18.325: Vortex Dynamics
|
|
|
- Pauline Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8.35: Vortex Dynamics Problem Sheet. Fluid is barotropic which means p = p(. The Euler equation, in presence of a conservative body force, is Du Dt = p χ. This can be written, on use of a vector identity, ( u t + u u ω = p χ. ( Take the curl: t (u ω = On use of a vector identity we get t ( p = p ( =. ( + u. ω ω. u u(.ω + ω(.u. (3 Now,.ω = since div curl=. Now use conservation of mass equation to substitute for.u:.u = D Dt (4 so Dω Dt ω. u ω D =. Dt (5 Dividing by gives the final result D Dt ( ω = ω. u. (6. Assume a barotropic fluid in a conservative force field. Let Γ = u.dl. (7 Take time derivative dγ dt = Du.dl + u.ddl Dt Dt But it is known that Ddl/Dt = du. Using this, together with the Euler equation, dγ ( dt = ( u p χ.dl + d (9 (8
2 But this can be written in the form ( dγ dt = dp d d χ + u.dl ( which is the integral, around a closed loop, of a total spatial differential of a single-valued function. It is therefore zero and yields Kelvin s circulation theorem for a barotropic fluid. 3. For a barotropic fluid, Euler s equation can be written in the form u t + + u + ω u = dp d d χ. ( First form of Bernoulli: Suppose the flow is steady. Taking the dot product of the Euler equation with u yields ( dp u. d d χ u ( which means that the quantity dp d d χ u (3 is constant on streamlines. Second form of Bernoulli: Suppose that the flow is irrotational. The Euler equation then says that ( dp d d + χ + u = (4 from which we deduce that dp d d + χ + u (5 is constant everywhere. Third form of Bernoulli: Suppose the flow is unsteady, but irrotational (note, by Q, we still have the persistence of irrotational flow for a barotropic fluid so this is a consistent statement. Then u = φ for some scalar φ. Then the Euler equation says that which means that ( φ t dp d d χ u = (6 φ t + dp d d + χ + u = H(t (7
3 for some function of time H(t. 4. Let u i and P be the velocity, density and pressure fields of any threedimensional steady solution of the incompressible Euler equation, i.e., u i u j + P =, (8 x j and (u i =. (9 onsider now the velocity, density and pressure fields û i, ˆ and ˆP given by where λ is assumed to be such that û i = λu i, ( ˆ = λ, ( ˆP = P ( u i λ =. (3 Note: this corresponds to the fact that λ is constant on streamlines. It must be shown that if (8, (9 and (3 hold then so do and û i û j + ˆ ˆP =, (4 x j (ˆû i =. (5 First, to show that (4 holds, note that by ( and (, û i û j + ˆ ˆP x j = λu j (λu j + λ x j ( = λ u i u j + P x j = P + λu i u j λ x j (6 where the last equality follows by (8 and provided (3 holds. 3
4 To show that (5 holds, note that (ˆû i = ( ui λ = (u i + u i λ = λ u λ i = ( λ (7 where we have used both (9 and (3. 5. Assume an ideal fluid and a flow field of the form u = (u r (r, z, t,, u z (r, z, t. (8 Taking the curl, in cylindrical polar coordinates, e r re θ e z ω = r θ z = (, ω(r, z, t, (9 u r (r, z, r u z (r, z, r where The vorticity equation is ω(r, z, t = u r z u z r. (3 t omputation of the right hand side gives = (u ω. (3 (, z (ωu z r (ωu r, (3 so only the azimuthal term gives a non-trivial equation i.e., or, equivalently, t + (ωu r + (ωu z r z ( t + ω ur r + u z + u r z r + u z z = (33 =. (34 But, the conservation of mass equation is.u = which, in cylindrical polar coordinates, takes the form u r r + u r r + u z z = (35 4
5 which can be used in the vorticity equation to reduce it to t ωu r + u r r r + u z z =. (36 But, dividing this by r, it is simply ( t + u r r + u (ω z = (37 z r which is the required result. Note that if the radius of a vortex ring increases then the vorticity equation just derived shows that the dynamics is such that the vorticity ω changes linearly with the radius, thus as a ring is stretched, the vorticity intensifies. 6. In spherical polars, the condition.u = takes the form or, multiplying by r sin θ, r r (r u r + r sin θ θ (sin θ u θ = (38 r (r sin θ u r + θ (r sin θ u θ =. (39 Therefore, introduce a streamfunction Ψ such that r sin θ u r = Ψ θ, r sin θ u θ = Ψ r. (4 omputing the vorticity field gives e r re θ r sin θe φ ω = r θ φ = (,, ω(r, θ, t (4 u r (r, θ, t u θ (r, θ, t where ω(r, θ, t = (ru θ u r r r r θ. (4 Substituting for u r and u θ in terms of Ψ then gives the final result ω = ( Ψ r sin θ r + Ψ r θ cot θ Ψ. (43 r θ For irrotational uniform flow past a sphere, we have ω = while u r U cos θ and u θ U sin θ as r. Therefore, as r, Ψ Ur sin θ/. This suggests trying a separable solution of the form Ψ(r, θ = f(r sin θ. (44 5
6 Substituting this ansatz into the vorticity equation just derived with ω = yields the ordinary differential equation which can be solved to yield = f (r f r (45 f(r = Ar + B r (46 where A and B are constants. From the far-field conditions, we must pick A = U/. On r = a (the spherical boundary, we need Ψ to be constant. Take Ψ = without loss of generality. This determines B and the final solution is Ψ = U (r a3 sin θ. (47 r Note: We will see this solution again when considering the Hill s spherical vortex. 7. Seek the solution of ψ = mδ(x x (48 that decays at infinity. Without loss of generality, take x =. Multiply this equation by e ik.x and integrate over all space (i.e. take a Fourier transform: e ik.x ψ = e ik.x mδ(x x (49 R 3 R 3 Green s identity says that R 3 ( u v v u dv = lim R S R (u v v u.ds (5 where S R is some radius-r spherical surface. The right side vanishes provided everything decays sufficiently fast at infinity. Letting u = ψ and v = e ik.x gives e ik.x ψdv = k Ψ(k (5 where Ψ(k is the Fourier transform of ψ, that is Ψ(k e ik.x ψdv. (5 R 3 Use of this in (48 gives the result Ψ(k = m k (53 6
7 Now, the easiest way to arrive at the result is to verify that the Fourier transform of m/(4πr is m/ k. But the Fourier transform of m/(4πr is π π R 4πr eik.x dv = 3 4πr ei k r cos θ r sin θdθdφdr (54 where we have adopted spherical polar coordinates to perform the integration. arrying out the φ integration gives π 4π (π dr dθe i k r cos θ r sin θdθ (55 but this allows a further integration with respect to θ yielding [ ] dr e i k r e i k r sin k r = dr = k i k k Im e i k z dz (56 where is the contour consisting of the infinite ray along the positive real z-axis. But e i k z is an analytic function of z in the first quadrant of the z-plane, moreover it decays exponentially on the contour R consisting of a large radius-r quarter-circle between the positive real and imaginary axes of the first quadrant. This means that auchy s theorem can be used to argue that the required integral is the same as k Im e i k z dz (57 where Ĉ is the ray consisting of the positive imaginary axis of the z-plane. Parametrizing this contour as z = iy for y < the integral becomes k Im Ĉ e k y idy = k (58 which verifies that the Fourier transform of /(4πr is / k as required. 8. From the Biot-Savart integral in 3d, u = 4π r (x 3 x ω(x dx dy dz (59 flow Now assume ω = everywhere off the plane z = and assume that x lies in this plane. Then u(x = (x x ω(x dx dy dz (6 4π [(x x + (y y + (z z ] 3/ flow so that, performing the z integration (using the hint, u(x = (x x ω(x dx dy 4π flow [(x x + (y y ] = (x x ω(x dx dy π ˆr flow (6 where ˆr = x x is the distance between two vectors x and x in the plane z =. This is precisely the d Biot-Savart result. 7
Continuum Mechanics Lecture 5 Ideal fluids
 Continuum Mechanics Lecture 5 Ideal fluids Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - Helmholtz decomposition - Divergence and curl theorem - Kelvin s circulation theorem - The vorticity equation
Continuum Mechanics Lecture 5 Ideal fluids Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - Helmholtz decomposition - Divergence and curl theorem - Kelvin s circulation theorem - The vorticity equation
Vortex motion. Wasilij Barsukow, July 1, 2016
 The concept of vorticity We call Vortex motion Wasilij Barsukow, mail@sturzhang.de July, 206 ω = v vorticity. It is a measure of the swirlyness of the flow, but is also present in shear flows where the
The concept of vorticity We call Vortex motion Wasilij Barsukow, mail@sturzhang.de July, 206 ω = v vorticity. It is a measure of the swirlyness of the flow, but is also present in shear flows where the
Week 2 Notes, Math 865, Tanveer
 Week 2 Notes, Math 865, Tanveer 1. Incompressible constant density equations in different forms Recall we derived the Navier-Stokes equation for incompressible constant density, i.e. homogeneous flows:
Week 2 Notes, Math 865, Tanveer 1. Incompressible constant density equations in different forms Recall we derived the Navier-Stokes equation for incompressible constant density, i.e. homogeneous flows:
3.5 Vorticity Equation
 .0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture 9.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Lecture 9 is structured as follows: In paragraph 3.5 we return to the full Navier-Stokes equations (unsteady, viscous
.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture 9.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Lecture 9 is structured as follows: In paragraph 3.5 we return to the full Navier-Stokes equations (unsteady, viscous
V (r,t) = i ˆ u( x, y,z,t) + ˆ j v( x, y,z,t) + k ˆ w( x, y, z,t)
 IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
7 EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR AN INVISCID FLUID
 7 EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR AN INISCID FLUID iscosity is a measure of the thickness of a fluid, and its resistance to shearing motions. Honey is difficult to stir because of its high viscosity, whereas water
7 EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR AN INISCID FLUID iscosity is a measure of the thickness of a fluid, and its resistance to shearing motions. Honey is difficult to stir because of its high viscosity, whereas water
F11AE1 1. C = ρν r r. r u z r
 F11AE1 1 Question 1 20 Marks) Consider an infinite horizontal pipe with circular cross-section of radius a, whose centre line is aligned along the z-axis; see Figure 1. Assume no-slip boundary conditions
F11AE1 1 Question 1 20 Marks) Consider an infinite horizontal pipe with circular cross-section of radius a, whose centre line is aligned along the z-axis; see Figure 1. Assume no-slip boundary conditions
5.1 Fluid momentum equation Hydrostatics Archimedes theorem The vorticity equation... 42
 Chapter 5 Euler s equation Contents 5.1 Fluid momentum equation........................ 39 5. Hydrostatics................................ 40 5.3 Archimedes theorem........................... 41 5.4 The
Chapter 5 Euler s equation Contents 5.1 Fluid momentum equation........................ 39 5. Hydrostatics................................ 40 5.3 Archimedes theorem........................... 41 5.4 The
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2007 2008 FLUIDS DYNAMICS WITH ADVANCED TOPICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt question ONE and FOUR other questions. Candidates must
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2007 2008 FLUIDS DYNAMICS WITH ADVANCED TOPICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt question ONE and FOUR other questions. Candidates must
3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity
 Version date: March 22, 21 1 3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity 3.1 The vorticity equation We start from Navier Stokes: u t + u u = 1 ρ p + ν 2 u 1) where we have not included a term describing a
Version date: March 22, 21 1 3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity 3.1 The vorticity equation We start from Navier Stokes: u t + u u = 1 ρ p + ν 2 u 1) where we have not included a term describing a
ENGI Gradient, Divergence, Curl Page 5.01
 ENGI 94 5. - Gradient, Divergence, Curl Page 5. 5. The Gradient Operator A brief review is provided here for the gradient operator in both Cartesian and orthogonal non-cartesian coordinate systems. Sections
ENGI 94 5. - Gradient, Divergence, Curl Page 5. 5. The Gradient Operator A brief review is provided here for the gradient operator in both Cartesian and orthogonal non-cartesian coordinate systems. Sections
Chapter 2 Dynamics of Perfect Fluids
 hapter 2 Dynamics of Perfect Fluids As discussed in the previous chapter, the viscosity of fluids induces tangential stresses in relatively moving fluids. A familiar example is water being poured into
hapter 2 Dynamics of Perfect Fluids As discussed in the previous chapter, the viscosity of fluids induces tangential stresses in relatively moving fluids. A familiar example is water being poured into
Exercise 9, Ex. 6.3 ( submarine )
 Exercise 9, Ex. 6.3 ( submarine The flow around a submarine moving at at velocity V can be described by the flow caused by a source and a sink with strength Q at a distance a from each other. V x Submarine
Exercise 9, Ex. 6.3 ( submarine The flow around a submarine moving at at velocity V can be described by the flow caused by a source and a sink with strength Q at a distance a from each other. V x Submarine
General Solution of the Incompressible, Potential Flow Equations
 CHAPTER 3 General Solution of the Incompressible, Potential Flow Equations Developing the basic methodology for obtaining the elementary solutions to potential flow problem. Linear nature of the potential
CHAPTER 3 General Solution of the Incompressible, Potential Flow Equations Developing the basic methodology for obtaining the elementary solutions to potential flow problem. Linear nature of the potential
Exercise 9: Model of a Submarine
 Fluid Mechanics, SG4, HT3 October 4, 3 Eample : Submarine Eercise 9: Model of a Submarine The flow around a submarine moving at a velocity V can be described by the flow caused by a source and a sink with
Fluid Mechanics, SG4, HT3 October 4, 3 Eample : Submarine Eercise 9: Model of a Submarine The flow around a submarine moving at a velocity V can be described by the flow caused by a source and a sink with
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4
 Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
2.25 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 2013
 .5 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 013 Solution to Problem 1-Final Exam- Fall 013 r j g u j ρ, µ,σ,u j u r 1 h(r) r = R Figure 1: Viscous Savart Sheet. Image courtesy: Villermaux et. al. [1]. This kind of
.5 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 013 Solution to Problem 1-Final Exam- Fall 013 r j g u j ρ, µ,σ,u j u r 1 h(r) r = R Figure 1: Viscous Savart Sheet. Image courtesy: Villermaux et. al. [1]. This kind of
Vorticity and Dynamics
 Vorticity and Dynamics In Navier-Stokes equation Nonlinear term ω u the Lamb vector is related to the nonlinear term u 2 (u ) u = + ω u 2 Sort of Coriolis force in a rotation frame Viscous term ν u = ν
Vorticity and Dynamics In Navier-Stokes equation Nonlinear term ω u the Lamb vector is related to the nonlinear term u 2 (u ) u = + ω u 2 Sort of Coriolis force in a rotation frame Viscous term ν u = ν
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK
 UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Faculty of Science and Engineering END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MA4607 SEMESTER: Autumn 2012-13 MODULE TITLE: Introduction to Fluids DURATION OF
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Faculty of Science and Engineering END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MA4607 SEMESTER: Autumn 2012-13 MODULE TITLE: Introduction to Fluids DURATION OF
Math 575-Lecture 19. In this lecture, we continue to investigate the solutions of the Stokes equations.
 Math 575-Lecture 9 In this lecture, we continue to investigate the solutions of the Stokes equations. Energy balance Rewrite the equation to σ = f. We begin the energy estimate by dotting u in the Stokes
Math 575-Lecture 9 In this lecture, we continue to investigate the solutions of the Stokes equations. Energy balance Rewrite the equation to σ = f. We begin the energy estimate by dotting u in the Stokes
ENGI Duffing s Equation Page 4.65
 ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
Summary of various integrals
 ummary of various integrals Here s an arbitrary compilation of information about integrals Moisés made on a cold ecember night. 1 General things o not mix scalars and vectors! In particular ome integrals
ummary of various integrals Here s an arbitrary compilation of information about integrals Moisés made on a cold ecember night. 1 General things o not mix scalars and vectors! In particular ome integrals
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability
 GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
Jim Lambers MAT 280 Summer Semester Practice Final Exam Solution. dy + xz dz = x(t)y(t) dt. t 3 (4t 3 ) + e t2 (2t) + t 7 (3t 2 ) dt
 Jim Lambers MAT 28 ummer emester 212-1 Practice Final Exam olution 1. Evaluate the line integral xy dx + e y dy + xz dz, where is given by r(t) t 4, t 2, t, t 1. olution From r (t) 4t, 2t, t 2, we obtain
Jim Lambers MAT 28 ummer emester 212-1 Practice Final Exam olution 1. Evaluate the line integral xy dx + e y dy + xz dz, where is given by r(t) t 4, t 2, t, t 1. olution From r (t) 4t, 2t, t 2, we obtain
Ma 1c Practical - Solutions to Homework Set 7
 Ma 1c Practical - olutions to omework et 7 All exercises are from the Vector Calculus text, Marsden and Tromba (Fifth Edition) Exercise 7.4.. Find the area of the portion of the unit sphere that is cut
Ma 1c Practical - olutions to omework et 7 All exercises are from the Vector Calculus text, Marsden and Tromba (Fifth Edition) Exercise 7.4.. Find the area of the portion of the unit sphere that is cut
One side of each sheet is blank and may be used as scratch paper.
 Math 244 Spring 2017 (Practice) Final 5/11/2017 Time Limit: 2 hours Name: No calculators or notes are allowed. One side of each sheet is blank and may be used as scratch paper. heck your answers whenever
Math 244 Spring 2017 (Practice) Final 5/11/2017 Time Limit: 2 hours Name: No calculators or notes are allowed. One side of each sheet is blank and may be used as scratch paper. heck your answers whenever
(Jim You have a note for yourself here that reads Fill in full derivation, this is a sloppy treatment ).
 Lecture. dministration Collect problem set. Distribute problem set due October 3, 004.. nd law of thermodynamics (Jim You have a note for yourself here that reads Fill in full derivation, this is a sloppy
Lecture. dministration Collect problem set. Distribute problem set due October 3, 004.. nd law of thermodynamics (Jim You have a note for yourself here that reads Fill in full derivation, this is a sloppy
MAC2313 Final A. (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Multiple Integrals 3. 2 Vector Fields 9
 MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
Practice Problems for Exam 3 (Solutions) 1. Let F(x, y) = xyi+(y 3x)j, and let C be the curve r(t) = ti+(3t t 2 )j for 0 t 2. Compute F dr.
 1. Let F(x, y) xyi+(y 3x)j, and let be the curve r(t) ti+(3t t 2 )j for t 2. ompute F dr. Solution. F dr b a 2 2 F(r(t)) r (t) dt t(3t t 2 ), 3t t 2 3t 1, 3 2t dt t 3 dt 1 2 4 t4 4. 2. Evaluate the line
1. Let F(x, y) xyi+(y 3x)j, and let be the curve r(t) ti+(3t t 2 )j for t 2. ompute F dr. Solution. F dr b a 2 2 F(r(t)) r (t) dt t(3t t 2 ), 3t t 2 3t 1, 3 2t dt t 3 dt 1 2 4 t4 4. 2. Evaluate the line
Copyright 2007 N. Komerath. Other rights may be specified with individual items. All rights reserved.
 Low Speed Aerodynamics Notes 5: Potential ti Flow Method Objective: Get a method to describe flow velocity fields and relate them to surface shapes consistently. Strategy: Describe the flow field as the
Low Speed Aerodynamics Notes 5: Potential ti Flow Method Objective: Get a method to describe flow velocity fields and relate them to surface shapes consistently. Strategy: Describe the flow field as the
18.04 Practice problems exam 1, Spring 2018 Solutions
 8.4 Practice problems exam, Spring 8 Solutions Problem. omplex arithmetic (a) Find the real and imaginary part of z + z. (b) Solve z 4 i =. (c) Find all possible values of i. (d) Express cos(4x) in terms
8.4 Practice problems exam, Spring 8 Solutions Problem. omplex arithmetic (a) Find the real and imaginary part of z + z. (b) Solve z 4 i =. (c) Find all possible values of i. (d) Express cos(4x) in terms
The vorticity field. A dust devil
 The vorticity field The vector ω = u curl u is twice the local angular velocity in the flow, and is called the vorticity of the flow (from Latin for a whirlpool). Vortex lines are everywhere in the direction
The vorticity field The vector ω = u curl u is twice the local angular velocity in the flow, and is called the vorticity of the flow (from Latin for a whirlpool). Vortex lines are everywhere in the direction
Chapter II. Complex Variables
 hapter II. omplex Variables Dates: October 2, 4, 7, 2002. These three lectures will cover the following sections of the text book by Keener. 6.1. omplex valued functions and branch cuts; 6.2.1. Differentiation
hapter II. omplex Variables Dates: October 2, 4, 7, 2002. These three lectures will cover the following sections of the text book by Keener. 6.1. omplex valued functions and branch cuts; 6.2.1. Differentiation
Before you begin read these instructions carefully.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part IB Tuesday, 3 June, 2014 9:00 am to 12:00 pm PAPER 2 Before you begin read these instructions carefully. Each question in Section II carries twice the number of marks of each question
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part IB Tuesday, 3 June, 2014 9:00 am to 12:00 pm PAPER 2 Before you begin read these instructions carefully. Each question in Section II carries twice the number of marks of each question
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring Final exam May 3rd. Suggested solutions
 alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
231 Outline Solutions Tutorial Sheet 4, 5 and November 2007
 31 Outline Solutions Tutorial Sheet 4, 5 and 6. 1 Problem Sheet 4 November 7 1. heck that the Jacobian for the transformation from cartesian to spherical polar coordinates is J = r sin θ. onsider the hemisphere
31 Outline Solutions Tutorial Sheet 4, 5 and 6. 1 Problem Sheet 4 November 7 1. heck that the Jacobian for the transformation from cartesian to spherical polar coordinates is J = r sin θ. onsider the hemisphere
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 4. Potential Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 4. Potential Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL EXAM. December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours)
 SOLUTIONS TO THE 18.02 FINAL EXAM BJORN POONEN December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours) 1) For each of (a)-(e) below: If the statement is true, write TRUE. If the statement is false, write FALSE. (Please
SOLUTIONS TO THE 18.02 FINAL EXAM BJORN POONEN December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours) 1) For each of (a)-(e) below: If the statement is true, write TRUE. If the statement is false, write FALSE. (Please
Vorticity Equation Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9. Return to viscous incompressible flow. N-S equation: v. Now: v = v + = 0 incompressible
 13.01 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 9 Copyright c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. Vorticity Equation 13.01 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Return to viscous incompressible
13.01 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 9 Copyright c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. Vorticity Equation 13.01 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Return to viscous incompressible
0 = p. 2 x + 2 w. z +ν w
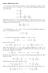 Solution (Elliptical pipe flow (a Using the Navier Stokes equations in three dimensional cartesian coordinates, given that u =, v = and w = w(x,y only, and assuming no body force, we are left with = p
Solution (Elliptical pipe flow (a Using the Navier Stokes equations in three dimensional cartesian coordinates, given that u =, v = and w = w(x,y only, and assuming no body force, we are left with = p
Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces
 Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces 21.1 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation According to Newton s Law of Universal Graviation, the force on a particle i of mass m i exerted by a particle j of
Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces 21.1 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation According to Newton s Law of Universal Graviation, the force on a particle i of mass m i exerted by a particle j of
Math 350 Solutions for Final Exam Page 1. Problem 1. (10 points) (a) Compute the line integral. F ds C. z dx + y dy + x dz C
 Math 35 Solutions for Final Exam Page Problem. ( points) (a) ompute the line integral F ds for the path c(t) = (t 2, t 3, t) with t and the vector field F (x, y, z) = xi + zj + xk. (b) ompute the line
Math 35 Solutions for Final Exam Page Problem. ( points) (a) ompute the line integral F ds for the path c(t) = (t 2, t 3, t) with t and the vector field F (x, y, z) = xi + zj + xk. (b) ompute the line
Math 31CH - Spring Final Exam
 Math 3H - Spring 24 - Final Exam Problem. The parabolic cylinder y = x 2 (aligned along the z-axis) is cut by the planes y =, z = and z = y. Find the volume of the solid thus obtained. Solution:We calculate
Math 3H - Spring 24 - Final Exam Problem. The parabolic cylinder y = x 2 (aligned along the z-axis) is cut by the planes y =, z = and z = y. Find the volume of the solid thus obtained. Solution:We calculate
Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics
 Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics Amey Joshi 07-Feb-018 1 Equations of ideal fluids onsider a volume element of a fluid of density ρ. If there are no sources or sinks in, the mass in it will change
Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics Amey Joshi 07-Feb-018 1 Equations of ideal fluids onsider a volume element of a fluid of density ρ. If there are no sources or sinks in, the mass in it will change
MATH 228: Calculus III (FALL 2016) Sample Problems for FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 228: Calculus III (FALL 216) Sample Problems for FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS MATH 228 Page 2 Problem 1. (2pts) Evaluate the line integral C xy dx + (x + y) dy along the parabola y x2 from ( 1, 1) to (2,
MATH 228: Calculus III (FALL 216) Sample Problems for FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS MATH 228 Page 2 Problem 1. (2pts) Evaluate the line integral C xy dx + (x + y) dy along the parabola y x2 from ( 1, 1) to (2,
Fluid Dynamics Problems M.Sc Mathematics-Second Semester Dr. Dinesh Khattar-K.M.College
 Fluid Dynamics Problems M.Sc Mathematics-Second Semester Dr. Dinesh Khattar-K.M.College 1. (Example, p.74, Chorlton) At the point in an incompressible fluid having spherical polar coordinates,,, the velocity
Fluid Dynamics Problems M.Sc Mathematics-Second Semester Dr. Dinesh Khattar-K.M.College 1. (Example, p.74, Chorlton) At the point in an incompressible fluid having spherical polar coordinates,,, the velocity
PRACTICE PROBLEMS. Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1. Mixed partial derivatives.
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1.1. Let Show that f is C 1 and yet How is that possible? 1. Mixed partial derivatives f(x, y) = {xy x
PRACTICE PROBLEMS Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1.1. Let Show that f is C 1 and yet How is that possible? 1. Mixed partial derivatives f(x, y) = {xy x
Homework Two. Abstract: Liu. Solutions for Homework Problems Two: (50 points total). Collected by Junyu
 Homework Two Abstract: Liu. Solutions for Homework Problems Two: (50 points total). Collected by Junyu Contents 1 BT Problem 13.15 (8 points) (by Nick Hunter-Jones) 1 2 BT Problem 14.2 (12 points: 3+3+3+3)
Homework Two Abstract: Liu. Solutions for Homework Problems Two: (50 points total). Collected by Junyu Contents 1 BT Problem 13.15 (8 points) (by Nick Hunter-Jones) 1 2 BT Problem 14.2 (12 points: 3+3+3+3)
MATH 18.01, FALL PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 181, FALL 17 - PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS Part II (5 points) 1 (Thurs, Oct 6; Second Fundamental Theorem; + + + + + = 16 points) Let sinc(x) denote the sinc function { 1 if x =, sinc(x) = sin x if
MATH 181, FALL 17 - PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS Part II (5 points) 1 (Thurs, Oct 6; Second Fundamental Theorem; + + + + + = 16 points) Let sinc(x) denote the sinc function { 1 if x =, sinc(x) = sin x if
3.1 Definition Physical meaning Streamfunction and vorticity The Rankine vortex Circulation...
 Chapter 3 Vorticity Contents 3.1 Definition.................................. 19 3.2 Physical meaning............................. 19 3.3 Streamfunction and vorticity...................... 21 3.4 The Rankine
Chapter 3 Vorticity Contents 3.1 Definition.................................. 19 3.2 Physical meaning............................. 19 3.3 Streamfunction and vorticity...................... 21 3.4 The Rankine
S12.1 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS 12 (ODD NUMBERS)
 OLUTION TO PROBLEM 2 (ODD NUMBER) 2. The electric field is E = φ = 2xi + 2y j and at (2, ) E = 4i + 2j. Thus E = 2 5 and its direction is 2i + j. At ( 3, 2), φ = 6i + 4 j. Thus the direction of most rapid
OLUTION TO PROBLEM 2 (ODD NUMBER) 2. The electric field is E = φ = 2xi + 2y j and at (2, ) E = 4i + 2j. Thus E = 2 5 and its direction is 2i + j. At ( 3, 2), φ = 6i + 4 j. Thus the direction of most rapid
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data
 On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
Final Exam May 4, 2016
 1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
Simplifications to Conservation Equations
 Chater 5 Simlifications to Conservation Equations 5.1 Steady Flow If fluid roerties at a oint in a field do not change with time, then they are a function of sace only. They are reresented by: ϕ = ϕq 1,
Chater 5 Simlifications to Conservation Equations 5.1 Steady Flow If fluid roerties at a oint in a field do not change with time, then they are a function of sace only. They are reresented by: ϕ = ϕq 1,
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics
 AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics for Aerodynamics B-: Flow Field Representations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics for Aerodynamics B-: Flow Field Representations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis
Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics
 Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics CDS 140b Joris Vankerschaver jv@caltech.edu CDS 01/29/08, 01/31/08 Joris Vankerschaver (CDS) Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics 01/29/08, 01/31/08 1 / 34 Outline
Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics CDS 140b Joris Vankerschaver jv@caltech.edu CDS 01/29/08, 01/31/08 Joris Vankerschaver (CDS) Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics 01/29/08, 01/31/08 1 / 34 Outline
MATH 52 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MAH 5 FINAL EXAM OLUION. (a) ketch the region R of integration in the following double integral. x xe y5 dy dx R = {(x, y) x, x y }. (b) Express the region R as an x-simple region. R = {(x, y) y, x y }
MAH 5 FINAL EXAM OLUION. (a) ketch the region R of integration in the following double integral. x xe y5 dy dx R = {(x, y) x, x y }. (b) Express the region R as an x-simple region. R = {(x, y) y, x y }
Physics 3323, Fall 2016 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 2016
 Physics 3323, Fall 26 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 26. What s my charge? A spherical region of radius R is filled with a charge distribution that gives rise to an electric field inside of the form E E /R 2
Physics 3323, Fall 26 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 26. What s my charge? A spherical region of radius R is filled with a charge distribution that gives rise to an electric field inside of the form E E /R 2
MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework
 MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
Math 1B Final Exam, Solution. Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring (6 points) Use substitution and integration by parts to find:
 Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Math 11 Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam
 Math 11 Fall 218 Practice Final Exam Disclaimer: This practice exam should give you an idea of the sort of questions we may ask on the actual exam. Since the practice exam (like the real exam) is not long
Math 11 Fall 218 Practice Final Exam Disclaimer: This practice exam should give you an idea of the sort of questions we may ask on the actual exam. Since the practice exam (like the real exam) is not long
F1.9AB2 1. r 2 θ2 + sin 2 α. and. p θ = mr 2 θ. p2 θ. (d) In light of the information in part (c) above, we can express the Hamiltonian in the form
 F1.9AB2 1 Question 1 (20 Marks) A cone of semi-angle α has its axis vertical and vertex downwards, as in Figure 1 (overleaf). A point mass m slides without friction on the inside of the cone under the
F1.9AB2 1 Question 1 (20 Marks) A cone of semi-angle α has its axis vertical and vertex downwards, as in Figure 1 (overleaf). A point mass m slides without friction on the inside of the cone under the
Continuum Mechanics Lecture 7 Theory of 2D potential flows
 Continuum Mechanics ecture 7 Theory of 2D potential flows Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - velocity potential and stream function - complex potential - elementary solutions - flow past a
Continuum Mechanics ecture 7 Theory of 2D potential flows Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - velocity potential and stream function - complex potential - elementary solutions - flow past a
Integration in the Complex Plane (Zill & Wright Chapter 18)
 Integration in the omplex Plane Zill & Wright hapter 18) 116-4-: omplex Variables Fall 11 ontents 1 ontour Integrals 1.1 Definition and Properties............................. 1. Evaluation.....................................
Integration in the omplex Plane Zill & Wright hapter 18) 116-4-: omplex Variables Fall 11 ontents 1 ontour Integrals 1.1 Definition and Properties............................. 1. Evaluation.....................................
ENGI Gradient, Divergence, Curl Page 5.01
 ENGI 940 5.0 - Gradient, Divergence, Curl Page 5.0 5. e Gradient Operator A brief review is provided ere for te gradient operator in bot Cartesian and ortogonal non-cartesian coordinate systems. Sections
ENGI 940 5.0 - Gradient, Divergence, Curl Page 5.0 5. e Gradient Operator A brief review is provided ere for te gradient operator in bot Cartesian and ortogonal non-cartesian coordinate systems. Sections
In this section, mathematical description of the motion of fluid elements moving in a flow field is
 Jun. 05, 015 Chapter 6. Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow 6.1 Fluid Element Kinematics In this section, mathematical description of the motion of fluid elements moving in a flow field is given. A small
Jun. 05, 015 Chapter 6. Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow 6.1 Fluid Element Kinematics In this section, mathematical description of the motion of fluid elements moving in a flow field is given. A small
APPENDIX 2.1 LINE AND SURFACE INTEGRALS
 2 APPENDIX 2. LINE AND URFACE INTEGRAL Consider a path connecting points (a) and (b) as shown in Fig. A.2.. Assume that a vector field A(r) exists in the space in which the path is situated. Then the line
2 APPENDIX 2. LINE AND URFACE INTEGRAL Consider a path connecting points (a) and (b) as shown in Fig. A.2.. Assume that a vector field A(r) exists in the space in which the path is situated. Then the line
Note: Each problem is worth 14 points except numbers 5 and 6 which are 15 points. = 3 2
 Math Prelim II Solutions Spring Note: Each problem is worth points except numbers 5 and 6 which are 5 points. x. Compute x da where is the region in the second quadrant between the + y circles x + y and
Math Prelim II Solutions Spring Note: Each problem is worth points except numbers 5 and 6 which are 5 points. x. Compute x da where is the region in the second quadrant between the + y circles x + y and
Staple or bind all pages together. DO NOT dog ear pages as a method to bind.
 Math 3337 Homework Instructions: Staple or bind all pages together. DO NOT dog ear pages as a method to bind. Hand-drawn sketches should be neat, clear, of reasonable size, with axis and tick marks appropriately
Math 3337 Homework Instructions: Staple or bind all pages together. DO NOT dog ear pages as a method to bind. Hand-drawn sketches should be neat, clear, of reasonable size, with axis and tick marks appropriately
Math 11 Fall 2016 Final Practice Problem Solutions
 Math 11 Fall 216 Final Practice Problem olutions Here are some problems on the material we covered since the second midterm. This collection of problems is not intended to mimic the final in length, content,
Math 11 Fall 216 Final Practice Problem olutions Here are some problems on the material we covered since the second midterm. This collection of problems is not intended to mimic the final in length, content,
Math 1272 Solutions for Fall 2005 Final Exam
 Math 7 Solutions for Fall 5 Final Exam ) This fraction appears in Problem 5 of the undated-? exam; a solution can be found in that solution set. (E) ) This integral appears in Problem 6 of the Fall 4 exam;
Math 7 Solutions for Fall 5 Final Exam ) This fraction appears in Problem 5 of the undated-? exam; a solution can be found in that solution set. (E) ) This integral appears in Problem 6 of the Fall 4 exam;
The Euler equations in fluid mechanics
 The Euler equations in fluid mechanics Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, niversity of Toronto April 14, 014 1 Continuity equation Let Ω be a domain in R n and let C (Ω R); perhaps
The Euler equations in fluid mechanics Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, niversity of Toronto April 14, 014 1 Continuity equation Let Ω be a domain in R n and let C (Ω R); perhaps
McGill University April 16, Advanced Calculus for Engineers
 McGill University April 16, 2014 Faculty of cience Final examination Advanced Calculus for Engineers Math 264 April 16, 2014 Time: 6PM-9PM Examiner: Prof. R. Choksi Associate Examiner: Prof. A. Hundemer
McGill University April 16, 2014 Faculty of cience Final examination Advanced Calculus for Engineers Math 264 April 16, 2014 Time: 6PM-9PM Examiner: Prof. R. Choksi Associate Examiner: Prof. A. Hundemer
Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus (Oxford Physics) Synopsis and Problem Sets; Hilary 2015
 Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus (Oxford Physics) Ramin Golestanian Synopsis and Problem Sets; Hilary 215 The outline of the material, which will be covered in 14 lectures, is as follows: 1. Introduction
Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus (Oxford Physics) Ramin Golestanian Synopsis and Problem Sets; Hilary 215 The outline of the material, which will be covered in 14 lectures, is as follows: 1. Introduction
Jim Lambers MAT 280 Fall Semester Practice Final Exam Solution
 Jim Lambers MAT 8 Fall emester 6-7 Practice Final Exam olution. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the point on the circle x + 4 closest to the point (, 5). olution We have f(x, ) (x ) + ( 5), the square
Jim Lambers MAT 8 Fall emester 6-7 Practice Final Exam olution. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the point on the circle x + 4 closest to the point (, 5). olution We have f(x, ) (x ) + ( 5), the square
Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 2, 3, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap. 2. 2π nx i a. ( ) = G n.
 Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Incompressible Flow Over Airfoils
 Chapter 7 Incompressible Flow Over Airfoils Aerodynamics of wings: -D sectional characteristics of the airfoil; Finite wing characteristics (How to relate -D characteristics to 3-D characteristics) How
Chapter 7 Incompressible Flow Over Airfoils Aerodynamics of wings: -D sectional characteristics of the airfoil; Finite wing characteristics (How to relate -D characteristics to 3-D characteristics) How
MATHS 267 Answers to Stokes Practice Dr. Jones
 MATH 267 Answers to tokes Practice Dr. Jones 1. Calculate the flux F d where is the hemisphere x2 + y 2 + z 2 1, z > and F (xz + e y2, yz, z 2 + 1). Note: the surface is open (doesn t include any of the
MATH 267 Answers to tokes Practice Dr. Jones 1. Calculate the flux F d where is the hemisphere x2 + y 2 + z 2 1, z > and F (xz + e y2, yz, z 2 + 1). Note: the surface is open (doesn t include any of the
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 27 May, 2004 1.30 to 3.30 PAPER 64 ASTROPHYSICAL FLUID DYNAMICS Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. Candidates
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 27 May, 2004 1.30 to 3.30 PAPER 64 ASTROPHYSICAL FLUID DYNAMICS Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. Candidates
lim = F F = F x x + F y y + F z
 Physics 361 Summary of Results from Lecture Physics 361 Derivatives of Scalar and Vector Fields The gradient of a scalar field f( r) is given by g = f. coordinates f g = ê x x + ê f y y + ê f z z Expressed
Physics 361 Summary of Results from Lecture Physics 361 Derivatives of Scalar and Vector Fields The gradient of a scalar field f( r) is given by g = f. coordinates f g = ê x x + ê f y y + ê f z z Expressed
MATH 0350 PRACTICE FINAL FALL 2017 SAMUEL S. WATSON. a c. b c.
 MATH 35 PRACTICE FINAL FALL 17 SAMUEL S. WATSON Problem 1 Verify that if a and b are nonzero vectors, the vector c = a b + b a bisects the angle between a and b. The cosine of the angle between a and c
MATH 35 PRACTICE FINAL FALL 17 SAMUEL S. WATSON Problem 1 Verify that if a and b are nonzero vectors, the vector c = a b + b a bisects the angle between a and b. The cosine of the angle between a and c
Candidates must show on each answer book the type of calculator used. Only calculators permitted under UEA Regulations may be used.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2011 2012 FLUID DYNAMICS MTH-3D41 Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt FIVE questions. Candidates must show on each answer book the type
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2011 2012 FLUID DYNAMICS MTH-3D41 Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt FIVE questions. Candidates must show on each answer book the type
Barotropic geophysical flows and two-dimensional fluid flows: Conserved Quantities
 Barotropic geophysical flows and two-dimensional fluid flows: Conserved Quantities Di Qi, and Andrew J. Majda Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2016 Advanced Topics in Applied Math Di Qi,
Barotropic geophysical flows and two-dimensional fluid flows: Conserved Quantities Di Qi, and Andrew J. Majda Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2016 Advanced Topics in Applied Math Di Qi,
HOMEWORK 8 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWOK 8 OLUTION. Let and φ = xdy dz + ydz dx + zdx dy. let be the disk at height given by: : x + y, z =, let X be the region in 3 bounded by the cone and the disk. We orient X via dx dy dz, then by definition
HOMEWOK 8 OLUTION. Let and φ = xdy dz + ydz dx + zdx dy. let be the disk at height given by: : x + y, z =, let X be the region in 3 bounded by the cone and the disk. We orient X via dx dy dz, then by definition
The Divergence Theorem Stokes Theorem Applications of Vector Calculus. Calculus. Vector Calculus (III)
 Calculus Vector Calculus (III) Outline 1 The Divergence Theorem 2 Stokes Theorem 3 Applications of Vector Calculus The Divergence Theorem (I) Recall that at the end of section 12.5, we had rewritten Green
Calculus Vector Calculus (III) Outline 1 The Divergence Theorem 2 Stokes Theorem 3 Applications of Vector Calculus The Divergence Theorem (I) Recall that at the end of section 12.5, we had rewritten Green
Review of fluid dynamics
 Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
MAE 101A. Homework 7 - Solutions 3/12/2018
 MAE 101A Homework 7 - Solutions 3/12/2018 Munson 6.31: The stream function for a two-dimensional, nonviscous, incompressible flow field is given by the expression ψ = 2(x y) where the stream function has
MAE 101A Homework 7 - Solutions 3/12/2018 Munson 6.31: The stream function for a two-dimensional, nonviscous, incompressible flow field is given by the expression ψ = 2(x y) where the stream function has
Physics 451/551 Theoretical Mechanics. G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 18
 Physics 451/551 Theoretical Mechanics G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 18 Theoretical Mechanics Fall 018 Properties of Sound Sound Waves Requires medium for propagation Mainly
Physics 451/551 Theoretical Mechanics G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 18 Theoretical Mechanics Fall 018 Properties of Sound Sound Waves Requires medium for propagation Mainly
Math 233. Practice Problems Chapter 15. i j k
 Math 233. Practice Problems hapter 15 1. ompute the curl and divergence of the vector field F given by F (4 cos(x 2 ) 2y)i + (4 sin(y 2 ) + 6x)j + (6x 2 y 6x + 4e 3z )k olution: The curl of F is computed
Math 233. Practice Problems hapter 15 1. ompute the curl and divergence of the vector field F given by F (4 cos(x 2 ) 2y)i + (4 sin(y 2 ) + 6x)j + (6x 2 y 6x + 4e 3z )k olution: The curl of F is computed
Study Guide for Exam #2
 Physical Mechanics METR103 November, 000 Study Guide for Exam # The information even below is meant to serve as a guide to help you to prepare for the second hour exam. The absence of a topic or point
Physical Mechanics METR103 November, 000 Study Guide for Exam # The information even below is meant to serve as a guide to help you to prepare for the second hour exam. The absence of a topic or point
Mathematical Concepts & Notation
 Mathematical Concepts & Notation Appendix A: Notation x, δx: a small change in x t : the partial derivative with respect to t holding the other variables fixed d : the time derivative of a quantity that
Mathematical Concepts & Notation Appendix A: Notation x, δx: a small change in x t : the partial derivative with respect to t holding the other variables fixed d : the time derivative of a quantity that
Math 212-Lecture 20. P dx + Qdy = (Q x P y )da. C
 15. Green s theorem Math 212-Lecture 2 A simple closed curve in plane is one curve, r(t) : t [a, b] such that r(a) = r(b), and there are no other intersections. The positive orientation is counterclockwise.
15. Green s theorem Math 212-Lecture 2 A simple closed curve in plane is one curve, r(t) : t [a, b] such that r(a) = r(b), and there are no other intersections. The positive orientation is counterclockwise.
FLUID DYNAMICS, THEORY AND COMPUTATION MTHA5002Y
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017 18 FLUID DYNAMICS, THEORY AND COMPUTATION MTHA5002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and THREE other questions.
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017 18 FLUID DYNAMICS, THEORY AND COMPUTATION MTHA5002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and THREE other questions.
The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics
 The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics A. Mignone October 24, 217 In this lecture we study some properties of the Euler equations of gasdynamics, + (u) = ( ) u + u u + p = a p + u p + γp u = where, p and u
The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics A. Mignone October 24, 217 In this lecture we study some properties of the Euler equations of gasdynamics, + (u) = ( ) u + u u + p = a p + u p + γp u = where, p and u
Complex Practice Exam 1
 Complex Practice Exam This practice exam contains sample questions. The actual exam will have fewer questions, and may contain questions not listed here.. Be prepared to explain the following concepts,
Complex Practice Exam This practice exam contains sample questions. The actual exam will have fewer questions, and may contain questions not listed here.. Be prepared to explain the following concepts,
Detailed Outline, M E 521: Foundations of Fluid Mechanics I
 Detailed Outline, M E 521: Foundations of Fluid Mechanics I I. Introduction and Review A. Notation 1. Vectors 2. Second-order tensors 3. Volume vs. velocity 4. Del operator B. Chapter 1: Review of Basic
Detailed Outline, M E 521: Foundations of Fluid Mechanics I I. Introduction and Review A. Notation 1. Vectors 2. Second-order tensors 3. Volume vs. velocity 4. Del operator B. Chapter 1: Review of Basic
