Diffractive self-imaging based on selective etching of a ferroelectric domain inversion grating
|
|
|
- August Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 COL 13(2), 02002(201) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS February 10, 201 Diffractive self-imaging based on selective etching of a ferroelectric domain inversion grating Yunlin Chen ( 陈云琳 )*, Tianwei Fan ( 范天伟 ), and Man Tong ( 曼佟 ) Institute of Applied Micro-Nano Materials, School of Science, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing , China *Corresponding author: ylchen@bjtu.edu.cn Received September 4, 2014; accepted November 28, 2014; posted online February 9, 201 A hexagonal array grating based on selective etching of a 2D ferroelectric domain inversion in a periodically poled MgO-doped LiNbO 3 crystal is fabricated. The effects to the diffractive self-imaging as a function of diffraction distance for a fixed phase difference and array duty cycle of the grating is theoretically analyzed. The Talbot diffractive self-imaging properties after selective etching of a 2D ferroelectric domain inversion grating under a fixed phase difference are experimentally demonstrated. A good agreement between theoretical and experimental results is observed. OCIS codes: , , doi: /COL The phenomenon of self-imaging of periodic objects, also known as the Talbot effect, was first observed by Talbot in 1836 [1]. The field diffracted from a periodic object illuminated by a plane wave was found to replicate the object transmittance at certain imaging planes, and has led to a variety of applications in imaging processing and synthesis, photolithography, optical testing, optical metrology, spectrometry, optical computing, as well as in near-field scanning optical microscopy [2]. Particularly, a Talbot interferometer becomes very useful in -ray imaging due to the lack of efficient lenses for -rays [3]. The Talbot effect is manifested when a grating is illuminated with a highly spatially coherent plane wave. Self-imaging is possible for periodic or also quasi-periodic objects (i.e., the Montgomery effect [4] ). The Talbot effect requires periodic objects, and images are produced solely by free-space propagation of a diffracted optical field at integer multiples of Talbot distances. Different optical elements have been made to exhibit self-imaging based on the Talbot effect [,6]. Among the various devices, a tunable array can be realized with spatial light modulators (SLMs) based on, for example, liquid crystals. However, a commercial SLM usually has relatively big pixel dimensions, which limits further applications. A LiNbO 3 (LN) crystal is a practical material for use in a Talbot phase array (TPA) due to its perfect optical characteristics [7]. However, applying a high external electric field restricts the Talbot diffractive self-imaging (TDSI) based on periodically poled LN (PPLN) to applications in optical integration and optical microstructure devices. PPLN and periodically poled LiTaO 3 (PPLT) can be used to realize second-harmonic self-imaging from 1D PPLN [8], and second-harmonic Talbot self-imaging from 1D and 2D PPLT [9]. A MgO LN (MgLN) crystal showed a shorter absorption edge and higher resistance to photorefractive damage than that of LN [10]. Moreover, because of it has a lower switching field, periodically poled MgLN (PPMgLN) has been expected to be fairly easily fabricated by means of electric-field poling [11]. These features are important to reduce the applied electric field, and improve TPA performance. A high flexibility for designing a TPA could be obtained if arbitrary surface-relief diffractive optical elements of high quality could be patterned in a MgLN crystal. Ferroelectric domains of opposite spontaneous polarization present different etching speeds when dipped in some acid mixtures. In this work, we theoretically analyzed the effects on TDSI based on 2D surface-relief diffraction grating from a diffraction distance. According to the theoretical simulation, we fabricated a 2D surface-relief diffraction grating based on PPMgLN by selective etching. The TDSI properties of the selective etching of a 2D ferroelectric domain inversion grating under a fixed phase difference are experimentally demonstrated. A 2D hexagonal array grating was designed because of its high efficiency with respect to luminous energy utilization and high compatibility with other optical devices. A hexagonal ferroelectric domain inversion grating is shown in Fig. 1, where t x and t y are the periods in the x and y-directions (respectively), and the period t x ¼ 2 μm, Fig. 1. Hexagonal array grating /201/02002(4) Chinese Optics Letters
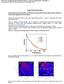
3 COL 13(2), 02002(201) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS February 10, 201 Fig. 2. Numerical simulation TDSI (for Δφ ¼ 0.3π); (a) (d) with respect to distance coefficient β ¼ 2, 3,, and 10; (e) (h) with respect to distance coefficient β ¼ 0.10, 0.33, 0.0, and p t y ¼ 3t x 43 μm, hexagon width l ¼ 14 μm, and duty cycle D ¼ l t x 6%. An expanded laser with a wavelength of 32 nm is used as the incident light source. Based on the theory of Fresnel images of plane periodic objects[12], a simple method of hexagonal array illumination based on the Talbot effect was reported[13]. The transmitted field of the hexagonal array structure within a period ðt x ; t y Þ can be written as uðx; yþ. Omitting a common phase factor, uðx; yþ can be expressed as uðx; yþ ¼ mx A exp i2π þ p ; tx 3t x mx u z ðδφ; x; yþ ¼ A exp i2π þ p tx 3t x 2 2 3m þ n : exp iπλz 3t 2x Then we substitute D ¼ l t x, Z t ¼ 3t 2x 2λ, and Z ¼ βz t into following equation, where Z t represents the Talbot distance, β is the coefficient of the Talbot distance, and λ is the input wavelength. Then u z ðδ; x; yþ can be rewritten as (1) u z ðδφ; x; yþ ¼ where m and n are positive integers, and A can be calculated as A00 ¼ exp½ iðδφþ þ cfexp½iðδφþ exp½ iðδφþ g; (2) where A00 represents the zeroth component. As shown in Fig. 1, for a ð0; πþ phase grating, A00 ¼ 0. in Ref. [13] ð 1Þn sinðδφþ A ¼ if1 þ exp½iπðn þ mþ g nðn 2 m2 Þπ 2 2m 3n nπ π 2n cos ðn þ mþ cos 2m þ 3n π : þ ðn mþ cos (4) i2πd mx þ p A exp l 3 πβ exp i ð3m 2 þ n 2 Þ : 2 () Through Eqs. (1) (), Fig. 2 shows the simulated TDSI at integer multiples of the Talbot distance and fractional values of the Talbot distance; the phase difference Δφ ¼ 0.3π and the duty cycle is 0.6. (3) When a hexagonal array grating is illuminated with a monochromatic plane wave, the diffracted field u z ðδφ; x; yþ at an arbitrary z-imaging plane can be expressed in the following Fourier series expansion Fig. 3. Waveform for the 2D ferroelectric domain inversion MgLN
4 COL 13(2), 02002(201) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS February 10, 201 Fig. 4. Fabricated MgLN domain inversion patterns; (a) optical microscope image; (b) SEM image. From numerical simulations, we knew that the intensity distribution of the TDSI is sensitive to the diffraction distance. The same TDSI is obtained at distances that are integer multiples of the Talbot distance Z t, and the intensity of the diffraction decreases with increasing distance coefficient β [as shown in Figs. 2(a) 2(d)]. A TDSI that is more complex occurs at fractional values of the Talbot [14,1] distance Z t as shown in Figs. 2(e) 2(h). A MgLN substrate allows light transmission over a wide spectral range, from the IR to the UV regions ( μm 30 nm). The sample was cut from a c-cut, optically polished, 1.0 mm thick wafer obtained from a mol.% MgO doping congruent LN crystal. A 2D grating of periodically inverted ferroelectric domains, along the z axis, in a 10 m 10 m 1 m ðx; y; zþ MgLN sample, was obtained by photolithographic and electric field poling processes. The periodic domain reversal poling process is shown in Fig. 3, which consists of three sections: an incubation stage, a poling stage, and a stabilization stage. The pitch of this hexagonal pattern is 2 μm. After poling, the sample was etched to obtain a ferroelectric domain inversion grating. In fact, more than 2 h of etching in a 90 C HNO 3 HF acid mixture results in differential etching of the opposite ferroelectric domain faces. In this way we obtain a 2D pattern in which each hexagonal domain became a truncated pyramid. The ferroelectric patterns were obtained in large areas (10 mm 10 mm) as required for photonics applications. Figure 4(a) shows an optical microscope image of the domains inversion patterns after the poling process, whereas Fig. 4(b) represents a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the obtained sample after the etching process. The sample had a duty cycle around 6% and a microstructure height of about 20 μm. Spatially resolved micro-raman spectroscopy was employed to investigate possible perturbations in the local structure of the crystalline material after polarization reversal [16,17]. The obtained spectra collected at the center of the original (no poling) inverted regions are shown in Fig.. As observed, little differences can be detected either in the position of the Raman peaks or in the spectral widths, the obtained spectra being identical. That is, no structural changes are observed which means that our poling process is a suitable technique to produce domain-inverted structures in MgLN crystals. We used a MgLN-based 2D (hexagonal) array of periodically inverted ferroelectric domains with a duty cycle 6%, and a pitch of size of 2 and 20 μm in depth, of a 10 mm 10 mm 1 mm ðx; y; zþ MgLN sample for studying TDSI. To this aim a simple optical setup was used, as depicted in Fig. 6. A diode laser operating at a wavelength of 32 nm illuminated the sample. For the 2D array sample, the Talbot distance is Z t ¼ 3t 2 x 2λ ¼ mm, where t x ¼ 2 μm is the period of the Fig.. Raman spectra collected at the original (noninverted) and domain inverted areas. Fig. 6. Experimental setup of diffraction self-imaging
5 COL 13(2), 02002(201) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS February 10, 201 Fig. 7. Experimental TDSI patterns obtains (Δφ ¼ 0.3π); (a) (d) on β ¼ 2, 3,, and 10 planes; (e) (h) on β ¼ 0.10, 0.33, 0.0, and 0.70 planes. hexagonal grating. The laser beam was remodeled by a double-lens telescope system in order to obtain a smaller laser spot size. When the plane wave propagates along the z axis to the sample, the TDSI will be magnified by a 40 microscope objective and recorded by a CCD camera. The distance between the sample and microscope objective is the diffraction distance. In order to investigate the influence of the diffraction distance on the self-imaging patterns, the phase difference was fixed at 0.3π. The TDSI patterns were recorded by a CCD camera. Pictures of the TDSI patterns obtained are shown in Fig. 7. The diffraction patterns in Figs. 7(a) 7(d) were recorded when β ¼ 2, 3,, and 10, and the patterns in Figs. 7(e) 7(h) were recorded when β ¼ 0.10, 0.33, 0.0, and It is obvious that the same TDSI is obtained at distances that are integer multiples of the Talbot distance Z t, and the TDSI with a high intensity-contrast is obtained with the distance coefficient β is decreased [as shown in Figs. 7(a) 7(d)]. A variety of interesting TDSIs have been obtained at fractional values of the Talbot distance Z t [as shown in Figs. 7(e) 7(h)]. The experiment results showed that the self-imaging patterns changed with the diffraction distance as the phase difference was fixed, which verified the numerical calculation results. In conclusion, we theoretically and experimentally study the TDSI of a 2D ferroelectric domain inversion grating based on selective etching of MgLN. Theoretical simulations are done for effects to the TDSI as a function of the diffraction distance for a fixed phase difference and array duty cycle of the grating. On the basis of the theoretical results, we fabricate a 2D hexagonal ferroelectric domain inversion array with duty cycle D ¼ 6% based on selective etching of PPMgLN. The TDSI properties after selective etching of a 2D ferroelectric domain inversion grating under a fixed phase difference are experimentally demonstrated. The work reported in this Letter shows that a TDSI with a high intensity-contrast is obtained when the distance coefficient β decreases in proportion to integer multiples of the Talbot distance Z t, and a variety of TDSIs are obtained at fractional values of the Talbot distance Z t. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No ) and the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (No ). References 1. H. F. Talbot, Philos. Mag. 9(4), 401 (1836). 2. K. Patorski, Prog. Opt. 27, 1 (1989). 3. W. Yashiro, Y. Takeda, A. Takeuchi, Y. Suzuki, and A. Momose, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, (2009). 4. W. D. Montgomery, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 7, 772 (1967).. G. Forte, A. Lencina, M. Tebaldi, and N. Bolognini, Appl. Opt. 1, 479 (2012). 6. N. Madamopoulos and N. A. Riza, Appl. Opt. 39, 4168 (2000). 7. M. Yamada, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 4010 (2000). 8. Y. Chen, J. Zhang, and H. Li, Chin. Opt. Lett. 11, (2013). 9. Y. Zhang, J. M. Wen, S. N. Zhu, and M. iao, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, (2010). 10. Y. L. Chen, G. Liu, and Y. Q. Zheng, Opt. Lett. 34, 2480 (2009). 11. Y. L. Chen, W. G. Yan, J. Guo, S. L. Chen, and G. Y. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, (200). 12. J. Winthrop and C. Worthington, J. Opt. Soc. Am., 373 (196). 13. P. i, C. H. Zhou, E. W. Dai, and L. R. Liu, Opt. Lett. 27, 228 (2002). 14. M. V. Berry and S. Klein, J. Mod. Opt. 43, 2139 (1996). 1. H. C. Rosu, J. S. Murguia, and A. Ludu, Physica A 392, 3780 (2013). 16. R. Hammoum, M. D. Fontana, P. Bourson, and V. Y. Shur, Appl. Phys. A 91, 6 (2008). 17. G. Stone, D. Lee, H. u, S. R. Phillpot, and V. Dierolf, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, (2013)
Acousto-optic tunable second-harmonic Talbot effect based on periodically poled LiNbO 3 crystals
 Liu et al. Vol. 29, No. 12 / December 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 3325 Acousto-optic tunable second-harmonic Talbot effect based on periodically poled LiNbO 3 crystals Dongmei Liu, 1 Yong Zhang, 1, * Zhenhua
Liu et al. Vol. 29, No. 12 / December 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 3325 Acousto-optic tunable second-harmonic Talbot effect based on periodically poled LiNbO 3 crystals Dongmei Liu, 1 Yong Zhang, 1, * Zhenhua
Multi-cycle THz pulse generation in poled lithium niobate crystals
 Laser Focus World April 2005 issue (pp. 67-72). Multi-cycle THz pulse generation in poled lithium niobate crystals Yun-Shik Lee and Theodore B. Norris Yun-Shik Lee is an assistant professor of physics
Laser Focus World April 2005 issue (pp. 67-72). Multi-cycle THz pulse generation in poled lithium niobate crystals Yun-Shik Lee and Theodore B. Norris Yun-Shik Lee is an assistant professor of physics
Periodic Poling of Stoichiometric Lithium Tantalate for High-Average Power Frequency Conversion
 VG04-123 Periodic Poling of Stoichiometric Lithium Tantalate for High-Average Power Frequency Conversion Douglas J. Bamford, David J. Cook, and Scott J. Sharpe Physical Sciences Inc. Jeffrey Korn and Peter
VG04-123 Periodic Poling of Stoichiometric Lithium Tantalate for High-Average Power Frequency Conversion Douglas J. Bamford, David J. Cook, and Scott J. Sharpe Physical Sciences Inc. Jeffrey Korn and Peter
Novel method for ultrashort laser pulse-width measurement based on the self-diffraction effect
 Novel method for ultrashort laser pulse-width measurement based on the self-diffraction effect Peng Xi, Changhe Zhou, Enwen Dai, and Liren Liu Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy
Novel method for ultrashort laser pulse-width measurement based on the self-diffraction effect Peng Xi, Changhe Zhou, Enwen Dai, and Liren Liu Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy
Channel Optical Waveguides with Spatial Longitudinal Modulation of Their Parameters Induced in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Samples
 Russian Forum of Young Scientists Volume 2018 Conference Paper Channel Optical Waveguides with Spatial Longitudinal Modulation of Their Parameters Induced in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Samples A D
Russian Forum of Young Scientists Volume 2018 Conference Paper Channel Optical Waveguides with Spatial Longitudinal Modulation of Their Parameters Induced in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Samples A D
High-power terahertz radiation from surface-emitted THz-wave parametric oscillator
 High-power terahertz radiation from surface-emitted THz-wave parametric oscillator Li Zhong-Yang( ) a)b), Yao Jian-Quan( ) a)b), Xu De-Gang( ) a)b), Zhong Kai( ) a)b), Wang Jing-Li( ) a)b), and Bing Pi-Bin(
High-power terahertz radiation from surface-emitted THz-wave parametric oscillator Li Zhong-Yang( ) a)b), Yao Jian-Quan( ) a)b), Xu De-Gang( ) a)b), Zhong Kai( ) a)b), Wang Jing-Li( ) a)b), and Bing Pi-Bin(
Two-dimensional nonlinear frequency converters
 Two-dimensional nonlinear frequency converters A. Arie, A. Bahabad, Y. Glickman, E. Winebrand, D. Kasimov and G. Rosenman Dept. of Physical Electronics, School of Electrical Engineering Tel-Aviv University,
Two-dimensional nonlinear frequency converters A. Arie, A. Bahabad, Y. Glickman, E. Winebrand, D. Kasimov and G. Rosenman Dept. of Physical Electronics, School of Electrical Engineering Tel-Aviv University,
GRATING CLASSIFICATION
 GRATING CLASSIFICATION SURFACE-RELIEF GRATING TYPES GRATING CLASSIFICATION Transmission or Reflection Classification based on Regime DIFFRACTION BY GRATINGS Acousto-Optics Diffractive Optics Integrated
GRATING CLASSIFICATION SURFACE-RELIEF GRATING TYPES GRATING CLASSIFICATION Transmission or Reflection Classification based on Regime DIFFRACTION BY GRATINGS Acousto-Optics Diffractive Optics Integrated
Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices
 Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices Xiaoyong Hu, Cuicui Lu, Yulan Fu, Yu Zhu, Yingbo Zhang, Hong Yang, Qihuang Gong Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China Contents Motivation
Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices Xiaoyong Hu, Cuicui Lu, Yulan Fu, Yu Zhu, Yingbo Zhang, Hong Yang, Qihuang Gong Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China Contents Motivation
A tunable corner-pumped Nd:YAG/YAG composite slab CW laser
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 21, No. 1 (212) 1428 A tunable corner-pumped Nd:YAG/YAG composite slab CW laser Liu Huan( 刘欢 ) and Gong Ma-Li( 巩马理 ) State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Center for Photonics and Electronics,
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 21, No. 1 (212) 1428 A tunable corner-pumped Nd:YAG/YAG composite slab CW laser Liu Huan( 刘欢 ) and Gong Ma-Li( 巩马理 ) State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Center for Photonics and Electronics,
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials
 Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light. Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film
 Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Ordered nano-scale domains in lithium niobate single crystals via. phase-mask assisted all-optical poling
 Ordered nano-scale domains in lithium niobate single crystals via phase-mask assisted all-optical poling I.T. Wellington *, C.E. Valdivia, T. J. Sono, C.L. Sones, S. Mailis and R.W. Eason. Optoelectronics
Ordered nano-scale domains in lithium niobate single crystals via phase-mask assisted all-optical poling I.T. Wellington *, C.E. Valdivia, T. J. Sono, C.L. Sones, S. Mailis and R.W. Eason. Optoelectronics
Double-distance propagation of Gaussian beams passing through a tilted cat-eye optical lens in a turbulent atmosphere
 Double-distance propagation of Gaussian beams passing through a tilted cat-eye optical lens in a turbulent atmosphere Zhao Yan-Zhong( ), Sun Hua-Yan( ), and Song Feng-Hua( ) Department of Photoelectric
Double-distance propagation of Gaussian beams passing through a tilted cat-eye optical lens in a turbulent atmosphere Zhao Yan-Zhong( ), Sun Hua-Yan( ), and Song Feng-Hua( ) Department of Photoelectric
Diffraction Interference Induced Superfocusing in Nonlinear Talbot Effect
 Diffraction Interference Induced Superfocusing in Nonlinear Talbot Effect Dongmei Liu, 1 Yong Zhang, 1,* Jianming Wen, 1,2, Zhenhua Chen, 1 Dunzhao Wei, 1 Xiaopeng Hu, 1 Gang Zhao, 1 S. N. Zhu, 1 and Min
Diffraction Interference Induced Superfocusing in Nonlinear Talbot Effect Dongmei Liu, 1 Yong Zhang, 1,* Jianming Wen, 1,2, Zhenhua Chen, 1 Dunzhao Wei, 1 Xiaopeng Hu, 1 Gang Zhao, 1 S. N. Zhu, 1 and Min
Initial Results on the Feasibility of Hybrid X-Ray Microscopy
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 43, NO. 5 OCTOBER 2005 Initial Results on the Feasibility of Hybrid X-Ray Microscopy P. K. Tseng, 1 W. F. Pong, 1 C. L. Chang, 1 C. P. Hsu, 1 F. Y. Lin, 2 C. S. Hwang, 2
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 43, NO. 5 OCTOBER 2005 Initial Results on the Feasibility of Hybrid X-Ray Microscopy P. K. Tseng, 1 W. F. Pong, 1 C. L. Chang, 1 C. P. Hsu, 1 F. Y. Lin, 2 C. S. Hwang, 2
All-optical isolator under arbitrary linearly polarized fundamental wave in an optical superlattice
 All-optical isolator under arbitrary linearly polarized fundamental wave in an optical superlattice Liang Yuan, 1 Jianhong Shi, 1,2 and Xianfeng Chen 1,3 1 Department of Physics; The State Key Laboratory
All-optical isolator under arbitrary linearly polarized fundamental wave in an optical superlattice Liang Yuan, 1 Jianhong Shi, 1,2 and Xianfeng Chen 1,3 1 Department of Physics; The State Key Laboratory
Multi-Purpose Nonlinear Optical Microscope. Principle and its Applications to Polar Thin Film Observation
 Multi-Purpose Nonlinear Optical Microscope. Principle and its Applications to Polar Thin Film Observation Y. Uesu, N. Kato Department of Physics, Waseda University 3 4 1 Okubo, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 169-8555,
Multi-Purpose Nonlinear Optical Microscope. Principle and its Applications to Polar Thin Film Observation Y. Uesu, N. Kato Department of Physics, Waseda University 3 4 1 Okubo, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 169-8555,
Efficient Generation of Second Harmonic Wave with Periodically. Poled MgO:LiNbO 3
 ISSN 2186-6570 Efficient Generation of Second Harmonic Wave with Periodically Poled MgO:LiNbO 3 Genta Masada Quantum ICT Research Institute, Tamagawa University 6-1-1 Tamagawa-gakuen, Machida, Tokyo 194-8610,
ISSN 2186-6570 Efficient Generation of Second Harmonic Wave with Periodically Poled MgO:LiNbO 3 Genta Masada Quantum ICT Research Institute, Tamagawa University 6-1-1 Tamagawa-gakuen, Machida, Tokyo 194-8610,
A tutorial on meta-materials and THz technology
 p.1/49 A tutorial on meta-materials and THz technology Thomas Feurer thomas.feurer@iap.unibe.ch Institute of Applied Physics Sidlerstr. 5, 3012 Bern Switzerland p.2/49 Outline Meta-materials Super-lenses
p.1/49 A tutorial on meta-materials and THz technology Thomas Feurer thomas.feurer@iap.unibe.ch Institute of Applied Physics Sidlerstr. 5, 3012 Bern Switzerland p.2/49 Outline Meta-materials Super-lenses
Efficient generation of >2 W of green light by single-pass frequency doubling in PPMgLN
 Efficient generation of >2 W of green light by single-pass frequency doubling in PPMgLN Author Pullen, Michael, Chapman, Justin, Kielpinski, David Published 2008 Journal Title Applied Optics DOI https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.47.001397
Efficient generation of >2 W of green light by single-pass frequency doubling in PPMgLN Author Pullen, Michael, Chapman, Justin, Kielpinski, David Published 2008 Journal Title Applied Optics DOI https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.47.001397
Nonlinear Physical Optics With Transversely Patterned Quasi-Phase-Matching Gratings
 660 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 Nonlinear Physical Optics With Transversely Patterned Quasi-Phase-Matching Gratings Jonathan R. Kurz, Andrew M.
660 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 Nonlinear Physical Optics With Transversely Patterned Quasi-Phase-Matching Gratings Jonathan R. Kurz, Andrew M.
Sub-wavelength focusing meta-lens
 Sub-wavelength focusing meta-lens Tapashree Roy, 1 Edward T. F. Rogers, 1 and Nikolay I. Zheludev 1,2,* 1 Optoelectronics Research Centre & Centre for Photonic Metamaterials, University of Southampton,
Sub-wavelength focusing meta-lens Tapashree Roy, 1 Edward T. F. Rogers, 1 and Nikolay I. Zheludev 1,2,* 1 Optoelectronics Research Centre & Centre for Photonic Metamaterials, University of Southampton,
Ultra-narrow-band tunable laserline notch filter
 Appl Phys B (2009) 95: 597 601 DOI 10.1007/s00340-009-3447-6 Ultra-narrow-band tunable laserline notch filter C. Moser F. Havermeyer Received: 5 December 2008 / Revised version: 2 February 2009 / Published
Appl Phys B (2009) 95: 597 601 DOI 10.1007/s00340-009-3447-6 Ultra-narrow-band tunable laserline notch filter C. Moser F. Havermeyer Received: 5 December 2008 / Revised version: 2 February 2009 / Published
Simultaneous optical parametric oscillation and intracavity second-harmonic generation based on a hexagonally poled lithium tantalate
 Simultaneous optical parametric oscillation and intracavity second-harmonic generation based on a hexagonally poled lithium tantalate P. Xu *, J. F. Wang, C. Li, Z. D. Xie, X. J. Lv, H. Y. Leng, J. S.
Simultaneous optical parametric oscillation and intracavity second-harmonic generation based on a hexagonally poled lithium tantalate P. Xu *, J. F. Wang, C. Li, Z. D. Xie, X. J. Lv, H. Y. Leng, J. S.
Unbalanced lensless ghost imaging with thermal light
 886 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A / Vol. 3, No. 4 / April 04 Gao et al. Unbalanced lensless ghost imaging with thermal light Lu Gao,,3 Xiao-long Liu, hiyuan heng, and Kaige Wang, * School of Science, China University
886 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A / Vol. 3, No. 4 / April 04 Gao et al. Unbalanced lensless ghost imaging with thermal light Lu Gao,,3 Xiao-long Liu, hiyuan heng, and Kaige Wang, * School of Science, China University
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 30 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 30 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 30 Mar 2010](/thumbs/83/87689638.jpg) Analytical vectorial structure of non-paraxial four-petal Gaussian beams in the far field Xuewen Long a,b, Keqing Lu a, Yuhong Zhang a,b, Jianbang Guo a,b, and Kehao Li a,b a State Key Laboratory of Transient
Analytical vectorial structure of non-paraxial four-petal Gaussian beams in the far field Xuewen Long a,b, Keqing Lu a, Yuhong Zhang a,b, Jianbang Guo a,b, and Kehao Li a,b a State Key Laboratory of Transient
Fast-Response Infrared Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Phase Modulators
 Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., Vol. 453, pp. 343 354, 2006 Copyright # Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 1542-1406 print=1563-5287 online DOI: 10.1080/15421400600653886 Fast-Response Infrared Ferroelectric Liquid
Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., Vol. 453, pp. 343 354, 2006 Copyright # Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 1542-1406 print=1563-5287 online DOI: 10.1080/15421400600653886 Fast-Response Infrared Ferroelectric Liquid
Supporting information. GaN Metalens for Pixel-Level Full-Color Routing at Visible Light
 Supporting information GaN Metalens for Pixel-Level Full-Color Routing at Visible Light Bo Han Chen 1,, Pin Chieh Wu 2,, Vin-Cent Su 3,, Yi-Chieh Lai 1,4, Cheng Hung Chu 2, I Chen Lee 5, Jia-Wern Chen
Supporting information GaN Metalens for Pixel-Level Full-Color Routing at Visible Light Bo Han Chen 1,, Pin Chieh Wu 2,, Vin-Cent Su 3,, Yi-Chieh Lai 1,4, Cheng Hung Chu 2, I Chen Lee 5, Jia-Wern Chen
Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch
 Vol 16 No 11, November 27 c 27 Chin. Phys. Soc. 19-1963/27/16(11/3285-5 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch Wang Xiang-Hui(
Vol 16 No 11, November 27 c 27 Chin. Phys. Soc. 19-1963/27/16(11/3285-5 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch Wang Xiang-Hui(
Focusing of Light by a Nano-Hole Array
 Focusing of Light by a Nano-Hole Array Fu Min Huang 1, Yifang Chen 2, F. Javier Garcia de Abajo 3 and Nikolay Zheludev 1 1 EPSRC Nanophotonics Portfolio Centre, School of Physics and Astronomy, University
Focusing of Light by a Nano-Hole Array Fu Min Huang 1, Yifang Chen 2, F. Javier Garcia de Abajo 3 and Nikolay Zheludev 1 1 EPSRC Nanophotonics Portfolio Centre, School of Physics and Astronomy, University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS2397 Strong-field physics with singular light beams M. Zürch, C. Kern, P. Hansinger, A. Dreischuh, and Ch. Spielmann Supplementary Information S.1 Spectrometric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS2397 Strong-field physics with singular light beams M. Zürch, C. Kern, P. Hansinger, A. Dreischuh, and Ch. Spielmann Supplementary Information S.1 Spectrometric
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION IN PERIODICALLY POLED NONLINEAR CRYSTALS WITH 1064 nm GAUSSIAN LASER PULSES
 SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION IN PERIODICALLY POLED NONLINEAR CRYSTALS WITH 1064 nm GAUSSIAN LASER PULSES LIVIU NEAGU National Institute for Laser, Plasma and Radiation Physics, P.O. Box MG-36, 077125, Bucharest,
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION IN PERIODICALLY POLED NONLINEAR CRYSTALS WITH 1064 nm GAUSSIAN LASER PULSES LIVIU NEAGU National Institute for Laser, Plasma and Radiation Physics, P.O. Box MG-36, 077125, Bucharest,
Analytical Study of Electromagnetic Wave Diffraction Through a Circular Aperture with Fringes on a Perfect Conducting Screen
 International Journal of High Energy Physics 016; 3(5): 33-40 http://wwwsciencepublishinggroupcom/j/ijhep doi: 1011648/jijhep016030511 ISSN: 376-7405 (Print); ISSN: 376-7448 (Online) Analytical Study of
International Journal of High Energy Physics 016; 3(5): 33-40 http://wwwsciencepublishinggroupcom/j/ijhep doi: 1011648/jijhep016030511 ISSN: 376-7405 (Print); ISSN: 376-7448 (Online) Analytical Study of
2008,, Jan 7 All-Paid US-Japan Winter School on New Functionalities in Glass. Controlling Light with Nonlinear Optical Glasses and Plasmonic Glasses
 2008,, Jan 7 All-Paid US-Japan Winter School on New Functionalities in Glass Photonic Glass Controlling Light with Nonlinear Optical Glasses and Plasmonic Glasses Takumi FUJIWARA Tohoku University Department
2008,, Jan 7 All-Paid US-Japan Winter School on New Functionalities in Glass Photonic Glass Controlling Light with Nonlinear Optical Glasses and Plasmonic Glasses Takumi FUJIWARA Tohoku University Department
Long- and short-term average intensity for multi-gaussian beam with a common axis in turbulence
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 0, No. 1 011) 01407 Long- and short-term average intensity for multi-gaussian beam with a common axis in turbulence Chu Xiu-Xiang ) College of Sciences, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 0, No. 1 011) 01407 Long- and short-term average intensity for multi-gaussian beam with a common axis in turbulence Chu Xiu-Xiang ) College of Sciences, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry
Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation angle dependence of electronic structure
 Supplementary Material for Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation angle dependence of electronic structure Kwanpyo Kim 1,2,3, Sinisa Coh 1,3, Liang Z. Tan 1,3, William
Supplementary Material for Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation angle dependence of electronic structure Kwanpyo Kim 1,2,3, Sinisa Coh 1,3, Liang Z. Tan 1,3, William
Measurement of novel micro bulk defects in semiconductive materials based on Mie scatter
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 45, April 2007, pp. 372-376 Measurement of novel micro bulk defects in semiconductive materials based on Mie scatter You Zheng, Li Yingpeng & Chen Jun Department
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 45, April 2007, pp. 372-376 Measurement of novel micro bulk defects in semiconductive materials based on Mie scatter You Zheng, Li Yingpeng & Chen Jun Department
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like. to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating
 Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
Supporting information
 Supporting information Vacuum ultraviolet laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging of single cells with submicron craters Jia Wang, 1, + Zhaoying Wang, 2, + Feng Liu, 1 Lesi Cai, 2 Jian-bin
Supporting information Vacuum ultraviolet laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging of single cells with submicron craters Jia Wang, 1, + Zhaoying Wang, 2, + Feng Liu, 1 Lesi Cai, 2 Jian-bin
Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Gratings in Electrooptic Polymer Devices
 Gratings in Electrooptic Polymer Devices Venkata N.P.Sivashankar 1, Edward M. McKenna 2 and Alan R.Mickelson 3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder,
Gratings in Electrooptic Polymer Devices Venkata N.P.Sivashankar 1, Edward M. McKenna 2 and Alan R.Mickelson 3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder,
Supporting information. Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via
 Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars
 Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Domain wall characterization in ferroelectrics by using localized nonlinearities
 Domain wall characterization in ferroelectrics by using localized nonlinearities Xuewei Deng and Xianfeng Chen* Department of Physics, the State Key Laboratory on Fiber Optic Local Area Communication Networks
Domain wall characterization in ferroelectrics by using localized nonlinearities Xuewei Deng and Xianfeng Chen* Department of Physics, the State Key Laboratory on Fiber Optic Local Area Communication Networks
Periodic microstructures fabricated by multiplex interfering femtosecond laser beams on graphene sheet
 Int. J. Nanomanufacturing, Vol. 8, No. 3, 2012 221 Periodic microstructures fabricated by multiplex interfering femtosecond laser beams on graphene sheet Yan Li TEDA Applied Physics School, Nankai University,
Int. J. Nanomanufacturing, Vol. 8, No. 3, 2012 221 Periodic microstructures fabricated by multiplex interfering femtosecond laser beams on graphene sheet Yan Li TEDA Applied Physics School, Nankai University,
Optimum Access Waveguide Width for 1xN Multimode. Interference Couplers on Silicon Nanomembrane
 Optimum Access Waveguide Width for 1xN Multimode Interference Couplers on Silicon Nanomembrane Amir Hosseini 1,*, Harish Subbaraman 2, David Kwong 1, Yang Zhang 1, and Ray T. Chen 1,* 1 Microelectronic
Optimum Access Waveguide Width for 1xN Multimode Interference Couplers on Silicon Nanomembrane Amir Hosseini 1,*, Harish Subbaraman 2, David Kwong 1, Yang Zhang 1, and Ray T. Chen 1,* 1 Microelectronic
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays. Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković
 Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
From optical graphene to topological insulator
 From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
Optical time-domain differentiation based on intensive differential group delay
 Optical time-domain differentiation based on intensive differential group delay Li Zheng-Yong( ), Yu Xiang-Zhi( ), and Wu Chong-Qing( ) Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information of the Ministry
Optical time-domain differentiation based on intensive differential group delay Li Zheng-Yong( ), Yu Xiang-Zhi( ), and Wu Chong-Qing( ) Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information of the Ministry
Coherently superposed efficient second harmonic. generation by domain wall series in ferroelectrics
 Coherently superposed efficient second harmonic generation by domain wall series in ferroelectrics Huaijin Ren, Xuewei Deng*, and Xianfeng Chen** Department of Physics, the State Key Laboratory on Fiber
Coherently superposed efficient second harmonic generation by domain wall series in ferroelectrics Huaijin Ren, Xuewei Deng*, and Xianfeng Chen** Department of Physics, the State Key Laboratory on Fiber
Direct measurement of electric-field-induced birefringence in a polymer-stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal composite
 Direct measurement of electric-field-induced birefringence in a polymer-stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal composite Jin Yan, Meizi Jiao, Linghui Rao, and Shin-Tson Wu* College of Optics and Photonics,
Direct measurement of electric-field-induced birefringence in a polymer-stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal composite Jin Yan, Meizi Jiao, Linghui Rao, and Shin-Tson Wu* College of Optics and Photonics,
Development of measurement technique to evaluate thermal conductivity of thermoelectric Bi 2 Te 3 submicron thin films by photothermal radiometry
 Development of measurement technique to evaluate thermal conductivity of thermoelectric Bi Te 3 submicron thin films by photothermal radiometry H Jitsukawa 1 and Y Nagasaka 1 School of Integrated Design
Development of measurement technique to evaluate thermal conductivity of thermoelectric Bi Te 3 submicron thin films by photothermal radiometry H Jitsukawa 1 and Y Nagasaka 1 School of Integrated Design
Micro- and Nano-Technology... for Optics
 Micro- and Nano-Technology...... for Optics U.D. Zeitner Fraunhofer Institut für Angewandte Optik und Feinmechanik Jena Today: 1. Introduction E. Bernhard Kley Institute of Applied Physics Friedrich-Schiller
Micro- and Nano-Technology...... for Optics U.D. Zeitner Fraunhofer Institut für Angewandte Optik und Feinmechanik Jena Today: 1. Introduction E. Bernhard Kley Institute of Applied Physics Friedrich-Schiller
Two-color ghost imaging
 Two-color ghost imaging Kam Wai Clifford Chan,* Malcolm N. O Sullivan, and Robert W. Boyd The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 14627, USA Received 10 September 2008; published
Two-color ghost imaging Kam Wai Clifford Chan,* Malcolm N. O Sullivan, and Robert W. Boyd The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 14627, USA Received 10 September 2008; published
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2016
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2016 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2016](/thumbs/93/113647721.jpg) August 28, 2018 arxiv:1601.02374v1 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2016 Abstract We report on efficient nonlinear generation of ultrafast, higher order perfect vortices at the green wavelength. Based on Fourier
August 28, 2018 arxiv:1601.02374v1 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2016 Abstract We report on efficient nonlinear generation of ultrafast, higher order perfect vortices at the green wavelength. Based on Fourier
Domain patterning in lithium niobate using spontaneous backswitching
 Domain patterning in lithium niobate using spontaneous backswitching R.G. Batchko*, G.D. Millerb, V. Ya. Shur', E. L. Rumyantsevc M.M. Fejer', and R.L. Byera ael Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University,
Domain patterning in lithium niobate using spontaneous backswitching R.G. Batchko*, G.D. Millerb, V. Ya. Shur', E. L. Rumyantsevc M.M. Fejer', and R.L. Byera ael Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL I: SEM IMAGE OF PHOTONIC CRYSTAL RESONATOR
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL I: SEM IMAGE OF PHOTONIC CRYSTAL RESONATOR Figure S1 below is a scanning electronic microscopy image of a typical evanescently coupled photonic crystal resonator used in these experiments.
1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL I: SEM IMAGE OF PHOTONIC CRYSTAL RESONATOR Figure S1 below is a scanning electronic microscopy image of a typical evanescently coupled photonic crystal resonator used in these experiments.
Supplementary Information. Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye. Nanostructures
 Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Broadband IR polarizing beam splitter using a subwavelength-structured one-dimensional photonic-crystal layer embedded in a high-index prism
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 9-10-2009 Broadband IR polarizing beam splitter using a subwavelength-structured
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 9-10-2009 Broadband IR polarizing beam splitter using a subwavelength-structured
Optical and Structural Properties of Bilayer Circular Filter Prepared by Glancing Angle Deposition
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 2, June 29, pp. 218-222 DOI:.387/JOSK.29.13.2.218 Optical and Structural Properties of Bilayer Circular Filter Prepared by Glancing Angle Deposition
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 2, June 29, pp. 218-222 DOI:.387/JOSK.29.13.2.218 Optical and Structural Properties of Bilayer Circular Filter Prepared by Glancing Angle Deposition
Application of high-precision temperature-controlled FBG f ilter and light source self-calibration technique in the BOTDR sensor system
 Application of high-precision temperature-controlled FBG f ilter and light source self-calibration technique in the BOTDR sensor system Jiacheng Hu ( ) 1,2, Fuchang Chen ( ) 1,2, Chengtao Zhang ( ) 1,2,
Application of high-precision temperature-controlled FBG f ilter and light source self-calibration technique in the BOTDR sensor system Jiacheng Hu ( ) 1,2, Fuchang Chen ( ) 1,2, Chengtao Zhang ( ) 1,2,
Periodic poling of magnesium-oxide-doped lithium niobate
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 91, NUMBER 7 1 APRIL 2002 Periodic poling of magnesium-oxide-doped lithium niobate Koichiro Nakamura, a) Jonathan Kurz, Krishnan Parameswaran, and M. M. Fejer Edward L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 91, NUMBER 7 1 APRIL 2002 Periodic poling of magnesium-oxide-doped lithium niobate Koichiro Nakamura, a) Jonathan Kurz, Krishnan Parameswaran, and M. M. Fejer Edward L.
Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light
 CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.97 Supplementary Information Far-field Imaging of Non-fluorescent Species with Sub-diffraction Resolution Pu Wang et al. 1. Theory of saturated transient absorption microscopy
DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.97 Supplementary Information Far-field Imaging of Non-fluorescent Species with Sub-diffraction Resolution Pu Wang et al. 1. Theory of saturated transient absorption microscopy
CHARACTERIZATION of NANOMATERIALS KHP
 CHARACTERIZATION of NANOMATERIALS Overview of the most common nanocharacterization techniques MAIN CHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES: 1.Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) 2. Scanning Electron Microscope
CHARACTERIZATION of NANOMATERIALS Overview of the most common nanocharacterization techniques MAIN CHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES: 1.Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) 2. Scanning Electron Microscope
Photon Energy Dependence of Contrast in Photoelectron Emission Microscopy of Si Devices
 Photon Energy Dependence of Contrast in Photoelectron Emission Microscopy of Si Devices V. W. Ballarotto, K. Siegrist, R. J. Phaneuf, and E. D. Williams University of Maryland and Laboratory for Physical
Photon Energy Dependence of Contrast in Photoelectron Emission Microscopy of Si Devices V. W. Ballarotto, K. Siegrist, R. J. Phaneuf, and E. D. Williams University of Maryland and Laboratory for Physical
Fabrication of micro-optical components in polymer using proton beam micro-machining and modification
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 210 (2003) 250 255 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Fabrication of micro-optical components in polymer using proton beam micro-machining and modification
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 210 (2003) 250 255 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Fabrication of micro-optical components in polymer using proton beam micro-machining and modification
Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices
 Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices Yunfeng Jiang, 1 Kaikai Huang, 1,2 and Xuanhui Lu 1, * 1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University,
Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices Yunfeng Jiang, 1 Kaikai Huang, 1,2 and Xuanhui Lu 1, * 1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University,
arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 18 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 18 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 18 Mar 2008](/thumbs/94/119245773.jpg) Real-time control of the periodicity of a standing wave: an optical accordion arxiv:0803.2733v1 [quant-ph] 18 Mar 2008 T. C. Li, H. Kelkar, D. Medellin, and M. G. Raizen Center for Nonlinear Dynamics and
Real-time control of the periodicity of a standing wave: an optical accordion arxiv:0803.2733v1 [quant-ph] 18 Mar 2008 T. C. Li, H. Kelkar, D. Medellin, and M. G. Raizen Center for Nonlinear Dynamics and
Assessment of Threshold for Nonlinear Effects in Ibsen Transmission Gratings
 Assessment of Threshold for Nonlinear Effects in Ibsen Transmission Gratings Temple University 13th & Norris Street Philadelphia, PA 19122 T: 1-215-204-1052 contact: johanan@temple.edu http://www.temple.edu/capr/
Assessment of Threshold for Nonlinear Effects in Ibsen Transmission Gratings Temple University 13th & Norris Street Philadelphia, PA 19122 T: 1-215-204-1052 contact: johanan@temple.edu http://www.temple.edu/capr/
Temperature Tuning Characteristics of Periodically Poled Lithium Niobate for Second Harmonic Generation at 490 nm
 Temperature Tuning Characteristics of Periodically Poled Lithium Niobate for Second Harmonic Generation at 490 nm Movva Sai Krishna *a, U.S. Tripathi a, Ashok Kaul a, K. Thyagarajan b, M.R. Shenoy b a
Temperature Tuning Characteristics of Periodically Poled Lithium Niobate for Second Harmonic Generation at 490 nm Movva Sai Krishna *a, U.S. Tripathi a, Ashok Kaul a, K. Thyagarajan b, M.R. Shenoy b a
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Large-scale lithography-free metasurface with spectrally tunable super
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Large-scale lithography-free metasurface with spectrally tunable super
Development of a nanostructural microwave probe based on GaAs
 Microsyst Technol (2008) 14:1021 1025 DOI 10.1007/s00542-007-0484-0 TECHNICAL PAPER Development of a nanostructural microwave probe based on GaAs Y. Ju Æ T. Kobayashi Æ H. Soyama Received: 18 June 2007
Microsyst Technol (2008) 14:1021 1025 DOI 10.1007/s00542-007-0484-0 TECHNICAL PAPER Development of a nanostructural microwave probe based on GaAs Y. Ju Æ T. Kobayashi Æ H. Soyama Received: 18 June 2007
Transmission matrices of random media: Means for spectral polarimetric measurements
 Reprint (R40) Transmission matrices of random media: Means for spectral polarimetric measurements Reprinted with permission by Thomas W. Kohlgraf-Owens, Aristide Dogariu CREOL, the College of Optics and
Reprint (R40) Transmission matrices of random media: Means for spectral polarimetric measurements Reprinted with permission by Thomas W. Kohlgraf-Owens, Aristide Dogariu CREOL, the College of Optics and
Nano fabrication and optical characterization of nanostructures
 Introduction to nanooptics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch Nano fabrication and optical characterization of nanostructures Lecture 12 1 Optical characterization
Introduction to nanooptics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch Nano fabrication and optical characterization of nanostructures Lecture 12 1 Optical characterization
Vectorial structure and beam quality of vector-vortex Bessel Gauss beams in the far field
 COL (Suppl., S6( CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS June 3, Vectorial structure and beam quality of vector-vortex Bessel Gauss beams in the far field Lina Guo (, and Zhilie Tang ( School of Physics and Telecommunication
COL (Suppl., S6( CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS June 3, Vectorial structure and beam quality of vector-vortex Bessel Gauss beams in the far field Lina Guo (, and Zhilie Tang ( School of Physics and Telecommunication
Birefringence dispersion in a quartz crystal retrieved from a channelled spectrum resolved by a fibre-optic spectrometer
 Birefringence dispersion in a quartz crystal retrieved from a channelled spectrum resolved by a fibre-optic spectrometer Petr Hlubina, Dalibor Ciprian Department of Physics, Technical University Ostrava,
Birefringence dispersion in a quartz crystal retrieved from a channelled spectrum resolved by a fibre-optic spectrometer Petr Hlubina, Dalibor Ciprian Department of Physics, Technical University Ostrava,
Large Scale Direct Synthesis of Graphene on Sapphire and Transfer-free Device Fabrication
 Supplementary Information Large Scale Direct Synthesis of Graphene on Sapphire and Transfer-free Device Fabrication Hyun Jae Song a, Minhyeok Son a, Chibeom Park a, Hyunseob Lim a, Mark P. Levendorf b,
Supplementary Information Large Scale Direct Synthesis of Graphene on Sapphire and Transfer-free Device Fabrication Hyun Jae Song a, Minhyeok Son a, Chibeom Park a, Hyunseob Lim a, Mark P. Levendorf b,
Miniaturization of an Optical Parametric Oscillator with a Bow-Tie. Configuration for Broadening a Spectrum of Squeezed Light
 ISSN 2186-6570 Miniaturization of an Optical Parametric Oscillator with a Bow-Tie Configuration for Broadening a Spectrum of Squeezed Light Genta Masada Quantum ICT Research Institute, Tamagawa University
ISSN 2186-6570 Miniaturization of an Optical Parametric Oscillator with a Bow-Tie Configuration for Broadening a Spectrum of Squeezed Light Genta Masada Quantum ICT Research Institute, Tamagawa University
Three-Dimensional Silicon Photonic Crystals
 Three-Dimensional Silicon Photonic Crystals Shawn-Yu Lin'*, J. G. Fleming', D.L. Hetherington', B.K. Smith', W. Zubrzycki', R. Biswas2, M.M. Sigalas2, and K.M. Ho2. 'Sandia National Laboratories, P.O.
Three-Dimensional Silicon Photonic Crystals Shawn-Yu Lin'*, J. G. Fleming', D.L. Hetherington', B.K. Smith', W. Zubrzycki', R. Biswas2, M.M. Sigalas2, and K.M. Ho2. 'Sandia National Laboratories, P.O.
Fundamentals of nanoscience
 Fundamentals of nanoscience Spectroscopy of nano-objects Mika Pettersson 1. Non-spatially resolved spectroscopy Traditionally, in spectroscopy, one is interested in obtaining information on the energy
Fundamentals of nanoscience Spectroscopy of nano-objects Mika Pettersson 1. Non-spatially resolved spectroscopy Traditionally, in spectroscopy, one is interested in obtaining information on the energy
PROBLEM OF X-RAY SYNCHROTRON BEAM COLLIMATION BY ZONE PLATE
 PROBLEM OF X-RAY SYNCHROTRON BEAM COLLIMATION BY ZONE PLATE A. Kuyumchyan* a, V. Kohn b, A. Snigirev c, I. Snigireva c, M. Grigorev a, S. Kouznetsov a Institute of Microelectronics Technology, RAS, 443,
PROBLEM OF X-RAY SYNCHROTRON BEAM COLLIMATION BY ZONE PLATE A. Kuyumchyan* a, V. Kohn b, A. Snigirev c, I. Snigireva c, M. Grigorev a, S. Kouznetsov a Institute of Microelectronics Technology, RAS, 443,
Characterizing the Nova600 microfocus X-ray sourc for use with the Talbot interferometer for phase-contrast imaging
 Characterizing the Nova600 microfocus X-ray sourc for use with the Talbot interferometer for phase-contrast imaging Miriam Robinson Department of Physics, ewis & Clark College, Portland, Oregon, 97219
Characterizing the Nova600 microfocus X-ray sourc for use with the Talbot interferometer for phase-contrast imaging Miriam Robinson Department of Physics, ewis & Clark College, Portland, Oregon, 97219
PHY410 Optics Exam #3
 PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Spectra Power and Bandwidth of Fiber Bragg Grating Under Influence of Gradient Strain
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 4, 216: 333 338 Spectra Power and Bandwidth of Fiber Bragg Grating Under Influence of Gradient Strain Qinpeng LIU *, Xueguang QIAO, Zhen an JIA, and Haiwei FU Key Laboratory
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 4, 216: 333 338 Spectra Power and Bandwidth of Fiber Bragg Grating Under Influence of Gradient Strain Qinpeng LIU *, Xueguang QIAO, Zhen an JIA, and Haiwei FU Key Laboratory
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Inverted Planar Solar Cell with 13% Efficiency and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Inverted Planar Solar Cell with 13% Efficiency and
Lecture 23 Optical MEMS (5)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 2005) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 23 Optical MEMS (5) Agenda: Microlenses Diffractive Microgratings Example Devices Reference: S. Sinzinger and J. Jahns, Chapter 6
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 2005) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 23 Optical MEMS (5) Agenda: Microlenses Diffractive Microgratings Example Devices Reference: S. Sinzinger and J. Jahns, Chapter 6
The near-infrared spectra and distribution of excited states of electrodeless discharge rubidium vapour lamps
 The near-infrared spectra and distribution of excited states of electrodeless discharge rubidium vapour lamps Sun Qin-Qing( ) a)b), Miao Xin-Yu( ) a), Sheng Rong-Wu( ) c), and Chen Jing-Biao( ) a)b) a)
The near-infrared spectra and distribution of excited states of electrodeless discharge rubidium vapour lamps Sun Qin-Qing( ) a)b), Miao Xin-Yu( ) a), Sheng Rong-Wu( ) c), and Chen Jing-Biao( ) a)b) a)
Real-time control of the periodicity of a standing wave: an optical accordion
 Real-time control of the periodicity of a standing wave: an optical accordion T. C. Li, H. Kelkar, D. Medellin, and M. G. Raizen Center for Nonlinear Dynamics and Department of Physics, The University
Real-time control of the periodicity of a standing wave: an optical accordion T. C. Li, H. Kelkar, D. Medellin, and M. G. Raizen Center for Nonlinear Dynamics and Department of Physics, The University
Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.31 Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature Chang-Hua Liu 1, You-Chia Chang 2, Ted Norris 1.2* and Zhaohui
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.31 Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature Chang-Hua Liu 1, You-Chia Chang 2, Ted Norris 1.2* and Zhaohui
Thermodynamics Study on the Decay Properties of Reversed Domains in LiNbO 3. Single Crystals
 DOI: 1.4172/221-6212.1178 Thermodynamics Study on the Decay Properties of Reversed Domains in LiNbO Single rystals Li LB 1,2*, Li GL 1, Kan Y 2, Lu XM 2 and Zhu JS 2 1 School of Physics and Engineering,
DOI: 1.4172/221-6212.1178 Thermodynamics Study on the Decay Properties of Reversed Domains in LiNbO Single rystals Li LB 1,2*, Li GL 1, Kan Y 2, Lu XM 2 and Zhu JS 2 1 School of Physics and Engineering,
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in. Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca
 Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Modification and Machining on Back Surface of a Silicon Substrate by Femtosecond Laser Pulses at 1552 nm
 Modification and Machining on Back Surface of a Silicon Substrate by Femtosecond Laser Pulses at 1552 nm Yoshiro ITO*, Hiroki SAKASHITA, Ryosuke SUZUKI, Mitsuru UEWADA, Khanh Phu LUONG and Rie TANABE Department
Modification and Machining on Back Surface of a Silicon Substrate by Femtosecond Laser Pulses at 1552 nm Yoshiro ITO*, Hiroki SAKASHITA, Ryosuke SUZUKI, Mitsuru UEWADA, Khanh Phu LUONG and Rie TANABE Department
Mechanical characterization of single crystal BaTiO 3 film and insitu. XRD observation of microstructure change due to
 76 Chapter 4 Mechanical characterization of single crystal BaTiO 3 film and insitu XRD observation of microstructure change due to mechanical loading 4.1 Introduction Ferroelectric materials have many
76 Chapter 4 Mechanical characterization of single crystal BaTiO 3 film and insitu XRD observation of microstructure change due to mechanical loading 4.1 Introduction Ferroelectric materials have many
Efficiency analysis of diffractive lenses
 86 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 8, No. / January 00 Levy et al. Efficiency analysis of diffractive lenses Uriel Levy, David Mendlovic, and Emanuel Marom Faculty of Engineering, Tel-Aviv University, 69978 Tel-Aviv,
86 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 8, No. / January 00 Levy et al. Efficiency analysis of diffractive lenses Uriel Levy, David Mendlovic, and Emanuel Marom Faculty of Engineering, Tel-Aviv University, 69978 Tel-Aviv,
Supplementary information: Photonic Crystal Microchip Laser
 Supplementary information: Photonic Crystal Microchip Laser Darius Gailevicius* 1, Volodymyr Koliadenko 2, Vytautas Purlys 1, Martynas Peckus 1, Victor Taranenko 2, and Kestutis Staliunas 3,4 1 Laser Research
Supplementary information: Photonic Crystal Microchip Laser Darius Gailevicius* 1, Volodymyr Koliadenko 2, Vytautas Purlys 1, Martynas Peckus 1, Victor Taranenko 2, and Kestutis Staliunas 3,4 1 Laser Research
Polarization anisotropic transmission through metallic Sierpinski-Carpet aperture array
 Polarization anisotropic transmission through metallic Sierpinski-Carpet aperture array Yuan Chen, Li Zhan, * Jian Wu, and Tianmeng Wang Department of Physics, Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry
Polarization anisotropic transmission through metallic Sierpinski-Carpet aperture array Yuan Chen, Li Zhan, * Jian Wu, and Tianmeng Wang Department of Physics, Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry
X-Ray Radiation Channeling through Micro-Channel Plates: spectroscopy with a Synchrotron Radiation Beam
 X-Ray Radiation Channeling through Micro-Channel Plates: spectroscopy with a Synchrotron Radiation Beam M.I. Mazuritskiy a, S.B. Dabagov b,c, A. Marcelli b, K. Dziedzic-Kocurek d and A.M. Lerer a a Southern
X-Ray Radiation Channeling through Micro-Channel Plates: spectroscopy with a Synchrotron Radiation Beam M.I. Mazuritskiy a, S.B. Dabagov b,c, A. Marcelli b, K. Dziedzic-Kocurek d and A.M. Lerer a a Southern
