CHEM What is Energy? Terminology: E = KE + PE. Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics
|
|
|
- Flora Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thermodynamics 2 Thermodynamics The study of energy changes accompanying physical and chemical processes. From the laws of thermodynamics, one can: 1. Predict the results of chemical reactions 2. Ascertain whether or not a reaction is possible 3. Predict quantitatively the effect of changes in the experimental conditions What is Energy? 1. Kinetic Energy (KE) the energy of motion due to the motion of the system's particles (translations, rotations, vibrations) 2. Potential Energy (PE) the stored energy in an object by virtue of its position or composition (chemical bonds, electric energy of the atoms within the molecules) Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. The total energy of the universe is a constant. Energy can, however, be converted from one form to another or transferred. 3 4 Terminology: is the portion of the physical world that is selected for a thermodynamic study. Examples: A beaker of water A polluted lake is the portion of the universe with which the system interacts. Isolated = + The total energy in any isolated system is constant. All substance possess internal energy, because the molecules of all substances all have kinetic energy and potential energy. Internal energy, represented by E, is essentially the thermal energy of the particles making up the system (all the atoms or molecules of the body due to their random motion and position). It is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles that form the system. E = KE + PE 5 6 1
2 E = KE + PE The simplest system is an ideal gas. In an ideal gas the molecules are so far apart that intermolecular forces can be ignored. Therefore, there is no potential energy. So all the energy is kinetic. Kinetic Molecular Theory assumes that the temperature of a gas is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of its particles. At T 1 At T 2 Calculate the internal energy of a pressurized bottle of Helium gas with volume m 3 at 1.01x10 7 Pa. You can use the gas law PV=nRT to express the internal energy in terms of pressure and volume: m x m x m = m 3 T 1 < T 2 The internal energy of an ideal monatomic gas is therefore directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. E = 3 / 2 nrt R = gas constant T = temperature in Kelvin 7 (1 atm = kpa) E = 3 / 2 nrt = 3 / 2 PV = 3 / 2 (1.01x10 7 Pa)( m³) = 7.54 x 10 5 Pa m³ = 7.54 x 10 5 J 8 The internal energy of other systems that are more complex than the ideal gas are harder to measure. But the internal energy of the system is still has a unique value for each temperature. E = f(t) Where f is monotonically increasing function. As the temperature of the system increases, the internal energy of the system also increases. Temperature, T Use a thermometer to measure a beaker of water at room temperature. T = 21.5 C This measurement describes the state of the system at a particular moment in time. It doesn t tell us how the water got to room temperature. Temperature is a state function The First Law of Thermodynamics Because the internal energy of the system has a fixed value for any temperature, internal energy is also a state function. (E depends on the state of the system in terms of P, V and T.) The total energy of the universe is constant. Energy can be transferred from the system to its surroundings and vice versa, but it cannot be created nor destroyed. Any change in the internal energy of the system is equal to the difference between its initial and final values. The energy lost by the system is gained by the surroundings such that E system = E final -E initial - E system = E surroundings E universe = E system + E surroundings =
3 Units of Energy There are two ways to change the internal energy of a system: 1. By flow of, q Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between the system and the surroundings 2. By doing work, w Calorie: One calorie is defined as the amount of required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 degree celsius. Joule: One joule is the work done when a force of one Newton is used to move an object one meter. 1 J = 1 N m Conversion: 1 calorie = joules Work can be converted into and vice versa. q and w are process dependent, and are not state functions Heat, q A form of energy Passes from one body to another as a result of a difference in temperature Heat flows from a higher temperature to a lower temperature Heat cannot be measured, but the effects which it produces is measurable. Measurement of the Effects of Heat The measurements of effects is known as calorimetry. The instrument used is the calorimeter. : the molecules inside the reaction chamber : the container holding the sample and the water bath Isolated : the calorimeter The condition under which the measurement is made is constant volume. This is a schematic of a bomb calorimeter Experiment 8 Measure E of a combustion reaction Experiment 8 Measure E of a combustion reaction Parr Bomb Combustion of Cyclohexanol 3
4 Measurement of the Effects of Heat In the isolated system containing Substance A q n A T Molar Heat Capacity is the quantity of necessary to raise the temperature of one mole of the material by one degree Celsius. where n A is the number of moles of substance A T = T 2 T 1 (T 2 = final temperature, T 1 = initial temperature) Introduce a proportionality constant, C A, such that Specific Heat is the quantity of necessary to raise the temperature of one gram of the material by one degree Celsius. q = n A C A T C A is the molar capacity; it is characteristic of the substance. q = m A c A T where m A is the mass of substance A T = T 2 T 1 c A is the specific of substance A Units of Heat Calorie: One calorie is defined as the amount of required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 degree Celsius. Heat Capacity varies as a function of temperature C 100 K is not the same as C 300 K Specific of water = 1.00 cal g -1 C -1 is different if the ing is done under constant pressure or under constant volume conditions Molar of water = 18.0 cal mole -1 C -1 Heat capacity measured under constant pressure is C p Heat capacity measured under constant volume is C v Conversion: 1 calorie = joules Specific of water = 4.18 J g -1 C -1 For liquids and solids, there is little difference between C p and C v. For gas, C p > C v Sign Convention Example: The internal energy and temperature of a system increase (E > 0) when the system gains from its surroundings. q > 0 when is added to the substance q > 0 when T 2 > T 1 (i.e. T>0) The internal energy and temperature of a system decrease(e < 0) when the system loses to its surroundings. q < 0 when is lost by the substance q < 0 when T 2 < T 1 (i.e. T<0) g of Pb ed to 100 C is dropped into g of water at 0 o C. What is the final temperature? Assume that transfer is between the two substances. Specific, C p, of Pb is cal g -1 C -1 Specific, C p, of water is 1.00 cal g -1 C -1 Heat lost by the Pb = Heat gained by the water - q Pb = q water - m Pb c Pb (T 2 -T 1 ) Pb =m water c water (T 2 -T 1 ) water T 2 =? T 1 = 100 C T 2 =? T 1 = 0 C T 2 = 23.6 C
5 Latent Heat Effects The effects associated with changes in physical state such as fusion and vapourization are known as latent effects. Latent Heat Effects Heat of Vaporization the required to vaporize a substance at its normal boiling temperature Heat of Fusion - the required to melt a substance at its normal melting temperature - the energy required to reorganize the intermolecular structure of a substance. Heat of fusion of ice is cal/g at 0 o C and 1 atm. Heat of vaporization of water is cal/g 100 o C and 1 atm. Let s up 1 g of water! Sign Convention Calculation : The internal energy and temperature of a system decrease (E < 0) when the system loses. Example 1: The internal energy and temperature increase (E > 0) when the system gains from its surroundings. HEAT A 1.00 g sample of the rocket fuel hydrazine, N 2 H 4, is burned in a bomb calorimeter containing g of water. The temperature rises From C to C. Taking the capacity of the calorimeter to be 200. cal C -1, calculate: (a)q for the combustion of the 1 g sample loses E < 0, q < 0 E > 0, q > 0 gains (b)the molar of combustion of hydrazine. (a) calories (b) kcal/mole 27 Calculation: Example 2: When 5.00 g of sodium hydroxide is added to 100. g of water, the temperature rises from 25.0 o C to 37.5 C. Calculate the molar of reaction for the process NaOH (s) Na + (aq) + OH - (aq) taking the specific of water to be 1.00 cal g -1 C -1 and that of NaOH to be 0.48 cal g -1 C -1. Calculation: Example 3: An experiment is designed to measure the of fusion of ice. 25 g of ice at 0 C was dropped into 195 g of water at 30 C. The water is contained in a copper calorimeter of mass 100 g. The final temperature was 18 C. Given the specific of copper is cal g -1 C -1, find the of fusion of ice kcal/mole Heat of fusion of ice = 80.1 cal/g 5
6 Calculation: Example 4: Steam at 100. C is condensed in a large calorimeter. The capacity of the calorimeter is expressed as water equivalent to 272 g. The calorimeter contains 2.82 kg of water at 5.0 C. The final temperature of 27.8 C is reached after 115 g of steam has been condensed. Find the latent of vaporization of water as given by these data. Heat of vaporization of water = 540 cal/g Work is done by the system Work is done on the system WORK Next we will talk about work! HEAT E < 0 E < 0, q < 0 E > 0 E > 0, q > 0 loses gains 32 6
CHEM Thermodynamics. Heat calculations
 Thermodynamics Heat calculations l Internal Energy, E The internal energy of other systems that are more complex than the ideal gas cannot be measured. But the internal energy of the system is still proportional
Thermodynamics Heat calculations l Internal Energy, E The internal energy of other systems that are more complex than the ideal gas cannot be measured. But the internal energy of the system is still proportional
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
Thermochemistry. Energy (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10. Energy. Energy
 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
CHEM Thermodynamics. Work. There are two ways to change the internal energy of a system:
 There are two ways to change the internal energy of a system: Thermodynamics Work 1. By flow of heat, q Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between and the surroundings 2. By doing work, w Work can
There are two ways to change the internal energy of a system: Thermodynamics Work 1. By flow of heat, q Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between and the surroundings 2. By doing work, w Work can
Thermochemistry 14.notebook. November 24, Thermochemistry. Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat. translational.
 Thermochemistry Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat POTENTIAL ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY (energy of motion) "stored" bond energy TEMPERATURE and HEAT vibrational rotational translational a measure
Thermochemistry Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat POTENTIAL ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY (energy of motion) "stored" bond energy TEMPERATURE and HEAT vibrational rotational translational a measure
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II. Unit 5
 Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Temperature and Its Measurement
 Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry
 Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
THE ENERGY OF THE UNIVERSE IS CONSTANT.
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry.notebook Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Jan 29 1:37 PM 6.1 The Nature of Energy Thermodynamics: The study of energy and its interconversions Energy: the capacity to do work or to
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry.notebook Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Jan 29 1:37 PM 6.1 The Nature of Energy Thermodynamics: The study of energy and its interconversions Energy: the capacity to do work or to
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry. 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin)
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin) 1 Thermodynamics The study of energy and its transformations is known as thermodynamics The relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes that
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin) 1 Thermodynamics The study of energy and its transformations is known as thermodynamics The relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes that
Topic 05 Energetics : Heat Change. IB Chemistry T05D01
 Topic 05 Energetics 5.1-5.2: Heat Change IB Chemistry T05D01 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions - 1 hour 5.1.1 Define the terms exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction and standard enthalpy change
Topic 05 Energetics 5.1-5.2: Heat Change IB Chemistry T05D01 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions - 1 hour 5.1.1 Define the terms exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction and standard enthalpy change
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes
 Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Topic 5: Energetics. Heat & Calorimetry. Thursday, March 22, 2012
 Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry. 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy
 I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
Thermochemistry. Section The flow of energy
 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 - The flow of energy What is Energy? Energy is the capacity for doing work or supplying heat Energy does not have mass or volume, and it can only be detected because of its
Thermochemistry Section 17.1 - The flow of energy What is Energy? Energy is the capacity for doing work or supplying heat Energy does not have mass or volume, and it can only be detected because of its
Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy
 Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change
 Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes
 Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Thermochemistry Chapter 4
 Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law
 Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
What are the states of Matter?
 What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
Vanden Bout/LaBrake. THERMODYNAMICS Quantifying Heat Flow Physical Change. Important Information EXAM 3 WRAPPER POSTED LATER TODAY OPEN 1 WEEK
 UNIT4DAY2-LaB Page 1 UNIT4DAY2-LaB Monday, November 12, 2012 10:00 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 THERMODYNAMICS Quantifying Heat Flow Physical Change UNIT 4 Day 2 Important Information LM28 & 29 DUE Th
UNIT4DAY2-LaB Page 1 UNIT4DAY2-LaB Monday, November 12, 2012 10:00 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 THERMODYNAMICS Quantifying Heat Flow Physical Change UNIT 4 Day 2 Important Information LM28 & 29 DUE Th
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20
 Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Energy Transformations
 Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
The Nature of Energy. Chapter Six: Kinetic vs. Potential Energy. Energy and Work. Temperature vs. Heat
 The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
Thermochemistry-Part 1
 Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS
 THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS Thermochemistry is the study of the study of relationships between chemistry and energy. All chemical changes and many physical changes involve exchange of energy with the
THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS Thermochemistry is the study of the study of relationships between chemistry and energy. All chemical changes and many physical changes involve exchange of energy with the
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry
 CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
Physics 111. Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, Latent Heats
 Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy
 Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 9.01 Law of Conservation of Energy Chemistry (11)(A)
Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 9.01 Law of Conservation of Energy Chemistry (11)(A)
3. When the external pressure is kpa torr, water will boil at what temperature? a C b C c. 100 C d. 18 C
 Chemistry EOC Review 5: Physical Behavior of Matter 1. Which gas is monatomic at STP? a. chlorine b. fluorine c. neon d. nitrogen 2. What Kelvin temperature is equal to 25 C? a. 248 K b. 298 K c. 100 K
Chemistry EOC Review 5: Physical Behavior of Matter 1. Which gas is monatomic at STP? a. chlorine b. fluorine c. neon d. nitrogen 2. What Kelvin temperature is equal to 25 C? a. 248 K b. 298 K c. 100 K
0 o K is called absolute zero. Water Freezes: 273 o K Water Boils: 373 o K
 Part I Notes Temperature and Heat The terms at the right all mean the same thing. The heat energy of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all of the atoms and molecules in the
Part I Notes Temperature and Heat The terms at the right all mean the same thing. The heat energy of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all of the atoms and molecules in the
Heat. Heat Terminology 04/12/2017. System Definitions. System Definitions
 System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
Physics 111. Lecture 35 (Walker: ) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics. Latent Heats. Latent Heat
 Physics 111 Lecture 35 (Walker: 17.4-5) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called the latent heat. The latent
Physics 111 Lecture 35 (Walker: 17.4-5) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called the latent heat. The latent
The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce Heat, q or Q, is ; flows due to temperature differences (always to )
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School
 Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School 1 From Greek therme (heat); study of energy changes in chemical reactions Energy: capacity do work or transfer heat Joules (J), kilo joules (kj) or
Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School 1 From Greek therme (heat); study of energy changes in chemical reactions Energy: capacity do work or transfer heat Joules (J), kilo joules (kj) or
Page 1 SPH3U. Heat. What is Heat? Thermal Physics. Waterloo Collegiate Institute. Some Definitions. Still More Heat
 SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
Ch. 7: Thermochemistry
 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics concerns itself with energy and its relationship to the large scale bulk properties of a system that are measurable: Volume, Temperature, Pressure, Heat
Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics concerns itself with energy and its relationship to the large scale bulk properties of a system that are measurable: Volume, Temperature, Pressure, Heat
Matter and Energy I. Matter Matter is anything that has mass and volume Mass Amount of matter Measured in grams (g) Volume Space matter occupies
 Matter and Energy I. Matter Matter is anything that has mass and volume Mass Amount of matter Measured in grams (g) Volume Space matter occupies Measured in milliliters (ml), liters (L) or cubic centimeters
Matter and Energy I. Matter Matter is anything that has mass and volume Mass Amount of matter Measured in grams (g) Volume Space matter occupies Measured in milliliters (ml), liters (L) or cubic centimeters
General Chemistry I. Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University. Module 4: Chemical Thermodynamics
 General Chemistry I Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University Module 4: Chemical Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics (state quantities:
General Chemistry I Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University Module 4: Chemical Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics (state quantities:
Physics 101: Lecture 25 Heat
 Final Physics 101: Lecture 25 Heat Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 14.1-14.5 Physics 101: Lecture 25, Pg 1 Internal Energy Energy of all molecules including Random motion of individual molecules»
Final Physics 101: Lecture 25 Heat Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 14.1-14.5 Physics 101: Lecture 25, Pg 1 Internal Energy Energy of all molecules including Random motion of individual molecules»
Properties of Matter
 Properties of Matter Chapter 4 Hein and Arena Version 1.0 Eugene Passer Chemistry Department Bronx Community 1 College John Wiley and Sons, Inc Properties of Substances 2 Properties of a Substance A property
Properties of Matter Chapter 4 Hein and Arena Version 1.0 Eugene Passer Chemistry Department Bronx Community 1 College John Wiley and Sons, Inc Properties of Substances 2 Properties of a Substance A property
Chapter 5 THERMO. THERMO chemistry. 5.4 Enthalpy of Reactions 5.5 Calorimetry 5.6 Hess s Law 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation
 Chapter 5 THERMO THERMO chemistry 5.4 Enthalpy of Reactions 5.5 Calorimetry 5.6 Hess s Law 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation Chemical Equations 1 st WRITE the Chemical Equation 2 nd BALANCE the Chemical Equation
Chapter 5 THERMO THERMO chemistry 5.4 Enthalpy of Reactions 5.5 Calorimetry 5.6 Hess s Law 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation Chemical Equations 1 st WRITE the Chemical Equation 2 nd BALANCE the Chemical Equation
Unit 6. Unit Vocabulary: Distinguish between the three phases of matter by identifying their different
 *STUDENT* Unit Objectives: Absolute Zero Avogadro s Law Normal Boiling Point Compound Cooling Curve Deposition Energy Element Evaporation Heat Heat of Fusion Heat of Vaporization Unit 6 Unit Vocabulary:
*STUDENT* Unit Objectives: Absolute Zero Avogadro s Law Normal Boiling Point Compound Cooling Curve Deposition Energy Element Evaporation Heat Heat of Fusion Heat of Vaporization Unit 6 Unit Vocabulary:
Chapter Practice Test Grosser
 Class: Date: Chapter 10-11 Practice Test Grosser Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of
Class: Date: Chapter 10-11 Practice Test Grosser Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of
11B, 11E Temperature and heat are related but not identical.
 Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
solid IMF>liquid IMF>gas IMF Draw a diagram to represent the 3 common states of matter of a given substance: solid liquid gas
 Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry Study of energy changes that accompany chemical rx s. I) Nature of Energy Energy / Capacity to do work Mechanical Work w = F x d Heat energy - energy used to cause the temperature
Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry Study of energy changes that accompany chemical rx s. I) Nature of Energy Energy / Capacity to do work Mechanical Work w = F x d Heat energy - energy used to cause the temperature
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 6 The States of Matter. Examples of Physical Properties of Three States of Matter
 Chapter 6 The States of Matter Examples of Physical Properties of Three States of Matter 1 Three States of Matter Solids: Fixed shape, fixed volume, particles are held rigidly in place. Liquids: Variable
Chapter 6 The States of Matter Examples of Physical Properties of Three States of Matter 1 Three States of Matter Solids: Fixed shape, fixed volume, particles are held rigidly in place. Liquids: Variable
February 16, Stoichiometry.notebook. Feb 4 8:11 PM. Feb 4 8:09 PM. Feb 4 8:13 PM. Feb 4 8:28 PM. Feb 4 8:13 PM.
 Stoichiometry You already know how to predict what products are produced. The goal of stoich is to predict how much products are produced. 4 Major Types of Stoichiometry Problems 1. Mole Mole 2. Mass Mass
Stoichiometry You already know how to predict what products are produced. The goal of stoich is to predict how much products are produced. 4 Major Types of Stoichiometry Problems 1. Mole Mole 2. Mass Mass
- Joule (J): SI unit for energy. It's defined based on the equation for kinetic energy. from. mass. velocity
 153 ENERGY UNITS - calorie (cal): the amount of energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin) 1g 1g add one calorie of energy - Calories in food? The
153 ENERGY UNITS - calorie (cal): the amount of energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin) 1g 1g add one calorie of energy - Calories in food? The
5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions
 Topic 5: Energetics 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions Chemical reactions involve the breaking and making of bonds. Breaking bonds requires energy,whereas energy is given out when new bonds are formed.
Topic 5: Energetics 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions Chemical reactions involve the breaking and making of bonds. Breaking bonds requires energy,whereas energy is given out when new bonds are formed.
2. If the volume of a container holding a gas is reduced, what will happen to the presure within the container?
 1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 24. Textbook Sections Lecture 25 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 24 Heat Textbook Sections 14.4 14.5 Lecture 25 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Exam 2 Average: 96.7 out of 150 Std Dev: 30.5 Lecture 25 Purdue University, Physics 220 2 Overview Last
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 24 Heat Textbook Sections 14.4 14.5 Lecture 25 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Exam 2 Average: 96.7 out of 150 Std Dev: 30.5 Lecture 25 Purdue University, Physics 220 2 Overview Last
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions
 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
A). Yes. B). No. Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury?
 Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury? A). Yes. B). No. The upward force is the weight of liquid displaced and the downward force is the weight of the ball. If the density of the
Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury? A). Yes. B). No. The upward force is the weight of liquid displaced and the downward force is the weight of the ball. If the density of the
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
 Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Thermal Physics. Temperature (Definition #1): a measure of the average random kinetic energy of all the particles of a system Units: o C, K
 Thermal Physics Internal Energy: total potential energy and random kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance Symbol: U Units: J Internal Kinetic Energy: arises from random translational, vibrational,
Thermal Physics Internal Energy: total potential energy and random kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance Symbol: U Units: J Internal Kinetic Energy: arises from random translational, vibrational,
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY. Mrs. Brayfield
 CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
Homework - Lecture 11.
 Homework - Lecture 11. Name: Topic: Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Type: Numerical 1. Two liquids, A and B, are mixed together, and the resulting temperature is 22 C. If liquid A has mass m and was initially
Homework - Lecture 11. Name: Topic: Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Type: Numerical 1. Two liquids, A and B, are mixed together, and the resulting temperature is 22 C. If liquid A has mass m and was initially
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Practice Packet: Energy. Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer. Practice Packet. Chapter 4: Energy.
 Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 4: Energy http:/drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Energy Objectives Define energy. Demonstrate the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions
Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 4: Energy http:/drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Energy Objectives Define energy. Demonstrate the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.)
 Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Unit 7 Kinetics and Thermodynamics
 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work Unit 7 Kinetics and Thermodynamics I. Energy Transformations A. Temperature 1. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter B. Heat
17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work Unit 7 Kinetics and Thermodynamics I. Energy Transformations A. Temperature 1. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter B. Heat
= (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj)
![= (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj) = (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj)](/thumbs/89/101004910.jpg) CHEM 101A ARMSTRONG SOLUTIONS TO TOPIC D PROBLEMS 1) For all problems involving energy, you may give your answer in either joules or kilojoules, unless the problem specifies a unit. (In general, though,
CHEM 101A ARMSTRONG SOLUTIONS TO TOPIC D PROBLEMS 1) For all problems involving energy, you may give your answer in either joules or kilojoules, unless the problem specifies a unit. (In general, though,
First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed.
 1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
Energetics. Topic
 Energetics Topic 5.1 5.2 Topic 5.1 Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?? total energy of the universe is a constant if a system loses energy, it must be gained by the surroundings, and vice versa Enthalpy
Energetics Topic 5.1 5.2 Topic 5.1 Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?? total energy of the universe is a constant if a system loses energy, it must be gained by the surroundings, and vice versa Enthalpy
AP* Chemistry THERMOCHEMISTRY
 AP* Chemistry THERMOCHEMISTRY Let s begin with terms for you to master: Energy (E) the ability to do work or produce heat ; the sum of all potential and kinetic energy in a system is known as the internal
AP* Chemistry THERMOCHEMISTRY Let s begin with terms for you to master: Energy (E) the ability to do work or produce heat ; the sum of all potential and kinetic energy in a system is known as the internal
CALORIEMETRY. Similar to the other forms of the energy, The S.I unit of heat is joule. joule is represented as J.
 CALORIEMETRY CALORIMETRY Heat is the kinetic energy due to random motion of the molecules of a substance is called heat energy. Heat is a an invisible energy, that causes in us the sensation of hotness
CALORIEMETRY CALORIMETRY Heat is the kinetic energy due to random motion of the molecules of a substance is called heat energy. Heat is a an invisible energy, that causes in us the sensation of hotness
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
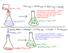 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
Figure 1.1. Relation between Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. From Figure 1.1. (1.1)
 CHAPTER I ELEMENTS OF APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 1.1. INTRODUCTION. The Air Conditioning systems extract heat from some closed location and deliver it to other places. To better understanding the principles
CHAPTER I ELEMENTS OF APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 1.1. INTRODUCTION. The Air Conditioning systems extract heat from some closed location and deliver it to other places. To better understanding the principles
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
 Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Introduction to Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry Unit. Definition. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology 07/04/2016. Chemistry 30
 Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
THERMODYNAMICS. Energy changes in reactions Text chapter 3, 4, 5, 6 & 7
 1 THERMODYNAMICS Energy changes in reactions Text chapter 3, 4, 5, 6 & 7 TERMINOLOGY: Thermodynamics: study of heat changes that occur during chemical reactions. Energy (J): Cannot be seen, touched, smelled,
1 THERMODYNAMICS Energy changes in reactions Text chapter 3, 4, 5, 6 & 7 TERMINOLOGY: Thermodynamics: study of heat changes that occur during chemical reactions. Energy (J): Cannot be seen, touched, smelled,
Chapter Notes: Temperature, Energy and Thermal Properties of Materials Mr. Kiledjian
 Chapter 10-11 Notes: Temperature, Energy and Thermal Properties of Materials Mr. Kiledjian 1) Temperature 2) Expansion of Matter 3) Ideal Gas Law 4) Kinetic Theory of Gases 5) Energy, Heat transfer and
Chapter 10-11 Notes: Temperature, Energy and Thermal Properties of Materials Mr. Kiledjian 1) Temperature 2) Expansion of Matter 3) Ideal Gas Law 4) Kinetic Theory of Gases 5) Energy, Heat transfer and
Energy Ability to produce change or do work. First Law of Thermodynamics. Heat (q) Quantity of thermal energy
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
q = m. C p. T q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C) UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
CHEMISTRY - TRO 4E CH.6 - THERMOCHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ENERGY CHANGES AND ENERGY CONSERVATION is the branch of physical science concerned with heat and its transformations to and from other forms of energy. is the branch of chemistry
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ENERGY CHANGES AND ENERGY CONSERVATION is the branch of physical science concerned with heat and its transformations to and from other forms of energy. is the branch of chemistry
Duncan. Q = m. C p. T. Q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat capacity (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C)
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES SECTION (A): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (B): phase(s) of matter = energy difference at same temp = temp is called the SECTION (C): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (D): phase(s) of matter
HEAT ENERGY NOTES SECTION (A): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (B): phase(s) of matter = energy difference at same temp = temp is called the SECTION (C): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (D): phase(s) of matter
States of Matter. We can explain the properties that we observe in the various states of matter with these postulates.
 States of Matter Kinetic Molecular Theory When discussing the properties of matter, it is not enough just to classify them. We must also create a model that helps to explain the properties that we see.
States of Matter Kinetic Molecular Theory When discussing the properties of matter, it is not enough just to classify them. We must also create a model that helps to explain the properties that we see.
CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 52 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW 1. Water at a temperature of 0 C is kept in a thermally insulated container.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 52 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW 1. Water at a temperature of 0 C is kept in a thermally insulated container.
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. Molecular Kinetic Energy -Translational energy E k, translational = 1/2mv 2 -Rotational energy 5.
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat is the transfer of energy due to the difference in temperature. The internal energy is the total energy of the object in its centerofmass reference
Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat is the transfer of energy due to the difference in temperature. The internal energy is the total energy of the object in its centerofmass reference
Chapter 14 Heat. Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Name Energy Test period Date
 Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Phase Change Diagram. Rank Solids, liquids and gases from weakest attractive forces to strongest:
 Unit 11 Kinetic molecular theory packet Page 1 of 13 Chemistry Unit 11 Kinetic Theory Unit Quiz: Test Objectives Be able to define pressure and memorize the basic pressure units. Be able to convert to/from:
Unit 11 Kinetic molecular theory packet Page 1 of 13 Chemistry Unit 11 Kinetic Theory Unit Quiz: Test Objectives Be able to define pressure and memorize the basic pressure units. Be able to convert to/from:
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry. Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake. Chapter 2. Energy and Matter Pearson Education, Inc.
 General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2.1 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat.
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2.1 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat.
