February 16, Stoichiometry.notebook. Feb 4 8:11 PM. Feb 4 8:09 PM. Feb 4 8:13 PM. Feb 4 8:28 PM. Feb 4 8:13 PM.
|
|
|
- Loreen Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stoichiometry You already know how to predict what products are produced. The goal of stoich is to predict how much products are produced. 4 Major Types of Stoichiometry Problems 1. Mole Mole 2. Mass Mass 3. Volume Volume 4. Mix Stoichiometry: the mathematical relationship between the reactants & products in a chemical rxn. Mole Ratio a proportion given by the coefficients in a BCE telling the relative number of moles of each substance. 5 Steps in Solving Stoichiometry Problems 1. Write the BCE (Balanced Chemical Equation) 2. Write down the given with units & labels 3. Set up a conversion 4. Using your new and improved road map (Y chart) to determine the bes route to get to your unknown. 5. Cross out and solve. Be sure to use the number of sig fig s from the given to report your answer and use units & label. Feb 4 8:09 PM Feb 4 8:11 PM Mole Mole Stoichiometry Problems Ex. 1: Nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas are combined to form ammonia. If I start with 250 moles of nitrogen, how many moles of ammonia will be produced? Ex. 2: When KCl 3 decomposes, how many moles of oxygen are produced if you start with 750 moles of the reactant. 5 Steps in Solving Stoichiometry Problems 1. Write the BCE (Balanced Chemical Equation) 2. Write down the given with units & labels 3. Set up a conversion 4. Using your new and improved road map (Y chart) to determine the bes route to get to your unknown. 5. Cross out and solve. Be sure to use the number of sig fig s from the given to report your answer and use units & label. Feb 4 8:28 PM Mass Mass Stoichiometry Problems Ex. 1: ow many grams of 2 would be made from 3.0g of 2? Volume Volume Stoichiometry Problems Ex. 1: If 5.0 L of methane (C 4 ) burns in the presence of oxygen, how many liters of C 2 will be produced? Ex. 2: 3Fe(s) + 42(g) Fe34(s) + 42(g) If 36.0g of 2 react completely, what is the mass of Fe34(s)? Ex. 2: In the space shuttle, exhaled carbon dioxide gas is removed from the air by passing it through canisters of lithium hydroxide; this reaction produces solid lithium carbonate & gaseous water. ow many liters of water are produced from 3.4 liters of exhaled carbon dioxide? Ex. 3: Nitrogen combines with oxygen in the atmosphere during lightning flashes to form nitrogen monoxide. If 42.1g of N are produced, how many grams of 2 are needed? 1
2 Energy in Chemical Rxn s Molar eat energy per mol of reactant release in a chemical reaction. the B. C. E. to determine molar heat. Use kJ 572kJ/2 mol 2 or 572kJ/1 mol 2 EX. n average, each person in the U.S. consumes 110 g of sugar daily. If all of this sugar is assumed to be glucose, how much heat energy form glucose is transferred to one person through respiration each day? C C 2(g) kJ Feb 4 8:14 PM Feb 15 8:15 AM Limiting Reactants Limiting Reactants limits the amount of products that can be produced Excess Reactant reactant that is left over after the reaction stops 5 Steps to Limiting Reactant Problems 1. Write BCE. 2. Determine moles of each reactant. 3. Determine the amount that you NEED using the mole ratio. 4. Determine Limiting Reactant. Compare what you have & need. 5. Use the limiting reactant to answer the question. Feb 4 8:33 PM Feb 11 11:17 AM Feb 11 11:25 AM Feb 12 8:12 AM 2
3 Thermodynamics (heat moving) Which had a greater average kinetic energy? Which has a greater total energy at the same temperature? Temperature T, is the measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules. Faster molecules means higher temperature The amount of substance doesn t matter Measured in Celsius or Kelvin Lower Limit = Absolute Zero (K.E. is 0) Upper Limit = There isn't one. Feb 11 11:44 AM Feb 11 11:45 AM Thermal Energy, the sum of all the energy of all the molecules in a object The amount of substance does matter Measured in Joules or calories 1 J = kg. m 2 /s J = 1 cal When I take pizza out of an oven, why can I burn myself on the sauce but not on the crust? They have different specific heats. Specific heat how much heat it takes to raise the temp of one kilogram of a substance one degree Kelvin or Celsius. Which has a higher specific heat, water or sand? Q = mcδt **Units must agree Feb 11 11:46 AM Mar 30 9:34 AM What is the specific heat of a metal with a mass of 38 kg if it absorbs 1.0 x 10 6 J while being heated for 26 o C to 180 o C? What metal is it? What metal is it? Brass J/g.o C Copper J/g.o C Gold J/g.o C Zinc 0.388J /g.o C Mar 30 9:36 AM Feb 19 2:13 PM 3
4 Conservation of Energy Energy can neither be created nor destroyed (What goes into the system must come out.) eat gained = eat lost Q G = Q L mcδt = mcδt Ex. 200g of 10 o water is contained in a calorimeter. If 95.0g of 90 o water is added, what is the equilibrium temperature of the system? Feb 19 2:28 PM Feb 20 7:15 AM *** When a substance changes states, adding energy (heat) doesn t increase temperature. eating Curve for Water. eat of Vaporization vap = cond, Energy needed to boil or condense eat of Fusion fus = melt, Energy needed to melt or freeze Feb 20 7:12 AM Feb 20 7:27 AM Feb 15 8:21 AM 4
5 Attachments MLE RELATINSIPS WITIN A CEMICAL REACTIN.doc Stoichiometry.doc mole rockets.doc eat Energy in Chemical Changes.doc
Reading Balanced Chemical Equations (see MHR Text p )
 Reading Balanced Chemical Equations (see MHR Text p. 114 118) 2 H 2(g) + O 2(g) 2 H 2 O (l) Read: 2 molecules of hydrogen gas reacts with 1 molecule of oxygen gas to produce 2 molecules of water or 2 moles
Reading Balanced Chemical Equations (see MHR Text p. 114 118) 2 H 2(g) + O 2(g) 2 H 2 O (l) Read: 2 molecules of hydrogen gas reacts with 1 molecule of oxygen gas to produce 2 molecules of water or 2 moles
Thermochemistry. Energy (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10. Energy. Energy
 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry
 CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions
 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Chapter 17: Energy and Kinetics
 Pages 510-547 S K K Chapter 17: Energy and Kinetics Thermochemistry: Causes of change in systems Kinetics: Rate of reaction progress (speed) Heat, Energy, and Temperature changes S J J Heat vs Temperature
Pages 510-547 S K K Chapter 17: Energy and Kinetics Thermochemistry: Causes of change in systems Kinetics: Rate of reaction progress (speed) Heat, Energy, and Temperature changes S J J Heat vs Temperature
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes
 Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Chemistry Heat Review. Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy:
 Chemistry Heat Review Name Date Vocabulary Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy: Formulas Heat of phase change Heat for temperature increase Heat of reaction Endothermic/Exothermic
Chemistry Heat Review Name Date Vocabulary Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy: Formulas Heat of phase change Heat for temperature increase Heat of reaction Endothermic/Exothermic
Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy
 Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 9.01 Law of Conservation of Energy Chemistry (11)(A)
Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 9.01 Law of Conservation of Energy Chemistry (11)(A)
Unit 7 Kinetics and Thermodynamics
 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work Unit 7 Kinetics and Thermodynamics I. Energy Transformations A. Temperature 1. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter B. Heat
17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work Unit 7 Kinetics and Thermodynamics I. Energy Transformations A. Temperature 1. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter B. Heat
Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change
 Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change Chemical reactions usually absorb or release energy. Section 1: Energy Section 2: Heat Section 3: Thermochemical Equations Section 4: Calculating Enthalpy Change Section
Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change Chemical reactions usually absorb or release energy. Section 1: Energy Section 2: Heat Section 3: Thermochemical Equations Section 4: Calculating Enthalpy Change Section
3. When the external pressure is kpa torr, water will boil at what temperature? a C b C c. 100 C d. 18 C
 Chemistry EOC Review 5: Physical Behavior of Matter 1. Which gas is monatomic at STP? a. chlorine b. fluorine c. neon d. nitrogen 2. What Kelvin temperature is equal to 25 C? a. 248 K b. 298 K c. 100 K
Chemistry EOC Review 5: Physical Behavior of Matter 1. Which gas is monatomic at STP? a. chlorine b. fluorine c. neon d. nitrogen 2. What Kelvin temperature is equal to 25 C? a. 248 K b. 298 K c. 100 K
Name Date Class THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK
 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK Section Review Objectives Explain the relationship between energy, heat, and work Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes Distinguish between heat
17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK Section Review Objectives Explain the relationship between energy, heat, and work Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes Distinguish between heat
_ + Units of Energy. Energy in Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry. Energy flow between system and surroundings. 100º C heat 50º C
 Units of Energy Like we saw with pressure, many different units are used throughout the world for energy. SI unit for energy 1kg m 1J = 2 s 2 Joule (J) calorie (cal) erg (erg) electron volts (ev) British
Units of Energy Like we saw with pressure, many different units are used throughout the world for energy. SI unit for energy 1kg m 1J = 2 s 2 Joule (J) calorie (cal) erg (erg) electron volts (ev) British
Outcomes: Interpret a balanced chemical equation in terms of moles, mass and volume of gases. Solve stoichiometric problems involving: moles, mass,
 Stoichiometry Outcomes: Interpret a balanced chemical equation in terms of moles, mass and volume of gases. Solve stoichiometric problems involving: moles, mass, volume, and heat of reaction. Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry Outcomes: Interpret a balanced chemical equation in terms of moles, mass and volume of gases. Solve stoichiometric problems involving: moles, mass, volume, and heat of reaction. Stoichiometry
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
 Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
11B, 11E Temperature and heat are related but not identical.
 Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy
 I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
Calculate the mass of L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure.
 148 Calculate the mass of 22650 L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure. 1 - Convert the volume of oxygen gas to moles using IDEAL GAS EQUATION 2 - Convert moles oxygen gas to mass using formula
148 Calculate the mass of 22650 L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure. 1 - Convert the volume of oxygen gas to moles using IDEAL GAS EQUATION 2 - Convert moles oxygen gas to mass using formula
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change
 Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state.
 Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
 Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce Heat, q or Q, is ; flows due to temperature differences (always to )
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Unit 14. States of Matter & Thermochemistry
 Unit 14 Flashback: States of Matter & Thermochemistry Characteristic Solids Liquids Gases Shape Volume Density Fluidity Compressibility Picture Phase Diagram Shows the relationship between solid, liquid,
Unit 14 Flashback: States of Matter & Thermochemistry Characteristic Solids Liquids Gases Shape Volume Density Fluidity Compressibility Picture Phase Diagram Shows the relationship between solid, liquid,
Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]?
![Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]?](/thumbs/78/77877522.jpg) Warm up 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? 4) What is the concentration of H 2 SO 4 if 30.1 ml
Warm up 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? 4) What is the concentration of H 2 SO 4 if 30.1 ml
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Energy & Chemistry Questions that need to be addressed: How do we measure
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Energy & Chemistry Questions that need to be addressed: How do we measure
Name Class Date. As you read Lesson 17.1, use the cause and effect chart below. Complete the chart with the terms system and surroundings.
 Name Class Date Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy As you read Lesson 17.1, use the cause and effect chart below. Complete the chart with the terms system and surroundings. Process Cause Effect endothermic
Name Class Date Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy As you read Lesson 17.1, use the cause and effect chart below. Complete the chart with the terms system and surroundings. Process Cause Effect endothermic
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes
 Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Ideal Gas & Gas Stoichiometry
 Ideal Gas & Gas Stoichiometry Avogadro s Law V a number of moles (n) V = constant x n Constant temperature Constant pressure V 1 /n 1 = V 2 /n 2 Ammonia burns in oxygen to form nitric oxide (NO) and water
Ideal Gas & Gas Stoichiometry Avogadro s Law V a number of moles (n) V = constant x n Constant temperature Constant pressure V 1 /n 1 = V 2 /n 2 Ammonia burns in oxygen to form nitric oxide (NO) and water
- Joule (J): SI unit for energy. It's defined based on the equation for kinetic energy. from. mass. velocity
 153 ENERGY UNITS - calorie (cal): the amount of energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin) 1g 1g add one calorie of energy - Calories in food? The
153 ENERGY UNITS - calorie (cal): the amount of energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin) 1g 1g add one calorie of energy - Calories in food? The
- The empirical gas laws (including the ideal gas equation) do not always apply.
 145 At 300 C, ammonium nitrate violently decomposes to produce nitrogen gas, oxygen gas, and water vapor. What is the total volume of gas that would be produced at 1.00 atm by the decomposition of 15.0
145 At 300 C, ammonium nitrate violently decomposes to produce nitrogen gas, oxygen gas, and water vapor. What is the total volume of gas that would be produced at 1.00 atm by the decomposition of 15.0
Quantity Relationships in Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 10 Relationships in Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Conversion Factors from a Chemical Equation Goal 1 The coefficients in a chemical equation give us the conversion factors to get from the number
Chapter 10 Relationships in Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Conversion Factors from a Chemical Equation Goal 1 The coefficients in a chemical equation give us the conversion factors to get from the number
Stoichiometry Dry Lab
 Stoichiometry Dry Lab Name: Mole-Mass Conversions The molar mass of a substance is the conversion factor that allows us to convert between the mass of a substance (in grams) and the number of moles of
Stoichiometry Dry Lab Name: Mole-Mass Conversions The molar mass of a substance is the conversion factor that allows us to convert between the mass of a substance (in grams) and the number of moles of
CHEM What is Energy? Terminology: E = KE + PE. Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics 2 Thermodynamics The study of energy changes accompanying physical and chemical processes. From the laws of thermodynamics, one can: 1. Predict the results of chemical reactions 2. Ascertain
Thermodynamics 2 Thermodynamics The study of energy changes accompanying physical and chemical processes. From the laws of thermodynamics, one can: 1. Predict the results of chemical reactions 2. Ascertain
Unit 6: Stoichiometry. How do manufacturers know how to make enough of their desired product?
 Unit 6: Stoichiometry How do manufacturers know how to make enough of their desired product? Chocolate Chip Cookies Using the following recipe, complete the questions. Cookie Recipe 1.5 c sugar 1 c. butter
Unit 6: Stoichiometry How do manufacturers know how to make enough of their desired product? Chocolate Chip Cookies Using the following recipe, complete the questions. Cookie Recipe 1.5 c sugar 1 c. butter
If Sally has 4.56 x atoms of oxygen in a sample of aluminum oxide, how many kilograms of aluminum does she have?
 If Sally has 4.56 x 10 34 atoms of oxygen in a sample of aluminum oxide, how many kilograms of aluminum does she have? Bertha has.025 milligrams of sodium that she got from a sample of Sodium phosphate,
If Sally has 4.56 x 10 34 atoms of oxygen in a sample of aluminum oxide, how many kilograms of aluminum does she have? Bertha has.025 milligrams of sodium that she got from a sample of Sodium phosphate,
Name: Thermochemistry. Practice Test C. General Chemistry Honors Chemistry
 Name: Thermochemistry C Practice Test C General Chemistry Honors Chemistry 1 Objective 1: Use the relationship between mass, specific heat, and temperature change to calculate the heat flow during a chemical
Name: Thermochemistry C Practice Test C General Chemistry Honors Chemistry 1 Objective 1: Use the relationship between mass, specific heat, and temperature change to calculate the heat flow during a chemical
Thermochemistry. Section The flow of energy
 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 - The flow of energy What is Energy? Energy is the capacity for doing work or supplying heat Energy does not have mass or volume, and it can only be detected because of its
Thermochemistry Section 17.1 - The flow of energy What is Energy? Energy is the capacity for doing work or supplying heat Energy does not have mass or volume, and it can only be detected because of its
Temp vs. Heat. Absolute Temperature Scales. Common Temperature Scales. Thermal Energy. Heat and Temperature are not the same!!
 Thermal Energy Heat and Temperature are not the same!! Cold is the absence of heat, not an energy Same concept as light/dark Cold can t come in, heat flows out Heat flows from High Temp Low Temp Temp vs.
Thermal Energy Heat and Temperature are not the same!! Cold is the absence of heat, not an energy Same concept as light/dark Cold can t come in, heat flows out Heat flows from High Temp Low Temp Temp vs.
Selected Questions on Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Selected Questions on Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Circle the correct answer: 1) At what velocity (m/s) must a 20.0 g object be moving in order to possess a kinetic energy of 1.00 J? A) 1.00 B) 100 10 2 C)
Selected Questions on Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Circle the correct answer: 1) At what velocity (m/s) must a 20.0 g object be moving in order to possess a kinetic energy of 1.00 J? A) 1.00 B) 100 10 2 C)
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
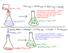 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
CHEM Thermodynamics. Heat calculations
 Thermodynamics Heat calculations l Internal Energy, E The internal energy of other systems that are more complex than the ideal gas cannot be measured. But the internal energy of the system is still proportional
Thermodynamics Heat calculations l Internal Energy, E The internal energy of other systems that are more complex than the ideal gas cannot be measured. But the internal energy of the system is still proportional
2. If the volume of a container holding a gas is reduced, what will happen to the presure within the container?
 1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry
 Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II. Unit 5
 Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Gravity is a force which keeps us stuck to the earth. The Electrostatic force attracts electrons to protons in an atom.
 Energy Relations in Chemistry: Thermochemistry The Nature of Energy Sugar you eat is "combusted" by your body to produce CO 2 and H 2 O. During this process energy is also released. This energy is used
Energy Relations in Chemistry: Thermochemistry The Nature of Energy Sugar you eat is "combusted" by your body to produce CO 2 and H 2 O. During this process energy is also released. This energy is used
Chemistry Chapter 16. Reaction Energy
 Chemistry Reaction Energy Section 16.1.I Thermochemistry Objectives Define temperature and state the units in which it is measured. Define heat and state its units. Perform specific-heat calculations.
Chemistry Reaction Energy Section 16.1.I Thermochemistry Objectives Define temperature and state the units in which it is measured. Define heat and state its units. Perform specific-heat calculations.
Stoichiometry Dry Lab
 Stoichiometry Dry Lab Name: Mole-Mass Conversions The molar mass of a substance is the conversion factor that allows us to convert between the mass of a substance (in grams) and the number of moles of
Stoichiometry Dry Lab Name: Mole-Mass Conversions The molar mass of a substance is the conversion factor that allows us to convert between the mass of a substance (in grams) and the number of moles of
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
2nd Semester Exam Review. C. K eq = [N 2][H 2 ]
![2nd Semester Exam Review. C. K eq = [N 2][H 2 ] 2nd Semester Exam Review. C. K eq = [N 2][H 2 ]](/thumbs/82/85457292.jpg) Name: ate: 1. Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound?. H 2 O, 4 H 6 O 4. HO, 6 H 12 O 6 8. Given the reaction at equilibrium: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g)
Name: ate: 1. Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound?. H 2 O, 4 H 6 O 4. HO, 6 H 12 O 6 8. Given the reaction at equilibrium: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g)
Chapter 4. Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
 Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions Stoichiometry The study of the numerical relationship between chemical quantities in a chemical reaction Making Pizza The number of pizzas you can make
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions Stoichiometry The study of the numerical relationship between chemical quantities in a chemical reaction Making Pizza The number of pizzas you can make
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY. Mrs. Brayfield
 CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 12, sections 1 and 2: Heat in Chemical Reactions
 Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 12, sections 1 and 2: Heat in Chemical Reactions Terms, definitions, topics Joule, calorie (Re-read p 57-58) Thermochemistry Exothermic reaction Endothermic reaction
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 12, sections 1 and 2: Heat in Chemical Reactions Terms, definitions, topics Joule, calorie (Re-read p 57-58) Thermochemistry Exothermic reaction Endothermic reaction
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes
 Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
How many ml of 0.250M potassium permangenate are needed to react with 3.36 g of iron(ii) sulfate?
 115 How many ml of 0.250M potassium permangenate are needed to react with 3.36 g of iron(ii) sulfate? 1) Convert 3.36 grams iron(ii) sulfate to moles. Use FORMULA WEIGHT. 2) Convert moles iron(ii) sulfate
115 How many ml of 0.250M potassium permangenate are needed to react with 3.36 g of iron(ii) sulfate? 1) Convert 3.36 grams iron(ii) sulfate to moles. Use FORMULA WEIGHT. 2) Convert moles iron(ii) sulfate
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
ENTHALPY CHANGE CHAPTER 4
 ENTHALPY CHANGE CHAPTER 4 ENTHALPY Is the total energy of a system. E k = Kinetic energy. Vibrational Rotational Translational E due to motion H = E k + E p E P = Potential energy Attractive force b/w
ENTHALPY CHANGE CHAPTER 4 ENTHALPY Is the total energy of a system. E k = Kinetic energy. Vibrational Rotational Translational E due to motion H = E k + E p E P = Potential energy Attractive force b/w
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Chemistry I Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Objective Sheet. Equation 1. Objectives: 1. Define stoichiometry
 Chemistry I Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Objective Sheet Equation 1 2 C 2 H 2 (g) + 5 O 2 (g) 4 CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (g), at STP C 2 H 2 (acetylene) 26 g/mol O 2 32 g/mol CO 2 44 g/mol H 2 O 18 g/mol Objectives:
Chemistry I Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Objective Sheet Equation 1 2 C 2 H 2 (g) + 5 O 2 (g) 4 CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (g), at STP C 2 H 2 (acetylene) 26 g/mol O 2 32 g/mol CO 2 44 g/mol H 2 O 18 g/mol Objectives:
Topic 5: Energetics. Heat & Calorimetry. Thursday, March 22, 2012
 Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
= (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj)
![= (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj) = (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj)](/thumbs/89/101004910.jpg) CHEM 101A ARMSTRONG SOLUTIONS TO TOPIC D PROBLEMS 1) For all problems involving energy, you may give your answer in either joules or kilojoules, unless the problem specifies a unit. (In general, though,
CHEM 101A ARMSTRONG SOLUTIONS TO TOPIC D PROBLEMS 1) For all problems involving energy, you may give your answer in either joules or kilojoules, unless the problem specifies a unit. (In general, though,
Name: Score: /100. Part I. Multiple choice. Write the letter of the correct answer for each problem. 3 points each
 Name: Score: /100 Part I. Multiple choice. Write the letter of the correct answer for each problem. 3 points each 1. Which of the following contains the greatest number of moles of O? A) 2.3 mol H 2 O
Name: Score: /100 Part I. Multiple choice. Write the letter of the correct answer for each problem. 3 points each 1. Which of the following contains the greatest number of moles of O? A) 2.3 mol H 2 O
Energy Ability to produce change or do work. First Law of Thermodynamics. Heat (q) Quantity of thermal energy
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
The following gas laws describes an ideal gas, where
 Alief ISD Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 4: Gases and Thermochemistry C.9.A Describe and calculate the relations between volume, pressure, number of moles, and temperature for an ideal gas as
Alief ISD Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 4: Gases and Thermochemistry C.9.A Describe and calculate the relations between volume, pressure, number of moles, and temperature for an ideal gas as
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Thermochemistry Chapter 4
 Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Name Energy Test period Date
 Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Section Using Gas Laws to Solve Problems
 Gases and Gas Laws Section 13.2 Using Gas Laws to Solve Problems Kinetic Molecular Theory Particles of matter are ALWAYS in motion Volume of individual particles is zero. Consists of large number of particles
Gases and Gas Laws Section 13.2 Using Gas Laws to Solve Problems Kinetic Molecular Theory Particles of matter are ALWAYS in motion Volume of individual particles is zero. Consists of large number of particles
A).5 atm B) 1 atm C) 1.5 atm D) 2 atm E) it is impossible to tell
 1. ne atmosphere is equivalent to A) 1.00 g ml 1 B) 22,400 ml ) 273 K D) 760. mmhg E) 298 K 2. A cylinder contains 2.50 L of air at a pressure of 5.00 atmospheres. At what volume, will the air exert a
1. ne atmosphere is equivalent to A) 1.00 g ml 1 B) 22,400 ml ) 273 K D) 760. mmhg E) 298 K 2. A cylinder contains 2.50 L of air at a pressure of 5.00 atmospheres. At what volume, will the air exert a
Energy Ability to produce change or do work. First Law of Thermodynamics. Heat (q) Quantity of thermal energy
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
q = m. C p. T q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C) UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
Heat. Heat Terminology 04/12/2017. System Definitions. System Definitions
 System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
Properties of Matter
 Properties of Matter Chapter 4 Hein and Arena Version 1.0 Eugene Passer Chemistry Department Bronx Community 1 College John Wiley and Sons, Inc Properties of Substances 2 Properties of a Substance A property
Properties of Matter Chapter 4 Hein and Arena Version 1.0 Eugene Passer Chemistry Department Bronx Community 1 College John Wiley and Sons, Inc Properties of Substances 2 Properties of a Substance A property
1. Fill in the blanks with the following: kinetic, potential, chemical, thermal. One word will be used twice.
 Thermo Worksheets Name Class Period Types of Energy and the Law of Conservation of Energy 1. Fill in the blanks with the following: kinetic, potential, chemical, thermal. One word will be used twice. Solar
Thermo Worksheets Name Class Period Types of Energy and the Law of Conservation of Energy 1. Fill in the blanks with the following: kinetic, potential, chemical, thermal. One word will be used twice. Solar
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Thermochemistry. Chapter 6. Dec 19 8:52 AM. Thermochemistry. Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat
 Chapter 6 Dec 19 8:52 AM Intro vocabulary Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat Potential Energy: Energy due to position or composition (distance and strength of bonds) Kinetic Energy: Energy
Chapter 6 Dec 19 8:52 AM Intro vocabulary Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat Potential Energy: Energy due to position or composition (distance and strength of bonds) Kinetic Energy: Energy
Chapter 4. Properties of Matter
 Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Changes and Properties of Matter
 Changes and Properties of Matter Physical Properties of Matter Physical Changes: Changes that change only the appearance of a substance, not its chemical identity. Physical Properties: Properties that
Changes and Properties of Matter Physical Properties of Matter Physical Changes: Changes that change only the appearance of a substance, not its chemical identity. Physical Properties: Properties that
Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy
 Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Stoichiometry. Consider the reaction in which the reactants are nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. They produce the product ammonia gas.
 1 1. Interpreting Chemical Equations Stoichiometry Calculations using balanced equations are called stoichiometric calculations. The starting point for any problem involving quantities of chemicals in
1 1. Interpreting Chemical Equations Stoichiometry Calculations using balanced equations are called stoichiometric calculations. The starting point for any problem involving quantities of chemicals in
Accelerated Chemistry Semester 2 Review Sheet
 Accelerated Chemistry Semester 2 Review Sheet The semester test will be given in two parts. The first part is a performance assessment and will be given the day before the semester test. This will include
Accelerated Chemistry Semester 2 Review Sheet The semester test will be given in two parts. The first part is a performance assessment and will be given the day before the semester test. This will include
Energy. Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.)
 Change in Energy Energy Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.) Heat - the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. Unit of heat
Change in Energy Energy Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.) Heat - the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. Unit of heat
Enthalpies of Reaction
 Enthalpies of Reaction Enthalpy is an extensive property Magnitude of H is directly related to the amount of reactant used up in a process. CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) H = 890 kj 2CH 4 (g)
Enthalpies of Reaction Enthalpy is an extensive property Magnitude of H is directly related to the amount of reactant used up in a process. CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) H = 890 kj 2CH 4 (g)
Thermochemistry-Part 1
 Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Start Part 2. Tro's "Introductory Chemistry", Chapter 3
 Start Part 2 1 Separation of Mixtures Separate mixtures based on different physical properties of the components. Physical change. Different Physical Property Boiling point State of matter (solid/liquid/gas)
Start Part 2 1 Separation of Mixtures Separate mixtures based on different physical properties of the components. Physical change. Different Physical Property Boiling point State of matter (solid/liquid/gas)
What are the states of Matter?
 What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
Name Date Class SECTION 16.1 PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS
 SOLUTIONS Practice Problems In your notebook, solve the following problems. SECTION 16.1 PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS 1. The solubility of CO 2 in water at 1.22 atm is 0.54 g/l. What is the solubility of carbon
SOLUTIONS Practice Problems In your notebook, solve the following problems. SECTION 16.1 PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS 1. The solubility of CO 2 in water at 1.22 atm is 0.54 g/l. What is the solubility of carbon
CHAPTER 16: REACTION ENERGY AND CHAPTER 17: REACTION KINETICS. Honors Chemistry Ms. Agostine
 CHAPTER 16: REACTION ENERGY AND CHAPTER 17: REACTION KINETICS Honors Chemistry Ms. Agostine 16.1 Thermochemistry Definition: study of the transfers of energy as heat that accompany chemical reactions and
CHAPTER 16: REACTION ENERGY AND CHAPTER 17: REACTION KINETICS Honors Chemistry Ms. Agostine 16.1 Thermochemistry Definition: study of the transfers of energy as heat that accompany chemical reactions and
Slide 1 / Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy (c) kinetic energy. a only b only c only a and c b and c
 Slide 1 / 84 1 Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy (c) kinetic energy A B C D E a only b only c only a and c b and c Slide 2 / 84 2 The internal energy of a system
Slide 1 / 84 1 Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy (c) kinetic energy A B C D E a only b only c only a and c b and c Slide 2 / 84 2 The internal energy of a system
2. What is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles? (A) heat capacity (B) molar enthalpy (C) specific heat (D) temperature
 Thermochemistry #1 Chemistry 3202 Name: 1. Classify the following systems as open or closed a) glass of cold water b) a gel filled freezer pack c) a burning candle d) a fluorescent lightbulb e) hot water
Thermochemistry #1 Chemistry 3202 Name: 1. Classify the following systems as open or closed a) glass of cold water b) a gel filled freezer pack c) a burning candle d) a fluorescent lightbulb e) hot water
Review of Terms. Additional Review. Energy, Enthalpy, & Thermochemistry
 Energy, Enthalpy, & Thermochemistry 9.1 The Nature of Energy 9. Enthalpy 9. Thermodynamics of Ideal Gases 9.4 alorimetry 9.5 Hess s Law 9.6 Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9.7 Present Sources of Energy
Energy, Enthalpy, & Thermochemistry 9.1 The Nature of Energy 9. Enthalpy 9. Thermodynamics of Ideal Gases 9.4 alorimetry 9.5 Hess s Law 9.6 Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9.7 Present Sources of Energy
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20
 Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Reaction Energy. Thermochemistry
 Reaction Energy Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the transfers of energy as heat that accompany chemical reactions & physical changes Thermochemistry -In studying heat changes, think of defining
Reaction Energy Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the transfers of energy as heat that accompany chemical reactions & physical changes Thermochemistry -In studying heat changes, think of defining
Name: Score: /100. Part I. Multiple choice. Write the letter of the correct answer for each problem. 3 points each
 Name: Score: /100 Part I. Multiple choice. Write the letter of the correct answer for each problem. 3 points each 1. Which of the following contains the greatest number of moles of O? A) 2.3 mol H 2 O
Name: Score: /100 Part I. Multiple choice. Write the letter of the correct answer for each problem. 3 points each 1. Which of the following contains the greatest number of moles of O? A) 2.3 mol H 2 O
Thermochemistry. Using Heats of Reaction - Hess s Law - Standard Enthalpies of Formation - Fuels Foods, Commercial Fuels, and Rocket Fuels
 Thermochemistry Understanding Heats of Reaction - Energy and Its Units - Heat of Reaction - Enthalpy and Enthalpy Change - Thermochemical Equations - Applying Stoichiometry to Heats of Reaction - Measuring
Thermochemistry Understanding Heats of Reaction - Energy and Its Units - Heat of Reaction - Enthalpy and Enthalpy Change - Thermochemical Equations - Applying Stoichiometry to Heats of Reaction - Measuring
Introduction to Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry Unit. Definition. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology 07/04/2016. Chemistry 30
 Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
