Inverse magnetoelectric effect in disk samples of ferrite piezoelectric composites
|
|
|
- Meryl Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science Research ; ( : -8 Published online Aril, (htt:// doi:.648/j.sr.. Inverse agnetoelectric effect in disk sales of ferrite iezoelectric coosites D. A. Filiov, T. A. Galkina, V. M. Laletin Novgorod State University, Russia, Velikii Novgorod Institute of Technical Acoustics, Belarus, Vitebsk Eail address: Ditry.Filiov@novsu.ru (D. A. Filiov, taisiya_galkina@ail.ru (T. A. Galkina, laletin57@rabler.ru (V. M. Laletin To cite this article: D. A. Filiov, T. A. Galkina, V. M. Laletin. Inverse Magnetoelectric Effect in Disk Sales of Ferrite Piezoelectric Coosites. Science Research. Vol., No.,,. -8. doi:.648/j.sr.. Abstract: A theory of the inverse agnetoelectric (ME effect in the region of electroechanical resonance (EMR for the sales in the for of a disk is resented. The exression for the coefficient of inverse ME-conversion on the effective araeter ethod is derived. It is shown that observed the eak increase of effect in the region of electroechanical resonance, resonance frequencies are differed for direct and inverse agnetoelectric effect. Resonance frequencies deendence on ferrite ercentage for ferrite-nickel sinel and lead zirconate titanate sales are investigated exerientally. Keywords: Inverse Magnetoelectric Effect, Electroechanical Resonance. Introduction The agnetoelectric (ME effect is relate to cross effects and consists in that olarization aears in a sale under the action of a agnetic field (direct ME effect and, vice versa, agnetization aears uon the alication of an electric field (inverse ME effect. This effect which was originally redicted by Dzyaloshinskii [] and then observed in exerients [, ], is of interest not only for basic science, but for alications as well, since it coules the values, that has different tensor diensions: olarization (olar vector with agnetizing intensity (axial vector, and, vice versa, agnetization (axial vector with electric intensity (olar vector. Presence of the ME effect in onocrystal directly couled with crystal syetry [4], and its arising is ride by joint action of sin-orbit interaction, odd art of intracrystalline field and external electric field [5]. ME effect in the ferrite iezoelectric coosite is individually absent in ferrite and in iezoelectric hases. Its arising is condition on echanical interaction between agnetostriction and iezoelectric subsystes. In the ferrite coonent, echanical stresses arise due to agnetostriction in a agnetic field, that are transferred to the iezoelectric hase, where occur an electric olarization. And, vice versa, for the inverse effect, deforations induced in the iezoelectric hase under the action of an electric field are transferred to the ferrite hase, where the agnetostriction leads to agnetization of the sale. Presently, the direct ME effect is known in uch detail [6], whereas the inverse effect is still insufficiently studied and even the nuber of ublications on this henoenon is very restricted [7 ]. In this works inverse ME effect investigated exerientally for the sales in the for of a late, where was used lead zirconate titanate (PZT iezoceraic as the iezoelectric, and aterials with large agnetostriction coefficient as the ferrite, to be exact: in [7] D-Terfenol (three-layer structure D-Terfenol-PZT-D- Terfenol, in [8] nickel (three-layer structure PZT-Ni-PZT and in [9,] galfenol (two-ly structure galfenol-pzt. In the resent works realized the easureent of coefficient of inverse ME-conversion frequency deendence and exerientally discovered, that this deendence has resonant nature, in a siilar as ME voltage coefficient frequency deendence for the direct effect. However detailed theoretical descrition of the inverse ME effect it not realized in this works. In work [] it is shown the theoretical descrition of the inverse ME effect for the sales in the for of a late. However the sales in the for of a disk are uch often used in ractice, but not in the for of a late. But data of work [] for the sales in the for of a disk can not be used. Detailed theoretical descrition of the inverse ME effect and exeriental results for the ferrite-nickel sinel and lead zirconate titanate sales in the for of a disk are resented in this work.. Theory of Effect
2 Science Research, ( : -8.. Longitudinal Effect Effective araeter ethod was got wide sread occurrence at the descrition of hysical henoenon in the ferrite iezoelectric coosites [, ]. This ethod consists in that coosition aterial fro the acroscoic oint of view considered as a hoogeneous ediu with soe effective araeters, which are found by cobined solved equations of elasto- and electrodynaics for the ferrite and iezoelectric hases with following averaging. Aarently that this ethod can be used, when the characteristic diensions of coosite building blocks uch saller than sound-wave-length. As the characteristic diensions of the building blocks in the tyical coosition aterials are order the decade of icron, that this descrition ethod can be used as far as frequency order by a hundred MHz. Consider a odel syste corising a sale of the ferrite iezoelectric coosite aterial in the for of a thin disk, with the sale radius R and thickness d. The thin etal electrodes have been alied on the to and on the botto surfaces of the disk, and on which the side face an induction coil, with N nubers of turns (fig.. Let the sale is olarized transversely to contacts lane (axis Z. Direct agnetic field directs either along the sales olarization (longitudinal effect. S + st + st + de qh =, ( S + st + st + de qh =, ( B H + q ( T + = µ. ( T where s ij is the effective coliance of the coosite, d ij and q ij is the effective iezoelectric and iezoagnetic coonents, ε ij is the effective erittivity, E i and H i is the rojections of the tensity vectors of variable electric and agnetic fields. Design rocedure of effective araeters of coosition aterial is resented in [4,5]. It is convenient to used the syetry of a roble and turn to the cylindrical co-ordinates z, r and θ, using the conversions resented in [6] for further calculations. The axial syetry results in nonzero coonents of the ressure and strain tensors T rr, T θθ, S rr and S θθ. Others coonents of the ressure and strain tensors equal to zero. Besides fro the axial syetry results, that the dislaceent coonent u θ equal to zero. We allowance for this, the above exression (- reduces to S rr strr + st + de + qh = θθ, (4 S rr + θθ = st + stθθ + de qh, (5 B = µ H + q( Trr + Tθθ. (6 The equation of otion of the ediu for the radial oscillation reduces to Trr r rr + ( T r Tθθ + ρω ur =, (7 where ρ is the density of coosite. Evaluate fro (4, 5 coonents of stress tensor through coonents of ressure tensor, as result we get: T = ( S S ( ( de qh rr + ν θθ + s ( ν ν, (8 rr + Figure. Scheatic diagra of the structure with: ( sale; ( etal electrodes; ( coil with N nubers of turns. Alternating electric field with frequency ω, that given on the sale, is give rise to oscillation in the sale, which are sread along the sale surface is the radial oscillation, and all along sale thickness is the thicknesses oscillation. In future we will coe to nothing ore than the consideration of the ost low-frequency radial oscillation. Let us assue that the dick is thin, i.e. d<<r.. That the surfaces of the coosite dick are free that is, the noral coonents of the stress tensor on these surfaces are vanishing. Since the dick is thin, we can assue that T = not only on the surface, but in the volue of the dick. Accordingly, the equations for coonents of the strain tensor Si and agnetic induction B can be written as follows: Tθθ = ( νs S ( ( de qh rr + θθ + + s ( ν ν, (9 where ν = s /s is the Poisson's ratio. In order to take the equation for the radial dislaceent, substitute (8, 9 into equation of otion of the ediu (7. After the transforations the equation (7 is reduced to Bessel equation u r r u + r r u r r + k u r r =, ( where k = ρ s ( ν ω. General solution of the ( can be resented as suerosition of the first and second order Bessel functions u r = c kr + cy ( kr. (
3 4 D. A. Filiov et al: Inverse agnetoelectric effect in disk sales of ferrite iezoelectric coosites Constants c and c are defined by the boundary conditions: the dislaceents are lacking in the disk centre, i.e. at r = dislaceent u r =, but the noral strains equal to zero on side surfaces, therefore at r = R strain T rr =. This is give for constants following exressions [7]: ( + ν R c =, c = ( qh + de. ( κj( Here introduced nondiensional variable κ=kr, which values are deends on frequency, disk radius and rate of elastic oscillation roagation. Substituting the values of constants c and c in ( and, exressing the deforation through the ediu dislaceent, we get exressions for the coonents of the strain tensors R ( ( ( κj kr ν J kr T = r ( qh d rr κj( + E ( R ( ( ( νκj kr + ν J kr T = r ( qh de κj( + (4 θθ The agnetization, which is aeared in the sale as a result of agnetostriction as a result of ediu echanical deforation, we define fro Eq. (6. Substituting the exressions ( and (4 in equation (6 we get: where q d ( + ν α B, L =, (7 r r = κj(. (8 The EMF induced in the coil by agnetic flux is ΦL εin = = N α t t π R dθ Brdr = iωnπr B, L E. (9 Suosing, that all absorbed voltage take lace on the easuring volteter, and the electric field strength in sale bound u with the inut voltage by E = Vin d, and for the voltage ratio (transforer coefficient k L = Vout Vin for the longitudinal ME effect is πr ω N αb. ( d k L =, L Accordingly, this structure can be used as a transforer, which has only one winding in contrast to traditional tye transforer... Transverse Effect For the transverse ME effect direct agnetic field H in the sale directs either along the sales olarization P. Alied to the contacts electrical field to rovoke the echanical oscillation in the sale, and change the agnetization in all along sale thickness at the result. For the exeriental investigation of transverse ME effect we use the structure reresented at fig.. q ( + ν κj( kr B = H + ( qh + de s ( J( ( ν κ κ ν κ µ (5 For the exeriental investigation of inverse ME effect, it is easured the EMF of induction, that originated in coil at the agnetic flux easuring, due to the change of the agnetization of caacitor agnetoelectric dielectric. Usually, the volteter resistance in these easureents is uch greater than the coil resistance at the exerient, we can assue that the oen-circuit condition is valid (I = and, hence, H =. We allowance for this, the above exression (5 for the agnetic induction reduces to: B = q d ( + ν κj ( kr κj( E. (6 The inverse ME conversion factor for the longitudinal configuration of fields is defined as α B, L = В Е, where < B > is the average agnetic induction in the sale that R B rdr πr π is deterined as. < B >= d θ Calculating the average agnetic induction and substituting this exression into the above definition, we eventually obtain the following exression: Figure. Scheatic diagra of the structure with: ( sale; ( etal electrodes; ( coil with N nubers of turns, t coil thickness. Equations (- for the ressure tensor Si and for the agnetic induction B for the transverse ME effect takes for: S = st + st + de + qh, ( S = st + st + de + qh, (
4 Science Research, ( : -8 5 B = µ +. ( H + qt qt Coonents of the strain tensors exression are get colicated by the direct agnetic field H break its syste axial syetry at the turn to the cylindrical co-ordinates. However, taking into account, that in the exerient used the oen circuit condition and alternating agnetic field strength equal to zero, the ediu oscillation are rovoke by alternating electric field, directed along axes X, as for the longitudinal effect. Equation of ediu otion for radial oscillation reduced to (, which solution given the coonents of the strain tensors: T rr = R ( ( ( κj kr ν J kr r de, (4 κj( R νκj ( kr + ( J ( kr r θθ = de. (5 κj( T Coonents of the strain tensors T and T connected with coonents T rr and T θθ by: T = Trr cos θ + Tθθ sin θ, (6 T = Trr sin θ + Tθθ cos θ, (7 Using this ratios, for the agnetic induction in the cylindrical co-ordinates we get: B = Trr ( q cos θ + q sin θ + Tθθ ( q sin θ + q cos. (8 θ In a siilar to longitudinal effect, inverse ME conversion factor is defined as α B, T = B E for the transverse effect. Substituting exressions ( and (4 in equation (8, and calculating the average agnetic induction < B >, we obtain the following exression for inverse ME conversion factor: ( q + q d ( + ν α BT, =, (9 r where r defined by (8. For the defined of EMF induced in the coil, we liited by the case, when coil thickness t is saller then disk radius R. At this aroxiation we can take, that agnetic flux, slitting the coil equal to ΦT = N R d and for transforer coefficient: values of iezoelectric d and iezoagnetic q i odules and inversely to coliance odule s value. However for the transverse effect the value of coefficient α B, T is roortional to roduct ( q + qd. And for the longitudinal effect the value α B, L is roortional to roduct q d. As ( q + q > q, that the value of the transverse effect bigger, than of longitudinal. Frequency deendence of the inverse ME conversion factor as the frequency deendence of the ME voltage coefficient α E for the direct effect, has the resonance nature. At the low frequency region, when araeter κ <<, the value of the inverse ME conversion factor ractically is not deend on frequency. However at the frequency, that corresonds to condition r =, it is observe the eak increase of coefficient. Roots of these equation take the nae resonant frequencies f res. The value of lower resonant frequency to average about f res khz for the ferrite-nickel sinel and lead zirconate titanate sales with radius nearly R 5. It should be noted that, in contrast to the inverse ME effect, the resonant growth α E =< E > / H in the direct ME effect is observed at an antiresonance frequency f anres that corresonds to the condition a =, where = / a K + K( + ν r. ( Where K = d ε is the square coefficient of electroechanical couling for radial oscillations. There are inverse ME conversion factor frequency deendences for the ferrite-nickel sinel and lead zirconate titanate sales in the for of a disk calculated by (7 and (9 resulted in the ictures and 4 for the transverse and longitudinal effects. Sale radius R= s. The following quantity values used at the calculations: Ferrite: s =6.8 - /N, s =.4 - /N, q =-88 - /A, q =556 - /A, ρ q = - /A, =5 kg/; Piezoelectric: s =5. - /N, s =5.4 - /N, d =75 - /V, ρ =7 8 kg/. k T ωn R αbt, =. (. Results Discussion Coarison with Exerient As following fro exression (7 and (9 for inverse ME conversion factor its value in roortion to roduct of Figure. Inverse ME conversion factor frequency deendences for longitudinal effects
5 6 D. A. Filiov et al: Inverse agnetoelectric effect in disk sales of ferrite iezoelectric coosites Figure 4. Inverse ME conversion factor frequency deendences for transverse effects Frequencies of resonance and antiresonance has at least the closely values, but they are distinguishable exerientally. Exeriental investigations of effect were realized for the sales of ferrite-nickel sinel and PZT. Sales has a disk for with radius R = Before easureent the sales was olarized by electric field with strength 4 kv/ during two hours at the teerature 8 С. It is used ethod, based on easuring of alternating voltage, that aearing at the suerosition of alternating and slowly changing agnetic field on the sale, for the investigations of direct ME effect. For the investigations of inverse ME effect we used ethod, based on easuring of alternating voltage, that aearing at the easuring coil when it lace in slowly changing agnetic field and when the alternating electric field aly to the sale. At first was investigated the field deendence of low-frequency ME signal. ME effect deendence of bias field strength was easured at the constant value of alternating agnetic field strength Oe. Then was investigated frequency deendence of agnetoelectric coefficient in the electroechanical resonance region at the bias field strength, that agree with a axiu of effect. The oen circuit condition realized very well at the easureent. Exeriental data are shown in table. Table. Table inforation Ferrite ercentage, % exressions (8 and ( for the value r for inverse effect and for the value a for direct effect are equal to zero. For the Poisson s coefficient ν =. 4 the equality to zero of these exressions is haen when value κ =. 74. This ilyies, that the resonant frequency defining by con- dition f res =.74/(π ρ s ( ν R. Piezoceraic density PZT ρ = 78 kg/, coliance odule s = 5. / N, ferrite-nickel sinel density ρ = 5 kg/, its coliance odule s = 6.5 / N. With increase of the ferrite ercentage it is occur of coosite effective density decrease and coosite effective coliance decrease, as result to increase of resonant and antiresonant frequency. Resonant and antiresonant frequency s difference defining by the coefficient of electroechanical couling K, as easily to see by exressions (8 and ( for r and for a. Really, suosing f = f + f and exanding exression anres res for a by sall araeter κ = f π ρ ν R for relative difference of frequencies we get: f ( + ν K. ( f κ ( / κ νj ( κ /( κ J ( κ res Or, substituting the nuerical values ν =. 4 and κ =.74, for relative difference of frequencies we get the resultant exression in the following for: f f res.4 K ( With increase of the ferrite ercentage, the coefficient of electroechanical connection increasing in consequence of coosite effective iezoodule value increase, as a result at the increase of resonant and antiresonant frequency difference. The exeriental and theoretical frequency deendences of inverse ME conversion factor α B for PZT(- 7 ass.%, NiFe,9Co,O4 ass.% structure reresented at fig.5. The exeriental easuring realized when value of bias field H = 8 Oe, that eet the axiu of ME interaction. f res, khz 89,9,4 4,8 59,7 78,8 9, f anres, khz,9 7,9 4,6 6,4 8,5 9,5 f, khz, 4,5,8,7,7,5 α ( = f, G c V 7 49 B, T f res / α E, T( f = fanres, V/( c Oe α ( f = khz, G c V,6,7,94,6,7,65 B, T / α E, T( f = khz, V/( c Oe As following fro exerient, in full accordance with theory, there is a eak increase of effect at the resonant and antiresonant frequency. This frequencies values defining by araeter κ = kr = ω ρ s ( R, at which the values of ν Figure 5. Inverse ME conversion factor B α frequency deendences for transverse effects for PZT(- 7 ass.%, NiFe,9Co,O4 ass.% structure, where the full line is the theoretical deendence, oints are the exeriental data
6 Science Research, ( : -8 7 In this case the inverse ME signal alification occurring at the frequency f res = 5 khz, and the inverse ME conversion factor resonant value three ties as any as its low-frequency value. In coarison with ultilayer coosites, this good quality accounted for the alied of iezoelectric with high good quality (Q and the selection of oerating ractices, that resulting to erforance of the echanical contact between slinters. There is a siilar effect was observed on the sales with other structures, but the resonance frequencies are vary deending on coosite ercentage coosition vary. The exeriental and theoretical resonant frequency deendences of ferrite content in coosite are reresented at fig.6. Figure 8. The difference of resonance and antiresonance frequencies, where the full line is the theoretical deendence, oints are the exeriental data With increase of the ferrite ercentage by iezoodule effective value decrease and decrease of electroechanical couling factor, as a resulted to decrease of resonance and antiresonance frequencies. Effect of coosite structure on the inverse ME conversion factor ( f res = 5 khz reresented at fig.9. We lotting of inverse ME conversion factor deendence of ferrite inclusion volue fraction by using the theoretical odel. Figure 6. Resonance frequency deendences of ferrite content in coosite, where the full line is the theoretical deendence, oints are the exeriental data As aears fro the fig. 6, with increase of ferrite ercentage there is a resonant frequency increase. This account for coosite effective density and effective coliance decrease by ferrite ercentage increase, that resulting in resonant frequency increase. The resonance and antiresonance frequencies deendences of ferrite content in coosite are reresented at fig.7. The difference of resonance and antiresonance frequencies reresented at fig.8. Figure 7. Resonance (the botto characteristic and antiresonance (the uer characteristic frequencies deendences of ferrite content in coosite, where the full line is the theoretical deendence, oints are the exeriental data Figure 9. Deendence of inverse ME conversion factor by ferrite inclusion volue fraction ( f res = 5 khz, where the full line is the theoretical deendence, oints are the exeriental data As can be seen by diagra (fig. 9, the deendence of inverse ME conversion factor by ferrite inclusion volue fraction has a axiu. The inverse ME conversion factor α B is roortional to roduct of effective values of iezoelectric and iezoagnetic odules and inversely roortional to odule of coosite coliance. With ferrite ercentage increase there is iezoodule decrease, that reducing to decrease of α B. As resulting to increase of coefficient with ferrite ercentage increase at first, then coefficient aounting to axiu, and then it has decreased. The inverse ME conversion factor α B is roortional to roduct of iezoelectric and iezoagnetic effective odules and inversely roortional to coosite coliance odule. With increase of the ferrite ercentage, on the one hand, there is increase of the iezoelectric odule s effective value and decrease of the coliance odule, that leading to increase of value α B, on the other hand, with increase of the ferrite ercentage, there is decrease of the iezoodule, that leading to decrease of value α B. As a
7 8 D. A. Filiov et al: Inverse agnetoelectric effect in disk sales of ferrite iezoelectric coosites consequence of that, the value of coefficient is increase at first with increase of the ferrite ercentage, is at the high and then is decrease. Siilarly leading oneself the ME voltage coefficient. Its value also is roortionally to roduct of iezoelectric and iezoagnetic effective odules. However it is inversely not only to coosite coliance odule, but is inversely to roduct of coliance odule and coosite erittivity coefficient, that value also decrease with increase of ferrite concentration. This is leading to that the ME voltage coefficient axiu account to the ost content of ferrite, than the inverse ME conversion factor axiu. References [] I. B. Dzyaloshinskii, Zh. Eks. Teor. Fiz. 7, 88 (959. [] D. N. Astrov, Zh. Eks. Teor. Fiz. 4, 5 (96. [] V.J. Folen, G.T. Rado, E.W. Stalder. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 67 (96. [4] Е.А.Turov. Physics-Usekhi 64, 5 (994. [5] Antonenkov O.V., Nikiforov I.S., Filiov D.A. Ferroelectrics. 79, 57 (. [6] M. Fiebig. J. Phys. D: Al. Phys. 8, (5. [7] S. Dong, J.F. Li, D.Viehland, J. Cheng, L.E. Cross. Al. Phys. Lett. 85, 54 (4. [8] Y.K. Fetisov, V.M. Petrov, G. Srinivasan. J. Mater. Res., 74 (7. [9] A. A. Bush, K. E. Kaentsev, V. F. Meshcheryakov, Y. K. Fetisov, D. V. Chashin and L. Y. Fetisov, Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 79 (9, 7 (9. [] Y.K. Fetisov, K.E. Kaentsev, D.V. Chashin, L.Y. Fetisov, G. Srinivasan. J. Al. Phys. 5, 98 (9. [] D.А. Filiov, Т.А. Galkina, G. Srinivasan. Pis a Zh. Tekh. 6,, (. [] G. Harshe, J.O. Dougherty, R. E. Newnha. Int. J. Al. Electroagn. Mater (99. [] G. Harshe, J.P. Dougherty, R.E. Newnha. Int. J. Al. Electroagn. Mater (99. [4] M.I. Bichurin, V.M. Petrov, G. Srinivasan. Phys. Rev. B (. [5] M.I. Bichurin, V.M. Petrov, D.А. Filiov, V.М. Laletin, G. Srinivasan. Persectivnye aterialy 6, 5 (4. [6] W.P. Mazon. Phys. Rev. 74, 4 (948. [7] D.А. Filiov, M.I. Bichurin, V.M. Petrov, V.М. Laletin, G. Srinivasan. FТТ, 46, 9, 6 (4.
Theory Analysis on Magnetoelectric Voltage Coefficients of the Terfoneol-D/PZT Composite Transducer
 heory Analysis on Magnetoelectric Voltage Coefficients of the erfoneol-d/pz Coosite ransducer Shuxiang Dong, JieFang Li, and Dwight Viehland Materials Science & ngineering, Virginia ech, Blacksburg, VA406
heory Analysis on Magnetoelectric Voltage Coefficients of the erfoneol-d/pz Coosite ransducer Shuxiang Dong, JieFang Li, and Dwight Viehland Materials Science & ngineering, Virginia ech, Blacksburg, VA406
1. (2.5.1) So, the number of moles, n, contained in a sample of any substance is equal N n, (2.5.2)
 Lecture.5. Ideal gas law We have already discussed general rinciles of classical therodynaics. Classical therodynaics is a acroscoic science which describes hysical systes by eans of acroscoic variables,
Lecture.5. Ideal gas law We have already discussed general rinciles of classical therodynaics. Classical therodynaics is a acroscoic science which describes hysical systes by eans of acroscoic variables,
CHAPTER 2 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER 2 HERMODYNAMICS 2.1 INRODUCION herodynaics is the study of the behavior of systes of atter under the action of external fields such as teerature and ressure. It is used in articular to describe
CHAPER 2 HERMODYNAMICS 2.1 INRODUCION herodynaics is the study of the behavior of systes of atter under the action of external fields such as teerature and ressure. It is used in articular to describe
5. Dimensional Analysis. 5.1 Dimensions and units
 5. Diensional Analysis In engineering the alication of fluid echanics in designs ake uch of the use of eirical results fro a lot of exerients. This data is often difficult to resent in a readable for.
5. Diensional Analysis In engineering the alication of fluid echanics in designs ake uch of the use of eirical results fro a lot of exerients. This data is often difficult to resent in a readable for.
[95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER. Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow
![[95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER. Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow [95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER. Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow](/thumbs/81/82687654.jpg) [95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow ABSTRACT The aer discusses a well-known condition [95%/95%],
[95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow ABSTRACT The aer discusses a well-known condition [95%/95%],
3 Thermodynamics and Statistical mechanics
 Therodynaics and Statistical echanics. Syste and environent The syste is soe ortion of atter that we searate using real walls or only in our ine, fro the other art of the universe. Everything outside the
Therodynaics and Statistical echanics. Syste and environent The syste is soe ortion of atter that we searate using real walls or only in our ine, fro the other art of the universe. Everything outside the
Derivation of stiffness matrix in constitutive modeling of magnetorheological elastomer
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Derivation of stiffness atrix in constitutive odeling of agnetorheological elastoer To cite this article: D Leng et al J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 4 8 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Derivation of stiffness atrix in constitutive odeling of agnetorheological elastoer To cite this article: D Leng et al J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 4 8 View the article online
Anomalous heat capacity for nematic MBBA near clearing point
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Anoalous heat caacity for neatic MA near clearing oint To cite this article: D A Lukashenko and M Khasanov J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 394 View the article online for udates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Anoalous heat caacity for neatic MA near clearing oint To cite this article: D A Lukashenko and M Khasanov J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 394 View the article online for udates
Frequency Domain Analysis of Rattle in Gear Pairs and Clutches. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 The 00 International Congress and Exosition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 9-, 00 Frequency Doain Analysis of Rattle in Gear Pairs and Clutches T. C. Ki and R. Singh Acoustics and
The 00 International Congress and Exosition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 9-, 00 Frequency Doain Analysis of Rattle in Gear Pairs and Clutches T. C. Ki and R. Singh Acoustics and
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volue 19, 2013 htt://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 1PAb: Acoustics in Microfluidics and for Particle
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volue 19, 2013 htt://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 1PAb: Acoustics in Microfluidics and for Particle
MATHEMATICAL MODELS AND OPTICAL INVESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE FLOWS IN WIND TUNNELS
 MATHEMATICAL MODELS AND OPTICAL INESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE FLOWS IN WIND TUNNELS *Central Aerohydrodynaic institute Keywords: wind tunnels, icing in suercooled drolets and non-sherical crystals, otical
MATHEMATICAL MODELS AND OPTICAL INESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE FLOWS IN WIND TUNNELS *Central Aerohydrodynaic institute Keywords: wind tunnels, icing in suercooled drolets and non-sherical crystals, otical
The Realm of Hydrogeology
 The Real of Hydrogeology In class exercise Stagnant Flow Plot hydraulic head and ressure vs. deth for (also indicate the hydrostatic line) Stagnant flow (no flow) Steady downward flow Steady uward flow
The Real of Hydrogeology In class exercise Stagnant Flow Plot hydraulic head and ressure vs. deth for (also indicate the hydrostatic line) Stagnant flow (no flow) Steady downward flow Steady uward flow
Minimizing Machinery Vibration Transmission in a Lightweight Building using Topology Optimization
 1 th World Congress on Structural and Multidiscilinary Otiization May 19-4, 13, Orlando, Florida, USA Miniizing Machinery Vibration ransission in a Lightweight Building using oology Otiization Niels Olhoff,
1 th World Congress on Structural and Multidiscilinary Otiization May 19-4, 13, Orlando, Florida, USA Miniizing Machinery Vibration ransission in a Lightweight Building using oology Otiization Niels Olhoff,
INTERIOR BALLISTIC PRINCIPLE OF HIGH/LOW PRESSURE CHAMBERS IN AUTOMATIC GRENADE LAUNCHERS
 XXXX IB08 19th International Syosiu of Ballistics, 7 11 May 001, Interlaken, Switzerland INTERIOR BALLISTIC PRINCIPLE OF HIGH/LOW PRESSURE CHAMBERS IN AUTOMATIC GRENADE LAUNCHERS S. Jaraaz1, D. Micković1,
XXXX IB08 19th International Syosiu of Ballistics, 7 11 May 001, Interlaken, Switzerland INTERIOR BALLISTIC PRINCIPLE OF HIGH/LOW PRESSURE CHAMBERS IN AUTOMATIC GRENADE LAUNCHERS S. Jaraaz1, D. Micković1,
STRAIN ENERGY DENSITY AS THE LINK BETWEEN GLOBAL AND LOCAL APPROACH TO FRACTURE
 eference ID: ICF100494O STAIN ENEGY DENSITY AS THE LIN BETWEEN GLOBAL AND LOCAL APPOACH TO FACTE Hans-Jakob Schindler Mat-Tec Ltd., Winterthur, Switzerland (forerly EMPA, Duebendorf, Switzerland) ABSTACT
eference ID: ICF100494O STAIN ENEGY DENSITY AS THE LIN BETWEEN GLOBAL AND LOCAL APPOACH TO FACTE Hans-Jakob Schindler Mat-Tec Ltd., Winterthur, Switzerland (forerly EMPA, Duebendorf, Switzerland) ABSTACT
Thermal conductivity, diffusivity and heat capacity of plasticized polyvinyl chloride
 Indian Journal of Pure & Alied Physics Vol. 43, February 25,. 132-136 heral conductivity, diffusivity and heat caacity of lasticized olyvinyl chloride P Dashora 1, G Guta 2 & J Dashora 1 1 Deartent of
Indian Journal of Pure & Alied Physics Vol. 43, February 25,. 132-136 heral conductivity, diffusivity and heat caacity of lasticized olyvinyl chloride P Dashora 1, G Guta 2 & J Dashora 1 1 Deartent of
Supplementary Information for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polymer Actuators
 Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Basic Thermodynamic Relations
 Basic herodynaic Relations Isolated syste: this is a syste that does not exchange energy with the surrounding edia. First Postulate (equilibriu theore) : Isolated syste always reaches the equilibriu state
Basic herodynaic Relations Isolated syste: this is a syste that does not exchange energy with the surrounding edia. First Postulate (equilibriu theore) : Isolated syste always reaches the equilibriu state
Properties of a one-dimensional metallophotonic crystal
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 70 035101 (004) Proerties of a one-diensional etallohotonic crystal J. T. Shen 1 * and P. M. Platzan 1 Deartent of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford California 94305
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 70 035101 (004) Proerties of a one-diensional etallohotonic crystal J. T. Shen 1 * and P. M. Platzan 1 Deartent of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford California 94305
A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 20 GHz
 A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 0 GHz A.M.Maedov (1), A. L. Levin (), and V. T. Potapov (3) (1) Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Acadey of
A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 0 GHz A.M.Maedov (1), A. L. Levin (), and V. T. Potapov (3) (1) Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Acadey of
Numerical Model of the Human Head under Side Impact
 J. Basic. Al. Sci. Res., 3(3)47-474, 3 3, TextRoad Publication ISSN 9-434 Journal of Basic and Alied Scientific Research www.textroad.co Nuerical Model of the Huan Head under Side Iact Behrooz Seehri (PHD),
J. Basic. Al. Sci. Res., 3(3)47-474, 3 3, TextRoad Publication ISSN 9-434 Journal of Basic and Alied Scientific Research www.textroad.co Nuerical Model of the Huan Head under Side Iact Behrooz Seehri (PHD),
CALCULATION of CORONA INCEPTION VOLTAGES in N 2 +SF 6 MIXTURES via GENETIC ALGORITHM
 CALCULATION of COONA INCPTION VOLTAGS in N +SF 6 MIXTUS via GNTIC ALGOITHM. Onal G. Kourgoz e-ail: onal@elk.itu.edu.tr e-ail: guven@itu.edu..edu.tr Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of lectric and
CALCULATION of COONA INCPTION VOLTAGS in N +SF 6 MIXTUS via GNTIC ALGOITHM. Onal G. Kourgoz e-ail: onal@elk.itu.edu.tr e-ail: guven@itu.edu..edu.tr Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of lectric and
THE CLAUSIUS-MOSSOTTI FACTOR IN LOW FREQUENCY FIELD OF THE POWDERS RESULTED FROM WASTES COMBUSTION
 THE CLAUSIUS-MOSSOTTI FACTOR IN LOW FREQUENCY FIELD OF THE POWDERS RESULTED FROM WASTES COMBUSTION R. GIUGIULAN 1, I. MALAESCU 1*, M. LUNGU 1, N. STRAMBEANU 2 1 West University of Tiisoara, Faculty of
THE CLAUSIUS-MOSSOTTI FACTOR IN LOW FREQUENCY FIELD OF THE POWDERS RESULTED FROM WASTES COMBUSTION R. GIUGIULAN 1, I. MALAESCU 1*, M. LUNGU 1, N. STRAMBEANU 2 1 West University of Tiisoara, Faculty of
Phase field modelling of microstructural evolution using the Cahn-Hilliard equation: A report to accompany CH-muSE
 Phase field odelling of icrostructural evolution using the Cahn-Hilliard equation: A reort to accoany CH-uSE 1 The Cahn-Hilliard equation Let us consider a binary alloy of average coosition c 0 occuying
Phase field odelling of icrostructural evolution using the Cahn-Hilliard equation: A reort to accoany CH-uSE 1 The Cahn-Hilliard equation Let us consider a binary alloy of average coosition c 0 occuying
Security Transaction Differential Equation
 Security Transaction Differential Equation A Transaction Volue/Price Probability Wave Model Shi, Leilei This draft: June 1, 4 Abstract Financial arket is a tyical colex syste because it is an oen trading
Security Transaction Differential Equation A Transaction Volue/Price Probability Wave Model Shi, Leilei This draft: June 1, 4 Abstract Financial arket is a tyical colex syste because it is an oen trading
CAUCHY PROBLEM FOR TECHNOLOGICAL CUMULATIVE CHARGE DESIGN. Christo Christov, Svetozar Botev
 SENS'6 Second Scientific Conference with International Particiation SPACE, ECOLOGY, NANOTECHNOLOGY, SAFETY 4 6 June 6, Varna, Bulgaria ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SENS'6 Second Scientific Conference with International Particiation SPACE, ECOLOGY, NANOTECHNOLOGY, SAFETY 4 6 June 6, Varna, Bulgaria ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AN EXPLICIT METHOD FOR NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF WAVE EQUATIONS
 The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beiing, China AN EXPLICIT ETHOD FOR NUERICAL SIULATION OF WAVE EQUATIONS Liu Heng and Liao Zheneng Doctoral Candidate, Det. of Structural
The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beiing, China AN EXPLICIT ETHOD FOR NUERICAL SIULATION OF WAVE EQUATIONS Liu Heng and Liao Zheneng Doctoral Candidate, Det. of Structural
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Simple Mechanical Systems
 Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
ULTRASONIC WELDING OF COMPOSITE MATERAILS. ULTRASONIC BOOSTER DESIGN AND FEM SIMULATION
 ULTRASONIC WELDING OF COMPOSITE MATERAILS. ULTRASONIC BOOSTER DESIGN AND FEM SIMULATION Gh. AMZA, Zoia Apostolescu, Dan NITOI University Politehnica fro Bucharest, aza@aza.cais.pub.ro Keywords: ultrasonic,
ULTRASONIC WELDING OF COMPOSITE MATERAILS. ULTRASONIC BOOSTER DESIGN AND FEM SIMULATION Gh. AMZA, Zoia Apostolescu, Dan NITOI University Politehnica fro Bucharest, aza@aza.cais.pub.ro Keywords: ultrasonic,
Isothermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. E. Feyzullahoglu
 Journal of the Balkan Tribological Association Vol. 15, No 3, 438 446 (009) 438 Elastohydrodynaic lubrication Isotheral Elastohydrodynaic Lubrication of Ellitic Contacts E. Feyzullahoglu Faculty of Engineering,
Journal of the Balkan Tribological Association Vol. 15, No 3, 438 446 (009) 438 Elastohydrodynaic lubrication Isotheral Elastohydrodynaic Lubrication of Ellitic Contacts E. Feyzullahoglu Faculty of Engineering,
EGN 3353C Fluid Mechanics
 Lecture 4 When nondiensionalizing an equation, nondiensional araeters often aear. Exale Consider an object falling due to gravity in a vacuu d z ays: (1) the conventional diensional aroach, and () diensionless
Lecture 4 When nondiensionalizing an equation, nondiensional araeters often aear. Exale Consider an object falling due to gravity in a vacuu d z ays: (1) the conventional diensional aroach, and () diensionless
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE BEHAVIOR OF AN EXPANSIVE SOIL
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 214, vol. 1, nu. 1 www.roceedings.blucher.co.br/evento/1wcc NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE BEHAVIOR OF AN EXPANSIVE SOIL L.M. Costa 1, S. R. M. Ferreira 2, I.
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 214, vol. 1, nu. 1 www.roceedings.blucher.co.br/evento/1wcc NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE BEHAVIOR OF AN EXPANSIVE SOIL L.M. Costa 1, S. R. M. Ferreira 2, I.
of particles an introduction Dielectrophoresis esis (DEP) Electro-rotation (ROT) Travelling wave (twdep)
 AC electrokinetic aniulation of articles an introduction Hywel Morgan University of Southaton OVRVIW: Dielectrohoresis esis (DP) lectro-rotation (ROT) Travelling wave (twdp) 1 lectrodes Polarisation of
AC electrokinetic aniulation of articles an introduction Hywel Morgan University of Southaton OVRVIW: Dielectrohoresis esis (DP) lectro-rotation (ROT) Travelling wave (twdp) 1 lectrodes Polarisation of
Dynamics and topology optimization of piezoelectric fans
 Theral Challenges in Next Generation Electronic Systes, Joshi & Gariella (eds) 00 Millress, Rotterda, ISBN 90-7707-0-8 Dynaics and toology otiization of iezoelectric fans Phili Bürann, Arvind Raan & Suresh
Theral Challenges in Next Generation Electronic Systes, Joshi & Gariella (eds) 00 Millress, Rotterda, ISBN 90-7707-0-8 Dynaics and toology otiization of iezoelectric fans Phili Bürann, Arvind Raan & Suresh
THE RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTIC OF FIXED DISPLACEMENT PUMP VARIABLE MOTOR SYSTEM
 Journal of Theoretical and Alied Inforation Technology th January 3. ol. 47 No. 5-3 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 THE RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTIC
Journal of Theoretical and Alied Inforation Technology th January 3. ol. 47 No. 5-3 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 THE RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTIC
An Investigation into the Effects of Roll Gyradius on Experimental Testing and Numerical Simulation: Troubleshooting Emergent Issues
 An Investigation into the Effects of Roll Gyradius on Exeriental esting and Nuerical Siulation: roubleshooting Eergent Issues Edward Dawson Maritie Division Defence Science and echnology Organisation DSO-N-140
An Investigation into the Effects of Roll Gyradius on Exeriental esting and Nuerical Siulation: roubleshooting Eergent Issues Edward Dawson Maritie Division Defence Science and echnology Organisation DSO-N-140
Binomial and Poisson Probability Distributions
 Binoial and Poisson Probability Distributions There are a few discrete robability distributions that cro u any ties in hysics alications, e.g. QM, SM. Here we consider TWO iortant and related cases, the
Binoial and Poisson Probability Distributions There are a few discrete robability distributions that cro u any ties in hysics alications, e.g. QM, SM. Here we consider TWO iortant and related cases, the
th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Germany, Parallel Connection of Piezoelectric Transformers
 004 35th Annual IEEE ower Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Gerany, 004 arallel Connection of iezoelectric Transforers Svetlana Bronstein, Gregory Ivensky and Sa Ben-Yaakov* ower Electronics Laboratory
004 35th Annual IEEE ower Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Gerany, 004 arallel Connection of iezoelectric Transforers Svetlana Bronstein, Gregory Ivensky and Sa Ben-Yaakov* ower Electronics Laboratory
General Physical Chemistry I
 General Physical Cheistry I Lecture 12 Aleksey Kocherzhenko Aril 2, 2015" Last tie " Gibbs free energy" In order to analyze the sontaneity of cheical reactions, we need to calculate the entroy changes
General Physical Cheistry I Lecture 12 Aleksey Kocherzhenko Aril 2, 2015" Last tie " Gibbs free energy" In order to analyze the sontaneity of cheical reactions, we need to calculate the entroy changes
Comparative Design of Radial and Transverse Flux PM Generators for Direct-Drive Wind Turbines
 Paer ID 1325 Coarative Design of Radial and Transverse Flux PM Generators for Direct-Drive Wind Turbines Deok-je Bang, Henk Polinder, Ghanshya Shrestha and Jan Abraha Ferreira Electrical Power Processing
Paer ID 1325 Coarative Design of Radial and Transverse Flux PM Generators for Direct-Drive Wind Turbines Deok-je Bang, Henk Polinder, Ghanshya Shrestha and Jan Abraha Ferreira Electrical Power Processing
Design and Experimental Research of Atomizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu WANG, Yin ZHEN, Juan SONG and A-chun ZHU
 217 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Autoation (AMMA 217) ISBN: 978-1-6595-479- Design and Experiental Research of Atoizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu
217 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Autoation (AMMA 217) ISBN: 978-1-6595-479- Design and Experiental Research of Atoizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu
In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on the following topics:
 Chapter 17 Waves II In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on the following topics: Speed of sound waves Relation between displaceent and pressure aplitude Interference of sound waves
Chapter 17 Waves II In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on the following topics: Speed of sound waves Relation between displaceent and pressure aplitude Interference of sound waves
doi: / (http://dx.doi.org/ / )
 doi:.7/978-3-642-3284-5(htt://dx.doi.org/.7/978-3-642-3284-5) A unified descrition of Toyoura sand Feng ZHANG ), Bin YE 2), Guanlin Ye 3) ) Nagoya Institute of Technology, Nagoya, Jaan 2) Tongji University,
doi:.7/978-3-642-3284-5(htt://dx.doi.org/.7/978-3-642-3284-5) A unified descrition of Toyoura sand Feng ZHANG ), Bin YE 2), Guanlin Ye 3) ) Nagoya Institute of Technology, Nagoya, Jaan 2) Tongji University,
On spinors and their transformation
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH, Science Huβ, htt:www.scihub.orgajsir ISSN: 5-69X On sinors and their transforation Anaitra Palit AuthorTeacher, P5 Motijheel Avenue, Flat C,Kolkata
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH, Science Huβ, htt:www.scihub.orgajsir ISSN: 5-69X On sinors and their transforation Anaitra Palit AuthorTeacher, P5 Motijheel Avenue, Flat C,Kolkata
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
1 (40) Gravitational Systems Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05R) objects are located at fixed positions along
 (40) Gravitational Systes Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05) objects are located at fixed positions along 2M 2M 0 an axis in space. The first ass is centered at r = 0 and has a ass of 2M. The second ass
(40) Gravitational Systes Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05) objects are located at fixed positions along 2M 2M 0 an axis in space. The first ass is centered at r = 0 and has a ass of 2M. The second ass
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.it.edu 8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics Fall 2008 For inforation about citing these aterials or our Ters of Use, isit: http://ocw.it.edu/ters. MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.it.edu 8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics Fall 2008 For inforation about citing these aterials or our Ters of Use, isit: http://ocw.it.edu/ters. MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
Suppress Parameter Cross-talk for Elastic Full-waveform Inversion: Parameterization and Acquisition Geometry
 Suress Paraeter Cross-talk for Elastic Full-wavefor Inversion: Paraeterization and Acquisition Geoetry Wenyong Pan and Kris Innanen CREWES Project, Deartent of Geoscience, University of Calgary Suary Full-wavefor
Suress Paraeter Cross-talk for Elastic Full-wavefor Inversion: Paraeterization and Acquisition Geoetry Wenyong Pan and Kris Innanen CREWES Project, Deartent of Geoscience, University of Calgary Suary Full-wavefor
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR. Mass Spectrometrically-Detected Statistical Aspects of Ligand Populations in Mixed Monolayer Au 25 L 18 Nanoparticles
 SUPPORTIG IFORMATIO FOR Mass Sectroetrically-Detected Statistical Asects of Lig Poulations in Mixed Monolayer Au 25 L 8 anoarticles Aala Dass,,a Kennedy Holt, Joseh F. Parer, Stehen W. Feldberg, Royce
SUPPORTIG IFORMATIO FOR Mass Sectroetrically-Detected Statistical Asects of Lig Poulations in Mixed Monolayer Au 25 L 8 anoarticles Aala Dass,,a Kennedy Holt, Joseh F. Parer, Stehen W. Feldberg, Royce
National 5 Summary Notes
 North Berwick High School Departent of Physics National 5 Suary Notes Unit 3 Energy National 5 Physics: Electricity and Energy 1 Throughout the Course, appropriate attention should be given to units, prefixes
North Berwick High School Departent of Physics National 5 Suary Notes Unit 3 Energy National 5 Physics: Electricity and Energy 1 Throughout the Course, appropriate attention should be given to units, prefixes
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction From The Faraday Acyclic Generator
 Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
Question number 1 to 8 carries 2 marks each, 9 to 16 carries 4 marks each and 17 to 18 carries 6 marks each.
 IIT-JEE5-PH-1 FIITJEE Solutions to IITJEE 5 Mains Paper Tie: hours Physics Note: Question nuber 1 to 8 carries arks each, 9 to 16 carries 4 arks each and 17 to 18 carries 6 arks each. Q1. whistling train
IIT-JEE5-PH-1 FIITJEE Solutions to IITJEE 5 Mains Paper Tie: hours Physics Note: Question nuber 1 to 8 carries arks each, 9 to 16 carries 4 arks each and 17 to 18 carries 6 arks each. Q1. whistling train
A multiscale nonequilibrium model for melting of metal. powder bed subjected to constant heat flux
 A ultiscale nonequilibriu odel for elting of etal owder bed subjected to constant heat flux Jin Wang 1,, Mo Yang 1, Yuwen Zhang, * 1 School of Energy and Power Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science
A ultiscale nonequilibriu odel for elting of etal owder bed subjected to constant heat flux Jin Wang 1,, Mo Yang 1, Yuwen Zhang, * 1 School of Energy and Power Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science
Ballistic Pendulum. Introduction
 Ballistic Pendulu Introduction The revious two activities in this odule have shown us the iortance of conservation laws. These laws rovide extra tools that allow us to analyze certain asects of hysical
Ballistic Pendulu Introduction The revious two activities in this odule have shown us the iortance of conservation laws. These laws rovide extra tools that allow us to analyze certain asects of hysical
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. Lectures 18-19
 H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER
 IEPC 003-0034 ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER A. Bober, M. Guelan Asher Space Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, 3000 Haifa, Israel
IEPC 003-0034 ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER A. Bober, M. Guelan Asher Space Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, 3000 Haifa, Israel
Department of Physics Preliminary Exam January 3 6, 2006
 Departent of Physics Preliinary Exa January 3 6, 2006 Day 1: Classical Mechanics Tuesday, January 3, 2006 9:00 a.. 12:00 p.. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a separate sheet of paper.
Departent of Physics Preliinary Exa January 3 6, 2006 Day 1: Classical Mechanics Tuesday, January 3, 2006 9:00 a.. 12:00 p.. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a separate sheet of paper.
2. Electric Current. E.M.F. of a cell is defined as the maximum potential difference between the two electrodes of the
 2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read the introduction to chapter 25 and sections 25.1 to 25.3 & 25.6.
 PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenomena. We will study the following topics:
 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
Efforts Towards a Validated Time-Domain Model of an Oscillating Water Column with Control Components
 Proceedings of the 11th Euroean Wave and Tidal Energy Conference 6-11th Set 215, Nantes, France Efforts Towards a Validated Tie-Doain Model of an Oscillating Water Colun with Control Coonents Thoas Kelly,
Proceedings of the 11th Euroean Wave and Tidal Energy Conference 6-11th Set 215, Nantes, France Efforts Towards a Validated Tie-Doain Model of an Oscillating Water Colun with Control Coonents Thoas Kelly,
III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynamics
 III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynaics As a first approxiation, we shall assue that in local equilibriu, the density f 1 at each point in space can be represented as in eq.iii.56, i.e. f 0 1 p, q, t = n q, t
III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynaics As a first approxiation, we shall assue that in local equilibriu, the density f 1 at each point in space can be represented as in eq.iii.56, i.e. f 0 1 p, q, t = n q, t
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
u = 1 (B 2 + E2 E B (16.2) + N = j E (16.3) One might be tempted to put u and N into a 4-vector N and write the equation in the form
 Chater 6 Energy-momentum tensor (Version., 3 November 7 Earlier, we obtained for the energy density and flux u = (B + E µ c (6. We also had a continuity equation N = µ E B (6. u t + N = j E (6.3 One might
Chater 6 Energy-momentum tensor (Version., 3 November 7 Earlier, we obtained for the energy density and flux u = (B + E µ c (6. We also had a continuity equation N = µ E B (6. u t + N = j E (6.3 One might
Chapter 1 Magnetic Materials
 Chapter 1 Magnetic Materials Figures cited with the notation [RCO] Fig. X.Y are fro O Handley, Robert C. Modern Magnetic Materials: Principles and Applications. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 2000. Courtesy
Chapter 1 Magnetic Materials Figures cited with the notation [RCO] Fig. X.Y are fro O Handley, Robert C. Modern Magnetic Materials: Principles and Applications. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 2000. Courtesy
2.141 Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems Assignment #2
 2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
7. Momentum balances Partly based on Chapter 7 of the De Nevers textbook (sections ).
 Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 7 Moentu balances Partly based on Chater 7 of the De Neers tetbook (sections 71-73) Introduction Net to ass and energy oentu is an iortant quantity fluid
Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 7 Moentu balances Partly based on Chater 7 of the De Neers tetbook (sections 71-73) Introduction Net to ass and energy oentu is an iortant quantity fluid
Optimum Design of Assembled Cavity Dies for Precision Forging Process
 International Syposiu on Material, Energy and Environent Enginee (ISM3E 2015) Optiu Design of Assebled Cavity Dies for Precision Forging Process Jun-song Jin1 and Xin-yun Wang1,* 1 State Key Laboratory
International Syposiu on Material, Energy and Environent Enginee (ISM3E 2015) Optiu Design of Assebled Cavity Dies for Precision Forging Process Jun-song Jin1 and Xin-yun Wang1,* 1 State Key Laboratory
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST 30 QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 15 MINUTES
 SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
Chapter 16 Solutions
 Chapter 16 Solutions 16.1 Replace x by x vt = x 4.5t to get y = 6 [(x 4.5t) + 3] 16. y (c) y (c) y (c) 6 4 4 4 t = s t = 1 s t = 1.5 s 0 6 10 14 x 0 6 10 14 x 0 6 10 14 x y (c) y (c) 4 t =.5 s 4 t = 3
Chapter 16 Solutions 16.1 Replace x by x vt = x 4.5t to get y = 6 [(x 4.5t) + 3] 16. y (c) y (c) y (c) 6 4 4 4 t = s t = 1 s t = 1.5 s 0 6 10 14 x 0 6 10 14 x 0 6 10 14 x y (c) y (c) 4 t =.5 s 4 t = 3
Final Exam Classical Mechanics
 Final Ea Classical Mechanics. Consider the otion in one diension of a article subjected to otential V= (where =constant). Use action-angle variables to find the eriod of the otion as a function of energ.
Final Ea Classical Mechanics. Consider the otion in one diension of a article subjected to otential V= (where =constant). Use action-angle variables to find the eriod of the otion as a function of energ.
Mistiming Performance Analysis of the Energy Detection Based ToA Estimator for MB-OFDM
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Mistiing Perforance Analysis of the Energy Detection Based ToA Estiator for MB-OFDM Huilin Xu, Liuqing Yang contact author, Y T Jade Morton and Mikel M Miller
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Mistiing Perforance Analysis of the Energy Detection Based ToA Estiator for MB-OFDM Huilin Xu, Liuqing Yang contact author, Y T Jade Morton and Mikel M Miller
STATIC OUTPUT FEEDBACK CONTROL FOR NON-LINEAR FLUTTER AND LIMIT CYCLE OSCILLATION.
 ICSV4 Cairns Australia 9- July, 007 SAIC OUPU FEEDBACK CONROL FOR NON-LINEAR FLUER AND LIMI CYCLE OSCILLAION Morteza Dardel and Firooz Bakhtiari-Nejad PhD Student, Mechanical Engineering, AirKabir Univeity
ICSV4 Cairns Australia 9- July, 007 SAIC OUPU FEEDBACK CONROL FOR NON-LINEAR FLUER AND LIMI CYCLE OSCILLAION Morteza Dardel and Firooz Bakhtiari-Nejad PhD Student, Mechanical Engineering, AirKabir Univeity
FRESNEL FORMULAE FOR SCATTERING OPERATORS
 elecounications and Radio Engineering, 70(9):749-758 (011) MAHEMAICAL MEHODS IN ELECROMAGNEIC HEORY FRESNEL FORMULAE FOR SCAERING OPERAORS I.V. Petrusenko & Yu.K. Sirenko A. Usikov Institute of Radio Physics
elecounications and Radio Engineering, 70(9):749-758 (011) MAHEMAICAL MEHODS IN ELECROMAGNEIC HEORY FRESNEL FORMULAE FOR SCAERING OPERAORS I.V. Petrusenko & Yu.K. Sirenko A. Usikov Institute of Radio Physics
DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS *
 IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
A PIEZOELECTRIC BERNOULLI-EULER BEAM THEORY CONSIDERING MODERATELY CONDUCTIVE AND INDUCTIVE ELECTRODES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Aores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5513 A PIEZOELECTRIC BERNOULLI-EULER
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Aores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5513 A PIEZOELECTRIC BERNOULLI-EULER
pp physics, RWTH, WS 2003/04, T.Hebbeker
 1. PP TH 03/04 Accelerators and Detectors 1 hysics, RWTH, WS 2003/04, T.Hebbeker 2003-12-03 1. Accelerators and Detectors In the following, we concentrate on the three machines SPS, Tevatron and LHC with
1. PP TH 03/04 Accelerators and Detectors 1 hysics, RWTH, WS 2003/04, T.Hebbeker 2003-12-03 1. Accelerators and Detectors In the following, we concentrate on the three machines SPS, Tevatron and LHC with
Phase transitions. Lectures in Physical Chemistry 4. Tamás Turányi Institute of Chemistry, ELTE. Phases
 Phase transitions Lectures in Physical Cheistry 4 Taás Turányi Institute of Cheistry, ELTE Phases DEF a syste is hoogeneous, if () it does not contain arts searated by acroscoic surfaces, and () all intensive
Phase transitions Lectures in Physical Cheistry 4 Taás Turányi Institute of Cheistry, ELTE Phases DEF a syste is hoogeneous, if () it does not contain arts searated by acroscoic surfaces, and () all intensive
Important Formulae & Basic concepts. Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER
 Iportant Forulae & Basic concepts Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER S. No. Forula Description 1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current
Iportant Forulae & Basic concepts Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER S. No. Forula Description 1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current
In the session you will be divided into groups and perform four separate experiments:
 Mechanics Lab (Civil Engineers) Nae (please print): Tutor (please print): Lab group: Date of lab: Experients In the session you will be divided into groups and perfor four separate experients: (1) air-track
Mechanics Lab (Civil Engineers) Nae (please print): Tutor (please print): Lab group: Date of lab: Experients In the session you will be divided into groups and perfor four separate experients: (1) air-track
VACUUM chambers have wide applications for a variety of
 JOURNAL OF THERMOPHYSICS AND HEAT TRANSFER Vol. 2, No., January March 27 Free Molecular Flows Between Two Plates Equied with Pus Chunei Cai ZONA Technology, Inc., Scottsdale, Arizona 85258 Iain D. Boyd
JOURNAL OF THERMOPHYSICS AND HEAT TRANSFER Vol. 2, No., January March 27 Free Molecular Flows Between Two Plates Equied with Pus Chunei Cai ZONA Technology, Inc., Scottsdale, Arizona 85258 Iain D. Boyd
MODELING AND CONTROL OF A MICROGRIPPER BASED ON ELECTROMAGNETIC ACTUATION
 MODELING AND CONTROL OF A MICROGRIPPER BASED ON ELECTROMAGNETIC ACTUATION Veronica DESPA, Adrian CATANGIU, Ioan Alexandru IVAN, Valentin GURGU, Miai ARDELEANU ) Valaia University of Targoviste ) Université
MODELING AND CONTROL OF A MICROGRIPPER BASED ON ELECTROMAGNETIC ACTUATION Veronica DESPA, Adrian CATANGIU, Ioan Alexandru IVAN, Valentin GURGU, Miai ARDELEANU ) Valaia University of Targoviste ) Université
A Constraint View of IBD Graphs
 A Constraint View of IBD Grahs Rina Dechter, Dan Geiger and Elizabeth Thoson Donald Bren School of Inforation and Couter Science University of California, Irvine, CA 92697 1 Introduction The reort rovides
A Constraint View of IBD Grahs Rina Dechter, Dan Geiger and Elizabeth Thoson Donald Bren School of Inforation and Couter Science University of California, Irvine, CA 92697 1 Introduction The reort rovides
Input-Output (I/O) Stability. -Stability of a System
 Inut-Outut (I/O) Stability -Stability of a Syste Outline: Introduction White Boxes and Black Boxes Inut-Outut Descrition Foralization of the Inut-Outut View Signals and Signal Saces he Notions of Gain
Inut-Outut (I/O) Stability -Stability of a Syste Outline: Introduction White Boxes and Black Boxes Inut-Outut Descrition Foralization of the Inut-Outut View Signals and Signal Saces he Notions of Gain
PH 221-2A Fall Waves - I. Lectures Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition)
 PH 1-A Fall 014 Waves - I Lectures 4-5 Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will
PH 1-A Fall 014 Waves - I Lectures 4-5 Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will
Problem T1. Main sequence stars (11 points)
 Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Quantum Mechanics I (8.04) Spring 2005 Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Quantu Mechanics I (8.04) Spring 2005 Solutions to Proble Set 4 By Kit Matan 1. X-ray production. (5 points) Calculate the short-wavelength liit for X-rays produced
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Quantu Mechanics I (8.04) Spring 2005 Solutions to Proble Set 4 By Kit Matan 1. X-ray production. (5 points) Calculate the short-wavelength liit for X-rays produced
Handout 6 Solutions to Problems from Homework 2
 CS 85/185 Fall 2003 Lower Bounds Handout 6 Solutions to Probles fro Hoewor 2 Ait Charabarti Couter Science Dartouth College Solution to Proble 1 1.2: Let f n stand for A 111 n. To decide the roerty f 3
CS 85/185 Fall 2003 Lower Bounds Handout 6 Solutions to Probles fro Hoewor 2 Ait Charabarti Couter Science Dartouth College Solution to Proble 1 1.2: Let f n stand for A 111 n. To decide the roerty f 3
Notes on Landau damping
 Notes on Landau daing by Youjun Hu Institute of Plasas, Chinese Acadey of Sciences Eail: yjhu@i.cas.cn In Sec. of this note, resonant wave article interactions are deonstrated by a sile testarticle siulation.
Notes on Landau daing by Youjun Hu Institute of Plasas, Chinese Acadey of Sciences Eail: yjhu@i.cas.cn In Sec. of this note, resonant wave article interactions are deonstrated by a sile testarticle siulation.
AN ACCURACY OF ASYMPTOTIC FORMULAS IN CALCULATIONS OF A RANDOM NETWORK RELIABILATY. Tsitsiashvili G.Sh., Losev A.S.
 Tsitsiashvili G, Losev A AN ACCUACY OF ASYMPTOTIC FOMULAS IN CALCULATIONS OF A ANDOM NETWOK ELIABILATY &ATA # 3 (Vol) 009, Seteber AN ACCUACY OF ASYMPTOTIC FOMULAS IN CALCULATIONS OF A ANDOM NETWOK ELIABILATY
Tsitsiashvili G, Losev A AN ACCUACY OF ASYMPTOTIC FOMULAS IN CALCULATIONS OF A ANDOM NETWOK ELIABILATY &ATA # 3 (Vol) 009, Seteber AN ACCUACY OF ASYMPTOTIC FOMULAS IN CALCULATIONS OF A ANDOM NETWOK ELIABILATY
The temperature dependences of electromechanical properties of PLZT ceramics
 The headers will be insert by the Publisher The headers will be insert by the Publisher The headers will be insert by the Publisher The teperature dependences of electroechanical properties of PLZT ceraics
The headers will be insert by the Publisher The headers will be insert by the Publisher The headers will be insert by the Publisher The teperature dependences of electroechanical properties of PLZT ceraics
New Set of Rotationally Legendre Moment Invariants
 New Set of Rotationally Legendre Moent Invariants Khalid M. Hosny Abstract Orthogonal Legendre oents are used in several attern recognition and iage rocessing alications. Translation and scale Legendre
New Set of Rotationally Legendre Moent Invariants Khalid M. Hosny Abstract Orthogonal Legendre oents are used in several attern recognition and iage rocessing alications. Translation and scale Legendre
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
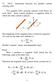 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications 3 rd Ed
 Fundaentals of Astrodynaics and Alications 3 rd Ed Errata June 0, 0 This listing is an on-going docuent of corrections and clarifications encountered in the book. I areciate any coents and questions you
Fundaentals of Astrodynaics and Alications 3 rd Ed Errata June 0, 0 This listing is an on-going docuent of corrections and clarifications encountered in the book. I areciate any coents and questions you
Physics 120. Exam #2. May 23, 2014
 Physics 10 Exa # May 3, 014 Nae Please read and follow these instructions carefully: ead all probles carefully before attepting to solve the. Your work ust be legible, and the organization clear. You ust
Physics 10 Exa # May 3, 014 Nae Please read and follow these instructions carefully: ead all probles carefully before attepting to solve the. Your work ust be legible, and the organization clear. You ust
Exploiting Matrix Symmetries and Physical Symmetries in Matrix Product States and Tensor Trains
 Exloiting Matrix Syetries and Physical Syetries in Matrix Product States and Tensor Trains Thoas K Huckle a and Konrad Waldherr a and Thoas Schulte-Herbrüggen b a Technische Universität München, Boltzannstr
Exloiting Matrix Syetries and Physical Syetries in Matrix Product States and Tensor Trains Thoas K Huckle a and Konrad Waldherr a and Thoas Schulte-Herbrüggen b a Technische Universität München, Boltzannstr
Chapter 28: Alternating Current
 hapter 8: Alternating urrent Phasors and Alternating urrents Alternating current (A current) urrent which varies sinusoidally in tie is called alternating current (A) as opposed to direct current (D).
hapter 8: Alternating urrent Phasors and Alternating urrents Alternating current (A current) urrent which varies sinusoidally in tie is called alternating current (A) as opposed to direct current (D).
Analysis of cold rolling a more accurate method
 Analysis of cold rolling a more accurate method 1.1 Rolling of stri more accurate slab analysis The revious lecture considered an aroximate analysis of the stri rolling. However, the deformation zone in
Analysis of cold rolling a more accurate method 1.1 Rolling of stri more accurate slab analysis The revious lecture considered an aroximate analysis of the stri rolling. However, the deformation zone in
