magnet Activity Guide Quick Reference Activity Guide Activity Materials Refrigerator magnet with removable probe strip Magnetic field diagrams Starting Points One of the great breakthroughs
MRSEC Refrigerator Magnet Activity Guide Quick Reference Activity Guide Activity Materials Refrigerator magnet with removable probe strip Magnetic field diagrams Starting Points One of the great breakthroughs
Superconducting-Insulating Quantum Phase Transition in Homogenous Thin Films
 Superconducting-Insulating Quantum Phase Transition in Homogenous Thin Films Jonathan K. Whitmer Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 1110 West Green Street, Urbana, IL 61801,
Superconducting-Insulating Quantum Phase Transition in Homogenous Thin Films Jonathan K. Whitmer Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 1110 West Green Street, Urbana, IL 61801,
Addition 1. Shear Stack Piezoelectric Elements and Shear Effect Basics
 120 Addition 1 Shear Stack Piezoelectric Elements and Shear Effect Basics Introduction The STM scanner built up in this work is a Besocke type scanner (see room temperature STM instrumental chapter). The
120 Addition 1 Shear Stack Piezoelectric Elements and Shear Effect Basics Introduction The STM scanner built up in this work is a Besocke type scanner (see room temperature STM instrumental chapter). The
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. how does STM work? the quantum mechanical picture example of images how can we understand what we see?
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy how does STM work? the quantum mechanical picture example of images how can we understand what we see? Observation of adatom diffusion with a field ion microscope Scanning
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy how does STM work? the quantum mechanical picture example of images how can we understand what we see? Observation of adatom diffusion with a field ion microscope Scanning
STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope
 STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Basic idea STM working principle Schematic representation of the sample-tip tunnel barrier Assume tip and sample described by two infinite plate electrodes Φ t +Φ s =
STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Basic idea STM working principle Schematic representation of the sample-tip tunnel barrier Assume tip and sample described by two infinite plate electrodes Φ t +Φ s =
Force-distance studies with piezoelectric tuning forks below 4.2K
 submitted to APPLIED SURFACE SCIENCE nc-afm 99, Pontresina Force-distance studies with piezoelectric tuning forks below 4.2K J. Rychen, T. Ihn, P. Studerus, A. Herrmann, K. Ensslin Solid State Physics
submitted to APPLIED SURFACE SCIENCE nc-afm 99, Pontresina Force-distance studies with piezoelectric tuning forks below 4.2K J. Rychen, T. Ihn, P. Studerus, A. Herrmann, K. Ensslin Solid State Physics
The effects of probe boundary conditions and propagation on nano- Raman spectroscopy
 The effects of probe boundary conditions and propagation on nano- Raman spectroscopy H. D. Hallen,* E. J. Ayars** and C. L. Jahncke*** * Physics Department, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC
The effects of probe boundary conditions and propagation on nano- Raman spectroscopy H. D. Hallen,* E. J. Ayars** and C. L. Jahncke*** * Physics Department, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC
MSE640: Advances in Investigation of Intermolecular & Surface Forces
 MSE640: Advances in Investigation of Forces Course Title Advances in investigation of Intermolecular & surface forces Course Code MSE640 Credit Hours 3 Pre-requisites (if any) MSE507, MSE508 or equivalent
MSE640: Advances in Investigation of Forces Course Title Advances in investigation of Intermolecular & surface forces Course Code MSE640 Credit Hours 3 Pre-requisites (if any) MSE507, MSE508 or equivalent
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy
 Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Observing the Doppler Absorption of Rubidium Using a Tunable Laser Diode System
 Observing the Doppler Absorption of Rubidium Using a Tunable Laser Diode System Ryan Prenger 5/5/00 Final Submission Purdue University Physics Department Abstract Using a tunable laser diode, Doppler absorption
Observing the Doppler Absorption of Rubidium Using a Tunable Laser Diode System Ryan Prenger 5/5/00 Final Submission Purdue University Physics Department Abstract Using a tunable laser diode, Doppler absorption
Crystalline Surfaces for Laser Metrology
 Crystalline Surfaces for Laser Metrology A.V. Latyshev, Institute of Semiconductor Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract: The number of methodological recommendations has been pronounced to describe
Crystalline Surfaces for Laser Metrology A.V. Latyshev, Institute of Semiconductor Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract: The number of methodological recommendations has been pronounced to describe
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy References: 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982); and ibid 50, 120 (1983). 2. J. Chen, Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy,
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy References: 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982); and ibid 50, 120 (1983). 2. J. Chen, Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy,
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
2 Symmetry. 2.1 Structure of carbon nanotubes
 2 Symmetry Carbon nanotubes are hollow cylinders of graphite sheets. They can be viewed as single molecules, regarding their small size ( nm in diameter and µm length), or as quasi-one dimensional crystals
2 Symmetry Carbon nanotubes are hollow cylinders of graphite sheets. They can be viewed as single molecules, regarding their small size ( nm in diameter and µm length), or as quasi-one dimensional crystals
THE LINE OF RESISTANCE
 ADDENDA TO: THE LINE OF RESISTANCE Dr. Lawrence D. Woolf General Atomics San Diego, CA 92121 Larry.Woolf@gat.com July 5, 2001 ADDENDUM TO 1A: ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY OF GRAPHITE There is another way to
ADDENDA TO: THE LINE OF RESISTANCE Dr. Lawrence D. Woolf General Atomics San Diego, CA 92121 Larry.Woolf@gat.com July 5, 2001 ADDENDUM TO 1A: ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY OF GRAPHITE There is another way to
Nanoscale characteristics by Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy
 Related Topics Tunneling effect, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), (STS), Local Density of States (LDOS), Band structure, Band Gap, k-space, Brioullin Zone, Metal, Semi-Metal, Semiconductor Principle
Related Topics Tunneling effect, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), (STS), Local Density of States (LDOS), Band structure, Band Gap, k-space, Brioullin Zone, Metal, Semi-Metal, Semiconductor Principle
CNPEM Laboratório de Ciência de Superfícies
 Investigating electrical charged samples by scanning probe microscopy: the influence to magnetic force microscopy and atomic force microscopy phase images. Carlos A. R. Costa, 1 Evandro M. Lanzoni, 1 Maria
Investigating electrical charged samples by scanning probe microscopy: the influence to magnetic force microscopy and atomic force microscopy phase images. Carlos A. R. Costa, 1 Evandro M. Lanzoni, 1 Maria
bio-molecular studies Physical methods in Semmelweis University Osváth Szabolcs
 Physical methods in bio-molecular studies Osváth Szabolcs Semmelweis University szabolcs.osvath@eok.sote.hu Light emission and absorption spectra Stokes shift is the difference (in wavelength or frequency
Physical methods in bio-molecular studies Osváth Szabolcs Semmelweis University szabolcs.osvath@eok.sote.hu Light emission and absorption spectra Stokes shift is the difference (in wavelength or frequency
Thermal properties of Engineering Materials
 Thermal properties of Engineering Materials Engineering materials are important in everyday life because of their versatile structural properties. Other than these properties, they do play an important
Thermal properties of Engineering Materials Engineering materials are important in everyday life because of their versatile structural properties. Other than these properties, they do play an important
(Scanning Probe Microscopy)
 (Scanning Probe Microscopy) Ing-Shouh Hwang (ishwang@phys.sinica.edu.tw) Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan References 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett.
(Scanning Probe Microscopy) Ing-Shouh Hwang (ishwang@phys.sinica.edu.tw) Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan References 1. G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, C. Gerber, and Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett.
Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors
 Abstract Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors Aliya Merali University of Florida REU Participant, Summer 2010 Advisor: Dr. Tarek Saab Preparations for a position calibration of cryogenic
Abstract Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors Aliya Merali University of Florida REU Participant, Summer 2010 Advisor: Dr. Tarek Saab Preparations for a position calibration of cryogenic
NIS: what can it be used for?
 AFM @ NIS: what can it be used for? Chiara Manfredotti 011 670 8382/8388/7879 chiara.manfredotti@to.infn.it Skype: khiaram 1 AFM: block scheme In an Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) a micrometric tip attached
AFM @ NIS: what can it be used for? Chiara Manfredotti 011 670 8382/8388/7879 chiara.manfredotti@to.infn.it Skype: khiaram 1 AFM: block scheme In an Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) a micrometric tip attached
Physics 312 Assignment 5
 Physics 31 Assignment 5 This assignment contains many short questions and a long one. Several questions are taken from Bloom eld Section 11., with some changes. 1. ( points) It is possible to combine the
Physics 31 Assignment 5 This assignment contains many short questions and a long one. Several questions are taken from Bloom eld Section 11., with some changes. 1. ( points) It is possible to combine the
Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics
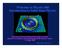 Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscope image of atoms placed on a surface, and confined quantum electron waves D. Eigler IBM Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 1
Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscope image of atoms placed on a surface, and confined quantum electron waves D. Eigler IBM Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 1
MAGNETIC FORCE MICROSCOPY
 University of Ljubljana Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Department of Physics SEMINAR MAGNETIC FORCE MICROSCOPY Author: Blaž Zupančič Supervisor: dr. Igor Muševič February 2003 Contents 1 Abstract 3
University of Ljubljana Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Department of Physics SEMINAR MAGNETIC FORCE MICROSCOPY Author: Blaž Zupančič Supervisor: dr. Igor Muševič February 2003 Contents 1 Abstract 3
Università degli Studi di Bari "Aldo Moro"
 Università degli Studi di Bari "Aldo Moro" Table of contents 1. Introduction to Atomic Force Microscopy; 2. Introduction to Raman Spectroscopy; 3. The need for a hybrid technique Raman AFM microscopy;
Università degli Studi di Bari "Aldo Moro" Table of contents 1. Introduction to Atomic Force Microscopy; 2. Introduction to Raman Spectroscopy; 3. The need for a hybrid technique Raman AFM microscopy;
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2491 Experimental Realization of Two-dimensional Boron Sheets Baojie Feng 1, Jin Zhang 1, Qing Zhong 1, Wenbin Li 1, Shuai Li 1, Hui Li 1, Peng Cheng 1, Sheng Meng 1,2, Lan Chen 1 and
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2491 Experimental Realization of Two-dimensional Boron Sheets Baojie Feng 1, Jin Zhang 1, Qing Zhong 1, Wenbin Li 1, Shuai Li 1, Hui Li 1, Peng Cheng 1, Sheng Meng 1,2, Lan Chen 1 and
EXPLORING SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY WITH MATHEMATICA
 EXPLORING SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY WITH MATHEMATICA Dror Sarid University of Arizona A WILEY-1NTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto CONTENTS
EXPLORING SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY WITH MATHEMATICA Dror Sarid University of Arizona A WILEY-1NTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto CONTENTS
Vacuum Kelvin Force Probe Research Richard Williams August 1st 2008
 Vacuum Kelvin Force Probe Research Richard Williams August 1st 2008 Introduction Kelvin Force Probe Microscopy is an analytical method to measure the contact potential difference between a reference material
Vacuum Kelvin Force Probe Research Richard Williams August 1st 2008 Introduction Kelvin Force Probe Microscopy is an analytical method to measure the contact potential difference between a reference material
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Institute for Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis Graz Centre for Electron Microscopy
 Institute for Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis Graz Centre for Electron Microscopy Micromechanics Ass.Prof. Priv.-Doz. DI Dr. Harald Plank a,b a Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis, Graz
Institute for Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis Graz Centre for Electron Microscopy Micromechanics Ass.Prof. Priv.-Doz. DI Dr. Harald Plank a,b a Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis, Graz
Principles and Applications of Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs)
 Principles and Applications of Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs) PHY 300 - Junior Phyics Laboratory Syed Ali Raza Roll no: 2012-10-0124 LUMS School of Science and Engineering Thursday,
Principles and Applications of Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs) PHY 300 - Junior Phyics Laboratory Syed Ali Raza Roll no: 2012-10-0124 LUMS School of Science and Engineering Thursday,
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes Fabrication of the scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) probes is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 1 and proceeds
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes Fabrication of the scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) probes is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 1 and proceeds
Carbon-nanotubes on graphite: alignment of lattice structure
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 (2003 818 822 PII: S0022-3727(0357144-3 Carbon-nanotubes on graphite: alignment of lattice structure C Rettig
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 (2003 818 822 PII: S0022-3727(0357144-3 Carbon-nanotubes on graphite: alignment of lattice structure C Rettig
SOLID STATE PHYSICS PHY F341. Dr. Manjuladevi.V Associate Professor Department of Physics BITS Pilani
 SOLID STATE PHYSICS PHY F341 Dr. Manjuladevi.V Associate Professor Department of Physics BITS Pilani 333031 manjula@bits-pilani.ac.in Characterization techniques SEM AFM STM BAM Outline What can we use
SOLID STATE PHYSICS PHY F341 Dr. Manjuladevi.V Associate Professor Department of Physics BITS Pilani 333031 manjula@bits-pilani.ac.in Characterization techniques SEM AFM STM BAM Outline What can we use
