Markov Chains and Web Ranking: a Multilevel Adaptive Aggregation Method
|
|
|
- Silvia Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Markov Chains and Web Ranking: a Multilevel Adaptive Aggregation Method Hans De Sterck Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo Quoc Nguyen; Steve McCormick, John Ruge, Tom Manteuffel (Boulder, Colorado)
2 1. Simple Markov Chain Example 5 states each outgoing edge same probability (random walk on directed graph)
3 Simple Markov Chain Example start in one state with probability 1: what is the stationary probability vector after number of steps? stationary probability:
4 2. Problem Statement B is column-stochastic B is irreducible (every state can be reached from every other state in the directed graph) (no probability sinks!)
5 Problem Statement B is column-stochastic B is irreducible B is a-periodic largest eigenvalue of B:
6 3. Traditional, One-Level Iterative Methods Power Method Weighted Jacobi Method (WJAC) normalization:
7 Traditional, One-Level Iterative Methods Power Method convergence factor: convergence is very slow when WJAC: similar
8 4. Aggregation form three coarse, aggregated states (Simon and Ando, 1961)
9 Aggregation (Krieger, Horton,...)
10 5. Two-Level Acceleration by Aggregation Iterative Aggregation/Disaggregation Algorithm (IAD) (Takahashi 1975, Koury et al 1984, Schweitzer and Kindle 1986, Krieger 1990, Marek and Mayer 1998,...)
11 6. Relation with Multigrid for PDEs high-frequency error is removed by relaxation low-frequency-error needs to be removed by coarse-grid correction
12 multigrid hierarchy: V-cycle multigrid V-cycle: relax (=smooth) on various grids transfer error using restriction (P T ) and interpolation (P)
13 7. Multilevel Adaptive Aggregation (MAA) Method (Krieger, Horton 1994, but no satisfactory way to build P)
14 8. Choosing Aggregates Based on Strength error equation: use strength of connection in define row-based strength (determine all states that strongly influence a row s state) state that has largest value in x i is seed point for new aggregate, and all unassigned states influenced by it join its aggregate repeat (similar to Brandt, McCormick and Ruge, 1983)
15 9. Web Matrix Regularization web adjacency matrix G, then B=N(G) needs to be made irreducible, a-periodic need to add in extra links, with coupling factor α
16 Web Matrix Regularization PageRank (used by Google):
17 Web Matrix Regularization BackButton (add reverse of each link):
18 Web Matrix Regularization second eigenvalue for PageRank: 1-α (α=0.15 and α=0.01)
19 Web Matrix Regularization second eigenvalue for BackButton (α=0.15 and α =0.01):
20 Web Matrix Regularization second eigenvalue for BackButton: 1- λ 2 O(1/n)
21 10. Performance of MAA total efficiency factor of MAA relative to WJAC: : MAA 2 times more efficient than WJAC : MAA 2 times less efficient than WJAC
22 Performance of MAA for PageRank convergence factors for α=0.15
23 Performance of MAA for BackButton
24 11. Web Matrix Regularizations as a Function of Coupling Factor α PageRank
25 Web Matrix Regularizations as a Function of Coupling Factor α BackButton
26 12. Conclusions PageRank regularization of webgraph with α=0.15 seems to be a pretty good model for web ranking
27 Conclusions MAA cannot beat Power Method speed for PageRank reasons: o λ 2 =0.85, independent of n o there are global connections on all scales o Power Method scales perfectly (also in parallel) o = =0.04 still: o MAA provides information about how web pages are clustered, at all levels
28 Conclusions MAA can dramatically outperform Power Method for Markov Chains for which λ 2 (n) 1 for large n reason: o multilevel nature of MAA allows to bridge scales (Markov Chain has only local connections in this case)
29 Comparison: Strength-based Aggregation major differences with previously considered multilevel methods for Markov chains (Horton, Krieger,...): o we use AMG strength of connection based on scaled problem matrix o our aggregates based on columns of strength matrix (~ AMG coarsening) IAD methods o normally only 2-level o aggregates fixed, based on previously known, regular structure of Markov chain
30 Two-Level Acceleration by Aggregation multiplicative correction: error equation
31 Web Matrix Regularization BackLink (to root page):
32 Web Matrix Regularization second eigenvalue for BackLink (α=0.15 and α =0.01):
33 Performance of MAA
34 Web Matrix Regularizations as a Function of Coupling Factor α BackLink
35 Web Matrix Regularizations as a Function of Coupling Factor α BackLink
MULTILEVEL ADAPTIVE AGGREGATION FOR MARKOV CHAINS, WITH APPLICATION TO WEB RANKING
 MULTILEVEL ADAPTIVE AGGREGATION FOR MARKOV CHAINS, WITH APPLICATION TO WEB RANKING H. DE STERCK, THOMAS A. MANTEUFFEL, STEPHEN F. MCCORMICK, QUOC NGUYEN, AND JOHN RUGE Abstract. A multilevel adaptive aggregation
MULTILEVEL ADAPTIVE AGGREGATION FOR MARKOV CHAINS, WITH APPLICATION TO WEB RANKING H. DE STERCK, THOMAS A. MANTEUFFEL, STEPHEN F. MCCORMICK, QUOC NGUYEN, AND JOHN RUGE Abstract. A multilevel adaptive aggregation
c 2010 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J. SCI. COMPUT. Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 40 61 c 2010 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics SMOOTHED AGGREGATION MULTIGRID FOR MARKOV CHAINS H. DE STERCK, T. A. MANTEUFFEL, S. F. MCCORMICK, K.
SIAM J. SCI. COMPUT. Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 40 61 c 2010 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics SMOOTHED AGGREGATION MULTIGRID FOR MARKOV CHAINS H. DE STERCK, T. A. MANTEUFFEL, S. F. MCCORMICK, K.
Aggregation Algorithms for K-cycle Aggregation Multigrid for Markov Chains
 Aggregation Algorithms for K-cycle Aggregation Multigrid for Markov Chains by Manda Winlaw A research paper presented to the University of Waterloo in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Aggregation Algorithms for K-cycle Aggregation Multigrid for Markov Chains by Manda Winlaw A research paper presented to the University of Waterloo in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Solving PDEs with Multigrid Methods p.1
 Solving PDEs with Multigrid Methods Scott MacLachlan maclachl@colorado.edu Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Colorado at Boulder Solving PDEs with Multigrid Methods p.1 Support and Collaboration
Solving PDEs with Multigrid Methods Scott MacLachlan maclachl@colorado.edu Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Colorado at Boulder Solving PDEs with Multigrid Methods p.1 Support and Collaboration
Algebraic Multigrid Preconditioners for Computing Stationary Distributions of Markov Processes
 Algebraic Multigrid Preconditioners for Computing Stationary Distributions of Markov Processes Elena Virnik, TU BERLIN Algebraic Multigrid Preconditioners for Computing Stationary Distributions of Markov
Algebraic Multigrid Preconditioners for Computing Stationary Distributions of Markov Processes Elena Virnik, TU BERLIN Algebraic Multigrid Preconditioners for Computing Stationary Distributions of Markov
Updating PageRank. Amy Langville Carl Meyer
 Updating PageRank Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC SCCM 11/17/2003 Indexing Google Must index key terms on each page Robots crawl the web software
Updating PageRank Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC SCCM 11/17/2003 Indexing Google Must index key terms on each page Robots crawl the web software
Bootstrap AMG. Kailai Xu. July 12, Stanford University
 Bootstrap AMG Kailai Xu Stanford University July 12, 2017 AMG Components A general AMG algorithm consists of the following components. A hierarchy of levels. A smoother. A prolongation. A restriction.
Bootstrap AMG Kailai Xu Stanford University July 12, 2017 AMG Components A general AMG algorithm consists of the following components. A hierarchy of levels. A smoother. A prolongation. A restriction.
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
New Multigrid Solver Advances in TOPS
 New Multigrid Solver Advances in TOPS R D Falgout 1, J Brannick 2, M Brezina 2, T Manteuffel 2 and S McCormick 2 1 Center for Applied Scientific Computing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, P.O.
New Multigrid Solver Advances in TOPS R D Falgout 1, J Brannick 2, M Brezina 2, T Manteuffel 2 and S McCormick 2 1 Center for Applied Scientific Computing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, P.O.
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank
 Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills Cedya p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance
Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills Cedya p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
UpdatingtheStationary VectorofaMarkovChain. Amy Langville Carl Meyer
 UpdatingtheStationary VectorofaMarkovChain Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC NSMC 9/4/2003 Outline Updating and Pagerank Aggregation Partitioning
UpdatingtheStationary VectorofaMarkovChain Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC NSMC 9/4/2003 Outline Updating and Pagerank Aggregation Partitioning
Link Analysis. Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016
 Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix. Steve Kirkland University of Regina
 Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix Steve Kirkland University of Regina June 5, 2006 Motivation: Google s PageRank algorithm finds the stationary vector of a stochastic
Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix Steve Kirkland University of Regina June 5, 2006 Motivation: Google s PageRank algorithm finds the stationary vector of a stochastic
Spectral element agglomerate AMGe
 Spectral element agglomerate AMGe T. Chartier 1, R. Falgout 2, V. E. Henson 2, J. E. Jones 4, T. A. Manteuffel 3, S. F. McCormick 3, J. W. Ruge 3, and P. S. Vassilevski 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Davidson
Spectral element agglomerate AMGe T. Chartier 1, R. Falgout 2, V. E. Henson 2, J. E. Jones 4, T. A. Manteuffel 3, S. F. McCormick 3, J. W. Ruge 3, and P. S. Vassilevski 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Davidson
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
An Algebraic Multigrid Method for Eigenvalue Problems
 An Algebraic Multigrid Method for Eigenvalue Problems arxiv:1503.08462v1 [math.na] 29 Mar 2015 Xiaole Han, Yunhui He, Hehu Xie and Chunguang You Abstract An algebraic multigrid method is proposed to solve
An Algebraic Multigrid Method for Eigenvalue Problems arxiv:1503.08462v1 [math.na] 29 Mar 2015 Xiaole Han, Yunhui He, Hehu Xie and Chunguang You Abstract An algebraic multigrid method is proposed to solve
AN AGGREGATION MULTILEVEL METHOD USING SMOOTH ERROR VECTORS
 AN AGGREGATION MULTILEVEL METHOD USING SMOOTH ERROR VECTORS EDMOND CHOW Abstract. Many algebraic multilevel methods for solving linear systems assume that the slowto-converge, or algebraically smooth error
AN AGGREGATION MULTILEVEL METHOD USING SMOOTH ERROR VECTORS EDMOND CHOW Abstract. Many algebraic multilevel methods for solving linear systems assume that the slowto-converge, or algebraically smooth error
Aggregation-based Adaptive Algebraic Multigrid for Sparse Linear Systems. Eran Treister
 Aggregation-based Adaptive Algebraic Multigrid for Sparse Linear Systems Eran Treister Aggregation-based Adaptive Algebraic Multigrid for Sparse Linear Systems Research Thesis In Partial Fulfillment of
Aggregation-based Adaptive Algebraic Multigrid for Sparse Linear Systems Eran Treister Aggregation-based Adaptive Algebraic Multigrid for Sparse Linear Systems Research Thesis In Partial Fulfillment of
Multigrid Methods for Linear Systems with Stochastic Entries Arising in Lattice QCD. Andreas Frommer
 Methods for Linear Systems with Stochastic Entries Arising in Lattice QCD Andreas Frommer Collaborators The Dirac operator James Brannick, Penn State University Björn Leder, Humboldt Universität Berlin
Methods for Linear Systems with Stochastic Entries Arising in Lattice QCD Andreas Frommer Collaborators The Dirac operator James Brannick, Penn State University Björn Leder, Humboldt Universität Berlin
A Generalized Eigensolver Based on Smoothed Aggregation (GES-SA) for Initializing Smoothed Aggregation Multigrid (SA)
 NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA WITH APPLICATIONS Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 2007; 07: 6 [Version: 2002/09/8 v.02] A Generalized Eigensolver Based on Smoothed Aggregation (GES-SA) for Initializing Smoothed Aggregation
NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA WITH APPLICATIONS Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 2007; 07: 6 [Version: 2002/09/8 v.02] A Generalized Eigensolver Based on Smoothed Aggregation (GES-SA) for Initializing Smoothed Aggregation
1998: enter Link Analysis
 1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
1. Fast Iterative Solvers of SLE
 1. Fast Iterative Solvers of crucial drawback of solvers discussed so far: they become slower if we discretize more accurate! now: look for possible remedies relaxation: explicit application of the multigrid
1. Fast Iterative Solvers of crucial drawback of solvers discussed so far: they become slower if we discretize more accurate! now: look for possible remedies relaxation: explicit application of the multigrid
LINK ANALYSIS. Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS
 LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
Parallel-in-Time Optimization with the General-Purpose XBraid Package
 Parallel-in-Time Optimization with the General-Purpose XBraid Package Stefanie Günther, Jacob Schroder, Robert Falgout, Nicolas Gauger 7th Workshop on Parallel-in-Time methods Wednesday, May 3 rd, 2018
Parallel-in-Time Optimization with the General-Purpose XBraid Package Stefanie Günther, Jacob Schroder, Robert Falgout, Nicolas Gauger 7th Workshop on Parallel-in-Time methods Wednesday, May 3 rd, 2018
Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 n page v Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xiii xvii 1 Background in Linear Algebra 1 1.1 Matrices................................. 1 1.2 Square Matrices and Eigenvalues....................
n page v Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xiii xvii 1 Background in Linear Algebra 1 1.1 Matrices................................. 1 1.2 Square Matrices and Eigenvalues....................
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
Finding steady states of communicating Markov processes combining aggregation/disaggregation with tensor techniques
 Finding steady states of communicating Markov processes combining aggregation/disaggregation with tensor techniques Francisco Macedo 1,2 1 EPF Lausanne, SB-MATHICSE-ANCHP, Station 8, CH-1015 Lausanne,
Finding steady states of communicating Markov processes combining aggregation/disaggregation with tensor techniques Francisco Macedo 1,2 1 EPF Lausanne, SB-MATHICSE-ANCHP, Station 8, CH-1015 Lausanne,
Algebraic Multigrid as Solvers and as Preconditioner
 Ò Algebraic Multigrid as Solvers and as Preconditioner Domenico Lahaye domenico.lahaye@cs.kuleuven.ac.be http://www.cs.kuleuven.ac.be/ domenico/ Department of Computer Science Katholieke Universiteit Leuven
Ò Algebraic Multigrid as Solvers and as Preconditioner Domenico Lahaye domenico.lahaye@cs.kuleuven.ac.be http://www.cs.kuleuven.ac.be/ domenico/ Department of Computer Science Katholieke Universiteit Leuven
The Removal of Critical Slowing Down. Lattice College of William and Mary
 The Removal of Critical Slowing Down Lattice 2008 College of William and Mary Michael Clark Boston University James Brannick, Rich Brower, Tom Manteuffel, Steve McCormick, James Osborn, Claudio Rebbi 1
The Removal of Critical Slowing Down Lattice 2008 College of William and Mary Michael Clark Boston University James Brannick, Rich Brower, Tom Manteuffel, Steve McCormick, James Osborn, Claudio Rebbi 1
Math 304 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks.
 Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Adaptive Multigrid for QCD. Lattice University of Regensburg
 Lattice 2007 University of Regensburg Michael Clark Boston University with J. Brannick, R. Brower, J. Osborn and C. Rebbi -1- Lattice 2007, University of Regensburg Talk Outline Introduction to Multigrid
Lattice 2007 University of Regensburg Michael Clark Boston University with J. Brannick, R. Brower, J. Osborn and C. Rebbi -1- Lattice 2007, University of Regensburg Talk Outline Introduction to Multigrid
Analysis of Google s PageRank
 Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills AN05 p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web page [Brin & Page 1998]
Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills AN05 p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web page [Brin & Page 1998]
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
Link Mining PageRank. From Stanford C246
 Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
An Introduction to Algebraic Multigrid (AMG) Algorithms Derrick Cerwinsky and Craig C. Douglas 1/84
 An Introduction to Algebraic Multigrid (AMG) Algorithms Derrick Cerwinsky and Craig C. Douglas 1/84 Introduction Almost all numerical methods for solving PDEs will at some point be reduced to solving A
An Introduction to Algebraic Multigrid (AMG) Algorithms Derrick Cerwinsky and Craig C. Douglas 1/84 Introduction Almost all numerical methods for solving PDEs will at some point be reduced to solving A
CONVERGENCE ANALYSIS OF A PAGERANK UPDATING ALGORITHM BY LANGVILLE AND MEYER
 CONVERGENCE ANALYSIS OF A PAGERANK UPDATING ALGORITHM BY LANGVILLE AND MEYER ILSE C.F. IPSEN AND STEVE KIRKLAND Abstract. The PageRank updating algorithm proposed by Langville and Meyer is a special case
CONVERGENCE ANALYSIS OF A PAGERANK UPDATING ALGORITHM BY LANGVILLE AND MEYER ILSE C.F. IPSEN AND STEVE KIRKLAND Abstract. The PageRank updating algorithm proposed by Langville and Meyer is a special case
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
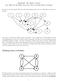 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Facebook Friends! and Matrix Functions
 Facebook Friends! and Matrix Functions! Graduate Research Day Joint with David F. Gleich, (Purdue), supported by" NSF CAREER 1149756-CCF Kyle Kloster! Purdue University! Network Analysis Use linear algebra
Facebook Friends! and Matrix Functions! Graduate Research Day Joint with David F. Gleich, (Purdue), supported by" NSF CAREER 1149756-CCF Kyle Kloster! Purdue University! Network Analysis Use linear algebra
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm
 Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
How works. or How linear algebra powers the search engine. M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University
 How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
Dynamic network sampling
 Dynamic network sampling Steve Thompson Simon Fraser University thompson@sfu.ca Graybill Conference Colorado State University June 10, 2013 Dynamic network sampling The population of interest has spatial
Dynamic network sampling Steve Thompson Simon Fraser University thompson@sfu.ca Graybill Conference Colorado State University June 10, 2013 Dynamic network sampling The population of interest has spatial
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Algebraic Representation of Networks
 Algebraic Representation of Networks 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Describing networks with matrices (1) Adjacency matrix A matrix with rows and columns labeled by
Algebraic Representation of Networks 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Describing networks with matrices (1) Adjacency matrix A matrix with rows and columns labeled by
Updating Markov Chains Carl Meyer Amy Langville
 Updating Markov Chains Carl Meyer Amy Langville Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC A. A. Markov Anniversary Meeting June 13, 2006 Intro Assumptions Very large irreducible
Updating Markov Chains Carl Meyer Amy Langville Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC A. A. Markov Anniversary Meeting June 13, 2006 Intro Assumptions Very large irreducible
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Today. Next lecture. (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models
 Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
The Second Eigenvalue of the Google Matrix
 The Second Eigenvalue of the Google Matrix Taher H. Haveliwala and Sepandar D. Kamvar Stanford University {taherh,sdkamvar}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We determine analytically the modulus of the second
The Second Eigenvalue of the Google Matrix Taher H. Haveliwala and Sepandar D. Kamvar Stanford University {taherh,sdkamvar}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We determine analytically the modulus of the second
MULTI-LEVEL TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOLUTION OF THE KINETIC EQUATIONS IN CONDENSING FLOWS SIMON GLAZENBORG
 MULTI-LEVEL TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOLUTION OF THE KINETIC EQUATIONS IN CONDENSING FLOWS SIMON GLAZENBORG CONTENTS Introduction Theory Test case: Nucleation pulse Conclusions & recommendations 2 WHAT IS CONDENSATION
MULTI-LEVEL TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOLUTION OF THE KINETIC EQUATIONS IN CONDENSING FLOWS SIMON GLAZENBORG CONTENTS Introduction Theory Test case: Nucleation pulse Conclusions & recommendations 2 WHAT IS CONDENSATION
Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
Aspects of Multigrid
 Aspects of Multigrid Kees Oosterlee 1,2 1 Delft University of Technology, Delft. 2 CWI, Center for Mathematics and Computer Science, Amsterdam, SIAM Chapter Workshop Day, May 30th 2018 C.W.Oosterlee (CWI)
Aspects of Multigrid Kees Oosterlee 1,2 1 Delft University of Technology, Delft. 2 CWI, Center for Mathematics and Computer Science, Amsterdam, SIAM Chapter Workshop Day, May 30th 2018 C.W.Oosterlee (CWI)
Iterative Methods and Multigrid
 Iterative Methods and Multigrid Part 1: Introduction to Multigrid 1 12/02/09 MG02.prz Error Smoothing 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Initial Solution=-Error 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 DCT:
Iterative Methods and Multigrid Part 1: Introduction to Multigrid 1 12/02/09 MG02.prz Error Smoothing 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Initial Solution=-Error 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 DCT:
ADAPTIVE ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID
 ADAPTIVE ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID M. BREZINA, R. FALGOUT, S. MACLACHLAN, T. MANTEUFFEL, S. MCCORMICK, AND J. RUGE Abstract. Efficient numerical simulation of physical processes is constrained by our ability
ADAPTIVE ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID M. BREZINA, R. FALGOUT, S. MACLACHLAN, T. MANTEUFFEL, S. MCCORMICK, AND J. RUGE Abstract. Efficient numerical simulation of physical processes is constrained by our ability
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Multigrid (MG) methods are used to approximate solutions to elliptic partial differential
 Title: Multigrid Methods Name: Luke Olson 1 Affil./Addr.: Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 61801 email: lukeo@illinois.edu url: http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/homes/lukeo/
Title: Multigrid Methods Name: Luke Olson 1 Affil./Addr.: Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 61801 email: lukeo@illinois.edu url: http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/homes/lukeo/
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2019 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2019 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2018 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2018 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y
 Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
MATH36001 Perron Frobenius Theory 2015
 MATH361 Perron Frobenius Theory 215 In addition to saying something useful, the Perron Frobenius theory is elegant. It is a testament to the fact that beautiful mathematics eventually tends to be useful,
MATH361 Perron Frobenius Theory 215 In addition to saying something useful, the Perron Frobenius theory is elegant. It is a testament to the fact that beautiful mathematics eventually tends to be useful,
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University.
 Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
IMPLEMENTATION OF A PARALLEL AMG SOLVER
 IMPLEMENTATION OF A PARALLEL AMG SOLVER Tony Saad May 2005 http://tsaad.utsi.edu - tsaad@utsi.edu PLAN INTRODUCTION 2 min. MULTIGRID METHODS.. 3 min. PARALLEL IMPLEMENTATION PARTITIONING. 1 min. RENUMBERING...
IMPLEMENTATION OF A PARALLEL AMG SOLVER Tony Saad May 2005 http://tsaad.utsi.edu - tsaad@utsi.edu PLAN INTRODUCTION 2 min. MULTIGRID METHODS.. 3 min. PARALLEL IMPLEMENTATION PARTITIONING. 1 min. RENUMBERING...
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation
 Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS
 LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS Markov Process and Markov Chains Hidden Markov Models Kalman Filters Types of dynamic systems Problem of future state prediction Predictability Observability Easily
LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS Markov Process and Markov Chains Hidden Markov Models Kalman Filters Types of dynamic systems Problem of future state prediction Predictability Observability Easily
Using an Auction Algorithm in AMG based on Maximum Weighted Matching in Matrix Graphs
 Using an Auction Algorithm in AMG based on Maximum Weighted Matching in Matrix Graphs Pasqua D Ambra Institute for Applied Computing (IAC) National Research Council of Italy (CNR) pasqua.dambra@cnr.it
Using an Auction Algorithm in AMG based on Maximum Weighted Matching in Matrix Graphs Pasqua D Ambra Institute for Applied Computing (IAC) National Research Council of Italy (CNR) pasqua.dambra@cnr.it
Slides based on those in:
 Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
(bu) = f in Ω, (1.1) u = g on Γ I, (1.2)
 A DUAL LEAST-SQUARES FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR LINEAR HYPERBOLIC PDES: A NUMERICAL STUDY LUKE OLSON Abstract. In this paper, we develop a least-squares finite element method for linear Partial Differential
A DUAL LEAST-SQUARES FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR LINEAR HYPERBOLIC PDES: A NUMERICAL STUDY LUKE OLSON Abstract. In this paper, we develop a least-squares finite element method for linear Partial Differential
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University.
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks
 Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks David Bindel Department of Computer Science Cornell University 26 Sep 2011 20 21 19 16 22 28 17 18 29 26 27 30 23 1 25 5 8 24 2 4 14 3 9 13 15 11 10 12
Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks David Bindel Department of Computer Science Cornell University 26 Sep 2011 20 21 19 16 22 28 17 18 29 26 27 30 23 1 25 5 8 24 2 4 14 3 9 13 15 11 10 12
An Introduction of Multigrid Methods for Large-Scale Computation
 An Introduction of Multigrid Methods for Large-Scale Computation Chin-Tien Wu National Center for Theoretical Sciences National Tsing-Hua University 01/4/005 How Large the Real Simulations Are? Large-scale
An Introduction of Multigrid Methods for Large-Scale Computation Chin-Tien Wu National Center for Theoretical Sciences National Tsing-Hua University 01/4/005 How Large the Real Simulations Are? Large-scale
Multigrid Solvers in Space and Time for Highly Concurrent Architectures
 Multigrid Solvers in Space and Time for Highly Concurrent Architectures Future CFD Technologies Workshop, Kissimmee, Florida January 6-7, 2018 Robert D. Falgout Center for Applied Scientific Computing
Multigrid Solvers in Space and Time for Highly Concurrent Architectures Future CFD Technologies Workshop, Kissimmee, Florida January 6-7, 2018 Robert D. Falgout Center for Applied Scientific Computing
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications
 Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and Applications p. 1/36 Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications Che-Rung Lee cherung@gmail.com National Tsing Hua University Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and
Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and Applications p. 1/36 Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications Che-Rung Lee cherung@gmail.com National Tsing Hua University Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and
Stabilization and Acceleration of Algebraic Multigrid Method
 Stabilization and Acceleration of Algebraic Multigrid Method Recursive Projection Algorithm A. Jemcov J.P. Maruszewski Fluent Inc. October 24, 2006 Outline 1 Need for Algorithm Stabilization and Acceleration
Stabilization and Acceleration of Algebraic Multigrid Method Recursive Projection Algorithm A. Jemcov J.P. Maruszewski Fluent Inc. October 24, 2006 Outline 1 Need for Algorithm Stabilization and Acceleration
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method
 eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Lecture 15: MCMC Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan. COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016
 Lecture 15: MCMC Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016 Course progress Learning from examples Definition + fundamental theorem of statistical learning,
Lecture 15: MCMC Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016 Course progress Learning from examples Definition + fundamental theorem of statistical learning,
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4)
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
for an m-state homogeneous irreducible Markov chain with transition probability matrix
 UPDATING MARKOV CHAINS AMY N LANGVILLE AND CARL D MEYER 1 Introduction Suppose that the stationary distribution vector φ T =(φ 1,φ 2,,φ m ) for an m-state homogeneous irreducible Markov chain with transition
UPDATING MARKOV CHAINS AMY N LANGVILLE AND CARL D MEYER 1 Introduction Suppose that the stationary distribution vector φ T =(φ 1,φ 2,,φ m ) for an m-state homogeneous irreducible Markov chain with transition
A theorethic treatment of the Partitioned Iterative Convergence methods
 A theorethic treatment of the Partitioned Iterative Convergence methods 1 Introduction Implementing an iterative algorithm in PIC can greatly reduce the run-time of the computation. In our experiments
A theorethic treatment of the Partitioned Iterative Convergence methods 1 Introduction Implementing an iterative algorithm in PIC can greatly reduce the run-time of the computation. In our experiments
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
VCMC: Variational Consensus Monte Carlo
 VCMC: Variational Consensus Monte Carlo Maxim Rabinovich, Elaine Angelino, Michael I. Jordan Berkeley Vision and Learning Center September 22, 2015 probabilistic models! sky fog bridge water grass object
VCMC: Variational Consensus Monte Carlo Maxim Rabinovich, Elaine Angelino, Michael I. Jordan Berkeley Vision and Learning Center September 22, 2015 probabilistic models! sky fog bridge water grass object
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
How does Google rank webpages?
 Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
OPERATOR-BASED INTERPOLATION FOR BOOTSTRAP ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID
 OPERATOR-BASED INTERPOLATION FOR BOOTSTRAP ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID T. MANTEUFFEL, S. MCCORMICK, M. PARK, AND J. RUGE Abstract. Bootstrap Algebraic Multigrid (BAMG) is a multigrid-based solver for matrix equations
OPERATOR-BASED INTERPOLATION FOR BOOTSTRAP ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID T. MANTEUFFEL, S. MCCORMICK, M. PARK, AND J. RUGE Abstract. Bootstrap Algebraic Multigrid (BAMG) is a multigrid-based solver for matrix equations
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Probability & Computing
 Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
