Mathematics 206 Solutions for HWK 22b Section 8.4 p399
|
|
|
- Chastity Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematics Solutions f HWK b Section 8. p99 Problem, 8. p99. Let T : P P be the linear transfmation defined by T(p(x)) = xp(x). (a) Find the matrix f T with respect to the standard bases B = {u, u, u }, B = {v, v, v, v } taken in the der u (x) =, u (x) = x, u (x) = x v (x) =, v (x) = x, v (x) = x, v (x) = x (b) Verify that this matrix functions as it should. In other wds, verify that multiplying the B-codinate matrix f p on the left by this matrix always produces the B -codinate matrix f T(p). Solution. (a) Since T() = x, T(x) = x, T(x ) = x, we have T(u ) = v, T(u ) = v, T(u ) = v. Therefe the matrix f T relative to B and B is A = T(u ) B T(u ) B T(u ) B = (b). With p given by p(x) = c + c x + c x, we should have T(p) B = Ap B Since T(p) is the function c x + c x + c x, we should have A c c c = c c c c c c c = c c Page of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
2 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 which is exactly right. Problem 5, 8. p99. Let T: R R be the linear transfmation defined by T( x x ) = x + x x (a) Find the matrix f T relative to the basis B = {u, u } f R and B = {v, v, v } f R, given that u =, u =, v =, v =, v = (b) Verify that this matrix functions as it should. In other wds, verify that multiplying the B-codinate matrix f v on the left by this matrix always produces the B -codinate matrix f T(v). Solution. (a). T(u ) = T( ) = 7 = + 8 = v v + 8 v so so T(u ) = T( T(u ) B = ) = 8 = v + v + v T(u ) B = Page of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
3 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 Therefe the matrix f T relative to B and B is T B,B = = 8 (b) We want to verify that f every u R we have With u = au + bu we would have T(u) B = T(au + bu ) B = T(a 8 T(u) B = u B 8 + b a b ) B = T( ) = a + b B 7a + b a + b B and so it should be that which does hold. u B = 8 8 a b = a + b a + 8b 7a + b (v + ( a + b)v + (a + 8b)v ) = a + b 7a + b ( a + b) + (a + 8b) = a + b a + b a + b + a + b a + b + 8a + b 8a + b = 7a + b = a + b 7a + b a + b Page of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
4 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 Problem, 8. p99. Let T: R R be the linear transfmation defined by T(x, x, x ) = (x x, x x, x x ) (a) Find the matrix f T relative to the basis B = {v, v, v }, given that v = (,,), v = (,, ), v = (,,) (b) Verify that this matrix functions as advertised. In other wds, verify that multiply the B- codinate matrix f v on the left by this matrix always produces the B-codinate matrix f T(v). Solution. (a). T(v ) = (,,) = v v T(v ) = (,, ) = v + v + v T(v ) = (,, ) = v + v v so the required matrix is A = (b). Given v R, with v = av + bv + cv we have T(v) = T (a(,, ) + b(,,) + c(,,)) = T(a + c, b + c, a + b) = (a b, b a, c b) Meover, Av B = a b + c a b = a + b + c c b c so we should have (a b + c)v + ( a + b + c)v + ( b c)v = (a b, b a, c b) Page of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
5 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 (a b + c)(,, ) +( a + b + c)(,,) +( b c)(,, ) = (a b, b a, c b) (a b + c,, a b + c) +(, a + b + c, a + b + c) +( b c, b c, ) = (a b, b a, c b) (a b + c + + b c, a + b + c + b c, a b + c a + b + c + ) = (a b, b a, c b) which does hold. (Vertical notation would have been a better choice here, but I won t retype.) Problem 9, 8. p99. Let and let v =, v = A = 5 be the matrix f the linear transfmation T : R R relative to the basis B = {v, v }. (a) Find T(v ) B and T(v ) B. (b) Find T(v ) and T(v ). (c) Find a fmula f T( x x ). Page 5 of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
6 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 (d) Use the fmula from (c) to compute T( ). Solution. (a). T(v ) B = first column of A = T(v ) B = second column of A = 5 (b). From (a), we have (c) We need to write x x and solve f a, b you should get T(v ) = v v = T(v ) = v + 5v = + = = 9 as a linear combination of v and v. If you set up the system a + b = x x a = 7 (x + x ), b = 7 ( x + x ) Therefe T ( x x ) = T( 7 (x + x )v + 7 ( x + x )v ) = 7 (x + x )T(v ) + 7 ( x + x )v )T(v ) = 7 (x + x ) ( x + x )v ) 9 = 7 (8x + x ) 7 ( 7x + x ) = 8 x 7 7 x (d). T( ) = = Page of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
7 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 Problem, 8. p99. Let A = 5 be the matrix f a linear transfmation T : P P relative to the basis B = {v, v, v } where v, v, v are given by v (x) = x + x, v (x) = + x + x, v (x) = + 7x + x (a) Find T(v ) B, T(v ) B, T(v ) B. (b) Find T(v ), T(v ), T(v ). (c) Find a fmula f T(a + a x + a x ). (d) Use the fmula from (c) to find T( + x ). Solution. (a). T(v ) B = first column of A = T(v ) B = second column of A = T(v ) B = third column of A = 5 (b) Use (a) to find: T(v ) = v + v + v = (x + x ) + ( + x + x ) + ( + 7x + x ) = + 5x + 9x T(v ) = v + v v = (x + x ) ( + 7x + x ) = 5x + 5x T(v ) = v + 5v + v = (x + x ) + 5( + x + x ) + ( + 7x + x ) = 7 + x + 5x (c). Write a + a x + a x = a(x +x )+ b( +x +x )+ c(+ 7x+ x ). Equate coefficients to find b + c = a a + b + 7c = a a + b + c = a Page 7 of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
8 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 Now solve f a, b, and c. (This might be a good time to use Joy of Mathematica.) You should get a = (a a + a ) b = 8 ( 5a + a a ) c = 8 (a + a a ) Therefe T(a + a x + a x ) = T(av + bv + cv ) = (a a + a )( + 5x + 9x ) + 8 ( 5a + a a )( 5x + 5x ) + 8 (a + a a )(7 + x + 5x ) = (9a a + 89a ) + 8 (a a + 7a )x + (a a + 7a )x With Joy of Mathematica, this last simplification isn t quite so tedious. (Use the Simplify command under the Algebra menu.) (d) T( + x ) = (9 + 89) + ( + 7)x + 8 ( + 7)x = + 5x + x Problem 5, 8. p99. Show that if T : V V is a contraction dilation of V, then the matrix f T relative to any basis f V is a positive scalar multiple of the identity matrix. Solution. F this problem to make sense we must assume that V is finite-dimensional. Say V has dimension n. Assume, as indicated, that T : V V is a contraction dilation by the fact k (f some k > ). This means that T(v) = kv f every v. Let B = {v,..., v n } be a basis f V, and let A be the matrix that represents T relative to the basis B. Then we must have T(v ) = kv, T(v ) = kv, and so fth f all the n basis vects. This tells us that the first column of A has k at the top and all its other entries. The second column of A has k in the second position, and all its other entries. Me generally, the j-th column of A will have k in the j-th position and all its other entries. But this description of A tells us that A = ki, where I is the n n identity matrix. Note, in particular, that with k = we have proven that the identity transfmation has the identity matrix as its representing matrix, no matter what basis is used f V. Page 8 of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
9 Math HWK b Solns contd 8. p99 Problem, 8. p99. Assume that B = {v, v, v, v } is a basis f some vect space V. Find the matrix with respect to B f the linear operat T : V V defined by the conditions T(v ) = v, T(v ) = v, T(v ) = v, T(v ) = v Solution. Finally, a nice simple problem. Denote the desired matrix by A. From T(v ) = v we conclude that the first column of A has the entries,,,, in that der. The entries in the second column are,,,, in that der. Those in the third column are,,,, and those in the fourth are,,,. Thus A = Problem 8b, 8. p99. Let D : P P be the differentiation operat (i.e. D(p) is the derivative function p ). Find the matrix f D relative to the basis B = {p, p, p }, given that p (x) =, p (x) = x, p (x) = x + 8x Solution. Let A be the specified matrix f D. A little bit of calculus mixed with a little bit of algebra gives us D(p ) = = p + p + p D(p ) = = p + p + p D(p ) = + x = p p + p so that A = = 9. Page 9 of 9 A. Sontag April 9,
Mathematics 206 Solutions for HWK 23 Section 6.3 p358
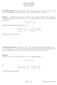 Mathematics 6 Solutions for HWK Section Problem 9. Given T(x, y, z) = (x 9y + z,6x + 5y z) and v = (,,), use the standard matrix for the linear transformation T to find the image of the vector v. Note
Mathematics 6 Solutions for HWK Section Problem 9. Given T(x, y, z) = (x 9y + z,6x + 5y z) and v = (,,), use the standard matrix for the linear transformation T to find the image of the vector v. Note
1 Last time: row reduction to (reduced) echelon form
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 8) Lecture Last time: row reduction to (reduced) echelon fm The leading entry in a nonzero row of a matrix is the first nonzero entry from left going right example, the row 7
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 8) Lecture Last time: row reduction to (reduced) echelon fm The leading entry in a nonzero row of a matrix is the first nonzero entry from left going right example, the row 7
Mathematics 206 Solutions for HWK 13b Section 5.2
 Mathematics 206 Solutions for HWK 13b Section 5.2 Section Problem 7ac. Which of the following are linear combinations of u = (0, 2,2) and v = (1, 3, 1)? (a) (2, 2,2) (c) (0,4, 5) Solution. Solution by
Mathematics 206 Solutions for HWK 13b Section 5.2 Section Problem 7ac. Which of the following are linear combinations of u = (0, 2,2) and v = (1, 3, 1)? (a) (2, 2,2) (c) (0,4, 5) Solution. Solution by
CALCULUS 3 February 6, st TEST
 MATH 400 (CALCULUS 3) Spring 008 1st TEST 1 CALCULUS 3 February, 008 1st TEST YOUR NAME: 001 A. Spina...(9am) 00 E. Wittenbn... (10am) 003 T. Dent...(11am) 004 J. Wiscons... (1pm) 005 A. Spina...(1pm)
MATH 400 (CALCULUS 3) Spring 008 1st TEST 1 CALCULUS 3 February, 008 1st TEST YOUR NAME: 001 A. Spina...(9am) 00 E. Wittenbn... (10am) 003 T. Dent...(11am) 004 J. Wiscons... (1pm) 005 A. Spina...(1pm)
Mathematics 205 HWK 18 Solutions Section 15.3 p725
 Mathematics 205 HWK 18 Solutions Section 15.3 p725 Problem 3, 15.3, p725. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values, if they exist, of f(x, y) = 3x 2y subject to the constraint x
Mathematics 205 HWK 18 Solutions Section 15.3 p725 Problem 3, 15.3, p725. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values, if they exist, of f(x, y) = 3x 2y subject to the constraint x
Direct Sums and Invariants. Direct Sums
 Math 5327 Direct Sums and Invariants Direct Sums Suppose that W and W 2 are both subspaces of a vector space V Recall from Chapter 2 that the sum W W 2 is the set "u v u " W v " W 2 # That is W W 2 is
Math 5327 Direct Sums and Invariants Direct Sums Suppose that W and W 2 are both subspaces of a vector space V Recall from Chapter 2 that the sum W W 2 is the set "u v u " W v " W 2 # That is W W 2 is
Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, and Diagonalization
 Math 240 TA: Shuyi Weng Winter 207 February 23, 207 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, and Diagonalization The concepts of eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and diagonalization are best studied with examples. We will
Math 240 TA: Shuyi Weng Winter 207 February 23, 207 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, and Diagonalization The concepts of eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and diagonalization are best studied with examples. We will
MTH5102 Spring 2017 HW Assignment 1: Prob. Set; Sec. 1.2, #7, 8, 12, 13, 20, 21 The due date for this assignment is 1/18/17.
 MTH5102 Spring 2017 HW Assignment 1: Prob. Set; Sec. 1.2, #7, 8, 12, 13, 20, 21 The due date for this assignment is 1/18/17. 7. Let S = {0, 1} and F = R. In F (S, R), show that f = g and f + g = h, where
MTH5102 Spring 2017 HW Assignment 1: Prob. Set; Sec. 1.2, #7, 8, 12, 13, 20, 21 The due date for this assignment is 1/18/17. 7. Let S = {0, 1} and F = R. In F (S, R), show that f = g and f + g = h, where
MATH Linear Algebra
 MATH 304 - Linear Algebra In the previous note we learned an important algorithm to produce orthogonal sequences of vectors called the Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization process. Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
MATH 304 - Linear Algebra In the previous note we learned an important algorithm to produce orthogonal sequences of vectors called the Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization process. Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
ftdt. We often drop the parentheses and write Tf instead of Tf. We could also write in this example Tfx 0
 Linear algebra: The study of linear transformations on vector spaces. Q: What s a linear transformation? What s a vector space? Linear transformations and matrices: We first discuss linear transformations
Linear algebra: The study of linear transformations on vector spaces. Q: What s a linear transformation? What s a vector space? Linear transformations and matrices: We first discuss linear transformations
Mathematics 205 Solutions for HWK 23. e x2 +y 2 dxdy
 Mathematics 5 Solutions for HWK Problem 1. 6. p7. Let D be the unit disk: x + y 1. Evaluate the integral e x +y dxdy by making a change of variables to polar coordinates. D Solution. Step 1. The integrand,
Mathematics 5 Solutions for HWK Problem 1. 6. p7. Let D be the unit disk: x + y 1. Evaluate the integral e x +y dxdy by making a change of variables to polar coordinates. D Solution. Step 1. The integrand,
1 Last time: inverses
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 8) Lecture 8 Last time: inverses The following all mean the same thing for a function f : X Y : f is invertible f is one-to-one and onto 3 For each b Y there is exactly one a
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 8) Lecture 8 Last time: inverses The following all mean the same thing for a function f : X Y : f is invertible f is one-to-one and onto 3 For each b Y there is exactly one a
Linear transformations
 Linear Algebra with Computer Science Application February 5, 208 Review. Review: linear combinations Given vectors v, v 2,..., v p in R n and scalars c, c 2,..., c p, the vector w defined by w = c v +
Linear Algebra with Computer Science Application February 5, 208 Review. Review: linear combinations Given vectors v, v 2,..., v p in R n and scalars c, c 2,..., c p, the vector w defined by w = c v +
EXERCISE SET 5.1. = (kx + kx + k, ky + ky + k ) = (kx + kx + 1, ky + ky + 1) = ((k + )x + 1, (k + )y + 1)
 EXERCISE SET 5. 6. The pair (, 2) is in the set but the pair ( )(, 2) = (, 2) is not because the first component is negative; hence Axiom 6 fails. Axiom 5 also fails. 8. Axioms, 2, 3, 6, 9, and are easily
EXERCISE SET 5. 6. The pair (, 2) is in the set but the pair ( )(, 2) = (, 2) is not because the first component is negative; hence Axiom 6 fails. Axiom 5 also fails. 8. Axioms, 2, 3, 6, 9, and are easily
Math 54 Homework 3 Solutions 9/
 Math 54 Homework 3 Solutions 9/4.8.8.2 0 0 3 3 0 0 3 6 2 9 3 0 0 3 0 0 3 a a/3 0 0 3 b b/3. c c/3 0 0 3.8.8 The number of rows of a matrix is the size (dimension) of the space it maps to; the number of
Math 54 Homework 3 Solutions 9/4.8.8.2 0 0 3 3 0 0 3 6 2 9 3 0 0 3 0 0 3 a a/3 0 0 3 b b/3. c c/3 0 0 3.8.8 The number of rows of a matrix is the size (dimension) of the space it maps to; the number of
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors week -2 Fall 26 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors The most simple linear transformation from R n to R n may be the transformation of the form: T (x,,, x n ) (λ x, λ 2,, λ n x n
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors week -2 Fall 26 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors The most simple linear transformation from R n to R n may be the transformation of the form: T (x,,, x n ) (λ x, λ 2,, λ n x n
MATH 145 Algebra, Solutions to Assignment 4
 MATH 145 Algebra, Solutions to Assignment 4 1: a Let a 975 and b161 Find d gcda, b and find s, t Z such that as + bt d Solution: The Euclidean Algorithm gives 161 975 1 + 86, 975 86 3 + 117, 86 117 + 5,
MATH 145 Algebra, Solutions to Assignment 4 1: a Let a 975 and b161 Find d gcda, b and find s, t Z such that as + bt d Solution: The Euclidean Algorithm gives 161 975 1 + 86, 975 86 3 + 117, 86 117 + 5,
Linear Algebra. 1.1 Introduction to vectors 1.2 Lengths and dot products. January 28th, 2013 Math 301. Monday, January 28, 13
 Linear Algebra 1.1 Introduction to vectors 1.2 Lengths and dot products January 28th, 2013 Math 301 Notation for linear systems 12w +4x + 23y +9z =0 2u + v +5w 2x +2y +8z =1 5u + v 6w +2x +4y z =6 8u 4v
Linear Algebra 1.1 Introduction to vectors 1.2 Lengths and dot products January 28th, 2013 Math 301 Notation for linear systems 12w +4x + 23y +9z =0 2u + v +5w 2x +2y +8z =1 5u + v 6w +2x +4y z =6 8u 4v
Lecture 16: 9.2 Geometry of Linear Operators
 Lecture 16: 9.2 Geometry of Linear Operators Wei-Ta Chu 2008/11/19 Theorem 9.2.1 If T: R 2 R 2 is multiplication by an invertible matrix A, then the geometric effect of T is the same as an appropriate
Lecture 16: 9.2 Geometry of Linear Operators Wei-Ta Chu 2008/11/19 Theorem 9.2.1 If T: R 2 R 2 is multiplication by an invertible matrix A, then the geometric effect of T is the same as an appropriate
Mathematics 116 HWK 25a Solutions 8.6 p610
 Mathematics 6 HWK 5a Solutions 8.6 p6 Problem, 8.6, p6 Fin a power series representation for the function f() = etermine the interval of convergence. an Solution. Begin with the geometric series = + +
Mathematics 6 HWK 5a Solutions 8.6 p6 Problem, 8.6, p6 Fin a power series representation for the function f() = etermine the interval of convergence. an Solution. Begin with the geometric series = + +
Calculus I Homework: The Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Page 1
 Calculus I Homework: The Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Page 1 Questions Example Differentiate the function y = ae v + b v + c v 2. Example Differentiate the function y = A + B x
Calculus I Homework: The Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Page 1 Questions Example Differentiate the function y = ae v + b v + c v 2. Example Differentiate the function y = A + B x
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 5. Eigenvectors & Eigenvalues Math 233 Linear Algebra 5. Eigenvectors & Eigenvalues Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan Chiu,
5. Eigenvectors & Eigenvalues Math 233 Linear Algebra 5. Eigenvectors & Eigenvalues Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan Chiu,
Matrices related to linear transformations
 Math 4326 Fall 207 Matrices related to linear transformations We have encountered several ways in which matrices relate to linear transformations. In this note, I summarize the important facts and formulas
Math 4326 Fall 207 Matrices related to linear transformations We have encountered several ways in which matrices relate to linear transformations. In this note, I summarize the important facts and formulas
Math 24 Spring 2012 Questions (mostly) from the Textbook
 Math 24 Spring 2012 Questions (mostly) from the Textbook 1. TRUE OR FALSE? (a) The zero vector space has no basis. (F) (b) Every vector space that is generated by a finite set has a basis. (c) Every vector
Math 24 Spring 2012 Questions (mostly) from the Textbook 1. TRUE OR FALSE? (a) The zero vector space has no basis. (F) (b) Every vector space that is generated by a finite set has a basis. (c) Every vector
Math 113 Solutions: Homework 8. November 28, 2007
 Math 113 Solutions: Homework 8 November 28, 27 3) Define c j = ja j, d j = 1 j b j, for j = 1, 2,, n Let c = c 1 c 2 c n and d = vectors in R n Then the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality on Euclidean n-space gives
Math 113 Solutions: Homework 8 November 28, 27 3) Define c j = ja j, d j = 1 j b j, for j = 1, 2,, n Let c = c 1 c 2 c n and d = vectors in R n Then the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality on Euclidean n-space gives
System of Linear Equations
 Math 20F Linear Algebra Lecture 2 1 System of Linear Equations Slide 1 Definition 1 Fix a set of numbers a ij, b i, where i = 1,, m and j = 1,, n A system of m linear equations in n variables x j, is given
Math 20F Linear Algebra Lecture 2 1 System of Linear Equations Slide 1 Definition 1 Fix a set of numbers a ij, b i, where i = 1,, m and j = 1,, n A system of m linear equations in n variables x j, is given
Properties of Transformations
 6. - 6.4 Properties of Transformations P. Danziger Transformations from R n R m. General Transformations A general transformation maps vectors in R n to vectors in R m. We write T : R n R m to indicate
6. - 6.4 Properties of Transformations P. Danziger Transformations from R n R m. General Transformations A general transformation maps vectors in R n to vectors in R m. We write T : R n R m to indicate
Systems. x 1 = ax 1 + bx 2, x 2 = cx 1 + dx 2,
 Systems We consider systems of differential equations of the fm x ax + bx, x cx + dx, where a,b,c, and d are real numbers At first glance the system may seem to be first-der; however, it is coupled, and
Systems We consider systems of differential equations of the fm x ax + bx, x cx + dx, where a,b,c, and d are real numbers At first glance the system may seem to be first-der; however, it is coupled, and
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET
 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
Finite. U-46 Curriculum Scope and Sequence. Reporting Strand Instructional Focus Standards Semester. Represent linear equations in matrices.
 Finite U-46 Curriculum Scope and Sequence Repting Strand Instructional Focus Standards Semester Represent linear equations in matrices. A.REI.8, A.REI.9 Matrices Perfm operations on matrices and use matrices
Finite U-46 Curriculum Scope and Sequence Repting Strand Instructional Focus Standards Semester Represent linear equations in matrices. A.REI.8, A.REI.9 Matrices Perfm operations on matrices and use matrices
Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra
 2.3 Composition Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra 2.3 Composition of Linear Transformations Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math4377
2.3 Composition Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra 2.3 Composition of Linear Transformations Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math4377
1 Last time: least-squares problems
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 07) Lecture Last time: least-squares problems Definition. If A is an m n matrix and b R m, then a least-squares solution to the linear system Ax = b is a vector x R n such that
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 07) Lecture Last time: least-squares problems Definition. If A is an m n matrix and b R m, then a least-squares solution to the linear system Ax = b is a vector x R n such that
ENGINEERING MATH 1 Fall 2009 VECTOR SPACES
 ENGINEERING MATH 1 Fall 2009 VECTOR SPACES A vector space, more specifically, a real vector space (as opposed to a complex one or some even stranger ones) is any set that is closed under an operation of
ENGINEERING MATH 1 Fall 2009 VECTOR SPACES A vector space, more specifically, a real vector space (as opposed to a complex one or some even stranger ones) is any set that is closed under an operation of
1.2 LECTURE 2. Scalar Product
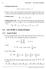 6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
MODEL PAPER - I MATHEMATICS. Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100
 MODEL PAPER - I MATHEMATICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maimum marks : General Instructions. All questions are compulsy.. The question paper consists of 9 questions divided into three sections A, B and C. Section
MODEL PAPER - I MATHEMATICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maimum marks : General Instructions. All questions are compulsy.. The question paper consists of 9 questions divided into three sections A, B and C. Section
Linear Equations in Linear Algebra
 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.3 VECTOR EQUATIONS VECTOR EQUATIONS Vectors in 2 A matrix with only one column is called a column vector, or simply a vector. An example of a vector with two entries
1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.3 VECTOR EQUATIONS VECTOR EQUATIONS Vectors in 2 A matrix with only one column is called a column vector, or simply a vector. An example of a vector with two entries
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations. Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve:
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
1. 10 apples for $6 is $0.60 per apple. 20 apples for $10 is $0.50 per apple. 25 $ $0.50 = 25 $0.10 = $2.50
 Fall 205. 0 apples for $6 is $0.60 per apple. 20 apples for $0 is $0.50 per apple. So the answer is B. $2.50 25 $0.60 25 $0.50 = 25 $0.0 = $2.50 2. Let s begin by finding the slopes of the two lines. ax
Fall 205. 0 apples for $6 is $0.60 per apple. 20 apples for $0 is $0.50 per apple. So the answer is B. $2.50 25 $0.60 25 $0.50 = 25 $0.0 = $2.50 2. Let s begin by finding the slopes of the two lines. ax
8. Diagonalization.
 8. Diagonalization 8.1. Matrix Representations of Linear Transformations Matrix of A Linear Operator with Respect to A Basis We know that every linear transformation T: R n R m has an associated standard
8. Diagonalization 8.1. Matrix Representations of Linear Transformations Matrix of A Linear Operator with Respect to A Basis We know that every linear transformation T: R n R m has an associated standard
Calculus II - Basic Matrix Operations
 Calculus II - Basic Matrix Operations Ryan C Daileda Terminology A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, for example 7,, 7 7 9, or / / /4 / / /4 / / /4 / /6 The numbers in any matrix are called its
Calculus II - Basic Matrix Operations Ryan C Daileda Terminology A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, for example 7,, 7 7 9, or / / /4 / / /4 / / /4 / /6 The numbers in any matrix are called its
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET
 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson
 Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson Name: TA Name and section: NO CALCULATORS, SHOW ALL WORK, NO OTHER PAPERS ON DESK. There is very little actual work to be done on this exam if
Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson Name: TA Name and section: NO CALCULATORS, SHOW ALL WORK, NO OTHER PAPERS ON DESK. There is very little actual work to be done on this exam if
Two Dimensional Linear Systems of ODEs
 34 CHAPTER 3 Two Dimensional Linear Sstems of ODEs A first-der, autonomous, homogeneous linear sstem of two ODEs has the fm x t ax + b, t cx + d where a, b, c, d are real constants The matrix fm is 31
34 CHAPTER 3 Two Dimensional Linear Sstems of ODEs A first-der, autonomous, homogeneous linear sstem of two ODEs has the fm x t ax + b, t cx + d where a, b, c, d are real constants The matrix fm is 31
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
We consider systems of differential equations of the form. x 1 = ax 1 + bx 2,
 Chapter 5 Systems We consider systems of differential equations of the fm (5) a + b, c + d, where a, b, c, and d are real numbers At first glance the system may seem to be first-der; however, it is coupled,
Chapter 5 Systems We consider systems of differential equations of the fm (5) a + b, c + d, where a, b, c, and d are real numbers At first glance the system may seem to be first-der; however, it is coupled,
Schur s Triangularization Theorem. Math 422
 Schur s Triangularization Theorem Math 4 The characteristic polynomial p (t) of a square complex matrix A splits as a product of linear factors of the form (t λ) m Of course, finding these factors is a
Schur s Triangularization Theorem Math 4 The characteristic polynomial p (t) of a square complex matrix A splits as a product of linear factors of the form (t λ) m Of course, finding these factors is a
Linear Algebra (MATH ) Spring 2011 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions
 Linear Algebra (MATH 4) Spring 2 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions Instructions: Try the following on your own, then use the book and notes where you need help. Afterwards, check your solutions with
Linear Algebra (MATH 4) Spring 2 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions Instructions: Try the following on your own, then use the book and notes where you need help. Afterwards, check your solutions with
Linear independence, span, basis, dimension - and their connection with linear systems
 Linear independence span basis dimension - and their connection with linear systems Linear independence of a set of vectors: We say the set of vectors v v..v k is linearly independent provided c v c v..c
Linear independence span basis dimension - and their connection with linear systems Linear independence of a set of vectors: We say the set of vectors v v..v k is linearly independent provided c v c v..c
Column 3 is fine, so it remains to add Row 2 multiplied by 2 to Row 1. We obtain
 Section Exercise : We are given the following augumented matrix 3 7 6 3 We have to bring it to the diagonal form The entries below the diagonal are already zero, so we work from bottom to top Adding the
Section Exercise : We are given the following augumented matrix 3 7 6 3 We have to bring it to the diagonal form The entries below the diagonal are already zero, so we work from bottom to top Adding the
Span and Linear Independence
 Span and Linear Independence It is common to confuse span and linear independence, because although they are different concepts, they are related. To see their relationship, let s revisit the previous
Span and Linear Independence It is common to confuse span and linear independence, because although they are different concepts, they are related. To see their relationship, let s revisit the previous
Homework For each of the following matrices, find the minimal polynomial and determine whether the matrix is diagonalizable.
 Math 5327 Fall 2018 Homework 7 1. For each of the following matrices, find the minimal polynomial and determine whether the matrix is diagonalizable. 3 1 0 (a) A = 1 2 0 1 1 0 x 3 1 0 Solution: 1 x 2 0
Math 5327 Fall 2018 Homework 7 1. For each of the following matrices, find the minimal polynomial and determine whether the matrix is diagonalizable. 3 1 0 (a) A = 1 2 0 1 1 0 x 3 1 0 Solution: 1 x 2 0
Chapter 2: Linear Independence and Bases
 MATH20300: Linear Algebra 2 (2016 Chapter 2: Linear Independence and Bases 1 Linear Combinations and Spans Example 11 Consider the vector v (1, 1 R 2 What is the smallest subspace of (the real vector space
MATH20300: Linear Algebra 2 (2016 Chapter 2: Linear Independence and Bases 1 Linear Combinations and Spans Example 11 Consider the vector v (1, 1 R 2 What is the smallest subspace of (the real vector space
Announcements September 19
 Announcements September 19 Please complete the mid-semester CIOS survey this week The first midterm will take place during recitation a week from Friday, September 3 It covers Chapter 1, sections 1 5 and
Announcements September 19 Please complete the mid-semester CIOS survey this week The first midterm will take place during recitation a week from Friday, September 3 It covers Chapter 1, sections 1 5 and
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated )
 Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
Solutions to Final Exam 2011 (Total: 100 pts)
 Page of 5 Introduction to Linear Algebra November 7, Solutions to Final Exam (Total: pts). Let T : R 3 R 3 be a linear transformation defined by: (5 pts) T (x, x, x 3 ) = (x + 3x + x 3, x x x 3, x + 3x
Page of 5 Introduction to Linear Algebra November 7, Solutions to Final Exam (Total: pts). Let T : R 3 R 3 be a linear transformation defined by: (5 pts) T (x, x, x 3 ) = (x + 3x + x 3, x x x 3, x + 3x
Math Lecture 26 : The Properties of Determinants
 Math 2270 - Lecture 26 : The Properties of Determinants Dylan Zwick Fall 202 The lecture covers section 5. from the textbook. The determinant of a square matrix is a number that tells you quite a bit about
Math 2270 - Lecture 26 : The Properties of Determinants Dylan Zwick Fall 202 The lecture covers section 5. from the textbook. The determinant of a square matrix is a number that tells you quite a bit about
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 7 Spring Practice problems for April Exam Problem Use the method of elimination to find the x-component of the general solution of x y = 6x 9x + y = x 6y 9y Soln: The system
Differential equations Math 7 Spring Practice problems for April Exam Problem Use the method of elimination to find the x-component of the general solution of x y = 6x 9x + y = x 6y 9y Soln: The system
Elementary maths for GMT
 Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 2: Matrices, Elimination and Determinant m n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1
Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 2: Matrices, Elimination and Determinant m n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1
2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution.
 1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
Linear Equations in Linear Algebra
 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.4 THE MATRIX EQUATION A = b MATRIX EQUATION A = b m n Definition: If A is an matri, with columns a 1, n, a n, and if is in, then the product of A and, denoted by
1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.4 THE MATRIX EQUATION A = b MATRIX EQUATION A = b m n Definition: If A is an matri, with columns a 1, n, a n, and if is in, then the product of A and, denoted by
MAT1302F Mathematical Methods II Lecture 19
 MAT302F Mathematical Methods II Lecture 9 Aaron Christie 2 April 205 Eigenvectors, Eigenvalues, and Diagonalization Now that the basic theory of eigenvalues and eigenvectors is in place most importantly
MAT302F Mathematical Methods II Lecture 9 Aaron Christie 2 April 205 Eigenvectors, Eigenvalues, and Diagonalization Now that the basic theory of eigenvalues and eigenvectors is in place most importantly
Math Linear algebra, Spring Semester Dan Abramovich
 Math 52 - Linear algebra, Spring Semester 22-23 Dan Abramovich Review We saw: an algorithm - row reduction, bringing to reduced echelon form - answers the questions: - consistency (no pivot on right) -
Math 52 - Linear algebra, Spring Semester 22-23 Dan Abramovich Review We saw: an algorithm - row reduction, bringing to reduced echelon form - answers the questions: - consistency (no pivot on right) -
1 Matrices and matrix algebra
 1 Matrices and matrix algebra 1.1 Examples of matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and/or variables. For instance 4 2 0 3 1 A = 5 1.2 0.7 x 3 π 3 4 6 27 is a matrix with 3 rows and 5 columns
1 Matrices and matrix algebra 1.1 Examples of matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and/or variables. For instance 4 2 0 3 1 A = 5 1.2 0.7 x 3 π 3 4 6 27 is a matrix with 3 rows and 5 columns
From Completing the Squares and Orthogonal Projection to Finite Element Methods
 From Completing the Squares and Orthogonal Projection to Finite Element Methods Mo MU Background In scientific computing, it is important to start with an appropriate model in order to design effective
From Completing the Squares and Orthogonal Projection to Finite Element Methods Mo MU Background In scientific computing, it is important to start with an appropriate model in order to design effective
Definition 1. A set V is a vector space over the scalar field F {R, C} iff. there are two operations defined on V, called vector addition
 6 Vector Spaces with Inned Product Basis and Dimension Section Objective(s): Vector Spaces and Subspaces Linear (In)dependence Basis and Dimension Inner Product 6 Vector Spaces and Subspaces Definition
6 Vector Spaces with Inned Product Basis and Dimension Section Objective(s): Vector Spaces and Subspaces Linear (In)dependence Basis and Dimension Inner Product 6 Vector Spaces and Subspaces Definition
Solving a system by back-substitution, checking consistency of a system (no rows of the form
 MATH 520 LEARNING OBJECTIVES SPRING 2017 BROWN UNIVERSITY SAMUEL S. WATSON Week 1 (23 Jan through 27 Jan) Definition of a system of linear equations, definition of a solution of a linear system, elementary
MATH 520 LEARNING OBJECTIVES SPRING 2017 BROWN UNIVERSITY SAMUEL S. WATSON Week 1 (23 Jan through 27 Jan) Definition of a system of linear equations, definition of a solution of a linear system, elementary
Final Exam Practice Problems Answers Math 24 Winter 2012
 Final Exam Practice Problems Answers Math 4 Winter 0 () The Jordan product of two n n matrices is defined as A B = (AB + BA), where the products inside the parentheses are standard matrix product. Is the
Final Exam Practice Problems Answers Math 4 Winter 0 () The Jordan product of two n n matrices is defined as A B = (AB + BA), where the products inside the parentheses are standard matrix product. Is the
Linear Algebra (Math-324) Lecture Notes
 Linear Algebra (Math-324) Lecture Notes Dr. Ali Koam and Dr. Azeem Haider September 24, 2017 c 2017,, Jazan All Rights Reserved 1 Contents 1 Real Vector Spaces 6 2 Subspaces 11 3 Linear Combination and
Linear Algebra (Math-324) Lecture Notes Dr. Ali Koam and Dr. Azeem Haider September 24, 2017 c 2017,, Jazan All Rights Reserved 1 Contents 1 Real Vector Spaces 6 2 Subspaces 11 3 Linear Combination and
Mathematics 116 HWK 14 Solutions Section 4.5 p305. Note: This set of solutions also includes 3 problems from HWK 12 (5,7,11 from 4.5).
 Mathematics 6 HWK 4 Solutions Section 4.5 p305 Note: This set of solutions also includes 3 problems from HWK 2 (5,7, from 4.5). Find the indicated it. Use l Hospital s Rule where appropriate. Consider
Mathematics 6 HWK 4 Solutions Section 4.5 p305 Note: This set of solutions also includes 3 problems from HWK 2 (5,7, from 4.5). Find the indicated it. Use l Hospital s Rule where appropriate. Consider
1 Last time: multiplying vectors matrices
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 7) Lecture Last time: multiplying vectors matrices Given a matrix A = a a a n a a a n and a vector v = a m a m a mn Av = v a a + v a a v v + + Rn we define a n a n a m a m a mn
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 7) Lecture Last time: multiplying vectors matrices Given a matrix A = a a a n a a a n and a vector v = a m a m a mn Av = v a a + v a a v v + + Rn we define a n a n a m a m a mn
Matrix-Vector Products and the Matrix Equation Ax = b
 Matrix-Vector Products and the Matrix Equation Ax = b A. Havens Department of Mathematics University of Massachusetts, Amherst January 31, 2018 Outline 1 Matrices Acting on Vectors Linear Combinations
Matrix-Vector Products and the Matrix Equation Ax = b A. Havens Department of Mathematics University of Massachusetts, Amherst January 31, 2018 Outline 1 Matrices Acting on Vectors Linear Combinations
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP Contents. 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2
 MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 10: Inverse matrix. Change of coordinates.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 10: Inverse matrix. Change of coordinates. Let V be a vector space and α = [v 1,...,v n ] be an ordered basis for V. Theorem 1 The coordinate mapping C : V F n given
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 10: Inverse matrix. Change of coordinates. Let V be a vector space and α = [v 1,...,v n ] be an ordered basis for V. Theorem 1 The coordinate mapping C : V F n given
Vectors: Introduction
 Vectors: Introduction Calculus II Josh Engwer TTU 23 April 2014 Josh Engwer (TTU) Vectors: Introduction 23 April 2014 1 / 30 Vectors & Scalars (Definition) Definition A vector v is a quantity that bears
Vectors: Introduction Calculus II Josh Engwer TTU 23 April 2014 Josh Engwer (TTU) Vectors: Introduction 23 April 2014 1 / 30 Vectors & Scalars (Definition) Definition A vector v is a quantity that bears
CHAPTER 1. FUNCTIONS 7
 CHAPTER 1. FUNCTIONS 7 1.3.2 Polynomials A polynomial is a function P with a general form P (x) a 0 + a 1 x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n, (1.4) where the coe cients a i (i 0, 1,...,n) are numbers and n is a non-negative
CHAPTER 1. FUNCTIONS 7 1.3.2 Polynomials A polynomial is a function P with a general form P (x) a 0 + a 1 x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n, (1.4) where the coe cients a i (i 0, 1,...,n) are numbers and n is a non-negative
Least Squares Regression
 Least Squares Regression Chemical Engineering 2450 - Numerical Methods Given N data points x i, y i, i 1 N, and a function that we wish to fit to these data points, fx, we define S as the sum of the squared
Least Squares Regression Chemical Engineering 2450 - Numerical Methods Given N data points x i, y i, i 1 N, and a function that we wish to fit to these data points, fx, we define S as the sum of the squared
Transformations and A Universal First Order Taylor Expansion
 Transformations and A Universal First Order Taylor Expansion MATH 1502 Calculus II Notes September 29, 2008 The first order Taylor approximation for f : R R at x = x 0 is given by P 1 (x) = f (x 0 )(x
Transformations and A Universal First Order Taylor Expansion MATH 1502 Calculus II Notes September 29, 2008 The first order Taylor approximation for f : R R at x = x 0 is given by P 1 (x) = f (x 0 )(x
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 0: Eigenvalues and diagonalization Section Eigenvalues and eigenvectors What you need to know already: Basic properties of linear transformations. Linear systems
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 0: Eigenvalues and diagonalization Section Eigenvalues and eigenvectors What you need to know already: Basic properties of linear transformations. Linear systems
SOLUTION OF THE ULAM STABILITY PROBLEM FOR CUBIC MAPPINGS. John Michael Rassias National and Capodistrian University of Athens, Greece
 GLASNIK MATEMATIČKI Vol. 36(56)(2001), 63 72 SOLUTION OF THE ULAM STABILITY PROBLEM FOR CUBIC MAPPINGS John Michael Rassias National and Capodistrian University of Athens, Greece Abstract. In 1968 S. M.
GLASNIK MATEMATIČKI Vol. 36(56)(2001), 63 72 SOLUTION OF THE ULAM STABILITY PROBLEM FOR CUBIC MAPPINGS John Michael Rassias National and Capodistrian University of Athens, Greece Abstract. In 1968 S. M.
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 12: Review for Test 1.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 12: Review for Test 1. Topics for Test 1 Vector spaces (F/I/S 1.1 1.7, 2.2, 2.4) Vector spaces: axioms and basic properties. Basic examples of vector spaces (coordinate
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 12: Review for Test 1. Topics for Test 1 Vector spaces (F/I/S 1.1 1.7, 2.2, 2.4) Vector spaces: axioms and basic properties. Basic examples of vector spaces (coordinate
Math 224, Fall 2007 Exam 3 Thursday, December 6, 2007
 Math 224, Fall 2007 Exam 3 Thursday, December 6, 2007 You have 1 hour and 20 minutes. No notes, books, or other references. You are permitted to use Maple during this exam, but you must start with a blank
Math 224, Fall 2007 Exam 3 Thursday, December 6, 2007 You have 1 hour and 20 minutes. No notes, books, or other references. You are permitted to use Maple during this exam, but you must start with a blank
. Let us consider the point P with coordinates y = R, z =0,0 x L. Evaluate the principal stresses and the principal stress directions.
 14 3. The linear 3-D elasticity mathematical model and substituting in (3.94) gives (n 1 ) =1 (n ) ( ) t n =λ 1 ( 1 (n ) ( ) ) + λ (n ) + λ 3 ( ) t n =λ 1 +(λ λ 1 )(n ) +(λ 3 λ 1 )( ). (3.95) Since λ 1
14 3. The linear 3-D elasticity mathematical model and substituting in (3.94) gives (n 1 ) =1 (n ) ( ) t n =λ 1 ( 1 (n ) ( ) ) + λ (n ) + λ 3 ( ) t n =λ 1 +(λ λ 1 )(n ) +(λ 3 λ 1 )( ). (3.95) Since λ 1
Chapter 4 & 5: Vector Spaces & Linear Transformations
 Chapter 4 & 5: Vector Spaces & Linear Transformations Philip Gressman University of Pennsylvania Philip Gressman Math 240 002 2014C: Chapters 4 & 5 1 / 40 Objective The purpose of Chapter 4 is to think
Chapter 4 & 5: Vector Spaces & Linear Transformations Philip Gressman University of Pennsylvania Philip Gressman Math 240 002 2014C: Chapters 4 & 5 1 / 40 Objective The purpose of Chapter 4 is to think
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54. Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues A = P DP 1 A = P DP T.
 Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54 Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues λ 1,, λ n (possibly repeated), and R n has an orthonormal basis v 1,, v n, where
Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54 Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues λ 1,, λ n (possibly repeated), and R n has an orthonormal basis v 1,, v n, where
Linear Algebra (wi1403lr) Lecture no.4
 Linear Algebra (wi1403lr) Lecture no.4 EWI / DIAM / Numerical Analysis group Matthias Möller 29/04/2014 M. Möller (EWI/NA group) LA (wi1403lr) 29/04/2014 1 / 28 Review of lecture no.3 1.5 Solution Sets
Linear Algebra (wi1403lr) Lecture no.4 EWI / DIAM / Numerical Analysis group Matthias Möller 29/04/2014 M. Möller (EWI/NA group) LA (wi1403lr) 29/04/2014 1 / 28 Review of lecture no.3 1.5 Solution Sets
MTH 362: Advanced Engineering Mathematics
 MTH 362: Advanced Engineering Mathematics Lecture 5 Jonathan A. Chávez Casillas 1 1 University of Rhode Island Department of Mathematics September 26, 2017 1 Linear Independence and Dependence of Vectors
MTH 362: Advanced Engineering Mathematics Lecture 5 Jonathan A. Chávez Casillas 1 1 University of Rhode Island Department of Mathematics September 26, 2017 1 Linear Independence and Dependence of Vectors
5.1 Polynomial Functions
 5.1 Polynomial Functions In this section, we will study the following topics: Identifying polynomial functions and their degree Determining end behavior of polynomial graphs Finding real zeros of polynomial
5.1 Polynomial Functions In this section, we will study the following topics: Identifying polynomial functions and their degree Determining end behavior of polynomial graphs Finding real zeros of polynomial
Homework 2 Solutions
 Math 312, Spring 2014 Jerry L. Kazdan Homework 2 s 1. [Bretscher, Sec. 1.2 #44] The sketch represents a maze of one-way streets in a city. The trac volume through certain blocks during an hour has been
Math 312, Spring 2014 Jerry L. Kazdan Homework 2 s 1. [Bretscher, Sec. 1.2 #44] The sketch represents a maze of one-way streets in a city. The trac volume through certain blocks during an hour has been
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS
 MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
SECTION 3.3. PROBLEM 22. The null space of a matrix A is: N(A) = {X : AX = 0}. Here are the calculations of AX for X = a,b,c,d, and e. =
 SECTION 3.3. PROBLEM. The null space of a matrix A is: N(A) {X : AX }. Here are the calculations of AX for X a,b,c,d, and e. Aa [ ][ ] 3 3 [ ][ ] Ac 3 3 [ ] 3 3 [ ] 4+4 6+6 Ae [ ], Ab [ ][ ] 3 3 3 [ ]
SECTION 3.3. PROBLEM. The null space of a matrix A is: N(A) {X : AX }. Here are the calculations of AX for X a,b,c,d, and e. Aa [ ][ ] 3 3 [ ][ ] Ac 3 3 [ ] 3 3 [ ] 4+4 6+6 Ae [ ], Ab [ ][ ] 3 3 3 [ ]
Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 9. Systems of Equations Solve the system of equations below. By this we mean, find pair(s) of numbers (x, y) (if possible) that satisfy both equations.
Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 9. Systems of Equations Solve the system of equations below. By this we mean, find pair(s) of numbers (x, y) (if possible) that satisfy both equations.
MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam. Topics
 MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam This study sheet will not be allowed during the test Books and notes will not be allowed during the test Calculators and cell phones
MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam This study sheet will not be allowed during the test Books and notes will not be allowed during the test Calculators and cell phones
0.1 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 0.. EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS MATH 22AL Computer LAB for Linear Algebra Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Dr. Daddel Please save your MATLAB Session (diary)as LAB9.text and submit. 0. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
0.. EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS MATH 22AL Computer LAB for Linear Algebra Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Dr. Daddel Please save your MATLAB Session (diary)as LAB9.text and submit. 0. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
MATH 110: LINEAR ALGEBRA HOMEWORK #2
 MATH 11: LINEAR ALGEBRA HOMEWORK #2 1.5: Linear Dependence and Linear Independence Problem 1. (a) False. The set {(1, ), (, 1), (, 1)} is linearly dependent but (1, ) is not a linear combination of the
MATH 11: LINEAR ALGEBRA HOMEWORK #2 1.5: Linear Dependence and Linear Independence Problem 1. (a) False. The set {(1, ), (, 1), (, 1)} is linearly dependent but (1, ) is not a linear combination of the
Discovery Guide. Beautiful, mysterious woman pursued by gunmen. Sounds like a spy story...
 Dv G W C T Gp, A T Af Hk T 39 Sp. M Mx Hk p j p v, f M P v...(!) Af Hk T 39 Sp, B,,, UNMISSABLE! T - f 4 p v 150 f-p f x v. Bf, k 4 p v 150. H k f f x? D,,,, v? W k, pf p f p? W f f f? W k k p? T p xp
Dv G W C T Gp, A T Af Hk T 39 Sp. M Mx Hk p j p v, f M P v...(!) Af Hk T 39 Sp, B,,, UNMISSABLE! T - f 4 p v 150 f-p f x v. Bf, k 4 p v 150. H k f f x? D,,,, v? W k, pf p f p? W f f f? W k k p? T p xp
ICS 6N Computational Linear Algebra Vector Equations
 ICS 6N Computational Linear Algebra Vector Equations Xiaohui Xie University of California, Irvine xhx@uci.edu January 17, 2017 Xiaohui Xie (UCI) ICS 6N January 17, 2017 1 / 18 Vectors in R 2 An example
ICS 6N Computational Linear Algebra Vector Equations Xiaohui Xie University of California, Irvine xhx@uci.edu January 17, 2017 Xiaohui Xie (UCI) ICS 6N January 17, 2017 1 / 18 Vectors in R 2 An example
and let s calculate the image of some vectors under the transformation T.
 Chapter 5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 5. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Let T : R n R n be a linear transformation. Then T can be represented by a matrix (the standard matrix), and we can write T ( v) =
Chapter 5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 5. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Let T : R n R n be a linear transformation. Then T can be represented by a matrix (the standard matrix), and we can write T ( v) =
3.2 Real and complex symmetric bilinear forms
 Then, the adjoint of f is the morphism 3 f + : Q 3 Q 3 ; x 5 0 x. 0 2 3 As a verification, you can check that 3 0 B 5 0 0 = B 3 0 0. 0 0 2 3 3 2 5 0 3.2 Real and complex symmetric bilinear forms Throughout
Then, the adjoint of f is the morphism 3 f + : Q 3 Q 3 ; x 5 0 x. 0 2 3 As a verification, you can check that 3 0 B 5 0 0 = B 3 0 0. 0 0 2 3 3 2 5 0 3.2 Real and complex symmetric bilinear forms Throughout
MTH5102 Spring 2017 HW Assignment 2: Sec. 1.3, #8, 16, 28, 31; Sec. 1.4, #5 (a), (e), (g), 10 The due date for this assignment is 1/25/17.
 MTH510 Spring 017 HW Assignment : Sec. 1. #8 16 8 1; Sec. 1.4 #5 (a (e (g 10 The due date for this assignment is 1/5/17. Sec. 1. #8. Determine whether the following sets are subspaces of the vector space
MTH510 Spring 017 HW Assignment : Sec. 1. #8 16 8 1; Sec. 1.4 #5 (a (e (g 10 The due date for this assignment is 1/5/17. Sec. 1. #8. Determine whether the following sets are subspaces of the vector space
