Cheat Sheet: Linear Regression
|
|
|
- Madison Parrish
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cheat Sheet: Linear Regression Measurement and Evaluation of HCC Systems Scenario Use regression if you want to test the simultaneous linear effect of several variables varx1, varx2, on a continuous outcome variable vary. In this scenario, you are predicting vary with varx1, varx2,. Power analysis for linear regression - There are several versions of power analysis for linear regression, but the most versatile one is F tests, Linear multiple regression: Fixed model, R 2 increase. - A power analysis has four variables: Effect size, a (usually.05), power (usually.85), and N. If you know three of these, G*Power will calculate the fourth. Select the correct type of power analysis, based on the information you have, and what you want to find out. - Number of tested predictors is the number of Xs that you want to test simultaneously. Often you want to test the effect of an individual X, in which case this field should say 1. - Total number of predictors is the total number of Xs in the model. - By clicking on Determine, you can compute the effect size f 2 from the partial R 2. This is the increase in R 2 caused by the predictors you want to test. - Click on Calculate to calculate the missing parameter. Plotting scatterplots with linear trend line - Use the ggplot2 package to plot a scatterplot with a linear trend line. ggplot(data, aes(varx1, vary)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method= lm, color= red, se=f) - (optional) To add a mean line, add: + geom_line(aes(y = mean(data$vary)), color= blue - Visually inspect if the relationship is indeed a linear one (see assumptions). You can also check if the scatterplot has a funnel shape, which may suggest heteroscedasticity (see assumptions). Repeat this procedure for varx2, etc.
2 Pre-testing assumptions - In a linear regression, Y should be independent, continuous, and unbounded. The error variance should be normally distributed, which is true if Y is normally distributed. - If your N is small: o Test for significant skewness, kurtosis, and Shapiro-Wilk test using stat.desc in the pastecs package. stat.desc(data$vary, basic=f, norm=t) o Multiply skew.2se and kurt.2se by 2 to get the Z-scores of skewness and kurtosis. Compare these values to typical cut-off values (Z > ±1.96: p <.05, Z > ±2.58: p <.01, Z > ±3.29: p <.001). The significance of the Shapiro-Wilk test is listed under normtest.p. - If your N is large: o Draw the histogram for vary, overlaid with normal curves (using ggplot2), and visually inspect whether they follow the normal distribution: ggplot(data, aes(vary)) + geom_histogram(aes(y=..density..), binwidth=1, color="black", fill="white") + stat_function(fun = dnorm, args = list(mean = mean(data$vary), sd = sd(data$vary))) o Change the binwidth setting based on what is suitable for your data. o Draw normal a Q-Q plot, and visually inspect whether the data follows the diagonal line: qplot(sample = data$vary, stat= qq ) - If you have dummy variables (see below), you want to test normality within each group (see the t test and ANOVA cheat sheets). - If your data has positive skew, and your data only has positive values, you can possibly fix this by transforming your Y variable: o Log transform: data$varylog <- log(data$vary + 1) o Or, square root transform: data$varysqrt <- sqrt(data$vary) - In other cases of violations of assumptions, you can conduct a robust test (see below). - Aside from normality, you also need to test for linearity, homoscedasticity and a lack of multicollinearity. You can do this after the test using the residual plots of the model. (optional) Preparing dummy variables - If one or more of your Xs are nominal variables, you need to create dummy variables for them. R does this automatically, as long as the nominal Xs are coded as factors. If they are coded as numerical values (e.g. 1, 2, 3 ), you can recode them as factors using the revalue
3 function in the plyr package: data$varx1 <- revalue(as.factor(data$varx1), c( 1 = cat1, 2 = cat2 )) - cat1 and cat2 are descriptive names of the different categories of the variable. You can revalue more categories if needed. - R automatically selects a baseline category against which all other categories are compared. If it chooses this category incorrectly, you can relevel the variable, e.g., to make cat1 the baseline category: data$varx1 <- relevel(data$varx1, ref= cat1 ) - Note that when you have a nominal variable with more than two categories, the automatically created dummies form a non-orthogonal contrast. This means that you should apply a correction (e.g. Bonferroni, Holm, or Benjamini-Hochberg) to the p-values of these contrasts. Alternatively, you can create orthogonal contrasts for such variables. Both are discussed in the ANOVA cheat sheet. Running the test - Run the regression model as follows (include additional Xs if needed): model1 <- lm(vary ~ varx1 + varx2, data = data) - Get the model summary: summary(model1) - In terms of overall model fit, this output will give you the Multiple R-squared, which is the proportion of the variance of vary explained by the model. The Adjusted R-squared is the expected R 2 if the test were to be repeated. - The F-statistic and its p-value tells us whether the model makes a significantly better prediction than the grand mean. - Each coefficient represents the effect of an X on Y, given all the other Xs. If X increases/decreases by 1, Y is expected to increase/decrease by this amount. For dummy variables, the coefficient represents the difference in Y between this category and the baseline category. - Each coefficient has a t test and a p-value to test if the effect is significant. Divide the p-value by 2 if you were conducting a one-sided test (i.e. if you had a directional hypothesis). You can get the effect size r using the formula r = (t 2 / t 2 + df)). - You can get confidence intervals for the coefficients using the confint function: confint(model1) - To compare the effects of different Xs, you need to standardize them using lm.beta in the QuantPsyc package: lm.beta(model1) This gives you the beta coefficients. If X increases/decreases by 1 standard deviation, Y is
4 expected to increase/decrease by this proportion of its standard deviation. Note: this does not work for dummy variables. (optional) Robust versions - You can bootstrap the regression coefficients (the bs) of a linear regression. First create a function for running the bootstrap sample (include additional Xs if needed): bootfun <- function(sample,i){ fit <- lm(vary~varx1+varx2, data=sample[i,]) return(coef(fit)) } - Then run the bootstrap sample over the function 2000 times: bootresult <- boot(data, bootfun, 2000) - Get the output; the original column shows the regression coefficient in the original sample, the bias column shows the difference between this and the coefficient in the bootstrap sample, and the std. error column shows the bootstrapped standard error. Row t1* shows the intercept, the subsequent rows show the coefficient b for each X: bootresult - Get the confidence interval of the first coefficient; the BCa version is the most robust variant: boot.ci(bootresult,index=2) - Repeat with index=3 etc. for the other coefficients. (optional) Testing additional variables - In any regression, always first decide on your outcome variable (Y) and the most important Xs. For additional Xs, only include them if they correlate with Y. Do not include Xs that are correlated too highly with any of the other Xs (r >.8 or r <.8), because this may lead to multicollinearity (see below). - If these additional Xs have a clear hierarchy (some are more interesting than others), then add them step-by-step in order of importance. Otherwise, add them all at once and remove non-significant ones one-by-one. - Models with more Xs always have a higher R 2. You can test whether this increase in R 2 is significant using an F-ratio test: anova(model1,model2) - Do not forget to assess the b estimates of the new model. Even the b estimates for the old parameters may have changed, especially when the new Xs are correlated with the old Xs. Post-testing assumptions - Run the plots of the model: plot(model1)
5 - The first plot shows the residuals e at different levels of Y. If this plot is funnel-shaped, you have heteroscedasticity. If the red mean line is not a straight line, you have non-linearity. - The next plot shows the normal Q-Q plot of the residuals. If they deviate strongly from the diagonal line, you have non-normality. - With any of these problems, you can possibly fix this by transforming your Y variable (see Pre-testing assumptions ), or by running a bootstrapped regression (see Robust versions ). - Test for multicollinearity of your Xs using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF); these should be below 5: vif(model1) - Check the average VIF. Ideally this should be 1, but values close to (say, up to 1.5) are permissible: mean(vif(model1)) - If you find any problems, some of your Xs are probably highly correlated with each other. Remove one of these Xs and start over. Inspecting outliers - Save the standardized residuals to your data: data$rstand <- rstandard(model1) - Create a filter for large standardized residuals: data$rstand.large <- (data$rstand > 1.96 data$rstand < -1.96) - Inspect these outliers: data[data$rstand.large,] - If these outliers comprise more than 5% of the data, you have too many data for which the model does not fit very well. Moreover, if more than 1% of the data has an rstand > 2.58, you have too many data for which the model is a very poor fit. Finally, any data with an rstand > 3.29 are extreme outliers: they will likely have to be removed. - Save Cook s distances, hat values (leverage), and covariance ratios to your data: data$cook <- cooks.distance(model1) data$leverage <- hatvalues(model1) data$covratio <- covratio(model1) - Check out the Cook s distances, hat values, and covariance ratio for the data with a large residual: data[data$rstand.large,c( cook, leverage, covratio )] - Cook s distance should be smaller than 1, leverage should be smaller than 3*(k+1)/N), and the covariance ratio should be between 1-(3(k+1)/N) and 1+(3(k+1)/N), where k is the number of Xs, and N is the sample size. - These metrics are a bit sensitive to sample size, so for large samples, focus on the Cook s distance. In case of problems, you can possibly fix this by removing the offending data point,
6 transforming your Y variable (see Pre-testing assumptions ), or running a bootstrapped regression (see Robust versions ). Reporting - Create a table to report your regression model(s); in the example below, model 1 has two continuous Xs, and model 2 adds a continuous X and a nominal X with 3 categories: DR 2 B SE B b P Model 1 [R 2 ] [p-value of model F-test] Constant [estimate] [std. error] [varx1] [estimate] [std. error] [beta coef.] [p-value] [varx2] [estimate] [std. error] [beta coef.] [p-value] Model 2 [R 2 increase] [p-value of F-ratio test between model 1 and 2] Constant [estimate] [std. error] [varx1] [estimate] [std. error] [beta coef.] [p-value] [varx2] [estimate] [std. error] [beta coef.] [p-value] [varx3] [estimate] [std. error] [beta coef.] [p-value] [varx4] baseline: [cat1] [cat2] [cat3] [estimate] [estimate] [std. error] [std. error] [p-value] [p-value] - You can additionally highlight and explain individual effects: o Controlling for [varx2], [varx3], and [varx4], each 1 point increase in [varx1] is related to [estimate] points increase in [vary], t([deg. freedom]) =.xx, p =.xxx. o Controlling for [varx1], [varx2], and [varx3], participants with [cat2] had a [estimate] points higher [vary] than participants with [cat1], t([deg. freedom]) =.xx, p =.xxx.
Cheat Sheet: ANOVA. Scenario. Power analysis. Plotting a line plot and a box plot. Pre-testing assumptions
 Cheat Sheet: ANOVA Measurement and Evaluation of HCC Systems Scenario Use ANOVA if you want to test the difference in continuous outcome variable vary between multiple levels (A, B, C, ) of a nominal variable
Cheat Sheet: ANOVA Measurement and Evaluation of HCC Systems Scenario Use ANOVA if you want to test the difference in continuous outcome variable vary between multiple levels (A, B, C, ) of a nominal variable
Cheat Sheet: factorial ANOVA
 Cheat Sheet: factorial ANOVA Measurement and Evaluation of HCC Systems Scenario Use factorial ANOVA if you want to test the effect of two (or more) nominal variables varx1 and varx2 on a continuous outcome
Cheat Sheet: factorial ANOVA Measurement and Evaluation of HCC Systems Scenario Use factorial ANOVA if you want to test the effect of two (or more) nominal variables varx1 and varx2 on a continuous outcome
Linear Regression Measurement & Evaluation of HCC Systems
 Linear Regression Measurement & Evaluation of HCC Systems Linear Regression Today s goal: Evaluate the effect of multiple variables on an outcome variable (regression) Outline: - Basic theory - Simple
Linear Regression Measurement & Evaluation of HCC Systems Linear Regression Today s goal: Evaluate the effect of multiple variables on an outcome variable (regression) Outline: - Basic theory - Simple
Review of Multiple Regression
 Ronald H. Heck 1 Let s begin with a little review of multiple regression this week. Linear models [e.g., correlation, t-tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA), multiple regression, path analysis, multivariate
Ronald H. Heck 1 Let s begin with a little review of multiple regression this week. Linear models [e.g., correlation, t-tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA), multiple regression, path analysis, multivariate
Checking model assumptions with regression diagnostics
 @graemeleehickey www.glhickey.com graeme.hickey@liverpool.ac.uk Checking model assumptions with regression diagnostics Graeme L. Hickey University of Liverpool Conflicts of interest None Assistant Editor
@graemeleehickey www.glhickey.com graeme.hickey@liverpool.ac.uk Checking model assumptions with regression diagnostics Graeme L. Hickey University of Liverpool Conflicts of interest None Assistant Editor
Regression Model Building
 Regression Model Building Setting: Possibly a large set of predictor variables (including interactions). Goal: Fit a parsimonious model that explains variation in Y with a small set of predictors Automated
Regression Model Building Setting: Possibly a large set of predictor variables (including interactions). Goal: Fit a parsimonious model that explains variation in Y with a small set of predictors Automated
Factorial ANOVA. Testing more than one manipulation
 Factorial ANOVA Testing more than one manipulation Factorial ANOVA Today s goal: Teach you about factorial ANOVA, the test used to evaluate more than two manipulations at the same time Outline: - Why Factorial
Factorial ANOVA Testing more than one manipulation Factorial ANOVA Today s goal: Teach you about factorial ANOVA, the test used to evaluate more than two manipulations at the same time Outline: - Why Factorial
Prepared by: Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti
 Prepared by: Prof Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang M L Regression is an extension to
Prepared by: Prof Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang M L Regression is an extension to
Simple Linear Regression
 Simple Linear Regression 1 Correlation indicates the magnitude and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. Linear Regression: variable Y (criterion) is predicted by variable X (predictor)
Simple Linear Regression 1 Correlation indicates the magnitude and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. Linear Regression: variable Y (criterion) is predicted by variable X (predictor)
Correlation and Simple Linear Regression
 Correlation and Simple Linear Regression Sasivimol Rattanasiri, Ph.D Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University E-mail: sasivimol.rat@mahidol.ac.th 1 Outline
Correlation and Simple Linear Regression Sasivimol Rattanasiri, Ph.D Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University E-mail: sasivimol.rat@mahidol.ac.th 1 Outline
Review of Statistics 101
 Review of Statistics 101 We review some important themes from the course 1. Introduction Statistics- Set of methods for collecting/analyzing data (the art and science of learning from data). Provides methods
Review of Statistics 101 We review some important themes from the course 1. Introduction Statistics- Set of methods for collecting/analyzing data (the art and science of learning from data). Provides methods
Hypothesis testing, part 2. With some material from Howard Seltman, Blase Ur, Bilge Mutlu, Vibha Sazawal
 Hypothesis testing, part 2 With some material from Howard Seltman, Blase Ur, Bilge Mutlu, Vibha Sazawal 1 CATEGORICAL IV, NUMERIC DV 2 Independent samples, one IV # Conditions Normal/Parametric Non-parametric
Hypothesis testing, part 2 With some material from Howard Seltman, Blase Ur, Bilge Mutlu, Vibha Sazawal 1 CATEGORICAL IV, NUMERIC DV 2 Independent samples, one IV # Conditions Normal/Parametric Non-parametric
Multicollinearity occurs when two or more predictors in the model are correlated and provide redundant information about the response.
 Multicollinearity Read Section 7.5 in textbook. Multicollinearity occurs when two or more predictors in the model are correlated and provide redundant information about the response. Example of multicollinear
Multicollinearity Read Section 7.5 in textbook. Multicollinearity occurs when two or more predictors in the model are correlated and provide redundant information about the response. Example of multicollinear
Inferences for Regression
 Inferences for Regression An Example: Body Fat and Waist Size Looking at the relationship between % body fat and waist size (in inches). Here is a scatterplot of our data set: Remembering Regression In
Inferences for Regression An Example: Body Fat and Waist Size Looking at the relationship between % body fat and waist size (in inches). Here is a scatterplot of our data set: Remembering Regression In
The Model Building Process Part I: Checking Model Assumptions Best Practice (Version 1.1)
 The Model Building Process Part I: Checking Model Assumptions Best Practice (Version 1.1) Authored by: Sarah Burke, PhD Version 1: 31 July 2017 Version 1.1: 24 October 2017 The goal of the STAT T&E COE
The Model Building Process Part I: Checking Model Assumptions Best Practice (Version 1.1) Authored by: Sarah Burke, PhD Version 1: 31 July 2017 Version 1.1: 24 October 2017 The goal of the STAT T&E COE
Regression in R. Seth Margolis GradQuant May 31,
 Regression in R Seth Margolis GradQuant May 31, 2018 1 GPA What is Regression Good For? Assessing relationships between variables This probably covers most of what you do 4 3.8 3.6 3.4 Person Intelligence
Regression in R Seth Margolis GradQuant May 31, 2018 1 GPA What is Regression Good For? Assessing relationships between variables This probably covers most of what you do 4 3.8 3.6 3.4 Person Intelligence
ST505/S697R: Fall Homework 2 Solution.
 ST505/S69R: Fall 2012. Homework 2 Solution. 1. 1a; problem 1.22 Below is the summary information (edited) from the regression (using R output); code at end of solution as is code and output for SAS. a)
ST505/S69R: Fall 2012. Homework 2 Solution. 1. 1a; problem 1.22 Below is the summary information (edited) from the regression (using R output); code at end of solution as is code and output for SAS. a)
Contents. Acknowledgments. xix
 Table of Preface Acknowledgments page xv xix 1 Introduction 1 The Role of the Computer in Data Analysis 1 Statistics: Descriptive and Inferential 2 Variables and Constants 3 The Measurement of Variables
Table of Preface Acknowledgments page xv xix 1 Introduction 1 The Role of the Computer in Data Analysis 1 Statistics: Descriptive and Inferential 2 Variables and Constants 3 The Measurement of Variables
Multiple Regression. More Hypothesis Testing. More Hypothesis Testing The big question: What we really want to know: What we actually know: We know:
 Multiple Regression Ψ320 Ainsworth More Hypothesis Testing What we really want to know: Is the relationship in the population we have selected between X & Y strong enough that we can use the relationship
Multiple Regression Ψ320 Ainsworth More Hypothesis Testing What we really want to know: Is the relationship in the population we have selected between X & Y strong enough that we can use the relationship
General and Generalized Linear Models
 General and Generalized Linear Models http://datascience.tntlab.org Module 9 Today s Agenda Some new tidyverse Correlations and covariances Review of lm() and glm() More plotting Stepwise and subsets Model
General and Generalized Linear Models http://datascience.tntlab.org Module 9 Today s Agenda Some new tidyverse Correlations and covariances Review of lm() and glm() More plotting Stepwise and subsets Model
holding all other predictors constant
 Multiple Regression Numeric Response variable (y) p Numeric predictor variables (p < n) Model: Y = b 0 + b 1 x 1 + + b p x p + e Partial Regression Coefficients: b i effect (on the mean response) of increasing
Multiple Regression Numeric Response variable (y) p Numeric predictor variables (p < n) Model: Y = b 0 + b 1 x 1 + + b p x p + e Partial Regression Coefficients: b i effect (on the mean response) of increasing
Daniel Boduszek University of Huddersfield
 Daniel Boduszek University of Huddersfield d.boduszek@hud.ac.uk Introduction to moderator effects Hierarchical Regression analysis with continuous moderator Hierarchical Regression analysis with categorical
Daniel Boduszek University of Huddersfield d.boduszek@hud.ac.uk Introduction to moderator effects Hierarchical Regression analysis with continuous moderator Hierarchical Regression analysis with categorical
AMS 7 Correlation and Regression Lecture 8
 AMS 7 Correlation and Regression Lecture 8 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, University of California, Santa Cruz Suumer 2014 1 / 18 Correlation pairs of continuous observations. Correlation
AMS 7 Correlation and Regression Lecture 8 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, University of California, Santa Cruz Suumer 2014 1 / 18 Correlation pairs of continuous observations. Correlation
Linear Regression. In this lecture we will study a particular type of regression model: the linear regression model
 1 Linear Regression 2 Linear Regression In this lecture we will study a particular type of regression model: the linear regression model We will first consider the case of the model with one predictor
1 Linear Regression 2 Linear Regression In this lecture we will study a particular type of regression model: the linear regression model We will first consider the case of the model with one predictor
Single and multiple linear regression analysis
 Single and multiple linear regression analysis Marike Cockeran 2017 Introduction Outline of the session Simple linear regression analysis SPSS example of simple linear regression analysis Additional topics
Single and multiple linear regression analysis Marike Cockeran 2017 Introduction Outline of the session Simple linear regression analysis SPSS example of simple linear regression analysis Additional topics
The Model Building Process Part I: Checking Model Assumptions Best Practice
 The Model Building Process Part I: Checking Model Assumptions Best Practice Authored by: Sarah Burke, PhD 31 July 2017 The goal of the STAT T&E COE is to assist in developing rigorous, defensible test
The Model Building Process Part I: Checking Model Assumptions Best Practice Authored by: Sarah Burke, PhD 31 July 2017 The goal of the STAT T&E COE is to assist in developing rigorous, defensible test
ANOVA. Testing more than 2 conditions
 ANOVA Testing more than 2 conditions ANOVA Today s goal: Teach you about ANOVA, the test used to measure the difference between more than two conditions Outline: - Why anova? - Contrasts and post-hoc tests
ANOVA Testing more than 2 conditions ANOVA Today s goal: Teach you about ANOVA, the test used to measure the difference between more than two conditions Outline: - Why anova? - Contrasts and post-hoc tests
Multivariate Lineare Modelle
 0-1 TALEB AHMAD CASE - Center for Applied Statistics and Economics Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Motivation 1-1 Motivation Multivariate regression models can accommodate many explanatory which simultaneously
0-1 TALEB AHMAD CASE - Center for Applied Statistics and Economics Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Motivation 1-1 Motivation Multivariate regression models can accommodate many explanatory which simultaneously
Longitudinal Data Analysis of Health Outcomes
 Longitudinal Data Analysis of Health Outcomes Longitudinal Data Analysis Workshop Running Example: Days 2 and 3 University of Georgia: Institute for Interdisciplinary Research in Education and Human Development
Longitudinal Data Analysis of Health Outcomes Longitudinal Data Analysis Workshop Running Example: Days 2 and 3 University of Georgia: Institute for Interdisciplinary Research in Education and Human Development
Statistical Modelling in Stata 5: Linear Models
 Statistical Modelling in Stata 5: Linear Models Mark Lunt Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit University of Manchester 07/11/2017 Structure This Week What is a linear model? How good is my model? Does
Statistical Modelling in Stata 5: Linear Models Mark Lunt Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit University of Manchester 07/11/2017 Structure This Week What is a linear model? How good is my model? Does
Using SPSS for One Way Analysis of Variance
 Using SPSS for One Way Analysis of Variance This tutorial will show you how to use SPSS version 12 to perform a one-way, between- subjects analysis of variance and related post-hoc tests. This tutorial
Using SPSS for One Way Analysis of Variance This tutorial will show you how to use SPSS version 12 to perform a one-way, between- subjects analysis of variance and related post-hoc tests. This tutorial
> modlyq <- lm(ly poly(x,2,raw=true)) > summary(modlyq) Call: lm(formula = ly poly(x, 2, raw = TRUE))
 School of Mathematical Sciences MTH5120 Statistical Modelling I Tutorial 4 Solutions The first two models were looked at last week and both had flaws. The output for the third model with log y and a quadratic
School of Mathematical Sciences MTH5120 Statistical Modelling I Tutorial 4 Solutions The first two models were looked at last week and both had flaws. The output for the third model with log y and a quadratic
Multiple Linear Regression
 Multiple Linear Regression University of California, San Diego Instructor: Ery Arias-Castro http://math.ucsd.edu/~eariasca/teaching.html 1 / 42 Passenger car mileage Consider the carmpg dataset taken from
Multiple Linear Regression University of California, San Diego Instructor: Ery Arias-Castro http://math.ucsd.edu/~eariasca/teaching.html 1 / 42 Passenger car mileage Consider the carmpg dataset taken from
LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS. MODULE XVI Lecture Exercises
 LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE XVI Lecture - 44 Exercises Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Exercise 1 The following data has been obtained on
LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE XVI Lecture - 44 Exercises Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Exercise 1 The following data has been obtained on
Regression Diagnostics Procedures
 Regression Diagnostics Procedures ASSUMPTIONS UNDERLYING REGRESSION/CORRELATION NORMALITY OF VARIANCE IN Y FOR EACH VALUE OF X For any fixed value of the independent variable X, the distribution of the
Regression Diagnostics Procedures ASSUMPTIONS UNDERLYING REGRESSION/CORRELATION NORMALITY OF VARIANCE IN Y FOR EACH VALUE OF X For any fixed value of the independent variable X, the distribution of the
Stat 427/527: Advanced Data Analysis I
 Stat 427/527: Advanced Data Analysis I Review of Chapters 1-4 Sep, 2017 1 / 18 Concepts you need to know/interpret Numerical summaries: measures of center (mean, median, mode) measures of spread (sample
Stat 427/527: Advanced Data Analysis I Review of Chapters 1-4 Sep, 2017 1 / 18 Concepts you need to know/interpret Numerical summaries: measures of center (mean, median, mode) measures of spread (sample
Contents. 1 Review of Residuals. 2 Detecting Outliers. 3 Influential Observations. 4 Multicollinearity and its Effects
 Contents 1 Review of Residuals 2 Detecting Outliers 3 Influential Observations 4 Multicollinearity and its Effects W. Zhou (Colorado State University) STAT 540 July 6th, 2015 1 / 32 Model Diagnostics:
Contents 1 Review of Residuals 2 Detecting Outliers 3 Influential Observations 4 Multicollinearity and its Effects W. Zhou (Colorado State University) STAT 540 July 6th, 2015 1 / 32 Model Diagnostics:
General Linear Model (Chapter 4)
 General Linear Model (Chapter 4) Outcome variable is considered continuous Simple linear regression Scatterplots OLS is BLUE under basic assumptions MSE estimates residual variance testing regression coefficients
General Linear Model (Chapter 4) Outcome variable is considered continuous Simple linear regression Scatterplots OLS is BLUE under basic assumptions MSE estimates residual variance testing regression coefficients
ECON 497 Midterm Spring
 ECON 497 Midterm Spring 2009 1 ECON 497: Economic Research and Forecasting Name: Spring 2009 Bellas Midterm You have three hours and twenty minutes to complete this exam. Answer all questions and explain
ECON 497 Midterm Spring 2009 1 ECON 497: Economic Research and Forecasting Name: Spring 2009 Bellas Midterm You have three hours and twenty minutes to complete this exam. Answer all questions and explain
Self-Assessment Weeks 8: Multiple Regression with Qualitative Predictors; Multiple Comparisons
 Self-Assessment Weeks 8: Multiple Regression with Qualitative Predictors; Multiple Comparisons 1. Suppose we wish to assess the impact of five treatments while blocking for study participant race (Black,
Self-Assessment Weeks 8: Multiple Regression with Qualitative Predictors; Multiple Comparisons 1. Suppose we wish to assess the impact of five treatments while blocking for study participant race (Black,
MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION IN MINITAB
 MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION IN MINITAB This document shows a complicated Minitab multiple regression. It includes descriptions of the Minitab commands, and the Minitab output is heavily annotated. Comments
MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION IN MINITAB This document shows a complicated Minitab multiple regression. It includes descriptions of the Minitab commands, and the Minitab output is heavily annotated. Comments
Psychology Seminar Psych 406 Dr. Jeffrey Leitzel
 Psychology Seminar Psych 406 Dr. Jeffrey Leitzel Structural Equation Modeling Topic 1: Correlation / Linear Regression Outline/Overview Correlations (r, pr, sr) Linear regression Multiple regression interpreting
Psychology Seminar Psych 406 Dr. Jeffrey Leitzel Structural Equation Modeling Topic 1: Correlation / Linear Regression Outline/Overview Correlations (r, pr, sr) Linear regression Multiple regression interpreting
Topic 1. Definitions
 S Topic. Definitions. Scalar A scalar is a number. 2. Vector A vector is a column of numbers. 3. Linear combination A scalar times a vector plus a scalar times a vector, plus a scalar times a vector...
S Topic. Definitions. Scalar A scalar is a number. 2. Vector A vector is a column of numbers. 3. Linear combination A scalar times a vector plus a scalar times a vector, plus a scalar times a vector...
Exam Applied Statistical Regression. Good Luck!
 Dr. M. Dettling Summer 2011 Exam Applied Statistical Regression Approved: Tables: Note: Any written material, calculator (without communication facility). Attached. All tests have to be done at the 5%-level.
Dr. M. Dettling Summer 2011 Exam Applied Statistical Regression Approved: Tables: Note: Any written material, calculator (without communication facility). Attached. All tests have to be done at the 5%-level.
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 63
 Stem-and-leaf diagram - vertical numbers on far left represent the 10s, numbers right of the line represent the 1s The mean should not be used if there are extreme scores, or for ranks and categories Unbiased
Stem-and-leaf diagram - vertical numbers on far left represent the 10s, numbers right of the line represent the 1s The mean should not be used if there are extreme scores, or for ranks and categories Unbiased
A discussion on multiple regression models
 A discussion on multiple regression models In our previous discussion of simple linear regression, we focused on a model in which one independent or explanatory variable X was used to predict the value
A discussion on multiple regression models In our previous discussion of simple linear regression, we focused on a model in which one independent or explanatory variable X was used to predict the value
Nonlinear Regression. Summary. Sample StatFolio: nonlinear reg.sgp
 Nonlinear Regression Summary... 1 Analysis Summary... 4 Plot of Fitted Model... 6 Response Surface Plots... 7 Analysis Options... 10 Reports... 11 Correlation Matrix... 12 Observed versus Predicted...
Nonlinear Regression Summary... 1 Analysis Summary... 4 Plot of Fitted Model... 6 Response Surface Plots... 7 Analysis Options... 10 Reports... 11 Correlation Matrix... 12 Observed versus Predicted...
Density Temp vs Ratio. temp
 Temp Ratio Density 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.12 Density 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1. (a) 170 175 180 185 temp 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 ratio The histogram shows that the temperature measures have two peaks,
Temp Ratio Density 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.12 Density 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1. (a) 170 175 180 185 temp 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 ratio The histogram shows that the temperature measures have two peaks,
ANOVA, ANCOVA and MANOVA as sem
 ANOVA, ANCOVA and MANOVA as sem Robin Beaumont 2017 Hoyle Chapter 24 Handbook of Structural Equation Modeling (2015 paperback), Examples converted to R and Onyx SEM diagrams. This workbook duplicates some
ANOVA, ANCOVA and MANOVA as sem Robin Beaumont 2017 Hoyle Chapter 24 Handbook of Structural Equation Modeling (2015 paperback), Examples converted to R and Onyx SEM diagrams. This workbook duplicates some
Introduction to Linear regression analysis. Part 2. Model comparisons
 Introduction to Linear regression analysis Part Model comparisons 1 ANOVA for regression Total variation in Y SS Total = Variation explained by regression with X SS Regression + Residual variation SS Residual
Introduction to Linear regression analysis Part Model comparisons 1 ANOVA for regression Total variation in Y SS Total = Variation explained by regression with X SS Regression + Residual variation SS Residual
Inferences About the Difference Between Two Means
 7 Inferences About the Difference Between Two Means Chapter Outline 7.1 New Concepts 7.1.1 Independent Versus Dependent Samples 7.1. Hypotheses 7. Inferences About Two Independent Means 7..1 Independent
7 Inferences About the Difference Between Two Means Chapter Outline 7.1 New Concepts 7.1.1 Independent Versus Dependent Samples 7.1. Hypotheses 7. Inferences About Two Independent Means 7..1 Independent
Last updated: Oct 18, 2012 LINEAR REGRESSION PSYC 3031 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS LABORATORY. J. Elder
 Last updated: Oct 18, 2012 LINEAR REGRESSION Acknowledgements 2 Some of these slides have been sourced or modified from slides created by A. Field for Discovering Statistics using R. Simple Linear Objectives
Last updated: Oct 18, 2012 LINEAR REGRESSION Acknowledgements 2 Some of these slides have been sourced or modified from slides created by A. Field for Discovering Statistics using R. Simple Linear Objectives
Heteroskedasticity. Part VII. Heteroskedasticity
 Part VII Heteroskedasticity As of Oct 15, 2015 1 Heteroskedasticity Consequences Heteroskedasticity-robust inference Testing for Heteroskedasticity Weighted Least Squares (WLS) Feasible generalized Least
Part VII Heteroskedasticity As of Oct 15, 2015 1 Heteroskedasticity Consequences Heteroskedasticity-robust inference Testing for Heteroskedasticity Weighted Least Squares (WLS) Feasible generalized Least
Regression Diagnostics for Survey Data
 Regression Diagnostics for Survey Data Richard Valliant Joint Program in Survey Methodology, University of Maryland and University of Michigan USA Jianzhu Li (Westat), Dan Liao (JPSM) 1 Introduction Topics
Regression Diagnostics for Survey Data Richard Valliant Joint Program in Survey Methodology, University of Maryland and University of Michigan USA Jianzhu Li (Westat), Dan Liao (JPSM) 1 Introduction Topics
Analysis of Covariance. The following example illustrates a case where the covariate is affected by the treatments.
 Analysis of Covariance In some experiments, the experimental units (subjects) are nonhomogeneous or there is variation in the experimental conditions that are not due to the treatments. For example, a
Analysis of Covariance In some experiments, the experimental units (subjects) are nonhomogeneous or there is variation in the experimental conditions that are not due to the treatments. For example, a
Introduction to Regression
 Regression Introduction to Regression If two variables covary, we should be able to predict the value of one variable from another. Correlation only tells us how much two variables covary. In regression,
Regression Introduction to Regression If two variables covary, we should be able to predict the value of one variable from another. Correlation only tells us how much two variables covary. In regression,
lm statistics Chris Parrish
 lm statistics Chris Parrish 2017-04-01 Contents s e and R 2 1 experiment1................................................. 2 experiment2................................................. 3 experiment3.................................................
lm statistics Chris Parrish 2017-04-01 Contents s e and R 2 1 experiment1................................................. 2 experiment2................................................. 3 experiment3.................................................
Chapter 8: Correlation & Regression
 Chapter 8: Correlation & Regression We can think of ANOVA and the two-sample t-test as applicable to situations where there is a response variable which is quantitative, and another variable that indicates
Chapter 8: Correlation & Regression We can think of ANOVA and the two-sample t-test as applicable to situations where there is a response variable which is quantitative, and another variable that indicates
Box-Cox Transformations
 Box-Cox Transformations Revised: 10/10/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Summary... 3 Analysis Options... 5 Plot of Fitted Model... 6 MSE Comparison Plot... 8 MSE Comparison Table... 9 Skewness
Box-Cox Transformations Revised: 10/10/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Summary... 3 Analysis Options... 5 Plot of Fitted Model... 6 MSE Comparison Plot... 8 MSE Comparison Table... 9 Skewness
Comparing Several Means: ANOVA
 Comparing Several Means: ANOVA Understand the basic principles of ANOVA Why it is done? What it tells us? Theory of one way independent ANOVA Following up an ANOVA: Planned contrasts/comparisons Choosing
Comparing Several Means: ANOVA Understand the basic principles of ANOVA Why it is done? What it tells us? Theory of one way independent ANOVA Following up an ANOVA: Planned contrasts/comparisons Choosing
1 The Classic Bivariate Least Squares Model
 Review of Bivariate Linear Regression Contents 1 The Classic Bivariate Least Squares Model 1 1.1 The Setup............................... 1 1.2 An Example Predicting Kids IQ................. 1 2 Evaluating
Review of Bivariate Linear Regression Contents 1 The Classic Bivariate Least Squares Model 1 1.1 The Setup............................... 1 1.2 An Example Predicting Kids IQ................. 1 2 Evaluating
Chapter 8: Correlation & Regression
 Chapter 8: Correlation & Regression We can think of ANOVA and the two-sample t-test as applicable to situations where there is a response variable which is quantitative, and another variable that indicates
Chapter 8: Correlation & Regression We can think of ANOVA and the two-sample t-test as applicable to situations where there is a response variable which is quantitative, and another variable that indicates
DISCOVERING STATISTICS USING R
 DISCOVERING STATISTICS USING R ANDY FIELD I JEREMY MILES I ZOE FIELD Los Angeles London New Delhi Singapore j Washington DC CONTENTS Preface How to use this book Acknowledgements Dedication Symbols used
DISCOVERING STATISTICS USING R ANDY FIELD I JEREMY MILES I ZOE FIELD Los Angeles London New Delhi Singapore j Washington DC CONTENTS Preface How to use this book Acknowledgements Dedication Symbols used
Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Chapter 3: Multiple Linear Regression Sections
 Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Chapter 3: Multiple Linear Regression Sections 3.4 3.6 by Iain Pardoe 3.4 Model assumptions 2 Regression model assumptions.............................................
Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Chapter 3: Multiple Linear Regression Sections 3.4 3.6 by Iain Pardoe 3.4 Model assumptions 2 Regression model assumptions.............................................
Multiple Regression. Peerapat Wongchaiwat, Ph.D.
 Peerapat Wongchaiwat, Ph.D. wongchaiwat@hotmail.com The Multiple Regression Model Examine the linear relationship between 1 dependent (Y) & 2 or more independent variables (X i ) Multiple Regression Model
Peerapat Wongchaiwat, Ph.D. wongchaiwat@hotmail.com The Multiple Regression Model Examine the linear relationship between 1 dependent (Y) & 2 or more independent variables (X i ) Multiple Regression Model
INTRODUCTION TO DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTS
 GEORGE W. COBB Mount Holyoke College INTRODUCTION TO DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTS Springer CONTENTS To the Instructor Sample Exam Questions To the Student Acknowledgments xv xxi xxvii xxix 1. INTRODUCTION
GEORGE W. COBB Mount Holyoke College INTRODUCTION TO DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTS Springer CONTENTS To the Instructor Sample Exam Questions To the Student Acknowledgments xv xxi xxvii xxix 1. INTRODUCTION
Multiple Regression Part I STAT315, 19-20/3/2014
 Multiple Regression Part I STAT315, 19-20/3/2014 Regression problem Predictors/independent variables/features Or: Error which can never be eliminated. Our task is to estimate the regression function f.
Multiple Regression Part I STAT315, 19-20/3/2014 Regression problem Predictors/independent variables/features Or: Error which can never be eliminated. Our task is to estimate the regression function f.
Chapter 1 Statistical Inference
 Chapter 1 Statistical Inference causal inference To infer causality, you need a randomized experiment (or a huge observational study and lots of outside information). inference to populations Generalizations
Chapter 1 Statistical Inference causal inference To infer causality, you need a randomized experiment (or a huge observational study and lots of outside information). inference to populations Generalizations
Classification & Regression. Multicollinearity Intro to Nominal Data
 Multicollinearity Intro to Nominal Let s Start With A Question y = β 0 + β 1 x 1 +β 2 x 2 y = Anxiety Level x 1 = heart rate x 2 = recorded pulse Since we can all agree heart rate and pulse are related,
Multicollinearity Intro to Nominal Let s Start With A Question y = β 0 + β 1 x 1 +β 2 x 2 y = Anxiety Level x 1 = heart rate x 2 = recorded pulse Since we can all agree heart rate and pulse are related,
Difference in two or more average scores in different groups
 ANOVAs Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Difference in two or more average scores in different groups Each participant tested once Same outcome tested in each group Simplest is one-way ANOVA (one variable as
ANOVAs Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Difference in two or more average scores in different groups Each participant tested once Same outcome tested in each group Simplest is one-way ANOVA (one variable as
" M A #M B. Standard deviation of the population (Greek lowercase letter sigma) σ 2
 Notation and Equations for Final Exam Symbol Definition X The variable we measure in a scientific study n The size of the sample N The size of the population M The mean of the sample µ The mean of the
Notation and Equations for Final Exam Symbol Definition X The variable we measure in a scientific study n The size of the sample N The size of the population M The mean of the sample µ The mean of the
Math 423/533: The Main Theoretical Topics
 Math 423/533: The Main Theoretical Topics Notation sample size n, data index i number of predictors, p (p = 2 for simple linear regression) y i : response for individual i x i = (x i1,..., x ip ) (1 p)
Math 423/533: The Main Theoretical Topics Notation sample size n, data index i number of predictors, p (p = 2 for simple linear regression) y i : response for individual i x i = (x i1,..., x ip ) (1 p)
Bivariate data analysis
 Bivariate data analysis Categorical data - creating data set Upload the following data set to R Commander sex female male male male male female female male female female eye black black blue green green
Bivariate data analysis Categorical data - creating data set Upload the following data set to R Commander sex female male male male male female female male female female eye black black blue green green
STAT Checking Model Assumptions
 STAT 704 --- Checking Model Assumptions Recall we assumed the following in our model: (1) The regression relationship between the response and the predictor(s) specified in the model is appropriate (2)
STAT 704 --- Checking Model Assumptions Recall we assumed the following in our model: (1) The regression relationship between the response and the predictor(s) specified in the model is appropriate (2)
Fractional Polynomial Regression
 Chapter 382 Fractional Polynomial Regression Introduction This program fits fractional polynomial models in situations in which there is one dependent (Y) variable and one independent (X) variable. It
Chapter 382 Fractional Polynomial Regression Introduction This program fits fractional polynomial models in situations in which there is one dependent (Y) variable and one independent (X) variable. It
Multivariate Analysis of Variance
 Chapter 15 Multivariate Analysis of Variance Jolicouer and Mosimann studied the relationship between the size and shape of painted turtles. The table below gives the length, width, and height (all in mm)
Chapter 15 Multivariate Analysis of Variance Jolicouer and Mosimann studied the relationship between the size and shape of painted turtles. The table below gives the length, width, and height (all in mm)
DETAILED CONTENTS PART I INTRODUCTION AND DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS. 1. Introduction to Statistics
 DETAILED CONTENTS About the Author Preface to the Instructor To the Student How to Use SPSS With This Book PART I INTRODUCTION AND DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Introduction to Statistics 1.1 Descriptive and
DETAILED CONTENTS About the Author Preface to the Instructor To the Student How to Use SPSS With This Book PART I INTRODUCTION AND DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Introduction to Statistics 1.1 Descriptive and
PBAF 528 Week 8. B. Regression Residuals These properties have implications for the residuals of the regression.
 PBAF 528 Week 8 What are some problems with our model? Regression models are used to represent relationships between a dependent variable and one or more predictors. In order to make inference from the
PBAF 528 Week 8 What are some problems with our model? Regression models are used to represent relationships between a dependent variable and one or more predictors. In order to make inference from the
Introduction to Linear Regression Rebecca C. Steorts September 15, 2015
 Introduction to Linear Regression Rebecca C. Steorts September 15, 2015 Today (Re-)Introduction to linear models and the model space What is linear regression Basic properties of linear regression Using
Introduction to Linear Regression Rebecca C. Steorts September 15, 2015 Today (Re-)Introduction to linear models and the model space What is linear regression Basic properties of linear regression Using
Basic Business Statistics 6 th Edition
 Basic Business Statistics 6 th Edition Chapter 12 Simple Linear Regression Learning Objectives In this chapter, you learn: How to use regression analysis to predict the value of a dependent variable based
Basic Business Statistics 6 th Edition Chapter 12 Simple Linear Regression Learning Objectives In this chapter, you learn: How to use regression analysis to predict the value of a dependent variable based
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression. Take random samples from each of m populations.
 22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 8: ANOVA NOTE: We will meet in the lab on Monday October 10. One-way ANOVA Focuses on testing for differences among group means. Take random samples from each
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 8: ANOVA NOTE: We will meet in the lab on Monday October 10. One-way ANOVA Focuses on testing for differences among group means. Take random samples from each
MANOVA is an extension of the univariate ANOVA as it involves more than one Dependent Variable (DV). The following are assumptions for using MANOVA:
 MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE MANOVA is an extension of the univariate ANOVA as it involves more than one Dependent Variable (DV). The following are assumptions for using MANOVA: 1. Cell sizes : o
MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE MANOVA is an extension of the univariate ANOVA as it involves more than one Dependent Variable (DV). The following are assumptions for using MANOVA: 1. Cell sizes : o
Multiple Linear Regression
 Andrew Lonardelli December 20, 2013 Multiple Linear Regression 1 Table Of Contents Introduction: p.3 Multiple Linear Regression Model: p.3 Least Squares Estimation of the Parameters: p.4-5 The matrix approach
Andrew Lonardelli December 20, 2013 Multiple Linear Regression 1 Table Of Contents Introduction: p.3 Multiple Linear Regression Model: p.3 Least Squares Estimation of the Parameters: p.4-5 The matrix approach
SPSS Output. ANOVA a b Residual Coefficients a Standardized Coefficients
 SPSS Output Homework 1-1e ANOVA a Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig. 1 Regression 351.056 1 351.056 11.295.002 b Residual 932.412 30 31.080 Total 1283.469 31 a. Dependent Variable: Sexual Harassment
SPSS Output Homework 1-1e ANOVA a Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig. 1 Regression 351.056 1 351.056 11.295.002 b Residual 932.412 30 31.080 Total 1283.469 31 a. Dependent Variable: Sexual Harassment
Chaper 5: Matrix Approach to Simple Linear Regression. Matrix: A m by n matrix B is a grid of numbers with m rows and n columns. B = b 11 b m1 ...
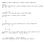 Chaper 5: Matrix Approach to Simple Linear Regression Matrix: A m by n matrix B is a grid of numbers with m rows and n columns B = b 11 b 1n b m1 b mn Element b ik is from the ith row and kth column A
Chaper 5: Matrix Approach to Simple Linear Regression Matrix: A m by n matrix B is a grid of numbers with m rows and n columns B = b 11 b 1n b m1 b mn Element b ik is from the ith row and kth column A
Ridge Regression. Summary. Sample StatFolio: ridge reg.sgp. STATGRAPHICS Rev. 10/1/2014
 Ridge Regression Summary... 1 Data Input... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Analysis Options... 6 Ridge Trace... 7 Regression Coefficients... 8 Standardized Regression Coefficients... 9 Observed versus Predicted...
Ridge Regression Summary... 1 Data Input... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Analysis Options... 6 Ridge Trace... 7 Regression Coefficients... 8 Standardized Regression Coefficients... 9 Observed versus Predicted...
401 Review. 6. Power analysis for one/two-sample hypothesis tests and for correlation analysis.
 401 Review Major topics of the course 1. Univariate analysis 2. Bivariate analysis 3. Simple linear regression 4. Linear algebra 5. Multiple regression analysis Major analysis methods 1. Graphical analysis
401 Review Major topics of the course 1. Univariate analysis 2. Bivariate analysis 3. Simple linear regression 4. Linear algebra 5. Multiple regression analysis Major analysis methods 1. Graphical analysis
Extensions of One-Way ANOVA.
 Extensions of One-Way ANOVA http://www.pelagicos.net/classes_biometry_fa18.htm What do I want You to Know What are two main limitations of ANOVA? What two approaches can follow a significant ANOVA? How
Extensions of One-Way ANOVA http://www.pelagicos.net/classes_biometry_fa18.htm What do I want You to Know What are two main limitations of ANOVA? What two approaches can follow a significant ANOVA? How
STATISTICS 479 Exam II (100 points)
 Name STATISTICS 79 Exam II (1 points) 1. A SAS data set was created using the following input statement: Answer parts(a) to (e) below. input State $ City $ Pop199 Income Housing Electric; (a) () Give the
Name STATISTICS 79 Exam II (1 points) 1. A SAS data set was created using the following input statement: Answer parts(a) to (e) below. input State $ City $ Pop199 Income Housing Electric; (a) () Give the
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression. There are a couple commonly used models for a one-way ANOVA with m groups. Chapter 8: ANOVA
 22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 8: ANOVA NOTE: We will meet in the lab on Monday October 10. One-way ANOVA Focuses on testing for differences among group means. Take random samples from each
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 8: ANOVA NOTE: We will meet in the lab on Monday October 10. One-way ANOVA Focuses on testing for differences among group means. Take random samples from each
Foundations of Correlation and Regression
 BWH - Biostatistics Intermediate Biostatistics for Medical Researchers Robert Goldman Professor of Statistics Simmons College Foundations of Correlation and Regression Tuesday, March 7, 2017 March 7 Foundations
BWH - Biostatistics Intermediate Biostatistics for Medical Researchers Robert Goldman Professor of Statistics Simmons College Foundations of Correlation and Regression Tuesday, March 7, 2017 March 7 Foundations
1 A Review of Correlation and Regression
 1 A Review of Correlation and Regression SW, Chapter 12 Suppose we select n = 10 persons from the population of college seniors who plan to take the MCAT exam. Each takes the test, is coached, and then
1 A Review of Correlation and Regression SW, Chapter 12 Suppose we select n = 10 persons from the population of college seniors who plan to take the MCAT exam. Each takes the test, is coached, and then
ECO220Y Simple Regression: Testing the Slope
 ECO220Y Simple Regression: Testing the Slope Readings: Chapter 18 (Sections 18.3-18.5) Winter 2012 Lecture 19 (Winter 2012) Simple Regression Lecture 19 1 / 32 Simple Regression Model y i = β 0 + β 1 x
ECO220Y Simple Regression: Testing the Slope Readings: Chapter 18 (Sections 18.3-18.5) Winter 2012 Lecture 19 (Winter 2012) Simple Regression Lecture 19 1 / 32 Simple Regression Model y i = β 0 + β 1 x
Regression: Main Ideas Setting: Quantitative outcome with a quantitative explanatory variable. Example, cont.
 TCELL 9/4/205 36-309/749 Experimental Design for Behavioral and Social Sciences Simple Regression Example Male black wheatear birds carry stones to the nest as a form of sexual display. Soler et al. wanted
TCELL 9/4/205 36-309/749 Experimental Design for Behavioral and Social Sciences Simple Regression Example Male black wheatear birds carry stones to the nest as a form of sexual display. Soler et al. wanted
BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 9 - Correlation and Bivariate Regression
 BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 9 - Correlation and Bivariate Regression Introduction to Correlation and Regression The procedures discussed in the previous ANOVA labs are most useful in cases where we are interested
BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 9 - Correlation and Bivariate Regression Introduction to Correlation and Regression The procedures discussed in the previous ANOVA labs are most useful in cases where we are interested
Final Exam. Name: Solution:
 Final Exam. Name: Instructions. Answer all questions on the exam. Open books, open notes, but no electronic devices. The first 13 problems are worth 5 points each. The rest are worth 1 point each. HW1.
Final Exam. Name: Instructions. Answer all questions on the exam. Open books, open notes, but no electronic devices. The first 13 problems are worth 5 points each. The rest are worth 1 point each. HW1.
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression. Chapter 8: 1-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) 2-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
 22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 8: 1-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) 2-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) We now consider an analysis with only categorical predictors (i.e. all predictors are
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 8: 1-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) 2-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) We now consider an analysis with only categorical predictors (i.e. all predictors are
Introduction and Single Predictor Regression. Correlation
 Introduction and Single Predictor Regression Dr. J. Kyle Roberts Southern Methodist University Simmons School of Education and Human Development Department of Teaching and Learning Correlation A correlation
Introduction and Single Predictor Regression Dr. J. Kyle Roberts Southern Methodist University Simmons School of Education and Human Development Department of Teaching and Learning Correlation A correlation
Multiple Linear Regression II. Lecture 8. Overview. Readings
 Multiple Linear Regression II Lecture 8 Image source:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:autobunnskr%c3%a4iz-ro-a201.jpg Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution
Multiple Linear Regression II Lecture 8 Image source:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:autobunnskr%c3%a4iz-ro-a201.jpg Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution
Multiple Linear Regression II. Lecture 8. Overview. Readings. Summary of MLR I. Summary of MLR I. Summary of MLR I
 Multiple Linear Regression II Lecture 8 Image source:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:autobunnskr%c3%a4iz-ro-a201.jpg Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution
Multiple Linear Regression II Lecture 8 Image source:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:autobunnskr%c3%a4iz-ro-a201.jpg Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution
