Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals
|
|
|
- Buddy McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution method for anti-differentiation. Reading: Textbook reading for Unit #10 : Study Sections 6.1, 7.1
2 2 The Relation between the Integral and the Derivative Graphs We saw last week that b a f(x) dx = F(b) F(a) if F(x) is an anti-derivative of f(x). Recognizing that finding anti-derivatives would be a central part of evaluating integrals, we introduced the notation f(x) dx = F(x)+C F (x) = f(x) Many times when we can t easily evaluate or find an anti-derivative by hand, we can at least sketch what the anti-derivative would look like; there are very clear relationships between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x).
3 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 3 Example: Consider the graph of f(x) shown below. Sketch two possible anti-derivatives of f(x)
4 4 Example: Consider the graph of g(x) = sin(x) shown below. Sketch two possible anti-derivatives of g(x).
5 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 5 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus lets us add additional detail to the antiderivative graph: b a f(x) dx = F(b) F(a) = F What does this statement tell up about the graph of F(x) and f(x)?
6 6 Re-sketch the earlier anti-derivative graph of sin(x), find the area underneath one arch of the sine graph.
7 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 7 Example: Use the area interpretation of F or F(b) F(a) to construct a detailed sketch of the anti-derivative of f(x) for which F(0) =
8 8 Example: f(x) is a continuous function, and f(0) = 1. The graph of f (x) is shown below Based only on the information in the f graph, identify the location of types of all the critical points of f(x) on the interval x [0,6].
9 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 9 Sketch the graph of f(x) on the interval [0, 6]
10 Question: Given the graph of f(x) above, which of the graphs below is an anti-derivative of f(x)? A B C D
11 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 11 Attheendoflastweek, weconsideredaspecialcasetoourtableofanti-derivatives. Example: What function, differentiated, gives f(x) = 1 x?
12 12 Below is the graph of f(x) = 1/x. Using the answer above, and our sketching techniques from today s class, sketch an anti-derivative of f(x). Use the points F(1) = 0 and F( 1) = 0.
13 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 13 Explain why we need to define 1 x dx = ln( x )+C, not simply ln(x)+c. Sketch the area implied by the integral the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus x dx, and find its value using
14 14 We now return to the challenge of finding a formula for an anti-derivative function. Wesawsimplecaseslastweek,andnowwewillextendourmethodstohandlemore complex integrals. Anti-differentiation by Inspection: The Guess-and-Check Method Reading: Section 7.1 Often, even if we do not see an anti-derivative immediately, we can make an educated guess and eventually arrive at the correct answer. [See also H-H, p ]
15 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 15 Example: Based on your knowledge of derivatives, what should the antiderivative of cos(3x), cos(3x) dx, look like?
16 16 Example: Find e 3x 2 dx.
17 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 17 Example: Both of our previous examples had linear inside functions. Here is an integral with a quadratic inside function: xe x2 dx Evaluate the integral. Why was it important that there be a factor x in front of e x2 in this integral?
18 18 Integration by Substitution We can formalize the guess-and-check method by defining an intermediate variable the represents the inside function. Reading: Section 7.1 Example: Show that x 3 x 4 +5 dx = 1 6 (x4 +5) 3/2 +C.
19 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 19 Relate this result to the chain rule.
20 20 Now use the method of substitution to evaluate x 3 x 4 +5 dx
21 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 21 Steps in the Method Of Substitution 1. Select a simple function w(x) that appears in the integral. Typically, you will also see w as a factor in the integrand as well. 2. Find dw by differentiating. Write it in the form dw =... dx dx 3. Rewrite the integral using only w and dw (no x nor dx). If you can now evaluate the integral, the substitution was effective. If you cannot remove all the x s, or the integral became harder instead of easier, then either try a different substitution, or a different integration method.
22 22 Example: Find tan(x) dx.
23 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 23 Though it is not required unless specifically requested, it can be reassuring to check the answer. Verify that the anti-derivative you found is correct.
24 24 Example: Find x 3 e x4 3 dx.
25 Example: For the integral, e x e x Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 25 (e x +e x ) 2dx both w = e x e x and w = e x +e x are seemingly reasonable substitutions. Question: Which substitution will change the integral into a simpler form? 1. w = e x e x 2. w = e x +e x
26 26 Compare both substitutions in practice. e x e x dx e x +e x with w = e x e x with w = e x +e x
27 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 27 Example: Find sin(x) 1+cos 2 (x) dx.
28 28 Using the Method of Substitution for Definite Integrals If we are asked to evaluate a definite integral such as π/2 0 sinx 1+cosx dx, where a substitution will ease the integration, we have two methods for handling the limits of integration (x = 0 and x = π/2). a) When we make our substitution, convert both the variables x and the limits (in x) to the new variable; or b) do the integration keeping the limits explicitly in terms of x, writing the final integral back in terms of the original x variable as well, and then evaluating.
29 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 29 Example: Use method a) to evaluate the integral π/2 0 sinx 1+cosx dx
30 30 Example: Use method b) method to evaluate x x dx.
31 Unit 10 Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals 31 Non-Obvious Substitution Integrals Sometimes a substitution will still simplify the integral, even if you don t see an obvious cue of function and its derivative in the integrand. Example: Find 1 dx. x+1
32
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
The Relation between the Integral and the Derivative Graphs. Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves. Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts
 Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Announcements. Topics: Homework:
 Announcements Topics: - sections 7.3 (the definite integral +area), 7.4 (FTC), 7.5 (additional techniques of integration) * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook! Homework: - review
Announcements Topics: - sections 7.3 (the definite integral +area), 7.4 (FTC), 7.5 (additional techniques of integration) * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook! Homework: - review
Announcements. Topics: Homework:
 Announcements Topics: - sections 7.4 (FTC), 7.5 (additional techniques of integration), 7.6 (applications of integration) * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook! Homework: - review
Announcements Topics: - sections 7.4 (FTC), 7.5 (additional techniques of integration), 7.6 (applications of integration) * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook! Homework: - review
5.5. The Substitution Rule
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
4.4 AREAS, INTEGRALS AND ANTIDERIVATIVES
 1 4.4 AREAS, INTEGRALS AND ANTIDERIVATIVES This section explores properties of functions defined as areas and examines some of the connections among areas, integrals and antiderivatives. In order to focus
1 4.4 AREAS, INTEGRALS AND ANTIDERIVATIVES This section explores properties of functions defined as areas and examines some of the connections among areas, integrals and antiderivatives. In order to focus
1.4 Techniques of Integration
 .4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
.4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
Calculus I Announcements
 Slide 1 Calculus I Announcements Read sections 4.2,4.3,4.4,4.1 and 5.3 Do the homework from sections 4.2,4.3,4.4,4.1 and 5.3 Exam 3 is Thursday, November 12th See inside for a possible exam question. Slide
Slide 1 Calculus I Announcements Read sections 4.2,4.3,4.4,4.1 and 5.3 Do the homework from sections 4.2,4.3,4.4,4.1 and 5.3 Exam 3 is Thursday, November 12th See inside for a possible exam question. Slide
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Integration by Substitution
 November 22, 2013 Introduction 7x 2 cos(3x 3 )dx =? 2xe x2 +5 dx =? Chain rule The chain rule: d dx (f (g(x))) = f (g(x)) g (x). Use the chain rule to find f (x) and then write the corresponding anti-differentiation
November 22, 2013 Introduction 7x 2 cos(3x 3 )dx =? 2xe x2 +5 dx =? Chain rule The chain rule: d dx (f (g(x))) = f (g(x)) g (x). Use the chain rule to find f (x) and then write the corresponding anti-differentiation
Math 111 lecture for Friday, Week 10
 Math lecture for Friday, Week Finding antiderivatives mean reversing the operation of taking derivatives. Today we ll consider reversing the chain rule and the product rule. Substitution technique. Recall
Math lecture for Friday, Week Finding antiderivatives mean reversing the operation of taking derivatives. Today we ll consider reversing the chain rule and the product rule. Substitution technique. Recall
Exploring Substitution
 I. Introduction Exploring Substitution Math Fall 08 Lab We use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part to evaluate a definite integral. If f is continuous on [a, b] b and F is any antiderivative of f
I. Introduction Exploring Substitution Math Fall 08 Lab We use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part to evaluate a definite integral. If f is continuous on [a, b] b and F is any antiderivative of f
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
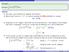 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3 Algebraic Methods. we can differentiate both sides implicitly to obtain a differential equation involving x and y:
 3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
Math 261 Calculus I. Test 1 Study Guide. Name. Decide whether the limit exists. If it exists, find its value. 1) lim x 1. f(x) 2) lim x -1/2 f(x)
 Math 261 Calculus I Test 1 Study Guide Name Decide whether the it exists. If it exists, find its value. 1) x 1 f(x) 2) x -1/2 f(x) Complete the table and use the result to find the indicated it. 3) If
Math 261 Calculus I Test 1 Study Guide Name Decide whether the it exists. If it exists, find its value. 1) x 1 f(x) 2) x -1/2 f(x) Complete the table and use the result to find the indicated it. 3) If
The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes. Marcel Proust
 The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes. Marcel Proust School of the Art Institute of Chicago Calculus Frank Timmes ftimmes@artic.edu flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.shtml
The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes. Marcel Proust School of the Art Institute of Chicago Calculus Frank Timmes ftimmes@artic.edu flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.shtml
Section 4.4. Using the Fundamental Theorem. Difference Equations to Differential Equations
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 4.4 Using the Fundamental Theorem As we saw in Section 4.3, using the Fundamental Theorem of Integral Calculus reduces the problem of evaluating a
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 4.4 Using the Fundamental Theorem As we saw in Section 4.3, using the Fundamental Theorem of Integral Calculus reduces the problem of evaluating a
Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) 1 / 28 Indefinite Integral Given a function f, if F is a function such that
Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) 1 / 28 Indefinite Integral Given a function f, if F is a function such that
School of the Art Institute of Chicago. Calculus. Frank Timmes. flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.
 School of the Art Institute of Chicago Calculus Frank Timmes ftimmes@artic.edu flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.shtml Syllabus 1 Aug 29 Pre-calculus 2 Sept 05 Rates and areas 3 Sept 12 Trapezoids
School of the Art Institute of Chicago Calculus Frank Timmes ftimmes@artic.edu flash.uchicago.edu/~fxt/class_pages/class_calc.shtml Syllabus 1 Aug 29 Pre-calculus 2 Sept 05 Rates and areas 3 Sept 12 Trapezoids
MTH4100 Calculus I. Bill Jackson School of Mathematical Sciences QMUL. Week 9, Semester 1, 2013
 MTH4100 School of Mathematical Sciences QMUL Week 9, Semester 1, 2013 Concavity Concavity In the literature concave up is often referred to as convex, and concave down is simply called concave. The second
MTH4100 School of Mathematical Sciences QMUL Week 9, Semester 1, 2013 Concavity Concavity In the literature concave up is often referred to as convex, and concave down is simply called concave. The second
Calculus I Review Solutions
 Calculus I Review Solutions. Compare and contrast the three Value Theorems of the course. When you would typically use each. The three value theorems are the Intermediate, Mean and Extreme value theorems.
Calculus I Review Solutions. Compare and contrast the three Value Theorems of the course. When you would typically use each. The three value theorems are the Intermediate, Mean and Extreme value theorems.
a x a y = a x+y a x a = y ax y (a x ) r = a rx and log a (xy) = log a (x) + log a (y) log a ( x y ) = log a(x) log a (y) log a (x r ) = r log a (x).
 You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
Integration by Parts
 Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
More on infinite series Antiderivatives and area
 More on infinite series Antiderivatives and area September 28, 2017 The eighth breakfast was on Monday: There are still slots available for the October 4 breakfast (Wednesday, 8AM), and there s a pop-in
More on infinite series Antiderivatives and area September 28, 2017 The eighth breakfast was on Monday: There are still slots available for the October 4 breakfast (Wednesday, 8AM), and there s a pop-in
Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem
 Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem Before we continue with the problem of describing graphs using calculus we shall briefly pause to examine some interesting applications of the derivative. In previous
Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem Before we continue with the problem of describing graphs using calculus we shall briefly pause to examine some interesting applications of the derivative. In previous
INTEGRATION: THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS
 INTEGRATION: THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS RECALL: ANTIDERIVATIVES When we last spoke of integration, we examined a physics problem where we saw that the area under the
INTEGRATION: THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS RECALL: ANTIDERIVATIVES When we last spoke of integration, we examined a physics problem where we saw that the area under the
4. Theory of the Integral
 4. Theory of the Integral 4.1 Antidifferentiation 4.2 The Definite Integral 4.3 Riemann Sums 4.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.5 Fundamental Integration Rules 4.6 U-Substitutions 4.1 Antidifferentiation
4. Theory of the Integral 4.1 Antidifferentiation 4.2 The Definite Integral 4.3 Riemann Sums 4.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.5 Fundamental Integration Rules 4.6 U-Substitutions 4.1 Antidifferentiation
INTEGRALS5 INTEGRALS
 INTEGRALS5 INTEGRALS INTEGRALS 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus In this section, we will learn about: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and its significance. FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS The
INTEGRALS5 INTEGRALS INTEGRALS 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus In this section, we will learn about: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and its significance. FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS The
f(x) = lim x 0 + x = lim f(x) =
 Infinite Limits Having discussed in detail its as x ±, we would like to discuss in more detail its where f(x) ±. Once again we would like to emphasize that ± are not numbers, so if we write f(x) = we are
Infinite Limits Having discussed in detail its as x ±, we would like to discuss in more detail its where f(x) ±. Once again we would like to emphasize that ± are not numbers, so if we write f(x) = we are
MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives
 MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives 1 Formal Definition of the Derivative We have seen plenty of limits so far, but very few applications. In particular, we have seen very few functions for which
MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives 1 Formal Definition of the Derivative We have seen plenty of limits so far, but very few applications. In particular, we have seen very few functions for which
Section 5.6. Integration By Parts. MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10
 Section 5.6 Integration By Parts MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10 Integration By Parts Manipulating the Product Rule d dx (f (x) g(x)) = f (x) g (x) + f (x) g(x)
Section 5.6 Integration By Parts MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10 Integration By Parts Manipulating the Product Rule d dx (f (x) g(x)) = f (x) g (x) + f (x) g(x)
In general, if we start with a function f and want to reverse the differentiation process, then we are finding an antiderivative of f.
 Math 1410 Worksheet #27: Section 4.9 Name: Our final application of derivatives is a prelude to what will come in later chapters. In many situations, it will be necessary to find a way to reverse the differentiation
Math 1410 Worksheet #27: Section 4.9 Name: Our final application of derivatives is a prelude to what will come in later chapters. In many situations, it will be necessary to find a way to reverse the differentiation
7 + 8x + 9x x + 12x x 6. x 3. (c) lim. x 2 + x 3 x + x 4 (e) lim. (d) lim. x 5
 Practice Exam 3 Fundamentals of Calculus, ch. 1-5 1 A falling rock has a height (in meters) as a function of time (in seconds) given by h(t) = pt 2 + qt + r, where p, q, and r are constants. (a) Infer
Practice Exam 3 Fundamentals of Calculus, ch. 1-5 1 A falling rock has a height (in meters) as a function of time (in seconds) given by h(t) = pt 2 + qt + r, where p, q, and r are constants. (a) Infer
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Distance and Velocity
 Distance and Velocity - Unit #8 : Goals: The Integral Determine how to calculate the area described by a function. Define the definite integral. Explore the relationship between the definite integral and
Distance and Velocity - Unit #8 : Goals: The Integral Determine how to calculate the area described by a function. Define the definite integral. Explore the relationship between the definite integral and
Practice Problems: Integration by Parts
 Practice Problems: Integration by Parts Answers. (a) Neither term will get simpler through differentiation, so let s try some choice for u and dv, and see how it works out (we can always go back and try
Practice Problems: Integration by Parts Answers. (a) Neither term will get simpler through differentiation, so let s try some choice for u and dv, and see how it works out (we can always go back and try
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued)
 Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
M152: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review
 M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
Integration by Substitution
 Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
M155 Exam 2 Concept Review
 M155 Exam 2 Concept Review Mark Blumstein DERIVATIVES Product Rule Used to take the derivative of a product of two functions u and v. u v + uv Quotient Rule Used to take a derivative of the quotient of
M155 Exam 2 Concept Review Mark Blumstein DERIVATIVES Product Rule Used to take the derivative of a product of two functions u and v. u v + uv Quotient Rule Used to take a derivative of the quotient of
The Definite Integral. Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area
 The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
Integrals. D. DeTurck. January 1, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Integrals 1 / 61
 Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Chapter 6. Techniques of Integration. 6.1 Differential notation
 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6. Techniques of Integration. 6.1 Differential notation
 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections
 Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Section 5.8. Taylor Series
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 5.8 Taylor Series In this section we will put together much of the work of Sections 5.-5.7 in the context of a discussion of Taylor series. We begin
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 5.8 Taylor Series In this section we will put together much of the work of Sections 5.-5.7 in the context of a discussion of Taylor series. We begin
(e) 2 (f) 2. (c) + (d). Limits at Infinity. 2.5) 9-14,25-34,41-43,46-47,56-57, (c) (d) 2
 Math 150A. Final Review Answers, Spring 2018. Limits. 2.2) 7-10, 21-24, 28-1, 6-8, 4-44. 1. Find the values, or state they do not exist. (a) (b) 1 (c) DNE (d) 1 (e) 2 (f) 2 (g) 2 (h) 4 2. lim f(x) = 2,
Math 150A. Final Review Answers, Spring 2018. Limits. 2.2) 7-10, 21-24, 28-1, 6-8, 4-44. 1. Find the values, or state they do not exist. (a) (b) 1 (c) DNE (d) 1 (e) 2 (f) 2 (g) 2 (h) 4 2. lim f(x) = 2,
Chapter 5 Integrals. 5.1 Areas and Distances
 Chapter 5 Integrals 5.1 Areas and Distances We start with a problem how can we calculate the area under a given function ie, the area between the function and the x-axis? If the curve happens to be something
Chapter 5 Integrals 5.1 Areas and Distances We start with a problem how can we calculate the area under a given function ie, the area between the function and the x-axis? If the curve happens to be something
7.2 Parts (Undoing the Product Rule)
 7.2 Parts (Undoing the Product Rule) 7.1 Substitution (Undoing the Chain Rule) Often w inside of some other function, dw up to constant What I want you to show me... w, dw, with respect to w 7.2 Parts
7.2 Parts (Undoing the Product Rule) 7.1 Substitution (Undoing the Chain Rule) Often w inside of some other function, dw up to constant What I want you to show me... w, dw, with respect to w 7.2 Parts
Question Details sp15 u sub intro 1(MEV) [ ]
![Question Details sp15 u sub intro 1(MEV) [ ] Question Details sp15 u sub intro 1(MEV) [ ]](/thumbs/74/69627605.jpg) 12 Basic: Integration by Substitution (9971904) Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Instructions Read today's Notes and Learning Goals 1. Question Details sp15 u sub intro 1(MEV) [3443269]
12 Basic: Integration by Substitution (9971904) Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Instructions Read today's Notes and Learning Goals 1. Question Details sp15 u sub intro 1(MEV) [3443269]
5 t + t2 4. (ii) f(x) = ln(x 2 1). (iii) f(x) = e 2x 2e x + 3 4
 Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
14 Increasing and decreasing functions
 14 Increasing and decreasing functions 14.1 Sketching derivatives READING Read Section 3.2 of Rogawski Reading Recall, f (a) is the gradient of the tangent line of f(x) at x = a. We can use this fact to
14 Increasing and decreasing functions 14.1 Sketching derivatives READING Read Section 3.2 of Rogawski Reading Recall, f (a) is the gradient of the tangent line of f(x) at x = a. We can use this fact to
Limits, Continuity, and the Derivative
 Unit #2 : Limits, Continuity, and the Derivative Goals: Study and define continuity Review limits Introduce the derivative as the limit of a difference quotient Discuss the derivative as a rate of change
Unit #2 : Limits, Continuity, and the Derivative Goals: Study and define continuity Review limits Introduce the derivative as the limit of a difference quotient Discuss the derivative as a rate of change
Ma 530 Power Series II
 Ma 530 Power Series II Please note that there is material on power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presentation of the topics that follow. Operations on Power Series
Ma 530 Power Series II Please note that there is material on power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presentation of the topics that follow. Operations on Power Series
Mathematic 108, Fall 2015: Solutions to assignment #7
 Mathematic 08, Fall 05: Solutions to assignment #7 Problem # Suppose f is a function with f continuous on the open interval I and so that f has a local maximum at both x = a and x = b for a, b I with a
Mathematic 08, Fall 05: Solutions to assignment #7 Problem # Suppose f is a function with f continuous on the open interval I and so that f has a local maximum at both x = a and x = b for a, b I with a
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I
 MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Fall 2017, WEEK 14 JoungDong Kim Week 14 Section 5.4, 5.5, 6.1, Indefinite Integrals and the Net Change Theorem, The Substitution Rule, Areas Between Curves. Section
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Fall 2017, WEEK 14 JoungDong Kim Week 14 Section 5.4, 5.5, 6.1, Indefinite Integrals and the Net Change Theorem, The Substitution Rule, Areas Between Curves. Section
Math 10b Ch. 8 Reading 1: Introduction to Taylor Polynomials
 Math 10b Ch. 8 Reading 1: Introduction to Taylor Polynomials Introduction: In applications, it often turns out that one cannot solve the differential equations or antiderivatives that show up in the real
Math 10b Ch. 8 Reading 1: Introduction to Taylor Polynomials Introduction: In applications, it often turns out that one cannot solve the differential equations or antiderivatives that show up in the real
Core Mathematics 3 Differentiation
 http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
MATH 250 TOPIC 13 INTEGRATION. 13B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules
 Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
Learning Objectives for Math 165
 Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 9
 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 9 Today we will study: Limits at infinity. L Hôpital s Rule. Mean Value Theorem. (11.5,11.6, 4.1) PS3 is due this Friday June 16. Next class: Applications of the Mean Value Theorem.
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 9 Today we will study: Limits at infinity. L Hôpital s Rule. Mean Value Theorem. (11.5,11.6, 4.1) PS3 is due this Friday June 16. Next class: Applications of the Mean Value Theorem.
Calculus I Homework: Linear Approximation and Differentials Page 1
 Calculus I Homework: Linear Approximation and Differentials Page Example (3..8) Find the linearization L(x) of the function f(x) = (x) /3 at a = 8. The linearization is given by which approximates the
Calculus I Homework: Linear Approximation and Differentials Page Example (3..8) Find the linearization L(x) of the function f(x) = (x) /3 at a = 8. The linearization is given by which approximates the
2015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution
 015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
Calculus I Homework: Linear Approximation and Differentials Page 1
 Calculus I Homework: Linear Approximation and Differentials Page Questions Example Find the linearization L(x) of the function f(x) = (x) /3 at a = 8. Example Find the linear approximation of the function
Calculus I Homework: Linear Approximation and Differentials Page Questions Example Find the linearization L(x) of the function f(x) = (x) /3 at a = 8. Example Find the linear approximation of the function
4.9 Anti-derivatives. Definition. An anti-derivative of a function f is a function F such that F (x) = f (x) for all x.
 4.9 Anti-derivatives Anti-differentiation is exactly what it sounds like: the opposite of differentiation. That is, given a function f, can we find a function F whose derivative is f. Definition. An anti-derivative
4.9 Anti-derivatives Anti-differentiation is exactly what it sounds like: the opposite of differentiation. That is, given a function f, can we find a function F whose derivative is f. Definition. An anti-derivative
Limit. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 9 Limit Limit is the foundation of calculus that it is so useful to understand more complicating chapters of calculus. Besides, Mathematics has black hole scenarios (dividing by zero, going to
Chapter 9 Limit Limit is the foundation of calculus that it is so useful to understand more complicating chapters of calculus. Besides, Mathematics has black hole scenarios (dividing by zero, going to
Lecture : The Indefinite Integral MTH 124
 Up to this point we have investigated the definite integral of a function over an interval. In particular we have done the following. Approximated integrals using left and right Riemann sums. Defined the
Up to this point we have investigated the definite integral of a function over an interval. In particular we have done the following. Approximated integrals using left and right Riemann sums. Defined the
MAT 122 Homework 7 Solutions
 MAT 1 Homework 7 Solutions Section 3.3, Problem 4 For the function w = (t + 1) 100, we take the inside function to be z = t + 1 and the outside function to be z 100. The derivative of the inside function
MAT 1 Homework 7 Solutions Section 3.3, Problem 4 For the function w = (t + 1) 100, we take the inside function to be z = t + 1 and the outside function to be z 100. The derivative of the inside function
f(x) g(x) = [f (x)g(x) dx + f(x)g (x)dx
 Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
What is on today. 1 Linear approximation. MA 123 (Calculus I) Lecture 17: November 2, 2017 Section A2. Professor Jennifer Balakrishnan,
 Professor Jennifer Balakrishnan, jbala@bu.edu What is on today 1 Linear approximation 1 1.1 Linear approximation and concavity....................... 2 1.2 Change in y....................................
Professor Jennifer Balakrishnan, jbala@bu.edu What is on today 1 Linear approximation 1 1.1 Linear approximation and concavity....................... 2 1.2 Change in y....................................
Families of Functions, Taylor Polynomials, l Hopital s
 Unit #6 : Rule Families of Functions, Taylor Polynomials, l Hopital s Goals: To use first and second derivative information to describe functions. To be able to find general properties of families of functions.
Unit #6 : Rule Families of Functions, Taylor Polynomials, l Hopital s Goals: To use first and second derivative information to describe functions. To be able to find general properties of families of functions.
8.7 MacLaurin Polynomials
 8.7 maclaurin polynomials 67 8.7 MacLaurin Polynomials In this chapter you have learned to find antiderivatives of a wide variety of elementary functions, but many more such functions fail to have an antiderivative
8.7 maclaurin polynomials 67 8.7 MacLaurin Polynomials In this chapter you have learned to find antiderivatives of a wide variety of elementary functions, but many more such functions fail to have an antiderivative
11.10a Taylor and Maclaurin Series
 11.10a 1 11.10a Taylor and Maclaurin Series Let y = f(x) be a differentiable function at x = a. In first semester calculus we saw that (1) f(x) f(a)+f (a)(x a), for all x near a The right-hand side of
11.10a 1 11.10a Taylor and Maclaurin Series Let y = f(x) be a differentiable function at x = a. In first semester calculus we saw that (1) f(x) f(a)+f (a)(x a), for all x near a The right-hand side of
Exam 3 MATH Calculus I
 Trinity College December 03, 2015 MATH 131-01 Calculus I By signing below, you attest that you have neither given nor received help of any kind on this exam. Signature: Printed Name: Instructions: Show
Trinity College December 03, 2015 MATH 131-01 Calculus I By signing below, you attest that you have neither given nor received help of any kind on this exam. Signature: Printed Name: Instructions: Show
b n x n + b n 1 x n b 1 x + b 0
 Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
1 Lesson 13: Methods of Integration
 Lesson 3: Methods of Integration Chapter 6 Material: pages 273-294 in the textbook: Lesson 3 reviews integration by parts and presents integration via partial fraction decomposition as the third of the
Lesson 3: Methods of Integration Chapter 6 Material: pages 273-294 in the textbook: Lesson 3 reviews integration by parts and presents integration via partial fraction decomposition as the third of the
Antiderivatives. DEFINITION: A function F is called an antiderivative of f on an (open) interval I if F (x) = f(x) for all x in I EXAMPLES:
 Antiderivatives 00 Kiryl Tsishchanka DEFINITION: A function F is called an antiderivative of f on an (open) interval I if F (x) = f(x) for all x in I EXAMPLES:. If f(x) = x, then F(x) = 3 x3, since ( )
Antiderivatives 00 Kiryl Tsishchanka DEFINITION: A function F is called an antiderivative of f on an (open) interval I if F (x) = f(x) for all x in I EXAMPLES:. If f(x) = x, then F(x) = 3 x3, since ( )
Math 230 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution
 Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
OBJECTIVES Use the area under a graph to find total cost. Use rectangles to approximate the area under a graph.
 4.1 The Area under a Graph OBJECTIVES Use the area under a graph to find total cost. Use rectangles to approximate the area under a graph. 4.1 The Area Under a Graph Riemann Sums (continued): In the following
4.1 The Area under a Graph OBJECTIVES Use the area under a graph to find total cost. Use rectangles to approximate the area under a graph. 4.1 The Area Under a Graph Riemann Sums (continued): In the following
O.K. But what if the chicken didn t have access to a teleporter.
 The intermediate value theorem, and performing algebra on its. This is a dual topic lecture. : The Intermediate value theorem First we should remember what it means to be a continuous function: A function
The intermediate value theorem, and performing algebra on its. This is a dual topic lecture. : The Intermediate value theorem First we should remember what it means to be a continuous function: A function
3. On the grid below, sketch and label graphs of the following functions: y = sin x, y = cos x, and y = sin(x π/2). π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2
 AP Physics C Calculus C.1 Name Trigonometric Functions 1. Consider the right triangle to the right. In terms of a, b, and c, write the expressions for the following: c a sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =. Using
AP Physics C Calculus C.1 Name Trigonometric Functions 1. Consider the right triangle to the right. In terms of a, b, and c, write the expressions for the following: c a sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =. Using
c) xy 3 = cos(7x +5y), y 0 = y3 + 7 sin(7x +5y) 3xy sin(7x +5y) d) xe y = sin(xy), y 0 = ey + y cos(xy) x(e y cos(xy)) e) y = x ln(3x + 5), y 0
 Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
1.10 Continuity Brian E. Veitch
 1.10 Continuity Definition 1.5. A function is continuous at x = a if 1. f(a) exists 2. lim x a f(x) exists 3. lim x a f(x) = f(a) If any of these conditions fail, f is discontinuous. Note: From algebra
1.10 Continuity Definition 1.5. A function is continuous at x = a if 1. f(a) exists 2. lim x a f(x) exists 3. lim x a f(x) = f(a) If any of these conditions fail, f is discontinuous. Note: From algebra
1. (16pts) Use the graph of the function to answer the following. Justify your answer if a limit does not exist. lim
 Spring 10/MAT 250/Exam 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (16pts) Use the graph of the function to answer the following. Justify your answer if a limit does not exist. lim x 1 +f(x) = lim x 3 f(x) = lim x
Spring 10/MAT 250/Exam 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (16pts) Use the graph of the function to answer the following. Justify your answer if a limit does not exist. lim x 1 +f(x) = lim x 3 f(x) = lim x
Lecture 7 - Separable Equations
 Lecture 7 - Separable Equations Separable equations is a very special type of differential equations where you can separate the terms involving only y on one side of the equation and terms involving only
Lecture 7 - Separable Equations Separable equations is a very special type of differential equations where you can separate the terms involving only y on one side of the equation and terms involving only
x n cos 2x dx. dx = nx n 1 and v = 1 2 sin(2x). Andreas Fring (City University London) AS1051 Lecture Autumn / 36
 We saw in Example 5.4. that we sometimes need to apply integration by parts several times in the course of a single calculation. Example 5.4.4: For n let S n = x n cos x dx. Find an expression for S n
We saw in Example 5.4. that we sometimes need to apply integration by parts several times in the course of a single calculation. Example 5.4.4: For n let S n = x n cos x dx. Find an expression for S n
Rolle s Theorem. The theorem states that if f (a) = f (b), then there is at least one number c between a and b at which f ' (c) = 0.
 Rolle s Theorem Rolle's Theorem guarantees that there will be at least one extreme value in the interior of a closed interval, given that certain conditions are satisfied. As with most of the theorems
Rolle s Theorem Rolle's Theorem guarantees that there will be at least one extreme value in the interior of a closed interval, given that certain conditions are satisfied. As with most of the theorems
Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide
 Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide 1. The Final Exam is on December 10 at 8:00-9:45pm in Hitchcock Hall (HI) 031 2. Take your BuckID to the exam. The use of notes, calculators, or other electronic
Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide 1. The Final Exam is on December 10 at 8:00-9:45pm in Hitchcock Hall (HI) 031 2. Take your BuckID to the exam. The use of notes, calculators, or other electronic
Topics and Concepts. 1. Limits
 Topics and Concepts 1. Limits (a) Evaluating its (Know: it exists if and only if the it from the left is the same as the it from the right) (b) Infinite its (give rise to vertical asymptotes) (c) Limits
Topics and Concepts 1. Limits (a) Evaluating its (Know: it exists if and only if the it from the left is the same as the it from the right) (b) Infinite its (give rise to vertical asymptotes) (c) Limits
Inverse Trig Functions
 6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
Techniques of Integration
 5 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives
5 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives
MA1021 Calculus I B Term, Sign:
 MA1021 Calculus I B Term, 2014 Final Exam Print Name: Sign: Write up your solutions neatly and show all your work. 1. (28 pts) Compute each of the following derivatives: You do not have to simplify your
MA1021 Calculus I B Term, 2014 Final Exam Print Name: Sign: Write up your solutions neatly and show all your work. 1. (28 pts) Compute each of the following derivatives: You do not have to simplify your
MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL
 05/05/2012 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Name: TA session: Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! (1) Calculate the following limits, using whatever tools are appropriate. State which results
05/05/2012 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Name: TA session: Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! (1) Calculate the following limits, using whatever tools are appropriate. State which results
Interpreting Derivatives, Local Linearity, Newton s
 Unit #4 : Method Interpreting Derivatives, Local Linearity, Newton s Goals: Review inverse trigonometric functions and their derivatives. Create and use linearization/tangent line formulas. Investigate
Unit #4 : Method Interpreting Derivatives, Local Linearity, Newton s Goals: Review inverse trigonometric functions and their derivatives. Create and use linearization/tangent line formulas. Investigate
24. Partial Differentiation
 24. Partial Differentiation The derivative of a single variable function, d f(x), always assumes that the independent variable dx is increasing in the usual manner. Visually, the derivative s value at
24. Partial Differentiation The derivative of a single variable function, d f(x), always assumes that the independent variable dx is increasing in the usual manner. Visually, the derivative s value at
4/8/2014: Second midterm practice A
 Math 1A: introduction to functions and calculus Oliver Knill, Spring 2014 4/8/2014: Second midterm practice A Your Name: Start by writing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the
Math 1A: introduction to functions and calculus Oliver Knill, Spring 2014 4/8/2014: Second midterm practice A Your Name: Start by writing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the
Calculus II Lecture Notes
 Calculus II Lecture Notes David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 206 edition Contents Contents 2 Review of Calculus I 5. Limits..................................... 7.2 Derivatives...................................3
Calculus II Lecture Notes David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 206 edition Contents Contents 2 Review of Calculus I 5. Limits..................................... 7.2 Derivatives...................................3
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
