Vorticity and Dynamics
|
|
|
- Clifford Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vorticity and Dynamics
2 In Navier-Stokes equation Nonlinear term ω u the Lamb vector is related to the nonlinear term u 2 (u ) u = + ω u 2 Sort of Coriolis force in a rotation frame Viscous term ν u = ν (.u) ( u) = ν ω
3 u t u 2 + ω u + = [ p 2 ρ ] ν ω taking the rotational ω t + (ω u) = ν ω Dynamical equation for Vorticity
4 Pressure is eliminated in the equation p =2ρ Q Q = 1 2 [1 2 ω2 e 2 ] Q>0 Q-Criterium to define a vortex region
5 e yx = e xy = 1 2 e xx = e yy =0 u = u x (y) e x ; u y Mixing layer u = u θ (r) e θ ; Vortex ω = u y ω 2 =2e ij e ij pressure is uniform ω z = 1 r e rr =0, e θθ =0, e rθ = r 2 (ru θ ) r r (u θ r ) Q =0
6 p =2ρ Q Q = 1 2r u 2 θ r Pressure can be computed using the first component of the Navier-Stokes equation in polar coordinates u 2 θ r = 1 p ρ r u 2 θ p(r) =p( ) ρ r r dr pressure decreases as we get near the vortex center : it is a pressure low.
7 Texte Q-vortex from Delcayre (2000)
8 Cavitation (Cadot et al)
9 Dissipation and Vorticity Internal dissipation Φ per unit volume particle deformation internal energy Φ =2µe ij e ij > 0 incompressibility assumed Φ = µ ω 2 +2µ. ω u + 12 (u 2 )
10 Φ dτ = µ v Dissipation and Vorticity v ω 2 dτ + µ surface [2 ω u + (u 2 )] nds the dissipation per unit mass used in turbulence = 1 ρ V v Φ dτ = ν V v ω 2 dτ There exists of a zone of dissipation around a vortex
11 Chaoticity and Vorticity u = u BS + φ Potential only depends on the boundary conditions since it satisfies at each time φ =0 n φ =(u u BS ) n Past history does not play a role for φ Vorticity precisely brings this historical aspect. Vorticity ω modifies velocityu Velocity u modifies with vorticity ω
12 This implies feedback loop Chaoticity and vortex Turbulence and vortex
13 Transport Equation for Vorticity : Incompressible Newtonian Fluid [ω u] = (u )ω (ω )u Dω Dt =[ t + u. ]ω = ω. u + ν ω Lagrangian Transport Stretching Viscous Diffusion Circulation theorem dγ dt = ν ω.dl C
14 Vorticity Diffusion #$%+ (-* #$+ (.* #$% #$#+ '! #!#$#+!#$%!#$%+!#$"!!!" # "! & " #!#$+!!!" # "! & U θ (r, t) = Lamb-Oseen Vortex Γ r2 [1 exp( 2πr a 2 )] Ω(r, t) = Γ r2 exp( πa2 a 2 ) a 2 (t) =a 2 (0) + 4νt
15 Inviscid incompressible flows Dω Dt =[ t + u. ]ω = ω. u Consider a vector element of a material line A B = δ l During time dt, points A and B move respectively to points A' and B' B B A B = δ l = δ l +(u B u A )δt A A Dδ l Dt = δ l δ l δt and Dδ l Dt =(δ l )u u B u A =( A B )u
16 Inviscid incompressible flows By comparing equations Dω Dt = ω. u Dδ l Dt =(δ l )u In the inviscid fluid, for a given fluid particle, vorticity evolves in time the same way as does a small material line with the same direction. (a) u (b) it may be tilted ω j (t) ω j (t + δt) ω i (t) ω i (t + δt) x j x i it may be stretched/compressed Concept used in numerical vortex methods.
17 Vorticity Enhancement by Strain Field Dω Dt =[ t + u. ]ω = ω. u + ν ω Stretching
18 Law of conservation : Helmholtz Laws for inviscid incompressible flows
19 First Law of conservation Circulation around a material loop Γ = C u.dl = d Du u dx = dt C(t) C(t) Dt dx S ω.ds d dt Γ = ν ω dx C(t) ν =0 d dt Γ =0 Circulation along a material line remains constant when convected by the fluid
20 Second Law of conservation Consider a fluid particle without vorticity All small loop around the particle would have zero circulation d dt Γ =0 all small loop remain of zero circulation ω =0 U y C b x C a A potential region remains potential when convected by the fluid in the inviscid context
21 Third Law of conservation. Vortex lines are material lines i.e. convected by the fluid Tilting and Stretching of Vortex lines First and Third laws imply that: Circulation of a vortex tube does not change with time
22 Helmholtz conservation laws in 2D For the two-dimensional case u(x,y), v(x,y), w=0 ω = ωe z = v y u e z y Vorticity lines are straight and there is no stretching (u ) ω =0 In 2D Euler, vorticity is such that Dω Dt =0 Vorticity of each particle is hence conserved
23 Helmholtz conservation laws in axisymmetric case axisymmetric vortex ring u = u r (r, z, t) e r + u z (r, z, t) e z ω = ω θ (r, z) e θ ω θ = u r z u z r Vorticity lines are rings and there is stretching In Euler, vorticity is such that D ωθ =0 Dt r ω θ r is hence conserved
V (r,t) = i ˆ u( x, y,z,t) + ˆ j v( x, y,z,t) + k ˆ w( x, y, z,t)
 IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity
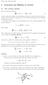 Version date: March 22, 21 1 3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity 3.1 The vorticity equation We start from Navier Stokes: u t + u u = 1 ρ p + ν 2 u 1) where we have not included a term describing a
Version date: March 22, 21 1 3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity 3.1 The vorticity equation We start from Navier Stokes: u t + u u = 1 ρ p + ν 2 u 1) where we have not included a term describing a
Continuum Mechanics Lecture 5 Ideal fluids
 Continuum Mechanics Lecture 5 Ideal fluids Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - Helmholtz decomposition - Divergence and curl theorem - Kelvin s circulation theorem - The vorticity equation
Continuum Mechanics Lecture 5 Ideal fluids Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - Helmholtz decomposition - Divergence and curl theorem - Kelvin s circulation theorem - The vorticity equation
3.5 Vorticity Equation
 .0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture 9.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Lecture 9 is structured as follows: In paragraph 3.5 we return to the full Navier-Stokes equations (unsteady, viscous
.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture 9.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Lecture 9 is structured as follows: In paragraph 3.5 we return to the full Navier-Stokes equations (unsteady, viscous
Chapter 5. The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws
 Chapter 5 The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws 1 5.1 Introduction Two primary methods in deriving the differential forms of fundamental laws: Gauss s Theorem: Allows area integrals of the equations
Chapter 5 The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws 1 5.1 Introduction Two primary methods in deriving the differential forms of fundamental laws: Gauss s Theorem: Allows area integrals of the equations
Vorticity Equation Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9. Return to viscous incompressible flow. N-S equation: v. Now: v = v + = 0 incompressible
 13.01 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 9 Copyright c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. Vorticity Equation 13.01 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Return to viscous incompressible
13.01 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 9 Copyright c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. Vorticity Equation 13.01 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 9 Return to viscous incompressible
Review of fluid dynamics
 Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course
 Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course January 15, 2014 A two dimensional flow field characterised by the following velocity components in polar coordinates is called a free vortex: u r
Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course January 15, 2014 A two dimensional flow field characterised by the following velocity components in polar coordinates is called a free vortex: u r
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability
 GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
The vorticity field. A dust devil
 The vorticity field The vector ω = u curl u is twice the local angular velocity in the flow, and is called the vorticity of the flow (from Latin for a whirlpool). Vortex lines are everywhere in the direction
The vorticity field The vector ω = u curl u is twice the local angular velocity in the flow, and is called the vorticity of the flow (from Latin for a whirlpool). Vortex lines are everywhere in the direction
CHAPTER 7 SEVERAL FORMS OF THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION
 CHAPTER 7 SEVERAL FORMS OF THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION 7.1 THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS Under the assumption of a Newtonian stress-rate-of-strain constitutive equation and a linear, thermally conductive medium,
CHAPTER 7 SEVERAL FORMS OF THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION 7.1 THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS Under the assumption of a Newtonian stress-rate-of-strain constitutive equation and a linear, thermally conductive medium,
Lecture 3: The Navier-Stokes Equations: Topological aspects
 Lecture 3: The Navier-Stokes Equations: Topological aspects September 9, 2015 1 Goal Topology is the branch of math wich studies shape-changing objects; objects which can transform one into another without
Lecture 3: The Navier-Stokes Equations: Topological aspects September 9, 2015 1 Goal Topology is the branch of math wich studies shape-changing objects; objects which can transform one into another without
TRANSIENT FLOW AROUND A VORTEX RING BY A VORTEX METHOD
 Proceedings of The Second International Conference on Vortex Methods, September 26-28, 21, Istanbul, Turkey TRANSIENT FLOW AROUND A VORTEX RING BY A VORTEX METHOD Teruhiko Kida* Department of Energy Systems
Proceedings of The Second International Conference on Vortex Methods, September 26-28, 21, Istanbul, Turkey TRANSIENT FLOW AROUND A VORTEX RING BY A VORTEX METHOD Teruhiko Kida* Department of Energy Systems
F1.9AB2 1. r 2 θ2 + sin 2 α. and. p θ = mr 2 θ. p2 θ. (d) In light of the information in part (c) above, we can express the Hamiltonian in the form
 F1.9AB2 1 Question 1 (20 Marks) A cone of semi-angle α has its axis vertical and vertex downwards, as in Figure 1 (overleaf). A point mass m slides without friction on the inside of the cone under the
F1.9AB2 1 Question 1 (20 Marks) A cone of semi-angle α has its axis vertical and vertex downwards, as in Figure 1 (overleaf). A point mass m slides without friction on the inside of the cone under the
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
 Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Tien-Tsan Shieh April 16, 2009 What is a Fluid? The key distinction between a fluid and a solid lies in the mode of resistance to change of shape. The fluid, unlike the
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Tien-Tsan Shieh April 16, 2009 What is a Fluid? The key distinction between a fluid and a solid lies in the mode of resistance to change of shape. The fluid, unlike the
AE/ME 339. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) K. M. Isaac. Momentum equation. Computational Fluid Dynamics (AE/ME 339) MAEEM Dept.
 AE/ME 339 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Momentum equation 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Consider the moving fluid element model shown in Figure.b Basis is Newton s nd Law which says
AE/ME 339 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Momentum equation 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Consider the moving fluid element model shown in Figure.b Basis is Newton s nd Law which says
0 = p. 2 x + 2 w. z +ν w
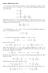 Solution (Elliptical pipe flow (a Using the Navier Stokes equations in three dimensional cartesian coordinates, given that u =, v = and w = w(x,y only, and assuming no body force, we are left with = p
Solution (Elliptical pipe flow (a Using the Navier Stokes equations in three dimensional cartesian coordinates, given that u =, v = and w = w(x,y only, and assuming no body force, we are left with = p
7 The Navier-Stokes Equations
 18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master Degree in Mechanical Engineering Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer 15-Convective Heat Transfer Fausto Arpino f.arpino@unicas.it Introduction In conduction problems the convection entered the analysis
Master Degree in Mechanical Engineering Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer 15-Convective Heat Transfer Fausto Arpino f.arpino@unicas.it Introduction In conduction problems the convection entered the analysis
Detailed Outline, M E 521: Foundations of Fluid Mechanics I
 Detailed Outline, M E 521: Foundations of Fluid Mechanics I I. Introduction and Review A. Notation 1. Vectors 2. Second-order tensors 3. Volume vs. velocity 4. Del operator B. Chapter 1: Review of Basic
Detailed Outline, M E 521: Foundations of Fluid Mechanics I I. Introduction and Review A. Notation 1. Vectors 2. Second-order tensors 3. Volume vs. velocity 4. Del operator B. Chapter 1: Review of Basic
6.2 Governing Equations for Natural Convection
 6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
AE/ME 339. K. M. Isaac Professor of Aerospace Engineering. 12/21/01 topic7_ns_equations 1
 AE/ME 339 Professor of Aerospace Engineering 12/21/01 topic7_ns_equations 1 Continuity equation Governing equation summary Non-conservation form D Dt. V 0.(2.29) Conservation form ( V ) 0...(2.33) t 12/21/01
AE/ME 339 Professor of Aerospace Engineering 12/21/01 topic7_ns_equations 1 Continuity equation Governing equation summary Non-conservation form D Dt. V 0.(2.29) Conservation form ( V ) 0...(2.33) t 12/21/01
18.325: Vortex Dynamics
 8.35: Vortex Dynamics Problem Sheet. Fluid is barotropic which means p = p(. The Euler equation, in presence of a conservative body force, is Du Dt = p χ. This can be written, on use of a vector identity,
8.35: Vortex Dynamics Problem Sheet. Fluid is barotropic which means p = p(. The Euler equation, in presence of a conservative body force, is Du Dt = p χ. This can be written, on use of a vector identity,
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data
 On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2007 2008 FLUIDS DYNAMICS WITH ADVANCED TOPICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt question ONE and FOUR other questions. Candidates must
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2007 2008 FLUIDS DYNAMICS WITH ADVANCED TOPICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt question ONE and FOUR other questions. Candidates must
The Role of Convection and Nearly Singular Behavior of the 3D Navier-Stokes Equations
 The Role of Convection and Nearly Singular Behavior of the 3D Navier-Stokes Equations Thomas Y. Hou Applied and Comput. Mathematics, Caltech PDE Conference in honor of Blake Temple, University of Michigan
The Role of Convection and Nearly Singular Behavior of the 3D Navier-Stokes Equations Thomas Y. Hou Applied and Comput. Mathematics, Caltech PDE Conference in honor of Blake Temple, University of Michigan
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK
 UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Faculty of Science and Engineering END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MA4607 SEMESTER: Autumn 2012-13 MODULE TITLE: Introduction to Fluids DURATION OF
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Faculty of Science and Engineering END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MA4607 SEMESTER: Autumn 2012-13 MODULE TITLE: Introduction to Fluids DURATION OF
J OURNAL OF TURBULENCE
 JOT J OURNAL OF TURBULENCE http://jot.iop.org/ Extension of the gridless vortex method into the compressible flow regime Monika Nitsche 1 and James H Strickland 2 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
JOT J OURNAL OF TURBULENCE http://jot.iop.org/ Extension of the gridless vortex method into the compressible flow regime Monika Nitsche 1 and James H Strickland 2 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics
 Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics Amey Joshi 07-Feb-018 1 Equations of ideal fluids onsider a volume element of a fluid of density ρ. If there are no sources or sinks in, the mass in it will change
Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics Amey Joshi 07-Feb-018 1 Equations of ideal fluids onsider a volume element of a fluid of density ρ. If there are no sources or sinks in, the mass in it will change
Mathematical Theory of Non-Newtonian Fluid
 Mathematical Theory of Non-Newtonian Fluid 1. Derivation of the Incompressible Fluid Dynamics 2. Existence of Non-Newtonian Flow and its Dynamics 3. Existence in the Domain with Boundary Hyeong Ohk Bae
Mathematical Theory of Non-Newtonian Fluid 1. Derivation of the Incompressible Fluid Dynamics 2. Existence of Non-Newtonian Flow and its Dynamics 3. Existence in the Domain with Boundary Hyeong Ohk Bae
Getting started: CFD notation
 PDE of p-th order Getting started: CFD notation f ( u,x, t, u x 1,..., u x n, u, 2 u x 1 x 2,..., p u p ) = 0 scalar unknowns u = u(x, t), x R n, t R, n = 1,2,3 vector unknowns v = v(x, t), v R m, m =
PDE of p-th order Getting started: CFD notation f ( u,x, t, u x 1,..., u x n, u, 2 u x 1 x 2,..., p u p ) = 0 scalar unknowns u = u(x, t), x R n, t R, n = 1,2,3 vector unknowns v = v(x, t), v R m, m =
Dynamics of the Coarse-Grained Vorticity
 (B) Dynamics of the Coarse-Grained Vorticity See T & L, Section 3.3 Since our interest is mainly in inertial-range turbulence dynamics, we shall consider first the equations of the coarse-grained vorticity.
(B) Dynamics of the Coarse-Grained Vorticity See T & L, Section 3.3 Since our interest is mainly in inertial-range turbulence dynamics, we shall consider first the equations of the coarse-grained vorticity.
Point Vortex Dynamics in Two Dimensions
 Spring School on Fluid Mechanics and Geophysics of Environmental Hazards 9 April to May, 9 Point Vortex Dynamics in Two Dimensions Ruth Musgrave, Mostafa Moghaddami, Victor Avsarkisov, Ruoqian Wang, Wei
Spring School on Fluid Mechanics and Geophysics of Environmental Hazards 9 April to May, 9 Point Vortex Dynamics in Two Dimensions Ruth Musgrave, Mostafa Moghaddami, Victor Avsarkisov, Ruoqian Wang, Wei
Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses
 Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses Shear stresses in a Newtonian fluid A fluid at rest can not resist shearing forces. Under the action of such forces it deforms continuously, however small
Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses Shear stresses in a Newtonian fluid A fluid at rest can not resist shearing forces. Under the action of such forces it deforms continuously, however small
Vortex stretching in incompressible and compressible fluids
 Vortex stretching in incompressible and compressible fluids Esteban G. Tabak, Fluid Dynamics II, Spring 00 1 Introduction The primitive form of the incompressible Euler equations is given by ( ) du P =
Vortex stretching in incompressible and compressible fluids Esteban G. Tabak, Fluid Dynamics II, Spring 00 1 Introduction The primitive form of the incompressible Euler equations is given by ( ) du P =
Nonlinear Evolution of a Vortex Ring
 Nonlinear Evolution of a Vortex Ring Yuji Hattori Kyushu Institute of Technology, JAPAN Yasuhide Fukumoto Kyushu University, JAPAN EUROMECH Colloquium 491 Vortex dynamics from quantum to geophysical scales
Nonlinear Evolution of a Vortex Ring Yuji Hattori Kyushu Institute of Technology, JAPAN Yasuhide Fukumoto Kyushu University, JAPAN EUROMECH Colloquium 491 Vortex dynamics from quantum to geophysical scales
Blow-up or No Blow-up? Fluid Dynamic Perspective of the Clay Millennium Problem
 Blow-up or No Blow-up? Fluid Dynamic Perspective of the Clay Millennium Problem Thomas Y. Hou Applied and Comput. Mathematics, Caltech Research was supported by NSF Theodore Y. Wu Lecture in Aerospace,
Blow-up or No Blow-up? Fluid Dynamic Perspective of the Clay Millennium Problem Thomas Y. Hou Applied and Comput. Mathematics, Caltech Research was supported by NSF Theodore Y. Wu Lecture in Aerospace,
Several forms of the equations of motion
 Chapter 6 Several forms of the equations of motion 6.1 The Navier-Stokes equations Under the assumption of a Newtonian stress-rate-of-strain constitutive equation and a linear, thermally conductive medium,
Chapter 6 Several forms of the equations of motion 6.1 The Navier-Stokes equations Under the assumption of a Newtonian stress-rate-of-strain constitutive equation and a linear, thermally conductive medium,
Exercise 5: Exact Solutions to the Navier-Stokes Equations I
 Fluid Mechanics, SG4, HT009 September 5, 009 Exercise 5: Exact Solutions to the Navier-Stokes Equations I Example : Plane Couette Flow Consider the flow of a viscous Newtonian fluid between two parallel
Fluid Mechanics, SG4, HT009 September 5, 009 Exercise 5: Exact Solutions to the Navier-Stokes Equations I Example : Plane Couette Flow Consider the flow of a viscous Newtonian fluid between two parallel
1. Introduction, tensors, kinematics
 1. Introduction, tensors, kinematics Content: Introduction to fluids, Cartesian tensors, vector algebra using tensor notation, operators in tensor form, Eulerian and Lagrangian description of scalar and
1. Introduction, tensors, kinematics Content: Introduction to fluids, Cartesian tensors, vector algebra using tensor notation, operators in tensor form, Eulerian and Lagrangian description of scalar and
SHORT WAVE INSTABILITIES OF COUNTER-ROTATING BATCHELOR VORTEX PAIRS
 Fifth International Conference on CFD in the Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 13-15 December 6 SHORT WAVE INSTABILITIES OF COUNTER-ROTATING BATCHELOR VORTEX PAIRS Kris RYAN, Gregory J. SHEARD
Fifth International Conference on CFD in the Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 13-15 December 6 SHORT WAVE INSTABILITIES OF COUNTER-ROTATING BATCHELOR VORTEX PAIRS Kris RYAN, Gregory J. SHEARD
TOPICS IN MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS: FLUID DYNAMICS
 TOPICS IN MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS: FLUID DYNAMICS PROF. VLADIMIR VLADIMIROV 1. The Kinematics of Continuous Medium 1.1. Lagrangian and Eulerian Coordinates General Idea Fluid flow is represented mathematically
TOPICS IN MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS: FLUID DYNAMICS PROF. VLADIMIR VLADIMIROV 1. The Kinematics of Continuous Medium 1.1. Lagrangian and Eulerian Coordinates General Idea Fluid flow is represented mathematically
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
Blow-up or No Blow-up? the Role of Convection in 3D Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations
 Blow-up or No Blow-up? the Role of Convection in 3D Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations Thomas Y. Hou Applied and Comput. Mathematics, Caltech Joint work with Zhen Lei; Congming Li, Ruo Li, and Guo
Blow-up or No Blow-up? the Role of Convection in 3D Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations Thomas Y. Hou Applied and Comput. Mathematics, Caltech Joint work with Zhen Lei; Congming Li, Ruo Li, and Guo
Math background. Physics. Simulation. Related phenomena. Frontiers in graphics. Rigid fluids
 Fluid dynamics Math background Physics Simulation Related phenomena Frontiers in graphics Rigid fluids Fields Domain Ω R2 Scalar field f :Ω R Vector field f : Ω R2 Types of derivatives Derivatives measure
Fluid dynamics Math background Physics Simulation Related phenomena Frontiers in graphics Rigid fluids Fields Domain Ω R2 Scalar field f :Ω R Vector field f : Ω R2 Types of derivatives Derivatives measure
5.1 Fluid momentum equation Hydrostatics Archimedes theorem The vorticity equation... 42
 Chapter 5 Euler s equation Contents 5.1 Fluid momentum equation........................ 39 5. Hydrostatics................................ 40 5.3 Archimedes theorem........................... 41 5.4 The
Chapter 5 Euler s equation Contents 5.1 Fluid momentum equation........................ 39 5. Hydrostatics................................ 40 5.3 Archimedes theorem........................... 41 5.4 The
Computational Fluid Dynamics 2
 Seite 1 Introduction Computational Fluid Dynamics 11.07.2016 Computational Fluid Dynamics 2 Turbulence effects and Particle transport Martin Pietsch Computational Biomechanics Summer Term 2016 Seite 2
Seite 1 Introduction Computational Fluid Dynamics 11.07.2016 Computational Fluid Dynamics 2 Turbulence effects and Particle transport Martin Pietsch Computational Biomechanics Summer Term 2016 Seite 2
Conservation of Mass. Computational Fluid Dynamics. The Equations Governing Fluid Motion
 http://www.nd.edu/~gtryggva/cfd-course/ http://www.nd.edu/~gtryggva/cfd-course/ Computational Fluid Dynamics Lecture 4 January 30, 2017 The Equations Governing Fluid Motion Grétar Tryggvason Outline Derivation
http://www.nd.edu/~gtryggva/cfd-course/ http://www.nd.edu/~gtryggva/cfd-course/ Computational Fluid Dynamics Lecture 4 January 30, 2017 The Equations Governing Fluid Motion Grétar Tryggvason Outline Derivation
(Jim You have a note for yourself here that reads Fill in full derivation, this is a sloppy treatment ).
 Lecture. dministration Collect problem set. Distribute problem set due October 3, 004.. nd law of thermodynamics (Jim You have a note for yourself here that reads Fill in full derivation, this is a sloppy
Lecture. dministration Collect problem set. Distribute problem set due October 3, 004.. nd law of thermodynamics (Jim You have a note for yourself here that reads Fill in full derivation, this is a sloppy
Topics in Fluid Dynamics: Classical physics and recent mathematics
 Topics in Fluid Dynamics: Classical physics and recent mathematics Toan T. Nguyen 1,2 Penn State University Graduate Student Seminar @ PSU Jan 18th, 2018 1 Homepage: http://math.psu.edu/nguyen 2 Math blog:
Topics in Fluid Dynamics: Classical physics and recent mathematics Toan T. Nguyen 1,2 Penn State University Graduate Student Seminar @ PSU Jan 18th, 2018 1 Homepage: http://math.psu.edu/nguyen 2 Math blog:
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/
Vortex motion. Wasilij Barsukow, July 1, 2016
 The concept of vorticity We call Vortex motion Wasilij Barsukow, mail@sturzhang.de July, 206 ω = v vorticity. It is a measure of the swirlyness of the flow, but is also present in shear flows where the
The concept of vorticity We call Vortex motion Wasilij Barsukow, mail@sturzhang.de July, 206 ω = v vorticity. It is a measure of the swirlyness of the flow, but is also present in shear flows where the
HIGH ORDER VORTEX METHODS WITH DEFORMING ELLIPTICAL GAUSSIAN BLOBS 1: DERIVATION AND VALIDATION
 HIGH ORDER VORTEX METHODS WITH DEFORMING ELLIPTICAL GAUSSIAN BLOBS 1: DERIVATION AND VALIDATION LOUIS F. ROSSI Key words. theory vortex methods, vorticity dynamics, computational fluid dynamics, convergence
HIGH ORDER VORTEX METHODS WITH DEFORMING ELLIPTICAL GAUSSIAN BLOBS 1: DERIVATION AND VALIDATION LOUIS F. ROSSI Key words. theory vortex methods, vorticity dynamics, computational fluid dynamics, convergence
Basic hydrodynamics. David Gurarie. 1 Newtonian fluids: Euler and Navier-Stokes equations
 Basic hydrodynamics David Gurarie 1 Newtonian fluids: Euler and Navier-Stokes equations The basic hydrodynamic equations in the Eulerian form consist of conservation of mass, momentum and energy. We denote
Basic hydrodynamics David Gurarie 1 Newtonian fluids: Euler and Navier-Stokes equations The basic hydrodynamic equations in the Eulerian form consist of conservation of mass, momentum and energy. We denote
Candidates must show on each answer book the type of calculator used. Only calculators permitted under UEA Regulations may be used.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2011 2012 FLUID DYNAMICS MTH-3D41 Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt FIVE questions. Candidates must show on each answer book the type
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics May/June UG Examination 2011 2012 FLUID DYNAMICS MTH-3D41 Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt FIVE questions. Candidates must show on each answer book the type
Quantum vortex reconnections
 Quantum vortex reconnections A.W. Baggaley 1,2, S. Zuccher 4, Carlo F Barenghi 2, 3, A.J. Youd 2 1 University of Glasgow 2 Joint Quantum Centre Durham-Newcastle 3 Newcastle University 4 University of Verona
Quantum vortex reconnections A.W. Baggaley 1,2, S. Zuccher 4, Carlo F Barenghi 2, 3, A.J. Youd 2 1 University of Glasgow 2 Joint Quantum Centre Durham-Newcastle 3 Newcastle University 4 University of Verona
Modeling, Simulating and Rendering Fluids. Thanks to Ron Fediw et al, Jos Stam, Henrik Jensen, Ryan
 Modeling, Simulating and Rendering Fluids Thanks to Ron Fediw et al, Jos Stam, Henrik Jensen, Ryan Applications Mostly Hollywood Shrek Antz Terminator 3 Many others Games Engineering Animating Fluids is
Modeling, Simulating and Rendering Fluids Thanks to Ron Fediw et al, Jos Stam, Henrik Jensen, Ryan Applications Mostly Hollywood Shrek Antz Terminator 3 Many others Games Engineering Animating Fluids is
J. Szantyr Lecture No. 4 Principles of the Turbulent Flow Theory The phenomenon of two markedly different types of flow, namely laminar and
 J. Szantyr Lecture No. 4 Principles of the Turbulent Flow Theory The phenomenon of two markedly different types of flow, namely laminar and turbulent, was discovered by Osborne Reynolds (184 191) in 1883
J. Szantyr Lecture No. 4 Principles of the Turbulent Flow Theory The phenomenon of two markedly different types of flow, namely laminar and turbulent, was discovered by Osborne Reynolds (184 191) in 1883
SHORT-WAVE INSTABILITY GROWTH IN CLOSELY SPACED VORTEX PAIRS
 Seventh International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 9-11 December 2009 SHORT-WAVE INSTABILITY GROWTH IN CLOSELY SPACED VORTEX PAIRS Nicholas BOUSTEAD
Seventh International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 9-11 December 2009 SHORT-WAVE INSTABILITY GROWTH IN CLOSELY SPACED VORTEX PAIRS Nicholas BOUSTEAD
Chapter 4: Fluid Kinematics
 Overview Fluid kinematics deals with the motion of fluids without considering the forces and moments which create the motion. Items discussed in this Chapter. Material derivative and its relationship to
Overview Fluid kinematics deals with the motion of fluids without considering the forces and moments which create the motion. Items discussed in this Chapter. Material derivative and its relationship to
A stochastic particle system for the Burgers equation.
 A stochastic particle system for the Burgers equation. Alexei Novikov Department of Mathematics Penn State University with Gautam Iyer (Carnegie Mellon) supported by NSF Burgers equation t u t + u x u
A stochastic particle system for the Burgers equation. Alexei Novikov Department of Mathematics Penn State University with Gautam Iyer (Carnegie Mellon) supported by NSF Burgers equation t u t + u x u
Lecture 1: Introduction to Linear and Non-Linear Waves
 Lecture 1: Introduction to Linear and Non-Linear Waves Lecturer: Harvey Segur. Write-up: Michael Bates June 15, 2009 1 Introduction to Water Waves 1.1 Motivation and Basic Properties There are many types
Lecture 1: Introduction to Linear and Non-Linear Waves Lecturer: Harvey Segur. Write-up: Michael Bates June 15, 2009 1 Introduction to Water Waves 1.1 Motivation and Basic Properties There are many types
Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection:
 Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection: K-H instability, vorticity dynamics, R-T instability, capillary action, and cavitation William A. Sirignano University of California, Irvine -- Round liquid columns
Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection: K-H instability, vorticity dynamics, R-T instability, capillary action, and cavitation William A. Sirignano University of California, Irvine -- Round liquid columns
Lecture 3: 1. Lecture 3.
 Lecture 3: 1 Lecture 3. Lecture 3: 2 Plan for today Summary of the key points of the last lecture. Review of vector and tensor products : the dot product (or inner product ) and the cross product (or vector
Lecture 3: 1 Lecture 3. Lecture 3: 2 Plan for today Summary of the key points of the last lecture. Review of vector and tensor products : the dot product (or inner product ) and the cross product (or vector
Lagrangian Dynamics & Mixing
 V Lagrangian Dynamics & Mixing See T&L, Ch. 7 The study of the Lagrangian dynamics of turbulence is, at once, very old and very new. Some of the earliest work on fluid turbulence in the 1920 s, 30 s and
V Lagrangian Dynamics & Mixing See T&L, Ch. 7 The study of the Lagrangian dynamics of turbulence is, at once, very old and very new. Some of the earliest work on fluid turbulence in the 1920 s, 30 s and
Implementation of a symmetry-preserving discretization in Gerris
 Implementation of a symmetry-preserving discretization in Gerris Daniel Fuster Cols: Pierre Sagaut, Stephane Popinet Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Institut Jean Le Rond D Alembert Introduction 10/11:
Implementation of a symmetry-preserving discretization in Gerris Daniel Fuster Cols: Pierre Sagaut, Stephane Popinet Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Institut Jean Le Rond D Alembert Introduction 10/11:
Vortices in accretion discs: formation process and dynamical evolution
 Vortices in accretion discs: formation process and dynamical evolution Geoffroy Lesur DAMTP (Cambridge UK) LAOG (Grenoble) John Papaloizou Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Giant vortex in Naruto straight (Japan)
Vortices in accretion discs: formation process and dynamical evolution Geoffroy Lesur DAMTP (Cambridge UK) LAOG (Grenoble) John Papaloizou Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Giant vortex in Naruto straight (Japan)
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 4. Potential Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 4. Potential Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Basic concepts in viscous flow
 Élisabeth Guazzelli and Jeffrey F. Morris with illustrations by Sylvie Pic Adapted from Chapter 1 of Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics 1 The fluid dynamic equations Navier-Stokes equations Dimensionless
Élisabeth Guazzelli and Jeffrey F. Morris with illustrations by Sylvie Pic Adapted from Chapter 1 of Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics 1 The fluid dynamic equations Navier-Stokes equations Dimensionless
Asymmetric vortex merger: mechanism and criterion
 Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. (2010) 24:163 167 DOI 10.1007/s00162-009-0154-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE L. K. Brandt T. K. Cichocki K. K. Nomura Asymmetric vortex merger: mechanism and criterion Received: 26 December
Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. (2010) 24:163 167 DOI 10.1007/s00162-009-0154-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE L. K. Brandt T. K. Cichocki K. K. Nomura Asymmetric vortex merger: mechanism and criterion Received: 26 December
Instabilities due a vortex at a density interface: gravitational and centrifugal effects
 Instabilities due a vortex at a density interface: gravitational and centrifugal effects Harish N Dixit and Rama Govindarajan Abstract A vortex placed at an initially straight density interface winds it
Instabilities due a vortex at a density interface: gravitational and centrifugal effects Harish N Dixit and Rama Govindarajan Abstract A vortex placed at an initially straight density interface winds it
OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT IN PLANE COUETTE FLOW
 OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT IN PLANE COUETTE FLOW Shingo Motoki, Genta Kawahara and Masaki Shimizu Graduate School of Engineering Science Osaka University 1-3 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka
OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT IN PLANE COUETTE FLOW Shingo Motoki, Genta Kawahara and Masaki Shimizu Graduate School of Engineering Science Osaka University 1-3 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka
M E 320 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 10
 M E 320 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 10 Today, we will: Finish our example problem rates of motion and deformation of fluid particles Discuss the Reynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) Show how the RTT
M E 320 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 10 Today, we will: Finish our example problem rates of motion and deformation of fluid particles Discuss the Reynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) Show how the RTT
Chapter 6: Incompressible Inviscid Flow
 Chapter 6: Incompressible Inviscid Flow 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Nondimensionalization of the NSE 6-3 Creeping Flow 6-4 Inviscid Regions of Flow 6-5 Irrotational Flow Approximation 6-6 Elementary Planar Irrotational
Chapter 6: Incompressible Inviscid Flow 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Nondimensionalization of the NSE 6-3 Creeping Flow 6-4 Inviscid Regions of Flow 6-5 Irrotational Flow Approximation 6-6 Elementary Planar Irrotational
Turbulent Rankine Vortices
 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Roger Kingdon April 2008 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Overview of key results in the theory of turbulence Motivation for a fresh perspective on turbulence The Rankine vortex CFD
Turbulent Rankine Vortices Roger Kingdon April 2008 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Overview of key results in the theory of turbulence Motivation for a fresh perspective on turbulence The Rankine vortex CFD
12.1 Viscous potential flow (VPF)
 1 Energy equation for irrotational theories of gas-liquid flow:: viscous potential flow (VPF), viscous potential flow with pressure correction (VCVPF), dissipation method (DM) 1.1 Viscous potential flow
1 Energy equation for irrotational theories of gas-liquid flow:: viscous potential flow (VPF), viscous potential flow with pressure correction (VCVPF), dissipation method (DM) 1.1 Viscous potential flow
2.25 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 2013
 .5 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 013 Solution to Problem 1-Final Exam- Fall 013 r j g u j ρ, µ,σ,u j u r 1 h(r) r = R Figure 1: Viscous Savart Sheet. Image courtesy: Villermaux et. al. [1]. This kind of
.5 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 013 Solution to Problem 1-Final Exam- Fall 013 r j g u j ρ, µ,σ,u j u r 1 h(r) r = R Figure 1: Viscous Savart Sheet. Image courtesy: Villermaux et. al. [1]. This kind of
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER
 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER Mohammad Goharkhah Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sahand Unversity of Technology, Tabriz, Iran CHAPTER 3 LAMINAR BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW LAMINAR BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW Boundary
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER Mohammad Goharkhah Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sahand Unversity of Technology, Tabriz, Iran CHAPTER 3 LAMINAR BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW LAMINAR BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW Boundary
Math 575-Lecture Viscous Newtonian fluid and the Navier-Stokes equations
 Math 575-Lecture 13 In 1845, tokes extended Newton s original idea to find a constitutive law which relates the Cauchy stress tensor to the velocity gradient, and then derived a system of equations. The
Math 575-Lecture 13 In 1845, tokes extended Newton s original idea to find a constitutive law which relates the Cauchy stress tensor to the velocity gradient, and then derived a system of equations. The
- Marine Hydrodynamics. Lecture 4. Knowns Equations # Unknowns # (conservation of mass) (conservation of momentum)
 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 4 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 4 Introduction Governing Equations so far: Knowns Equations # Unknowns # density ρ( x, t) Continuity 1 velocities
2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 4 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 4 Introduction Governing Equations so far: Knowns Equations # Unknowns # density ρ( x, t) Continuity 1 velocities
The Polymers Tug Back
 Tugging at Polymers in Turbulent Flow The Polymers Tug Back Jean-Luc Thiffeault http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/ jeanluc Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University Tugging
Tugging at Polymers in Turbulent Flow The Polymers Tug Back Jean-Luc Thiffeault http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/ jeanluc Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University Tugging
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master Degree in Mechanical Engineering Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer 19 Turbulent Flows Fausto Arpino f.arpino@unicas.it Introduction All the flows encountered in the engineering practice become unstable
Master Degree in Mechanical Engineering Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer 19 Turbulent Flows Fausto Arpino f.arpino@unicas.it Introduction All the flows encountered in the engineering practice become unstable
Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik
 ASDEX Upgrade Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 2D Fluid Turbulence Florian Merz Seminar on Turbulence, 08.09.05 2D turbulence? strictly speaking, there are no two-dimensional flows in nature approximately
ASDEX Upgrade Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 2D Fluid Turbulence Florian Merz Seminar on Turbulence, 08.09.05 2D turbulence? strictly speaking, there are no two-dimensional flows in nature approximately
The Turbulent Rotational Phase Separator
 The Turbulent Rotational Phase Separator J.G.M. Kuerten and B.P.M. van Esch Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands j.g.m.kuerten@tue.nl Summary. The Rotational
The Turbulent Rotational Phase Separator J.G.M. Kuerten and B.P.M. van Esch Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands j.g.m.kuerten@tue.nl Summary. The Rotational
Vortex Dynamos. Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD)
 Vortex Dynamos Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD) An introduction to vortices Vortices are ubiquitous in geophysical and astrophysical fluid mechanics (stratification & rotation).
Vortex Dynamos Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD) An introduction to vortices Vortices are ubiquitous in geophysical and astrophysical fluid mechanics (stratification & rotation).
Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics
 Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics CDS 140b Joris Vankerschaver jv@caltech.edu CDS 01/29/08, 01/31/08 Joris Vankerschaver (CDS) Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics 01/29/08, 01/31/08 1 / 34 Outline
Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics CDS 140b Joris Vankerschaver jv@caltech.edu CDS 01/29/08, 01/31/08 Joris Vankerschaver (CDS) Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics 01/29/08, 01/31/08 1 / 34 Outline
AA210A Fundamentals of Compressible Flow. Chapter 1 - Introduction to fluid flow
 AA210A Fundamentals of Compressible Flow Chapter 1 - Introduction to fluid flow 1 1.2 Conservation of mass Mass flux in the x-direction [ ρu ] = M L 3 L T = M L 2 T Momentum per unit volume Mass per unit
AA210A Fundamentals of Compressible Flow Chapter 1 - Introduction to fluid flow 1 1.2 Conservation of mass Mass flux in the x-direction [ ρu ] = M L 3 L T = M L 2 T Momentum per unit volume Mass per unit
Chapter 3 Burgers Equation
 Chapter 3 Burgers Equation One of the major challenges in the field of comple systems is a thorough understanding of the phenomenon of turbulence. Direct numerical simulations (DNS) have substantially
Chapter 3 Burgers Equation One of the major challenges in the field of comple systems is a thorough understanding of the phenomenon of turbulence. Direct numerical simulations (DNS) have substantially
MAE210C: Fluid Mechanics III Spring Quarter sgls/mae210c 2013/ Solution II
 MAE210C: Fluid Mechanics III Spring Quarter 2013 http://web.eng.ucsd.edu/ sgls/mae210c 2013/ Solution II D 4.1 The equations are exactly the same as before, with the difference that the pressure in the
MAE210C: Fluid Mechanics III Spring Quarter 2013 http://web.eng.ucsd.edu/ sgls/mae210c 2013/ Solution II D 4.1 The equations are exactly the same as before, with the difference that the pressure in the
Computational Analysis of an Imploding Gas:
 1/ 31 Direct Numerical Simulation of Navier-Stokes Equations Stephen Voelkel University of Notre Dame October 19, 2011 2/ 31 Acknowledges Christopher M. Romick, Ph.D. Student, U. Notre Dame Dr. Joseph
1/ 31 Direct Numerical Simulation of Navier-Stokes Equations Stephen Voelkel University of Notre Dame October 19, 2011 2/ 31 Acknowledges Christopher M. Romick, Ph.D. Student, U. Notre Dame Dr. Joseph
DNS STUDY OF TURBULENT HEAT TRANSFER IN A SPANWISE ROTATING SQUARE DUCT
 10 th International Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena (TSFP10), Chicago, USA, July, 2017 DNS STUDY OF TURBULENT HEAT TRANSFER IN A SPANWISE ROTATING SQUARE DUCT Bing-Chen Wang Department
10 th International Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena (TSFP10), Chicago, USA, July, 2017 DNS STUDY OF TURBULENT HEAT TRANSFER IN A SPANWISE ROTATING SQUARE DUCT Bing-Chen Wang Department
FORMULA SHEET. General formulas:
 FORMULA SHEET You may use this formula sheet during the Advanced Transport Phenomena course and it should contain all formulas you need during this course. Note that the weeks are numbered from 1.1 to
FORMULA SHEET You may use this formula sheet during the Advanced Transport Phenomena course and it should contain all formulas you need during this course. Note that the weeks are numbered from 1.1 to
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN
 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN FLUID DYNAMICS Part 6: Particles transport model Marcela B. Goldschmit 2 3 Lagrangean Model The particles movement equations are solved. The trajectory of each particles can be
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN FLUID DYNAMICS Part 6: Particles transport model Marcela B. Goldschmit 2 3 Lagrangean Model The particles movement equations are solved. The trajectory of each particles can be
F11AE1 1. C = ρν r r. r u z r
 F11AE1 1 Question 1 20 Marks) Consider an infinite horizontal pipe with circular cross-section of radius a, whose centre line is aligned along the z-axis; see Figure 1. Assume no-slip boundary conditions
F11AE1 1 Question 1 20 Marks) Consider an infinite horizontal pipe with circular cross-section of radius a, whose centre line is aligned along the z-axis; see Figure 1. Assume no-slip boundary conditions
Chapter 2: Fluid Dynamics Review
 7 Chapter 2: Fluid Dynamics Review This chapter serves as a short review of basic fluid mechanics. We derive the relevant transport equations (or conservation equations), state Newton s viscosity law leading
7 Chapter 2: Fluid Dynamics Review This chapter serves as a short review of basic fluid mechanics. We derive the relevant transport equations (or conservation equations), state Newton s viscosity law leading
Soft Bodies. Good approximation for hard ones. approximation breaks when objects break, or deform. Generalization: soft (deformable) bodies
 Soft-Body Physics Soft Bodies Realistic objects are not purely rigid. Good approximation for hard ones. approximation breaks when objects break, or deform. Generalization: soft (deformable) bodies Deformed
Soft-Body Physics Soft Bodies Realistic objects are not purely rigid. Good approximation for hard ones. approximation breaks when objects break, or deform. Generalization: soft (deformable) bodies Deformed
INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES
 INTRODUCTION The transport of particles in laminar and turbulent flows has numerous applications in engineering, biological and environmental systems. The deposition of aerosol particles in channels and
INTRODUCTION The transport of particles in laminar and turbulent flows has numerous applications in engineering, biological and environmental systems. The deposition of aerosol particles in channels and
Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics
 Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
PAPER 331 HYDRODYNAMIC STABILITY
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday, 6 May, 016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm PAPER 331 HYDRODYNAMIC STABILITY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday, 6 May, 016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm PAPER 331 HYDRODYNAMIC STABILITY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal
Exam in Fluid Mechanics 5C1214
 Eam in Fluid Mechanics 5C1214 Final eam in course 5C1214 13/01 2004 09-13 in Q24 Eaminer: Prof. Dan Henningson The point value of each question is given in parenthesis and you need more than 20 points
Eam in Fluid Mechanics 5C1214 Final eam in course 5C1214 13/01 2004 09-13 in Q24 Eaminer: Prof. Dan Henningson The point value of each question is given in parenthesis and you need more than 20 points
