THE A-TEMPORAL COSMIC SPACE AND A GENERALIZATION OF THE DIRAC EQUATION
|
|
|
- Morgan Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE -TEMPORL COMC PCE N GENERLZTON OF THE RC EQUTON avide Fisaletti aelife nstitute an Loenzo in Camo PU taly fisalettidavide@libeo.it bstat model desibing an a-temoal sae-gavity endowed with a quantum wave stutue is oosed. n this model the most fundamental hysial quantities ae the density of osmi sae hysial quantity whih deends on the amount of matte esent in the egion into onsideation the eleti density of sae hysial quantity whih indiates the amount of hage esent in the egion into onsideation and a quantum numbe indiating a sot of otation-oientation of eah oint of sae. mathematial fomalism egading the wave funtion of quantum-gavity sae is develoed whih is based on a genealized Fisaletti-ia equation fo the density of osmi sae. genealized Fisaletti-ia equation fo the density of osmi sae ouled with eletomagneti inteation is also intodued.. ntodution t the beginning of the new millennium a etain onetual onfusion is evident in diffeent hysial theoies models and ideas fo eamle elativity theoies standad model quantum gavity natue of sae time and mass and sense of highe sae dimensions to name a few. t is tue that quantum mehanis and geneal elativity the two fundamental XX entuy hysial theoies have obtained huge suess fom the editive oint of view but it is also tue that they ovide a itue of the wold whih is somewhat inomlete and fagmented. The most imotant hallenge in today s fundamental hysis is to find a oheent and satisfatoy unifiation of these theoies and thus to inooate onsistently gavity in the quantum mehanial sheme. s egads the hallenge of quantum gavity in ode to omlete the evolution oened by geneal elativity and quantum mehanis loo quantum gavity edits that at the most fundamental level hysial sae has a ganula stutue namely is omosed by elementay gains a net of inteseting loos also defined sin elements o sin netwos beause thei quantum numbes and thei algeba loo lie the sin angula momentum numbes of elementay atiles having the Plan size. On the gound of the esults of loo quantum gavity nodes of sin netwos eesent the elementay gains of sae and thei volume is given by a quantum numbe that is assoiated with the node in units of the elementay Plan volume / V G / whee is Plan s edued-onstant G is the univesal gavitation onstant and is the seed of light. n this atile following the hilosohy of loo quantum gavity we want to suggest a new view a new hysial model whih stats fom the idea that gavity-sae is a- temoal in the sense that time eists only as a steam of mateial movements and hanges and is haateized by a quantum wave and ganula stutue. The ental idea suggested by this model is that hysial univese an be desibed by intoduing a fundamental level of desition whih an be alled quantum-gavity sae whih is a
2 gavitational sae that ehibits wave stutue and ganula stutue. n atiula in this model eah egion of sae an be haateized by a wave funtion whih deends on two fundamental quantities: the density of osmi sae whih is lined to the amount of matte esent in the egion unde onsideation and a quantum numbe indiating a sot of otation-oientation of eah oint of sae. e will show that this wave funtion satisfy a fundamental genealization of the ia equation fo the density of osmi sae and that the standad ia equation of quantum theoy an be obtained fom this genealized ia equation in a atiula ase. e will analyze also the situation in whih the density of osmi sae is ouled with an eletomagneti inteation by intoduing a genealized ia equation fo the density of osmi sae with eletomagneti inteation.. The density of osmi sae and the gavitational inteation the eleti density of sae and the eletostati inteation On the basis of elementay eetion the assing of the time annot be eeived dietly as matte and sae; we an eeive only the ievesible hanges of matte in sae. Time annot be onsideed a eal hysial entity: it has not an autonomous eistene but eists only as a steam of ievesible mateial hanges haening in an a- temoal sae. t is emissible to assume on the gound of ou elementay eetion that hange does not un in time but hange itself is time. Time means hange movement and theefoe when thee is no hange thee is no time. Clos un in a- temoal sae. ith los we measue the duation and the numeial ode of all hanges. Phenomena un in sae-time only in the mathematial models of eality whih sometimes beome moe eal than eality itself whih instead on the gound of ou elementay eetion tuns out to be a-temoal. The stage in whih natual henomena haen is not sae-time but is an a-temoal sae. This is an altenative diffeent oint of view fom that onventionally adoted in hysis but is ehas moe oet and aoiate beause is moe oheent with eeimental fats i.e. with the fat that thee is no evidene that mateial objets move in time 4. tating fom the idea that sae is a-temoal inteesting esetives ae oened in theoetial hysis. n atiula in a-temoal hysial sae the fundamental inteations and hysial fields an be inteeted as seial states of sae unde etain iumstanes an be seen as entities whih deive fom eal oeties of sae 5. f time eists only as a steam of ievesible mateial hanges haening in sae we ae esented with the ossibility to ovide a new a-temoal inteetation of gavitational inteation. oding to this inteetation gavitational inteation is immediate in the sense that ats instantly though the density of osmi sae. Moeove gavitational foe is a-temoal: no movement of atile-wave is needed fo its ating. Gavity is tansmitted by the density of osmi sae eisting in eah oint of sae. The density of osmi sae an be onsideed the fundamental hysial oety whih haateizes univesal sae. t deends on the amount of matte esent in the egion into onsideation. The density of osmi sae assoiated with a mateial objet of mass m in the oints situated at distane fom the ente of this objet is defined by the Gm elation whee G is gavitational onstant. hile in the Newtonian view the soue of the gavitational field is mass in this model we suggest the idea that the gavitational field in eah oint of sae is a oety
3 that deends on the density of osmi sae eisting in that oint. t is the density of osmi sae that detemines the aeaane of a gavitational field in eah oint of sae. ntoduing the onet of the density of osmi sae assoiated with a given Gm mass m on the basis of elation the gavitational field assoiated with that density of osmi sae in the oints situated at distane fom its ente assumes the fom g ˆ. Equation shows that the gavitational field deives dietly fom the density of osmi sae haateizing a given oint. The fundamental ideas of the aoah hee suggested an be also eessed in the following way. e an say that if a egion of sae is haateized by a density of osmi sae given by in the oints situated at distane fom a given oint P this means that in the egion thee is a mateial objet of mass m and that the oint P is the ente of this mateial objet. t is the density of osmi sae that detemines the aeaane of a mateial objet in a given egion of sae. n othe wods onsideing a etain egion of sae the mass of a atile an be seen as the otion of that egion whee the density of osmi sae is bigge. This view allows us to inteet mass as a quantity whih is not muh diffeent fom sae as a onsequene of a oety of osmi sae namely its density. Newton s gavitational attation between two masses m and m situated at distane an be seen as a onsequene of a moe fundamental attation of two oints Gm of sae haateized by a diffeent density of osmi sae. n fat if is the density of osmi sae assoiated with a mateial objet of mass m in a given oint Gm of sae situated at distane fom its ente 4 is the density of osmi sae assoiated with a mateial objet of mass m in a given oint of sae situated at distane fom its ente is the distane between these two atiula oints we an wite: F g ˆ 5 whih eesents the geneal law of inteation G between these two densities of osmi sae the one assoiated with the mass m the othe assoiated with the mass m. Taing into aount elations and 4 equation 5 m m tuns out to be omletely omatible with equation F g G ˆ 6 whih is Newton s law of gavitational inteation witten in the standad fom. e an say that intoduing the density of osmi sae Newton s law 6 an be onsideed as a atiula ase of a moe geneal equation the equation 5 whih desibes the inteation between two densities of osmi sae the one assoiated with the mass m the othe assoiated with the mass m. The a-temoal model of gavitation inteation hee oosed oens theefoe this imotant esetive in theoetial hysis: two oints of sae haateized by a diffeent density of osmi sae attat eah othe and this onens all the oints of sae satisfying this ondition. nd the following inteetation of masses inteation deives: the mateial objets move in the dietion whee the density of osmi sae is ineasing. n othe wods a-temoal hysial sae an be seen as an elasti medium whih has a tendeny to shin. The moe medium is dense the stonge the foe of shining. The foe of shining is the gavitational foe 6. oding to the model hee oosed aeas of lowe density have a tendeny to move towads aeas of highe density. This is
4 the eason why objets with lowe mass have a tendeny to move towads objets with bigge mass. f the density of osmi sae is the most univesal hysial oety of a-temoal sae thee is howeve also anothe imotant hysial oety whih an be onsideed fundamental namely the eleti density of sae. The eleti density of sae is the hysial quantity whih indiates the amount of hage haateizing the egion of sae into onsideation and theefoe whih indiates the eleti oeties of a given egion of hysial sae. f we have a haged atile still in a given oint of sae this hage detemines a modifiation in the oeties of a-temoal osmi sae onening in atiula the tajetoies of othe haged atiles situated in that egion. n atiula the eleti density of sae assoiated to a hage q in the oints situated at Kq distane fom its ente an be defined though the elation e 7 whee l K is the onstant indiating the stength of the eleti foe with ε being the 4πε dieleti onstant of the vauum is the distane fom the ental quantum of sae. f a egion of sae is haateized by an eleti density of sae given by elation 7 this means that in this egion thee is a atile of hage q 7. Taing into onsideation its hysial dimensions the eleti density of sae an be inteeted as a measue of the eleti field fo unit of volume namely fo Plan volume l. ntoduing the onet of the eleti density of sae we an say that eah oint of a given egion endowed with the eleti density of sae 7 esents an eletostati field as a onsequene of this eleti density of sae. n atiula the eletostati field due to an eleti density of sae in a given oint at distane fom the ente of this eleti density an be eessed in the following way E l ˆ 8. Equation 8 shows lealy that the eleti field is a oety of sae deending on the value of the eleti density of sae haateizing that oint. e an say theefoe that the soue of the eleti field is not oely the eleti hage but the eleti density of sae. f mass an be seen as a stutue of sae deiving fom the density of osmi sae in a simila way hage an be seen as a oety of sae deiving fom the eleti density of sae. t is the eleti density of sae 7 that detemines the aeaane of a haged atile in a given egion of sae. n othe wods onsideing a etain egion of sae a hage an be seen as the otion of that egion whee an ootune eleti density of sae assumes its maimum value. n the lassial domain the eletostati foe ating between two hages q and q situated at distane an be seen as a onsequene of a moe fundamental inteation between two oints of sae haateized by a diffeent eleti density of sae. n fat Kq if e is the density of osmi sae assoiated with a atile of hage q in a l Kq given oint of sae situated at distane fom its ente e is the eleti l density of sae assoiated with a atile of hage q in a given oint of sae situated at distane fom its ente is the distane between these two atiula oints of 6 e e l sae we an wite: Fe ˆ 9 whih eesents the geneal law K of inteation between two eleti densities of osmi sae the one assoiated with the e 4
5 hage q the othe assoiated with the hage q. Equation 9 establishes that eletostati foe ats between egions of sae endowed with diffeent eleti densities of sae. t is imotant to obseve that taing into aount the definition of the eleti q q density of sae 7 Coulomb s law F e K ˆ is efetly equivalent to equation 9. e an theefoe onlude that intoduing the onet of the eleti density of sae Coulomb s law an be onsideed as a atiula ase of a moe geneal equation the equation 9 whih desibes the inteation between two eleti densities of sae. e ae esented theefoe with this inteesting esetive: two oints of sae haateized by a diffeent eleti density of sae inteat eah othe and this onens all the ais of oints of sae satisfying this ondition. nd the following inteetation of eletostati inteation deives: as eah oint of sae is haateized by the oety of the eleti density of sae not only the entes of the haged atiles move but also all the othe oints move aoding to equation 9.. -temoal gavitodynamis: the wave funtion of quantum-gavity sae and the Fisaletti-ia equation fo the density of osmi sae eveal authos have taen into onsideation the ossibility that sae is endowed with gavito/magneti oeties. n atiula in some eent atiles 8 9 Tuanyanin oosed the idea of a gavity-sae henomenon haateized by a non linea wave dynamis in whih the wave funtion desibing the state of sae is eessed in tems of G M two fields the gavitostati/eleti field E g ˆ having hysial dimensions of a G J wave veto l and the gavitoineti/magneti field B g having hysial dimensions of a fequeny t whee J L s L Mv is the obital angula momentum of the soue M is the soue mass s is the sin angula momentum of the soue. awing a stating oint fom these esults we want to suggest now a new view of a hysial sae endowed with a wave stutue and in whih time eists only as an ievesible motion of matte. oding to this inteetation the most fundamental hysial quantities desibing sae ae the density of osmi sae and a quantum veto Gs j defined as j and theefoe having the dimensions of an angula momentum fo unit of volume and multilied with the gavitation univesal onstant. This quantum veto j an be theefoe onsideed as a sot of otation-oientation of eah oint of sae. The quantum numbe j multilied fo / G an assume intege o halfintege multile values of the Plan edued onstant in ode to assue onsisteny with the esults of standad quantum mehanis. e will say thus that eah oint of sae is haateized by a deteminate value of the density of osmi sae and is endowed with a atiula otation-oientation lined to a atiula value of the quantum numbe j whih G an assume intege of half intege multile values of. n analogy with the oosal of Tuanyanin in the theoy hee suggested sae is desibed in tems of two fields: the gavistostati/eleti field defined on the basis of the 5
6 elation E g ˆ 4 whih is omletely omatible with and the v senϑ gavitoineti/magneti field defined on the basis of the elation ˆ j B g b 5 whee ϑ is the angle between and v bˆ is an unitay veto identifying dietion and vesus of L mv m being the mass of the atile assoiated with the density of osmi sae. The modulus of B g is B g v sen ϑ j v senϑ j os 6 whee is the angle between bˆ and j. t is imotant to obseve that the gavitostati/eleti field and the gavitoineti/magneti field hee defined have the hysial dimensions of a wave veto and a fequeny esetively. t aeas thus legitimate to intodue the wave funtion of sae ψ ˆ e πi v sen ϑ j v senϑ j os t ϕ 7 whee the amlitude is a funtion of the oint yz of sae. ine the density of osmi sae is the univesal hysial oety of sae will deend in geneal on the density of osmi sae and the seed of the atile detemined by this density of osmi sae. The wave funtion 7 of quantum-gavity sae an be onsideed the statingoint of an a-temoal inteetation of the univese in whih time eists only as motion of matte. n fat fo v and j onditions whih mean no motion one an easily see that this wave funtion assumes the fom ψ ˆ e πi ϕ 8 namely tuns out to be indeendent fom time: this means just that when thee is no motion thee is no time. G Now we want to analyze the atiula ase j and develo a mathematial G fomalism fo this. ine j oesonds to the aeaane of a atile of sin ½ one an intodue in this ase the idea of a geneal wave funtion of quantum-gavity sae ψ satisfying a ia-tye equation fo the density of osmi sae iγ ψ 9 whee t and γ ae the well-nown i elativisti maties γ γ σ i and σ ae the Pauli maties whih ae lined to σ j though the elation j G. Equation 9 an be onsideed the equation whih desibes a egion of sae haateized by a density of osmi sae whih detemines the esene of a atile of sin ½ without eletomagneti inteation namely in whih the density of osmi sae is not ouled with an eletomagneti inteation. The geneal solution of equation 9 an be eessed as P P ψ ψ ψ whee ψ eesents the wave funtion of sae assoiated with the aeaane of atiles of sin ½ and ψ eesents the wave funtion of sae assoiated with the aeaane of the oesonding antiatiles. P These two set of wave funtions of sae an be eanded as ψ b u 6
7 7 v d * ψ esetively. Hee u ae ositive-fequeny 4-sinos of sae while v ae negative fequeny 4-sinos of sae; they togethe fom a omlete set of othonomal solutions to 9. The label is an abbeviation fo the set j whee is the -momentum and Gs j with s is the label of the otationoientation of the genei oint of sae at distane fom the ente of the density of osmi sae namely whee assumes its maimum value. s egads the eessions of u and v equation 9 leads to the following esults: i u z e with z and i v z e 4 with z4 whee and E i E E 5 E E i E 6 E i E E 7 4 E E i E 8. whee E is the enegy of the atile assoiated with the density of osmi sae. Now by intoduing the quantities Ω P u u 9 Ω v v one an obtain P ψ and ψ fom ψ using P P d ψ ψ Ω and d ψ ψ Ω whee t t. One an also intodue the atile and antiatile uents assoiated esetively with
8 P the atile wave of sae ψ and the antiatile wave of sae ψ defined as ψ γ ψ P P P P J ψ γ ψ J whee ψ ψ γ. ine ψ and ψ seaately satisfies the ia-tye equation 9 the uents P J J P J and J ae seaately onseved. Theefoe one an intodue the idea of tajetoies of atiles P and antiatiles whih deive fom ψ and ψ on the basis of the equations: P P P d J t d J t P 4 P 5 esetively whee J J J J. dt J t dt J t t is also inteesting to obseve that the well-nown ia equation fo elativisti m atiles of sin ½ of standad quantum theoy i γ ψ 6 an be seen as a atiula ase of the equation 9. n fat equation 6 an be dietly obtained fom m m 9 in the ondition namely that is l and in oesondene the wave funtions and 4 beome the standad 4-sinos whih ae solutions of the standad ia equation of the standad quantum theoy fo atiles. This onsideation allows us to oen the following imotant esetive: equation 6 an be inteeted as the equation of the density of osmi sae fo the atiula oints of sae situated at distane l fom the ente of the density of osmi sae into onsideation. n othe wods the standad wave funtions of ia atiles an be seen as atiula ases of moe geneal wave funtions of quantum-gavity sae fo the atiula oints situated at distane l fom the ente of the density of osmi sae into onsideation. e ae theefoe esented with the ossibility that equation 9 an be onsideed as a moe fundamental equation than the standad ia equation 6: we an all equation 9 as the genealized ia equation fo the wave funtion of quantum-gavity sae without eletomagneti inteation o the Fisaletti-ia equation without eletomagneti inteation. Finally let us onside now a egion of sae haateized by a density of osmi sae whih detemines the esene of a atile of sin ½ whih is subjeted to an eletomagneti inteation namely a egion of sae in whih the density of osmi sae is ouled with eletomagneti inteation. n this ase we an intodue the idea of a wave funtion of quantum-gavity sae ψ satisfying a genealized ia-tye equation fo the density of osmi sae with eletomagneti inteation e l G iγ 4 ψ 7 whee e is the eleti density of sae K is K the eletostati onstant is the eletomagneti otential. The well nown ia equation fo elativisti atiles of sin ½ with eletomagneti inteation q m i γ ψ 8 an be seen as a atiula ase of the equation. n q e l G fat equation 8 an be dietly obtained fom 7 in the onditions 4 K Kq m m namely e and namely whih togethe oesond to Gl the ondition l. This onsideation allows us to oen the following imotant 8
9 esetive: equation 8 an be inteeted as the equation of the density of osmi sae ouled with eleti density of sae and eletomagneti inteation fo the atiula oints of sae situated at distane l fom the ente of the density of osmi sae and the eleti density of sae into onsideation. This imlies also that the standad wave funtions of ia atiles with eletomagneti inteation an be seen as atiula ases of moe geneal wave funtions of quantum-gavity sae ouled with eletomagneti inteation fo the atiula oints situated at distane l fom the ente of the density of osmi sae and the eleti density of sae into onsideation. e ae theefoe esented with the ossibility that equation 8 an be onsideed as a moe fundamental equation than the standad ia equation 55: we an all equation 8 as the genealized ia equation fo the wave funtion of quantumgavity sae with eletomagneti inteation o the Fisaletti-ia equation with eletomagneti inteation. The ossibility is oened that the Fisaletti-ia equation with eletomagneti inteation 7 an be esolved analogously to the oesonding standad ia equation of quantum theoy by intoduing a Feynman oagato inside a etubative method with eset to the eleti density of sae 7. n absene of the eleti density of sae we have the wave funtions of quantum-gavity sae without eletomagneti inteation solutions to the Fisaletti-ia equation these solutions on the basis of this etubative teatment an be inteeted as aoimations at the zeoth ode of the solutions to the Fisaletti-ia equation with eletomagneti inteation 7. hen the eleti density of sae is esent and is lead to its hysial value we have the solutions to the Fisaletti-ia equation fo the density of osmi sae with eletomagneti inteation 7 at the fist ode. bout the solutions of the Fisaletti-ia equation with eletomagneti inteation 7 and thei onsequenes futhe eseah will give you moe infomation. 4. Conlusions tating fom the idea that hysial sae is a-temoal in the sense that time eists only as motion of matte and intoduing the onets of the density of osmi sae the eleti density of sae and of the otation-oientation of eah oint of sae a new view of quantum-gavity sae aises. n this view sae an be desibed in tems of two fields the gavitostati field and the gavitoineti field whih ae defined in tems of the density of osmi sae and of the otation-oientation of eah oint of sae. n vitue of the natue of these fields a wave funtion of gavity-sae and theefoe the idea of a G wave quantum-gavity sae an be intodued. n the atiula ase j whih oesonds to the aeaane of a atile of sin ½ genealized Fisaletti-ia equations fo the density of osmi sae both without eletomagneti inteation and theefoe without the ouling with an eleti density of sae and with eletomagneti inteation and thus with the ouling of an eleti density of sae have been intodued. The well nown ia equations without eletomagneti inteation and with eletomagneti inteation fo elementay atiles of standad quantum theoy an be seen as seial ases of the genealized Fisaletti-ia equations fo the density of osmi sae without eletomagneti inteation and with eletomagneti inteation esetively. The lin between the standad ia equations without eletomagneti inteation and with eletomagneti inteation fo elementay atiles and the genealized Fisaletti-ia equations fo the density of osmi sae without eletomagneti inteation and with eletomagneti inteation has the imotant 9
10 onsequene that hysial sae tuns out to be not indefinitely divisible but to have a minimal size equal to Plan length. n this way the model hee suggested ovides an imotant justifiation of the fat that in a etain sense the idea of a wave stutue of sae must not be onsideed inomatible with the idea of a ganula stutue of sae. n sum the inteetation of quantum-gavity sae oosed in this atile an be onsideed the stating-oint of a modifiation in the th entuy field-geomety aadigm towads a eal ganula-wave-dynami itue and deely holisti view of the univese. Refeenes. oli. and Fisaletti. 5. tive Galati Nuleus s a Renewing ystem Of the Univese. Eletoni Jounal of Theoetial Physis Rovelli C.. Loo Quantum Gavity. Physis old oli. and oli. 4. Mathematial Time nd Physial Time n The Theoy Of Relativity. Eletoni Jounal of Theoetial Physis htt:// 4. oli. and oli. 4. -temoal gavitation. Eletoni Jounal of Theoetial Physis Fisaletti. and oli. 5. Towad an a-temoal inteetation of quantum otential. Fontie Pesetives oli. and oli. 5. -temoal gavitation and hyothetial gavitational waves. Eletoni Jounal of Theoetial Physis Puell E.M. 97. La fisia di Beeley Vol. : Elettiità e magnetismo. Bologna: Zanihelli. 8. Tuanyanin. 5. ave Gavity the way towads Plan sale. Millennium Relativity Paes etion. 9. Tuanyanin. 6. ave dynamis of quantum gavity-sae. Geneal iene Jounal.. Fisaletti. 8. Pesetives towads the density theoy of eveything ; ientifi nquiy Nioli H. 4. Bohmian atile tajetoies in elativisti femioni quantum field theoy. axiv:quant-h/5 v 7 et 4.. Nioli H. 4. Found. Phys. Lett Bjoen J.. and ell Relativisti quantum mehanis. New Yo: MGaw-Hill.
dp p v= = ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945).
 ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
Journal of Theoretics
 Jounal of Theoetis Volume 6-1, Feb-Mah 4 An Altenative Exlanation of the Cosmologial Redshift by the Tahyon Plasma Field in Integalati Sae Takaaki Musha musha@jda-tdi.go.j, musha@jg.ejnet.ne.j MRI, -11-7-61,
Jounal of Theoetis Volume 6-1, Feb-Mah 4 An Altenative Exlanation of the Cosmologial Redshift by the Tahyon Plasma Field in Integalati Sae Takaaki Musha musha@jda-tdi.go.j, musha@jg.ejnet.ne.j MRI, -11-7-61,
Dynamic Quantum Vacuum and Relativity
 Dynami Quantum Vauum and Relativity Davide Fisaletti*, Amit Soli** *SaeLife Institute, San Loenzo in Camo (PU), Italy **Foundations of Physis Institute, Idija, Slovenia soli.amit@gmail.om saelife.institute@gmail.om
Dynami Quantum Vauum and Relativity Davide Fisaletti*, Amit Soli** *SaeLife Institute, San Loenzo in Camo (PU), Italy **Foundations of Physis Institute, Idija, Slovenia soli.amit@gmail.om saelife.institute@gmail.om
From E.G. Haug Escape Velocity To the Golden Ratio at the Black Hole. Branko Zivlak, Novi Sad, May 2018
 Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
ASuggestedBoundaryforHeisenberg suncertaintyprinciple
 ASuggestedBoundayfoHeisenbeg sunetaintypinile Esen aade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Januay 9, 08 Abstat In this ae we ae ombining Heisenbeg s unetainty inile with Haug s suggested maimum veloity
ASuggestedBoundayfoHeisenbeg sunetaintypinile Esen aade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Januay 9, 08 Abstat In this ae we ae ombining Heisenbeg s unetainty inile with Haug s suggested maimum veloity
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A realistic approach
 Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
In electrostatics, the electric field E and its sources (charges) are related by Gauss s law: Surface
 Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
The Mystery of Mass as Understood from Atomism
 The Mystey of Mass as Undestood fom Atomism Esen Gaade Haug June, 08 Abstat Ove the ast few yeas I have esented a theoy of moden atomism suoted by mathematis [, ]. In eah aea of analysis undetaken in this
The Mystey of Mass as Undestood fom Atomism Esen Gaade Haug June, 08 Abstat Ove the ast few yeas I have esented a theoy of moden atomism suoted by mathematis [, ]. In eah aea of analysis undetaken in this
PROPAGATION OF PHOTON IN RESTING AND MOVING MEDIUM. J. Zaleśny. Institute of Physics, Technical University of Szczecin, A b s t r a c t
 PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
Revised Newtonian Formula of Gravity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat Space-Time Transformed from Schwarzschild Solution
 Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematical Model of Dust Whirl
 Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Electric Anisotropy, Magnetic Anisotropy, Uniaxial and Biaxial Materials, Bianisotropic Media (Definitions)
 leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Special Relativity in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Waves Without Phase Invariance and Lorentz Transformations 1. Introduction n k.
 Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Mass- and light-horizons, black holes' radii, the Schwartzschild metric and the Kerr metric
 006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
A thermodynamic degree of freedom solution to the galaxy cluster problem of MOND. Abstract
 A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior P.V.T Relationships for Liquid and Solid:
 hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH 1. INTRODUCTION
 DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
4) Magnetic confinement of plasma
 4) Magneti onfineent of plasa Due to the shielding in the plasa, thee is alost no ontol with eleti fields. A ontol is possible with agneti fields, as patiles ae bound to the field lines. This is alled
4) Magneti onfineent of plasa Due to the shielding in the plasa, thee is alost no ontol with eleti fields. A ontol is possible with agneti fields, as patiles ae bound to the field lines. This is alled
Time Dilation in Gravity Wells
 Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
A Theory of the Podkletnov Effect based on General Relativity: Anti-Gravity Force due to the Perturbed Non-Holonomic Background of Space
 July, 007 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Volume 3 SPECIAL REPORT A Theoy of the Podkletnov Effet based on Geneal Relativity: Anti-Gavity Foe due to the Petubed Non-Holonomi Bakgound of Spae Dmiti Rabounski and Laissa
July, 007 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Volume 3 SPECIAL REPORT A Theoy of the Podkletnov Effet based on Geneal Relativity: Anti-Gavity Foe due to the Petubed Non-Holonomi Bakgound of Spae Dmiti Rabounski and Laissa
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Planck Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gravitation
 Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Classical Approach to the Theory of Elementary Particles
 Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Recitation PHYS 131. must be one-half of T 2
 Reitation PHYS 131 Ch. 5: FOC 1, 3, 7, 10, 15. Pobles 4, 17, 3, 5, 36, 47 & 59. Ch 5: FOC Questions 1, 3, 7, 10 & 15. 1. () The eloity of a has a onstant agnitude (speed) and dietion. Sine its eloity is
Reitation PHYS 131 Ch. 5: FOC 1, 3, 7, 10, 15. Pobles 4, 17, 3, 5, 36, 47 & 59. Ch 5: FOC Questions 1, 3, 7, 10 & 15. 1. () The eloity of a has a onstant agnitude (speed) and dietion. Sine its eloity is
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
Suppose you have a bank account that earns interest at rate r, and you have made an initial deposit of X 0
 IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
CMSC 425: Lecture 5 More on Geometry and Geometric Programming
 CMSC 425: Lectue 5 Moe on Geomety and Geometic Pogamming Moe Geometic Pogamming: In this lectue we continue the discussion of basic geometic ogamming fom the eious lectue. We will discuss coodinate systems
CMSC 425: Lectue 5 Moe on Geomety and Geometic Pogamming Moe Geometic Pogamming: In this lectue we continue the discussion of basic geometic ogamming fom the eious lectue. We will discuss coodinate systems
Appendix B The Relativistic Transformation of Forces
 Appendix B The Relativistic Tansfomation of oces B. The ou-foce We intoduced the idea of foces in Chapte 3 whee we saw that the change in the fou-momentum pe unit time is given by the expession d d w x
Appendix B The Relativistic Tansfomation of oces B. The ou-foce We intoduced the idea of foces in Chapte 3 whee we saw that the change in the fou-momentum pe unit time is given by the expession d d w x
not to be republished NCERT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Chapter Eight MCQ I
 Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Lorentz-invariant theory of gravitation
 oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (summay) Alexande G. Kyiakos * Annotation This atile is a summay of the non-geometial oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (IGT) (efeenes and itations hee allow to familiaize
oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (summay) Alexande G. Kyiakos * Annotation This atile is a summay of the non-geometial oentz-invaiant theoy of gavitation (IGT) (efeenes and itations hee allow to familiaize
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6- THE LAW OF GRAVITATION Essential Idea: The Newtonian idea of gavitational foce acting between two spheical bodies and the laws of mechanics
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6- THE LAW OF GRAVITATION Essential Idea: The Newtonian idea of gavitational foce acting between two spheical bodies and the laws of mechanics
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B. Calculations for Sample Cross-Section 2
 SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
The Convergence-Confinement Method: Roles and Limits in Modern Geomechanical Tunnel Design
 Ameian Jounal of Aied Sienes 6 (4): 757-771, 009 ISSN 1546-939 009 Siene Publiations The Convegene-Confinement Method: oles and Limits in Moden Geomehanial Tunnel Design Pieaolo Oeste Deatment of Land,
Ameian Jounal of Aied Sienes 6 (4): 757-771, 009 ISSN 1546-939 009 Siene Publiations The Convegene-Confinement Method: oles and Limits in Moden Geomehanial Tunnel Design Pieaolo Oeste Deatment of Land,
d 2 x 0a d d =0. Relative to an arbitrary (accelerating frame) specified by x a = x a (x 0b ), the latter becomes: d 2 x a d 2 + a dx b dx c
 Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Rigid Body Dynamics 2. CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018
 Rigid Body Dynamics 2 CSE169: Compute Animation nstucto: Steve Rotenbeg UCSD, Winte 2018 Coss Poduct & Hat Opeato Deivative of a Rotating Vecto Let s say that vecto is otating aound the oigin, maintaining
Rigid Body Dynamics 2 CSE169: Compute Animation nstucto: Steve Rotenbeg UCSD, Winte 2018 Coss Poduct & Hat Opeato Deivative of a Rotating Vecto Let s say that vecto is otating aound the oigin, maintaining
Solving Problems of Advance of Mercury s Perihelion and Deflection of. Photon Around the Sun with New Newton s Formula of Gravity
 Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Kepler s problem gravitational attraction
 Kele s oblem gavitational attaction Summay of fomulas deived fo two-body motion Let the two masses be m and m. The total mass is M = m + m, the educed mass is µ = m m /(m + m ). The gavitational otential
Kele s oblem gavitational attaction Summay of fomulas deived fo two-body motion Let the two masses be m and m. The total mass is M = m + m, the educed mass is µ = m m /(m + m ). The gavitational otential
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
KEPLER S LAWS AND PLANETARY ORBITS
 KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
Reflectance spectra for Si
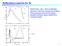 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
The Kerr-metric, mass- and light-horizons, and black holes' radii.
 006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
A Relativistic BCS Theory of S-Wave Superconductivity
 A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
Determine the Stress Calculating Mode of Sliding Failure of Soil Mass under the Push-Extend Multi-under-Reamed Pile
 Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Q. Obtain the Hamiltonian for a one electron atom in the presence of an external magnetic field.
 Syed Ashad Hussain Lectue Deatment of Physics Tiua Univesity www.sahussaintu.wodess.com Q. Obtain the Hamiltonian fo a one electon atom in the esence of an extenal magnetic field. To have an idea about
Syed Ashad Hussain Lectue Deatment of Physics Tiua Univesity www.sahussaintu.wodess.com Q. Obtain the Hamiltonian fo a one electon atom in the esence of an extenal magnetic field. To have an idea about
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
Relativity for Global Navigation Satellite Systems
 Relativity fo Global Navigation Satellite Systems Notes by Anna Heffenan based on the Living eviews atile, Relativity in the Global Positioning Systems, Neil Ashby, Living Rev. Relativity 6, (003),1 whih
Relativity fo Global Navigation Satellite Systems Notes by Anna Heffenan based on the Living eviews atile, Relativity in the Global Positioning Systems, Neil Ashby, Living Rev. Relativity 6, (003),1 whih
Physics 161 Fall 2011 Extra Credit 2 Investigating Black Holes - Solutions The Following is Worth 50 Points!!!
 Physics 161 Fall 011 Exta Cedit Investigating Black Holes - olutions The Following is Woth 50 Points!!! This exta cedit assignment will investigate vaious popeties of black holes that we didn t have time
Physics 161 Fall 011 Exta Cedit Investigating Black Holes - olutions The Following is Woth 50 Points!!! This exta cedit assignment will investigate vaious popeties of black holes that we didn t have time
Representation of gravity field equation and solutions, Hawking Radiation in Data General Relativity theory
 epesentation of gavity field equation and solutions Hawking adiation in Data Geneal elativity theoy Sangwha-Yi Depatment of Math aejon Univesity 300-76 ABSAC In the geneal elativity theoy we find the epesentation
epesentation of gavity field equation and solutions Hawking adiation in Data Geneal elativity theoy Sangwha-Yi Depatment of Math aejon Univesity 300-76 ABSAC In the geneal elativity theoy we find the epesentation
Correspondence Analysis & Related Methods
 Coespondene Analysis & Related Methods Oveview of CA and basi geometi onepts espondents, all eades of a etain newspape, osstabulated aoding to thei eduation goup and level of eading of the newspape Mihael
Coespondene Analysis & Related Methods Oveview of CA and basi geometi onepts espondents, all eades of a etain newspape, osstabulated aoding to thei eduation goup and level of eading of the newspape Mihael
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
Newton s Laws, Kepler s Laws, and Planetary Orbits
 Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Circular Motion Problem Solving
 iula Motion Poblem Soling Aeleation o a hange in eloity i aued by a net foe: Newton nd Law An objet aeleate when eithe the magnitude o the dietion of the eloity hange We aw in the lat unit that an objet
iula Motion Poblem Soling Aeleation o a hange in eloity i aued by a net foe: Newton nd Law An objet aeleate when eithe the magnitude o the dietion of the eloity hange We aw in the lat unit that an objet
A New Approach to General Relativity
 Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
5.111 Lecture Summary #6 Monday, September 15, 2014
 5.111 Lectue Summay #6 Monday, Septembe 15, 014 Readings fo today: Section 1.9 Atomic Obitals. Section 1.10 Electon Spin, Section 1.11 The Electonic Stuctue of Hydogen. (Same sections in 4 th ed.) Read
5.111 Lectue Summay #6 Monday, Septembe 15, 014 Readings fo today: Section 1.9 Atomic Obitals. Section 1.10 Electon Spin, Section 1.11 The Electonic Stuctue of Hydogen. (Same sections in 4 th ed.) Read
The Radii of Baryons
 Jounal Heading Yea; Vol. (No.): page ange DOI: 0.592/j.xxx.xxxxxxxx.xx The Radii of Bayons Maio Evealdo de Souza Depatmento de Físia, Univesidade Fedeal de Segipe, São Cistovão, 4900-000, Bazil Astat Consideing
Jounal Heading Yea; Vol. (No.): page ange DOI: 0.592/j.xxx.xxxxxxxx.xx The Radii of Bayons Maio Evealdo de Souza Depatmento de Físia, Univesidade Fedeal de Segipe, São Cistovão, 4900-000, Bazil Astat Consideing
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Galilean Transformation vs E&M y. Historical Perspective. Chapter 2 Lecture 2 PHYS Special Relativity. Sep. 1, y K K O.
 PHYS-2402 Chapte 2 Lectue 2 Special Relativity 1. Basic Ideas Sep. 1, 2016 Galilean Tansfomation vs E&M y K O z z y K In 1873, Maxwell fomulated Equations of Electomagnetism. v Maxwell s equations descibe
PHYS-2402 Chapte 2 Lectue 2 Special Relativity 1. Basic Ideas Sep. 1, 2016 Galilean Tansfomation vs E&M y K O z z y K In 1873, Maxwell fomulated Equations of Electomagnetism. v Maxwell s equations descibe
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
Analysis of Arithmetic. Analysis of Arithmetic. Analysis of Arithmetic Round-Off Errors. Analysis of Arithmetic. Analysis of Arithmetic
 In the fixed-oint imlementation of a digital filte only the esult of the multilication oeation is quantied The eesentation of a actical multilie with the quantie at its outut is shown below u v Q ^v The
In the fixed-oint imlementation of a digital filte only the esult of the multilication oeation is quantied The eesentation of a actical multilie with the quantie at its outut is shown below u v Q ^v The
THE SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY - A CLASSICAL APPROACH PETER G. BASS
 THE SPECIAL THEORY O RELATIVITY A CLASSICAL APPROACH PETER G. BASS P.G.Bass Deebe R Vesion.4. www.elativityoains.o Otobe 8 ABSTRACT The uose of this ae is to esent a new silifie aoah to the atheatial foulation
THE SPECIAL THEORY O RELATIVITY A CLASSICAL APPROACH PETER G. BASS P.G.Bass Deebe R Vesion.4. www.elativityoains.o Otobe 8 ABSTRACT The uose of this ae is to esent a new silifie aoah to the atheatial foulation
5. Mass Action and Concentration Dependence of the Chemical Potential. Topic: Concentration dependence of μ and the most important applications.
 5 Mass Ation and Conentation Deendene of the Chemial Potential 5 Mass Ation and Conentation Deendene of the Chemial Potential Toi: Conentation deendene of μ and the most imotant aliations 51 The onet of
5 Mass Ation and Conentation Deendene of the Chemial Potential 5 Mass Ation and Conentation Deendene of the Chemial Potential Toi: Conentation deendene of μ and the most imotant aliations 51 The onet of
ASuggestedBoundaryforHeisenberg suncertaintyprinciple
 ASuggestedBoundayfoHeisenbeg suncetaintypincile Esen aade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sciences Januay, 07 Abstact In this ae we ae combining Heisenbeg s uncetainty incile with Haug s suggested maimum
ASuggestedBoundayfoHeisenbeg suncetaintypincile Esen aade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sciences Januay, 07 Abstact In this ae we ae combining Heisenbeg s uncetainty incile with Haug s suggested maimum
Chapter 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
GRAVITATION EXPLAINED BY THE THEORY OF INFORMATONS
 GRAVITATION XLAIND BY TH THORY OF INFORMATONS Antoine Ake * ABSTRACT The theoy of infomatons explains the avitational inteations by the hypothesis that infomation is the substane of avitational fields
GRAVITATION XLAIND BY TH THORY OF INFORMATONS Antoine Ake * ABSTRACT The theoy of infomatons explains the avitational inteations by the hypothesis that infomation is the substane of avitational fields
AST 121S: The origin and evolution of the Universe. Introduction to Mathematical Handout 1
 Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Numerical Integration
 MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
Vibrational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Particle Pair in a Complex Plasma
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < Vibational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Patile Pai in a Comple Plasma K. Qiao, L. S. Matthews, and T. W. Hyde,
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < Vibational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Patile Pai in a Comple Plasma K. Qiao, L. S. Matthews, and T. W. Hyde,
Electric Field, Potential Energy, & Voltage
 Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Physics 2B Chapter 22 Notes - Magnetic Field Spring 2018
 Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I
 556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I CHAPTER 5: STOCHASTIC CONVERGENCE The following efinitions ae state in tems of scala anom vaiables, but exten natually to vecto anom vaiables efine on the same obability
556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I CHAPTER 5: STOCHASTIC CONVERGENCE The following efinitions ae state in tems of scala anom vaiables, but exten natually to vecto anom vaiables efine on the same obability
Special relativity with clock synchronization
 Speial elativity with lok synhonization Benhad Rothenstein ), Stefan Popesu ) and Geoge J. Spi 3) ) Politehnia Univesity of Timisoaa, Physis Depatment, Timisoaa, Romania, benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om ) Siemens
Speial elativity with lok synhonization Benhad Rothenstein ), Stefan Popesu ) and Geoge J. Spi 3) ) Politehnia Univesity of Timisoaa, Physis Depatment, Timisoaa, Romania, benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om ) Siemens
Numerical Modeling in Biomedical Systems
 Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
AP-C WEP. h. Students should be able to recognize and solve problems that call for application both of conservation of energy and Newton s Laws.
 AP-C WEP 1. Wok a. Calculate the wok done by a specified constant foce on an object that undegoes a specified displacement. b. Relate the wok done by a foce to the aea unde a gaph of foce as a function
AP-C WEP 1. Wok a. Calculate the wok done by a specified constant foce on an object that undegoes a specified displacement. b. Relate the wok done by a foce to the aea unde a gaph of foce as a function
Quantum theory of angular momentum
 Quantum theoy of angula momentum Igo Mazets igo.mazets+e141@tuwien.ac.at (Atominstitut TU Wien, Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien Time: Fiday, 13:00 14:30 Place: Feihaus, Sem.R. DA gün 06B (exception date 18 Nov.:
Quantum theoy of angula momentum Igo Mazets igo.mazets+e141@tuwien.ac.at (Atominstitut TU Wien, Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien Time: Fiday, 13:00 14:30 Place: Feihaus, Sem.R. DA gün 06B (exception date 18 Nov.:
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Today in Physics 218: radiation from moving charges
 Today in Physics 218: adiation fom moving chages Poblems with moving chages Motion, snapshots and lengths The Liénad-Wiechet potentials Fields fom moving chages Radio galaxy Cygnus A, obseved by Rick Peley
Today in Physics 218: adiation fom moving chages Poblems with moving chages Motion, snapshots and lengths The Liénad-Wiechet potentials Fields fom moving chages Radio galaxy Cygnus A, obseved by Rick Peley
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
Fri Angular Momentum Quiz 10 RE 11.a; HW10: 13*, 21, 30, 39 Mon , (.12) Rotational + Translational RE 11.b Tues.
 Fi. 11.1 Angula Momentum Quiz 10 R 11.a; HW10: 13*, 1, 30, 39 Mon. 11.-.3, (.1) Rotational + Tanslational R 11.b Tues. P10 Mon. 11.4-.6, (.13) Angula Momentum & Toque Tues. Wed. 11.7 -.9, (.11) Toque R
Fi. 11.1 Angula Momentum Quiz 10 R 11.a; HW10: 13*, 1, 30, 39 Mon. 11.-.3, (.1) Rotational + Tanslational R 11.b Tues. P10 Mon. 11.4-.6, (.13) Angula Momentum & Toque Tues. Wed. 11.7 -.9, (.11) Toque R
Projection Gravitation, a Projection Force from 5-dimensional Space-time into 4-dimensional Space-time
 Intenational Jounal of Physics, 17, Vol. 5, No. 5, 181-196 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/5/6 Science and ducation Publishing DOI:1.1691/ijp-5-5-6 Pojection Gavitation, a Pojection Foce
Intenational Jounal of Physics, 17, Vol. 5, No. 5, 181-196 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/5/6 Science and ducation Publishing DOI:1.1691/ijp-5-5-6 Pojection Gavitation, a Pojection Foce
An Estimate of Incomplete Mixed Character Sums 1 2. Mei-Chu Chang 3. Dedicated to Endre Szemerédi for his 70th birthday.
 An Estimate of Incomlete Mixed Chaacte Sums 2 Mei-Chu Chang 3 Dedicated to Ende Szemeédi fo his 70th bithday. 4 In this note we conside incomlete mixed chaacte sums ove a finite field F n of the fom x
An Estimate of Incomlete Mixed Chaacte Sums 2 Mei-Chu Chang 3 Dedicated to Ende Szemeédi fo his 70th bithday. 4 In this note we conside incomlete mixed chaacte sums ove a finite field F n of the fom x
Cross section dependence on ski pole sti ness
 Coss section deendence on ski ole sti ness Johan Bystöm and Leonid Kuzmin Abstact Ski equiment oduce SWIX has ecently esented a new ai of ski oles, called SWIX Tiac, which di es fom conventional (ound)
Coss section deendence on ski ole sti ness Johan Bystöm and Leonid Kuzmin Abstact Ski equiment oduce SWIX has ecently esented a new ai of ski oles, called SWIX Tiac, which di es fom conventional (ound)
Gravitation. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
= e2. = 2e2. = 3e2. V = Ze2. where Z is the atomic numnber. Thus, we take as the Hamiltonian for a hydrogenic. H = p2 r. (19.4)
 Chapte 9 Hydogen Atom I What is H int? That depends on the physical system and the accuacy with which it is descibed. A natual stating point is the fom H int = p + V, (9.) µ which descibes a two-paticle
Chapte 9 Hydogen Atom I What is H int? That depends on the physical system and the accuacy with which it is descibed. A natual stating point is the fom H int = p + V, (9.) µ which descibes a two-paticle
Lab #4: Newton s Second Law
 Lab #4: Newton s Second Law Si Isaac Newton Reading Assignment: bon: Januay 4, 1643 Chapte 5 died: Mach 31, 1727 Chapte 9, Section 9-7 Intoduction: Potait of Isaac Newton by Si Godfey Knelle http://www.newton.cam.ac.uk/at/potait.html
Lab #4: Newton s Second Law Si Isaac Newton Reading Assignment: bon: Januay 4, 1643 Chapte 5 died: Mach 31, 1727 Chapte 9, Section 9-7 Intoduction: Potait of Isaac Newton by Si Godfey Knelle http://www.newton.cam.ac.uk/at/potait.html
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
Fifth force potentials, compared to Yukawa modification of Gravity for massive Gravitons, to link Gravitation, and NLED modified GR
 1 Fifth foce potentials, compaed to Yukawa modification of Gavity fo massive Gavitons, to link Gavitation, and NED modified GR A. B. Beckwith Physics Depatment, Chongqing Univesity, Chongqing 40014, PRC
1 Fifth foce potentials, compaed to Yukawa modification of Gavity fo massive Gavitons, to link Gavitation, and NED modified GR A. B. Beckwith Physics Depatment, Chongqing Univesity, Chongqing 40014, PRC
Study of the Parameters Affecting Cylindrical Cloak Using Dispersive FDTD
 Intenational Jounal of Otis and Photonis (IJOP) Vol. 9, No., Winte-Sing, 5 Study of the Paametes Affeting Cylindial Cloak Using Disesive FDTD Hossein Vejdani Shoja a,*, Ali Aab a, and Minoo Shojae Fa b
Intenational Jounal of Otis and Photonis (IJOP) Vol. 9, No., Winte-Sing, 5 Study of the Paametes Affeting Cylindial Cloak Using Disesive FDTD Hossein Vejdani Shoja a,*, Ali Aab a, and Minoo Shojae Fa b
