Exponential Families and Friends: Learning the Parameters of the a Fully Observed BN. Kayhan Batmanghelich
|
|
|
- Muriel Russell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Epoetia Famiies ad Frieds: Learig te Parameters of te a Fuy Observed BN Kaya Batmageic
2 Macie Learig Te data ispires te structures we wat to predict Iferece fids {best structure, margias, partitio fuctio} for a ew observatio Iferece is usuay caed as a subroutie i earig Domai Kowedge Combiatoria Optimizatio ML Matematica Modeig Optimizatio Our mode defies a score for eac structure It aso tes us wat to optimize Learig tues te parameters of te mode 2
3 Macie Learig Data Mode X time fies ike a arrow X2 X 3 X 4 X 5 Objective Iferece Learig Iferece is usuay caed as a subroutie i earig 3
4 Today s Lecture X2 X X 3 X 4 X 5 px,x 2,X 3,X 4,X 5 px 5 X 3 px 4 X 2,X 3 px 3 px 2 X px 4
5 Today s Lecture X2 X X 3 X 4 X 5 px,x 2,X 3,X 4,X 5 px 5 X 3 px 4 X 2,X 3 px 3 px 2 X px 5
6 Today s Lecture X2 X X 3 X 4 X 5 px,x 2,X 3,X 4,X 5 px 5 X 3 px 4 X 2,X 3 px 3 px 2 X px How do we defie ad ear tese coditioa ad margia distributios for a Bayes Net? 6
7 Today s Lecture. Epoetia Famiy Distributios A cadidate for margia distributios, px i 2. Geeraized Liear Modes Coveiet form for coditioa distributios, px j X i 3. Learig Fuy Observed Bayes Nets Easy taks to decomposabiity 7
8 A cadidate for margia distributios, px i. EXPONENTIAL FAMILY 8
9 Wy te Epoetia Famiy?. Pitma-Koopma-Darmois teorem: it is te oy famiy of distributios wit sufficiet statistics tat do ot grow wit te size of te dataset 2. Oy famiy of distributios for wic cojugate priors eist see Murpy tetbook for a descriptio 3. It is te distributio tat is cosest to uiform i.e. maimizes etropy subject to momet matcig costraits 4. Key to Geeraized Liear Modes et sectio 5. Icudes some of your favorite distributios! Adapted from Murpy 202 tetbook 9
10 Witeboard Defiitio of mutivariate epoetia famiy 0
11 Witeboard Eampe : Categorica distributio
12 Witeboard Eampe 2: Mutivariate Gaussia distributio 2
13 Momets ad te Partitio Fuctio p; ep T A 3
14 Momets ad te Partitio Fuctio p; ep T T A r A E[T ] r 2 A E[T T T ] E[T ]E[T ] T 4
15 Sufficiecy For!#; %, T is sufficiet for q if tere is o iformatio i X regardig q beyod tat i T. We ca trow away X for te purpose of iferece w.r.t. q. Bayesia view X T p q T, p q T q Frequetist view X T p T, q p T q Te Neyma factorizatio teorem T is sufficiet for q if X T q p y 2, T, q y T, q, T Þ p q g T, q, T Eric CMU,
16 Sufficiecy p; ep T T A Let s assume i iid p,, ; p; Y j A ep T X T j A A j j 6
17 MLE for Epoetia Famiy For iid data, te og-ikeiood is Take derivatives ad set to zero: Tis amouts to momet matcig. We ca ifer te caoica parameters usig Eric CMU, { } å å Õ - ø ö ç è æ + - T T NA T A T D og ep og ; å å å Þ - MLE T N T N A A N T 0 µ! MLE MLE µ y!!
18 Eampes Gaussia: Mutiomia: Poisso: Eric CMU, [ ] [ ] / og ; vec vec ; k T T A T S + S S - S p µ µ µ å å Þ MLE N T N µ [ ] 0 ø ö ç è æ ø ö ç è æ - - ú û ù ê ë é ø ö ç è æ å å - ; e A T K k K k k K k k p p p å Þ MLE N µ! og e A T å Þ MLE N µ
19 Witeboard Bayesia estimatio of epoetia famiy p; ep T T A We ave observed iid sampes ad we are iterested i p {,, {z } D 25
20 Posterior Mea Uder Cojugate Prior p; ep T T p ;, 0 ep A T 0 A Ã, 0 p D p ; + X i T i ; + 0 Posterior mea of! E[ D] + 0 P i T i
21 Coveiet form for coditioa distributios, px j X i 2. GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS 27
22 Wy Geeraized Liear Modes? GLIMs. Geeraizatio of iear regressio, ogistic regressio, probit regressio, etc. 2. Provides a framework for creatig ew coditioa distributios tat come wit some coveiet properties 3. Specia case: GLMs wit caoica respose fuctios are easy to trai wit MLE. 4. No Free Luc: Wat about Bayesia estimatio of GLMs? Ufortuatey, we ave to tur to approimatio teciques sice, i geera, tere is't a cosed form of te posterior. 28
23 Geeraized Liear Modes GLMs GLM Te observed iput is assumed to eter ito te mode T via a iear combiatio of its eemets q Te coditioa mea µ is represeted as a fuctio f of, were f is kow as te respose fuctio Te observed output y is assumed to be caracterized by a epoetia famiy distributio wit coditioa mea µ. X Y N Eric CMU,
24 Witeboard Costructive defiitio of GLMs Defiitio of GLMs wit caoica respose fuctios 30
25 Eampes of te caoica respose fuctios 3
26 Witeboard MLE wit GLM wit Caoica respose 32
27 MLE for GLMs wit caoica respose Log-ikeiood Lw X i og y i + X i Derivative of Log-ikeiood y i w T i A i r w Lw X i i y i da i d i d i é- - ê ê - - X ê! ê ë- - é y ù ê ú ê y y " 2 ú ê! ú ê ú ëy û! 2 - -ù - - ú ú! ú ú - -û X i y i µ i i Oie earig for caoica GLMs X T y µ Tis is a fuctio of! Stocastic gradiet ascet east mea squares LMS agoritm: w t+ w t + y i µ t i i Step egt 33
28 Batc earig for caoica GLMs Te Hessia matri é- - ê ê - - X ê! ê ë- - é y ù ê ú ê y y " 2 ú ê! ú ê ú ëy û! 2 - -ù - - ú ú! ú ú - -û Ivoves te secod derivative of!# 34
29 Iterativey Reweigted Least Squares IRLS r w Lw X T y µ Reca Newto-Rapso metods wit cost fuctio w t+ w t + H w t rlw t X T Sw t X X T Sw t Xw t + X T y µ X T Sw t X X T Sw t z t z t Xw t + Sw t y µ t 35
30 Iterativey Reweigted Least Squares IRLS r w Lw X T y µ Reca Newto-Rapso metods wit cost fuctio w t+ w t + H w t rlw t X T Sw t X X T Sw t Xw t + X T y µ X T Sw t X X T Sw t z t z t Xw t + Sw t y µ t It ooks ike! "! #$! " % 36
31 Iterativey Reweigted Least Squares IRLS r w Lw X T y µ Reca Newto-Rapso metods wit cost fuctio w t+ w t + H w t rlw t X T Sw t X X T Sw t Xw t + X T y µ X T Sw t X X T Sw t z t z t Xw t + Sw t y µ t Tis ca be uderstood as sovig te foowig " Iterativey reweigted east squares " probem 37
32 Eampes r w Lw X T y µ Reca Newto-Rapso metods wit cost fuctio w t+ w t + H w t rlw t X T Sw t X X T Sw t Xw t + X T y µ X T Sw t X X T Sw t z t z t Xw t + Sw t y µ t 38
33 Practica Issues 39 It is very commo to use reguarized maimum ikeiood. IRLS takes!#$ % per iteratio, were N umber of traiig cases ad d dimesio of iput. Quasi-Newto metods, tat approimate te Hessia, work faster. Cojugate gradiet takes!#$ per iteratio, ad usuay works best i practice. Stocastic gradiet descet ca aso be used if N is arge c.f. perceptro rue. Eric CMU, q q q s q q q s q q T T T y y I p y e y p T ± å - - og, Norma ~,
34 Today s Lecture. Epoetia Famiy Distributios A cadidate for margia distributios, px i 2. Geeraized Liear Modes Coveiet form for coditioa distributios, px j X i 3. Learig Fuy Observed Bayes Nets Easy taks to decomposabiity 50
35 Easy taks to decomposabiity 3. LEARNING FULLY OBSERVED BNS 5
36 Simpe GMs are te buidig bocks of compe BNs Desity estimatio Parametric ad oparametric metods Regressio Liear, coditioa miture, oparametric Cassificatio Geerative ad discrimiative approac X X Q X µ,s X Y Q X Eric CMU,
37 Decomposabe ikeiood of a BN Reca from Lecture 2 Cosider te distributio defied by te directed acycic GM: p q p q p 2, q2 p 3, q3 p 4 2, 3, q4 Tis is eacty ike earig four separate sma BNs, eac of wic cosists of a ode ad its parets. X X X X X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3 X 4 X 4 Eric CMU,
38 Learig Fuy Observed BNs X2 X X 3 argma argma og px,x 2,X 3,X 4,X 5 og px 5 X 3, 5 + og px 4 X 2,X 3, 4 + og px og px 2 X, 2 + og px X 4 X 5 argma og px 2 argma 2 og px 2 X, 2 3 argma 3 og px argma 4 og px 4 X 2,X 3, 4 5 argma 5 og px 5 X 3, 5 54
39 Summary. Epoetia Famiy Distributios A cadidate for margia distributios, px i Eampes: Mutiomia, Diricet, Gaussia, Gamma, Poisso MLE as cosed form soutio Bayesia estimatio easy wit cojugate priors Sufficiet statistics by ispectio 2. Geeraized Liear Modes Coveiet form for coditioa distributios, px j X i Specia case: GLIMs wit caoica respose Output y foows a epoetia famiy Iput itroduced via a iear combiatio MLE for GLIMs wit caoica respose by SGD I geera, Bayesia estimatio reies o approimatios 3. Learig Fuy Observed Bayes Nets Easy taks to decomposabiity 55
5 : Exponential Family and Generalized Linear Models
 0-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 0-708, Sprig 206 5 : Expoetial Family ad Geeralized Liear Models Lecturer: Matthew Gormley Scribes: Yua Li, Yichog Xu, Silu Wag Expoetial Family Probability desity
0-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 0-708, Sprig 206 5 : Expoetial Family ad Geeralized Liear Models Lecturer: Matthew Gormley Scribes: Yua Li, Yichog Xu, Silu Wag Expoetial Family Probability desity
Machine Learning. Logistic Regression -- generative verses discriminative classifier. Le Song /15-781, Spring 2008
 Machie Learig 070/578 Srig 008 Logistic Regressio geerative verses discrimiative classifier Le Sog Lecture 5 Setember 4 0 Based o slides from Eric Xig CMU Readig: Cha. 3..34 CB Geerative vs. Discrimiative
Machie Learig 070/578 Srig 008 Logistic Regressio geerative verses discrimiative classifier Le Sog Lecture 5 Setember 4 0 Based o slides from Eric Xig CMU Readig: Cha. 3..34 CB Geerative vs. Discrimiative
Pattern Classification
 Patter Classificatio All materials i these slides were tae from Patter Classificatio (d ed) by R. O. Duda, P. E. Hart ad D. G. Stor, Joh Wiley & Sos, 000 with the permissio of the authors ad the publisher
Patter Classificatio All materials i these slides were tae from Patter Classificatio (d ed) by R. O. Duda, P. E. Hart ad D. G. Stor, Joh Wiley & Sos, 000 with the permissio of the authors ad the publisher
Elementary manipulations of probabilities
 Elemetary maipulatios of probabilities Set probability of multi-valued r.v. {=Odd} = +3+5 = /6+/6+/6 = ½ X X,, X i j X i j Multi-variat distributio: Joit probability: X true true X X,, X X i j i j X X
Elemetary maipulatios of probabilities Set probability of multi-valued r.v. {=Odd} = +3+5 = /6+/6+/6 = ½ X X,, X i j X i j Multi-variat distributio: Joit probability: X true true X X,, X X i j i j X X
Chapter 6 Principles of Data Reduction
 Chapter 6 for BST 695: Special Topics i Statistical Theory. Kui Zhag, 0 Chapter 6 Priciples of Data Reductio Sectio 6. Itroductio Goal: To summarize or reduce the data X, X,, X to get iformatio about a
Chapter 6 for BST 695: Special Topics i Statistical Theory. Kui Zhag, 0 Chapter 6 Priciples of Data Reductio Sectio 6. Itroductio Goal: To summarize or reduce the data X, X,, X to get iformatio about a
CS434a/541a: Pattern Recognition Prof. Olga Veksler. Lecture 5
 CS434a/54a: Patter Recogitio Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 5 Today Itroductio to parameter estimatio Two methods for parameter estimatio Maimum Likelihood Estimatio Bayesia Estimatio Itroducto Bayesia Decisio
CS434a/54a: Patter Recogitio Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 5 Today Itroductio to parameter estimatio Two methods for parameter estimatio Maimum Likelihood Estimatio Bayesia Estimatio Itroducto Bayesia Decisio
Lecture 13: Maximum Likelihood Estimation
 ECE90 Sprig 007 Statistical Learig Theory Istructor: R. Nowak Lecture 3: Maximum Likelihood Estimatio Summary of Lecture I the last lecture we derived a risk (MSE) boud for regressio problems; i.e., select
ECE90 Sprig 007 Statistical Learig Theory Istructor: R. Nowak Lecture 3: Maximum Likelihood Estimatio Summary of Lecture I the last lecture we derived a risk (MSE) boud for regressio problems; i.e., select
Classification with linear models
 Lecture 8 Classificatio with liear models Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Seott Square Geerative approach to classificatio Idea:. Represet ad lear the distributio, ). Use it to defie probabilistic
Lecture 8 Classificatio with liear models Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Seott Square Geerative approach to classificatio Idea:. Represet ad lear the distributio, ). Use it to defie probabilistic
The Bayesian Learning Framework. Back to Maximum Likelihood. Naïve Bayes. Simple Example: Coin Tosses. Given a generative model
 Back to Maximum Likelihood Give a geerative model f (x, y = k) =π k f k (x) Usig a geerative modellig approach, we assume a parametric form for f k (x) =f (x; k ) ad compute the MLE θ of θ =(π k, k ) k=
Back to Maximum Likelihood Give a geerative model f (x, y = k) =π k f k (x) Usig a geerative modellig approach, we assume a parametric form for f k (x) =f (x; k ) ad compute the MLE θ of θ =(π k, k ) k=
x x x 2x x N ( ) p NUMERICAL METHODS UNIT-I-SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS AND EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS By Newton-Raphson formula
 NUMERICAL METHODS UNIT-I-SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS AND EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS. If g( is cotiuous i [a,b], te uder wat coditio te iterative (or iteratio metod = g( as a uique solutio i [a,b]? '( i [a,b].. Wat
NUMERICAL METHODS UNIT-I-SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS AND EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS. If g( is cotiuous i [a,b], te uder wat coditio te iterative (or iteratio metod = g( as a uique solutio i [a,b]? '( i [a,b].. Wat
The picture in figure 1.1 helps us to see that the area represents the distance traveled. Figure 1: Area represents distance travelled
 1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
LECTURE 2 LEAST SQUARES CROSS-VALIDATION FOR KERNEL DENSITY ESTIMATION
 Jauary 3 07 LECTURE LEAST SQUARES CROSS-VALIDATION FOR ERNEL DENSITY ESTIMATION Noparametric kerel estimatio is extremely sesitive to te coice of badwidt as larger values of result i averagig over more
Jauary 3 07 LECTURE LEAST SQUARES CROSS-VALIDATION FOR ERNEL DENSITY ESTIMATION Noparametric kerel estimatio is extremely sesitive to te coice of badwidt as larger values of result i averagig over more
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 016 MODULE : Statistical Iferece Time allowed: Three hours Cadidates should aswer FIVE questios. All questios carry equal marks. The umber
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 016 MODULE : Statistical Iferece Time allowed: Three hours Cadidates should aswer FIVE questios. All questios carry equal marks. The umber
10-701/ Machine Learning Mid-term Exam Solution
 0-70/5-78 Machie Learig Mid-term Exam Solutio Your Name: Your Adrew ID: True or False (Give oe setece explaatio) (20%). (F) For a cotiuous radom variable x ad its probability distributio fuctio p(x), it
0-70/5-78 Machie Learig Mid-term Exam Solutio Your Name: Your Adrew ID: True or False (Give oe setece explaatio) (20%). (F) For a cotiuous radom variable x ad its probability distributio fuctio p(x), it
Lecture 12: September 27
 36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 207 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 2: September 27 Today we will discuss sufficiecy i more detail ad the begi to discuss some geeral strategies for costructig estimators.
36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 207 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 2: September 27 Today we will discuss sufficiecy i more detail ad the begi to discuss some geeral strategies for costructig estimators.
Topics Machine learning: lecture 3. Linear regression. Linear regression. Linear regression. Linear regression
 6.867 Machie learig: lecture 3 Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL tommi@csail.mit.edu Topics Beod liear regressio models additive regressio models, eamples geeralizatio ad cross-validatio populatio miimizer Statistical
6.867 Machie learig: lecture 3 Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL tommi@csail.mit.edu Topics Beod liear regressio models additive regressio models, eamples geeralizatio ad cross-validatio populatio miimizer Statistical
8 : Learning Partially Observed GM: the EM algorithm
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Sprig 2015 8 : Learig Partially Observed GM: the EM algorithm Lecturer: Eric P. Xig Scribes: Auric Qiao, Hao Zhag, Big Liu 1 Itroductio Two fudametal questios i
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Sprig 2015 8 : Learig Partially Observed GM: the EM algorithm Lecturer: Eric P. Xig Scribes: Auric Qiao, Hao Zhag, Big Liu 1 Itroductio Two fudametal questios i
Lecture 9: September 19
 36-700: Probability ad Mathematical Statistics I Fall 206 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 9: September 9 9. Review ad Outlie Last class we discussed: Statistical estimatio broadly Pot estimatio Bias-Variace
36-700: Probability ad Mathematical Statistics I Fall 206 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 9: September 9 9. Review ad Outlie Last class we discussed: Statistical estimatio broadly Pot estimatio Bias-Variace
Exponential Families and Bayesian Inference
 Computer Visio Expoetial Families ad Bayesia Iferece Lecture Expoetial Families A expoetial family of distributios is a d-parameter family f(x; havig the followig form: f(x; = h(xe g(t T (x B(, (. where
Computer Visio Expoetial Families ad Bayesia Iferece Lecture Expoetial Families A expoetial family of distributios is a d-parameter family f(x; havig the followig form: f(x; = h(xe g(t T (x B(, (. where
ON LOCAL LINEAR ESTIMATION IN NONPARAMETRIC ERRORS-IN-VARIABLES MODELS 1
 Teory of Stocastic Processes Vol2 28, o3-4, 2006, pp*-* SILVELYN ZWANZIG ON LOCAL LINEAR ESTIMATION IN NONPARAMETRIC ERRORS-IN-VARIABLES MODELS Local liear metods are applied to a oparametric regressio
Teory of Stocastic Processes Vol2 28, o3-4, 2006, pp*-* SILVELYN ZWANZIG ON LOCAL LINEAR ESTIMATION IN NONPARAMETRIC ERRORS-IN-VARIABLES MODELS Local liear metods are applied to a oparametric regressio
Clustering. CM226: Machine Learning for Bioinformatics. Fall Sriram Sankararaman Acknowledgments: Fei Sha, Ameet Talwalkar.
 Clusterig CM226: Machie Learig for Bioiformatics. Fall 216 Sriram Sakararama Ackowledgmets: Fei Sha, Ameet Talwalkar Clusterig 1 / 42 Admiistratio HW 1 due o Moday. Email/post o CCLE if you have questios.
Clusterig CM226: Machie Learig for Bioiformatics. Fall 216 Sriram Sakararama Ackowledgmets: Fei Sha, Ameet Talwalkar Clusterig 1 / 42 Admiistratio HW 1 due o Moday. Email/post o CCLE if you have questios.
ECE 901 Lecture 12: Complexity Regularization and the Squared Loss
 ECE 90 Lecture : Complexity Regularizatio ad the Squared Loss R. Nowak 5/7/009 I the previous lectures we made use of the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds for our aalysis of classifier errors. Hoeffdig s iequality
ECE 90 Lecture : Complexity Regularizatio ad the Squared Loss R. Nowak 5/7/009 I the previous lectures we made use of the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds for our aalysis of classifier errors. Hoeffdig s iequality
Stat 543 Exam 3 Spring 2016
 Stat 543 Exam 3 Sprig 06 I have either give or received uauthorized assistace o this exam. Name Siged Date Name Prited This exam cosists of parts. Do at east 8 of them. I wi score aswers at 0 poits apiece
Stat 543 Exam 3 Sprig 06 I have either give or received uauthorized assistace o this exam. Name Siged Date Name Prited This exam cosists of parts. Do at east 8 of them. I wi score aswers at 0 poits apiece
Expectation-Maximization Algorithm.
 Expectatio-Maximizatio Algorithm. Petr Pošík Czech Techical Uiversity i Prague Faculty of Electrical Egieerig Dept. of Cyberetics MLE 2 Likelihood.........................................................................................................
Expectatio-Maximizatio Algorithm. Petr Pošík Czech Techical Uiversity i Prague Faculty of Electrical Egieerig Dept. of Cyberetics MLE 2 Likelihood.........................................................................................................
Lecture 2 October 11
 Itroductio to probabilistic graphical models 203/204 Lecture 2 October Lecturer: Guillaume Oboziski Scribes: Aymeric Reshef, Claire Verade Course webpage: http://www.di.es.fr/~fbach/courses/fall203/ 2.
Itroductio to probabilistic graphical models 203/204 Lecture 2 October Lecturer: Guillaume Oboziski Scribes: Aymeric Reshef, Claire Verade Course webpage: http://www.di.es.fr/~fbach/courses/fall203/ 2.
Naïve Bayes. Naïve Bayes
 Statistical Data Miig ad Machie Learig Hilary Term 206 Dio Sejdiovic Departmet of Statistics Oxford Slides ad other materials available at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdiov/sdmml : aother plug-i classifier
Statistical Data Miig ad Machie Learig Hilary Term 206 Dio Sejdiovic Departmet of Statistics Oxford Slides ad other materials available at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdiov/sdmml : aother plug-i classifier
Differentiation Techniques 1: Power, Constant Multiple, Sum and Difference Rules
 Differetiatio Teciques : Power, Costat Multiple, Sum ad Differece Rules 97 Differetiatio Teciques : Power, Costat Multiple, Sum ad Differece Rules Model : Fidig te Equatio of f '() from a Grap of f ()
Differetiatio Teciques : Power, Costat Multiple, Sum ad Differece Rules 97 Differetiatio Teciques : Power, Costat Multiple, Sum ad Differece Rules Model : Fidig te Equatio of f '() from a Grap of f ()
Improving The Problem Not the Code
 mprovig Te Probem Not te Code Fidig Te Max ad Mi of a Number Comparig two adjacet umbers ad fidig te maximum ad miimum e.g. 5 7 8 9 10 1 3 Normay T()= N- Compariso wit a orace, i tis case a touramet teory
mprovig Te Probem Not te Code Fidig Te Max ad Mi of a Number Comparig two adjacet umbers ad fidig te maximum ad miimum e.g. 5 7 8 9 10 1 3 Normay T()= N- Compariso wit a orace, i tis case a touramet teory
Topics Machine learning: lecture 2. Review: the learning problem. Hypotheses and estimation. Estimation criterion cont d. Estimation criterion
 .87 Machie learig: lecture Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL tommi@csail.mit.edu Topics The learig problem hypothesis class, estimatio algorithm loss ad estimatio criterio samplig, empirical ad epected losses
.87 Machie learig: lecture Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL tommi@csail.mit.edu Topics The learig problem hypothesis class, estimatio algorithm loss ad estimatio criterio samplig, empirical ad epected losses
CSIE/GINM, NTU 2009/11/30 1
 Itroductio ti to Machie Learig (Part (at1: Statistical Machie Learig Shou de Li CSIE/GINM, NTU sdli@csie.tu.edu.tw 009/11/30 1 Syllabus of a Itro ML course ( Machie Learig, Adrew Ng, Staford, Autum 009
Itroductio ti to Machie Learig (Part (at1: Statistical Machie Learig Shou de Li CSIE/GINM, NTU sdli@csie.tu.edu.tw 009/11/30 1 Syllabus of a Itro ML course ( Machie Learig, Adrew Ng, Staford, Autum 009
MATH 320: Probability and Statistics 9. Estimation and Testing of Parameters. Readings: Pruim, Chapter 4
 MATH 30: Probability ad Statistics 9. Estimatio ad Testig of Parameters Estimatio ad Testig of Parameters We have bee dealig situatios i which we have full kowledge of the distributio of a radom variable.
MATH 30: Probability ad Statistics 9. Estimatio ad Testig of Parameters Estimatio ad Testig of Parameters We have bee dealig situatios i which we have full kowledge of the distributio of a radom variable.
Section 14. Simple linear regression.
 Sectio 14 Simple liear regressio. Let us look at the cigarette dataset from [1] (available to dowload from joural s website) ad []. The cigarette dataset cotais measuremets of tar, icotie, weight ad carbo
Sectio 14 Simple liear regressio. Let us look at the cigarette dataset from [1] (available to dowload from joural s website) ad []. The cigarette dataset cotais measuremets of tar, icotie, weight ad carbo
Estimation for Complete Data
 Estimatio for Complete Data complete data: there is o loss of iformatio durig study. complete idividual complete data= grouped data A complete idividual data is the oe i which the complete iformatio of
Estimatio for Complete Data complete data: there is o loss of iformatio durig study. complete idividual complete data= grouped data A complete idividual data is the oe i which the complete iformatio of
PHYS-3301 Lecture 9. CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I. 5.3: Electron Scattering. Bohr s Quantization Condition
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter ad Quatum Mecaics I PHYS-3301 Lecture 9 Sep. 5, 018 5.1 X-Ray Scatterig 5. De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electro Scatterig 5.4 Wave Motio 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Ucertaity
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter ad Quatum Mecaics I PHYS-3301 Lecture 9 Sep. 5, 018 5.1 X-Ray Scatterig 5. De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electro Scatterig 5.4 Wave Motio 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Ucertaity
Nonparametric regression: minimax upper and lower bounds
 Capter 4 Noparametric regressio: miimax upper ad lower bouds 4. Itroductio We cosider oe of te two te most classical o-parametric problems i tis example: estimatig a regressio fuctio o a subset of te real
Capter 4 Noparametric regressio: miimax upper ad lower bouds 4. Itroductio We cosider oe of te two te most classical o-parametric problems i tis example: estimatig a regressio fuctio o a subset of te real
Pattern Classification
 Patter Classificatio All materials i these slides were tae from Patter Classificatio (d ed) by R. O. Duda, P. E. Hart ad D. G. Stor, Joh Wiley & Sos, 000 with the permissio of the authors ad the publisher
Patter Classificatio All materials i these slides were tae from Patter Classificatio (d ed) by R. O. Duda, P. E. Hart ad D. G. Stor, Joh Wiley & Sos, 000 with the permissio of the authors ad the publisher
Apply change-of-basis formula to rewrite x as a linear combination of eigenvectors v j.
 Eigevalue-Eigevector Istructor: Nam Su Wag eigemcd Ay vector i real Euclidea space of dimesio ca be uiquely epressed as a liear combiatio of liearly idepedet vectors (ie, basis) g j, j,,, α g α g α g α
Eigevalue-Eigevector Istructor: Nam Su Wag eigemcd Ay vector i real Euclidea space of dimesio ca be uiquely epressed as a liear combiatio of liearly idepedet vectors (ie, basis) g j, j,,, α g α g α g α
ECE 901 Lecture 13: Maximum Likelihood Estimation
 ECE 90 Lecture 3: Maximum Likelihood Estimatio R. Nowak 5/7/009 The focus of this lecture is to cosider aother approach to learig based o maximum likelihood estimatio. Ulike earlier approaches cosidered
ECE 90 Lecture 3: Maximum Likelihood Estimatio R. Nowak 5/7/009 The focus of this lecture is to cosider aother approach to learig based o maximum likelihood estimatio. Ulike earlier approaches cosidered
Statistical Inference Based on Extremum Estimators
 T. Rotheberg Fall, 2007 Statistical Iferece Based o Extremum Estimators Itroductio Suppose 0, the true value of a p-dimesioal parameter, is kow to lie i some subset S R p : Ofte we choose to estimate 0
T. Rotheberg Fall, 2007 Statistical Iferece Based o Extremum Estimators Itroductio Suppose 0, the true value of a p-dimesioal parameter, is kow to lie i some subset S R p : Ofte we choose to estimate 0
Empirical Process Theory and Oracle Inequalities
 Stat 928: Statistical Learig Theory Lecture: 10 Empirical Process Theory ad Oracle Iequalities Istructor: Sham Kakade 1 Risk vs Risk See Lecture 0 for a discussio o termiology. 2 The Uio Boud / Boferoi
Stat 928: Statistical Learig Theory Lecture: 10 Empirical Process Theory ad Oracle Iequalities Istructor: Sham Kakade 1 Risk vs Risk See Lecture 0 for a discussio o termiology. 2 The Uio Boud / Boferoi
MATH 6101 Fall 2008 Newton and Differential Equations
 MATH 611 Fall 8 Newto ad Differetial Equatios A Differetial Equatio What is a differetial equatio? A differetial equatio is a equatio relatig the quatities x, y ad y' ad possibly higher derivatives of
MATH 611 Fall 8 Newto ad Differetial Equatios A Differetial Equatio What is a differetial equatio? A differetial equatio is a equatio relatig the quatities x, y ad y' ad possibly higher derivatives of
Mathematical Statistics Anna Janicka
 Mathematical Statistics Aa Jaicka Lecture XIV, 5.06.07 BAYESIAN STATISTICS Pla for Today. BayesiaStatistics a priori ad a posteriori distributios Bayesia estimatio: Maximum a posteriori probability(map)
Mathematical Statistics Aa Jaicka Lecture XIV, 5.06.07 BAYESIAN STATISTICS Pla for Today. BayesiaStatistics a priori ad a posteriori distributios Bayesia estimatio: Maximum a posteriori probability(map)
Here are some solutions to the sample problems concerning series solution of differential equations with non-constant coefficients (Chapter 12).
 Lecture Appedi B: Some sampe probems from Boas Here are some soutios to the sampe probems cocerig series soutio of differetia equatios with o-costat coefficiets (Chapter ) : Soutio: We wat to cosider the
Lecture Appedi B: Some sampe probems from Boas Here are some soutios to the sampe probems cocerig series soutio of differetia equatios with o-costat coefficiets (Chapter ) : Soutio: We wat to cosider the
Lecture 4. Hw 1 and 2 will be reoped after class for every body. New deadline 4/20 Hw 3 and 4 online (Nima is lead)
 Lecture 4 Homework Hw 1 ad 2 will be reoped after class for every body. New deadlie 4/20 Hw 3 ad 4 olie (Nima is lead) Pod-cast lecture o-lie Fial projects Nima will register groups ext week. Email/tell
Lecture 4 Homework Hw 1 ad 2 will be reoped after class for every body. New deadlie 4/20 Hw 3 ad 4 olie (Nima is lead) Pod-cast lecture o-lie Fial projects Nima will register groups ext week. Email/tell
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Itroductio to Probability ad Statistics Lecture 23: Cotiuous radom variables- Iequalities, CLT Puramrita Sarkar Departmet of Statistics ad Data Sciece The Uiversity of Texas at Austi www.cs.cmu.edu/
SDS 321: Itroductio to Probability ad Statistics Lecture 23: Cotiuous radom variables- Iequalities, CLT Puramrita Sarkar Departmet of Statistics ad Data Sciece The Uiversity of Texas at Austi www.cs.cmu.edu/
Regression and generalization
 Regressio ad geeralizatio CE-717: Machie Learig Sharif Uiversity of Techology M. Soleymai Fall 2016 Curve fittig: probabilistic perspective Describig ucertaity over value of target variable as a probability
Regressio ad geeralizatio CE-717: Machie Learig Sharif Uiversity of Techology M. Soleymai Fall 2016 Curve fittig: probabilistic perspective Describig ucertaity over value of target variable as a probability
Statistical Pattern Recognition
 Statistical Patter Recogitio Classificatio: No-Parametric Modelig Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi Sprig 2014 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/92-93/2/ce725-2/ Ageda Parametric Modelig No-Parametric Modelig
Statistical Patter Recogitio Classificatio: No-Parametric Modelig Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi Sprig 2014 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/92-93/2/ce725-2/ Ageda Parametric Modelig No-Parametric Modelig
n n i=1 Often we also need to estimate the variance. Below are three estimators each of which is optimal in some sense: n 1 i=1 k=1 i=1 k=1 i=1 k=1
 MATH88T Maria Camero Cotets Basic cocepts of statistics Estimators, estimates ad samplig distributios 2 Ordiary least squares estimate 3 3 Maximum lielihood estimator 3 4 Bayesia estimatio Refereces 9
MATH88T Maria Camero Cotets Basic cocepts of statistics Estimators, estimates ad samplig distributios 2 Ordiary least squares estimate 3 3 Maximum lielihood estimator 3 4 Bayesia estimatio Refereces 9
Economics 241B Relation to Method of Moments and Maximum Likelihood OLSE as a Maximum Likelihood Estimator
 Ecoomics 24B Relatio to Method of Momets ad Maximum Likelihood OLSE as a Maximum Likelihood Estimator Uder Assumptio 5 we have speci ed the distributio of the error, so we ca estimate the model parameters
Ecoomics 24B Relatio to Method of Momets ad Maximum Likelihood OLSE as a Maximum Likelihood Estimator Uder Assumptio 5 we have speci ed the distributio of the error, so we ca estimate the model parameters
Summary. Recap ... Last Lecture. Summary. Theorem
 Last Lecture Biostatistics 602 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 23 Hyu Mi Kag April 11th, 2013 What is p-value? What is the advatage of p-value compared to hypothesis testig procedure with size α? How ca
Last Lecture Biostatistics 602 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 23 Hyu Mi Kag April 11th, 2013 What is p-value? What is the advatage of p-value compared to hypothesis testig procedure with size α? How ca
Discrete Fourier Transform
 Discrete Fourier Trasform ) Purpose The purpose is to represet a determiistic or stochastic siga u( t ) as a fiite Fourier sum, whe observatios of u() t ( ) are give o a reguar grid, each affected by a
Discrete Fourier Trasform ) Purpose The purpose is to represet a determiistic or stochastic siga u( t ) as a fiite Fourier sum, whe observatios of u() t ( ) are give o a reguar grid, each affected by a
Expectation and Variance of a random variable
 Chapter 11 Expectatio ad Variace of a radom variable The aim of this lecture is to defie ad itroduce mathematical Expectatio ad variace of a fuctio of discrete & cotiuous radom variables ad the distributio
Chapter 11 Expectatio ad Variace of a radom variable The aim of this lecture is to defie ad itroduce mathematical Expectatio ad variace of a fuctio of discrete & cotiuous radom variables ad the distributio
f(x i ; ) L(x; p) = i=1 To estimate the value of that maximizes L or equivalently ln L we will set =0, for i =1, 2,...,m p x i (1 p) 1 x i i=1
 Parameter Estimatio Samples from a probability distributio F () are: [,,..., ] T.Theprobabilitydistributio has a parameter vector [,,..., m ] T. Estimator: Statistic used to estimate ukow. Estimate: Observed
Parameter Estimatio Samples from a probability distributio F () are: [,,..., ] T.Theprobabilitydistributio has a parameter vector [,,..., m ] T. Estimator: Statistic used to estimate ukow. Estimate: Observed
Last time: Moments of the Poisson distribution from its generating function. Example: Using telescope to measure intensity of an object
 6.3 Stochastic Estimatio ad Cotrol, Fall 004 Lecture 7 Last time: Momets of the Poisso distributio from its geeratig fuctio. Gs () e dg µ e ds dg µ ( s) µ ( s) µ ( s) µ e ds dg X µ ds X s dg dg + ds ds
6.3 Stochastic Estimatio ad Cotrol, Fall 004 Lecture 7 Last time: Momets of the Poisso distributio from its geeratig fuctio. Gs () e dg µ e ds dg µ ( s) µ ( s) µ ( s) µ e ds dg X µ ds X s dg dg + ds ds
Bayesian and E- Bayesian Method of Estimation of Parameter of Rayleigh Distribution- A Bayesian Approach under Linex Loss Function
 Iteratioal Joural of Statistics ad Systems ISSN 973-2675 Volume 12, Number 4 (217), pp. 791-796 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com Bayesia ad E- Bayesia Method of Estimatio of Parameter
Iteratioal Joural of Statistics ad Systems ISSN 973-2675 Volume 12, Number 4 (217), pp. 791-796 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com Bayesia ad E- Bayesia Method of Estimatio of Parameter
Machine Learning Theory (CS 6783)
 Machie Learig Theory (CS 6783) Lecture 2 : Learig Frameworks, Examples Settig up learig problems. X : istace space or iput space Examples: Computer Visio: Raw M N image vectorized X = 0, 255 M N, SIFT
Machie Learig Theory (CS 6783) Lecture 2 : Learig Frameworks, Examples Settig up learig problems. X : istace space or iput space Examples: Computer Visio: Raw M N image vectorized X = 0, 255 M N, SIFT
Lecture 9: Regression: Regressogram and Kernel Regression
 STAT 425: Itroductio to Noparametric Statistics Witer 208 Lecture 9: Regressio: Regressogram ad erel Regressio Istructor: Ye-Ci Ce Referece: Capter 5 of All of oparametric statistics 9 Itroductio Let X,
STAT 425: Itroductio to Noparametric Statistics Witer 208 Lecture 9: Regressio: Regressogram ad erel Regressio Istructor: Ye-Ci Ce Referece: Capter 5 of All of oparametric statistics 9 Itroductio Let X,
Linear regression. Daniel Hsu (COMS 4771) (y i x T i β)2 2πσ. 2 2σ 2. 1 n. (x T i β y i ) 2. 1 ˆβ arg min. β R n d
 Liear regressio Daiel Hsu (COMS 477) Maximum likelihood estimatio Oe of the simplest liear regressio models is the followig: (X, Y ),..., (X, Y ), (X, Y ) are iid radom pairs takig values i R d R, ad Y
Liear regressio Daiel Hsu (COMS 477) Maximum likelihood estimatio Oe of the simplest liear regressio models is the followig: (X, Y ),..., (X, Y ), (X, Y ) are iid radom pairs takig values i R d R, ad Y
CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES
 CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES CONTENTS PAGE 4. Periodic Fuctio 4. Eve ad Odd Fuctio 3 4.3 Fourier Series for Periodic Fuctio 9 4.4 Fourier Series for Haf Rage Epasios 4.5 Approimate Sum of the Ifiite Series
CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES CONTENTS PAGE 4. Periodic Fuctio 4. Eve ad Odd Fuctio 3 4.3 Fourier Series for Periodic Fuctio 9 4.4 Fourier Series for Haf Rage Epasios 4.5 Approimate Sum of the Ifiite Series
Hypothesis Testing. Evaluation of Performance of Learned h. Issues. Trade-off Between Bias and Variance
 Hypothesis Testig Empirically evaluatig accuracy of hypotheses: importat activity i ML. Three questios: Give observed accuracy over a sample set, how well does this estimate apply over additioal samples?
Hypothesis Testig Empirically evaluatig accuracy of hypotheses: importat activity i ML. Three questios: Give observed accuracy over a sample set, how well does this estimate apply over additioal samples?
Estimating the Population Mean using Stratified Double Ranked Set Sample
 Estimatig te Populatio Mea usig Stratified Double Raked Set Sample Mamoud Syam * Kamarulzama Ibraim Amer Ibraim Al-Omari Qatar Uiversity Foudatio Program Departmet of Mat ad Computer P.O.Box (7) Doa State
Estimatig te Populatio Mea usig Stratified Double Raked Set Sample Mamoud Syam * Kamarulzama Ibraim Amer Ibraim Al-Omari Qatar Uiversity Foudatio Program Departmet of Mat ad Computer P.O.Box (7) Doa State
Mixtures of Gaussians and the EM Algorithm
 Mixtures of Gaussias ad the EM Algorithm CSE 6363 Machie Learig Vassilis Athitsos Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Departmet Uiversity of Texas at Arligto 1 Gaussias A popular way to estimate probability desity
Mixtures of Gaussias ad the EM Algorithm CSE 6363 Machie Learig Vassilis Athitsos Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Departmet Uiversity of Texas at Arligto 1 Gaussias A popular way to estimate probability desity
Improved Estimation of Rare Sensitive Attribute in a Stratified Sampling Using Poisson Distribution
 Ope Joural of Statistics, 06, 6, 85-95 Publised Olie February 06 i SciRes ttp://wwwscirporg/joural/ojs ttp://dxdoiorg/0436/ojs0660 Improved Estimatio of Rare Sesitive ttribute i a Stratified Samplig Usig
Ope Joural of Statistics, 06, 6, 85-95 Publised Olie February 06 i SciRes ttp://wwwscirporg/joural/ojs ttp://dxdoiorg/0436/ojs0660 Improved Estimatio of Rare Sesitive ttribute i a Stratified Samplig Usig
Solutions: Homework 3
 Solutios: Homework 3 Suppose that the radom variables Y,...,Y satisfy Y i = x i + " i : i =,..., IID where x,...,x R are fixed values ad ",...," Normal(0, )with R + kow. Fid ˆ = MLE( ). IND Solutio: Observe
Solutios: Homework 3 Suppose that the radom variables Y,...,Y satisfy Y i = x i + " i : i =,..., IID where x,...,x R are fixed values ad ",...," Normal(0, )with R + kow. Fid ˆ = MLE( ). IND Solutio: Observe
Machine Learning Brett Bernstein
 Machie Learig Brett Berstei Week 2 Lecture: Cocept Check Exercises Starred problems are optioal. Excess Risk Decompositio 1. Let X = Y = {1, 2,..., 10}, A = {1,..., 10, 11} ad suppose the data distributio
Machie Learig Brett Berstei Week 2 Lecture: Cocept Check Exercises Starred problems are optioal. Excess Risk Decompositio 1. Let X = Y = {1, 2,..., 10}, A = {1,..., 10, 11} ad suppose the data distributio
EECS564 Estimation, Filtering, and Detection Hwk 2 Solns. Winter p θ (z) = (2θz + 1 θ), 0 z 1
 EECS564 Estimatio, Filterig, ad Detectio Hwk 2 Sols. Witer 25 4. Let Z be a sigle observatio havig desity fuctio where. p (z) = (2z + ), z (a) Assumig that is a oradom parameter, fid ad plot the maximum
EECS564 Estimatio, Filterig, ad Detectio Hwk 2 Sols. Witer 25 4. Let Z be a sigle observatio havig desity fuctio where. p (z) = (2z + ), z (a) Assumig that is a oradom parameter, fid ad plot the maximum
Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Complexity Regularization
 ECE90 Sprig 004 Statistical Regularizatio ad Learig Theory Lecture: 4 Maximum Likelihood Estimatio ad Complexity Regularizatio Lecturer: Rob Nowak Scribe: Pam Limpiti Review : Maximum Likelihood Estimatio
ECE90 Sprig 004 Statistical Regularizatio ad Learig Theory Lecture: 4 Maximum Likelihood Estimatio ad Complexity Regularizatio Lecturer: Rob Nowak Scribe: Pam Limpiti Review : Maximum Likelihood Estimatio
Properties of Joints Chris Piech CS109, Stanford University
 Properties of Joits Chris Piech CS09, Staford Uiversity Titaic Probability 7% of passegers were from the Ottoma Empire Biometric Keystroes Altruism? Scores for a stadardized test that studets i Polad
Properties of Joits Chris Piech CS09, Staford Uiversity Titaic Probability 7% of passegers were from the Ottoma Empire Biometric Keystroes Altruism? Scores for a stadardized test that studets i Polad
The Sampling Distribution of the Maximum. Likelihood Estimators for the Parameters of. Beta-Binomial Distribution
 Iteratioal Mathematical Forum, Vol. 8, 2013, o. 26, 1263-1277 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://d.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2013.3475 The Samplig Distributio of the Maimum Likelihood Estimators for the Parameters
Iteratioal Mathematical Forum, Vol. 8, 2013, o. 26, 1263-1277 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://d.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2013.3475 The Samplig Distributio of the Maimum Likelihood Estimators for the Parameters
Lecture 5. Power properties of EL and EL for vectors
 Stats 34 Empirical Likelihood Oct.8 Lecture 5. Power properties of EL ad EL for vectors Istructor: Art B. Owe, Staford Uiversity. Scribe: Jigshu Wag Power properties of empirical likelihood Power of the
Stats 34 Empirical Likelihood Oct.8 Lecture 5. Power properties of EL ad EL for vectors Istructor: Art B. Owe, Staford Uiversity. Scribe: Jigshu Wag Power properties of empirical likelihood Power of the
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence CAP 4601 Summer 2013 Midterm Exam
 Itroductio to Artificial Itelligece CAP 601 Summer 013 Midterm Exam 1. Termiology (7 Poits). Give the followig task eviromets, eter their properties/characteristics. The properties/characteristics of the
Itroductio to Artificial Itelligece CAP 601 Summer 013 Midterm Exam 1. Termiology (7 Poits). Give the followig task eviromets, eter their properties/characteristics. The properties/characteristics of the
Mathematical Statistics - MS
 Paper Specific Istructios. The examiatio is of hours duratio. There are a total of 60 questios carryig 00 marks. The etire paper is divided ito three sectios, A, B ad C. All sectios are compulsory. Questios
Paper Specific Istructios. The examiatio is of hours duratio. There are a total of 60 questios carryig 00 marks. The etire paper is divided ito three sectios, A, B ad C. All sectios are compulsory. Questios
Outline. CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Outline. Prof. Victor Adamchik. Mar. 26, 2019
 Outlie CSCI-567: Machie Learig Sprig 209 Gaussia mixture models Prof. Victor Adamchik 2 Desity estimatio U of Souther Califoria Mar. 26, 209 3 Naive Bayes Revisited March 26, 209 / 57 March 26, 209 2 /
Outlie CSCI-567: Machie Learig Sprig 209 Gaussia mixture models Prof. Victor Adamchik 2 Desity estimatio U of Souther Califoria Mar. 26, 209 3 Naive Bayes Revisited March 26, 209 / 57 March 26, 209 2 /
Step 1: Function Set. Otherwise, output C 2. Function set: Including all different w and b
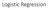 Logistic Regressio Step : Fuctio Set We wat to fid P w,b C x σ z = + exp z If P w,b C x.5, output C Otherwise, output C 2 z P w,b C x = σ z z = w x + b = w i x i + b i z Fuctio set: f w,b x = P w,b C x
Logistic Regressio Step : Fuctio Set We wat to fid P w,b C x σ z = + exp z If P w,b C x.5, output C Otherwise, output C 2 z P w,b C x = σ z z = w x + b = w i x i + b i z Fuctio set: f w,b x = P w,b C x
Exercises Advanced Data Mining: Solutions
 Exercises Advaced Data Miig: Solutios Exercise 1 Cosider the followig directed idepedece graph. 5 8 9 a) Give the factorizatio of P (X 1, X 2,..., X 9 ) correspodig to this idepedece graph. P (X) = 9 P
Exercises Advaced Data Miig: Solutios Exercise 1 Cosider the followig directed idepedece graph. 5 8 9 a) Give the factorizatio of P (X 1, X 2,..., X 9 ) correspodig to this idepedece graph. P (X) = 9 P
Let us give one more example of MLE. Example 3. The uniform distribution U[0, θ] on the interval [0, θ] has p.d.f.
![Let us give one more example of MLE. Example 3. The uniform distribution U[0, θ] on the interval [0, θ] has p.d.f. Let us give one more example of MLE. Example 3. The uniform distribution U[0, θ] on the interval [0, θ] has p.d.f.](/thumbs/91/105380228.jpg) Lecture 5 Let us give oe more example of MLE. Example 3. The uiform distributio U[0, ] o the iterval [0, ] has p.d.f. { 1 f(x =, 0 x, 0, otherwise The likelihood fuctio ϕ( = f(x i = 1 I(X 1,..., X [0,
Lecture 5 Let us give oe more example of MLE. Example 3. The uiform distributio U[0, ] o the iterval [0, ] has p.d.f. { 1 f(x =, 0 x, 0, otherwise The likelihood fuctio ϕ( = f(x i = 1 I(X 1,..., X [0,
ECE 901 Lecture 14: Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Complexity Regularization
 ECE 90 Lecture 4: Maximum Likelihood Estimatio ad Complexity Regularizatio R Nowak 5/7/009 Review : Maximum Likelihood Estimatio We have iid observatios draw from a ukow distributio Y i iid p θ, i,, where
ECE 90 Lecture 4: Maximum Likelihood Estimatio ad Complexity Regularizatio R Nowak 5/7/009 Review : Maximum Likelihood Estimatio We have iid observatios draw from a ukow distributio Y i iid p θ, i,, where
Overview of Estimation
 Topic Iferece is the problem of turig data ito kowledge, where kowledge ofte is expressed i terms of etities that are ot preset i the data per se but are preset i models that oe uses to iterpret the data.
Topic Iferece is the problem of turig data ito kowledge, where kowledge ofte is expressed i terms of etities that are ot preset i the data per se but are preset i models that oe uses to iterpret the data.
Learning Fully Observed Undirected Graphical Models
 Learning Fuy Observed Undirected Graphica Modes Sides Credit: Matt Gormey (2016) Kayhan Batmangheich 1 Machine Learning The data inspires the structures we want to predict Inference finds {best structure,
Learning Fuy Observed Undirected Graphica Modes Sides Credit: Matt Gormey (2016) Kayhan Batmangheich 1 Machine Learning The data inspires the structures we want to predict Inference finds {best structure,
Lecture 27: Optimal Estimators and Functional Delta Method
 Stat210B: Theoretical Statistics Lecture Date: April 19, 2007 Lecture 27: Optimal Estimators ad Fuctioal Delta Method Lecturer: Michael I. Jorda Scribe: Guilherme V. Rocha 1 Achievig Optimal Estimators
Stat210B: Theoretical Statistics Lecture Date: April 19, 2007 Lecture 27: Optimal Estimators ad Fuctioal Delta Method Lecturer: Michael I. Jorda Scribe: Guilherme V. Rocha 1 Achievig Optimal Estimators
Direction: This test is worth 250 points. You are required to complete this test within 50 minutes.
 Term Test October 3, 003 Name Math 56 Studet Number Directio: This test is worth 50 poits. You are required to complete this test withi 50 miutes. I order to receive full credit, aswer each problem completely
Term Test October 3, 003 Name Math 56 Studet Number Directio: This test is worth 50 poits. You are required to complete this test withi 50 miutes. I order to receive full credit, aswer each problem completely
Factor Analysis. Lecture 10: Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis. Sam Roweis
 Lecture 10: Factor Aalysis ad Pricipal Compoet Aalysis Sam Roweis February 9, 2004 Whe we assume that the subspace is liear ad that the uderlyig latet variable has a Gaussia distributio we get a model
Lecture 10: Factor Aalysis ad Pricipal Compoet Aalysis Sam Roweis February 9, 2004 Whe we assume that the subspace is liear ad that the uderlyig latet variable has a Gaussia distributio we get a model
Machine Learning Theory Tübingen University, WS 2016/2017 Lecture 11
 Machie Learig Theory Tübige Uiversity, WS 06/07 Lecture Tolstikhi Ilya Abstract We will itroduce the otio of reproducig kerels ad associated Reproducig Kerel Hilbert Spaces (RKHS). We will cosider couple
Machie Learig Theory Tübige Uiversity, WS 06/07 Lecture Tolstikhi Ilya Abstract We will itroduce the otio of reproducig kerels ad associated Reproducig Kerel Hilbert Spaces (RKHS). We will cosider couple
Pattern recognition systems Laboratory 10 Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron Algorithm
 Patter recogitio systems Laboratory 10 Liear Classifiers ad the Perceptro Algorithm 1. Objectives his laboratory sessio presets the perceptro learig algorithm for the liear classifier. We will apply gradiet
Patter recogitio systems Laboratory 10 Liear Classifiers ad the Perceptro Algorithm 1. Objectives his laboratory sessio presets the perceptro learig algorithm for the liear classifier. We will apply gradiet
Machine Learning Regression I Hamid R. Rabiee [Slides are based on Bishop Book] Spring
![Machine Learning Regression I Hamid R. Rabiee [Slides are based on Bishop Book] Spring Machine Learning Regression I Hamid R. Rabiee [Slides are based on Bishop Book] Spring](/thumbs/84/90654010.jpg) Machie Learig Regressio I Hamid R. Rabiee [Slides are based o Bishop Book] Sprig 015 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/93-94//ce717-1 Liear Regressio Liear regressio: ivolves a respose variable ad a sigle predictor
Machie Learig Regressio I Hamid R. Rabiee [Slides are based o Bishop Book] Sprig 015 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/93-94//ce717-1 Liear Regressio Liear regressio: ivolves a respose variable ad a sigle predictor
6.867 Machine learning, lecture 7 (Jaakkola) 1
 6.867 Machie learig, lecture 7 (Jaakkola) 1 Lecture topics: Kerel form of liear regressio Kerels, examples, costructio, properties Liear regressio ad kerels Cosider a slightly simpler model where we omit
6.867 Machie learig, lecture 7 (Jaakkola) 1 Lecture topics: Kerel form of liear regressio Kerels, examples, costructio, properties Liear regressio ad kerels Cosider a slightly simpler model where we omit
CONCENTRATION INEQUALITIES
 CONCENTRATION INEQUALITIES MAXIM RAGINSKY I te previous lecture, te followig result was stated witout proof. If X 1,..., X are idepedet Beroulliθ radom variables represetig te outcomes of a sequece of
CONCENTRATION INEQUALITIES MAXIM RAGINSKY I te previous lecture, te followig result was stated witout proof. If X 1,..., X are idepedet Beroulliθ radom variables represetig te outcomes of a sequece of
Resampling Methods. X (1/2), i.e., Pr (X i m) = 1/2. We order the data: X (1) X (2) X (n). Define the sample median: ( n.
 Jauary 1, 2019 Resamplig Methods Motivatio We have so may estimators with the property θ θ d N 0, σ 2 We ca also write θ a N θ, σ 2 /, where a meas approximately distributed as Oce we have a cosistet estimator
Jauary 1, 2019 Resamplig Methods Motivatio We have so may estimators with the property θ θ d N 0, σ 2 We ca also write θ a N θ, σ 2 /, where a meas approximately distributed as Oce we have a cosistet estimator
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. BACKGROUND EXAM September 30, 2004.
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Sciece 6.34 Discrete Time Sigal Processig Fall 24 BACKGROUND EXAM September 3, 24. Full Name: Note: This exam is closed
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Sciece 6.34 Discrete Time Sigal Processig Fall 24 BACKGROUND EXAM September 3, 24. Full Name: Note: This exam is closed
Machine Learning: Logistic Regression. Lecture 04
 Machie Learig: Logistic Regressio Razva C. Buescu School of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Sciece buescu@ohio.edu Supervised Learig ask = lear a uko fuctio t : X that maps iput istaces x Î X to output
Machie Learig: Logistic Regressio Razva C. Buescu School of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Sciece buescu@ohio.edu Supervised Learig ask = lear a uko fuctio t : X that maps iput istaces x Î X to output
1.010 Uncertainty in Engineering Fall 2008
 MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.00 Ucertaity i Egieerig Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu.terms. .00 - Brief Notes # 9 Poit ad Iterval
MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.00 Ucertaity i Egieerig Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu.terms. .00 - Brief Notes # 9 Poit ad Iterval
1 Approximating Integrals using Taylor Polynomials
 Seughee Ye Ma 8: Week 7 Nov Week 7 Summary This week, we will lear how we ca approximate itegrals usig Taylor series ad umerical methods. Topics Page Approximatig Itegrals usig Taylor Polyomials. Defiitios................................................
Seughee Ye Ma 8: Week 7 Nov Week 7 Summary This week, we will lear how we ca approximate itegrals usig Taylor series ad umerical methods. Topics Page Approximatig Itegrals usig Taylor Polyomials. Defiitios................................................
Singular value decomposition. Mathématiques appliquées (MATH0504-1) B. Dewals, Ch. Geuzaine
 Lecture 11 Sigular value decompositio Mathématiques appliquées (MATH0504-1) B. Dewals, Ch. Geuzaie V1.2 07/12/2018 1 Sigular value decompositio (SVD) at a glace Motivatio: the image of the uit sphere S
Lecture 11 Sigular value decompositio Mathématiques appliquées (MATH0504-1) B. Dewals, Ch. Geuzaie V1.2 07/12/2018 1 Sigular value decompositio (SVD) at a glace Motivatio: the image of the uit sphere S
NYU Center for Data Science: DS-GA 1003 Machine Learning and Computational Statistics (Spring 2018)
 NYU Ceter for Data Sciece: DS-GA 003 Machie Learig ad Computatioal Statistics (Sprig 208) Brett Berstei, David Roseberg, Be Jakubowski Jauary 20, 208 Istructios: Followig most lab ad lecture sectios, we
NYU Ceter for Data Sciece: DS-GA 003 Machie Learig ad Computatioal Statistics (Sprig 208) Brett Berstei, David Roseberg, Be Jakubowski Jauary 20, 208 Istructios: Followig most lab ad lecture sectios, we
Machine Learning, Spring 2011: Homework 1 Solution
 10-701 Machie Learig, Sprig 011: Homework 1 Solutio February 1, 011 Istructios There are 3 questios o this assigmet. The last questio ivolves codig. Attach your code to the writeup. Please submit your
10-701 Machie Learig, Sprig 011: Homework 1 Solutio February 1, 011 Istructios There are 3 questios o this assigmet. The last questio ivolves codig. Attach your code to the writeup. Please submit your
Week 6. Intuition: Let p (x, y) be the joint density of (X, Y ) and p (x) be the marginal density of X. Then. h dy =
 Week 6 Lecture Kerel regressio ad miimax rates Model: Observe Y i = f (X i ) + ξ i were ξ i, i =,,,, iid wit Eξ i = 0 We ofte assume X i are iid or X i = i/ Nadaraya Watso estimator Let w i (x) = K ( X
Week 6 Lecture Kerel regressio ad miimax rates Model: Observe Y i = f (X i ) + ξ i were ξ i, i =,,,, iid wit Eξ i = 0 We ofte assume X i are iid or X i = i/ Nadaraya Watso estimator Let w i (x) = K ( X
January 25, 2017 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS
 Jauary 25, 207 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS Abstract. A basic itroductio to statistics assumig kowledge of probability theory.. Probability I a typical udergraduate problem i probability, we
Jauary 25, 207 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS Abstract. A basic itroductio to statistics assumig kowledge of probability theory.. Probability I a typical udergraduate problem i probability, we
Uniformly Consistency of the Cauchy-Transformation Kernel Density Estimation Underlying Strong Mixing
 Appl. Mat. If. Sci. 7, No. L, 5-9 (203) 5 Applied Matematics & Iformatio Scieces A Iteratioal Joural c 203 NSP Natural Scieces Publisig Cor. Uiformly Cosistecy of te Caucy-Trasformatio Kerel Desity Estimatio
Appl. Mat. If. Sci. 7, No. L, 5-9 (203) 5 Applied Matematics & Iformatio Scieces A Iteratioal Joural c 203 NSP Natural Scieces Publisig Cor. Uiformly Cosistecy of te Caucy-Trasformatio Kerel Desity Estimatio
EE 6885 Statistical Pattern Recognition
 EE 6885 Statistical Patter Recogitio Fall 5 Prof. Shih-Fu Chag http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~sfchag Lecture 6 (9/8/5 EE6887-Chag 6- Readig EM for Missig Features Textboo, DHS 3.9 Bayesia Parameter Estimatio
EE 6885 Statistical Patter Recogitio Fall 5 Prof. Shih-Fu Chag http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~sfchag Lecture 6 (9/8/5 EE6887-Chag 6- Readig EM for Missig Features Textboo, DHS 3.9 Bayesia Parameter Estimatio
