More about the Perceptron
|
|
|
- Elisabeth McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III
2 Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive from negative examples y = sign(w T x + b) Perceptron training Finds such a hyperplane Online & error-driven
3 Recap: Perceptron updates Update for a misclassified positive example:
4 Recap: Perceptron updates Update for a misclassified negative example:
5 Today Example of perceptron + averaged perceptron training Perceptron convergence proof Fundamental Machine Learning Concepts Linear separability and margin of a data set
6 Standard Perceptron: predict based on final parameters
7 Averaged Perceptron: predict based on average of intermediate parameters
8 Convergence of Perceptron The perceptron has converged if it can classify every training example correctly i.e. if it has found a hyperplane that correctly separates positive and negative examples Under which conditions does the perceptron converge and how long does it take?
9 Convergence of Perceptron Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, Then perceptron training converges after R2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x). γ 2
10 Margin of a data set D Distance between the hyperplane (w,b) and the nearest point in D Largest attainable margin on D
11 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
12 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
13 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
14 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
15 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
16 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
17 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x).
18 Theorem (Block & Novikoff, 1962) If the training data D = { x 1, y 1,, x N, y N } is linearly separable with margin γ by a unit norm hyperplane w ( w = 1 with b = 0, then perceptron training converges after R2 γ2 errors during training (assuming ( x < R for all x). What does this mean? Perceptron converges quickly when the margin is large, slowly when it is small Bound doesn t depend on the number of examples N, nor on their dimension d! Important note: proof guarantees that perceptron converges, but it doesn t necessarily converge to the max margin separator!!
19 What you should know Perceptron training and prediction algorithms (standard, voting, averaged) Convergence theorem and what practical guarantees it gives us Draw/describe the decision boundary of a perceptron classifier Fundamental ML concepts: Determine whether a data set is linearly separable, and define its margin Determine whether a training algorithm is error-driven or not, online or not
Perceptron. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. 3 February February 2015
 Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
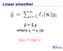 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear Classifiers: predictions Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear Classifiers: predictions Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next
The Perceptron Algorithm
 The Perceptron Algorithm Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Outline The Perceptron Algorithm Perceptron Mistake Bound Variants of Perceptron 2 Where are we? The Perceptron
The Perceptron Algorithm Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Outline The Perceptron Algorithm Perceptron Mistake Bound Variants of Perceptron 2 Where are we? The Perceptron
CSE 151 Machine Learning. Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri
 CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression
 Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
Binary Classification / Perceptron
 Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
MIRA, SVM, k-nn. Lirong Xia
 MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt.
 1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab.
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Lecture 4: Linear predictors and the Perceptron
 Lecture 4: Linear predictors and the Perceptron Introduction to Learning and Analysis of Big Data Kontorovich and Sabato (BGU) Lecture 4 1 / 34 Inductive Bias Inductive bias is critical to prevent overfitting.
Lecture 4: Linear predictors and the Perceptron Introduction to Learning and Analysis of Big Data Kontorovich and Sabato (BGU) Lecture 4 1 / 34 Inductive Bias Inductive bias is critical to prevent overfitting.
ML in Practice: CMSC 422 Slides adapted from Prof. CARPUAT and Prof. Roth
 ML in Practice: CMSC 422 Slides adapted from Prof. CARPUAT and Prof. Roth N-fold cross validation Instead of a single test-training split: train test Split data into N equal-sized parts Train and test
ML in Practice: CMSC 422 Slides adapted from Prof. CARPUAT and Prof. Roth N-fold cross validation Instead of a single test-training split: train test Split data into N equal-sized parts Train and test
Linear Classifiers. Michael Collins. January 18, 2012
 Linear Classifiers Michael Collins January 18, 2012 Today s Lecture Binary classification problems Linear classifiers The perceptron algorithm Classification Problems: An Example Goal: build a system that
Linear Classifiers Michael Collins January 18, 2012 Today s Lecture Binary classification problems Linear classifiers The perceptron algorithm Classification Problems: An Example Goal: build a system that
COMP 652: Machine Learning. Lecture 12. COMP Lecture 12 1 / 37
 COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM
 Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM Corso di AA, anno 2018/19, Padova Fabio Aiolli 19/26 Novembre 2018 Fabio Aiolli Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM 19/26 Novembre 2018 1 / 36 Outline Linear methods
Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM Corso di AA, anno 2018/19, Padova Fabio Aiolli 19/26 Novembre 2018 Fabio Aiolli Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM 19/26 Novembre 2018 1 / 36 Outline Linear methods
Perceptron (Theory) + Linear Regression
 10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
Multi-class SVMs. Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University
 Multi-class SVMs Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University Administrative We will have a make-up lecture on Saturday April 23, 2016. Project progress reports are due April 21, 2016 2 days
Multi-class SVMs Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University Administrative We will have a make-up lecture on Saturday April 23, 2016. Project progress reports are due April 21, 2016 2 days
A Course in Machine Learning
 A Course in Machine Learning Hal Daumé III 3 THE PERCEPTRON Learning Objectives: Describe the biological motivation behind the perceptron. Classify learning algorithms based on whether they are error-driven
A Course in Machine Learning Hal Daumé III 3 THE PERCEPTRON Learning Objectives: Describe the biological motivation behind the perceptron. Classify learning algorithms based on whether they are error-driven
Neural networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 MARINE CARPUAT. Slides credit: Graham Neubig
 Neural networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Slides credit: Graham Neubig Outline Perceptron: recap and limitations Neural networks Multi-layer perceptron Forward propagation
Neural networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Slides credit: Graham Neubig Outline Perceptron: recap and limitations Neural networks Multi-layer perceptron Forward propagation
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm
 CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Logistic Regression & Neural Networks
 Logistic Regression & Neural Networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Graham Neubig, Jacob Eisenstein Logistic Regression Perceptron & Probabilities What if we want a probability
Logistic Regression & Neural Networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Graham Neubig, Jacob Eisenstein Logistic Regression Perceptron & Probabilities What if we want a probability
The Perceptron Algorithm
 The Perceptron Algorithm Greg Grudic Greg Grudic Machine Learning Questions? Greg Grudic Machine Learning 2 Binary Classification A binary classifier is a mapping from a set of d inputs to a single output
The Perceptron Algorithm Greg Grudic Greg Grudic Machine Learning Questions? Greg Grudic Machine Learning 2 Binary Classification A binary classifier is a mapping from a set of d inputs to a single output
Training the linear classifier
 215, Training the linear classifier A natural way to train the classifier is to minimize the number of classification errors on the training data, i.e. choosing w so that the training error is minimized.
215, Training the linear classifier A natural way to train the classifier is to minimize the number of classification errors on the training data, i.e. choosing w so that the training error is minimized.
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning. Nakul Verma
 COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Support Vector Machines. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost 2 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost Produce
Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost 2 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost Produce
The Perceptron Algorithm 1
 CS 64: Machine Learning Spring 5 College of Computer and Information Science Northeastern University Lecture 5 March, 6 Instructor: Bilal Ahmed Scribe: Bilal Ahmed & Virgil Pavlu Introduction The Perceptron
CS 64: Machine Learning Spring 5 College of Computer and Information Science Northeastern University Lecture 5 March, 6 Instructor: Bilal Ahmed Scribe: Bilal Ahmed & Virgil Pavlu Introduction The Perceptron
Inf2b Learning and Data
 Inf2b Learning and Data Lecture : Single layer Neural Networks () (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murray and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR) School of Informatics University
Inf2b Learning and Data Lecture : Single layer Neural Networks () (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murray and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR) School of Informatics University
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F10 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers
 Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Reading: Ben-Hur & Weston, A User s Guide to Support Vector Machines (linked from class web page) Notation Assume a binary classification problem. Instances are represented by vector
Support Vector Machines Reading: Ben-Hur & Weston, A User s Guide to Support Vector Machines (linked from class web page) Notation Assume a binary classification problem. Instances are represented by vector
The Perceptron algorithm
 The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
Logistic Regression Logistic
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Machine Learning : Support Vector Machines
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines 05/01/2014 Machine Learning : Support Vector Machines Linear Classifiers (recap) A building block for almost all a mapping, a partitioning of the input space into
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines 05/01/2014 Machine Learning : Support Vector Machines Linear Classifiers (recap) A building block for almost all a mapping, a partitioning of the input space into
AN INTRODUCTION TO NEURAL NETWORKS. Scott Kuindersma November 12, 2009
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NEURAL NETWORKS Scott Kuindersma November 12, 2009 SUPERVISED LEARNING We are given some training data: We must learn a function If y is discrete, we call it classification If it is
AN INTRODUCTION TO NEURAL NETWORKS Scott Kuindersma November 12, 2009 SUPERVISED LEARNING We are given some training data: We must learn a function If y is discrete, we call it classification If it is
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Single layer NN. Neuron Model
 Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression. 1 Linearly Separable Data: Hard Margin SVMs
 E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
Linear Discrimination Functions
 Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Chapter 2 Single Layer Feedforward Networks
 Chapter 2 Single Layer Feedforward Networks By Rosenblatt (1962) Perceptrons For modeling visual perception (retina) A feedforward network of three layers of units: Sensory, Association, and Response Learning
Chapter 2 Single Layer Feedforward Networks By Rosenblatt (1962) Perceptrons For modeling visual perception (retina) A feedforward network of three layers of units: Sensory, Association, and Response Learning
Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions
 CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron
 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron
 Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Andrey Kan Copyright: University of Melbourne This lecture Notes on linear algebra Vectors
Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Andrey Kan Copyright: University of Melbourne This lecture Notes on linear algebra Vectors
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017
 COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University FEATURE EXPANSIONS FEATURE EXPANSIONS
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University FEATURE EXPANSIONS FEATURE EXPANSIONS
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9
 Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan Boulder 1 of 39 Recap Supervised learning Previously: KNN, naïve
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan Boulder 1 of 39 Recap Supervised learning Previously: KNN, naïve
6.867 Machine learning
 6.867 Machine learning Mid-term eam October 8, 6 ( points) Your name and MIT ID: .5.5 y.5 y.5 a).5.5 b).5.5.5.5 y.5 y.5 c).5.5 d).5.5 Figure : Plots of linear regression results with different types of
6.867 Machine learning Mid-term eam October 8, 6 ( points) Your name and MIT ID: .5.5 y.5 y.5 a).5.5 b).5.5.5.5 y.5 y.5 c).5.5 d).5.5 Figure : Plots of linear regression results with different types of
Machine Learning Linear Models
 Machine Learning Linear Models Outline II - Linear Models 1. Linear Regression (a) Linear regression: History (b) Linear regression with Least Squares (c) Matrix representation and Normal Equation Method
Machine Learning Linear Models Outline II - Linear Models 1. Linear Regression (a) Linear regression: History (b) Linear regression with Least Squares (c) Matrix representation and Normal Equation Method
Name (NetID): (1 Point)
 CS446: Machine Learning Fall 2016 October 25 th, 2016 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains four
CS446: Machine Learning Fall 2016 October 25 th, 2016 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains four
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 7 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Jordan Boyd-Graber Boulder Support Vector Machines 1 of
Support Vector Machines Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 7 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Jordan Boyd-Graber Boulder Support Vector Machines 1 of
Support Vector Machine
 Support Vector Machine Kernel: Kernel is defined as a function returning the inner product between the images of the two arguments k(x 1, x 2 ) = ϕ(x 1 ), ϕ(x 2 ) k(x 1, x 2 ) = k(x 2, x 1 ) modularity-
Support Vector Machine Kernel: Kernel is defined as a function returning the inner product between the images of the two arguments k(x 1, x 2 ) = ϕ(x 1 ), ϕ(x 2 ) k(x 1, x 2 ) = k(x 2, x 1 ) modularity-
10/05/2016. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Kernels. Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. October 28, Carlos Guestrin
 Kernels Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 28, 2013 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2013 1 Linear Separability: More formally, Using Margin Data linearly separable, if there
Kernels Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 28, 2013 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2013 1 Linear Separability: More formally, Using Margin Data linearly separable, if there
Vote. Vote on timing for night section: Option 1 (what we have now) Option 2. Lecture, 6:10-7:50 25 minute dinner break Tutorial, 8:15-9
 Vote Vote on timing for night section: Option 1 (what we have now) Lecture, 6:10-7:50 25 minute dinner break Tutorial, 8:15-9 Option 2 Lecture, 6:10-7 10 minute break Lecture, 7:10-8 10 minute break Tutorial,
Vote Vote on timing for night section: Option 1 (what we have now) Lecture, 6:10-7:50 25 minute dinner break Tutorial, 8:15-9 Option 2 Lecture, 6:10-7 10 minute break Lecture, 7:10-8 10 minute break Tutorial,
Part of the slides are adapted from Ziko Kolter
 Part of the slides are adapted from Ziko Kolter OUTLINE 1 Supervised learning: classification........................................................ 2 2 Non-linear regression/classification, overfitting,
Part of the slides are adapted from Ziko Kolter OUTLINE 1 Supervised learning: classification........................................................ 2 2 Non-linear regression/classification, overfitting,
Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155. Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent
 Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155 Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent Announcements Homework 1 is out Due Tuesday Jan 12 th at 2pm Via Moodle Sign up for Moodle & Piazza if you haven
Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155 Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent Announcements Homework 1 is out Due Tuesday Jan 12 th at 2pm Via Moodle Sign up for Moodle & Piazza if you haven
Warm up. Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not instructors.
 Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Perceptron. by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab POSTECH. Table of Contents
 Perceptron by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I.. Supervised Learning II.. Classification III. 3. Perceptron I. 3.. Linear Classifier II. 3..
Perceptron by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I.. Supervised Learning II.. Classification III. 3. Perceptron I. 3.. Linear Classifier II. 3..
4 THE PERCEPTRON. 4.1 Bio-inspired Learning. Learning Objectives:
 4 THE PERCEPTRON Algebra is nothing more than geometry, in words; geometry is nothing more than algebra, in pictures. Sophie Germain Learning Objectives: Describe the biological motivation behind the perceptron.
4 THE PERCEPTRON Algebra is nothing more than geometry, in words; geometry is nothing more than algebra, in pictures. Sophie Germain Learning Objectives: Describe the biological motivation behind the perceptron.
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification
 Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
a b = a T b = a i b i (1) i=1 (Geometric definition) The dot product of two Euclidean vectors a and b is defined by a b = a b cos(θ a,b ) (2)
 This is my preperation notes for teaching in sections during the winter 2018 quarter for course CSE 446. Useful for myself to review the concepts as well. More Linear Algebra Definition 1.1 (Dot Product).
This is my preperation notes for teaching in sections during the winter 2018 quarter for course CSE 446. Useful for myself to review the concepts as well. More Linear Algebra Definition 1.1 (Dot Product).
The Perceptron. Volker Tresp Summer 2014
 The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2014 1 Introduction One of the first serious learning machines Most important elements in learning tasks Collection and preprocessing of training data Definition of a
The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2014 1 Introduction One of the first serious learning machines Most important elements in learning tasks Collection and preprocessing of training data Definition of a
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression
 CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 04, 207 Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may
CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 04, 207 Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may
Machine Learning A Geometric Approach
 Machine Learning A Geometric Approach Linear Classification: Perceptron Professor Liang Huang some slides from Alex Smola (CMU) Perceptron Frank Rosenblatt deep learning multilayer perceptron linear regression
Machine Learning A Geometric Approach Linear Classification: Perceptron Professor Liang Huang some slides from Alex Smola (CMU) Perceptron Frank Rosenblatt deep learning multilayer perceptron linear regression
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Neural Networks, Computation Graphs. CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat
 Neural Networks, Computation Graphs CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat Binary Classification with a Multi-layer Perceptron φ A = 1 φ site = 1 φ located = 1 φ Maizuru = 1 φ, = 2 φ in = 1 φ Kyoto = 1 φ priest = 0 φ
Neural Networks, Computation Graphs CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat Binary Classification with a Multi-layer Perceptron φ A = 1 φ site = 1 φ located = 1 φ Maizuru = 1 φ, = 2 φ in = 1 φ Kyoto = 1 φ priest = 0 φ
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Preliminaries. Definition: The Euclidean dot product between two vectors is the expression. i=1
 90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
Linear Support Vector Machine. Classification. Linear SVM. Huiping Cao. Huiping Cao, Slide 1/26
 Huiping Cao, Slide 1/26 Classification Linear SVM Huiping Cao linear hyperplane (decision boundary) that will separate the data Huiping Cao, Slide 2/26 Support Vector Machines rt Vector Find a linear Machines
Huiping Cao, Slide 1/26 Classification Linear SVM Huiping Cao linear hyperplane (decision boundary) that will separate the data Huiping Cao, Slide 2/26 Support Vector Machines rt Vector Find a linear Machines
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771
 Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Classification, Linear Models, Naïve Bayes
 Classification, Linear Models, Naïve Bayes CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Dan Jurafsky & James Martin, Jacob Eisenstein Today Text classification problems and their evaluation Linear classifiers
Classification, Linear Models, Naïve Bayes CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Dan Jurafsky & James Martin, Jacob Eisenstein Today Text classification problems and their evaluation Linear classifiers
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning: Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Machine Learning: Jordan
Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning: Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Machine Learning: Jordan
Machine Learning. Linear Models. Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017
 Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers
 Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers / 6 Outline What Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers Do 2 Margin I 3 Loss and Regularized
Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers / 6 Outline What Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers Do 2 Margin I 3 Loss and Regularized
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
1 Learning Linear Separators
 10-601 Machine Learning Maria-Florina Balcan Spring 2015 Plan: Perceptron algorithm for learning linear separators. 1 Learning Linear Separators Here we can think of examples as being from {0, 1} n or
10-601 Machine Learning Maria-Florina Balcan Spring 2015 Plan: Perceptron algorithm for learning linear separators. 1 Learning Linear Separators Here we can think of examples as being from {0, 1} n or
L5 Support Vector Classification
 L5 Support Vector Classification Support Vector Machine Problem definition Geometrical picture Optimization problem Optimization Problem Hard margin Convexity Dual problem Soft margin problem Alexander
L5 Support Vector Classification Support Vector Machine Problem definition Geometrical picture Optimization problem Optimization Problem Hard margin Convexity Dual problem Soft margin problem Alexander
Brief Introduction to Machine Learning
 Brief Introduction to Machine Learning Yuh-Jye Lee Lab of Data Science and Machine Intelligence Dept. of Applied Math. at NCTU August 29, 2016 1 / 49 1 Introduction 2 Binary Classification 3 Support Vector
Brief Introduction to Machine Learning Yuh-Jye Lee Lab of Data Science and Machine Intelligence Dept. of Applied Math. at NCTU August 29, 2016 1 / 49 1 Introduction 2 Binary Classification 3 Support Vector
GRADIENT DESCENT AND LOCAL MINIMA
 GRADIENT DESCENT AND LOCAL MINIMA 25 20 5 15 10 3 2 1 1 2 5 2 2 4 5 5 10 Suppose for both functions above, gradient descent is started at the point marked red. It will walk downhill as far as possible,
GRADIENT DESCENT AND LOCAL MINIMA 25 20 5 15 10 3 2 1 1 2 5 2 2 4 5 5 10 Suppose for both functions above, gradient descent is started at the point marked red. It will walk downhill as far as possible,
COMP 875 Announcements
 Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Multiclass Classification-1
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
Introduction to Machine Learning
 1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
Learning Theory. Piyush Rai. CS5350/6350: Machine Learning. September 27, (CS5350/6350) Learning Theory September 27, / 14
 Learning Theory Piyush Rai CS5350/6350: Machine Learning September 27, 2011 (CS5350/6350) Learning Theory September 27, 2011 1 / 14 Why Learning Theory? We want to have theoretical guarantees about our
Learning Theory Piyush Rai CS5350/6350: Machine Learning September 27, 2011 (CS5350/6350) Learning Theory September 27, 2011 1 / 14 Why Learning Theory? We want to have theoretical guarantees about our
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
Online Passive- Aggressive Algorithms
 Online Passive- Aggressive Algorithms Jean-Baptiste Behuet 28/11/2007 Tutor: Eneldo Loza Mencía Seminar aus Maschinellem Lernen WS07/08 Overview Online algorithms Online Binary Classification Problem Perceptron
Online Passive- Aggressive Algorithms Jean-Baptiste Behuet 28/11/2007 Tutor: Eneldo Loza Mencía Seminar aus Maschinellem Lernen WS07/08 Overview Online algorithms Online Binary Classification Problem Perceptron
Linear models and the perceptron algorithm
 8/5/6 Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, 3 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression dx T x = i x i The dot product is also referred to as
8/5/6 Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, 3 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression dx T x = i x i The dot product is also referred to as
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision. 8C-L3 Support Vector Machines
 CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 8C-L3 Support Vector Machines Discriminative classifiers Discriminative classifiers find a division (surface) in feature space that separates the classes Several
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 8C-L3 Support Vector Machines Discriminative classifiers Discriminative classifiers find a division (surface) in feature space that separates the classes Several
TDT4173 Machine Learning
 TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 9 Learning Classifiers: Bagging & Boosting Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline
TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 9 Learning Classifiers: Bagging & Boosting Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
CS 446: Machine Learning Lecture 4, Part 2: On-Line Learning
 CS 446: Machine Learning Lecture 4, Part 2: On-Line Learning 0.1 Linear Functions So far, we have been looking at Linear Functions { as a class of functions which can 1 if W1 X separate some data and not
CS 446: Machine Learning Lecture 4, Part 2: On-Line Learning 0.1 Linear Functions So far, we have been looking at Linear Functions { as a class of functions which can 1 if W1 X separate some data and not
Linear Classification. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Linear Classification CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Example of Linear Classification Red points: patterns belonging
Linear Classification CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Example of Linear Classification Red points: patterns belonging
1 Machine Learning Concepts (16 points)
 CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
Support Vector and Kernel Methods
 SIGIR 2003 Tutorial Support Vector and Kernel Methods Thorsten Joachims Cornell University Computer Science Department tj@cs.cornell.edu http://www.joachims.org 0 Linear Classifiers Rules of the Form:
SIGIR 2003 Tutorial Support Vector and Kernel Methods Thorsten Joachims Cornell University Computer Science Department tj@cs.cornell.edu http://www.joachims.org 0 Linear Classifiers Rules of the Form:
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 28, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Today Two important concepts: Margins Kernels Large Margin Classification
Support Vector Machines INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 28, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Today Two important concepts: Margins Kernels Large Margin Classification
ESS2222. Lecture 4 Linear model
 ESS2222 Lecture 4 Linear model Hosein Shahnas University of Toronto, Department of Earth Sciences, 1 Outline Logistic Regression Predicting Continuous Target Variables Support Vector Machine (Some Details)
ESS2222 Lecture 4 Linear model Hosein Shahnas University of Toronto, Department of Earth Sciences, 1 Outline Logistic Regression Predicting Continuous Target Variables Support Vector Machine (Some Details)
