Conveyance Estimation System (CES) Launch
|
|
|
- Berenice Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (CES) Launch Conveyance Principles Caroline McGahey 10 June 2004
2 Why is there a new approach? Existing 1D software still based on historic hand-calculation methods - not based in rigorous physics - as SCM poor predictions for overbank flow - as DCM ignores lateral shearing - all physical processes lumped into one catch-all parameter - Manning n
3 Why is there a new approach? Research advances over past 20 years understanding flow mechanisms quantifying associated energy losses Quality data sets from: - experimental set-ups e.g. FCF - purpose-made river measurements - large scale rivers - EA gauging sites Advent of computing power enabled coding & testing of methods against extensive database
4 Energy transfer mechanisms 2. Momentum Transfer 2. Shear layer Direction of flow 1. Boundary shear stresses 3. Secondary flows
5 Meandering mechanisms
6 Observed flow features Ikeda et al 2001 Shiono & Muto 1998 Sellin 1964 Shiono & Muto 1998 Ikeda et al 2001
7 Meandering velocity profiles U d AA A A AA BB B B C BB C CC Distance across section
8 Conveyance calculation Depth integration of Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes equations dy Integrate unit flow rate q (m 2 /s) Q = qdy 2 K = Q / S f 1
9 Conveyance calculation ghs o β f q 2 8H 2 + y λ H f q y q H = α Γ+ (1 α) y C uvq H 2 I II III IV V I II III IV V hydrostatic pressure boundary friction turbulence due to lateral shear straight secondary flow losses meandering secondary flow losses
10 Calibration coefficients Terms to cover all energy losses - coefficients for: - skin friction f based on RA unit roughness n l - lateral shearing - dimensionless eddy viscosity λ - straight secondary flow losses Γ - meandering secondary flow losses C uv Form loss is not accounted for
11 Calibration parameters f - complete Colebrook-White equation 1 k s 3.09ν = 2.03log + f 12.27H 4q f λ function of relative depth λ ( ) = λ mc Dr
12 Secondary flow model Γ = khρ gs o straight C uv = f ( σ, Dr ) Secondary flow term straight transitional fully meandering Key: C uv Γ total Relative depth Sinuosity
13 Typical distributions f λ Γ C uv Colebrook-White λ = f (λ mc, D r ) Γ fp (-ve) Γ mc (+ve) Γ fp (-ve) Varies with σ, D r Top of bank
14 CES Outputs Cross-section: total flow Q area A conveyance K ave velocity U Re number Fr number α, β Across section: unit flow q unit conveyance k depth-ave U d bed shear stress τ shear velocity U * Fr number f,n l with depth
15 FCF Straight: Large Scale Bed level (m) Depth = 0.249m Lateral distance across channel (m) Bed shear stress (N/m 2 ) Lateral distance across channel (m) Depth-averaged velocity (m/s) Lateral distance cross channel (m)
16 River Blackwater Model Sinuosity = Bed level (m) Lateral distance across channel (m) Depth-averaged velocity (m/s) Lateral distance across channel (m)
17 River Severn, Shrewsbury 1.2 Sinuosity = Depth-averaged velocity (m/s) Elevation (m) Lateral distance across channel (m)
18 Comparison to isis method 0.16 isis 0.14 CES prediction data Stage (m) Glasgow Flume Discharge (m 3 /s)
19 Comparison to isis method River 7.8 Severn at Montford Bridge isis CES Prediction 7.2 data Stage (m) Discharge (m 3 /s) Bed level (m) Lateral distance across channel (m)
20 CES stage-discharge River 2 Main CES central estimate Measured data Credible upper / lower bands Stage m Bed elevation (m) Lateral distance across channel - offset (m) Discharge m 3 /s
This is a repository copy of An analytical model for lateral depth-averaged velocity distributions along a meander in curved compound channels.
 This is a repository copy of An analytical model for lateral depth-averaged velocity distributions along a meander in curved compound channels. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/80340/
This is a repository copy of An analytical model for lateral depth-averaged velocity distributions along a meander in curved compound channels. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/80340/
Discharge estimation in compound channels with fixed and mobile bed
 Sādhanā Vol. 34, Part 6, December 2009, pp. 923 945. Indian Academy of Sciences Discharge estimation in compound channels with fixed and mobile bed GALIP SECKIN 1, MUSTAFA MAMAK 1, SERTER ATABAY 2 and
Sādhanā Vol. 34, Part 6, December 2009, pp. 923 945. Indian Academy of Sciences Discharge estimation in compound channels with fixed and mobile bed GALIP SECKIN 1, MUSTAFA MAMAK 1, SERTER ATABAY 2 and
Stage Discharge Prediction in a Prismatic Compound Channel
 International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 227-232 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Stage Discharge Prediction
International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 227-232 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Stage Discharge Prediction
Accounting for increased flow resistance due to lateral momentum loss in restoration designs using 2-stage channels
 Skamania 2005 Accounting for increased flow resistance due to lateral momentum loss in restoration designs using 2-stage channels Outline Aim and Objectives Definition Use of 2-stage channels in stream
Skamania 2005 Accounting for increased flow resistance due to lateral momentum loss in restoration designs using 2-stage channels Outline Aim and Objectives Definition Use of 2-stage channels in stream
EQUATIONS FOR DISCHARGE CALCULATION IN COMPOUND CHANNELS HAVING HOMOGENEOUS ROUGHNESS * S. M. HOSSEINI **
 Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Transaction B, Vol. 28, No. B5 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2004 Shiraz University EQUATIONS FOR DISCHARGE CALCULATION IN COMPOUND CHANNELS HAVING HOMOGENEOUS
Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Transaction B, Vol. 28, No. B5 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2004 Shiraz University EQUATIONS FOR DISCHARGE CALCULATION IN COMPOUND CHANNELS HAVING HOMOGENEOUS
conservation of linear momentum 1+8Fr = 1+ Sufficiently short that energy loss due to channel friction is negligible h L = 0 Bernoulli s equation.
 174 Review Flow through a contraction Critical and choked flows The hydraulic jump conservation of linear momentum y y 1 = 1+ 1+8Fr 1 8.1 Rapidly Varied Flows Weirs 8.1.1 Broad-Crested Weir Consider the
174 Review Flow through a contraction Critical and choked flows The hydraulic jump conservation of linear momentum y y 1 = 1+ 1+8Fr 1 8.1 Rapidly Varied Flows Weirs 8.1.1 Broad-Crested Weir Consider the
Defra / Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R&D Programme
 Defra / Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R&D Programme Reducing uncertainty in river flood conveyance, Phase 2 Conveyance Manual Project Record W5A-057/PR/1 Defra / Environment Agency Flood
Defra / Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R&D Programme Reducing uncertainty in river flood conveyance, Phase 2 Conveyance Manual Project Record W5A-057/PR/1 Defra / Environment Agency Flood
Analysis of Depth Averaged Velocity in Meandering Compound Channels
 Analysis of Depth Averaged Velocity in Meandering Compound Channels Prof. K.C.Patra, Ellora Padhi, Laxmipriya Mohanty & Manaswinee Patnaik. Department of Water Resources Engineering, National Institute
Analysis of Depth Averaged Velocity in Meandering Compound Channels Prof. K.C.Patra, Ellora Padhi, Laxmipriya Mohanty & Manaswinee Patnaik. Department of Water Resources Engineering, National Institute
Two-dimensional analytical solution for compound channel flows with vegetated floodplains
 Appl. Math. Mech. -Engl. Ed. 3(9), 2 3 (29) DOI:.7/s483-9-96-z c Shanghai University and Springer-Verlag 29 Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) Two-dimensional analytical solution or compound
Appl. Math. Mech. -Engl. Ed. 3(9), 2 3 (29) DOI:.7/s483-9-96-z c Shanghai University and Springer-Verlag 29 Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) Two-dimensional analytical solution or compound
Uniform Channel Flow Basic Concepts. Definition of Uniform Flow
 Uniform Channel Flow Basic Concepts Hydromechanics VVR090 Uniform occurs when: Definition of Uniform Flow 1. The depth, flow area, and velocity at every cross section is constant 2. The energy grade line,
Uniform Channel Flow Basic Concepts Hydromechanics VVR090 Uniform occurs when: Definition of Uniform Flow 1. The depth, flow area, and velocity at every cross section is constant 2. The energy grade line,
Overbank flow depth prediction in alluvial compound channels
 Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Overbank flow depth prediction in alluvial
Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Overbank flow depth prediction in alluvial
Influence of Two-line Emergent Floodplain Vegetation on A Straight Compound Channel Flow
 International Journal of Integrated Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 1 (2013) p. 58-63 Influence of Two-line Emergent Floodplain Vegetation on A Straight Compound Channel Flow Mazlin Jumain 1,*, Zulkiflee Ibrahim
International Journal of Integrated Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 1 (2013) p. 58-63 Influence of Two-line Emergent Floodplain Vegetation on A Straight Compound Channel Flow Mazlin Jumain 1,*, Zulkiflee Ibrahim
7.6 Example von Kármán s Laminar Boundary Layer Problem
 CEE 3310 External Flows (Boundary Layers & Drag, Nov. 11, 2016 157 7.5 Review Non-Circular Pipes Laminar: f = 64/Re DH ± 40% Turbulent: f(re DH, ɛ/d H ) Moody chart for f ± 15% Bernoulli-Based Flow Metering
CEE 3310 External Flows (Boundary Layers & Drag, Nov. 11, 2016 157 7.5 Review Non-Circular Pipes Laminar: f = 64/Re DH ± 40% Turbulent: f(re DH, ɛ/d H ) Moody chart for f ± 15% Bernoulli-Based Flow Metering
APPARENT SHEAR STRESS IN A COMPOUND CHANNEL
 APPARENT SHEAR STRESS IN A COMPOUND CHANNEL K. K. Khatua K. C. Patra R. Jha Asst. Professor Professor Professor Email: kkkhatua@yahoo.com/ kkkhatua@nitrkl.ac.in Department of Civil Engineering, N.I.T.Rourkela,
APPARENT SHEAR STRESS IN A COMPOUND CHANNEL K. K. Khatua K. C. Patra R. Jha Asst. Professor Professor Professor Email: kkkhatua@yahoo.com/ kkkhatua@nitrkl.ac.in Department of Civil Engineering, N.I.T.Rourkela,
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel. February 24 th, UMSRS
 Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
MEANDERING EFFECT FOR EVALUATION OF ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENTS IN OPEN CHANNEL FLOW
 Conference on Advances in Fluid Mechanics, 5th -7th September 00, Algarve-Portugal MEANDERING EFFECT FOR EVALUATION OF ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENTS IN OPEN CHANNEL FLOW K. K. Khatua, K.C.Patra and P.Nayak Department
Conference on Advances in Fluid Mechanics, 5th -7th September 00, Algarve-Portugal MEANDERING EFFECT FOR EVALUATION OF ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENTS IN OPEN CHANNEL FLOW K. K. Khatua, K.C.Patra and P.Nayak Department
Sediment transport and river bed evolution
 1 Chapter 1 Sediment transport and river bed evolution 1.1 What is the sediment transport? What is the river bed evolution? System of the interaction between flow and river beds Rivers transport a variety
1 Chapter 1 Sediment transport and river bed evolution 1.1 What is the sediment transport? What is the river bed evolution? System of the interaction between flow and river beds Rivers transport a variety
An experimental study of longitudinal velocity distribution at cross-over and bend section of a compound meandering channel
 American Journal of Civil Engineering 2013; 1(3): 124-128 Published online November 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20130103.16 An experimental study of longitudinal
American Journal of Civil Engineering 2013; 1(3): 124-128 Published online November 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20130103.16 An experimental study of longitudinal
1. Introduction. Keywords Compound channel, Momentum transfer, Relative roughness, Relative depth, Relative width
 International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, (): -8 DOI:.9/j.ijhe.. Investigating the Effect of and Relative Roughness on Momentum Transfer in Symmetric Rectangular Compound Channels with Varius Relative
International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, (): -8 DOI:.9/j.ijhe.. Investigating the Effect of and Relative Roughness on Momentum Transfer in Symmetric Rectangular Compound Channels with Varius Relative
Turbulence is a ubiquitous phenomenon in environmental fluid mechanics that dramatically affects flow structure and mixing.
 Turbulence is a ubiquitous phenomenon in environmental fluid mechanics that dramatically affects flow structure and mixing. Thus, it is very important to form both a conceptual understanding and a quantitative
Turbulence is a ubiquitous phenomenon in environmental fluid mechanics that dramatically affects flow structure and mixing. Thus, it is very important to form both a conceptual understanding and a quantitative
Channel Pattern. Channel Pattern, Meanders, and Confluences. Description of Channel Pattern. Bridge (2003)
 Channel Pattern Channel Pattern, Meanders, and Confluences Outline Description of channel pattern Alternate bars Channel pattern continua and evolution Controls of channel pattern Description of Channel
Channel Pattern Channel Pattern, Meanders, and Confluences Outline Description of channel pattern Alternate bars Channel pattern continua and evolution Controls of channel pattern Description of Channel
Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped outer bank
 River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
Prediction of bed form height in straight and meandering compound channels
 Water Resources Management III 311 Prediction of bed form height in straight and meandering compound channels R. D. Karamisheva, J. F. Lyness, W. R. C. Myers, J. O Sullivan & J. B. C. Cassells School of
Water Resources Management III 311 Prediction of bed form height in straight and meandering compound channels R. D. Karamisheva, J. F. Lyness, W. R. C. Myers, J. O Sullivan & J. B. C. Cassells School of
7. Basics of Turbulent Flow Figure 1.
 1 7. Basics of Turbulent Flow Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. The ratio of inertial to viscous forces is the Reynolds
1 7. Basics of Turbulent Flow Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. The ratio of inertial to viscous forces is the Reynolds
CHAPTER 2- BACKGROUND. INVESTIGATIONS OF COMPOSITE ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT IN A RIVER WITH LOW FLOW
 2. Background 2.1 Introduction The estimation of resistant coefficient and hence discharge capacity in a channel or river is one of the fundamental problems facing river engineers. When applying Manning
2. Background 2.1 Introduction The estimation of resistant coefficient and hence discharge capacity in a channel or river is one of the fundamental problems facing river engineers. When applying Manning
Extreme Mixing Events in Rivers
 PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., E-10 (406), 2008 Extreme Mixing Events in Rivers Russell MANSON 1 and Steve WALLIS 2 1 The Richard Stockton College of New Jersey, School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics,
PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., E-10 (406), 2008 Extreme Mixing Events in Rivers Russell MANSON 1 and Steve WALLIS 2 1 The Richard Stockton College of New Jersey, School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics,
y 2 = 1 + y 1 This is known as the broad-crested weir which is characterized by:
 CEE 10 Open Channel Flow, Dec. 1, 010 18 8.16 Review Flow through a contraction Critical and choked flows The hydraulic jump conservation of linear momentum y = 1 + y 1 1 + 8Fr 1 8.17 Rapidly Varied Flows
CEE 10 Open Channel Flow, Dec. 1, 010 18 8.16 Review Flow through a contraction Critical and choked flows The hydraulic jump conservation of linear momentum y = 1 + y 1 1 + 8Fr 1 8.17 Rapidly Varied Flows
UNIFORM FLOW CRITICAL FLOW GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW
 UNIFORM FLOW CRITICAL FLOW GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW Derivation of uniform flow equation Dimensional analysis Computation of normal depth UNIFORM FLOW 1. Uniform flow is the flow condition obtained from a
UNIFORM FLOW CRITICAL FLOW GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW Derivation of uniform flow equation Dimensional analysis Computation of normal depth UNIFORM FLOW 1. Uniform flow is the flow condition obtained from a
THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL
 Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 281 THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL Karima Attia 1 and Gamal El Saied 2 1
Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 281 THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL Karima Attia 1 and Gamal El Saied 2 1
STAGE DISCHARGE PREDICTION FOR MEANDERING CHANNELS
 K.K. Khatua, et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 1, No. 1 (2013) 80 92 STAGE DISCHARGE PREDICTION FOR MEANDERING CHANNELS K. K. KHATUA, K.C. PATRA, P. NAYAK & N. SAHOO Department of Civil
K.K. Khatua, et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 1, No. 1 (2013) 80 92 STAGE DISCHARGE PREDICTION FOR MEANDERING CHANNELS K. K. KHATUA, K.C. PATRA, P. NAYAK & N. SAHOO Department of Civil
Hydromechanics: Course Summary
 Hydromechanics: Course Summary Hydromechanics VVR090 Material Included; French: Chapters to 9 and 4 + Sample problems Vennard & Street: Chapters 8 + 3, and (part of it) Roberson & Crowe: Chapter Collection
Hydromechanics: Course Summary Hydromechanics VVR090 Material Included; French: Chapters to 9 and 4 + Sample problems Vennard & Street: Chapters 8 + 3, and (part of it) Roberson & Crowe: Chapter Collection
Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering. Gene-Expression Programming to Predict Manning s n in Meandering Flows
 Gene-Expression Programming to Predict Manning s n in Meandering Flows Journal: Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering Manuscript ID cjce-2016-0569.r2 Manuscript Type: Article Date Submitted by the Author:
Gene-Expression Programming to Predict Manning s n in Meandering Flows Journal: Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering Manuscript ID cjce-2016-0569.r2 Manuscript Type: Article Date Submitted by the Author:
Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke
 1 Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke with contributions from Norwegian and international project partners 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Basic ideas of flow
1 Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke with contributions from Norwegian and international project partners 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Basic ideas of flow
OE4625 Dredge Pumps and Slurry Transport. Vaclav Matousek October 13, 2004
 OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 1 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie Transport OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie
OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 1 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie Transport OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie
External Flow and Boundary Layer Concepts
 1 2 Lecture (8) on Fayoum University External Flow and Boundary Layer Concepts By Dr. Emad M. Saad Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical
1 2 Lecture (8) on Fayoum University External Flow and Boundary Layer Concepts By Dr. Emad M. Saad Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical
CEE 3310 Open Channel Flow, Nov. 26,
 CEE 3310 Open Channel Flow, Nov. 6, 018 175 8.10 Review Open Channel Flow Gravity friction balance. y Uniform Flow x = 0 z = S 0L = h f y Rapidly Varied Flow x 1 y Gradually Varied Flow x 1 In general
CEE 3310 Open Channel Flow, Nov. 6, 018 175 8.10 Review Open Channel Flow Gravity friction balance. y Uniform Flow x = 0 z = S 0L = h f y Rapidly Varied Flow x 1 y Gradually Varied Flow x 1 In general
Geology 550 Spring 2005 LAB 3: HYDRAULICS OF PRAIRIE CREEK
 Geology 550 Spring 2005 LAB 3: HYDRAULICS OF PRAIRIE CREEK Objectives: 1. To examine the distribution of velocity in a stream channel 2. To characterize the state of flow using dimensionless variables
Geology 550 Spring 2005 LAB 3: HYDRAULICS OF PRAIRIE CREEK Objectives: 1. To examine the distribution of velocity in a stream channel 2. To characterize the state of flow using dimensionless variables
150A Review Session 2/13/2014 Fluid Statics. Pressure acts in all directions, normal to the surrounding surfaces
 Fluid Statics Pressure acts in all directions, normal to the surrounding surfaces or Whenever a pressure difference is the driving force, use gauge pressure o Bernoulli equation o Momentum balance with
Fluid Statics Pressure acts in all directions, normal to the surrounding surfaces or Whenever a pressure difference is the driving force, use gauge pressure o Bernoulli equation o Momentum balance with
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FOUR. Stream flow measurement. Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib
 Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FOUR Stream flow measurement Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib -١ 4.1 Introduction - Surface water hydrology deals with the movement of water
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FOUR Stream flow measurement Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib -١ 4.1 Introduction - Surface water hydrology deals with the movement of water
Turbulent structures in the flow through compound meandering channels
 River Flow 2010 - Dittrich, Koll, Aberle & Geisenhainer (eds) - 2010 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-00-7 Turbulent structures in the flow through compound meandering channels I. Moncho-Esteve
River Flow 2010 - Dittrich, Koll, Aberle & Geisenhainer (eds) - 2010 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-00-7 Turbulent structures in the flow through compound meandering channels I. Moncho-Esteve
Lecture 10: River Channels
 GEOG415 Lecture 10: River Channels 10-1 Importance of channel characteristics Prediction of flow was the sole purpose of hydrology, and still is a very important aspect of hydrology. - Water balance gives
GEOG415 Lecture 10: River Channels 10-1 Importance of channel characteristics Prediction of flow was the sole purpose of hydrology, and still is a very important aspect of hydrology. - Water balance gives
Uniform Channel Flow Basic Concepts Hydromechanics VVR090
 Uniform Channel Flow Basic Concepts Hydromechanics VVR090 ppt by Magnus Larson; revised by Rolf L Feb 2014 SYNOPSIS 1. Definition of Uniform Flow 2. Momentum Equation for Uniform Flow 3. Resistance equations
Uniform Channel Flow Basic Concepts Hydromechanics VVR090 ppt by Magnus Larson; revised by Rolf L Feb 2014 SYNOPSIS 1. Definition of Uniform Flow 2. Momentum Equation for Uniform Flow 3. Resistance equations
The Importance of Riparian Vegetation in Channel Restoration: Moving Towards Quantification in Design
 The Importance of Riparian Vegetation in Channel Restoration: Moving Towards Quantification in Design Rob Millar Department of Civil Engineering The University of British Columbia "Nothing is as practical
The Importance of Riparian Vegetation in Channel Restoration: Moving Towards Quantification in Design Rob Millar Department of Civil Engineering The University of British Columbia "Nothing is as practical
Transverse Distribution of Shear Stress in Compound Meandering Channel
 e-issn: 2278-1684, p-issn: 232-334X. Transverse Distribution of Shear Stress in Compound Meandering Channel A.sahu 1, L.Mohanty 2, K.K.Khatua³ 1,2 ( Department of Civil Engineering, VSSUT burla, India)
e-issn: 2278-1684, p-issn: 232-334X. Transverse Distribution of Shear Stress in Compound Meandering Channel A.sahu 1, L.Mohanty 2, K.K.Khatua³ 1,2 ( Department of Civil Engineering, VSSUT burla, India)
Steven Burian Civil & Environmental Engineering September 25, 2013
 Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mechanics Steven Burian Civil & Environmental Engineering September 25, 2013 s and FE Morning ( Mechanics) A. Flow measurement 7% of FE Morning B. properties Session
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mechanics Steven Burian Civil & Environmental Engineering September 25, 2013 s and FE Morning ( Mechanics) A. Flow measurement 7% of FE Morning B. properties Session
Flow structures in a compound meandering channel with flat and natural bedforms
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Flow structures in a compound meandering channel with flat and natural bedforms This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Flow structures in a compound meandering channel with flat and natural bedforms This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
APPLICATION OF ADAPTIVE NEURO-FUZZY INFERENCE SYSTEM FOR THE ESTIMATION OF ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT OF A MEANDERING OPEN-CHANNEL FLOW
 S. Moharana et al., Int. J. Sus. Dev. Plann. Vol. 10, No. 1 (2015) 87 99 APPLICATION OF ADAPTIVE NEURO-FUZZY INFERENCE SYSTEM FOR THE ESTIMATION OF ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT OF A MEANDERING OPEN-CHANNEL FLOW
S. Moharana et al., Int. J. Sus. Dev. Plann. Vol. 10, No. 1 (2015) 87 99 APPLICATION OF ADAPTIVE NEURO-FUZZY INFERENCE SYSTEM FOR THE ESTIMATION OF ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT OF A MEANDERING OPEN-CHANNEL FLOW
Lecture 3: Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: fluid properties and types; Boundary layer structure; unidirectional flows
 GEOL 440 Sedimentology and stratigraphy: processes, environments and deposits Lecture 3: Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: fluid properties and types; Boundary layer structure; unidirectional flows Why study
GEOL 440 Sedimentology and stratigraphy: processes, environments and deposits Lecture 3: Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: fluid properties and types; Boundary layer structure; unidirectional flows Why study
Estimation of State Noise for the Ensemble Kalman filter algorithm for 2D shallow water equations.
 Estimation of State Noise for the Ensemble Kalman filter algorithm for 2D shallow water equations. May 6, 2009 Motivation Constitutive Equations EnKF algorithm Some results Method Navier Stokes equations
Estimation of State Noise for the Ensemble Kalman filter algorithm for 2D shallow water equations. May 6, 2009 Motivation Constitutive Equations EnKF algorithm Some results Method Navier Stokes equations
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 One-dimensional unsteady flow computation in channels with floodplains D. Bousmar, R. Scherer & Y. Zech Civil Engineering Dept., Universite Catholique de Louvain, Place du Levant, 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
One-dimensional unsteady flow computation in channels with floodplains D. Bousmar, R. Scherer & Y. Zech Civil Engineering Dept., Universite Catholique de Louvain, Place du Levant, 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics in a Compound Meandering River
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
Conclusion Evaluating Methods for 3D CFD Models in Sediment Transport Computations
 Conclusion Evaluating Methods for 3D CFD Models in Sediment Transport Computations Hamid Reza Madihi* 1, Bagher Keshtgar 2, Sina Hosseini Fard 3 1, 2, 3 M.Sc. Coastal Environmental Engineering, Graduate
Conclusion Evaluating Methods for 3D CFD Models in Sediment Transport Computations Hamid Reza Madihi* 1, Bagher Keshtgar 2, Sina Hosseini Fard 3 1, 2, 3 M.Sc. Coastal Environmental Engineering, Graduate
How Wrong is Your Flood Model? Bill Syme, Senior Principal, BMT Water & Environment
 How Wrong is Your Flood Model? Bill Syme, Senior Principal, BMT Water & Environment Always! Really Accurate How Accurate is my Model? Sufficiently Accurate Young Modeller (or Salesperson!) Old Modeller
How Wrong is Your Flood Model? Bill Syme, Senior Principal, BMT Water & Environment Always! Really Accurate How Accurate is my Model? Sufficiently Accurate Young Modeller (or Salesperson!) Old Modeller
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOLOGICAL IMPACT OF GROYNE LENGTHENING I. RÁTKY, ÉVA RÁTKY
 ESTIMATION OF MORPHOLOGICAL IMPACT OF GROYNE LENGTHENING I. RÁTKY, ÉVA RÁTKY Abstract. Hydraulic-morphological calculations in open channel flows still cause problems for modellers, partially because of
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOLOGICAL IMPACT OF GROYNE LENGTHENING I. RÁTKY, ÉVA RÁTKY Abstract. Hydraulic-morphological calculations in open channel flows still cause problems for modellers, partially because of
HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF STRAIGHT COMPOUND CHANNELS. P Ackers, Hydraulics Consultant. Contents of Volume 1
 HR Wallingiord HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF STRAIGHT COMPOUND CHANNELS VOLUME 1 by P Ackers, Hydraulics Consultant Contents of Volume 1 Summary and design method Detailed development of design method, - Part 1
HR Wallingiord HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF STRAIGHT COMPOUND CHANNELS VOLUME 1 by P Ackers, Hydraulics Consultant Contents of Volume 1 Summary and design method Detailed development of design method, - Part 1
Engineering Fluid Mechanics
 Engineering Fluid Mechanics Eighth Edition Clayton T. Crowe WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY, PULLMAN Donald F. Elger UNIVERSITY OF IDAHO, MOSCOW John A. Roberson WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY, PULLMAN WILEY
Engineering Fluid Mechanics Eighth Edition Clayton T. Crowe WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY, PULLMAN Donald F. Elger UNIVERSITY OF IDAHO, MOSCOW John A. Roberson WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY, PULLMAN WILEY
Turbulent flow across a natural compound channel
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 12, 1270, doi:10.1029/2001wr000902, 2002 Turbulent flow across a natural compound channel P. A. Carling and Zhixian Cao Department of Geography, University of Southampton,
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 12, 1270, doi:10.1029/2001wr000902, 2002 Turbulent flow across a natural compound channel P. A. Carling and Zhixian Cao Department of Geography, University of Southampton,
Analytical Models Evaluation for Predicting Vertical Velocity Flows through Submerged Vegetation
 From the SelectedWorks of Innovative Research Publications IRP India Winter January, 205 Analytical Models Evaluation for Predicting Vertical Velocity Flows through Submerged Vegetation Innovative Research
From the SelectedWorks of Innovative Research Publications IRP India Winter January, 205 Analytical Models Evaluation for Predicting Vertical Velocity Flows through Submerged Vegetation Innovative Research
ANALYSIS OF FLOW ALONG THE MEANDER PATH OF A HIGHLY SINUOUS RIGID CHANNEL
 ANALYSIS OF FLOW ALONG THE MEANDER PATH OF A HIGHLY SINUOUS RIGID CHANNEL A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirement for the Degree of Master of Technology In Civil Engineering ARPAN PRADHAN
ANALYSIS OF FLOW ALONG THE MEANDER PATH OF A HIGHLY SINUOUS RIGID CHANNEL A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirement for the Degree of Master of Technology In Civil Engineering ARPAN PRADHAN
Keywords: flow characteristics, compound straight channel, bed morphology, floodplain
 Flow Characteristics on Floodplain Vegetation in Compound Straight Channels Nur Amirah Nabilah Mohd Zamri 1, a, Zulhilmi Ismail 1,b,Zulkiflee Ibrahim 1,c 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
Flow Characteristics on Floodplain Vegetation in Compound Straight Channels Nur Amirah Nabilah Mohd Zamri 1, a, Zulhilmi Ismail 1,b,Zulkiflee Ibrahim 1,c 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
Physical and numerical modeling of overbank flow with a groyne on the floodplain
 Physical and numerical modeling of overbank flow with a groyne on the floodplain (1) Y. Peltier, (1) S. Proust, (2) A. Bourdat, (1) F. Thollet, (3) N. Rivière, (1) A. Paquier (1) Hydrology-Hydraulics Research
Physical and numerical modeling of overbank flow with a groyne on the floodplain (1) Y. Peltier, (1) S. Proust, (2) A. Bourdat, (1) F. Thollet, (3) N. Rivière, (1) A. Paquier (1) Hydrology-Hydraulics Research
Discharge estimation for equatorial natural rivers with overbank flow
 Intl. J. River Basin Management Vol. 6, No. (28), pp. 3 2 28 IAHR, INBO & IAHS Discharge estimation for equatorial natural rivers with overbank flow LAI SAI HIN, Lecturer, River Engineering and Urban Drainage
Intl. J. River Basin Management Vol. 6, No. (28), pp. 3 2 28 IAHR, INBO & IAHS Discharge estimation for equatorial natural rivers with overbank flow LAI SAI HIN, Lecturer, River Engineering and Urban Drainage
Watershed Sciences 6900 FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS & ECOHYDRAULICS
 Watershed Sciences 6900 FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS & ECOHYDRAULICS WEEK Four Lecture 6 VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION Joe Wheaton FOR TODAY, YOU SHOULD HAVE READ 1 LET S GET ON WITH IT TODAY S PLAN VELOCITY DISTRIBUTIONS
Watershed Sciences 6900 FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS & ECOHYDRAULICS WEEK Four Lecture 6 VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION Joe Wheaton FOR TODAY, YOU SHOULD HAVE READ 1 LET S GET ON WITH IT TODAY S PLAN VELOCITY DISTRIBUTIONS
We will assume straight channels with simple geometries (prismatic channels) and steady state flow (in time).
 56 Review Drag & Lift Laminar vs Turbulent Boundary Layer Turbulent boundary layers stay attached to bodies longer Narrower wake! Lower pressure drag! 8. Open-Channel Flow Pipe/duct flow closed, full,
56 Review Drag & Lift Laminar vs Turbulent Boundary Layer Turbulent boundary layers stay attached to bodies longer Narrower wake! Lower pressure drag! 8. Open-Channel Flow Pipe/duct flow closed, full,
Composite roughness for rough compound channels
 Composite roughness for rough compound channels S. Pradhan Research Scholar (Ph. D), Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Orissa, India K.K.Khatua Associate Professor,
Composite roughness for rough compound channels S. Pradhan Research Scholar (Ph. D), Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Orissa, India K.K.Khatua Associate Professor,
A note on critical flow section in collector channels
 Sādhan ā, Vol. 26, Part 5, October 2001, pp. 439 445. Printed in India A note on critical flow section in collector channels 1. Introduction SUBHASISH DEY Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute
Sādhan ā, Vol. 26, Part 5, October 2001, pp. 439 445. Printed in India A note on critical flow section in collector channels 1. Introduction SUBHASISH DEY Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute
Evaluating methods for 3D CFD Models in sediment transport computations
 American Journal of Civil Engineering 2015; 3(2-2): 33-37 Published online February 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.s.2015030202.17 ISSN: 2330-8729 (Print);
American Journal of Civil Engineering 2015; 3(2-2): 33-37 Published online February 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.s.2015030202.17 ISSN: 2330-8729 (Print);
Estimating longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural channels
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 017 Estimating longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural channels Yuqi Song Iowa State University Follow
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 017 Estimating longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural channels Yuqi Song Iowa State University Follow
Computation of vertically averaged velocities in irregular sections of straight channels
 doi:10.5194/hess-19-3857-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Computation of vertically averaged velocities in irregular sections of straight channels E. Spada 1, T. Tucciarelli 1, M. Sinagra
doi:10.5194/hess-19-3857-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Computation of vertically averaged velocities in irregular sections of straight channels E. Spada 1, T. Tucciarelli 1, M. Sinagra
Hydraulic characteristics of meandering mobile bed compound channels
 Hydraulic characteristics of meandering mobile bed compound channels J. F. Lyness, MSc, PhD, MICE, W.R.C.Myers,BA, BSc, PhD, MICE and J. J. O'Sullivan, BA, BAI, MSc Proc. Instn Civ. Engrs Wat., Marit.
Hydraulic characteristics of meandering mobile bed compound channels J. F. Lyness, MSc, PhD, MICE, W.R.C.Myers,BA, BSc, PhD, MICE and J. J. O'Sullivan, BA, BAI, MSc Proc. Instn Civ. Engrs Wat., Marit.
Flow Analysis of Compound Channels With Wide Flood Plains
 Flow Analysis of Compound Channels With Wide Flood Plains Prabir Kumar Mohanty Flow Analysis of Compound Channels with Wide Flood Plains Thesis Submitted to the Department of Civil Engineering National
Flow Analysis of Compound Channels With Wide Flood Plains Prabir Kumar Mohanty Flow Analysis of Compound Channels with Wide Flood Plains Thesis Submitted to the Department of Civil Engineering National
15. Physics of Sediment Transport William Wilcock
 15. Physics of Sediment Transport William Wilcock (based in part on lectures by Jeff Parsons) OCEAN/ESS 410 Lecture/Lab Learning Goals Know how sediments are characteried (sie and shape) Know the definitions
15. Physics of Sediment Transport William Wilcock (based in part on lectures by Jeff Parsons) OCEAN/ESS 410 Lecture/Lab Learning Goals Know how sediments are characteried (sie and shape) Know the definitions
ECOHYDRAULICS. Introduction to 2D Modeling
 Introduction to 2D Modeling No one believes a model, except the person who wrote it; Everyone believes data, except the person who collected it. unknown wise scientist Two dimensional (depth averaged)
Introduction to 2D Modeling No one believes a model, except the person who wrote it; Everyone believes data, except the person who collected it. unknown wise scientist Two dimensional (depth averaged)
2.3 The Turbulent Flat Plate Boundary Layer
 Canonical Turbulent Flows 19 2.3 The Turbulent Flat Plate Boundary Layer The turbulent flat plate boundary layer (BL) is a particular case of the general class of flows known as boundary layer flows. The
Canonical Turbulent Flows 19 2.3 The Turbulent Flat Plate Boundary Layer The turbulent flat plate boundary layer (BL) is a particular case of the general class of flows known as boundary layer flows. The
Flow and Bed Topography in a 180 Curved Channel
 Flow and Bed Topography in a 180 Curved Channel Jae Wook Jung 1, Sei Eui Yoon 2 Abstract The characteristics of flow and bed topography has been analyzed by changing the bed materials in a 180-degree,
Flow and Bed Topography in a 180 Curved Channel Jae Wook Jung 1, Sei Eui Yoon 2 Abstract The characteristics of flow and bed topography has been analyzed by changing the bed materials in a 180-degree,
Thelongwaveequations
 Alternative Hydraulics Paper 1, January 2010 Thelongwaveequations Institute of Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering Vienna University of Technology, Karlsplatz 13/222, 1040 Vienna, Austria URL: http://johndfenton.com/
Alternative Hydraulics Paper 1, January 2010 Thelongwaveequations Institute of Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering Vienna University of Technology, Karlsplatz 13/222, 1040 Vienna, Austria URL: http://johndfenton.com/
LECTURE 2: FLUID MECHANICS
 LECTURE 2: FLUID MECHANICS Introduction Conservation of mass and momentum General types of flow Laminar vs. turbulent flow Shear Stress Reach-average shear stress Bed roughness and reach average flow velocity
LECTURE 2: FLUID MECHANICS Introduction Conservation of mass and momentum General types of flow Laminar vs. turbulent flow Shear Stress Reach-average shear stress Bed roughness and reach average flow velocity
Hydraulics of bendway weirs
 River Basin Management IV 389 Hydraulics of bendway weirs C. Thornton 1, S. Abt 1, D. Baird 2 & R. Padilla 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA 2 U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO,
River Basin Management IV 389 Hydraulics of bendway weirs C. Thornton 1, S. Abt 1, D. Baird 2 & R. Padilla 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA 2 U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO,
Beaver Creek Corridor Design and Analysis. By: Alex Previte
 Beaver Creek Corridor Design and Analysis By: Alex Previte Overview Introduction Key concepts Model Development Design Accuracy Conclusion Refresh v = Beaver Creek Site = Wittenberg Introduction Low head
Beaver Creek Corridor Design and Analysis By: Alex Previte Overview Introduction Key concepts Model Development Design Accuracy Conclusion Refresh v = Beaver Creek Site = Wittenberg Introduction Low head
Discharge. Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1. Velocity. Area
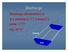 Discharge Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1 Velocity Area Where is the average velocity?? 3 Source: Brooks et al., Hydrology and the Management
Discharge Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1 Velocity Area Where is the average velocity?? 3 Source: Brooks et al., Hydrology and the Management
EXAMPLES (SEDIMENT TRANSPORT) AUTUMN 2018
 EXAMPLES (SEDIMENT TRANSPORT) AUTUMN 2018 Q1. Using Cheng s formula estimate the settling velocity of a sand particle of diameter 1 mm in: (a) air; (b) water. Q2. Find the critical Shields parameter diameter
EXAMPLES (SEDIMENT TRANSPORT) AUTUMN 2018 Q1. Using Cheng s formula estimate the settling velocity of a sand particle of diameter 1 mm in: (a) air; (b) water. Q2. Find the critical Shields parameter diameter
Visualization of Shear Layers in Compound Channel Flows
 Visualization of Shear Layers in Compound Channel Flows Saad Mulahasan*, Professor Thorsten Stoesser and Fernando Alvarez Hydro-environmental Research Centre, School of Engineering, Cardiff University,
Visualization of Shear Layers in Compound Channel Flows Saad Mulahasan*, Professor Thorsten Stoesser and Fernando Alvarez Hydro-environmental Research Centre, School of Engineering, Cardiff University,
ACCOUNTING FOR FRICTION IN THE BERNOULLI EQUATION FOR FLOW THROUGH PIPES
 ACCOUNTING FOR FRICTION IN THE BERNOULLI EQUATION FOR FLOW THROUGH PIPES Some background information first: We have seen that a major limitation of the Bernoulli equation is that it does not account for
ACCOUNTING FOR FRICTION IN THE BERNOULLI EQUATION FOR FLOW THROUGH PIPES Some background information first: We have seen that a major limitation of the Bernoulli equation is that it does not account for
DISTRIBUTION OF THE HYDRAULIC PARAMETERS AT RIVER BENDS
 DISTRIBUTION OF THE HYDRAULIC PARAMETERS AT RIVER BENDS Isa Issa Oran *, Riyad Hassan Al-Anbari ** and Walaa Khalil Ali *** * Assist. Professor, Foundation of Technical Education ** Assist. Professor,
DISTRIBUTION OF THE HYDRAULIC PARAMETERS AT RIVER BENDS Isa Issa Oran *, Riyad Hassan Al-Anbari ** and Walaa Khalil Ali *** * Assist. Professor, Foundation of Technical Education ** Assist. Professor,
s and FE X. A. Flow measurement B. properties C. statics D. impulse, and momentum equations E. Pipe and other internal flow 7% of FE Morning Session I
 Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam General Section Steven Burian Civil & Environmental Engineering October 26, 2010 s and FE X. A. Flow measurement B. properties C. statics D. impulse, and momentum
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam General Section Steven Burian Civil & Environmental Engineering October 26, 2010 s and FE X. A. Flow measurement B. properties C. statics D. impulse, and momentum
Numerical Study of Turbulent Structure. Hitoshi SUGIYAMA, Mitsunobu AKIYAMA and Mieko TANAKA
 Vol.1 (1998 9 ) Numerical Study of Turbulent Structure in Curved Open-Channel Flow with Flood Plains Hitoshi SUGIYAMA, Mitsunobu AKIYAMA and Mieko TANAKA ( 31-8585 753) Ph.D. ( 31-8585 753) ( 31-8585 753)
Vol.1 (1998 9 ) Numerical Study of Turbulent Structure in Curved Open-Channel Flow with Flood Plains Hitoshi SUGIYAMA, Mitsunobu AKIYAMA and Mieko TANAKA ( 31-8585 753) Ph.D. ( 31-8585 753) ( 31-8585 753)
Stream flow measurements are fundamental in water management and. Different streams and rivers require
 Stream Flow Measurements Introduction Stream flow measurements are fundamental in water management and projects Different streams and rivers require appropriate flow measurement methods Weirs and Flumes
Stream Flow Measurements Introduction Stream flow measurements are fundamental in water management and projects Different streams and rivers require appropriate flow measurement methods Weirs and Flumes
NATURE OF RIVERS B-1. Channel Function... ALLUVIAL FEATURES. ... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed. ...dissipate energy.
 1 2 Function... Sevier River... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed....dissipate energy. 3 ALLUVIAL FEATURES 4 CHANNEL DIMENSION The purpose of a stream is to carry water and sediment
1 2 Function... Sevier River... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed....dissipate energy. 3 ALLUVIAL FEATURES 4 CHANNEL DIMENSION The purpose of a stream is to carry water and sediment
Uniform flow formulas for irregular sections in straight channels
 1 Uniform flow formulas for irregular sections in straight channels 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 ELEONORA SPADA, PhD student, Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Ambientale,Aerospaziale,
1 Uniform flow formulas for irregular sections in straight channels 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 ELEONORA SPADA, PhD student, Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Ambientale,Aerospaziale,
39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow
 39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow Gradually varied unsteady low occurs when the low variables such as the low depth and velocity do not change rapidly in time and space. Such lows are very common in
39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow Gradually varied unsteady low occurs when the low variables such as the low depth and velocity do not change rapidly in time and space. Such lows are very common in
DAY 19: Boundary Layer
 DAY 19: Boundary Layer flat plate : let us neglect the shape of the leading edge for now flat plate boundary layer: in blue we highlight the region of the flow where velocity is influenced by the presence
DAY 19: Boundary Layer flat plate : let us neglect the shape of the leading edge for now flat plate boundary layer: in blue we highlight the region of the flow where velocity is influenced by the presence
CE 6403 APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING UNIT - II GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW
 CE 6403 APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING UNIT - II GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW Dynamic equations of gradually varied and spatially varied flows - Water surface flow profile classifications: Hydraulic Slope, Hydraulic
CE 6403 APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING UNIT - II GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW Dynamic equations of gradually varied and spatially varied flows - Water surface flow profile classifications: Hydraulic Slope, Hydraulic
Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber
 Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber by Richard L. Stockstill BACKGROUND: Extensive research has been conducted in the area of modeling mooring systems in sea environments where the forcing function
Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber by Richard L. Stockstill BACKGROUND: Extensive research has been conducted in the area of modeling mooring systems in sea environments where the forcing function
 http://water.usgs.gov/waterwatch/ Stream Flow Measurement: Velocity-Area method Stream discharge = Q = U * A Q = volumetric flow rate in [L 3 T -1 ] U= average stream velocity [L 2 T -1 ] A = cross sectional
http://water.usgs.gov/waterwatch/ Stream Flow Measurement: Velocity-Area method Stream discharge = Q = U * A Q = volumetric flow rate in [L 3 T -1 ] U= average stream velocity [L 2 T -1 ] A = cross sectional
Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels
 Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels by Richard L. Stockstill PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) investigates lateral flow discharging into a high-velocity channel.
Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels by Richard L. Stockstill PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) investigates lateral flow discharging into a high-velocity channel.
Introduction to BASEMENT Basic Simulation Environment for Computation of Environmental Flow and Natural Hazard Simulation
 Introduction to BASEMENT Basic Simulation Environment for Computation of Environmental Flow and Natural Hazard Simulation Numerical Hydraulics Autumn semester 2016 Prof. Dr. Markus Holzner Author: Pascal
Introduction to BASEMENT Basic Simulation Environment for Computation of Environmental Flow and Natural Hazard Simulation Numerical Hydraulics Autumn semester 2016 Prof. Dr. Markus Holzner Author: Pascal
VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL *Satish Patel 1 and Bimlesh Kumar 2
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 3678 3685 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 3678 3685 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL
Flood Capacity of Shirakawa River at Tatsudajinnnai Area in Kumamoto Prefecture
 International Journal of Economy, Energy and Environment 218; 3(5): 51-57 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijeee doi: 1.11648/j.ijeee.21835.13 ISSN: 2575-513 (Print); ISSN: 2575-521 (Online) Flood
International Journal of Economy, Energy and Environment 218; 3(5): 51-57 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijeee doi: 1.11648/j.ijeee.21835.13 ISSN: 2575-513 (Print); ISSN: 2575-521 (Online) Flood
6. Laminar and turbulent boundary layers
 6. Laminar and turbulent boundary layers John Richard Thome 8 avril 2008 John Richard Thome (LTCM - SGM - EPFL) Heat transfer - Convection 8 avril 2008 1 / 34 6.1 Some introductory ideas Figure 6.1 A boundary
6. Laminar and turbulent boundary layers John Richard Thome 8 avril 2008 John Richard Thome (LTCM - SGM - EPFL) Heat transfer - Convection 8 avril 2008 1 / 34 6.1 Some introductory ideas Figure 6.1 A boundary
VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION IN TRAPEZOIDAL MEANDERING CHANNEL. A thesis submitted to. National Institute of Technology, Rourkela
 VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION IN TRAPEZOIDAL MEANDERING CHANNEL A thesis submitted to National Institute of Technology, Rourkela In partial fulfillment for the award of the degree of Master of Technology in Civil
VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION IN TRAPEZOIDAL MEANDERING CHANNEL A thesis submitted to National Institute of Technology, Rourkela In partial fulfillment for the award of the degree of Master of Technology in Civil
