Design of an interferometric displacement sensor with picometer resolution for the Galileo-Galilei mission
|
|
|
- Marshall Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design of an interferometric displacement sensor with picometer resolution for the Galileo-Galilei mission Marco Pisani and Giovanni Mana Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica INRIM Torino, Italy Anna M. Nobili Department of Physics E. Fermi, University of Pisa and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Pisa, Italy Abstract The Galileo-Galilei (GG) mission aims at testing the Weak Equivalence Principle. It requires the measurement of the differential displacement between two test masses with a resolution of 1 pm/ Hz at 1 Hz. An optical interferometer has been designed to the purpose. The principle and the preliminary design of the interferometer will be illustrated. Keywords Laser interferometer, I. INTRODUCTION General Relativity stands on the experimental fact that all bodies fall in a gravitational field with the same acceleration regardless of their mass and composition. This is the Universality of Free Fall (UFF) or the Weak Equivalence Principle (WEP). GG will test UFF/WEP to 1 part in [1]. It will do it by measuring the fractional differential acceleration of two test masses of different composition in the gravitational field of Earth while orbiting around it at low altitude. GG will improve the best tests to date currently at sensitivity level [2-4] by four orders of magnitude, deeply probing a totally unexplored physical domain. The improvement on the best drop tests with cold atoms [5-8] will be huge, by 10 orders of magnitude. An experimental evidence of a UFF/WEP violation would mean that either General Relativity is to be amended, or that a new force of nature is at play. It would amount to a scientific revolution, while a UFF/WEP confirmation at this sensitivity level would strongly constrain physical theories. There is no firm target as to the level at which violation should occur, but the higher the test sensitivity, the higher the chances to find new physics. The GG sensor is sensitive to the differential accelerations acting in the plane perpendicular to the spin/symmetry axis (such as the violation signal). It is made of two concentric, hollow cylinders weakly coupled to form a balance whose beam is the symmetry and spin axis. The capacitance readout of the early GG design has now been replaced by a laser interferometry gauge, which is ideal for rejecting common mode effects, it is linear, works at any distance and allows a gap several times larger than cap sensors (thus reducing many error sources). This paper relates about the design of a laser interferometer to be used to measure the differential displacement of the two cylinders. II. THE PRINCIPLE OF GG MEASUREMENT In the GG design, the test cylinders, together with the whole spacecraft surrounding them, spin around the symmetry axis. The proof masses form a rotating 2D harmonic oscillator characterized by weak coupling and fast rotation, that is, above the natural coupling frequency. This ensures the self-centering of their centers of mass, no active centering being required. Thus, one-axis rotation (e.g. at 1 Hz) stabilizes the satellite while, at the same time, modulates the violation signal (see Fig. 1). Fig. 1. A violation signal is shown to the right, as it affects the GG test cylinders in the orbit plane. The signal points to the Earth and in the simple case of a circular orbit has constant size. The sketch to the left shows the GG concentric cylinders coupled as a mechanical oscillator in 2D (the plane perpendicular to the spin/symmetry axis). The rotation upconverts the low frequency violation signal by a factor of 5800, from the orbital frequency to the spin frequency. III. DESIGN OF THE NEW LASER GAUGE GG uses nine laser gauges with sub-picometer performance to measure the relative displacements and, thus, the differential acceleration of the two test masses. Its conceptual layout is shown in Figs. 2 and 3, where three series of laser gauges are placed symmetrically at each end of the test masses and at the center /15/$ IEEE 591
2 Fig. 2. A view of the nine laser gauges fixed to the PGB (Pico Gravity Box, an intermediate suspended stage, also of cylindrical shape, between the test masses and the spacecraft outer shell) aiming at the cylindrical test masses. Fig. 4. Interferometer output obtained in laboratory with a breadboard of the spatially separated heterodyne interferometer realized as in [9]. The subdemonstrated. picometer noise around 1 Hz is Fig. 3. Cylindrical test masses (10 kg each) with opto-mechanicato host the metrology system. The holes in the external cylinder allow machining the interferometer beam to measure the internal cylinder. This layout allows the differential acceleration defined by four degrees of freedom (two translationss and two tip/tilt) between the two cylinders to be measured with some redundancy. Systematic errors, such as uniform thermal expansions of the cylinders, are taken out among the nine symmetric laser gauges. The GG laser gauge (LG) is based on the common-path heterodyne interferometer originally developed for the SIM mission [9]. The LG is based on a heterodyne Michelson interferometer where the two arms are spatially separated (and recombined) by an arrangement of physical stops, iris and mirrors without using polarizing optics. The result is a quasi-complete cancellation of the typical polarization mixing induced nonlinearities. Picometer performance has been demonstrated at the laser sensor level and higher systems levels (Fig. 4). Similar performances have been demonstrated in alternative layouts realized by the authors of this paper in [10 and 11]. The concept of spatial separation of the interferometer arms to minimize non linearity effects is shown in Fig. 5. The interferometer is fed by two laser sources (red and blue in the sketch) and has two optical outputs (green in the sketch). Fig. 5. Principle of the spatial separation of the interferometer arms to minimize non linearity effects in the laser gauge. a) a simplified schematic of the LG set-up as described in the text. b) path of the portion of the laser which goes towards the inner mass through a hole in the external mass, is reflected back, is redirected to the right side by the partially reflected mirror and finally is redirected towards one of the two detector lenses by a small mirror. The dimension of the mirror is such 592
3 that only the right part of the beam is «seen» by the detector. c) path of the beam going towards the external mass behaving as a ring shaped mirror, reflected back, redirected to the right side and finally passing over the small mirror now acting as a circular stop so that only the right part of the beam is collected by the lens. The four laser lines are fiber coupled via collimating lenses (light blue in the sketch). The red laser source having frequency 1 is sent towards the test masses here represented as flat mirrors. The outer mass (blue line) has a hole that allows part of the beam to reach the inner mass (green line). Both mirrors reflect back the laser light to the beam splitter, which has experienced two different optical paths. The same beam splitter is illuminated by the blue laser source having frequency 2 ; here, the two laser beams interfere and generate an heterodyne signal at the frequency = 2 1. The central part of the superposed beams delivers information about the inner mass position, the external part about the outer mass position. The two parts are eventually separated by a mirror so that they are sent by two different fibers to photo-detectors. The phase difference between the two heterodyne signals is measured with a phase meter. The differential displacement between the two test masses is then obtained by multiplying measured phase difference by /2 times the laser wavelength. For displacements larger than /2, the phase meter tracks integer counts. Fig. 7. Possible realization of the beam launcher (BL) fixed on the PGB (not visible) and aiming at the test masses. The BL assembly consists in four fibers (two inputs and two outputs) plus collimating lenses, as depicted in Fig. 5. No electronics is present on the BL assembly. The collimated laser beams are folded, split and combined by means of optical prisms. The detail of a possible realization of the beam launcher and separation scheme is shown in Fig. 7. A scheme of the reflectors system (CCR) based on a split corner cube is shown in Fig. 8: a CCR with truncated vertex is embedded into the outer mass and retroreflects the external part of the laser beam. The central part of the laser beam passes through the polished surfaces of the truncated CCR and is reflected back by a smaller CCR embedded in the inner mass. Fig. 6. schematic diagram of the opto-electronic set-up of the laser gauge. A schematic diagram of the GG laser metrology system is shown in Fig. 6. The laser source is a continuous-wave nonplanar ring-cavity oscillator (NPRO) with wavelength = μm. The laser beam is split into two parts and undergoes differential frequency shift with the use of two acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) to generate 2 and 1. One laser frequency is used as the measurement beam, the other as the common local oscillator. Optical fiber couplers split the laser beams into nine parts to feed the nine laser gauges mounted around the test masses. The interferometer s beam launchers send the measurement beams to interrogate the outer and inner test masses. The power of the laser beams reflected on the test masses is kept as low as 1 μw in order to have a negligible effect due to the radiation pressure on the displacement of the masses. This power level, on the other hand, is high enough to guarantee the S/N level to the interferometric signal. Fig. 8. Conceptual schematic of the possible launch optics for the laser gauge based on split corner-cube-retro-reflectors. A 3D representation of the two CCR is shown at the right. IV. THE DIFFRACTION ISSUE As explained in the previous chapter, the main error source in heterodyne interferometers is the cross-talk between the two optical paths that causes nonlinearities in the displacement vs phase function. In the proposed interferometer the beam separation is based on physical separation between two concentric optical paths. A simplified sketch is represented in Fig 9. In a practical realization, because of the limited dimensions of the optical head, the apertures and stops that implement the spatial separation will unavoidably cause diffraction. That means that part of the rays are deflected from 593
4 their straight path, thus going in the wroong direction. In other words, part of the signal that should go onto one detector, in fact, goes onto the other onne (see Fig. 10). Roughly speaking, the proportion of the mixing m effect (ratio between the unwanted and the wanted signal) generate proportional nonlinearity. The displacemennt error caused by diffraction is a fraction of the maximum displacement d error given by the ratio of the test masses relative displacement over o the masses, the λ/4: the smaller the relative displacement of smaller the effect of the diffraction error on the measured displacement. In GG, with 1 nm separationn between the test masses, nonlinearities to the level of 0.01% would w give 0.2 pm displacement error. Fig. 9. Simplified representation of the measuremennt beams in the laser gauge. For the sake of clarity, the mass reflectors are represented in their own function as stop for a portion of the beam (first stop starting from the left). The beam is represented in a straight paath from the fiber laser source (left), to the fiber detector (right). a) path of o the laser reflected on the external mass reaching the detector D1. b) patth of the laser reflected on the internal mass reaching detector D2. c) pathh of the laser reflected on the external mass stopped to prevent reaching detector D1. d) path of the laser reflected by the internal mass stopped to prevent reaching C sensor and the profiles are recorded by a high dynamic CCD compared with the numerical simulation. The results of the experiment are shown in Figs. 12 to 14. Fig. 11. experimental set-up for the evvaluation of the diffraction effect. The first stop represent the mass mirrror and can be an aperture (simulating the internal mass) or a stop (sim mulating the external mass). The second stop represents the mirror useed to redirect the beam towards the detectors. Different stop and iris diameters have been used. The diameter size and the distance between thhe stops and the detector are scaled to take in account the difference between b the simulator wavelength (633 nm) and the laser gauge wavelenggth (1064 nm). Fig. 12. Diffraction patterns and diffrraction profiles. a) a 7 mm iris placed along the laser path selects the ceentral part of the beam (representing the inner mass mirror). Diffractionn distortion near the circumference is evident. The curve at the center is i the normalized intensity profile along the diameter. The curve at thee right side is a numerical simulation obtained with similar geomatricaal configuration. b) The iris is removed and a 7 mm circular stop is placed close to the camera. detector D2. Fig. 10. Effect of the diffraction on the laser beam pathhs. Whenever the laser beam is truncated by a stop, diffraction occurs (red ( paths). This effect causes part of the beam to deviate off the right patth and eventually reach the «wrong» detector. In other words in a real im mplementation the stops are not able to completely cancel the undesired siggnal In order to evaluate the feasibility of a miiniaturized optical head keeping the diffraction effect below the maximum allowed level, we have carried out numericcal simulations as well as a preliminary experiment. The simple s diffraction experiment (shown in Fig. 11) is based on a red laser source (633 nm) and makes use of irises and stops s of the size foreseen for the GG-LG, scaled for the wavelength w factor between 633 nm/1064 nm. The diffracttion patterns are 594 Fig. 13. Effect of the combination of ris and stop (simulator of the internal mass signal). The two objects of figure 12 are now on the beam, simulating one of the configuratiions of fig 10. A residual undesired ring is visible. The residual power iss close to 1 % of the overall signal. A similar result is obtained with thhe numerical simulation at the up right side.
5 Fig. 14. Minimization of the spurious radiation. In order to reduce the spurious signal a 8 mm stop is used in place of the 7 mm one. The residual diffracted power is greatly reduced. Note that the image and the intensity profile are on x10 scale with respect to figure 13. The ratio between the residual and the wanted signal is now close to Both experimental and numerical results shown in figures 12 and 13 demonstrate that by using iris and stop of the same size a residual diffraction effect (ratio between the spurious and wanted signal) of the order of 1% is obtained. It is easy to demonstrate that by using a slightly larger stop the effect can be reduced down to 0.01% (see Fig. 14). That means that a separation of the two measurement channels to the required level can be easily obtained with a proper sizing of the apertures with a minimum effect on the intensity of the overall signal. V. CONCLUSIONS GG requires a metrology system to measure the differential displacement between the test masses with a resolution of 1 pm/ Hz at the spin frequency of 1 Hz to which the target signal is up-converted from the low orbital frequency of 1.7x10-4 Hz. It is well established that a readout based on laser interferometry can perform better than capacitance sensors. The laser interferometers envisaged for GG exploit spatial separation between the measurement arms in order to reduce nonlinearities to the required level. A preliminary experiment has demonstrated the feasibility of the reduction of the diffraction effect to the required 0.01%. A breadboard of the laser gauge will be realized: a prototype of the beam launcher will be built and tested against a split corner-cube target in a vibration-controlled environment and in vacuum in order to test the performances at the real scale and to optimize the optoelectronic set up. The breadboard will be realized making use of standard components (laser, detectors optical elements etc.).. REFERENCES [1] A.M. Nobili et al., Class. Quantum Grav. 29, (2012) [2] S. Schlamminger et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, (2008) [3] J. Mueller, F. Homan & L. Biskupek, Class. Quantum Grav. 29, (2012) [4] J. G. Williams, S. G. Turyshev & D. H. Boggs, Class. Quantum Grav. 29, (2012) [5] S. Fray et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, (2004) [6] A. Bonnin,. et. Al., Phys. Rev. A 88, (5pp) (2013) [7] D. Schlippert et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, (2014) [8] M. G. Tarallo et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, (2014) [9] M. Shao SIM: the space interferometry mission, Proc. SPIE 3350, Astronomical Interferometry, 536 (1998); doi: / [10] M. Pisani et al., Metrologia (2012); doi: / /49/4/455 [11] G. Cavagnero et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, (2005); doi: /
LIG: a miniature 10 pm accuracy Laser Interferometer Gauge Report of work performed under ESA contract ITI /16/NL/MH/GM
 LIG: a miniature 10 pm accuracy Laser Interferometer Gauge Report of work performed under ESA contract ITI 4000116275/16/NL/MH/GM Written by Anna M. Nobili, Marco Pisani & Massimo Zucco March 2017; Final
LIG: a miniature 10 pm accuracy Laser Interferometer Gauge Report of work performed under ESA contract ITI 4000116275/16/NL/MH/GM Written by Anna M. Nobili, Marco Pisani & Massimo Zucco March 2017; Final
Characterization of Picometer Repeatability Displacement Metrology Gauges
 Characterization of Picometer Repeatability Displacement Metrology Gauges This paper was presented at ODIMAP III, the 3 rd Topical Meeting on Optoelectronic Distance/Displacement Measurements and Applications,
Characterization of Picometer Repeatability Displacement Metrology Gauges This paper was presented at ODIMAP III, the 3 rd Topical Meeting on Optoelectronic Distance/Displacement Measurements and Applications,
Optical Metrology Applications at TAS-I in support of Gravity and Fundamental Physics
 Optical Metrology Applications at TAS-I in support of Gravity and Fundamental Physics Template reference : 100181670S-EN Stefano Cesare, Thales Alenia Space Italia, Torino Workshop GG/GGG: state of the
Optical Metrology Applications at TAS-I in support of Gravity and Fundamental Physics Template reference : 100181670S-EN Stefano Cesare, Thales Alenia Space Italia, Torino Workshop GG/GGG: state of the
Renewal of the gage-block interferometer at INRIM
 Renewal of the gage-block interferometer at INRIM R. Bellotti, M. Franco, G. B. Picotto* and M. Pometto Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM), Strada delle Cacce 73, 10135 Torino, Italy * Corresponding
Renewal of the gage-block interferometer at INRIM R. Bellotti, M. Franco, G. B. Picotto* and M. Pometto Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM), Strada delle Cacce 73, 10135 Torino, Italy * Corresponding
Pioneer anomaly: Implications for LISA?
 Pioneer anomaly: Implications for LISA? Denis Defrère Astrophysics and Geophysics Institute of Liege (Belgium) Andreas Rathke EADS Astrium GmbH Friedrichshafen (Germany) ISSI Meeting - Bern November 10th
Pioneer anomaly: Implications for LISA? Denis Defrère Astrophysics and Geophysics Institute of Liege (Belgium) Andreas Rathke EADS Astrium GmbH Friedrichshafen (Germany) ISSI Meeting - Bern November 10th
arxiv:gr-qc/ v2 16 Feb 2006
 Acceleration disturbances due to local gravity gradients in ASTROD I arxiv:gr-qc/0510045v2 16 Feb 2006 Sachie Shiomi Department of Physics, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan 30013 R.O.C. E-mail:
Acceleration disturbances due to local gravity gradients in ASTROD I arxiv:gr-qc/0510045v2 16 Feb 2006 Sachie Shiomi Department of Physics, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan 30013 R.O.C. E-mail:
Low Coherence Vibration Insensitive Fizeau Interferometer
 Low Coherence Vibration Insensitive Fizeau Interferometer Brad Kimbrough, James Millerd, James Wyant, John Hayes 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop, Suite 146, Tucson, AZ 85706 (520) 294-5600,
Low Coherence Vibration Insensitive Fizeau Interferometer Brad Kimbrough, James Millerd, James Wyant, John Hayes 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop, Suite 146, Tucson, AZ 85706 (520) 294-5600,
A rotating differential accelerometer for testing the equivalence principle in space: results from laboratory tests of a ground prototype
 A rotating differential accelerometer for testing the equivalence principle in space: results from laboratory tests of a ground prototype A.M. Nobili, D. Bramanti, G. Comandi, R. Toncelli Space Mechanics
A rotating differential accelerometer for testing the equivalence principle in space: results from laboratory tests of a ground prototype A.M. Nobili, D. Bramanti, G. Comandi, R. Toncelli Space Mechanics
1
 Daniel.Schuetze@aei.mpg.de 1 Satellite gravimetry Mapping the global gravity field Static and dynamic components Many applications in geosciences Techniques Orbit determination and tracking Satellite-to-satellite
Daniel.Schuetze@aei.mpg.de 1 Satellite gravimetry Mapping the global gravity field Static and dynamic components Many applications in geosciences Techniques Orbit determination and tracking Satellite-to-satellite
GG studies at TAS-I: state of the art
 GG studies at TAS-I: state of the art A. Anselmi INRIM, 24-10-2014 83230350-DOC-TAS-EN-002 GG@ThalesAleniaSpace! 1996 Early experiment concept presented to ESA HQ! Industrial support on satellite & drag-free
GG studies at TAS-I: state of the art A. Anselmi INRIM, 24-10-2014 83230350-DOC-TAS-EN-002 GG@ThalesAleniaSpace! 1996 Early experiment concept presented to ESA HQ! Industrial support on satellite & drag-free
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors
 Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors Rene Zehnder, James H. Burge and Chunyu Zhao College of Optical Sciences, the University of Arizona 1630 E. University Blvd,
Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors Rene Zehnder, James H. Burge and Chunyu Zhao College of Optical Sciences, the University of Arizona 1630 E. University Blvd,
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
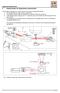 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Nanosat Science Instruments for Modular Gravitational Reference Sensor (MGRS)
 Microgravity White Paper Decadal Survey on Biological and Physical Sciences in Space Fundamental Physics Sciences (FPS) Applied Physical Sciences (APS) Nanosat Science Instruments for Modular Gravitational
Microgravity White Paper Decadal Survey on Biological and Physical Sciences in Space Fundamental Physics Sciences (FPS) Applied Physical Sciences (APS) Nanosat Science Instruments for Modular Gravitational
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5955/974/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Observation of Half-Quantum Vortices in an Exciton-Polariton Condensate K. G. Lagoudakis,* T. Ostatnický, A. V. Kavokin,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5955/974/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Observation of Half-Quantum Vortices in an Exciton-Polariton Condensate K. G. Lagoudakis,* T. Ostatnický, A. V. Kavokin,
1 N star coupler as a distributed fiber-optic strain sensor in a white-light interferometer
 1 star coupler as a distributed fiber-optic strain sensor in a white-light interferometer Libo Yuan and Limin Zhou A novel technique of using a 1 star fiber optic coupler as a distributed strain sensor
1 star coupler as a distributed fiber-optic strain sensor in a white-light interferometer Libo Yuan and Limin Zhou A novel technique of using a 1 star fiber optic coupler as a distributed strain sensor
A broad band detector of Gravitational Waves: The dual torus
 A broad band detector of Gravitational Waves: The dual torus M.BONALDI 1, M.CERDONIO 2, L.CONTI 2, M.PINARD 3, G.A.PRODI 4, L.TAFFARELLO 5, J.P.ZENDRI 5 1 Istituto di Fotonica e Nanotecnologie, ITC-CNR,
A broad band detector of Gravitational Waves: The dual torus M.BONALDI 1, M.CERDONIO 2, L.CONTI 2, M.PINARD 3, G.A.PRODI 4, L.TAFFARELLO 5, J.P.ZENDRI 5 1 Istituto di Fotonica e Nanotecnologie, ITC-CNR,
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
INTERNAL THALES ALENIA SPACE
 Workshop Galileo Galilei (GG) and GGG lab prototype: state of the art and new possibilities Template reference : 100181670S-EN GG error budget from the end-to-end simulator developed at TAS-I Giuseppe
Workshop Galileo Galilei (GG) and GGG lab prototype: state of the art and new possibilities Template reference : 100181670S-EN GG error budget from the end-to-end simulator developed at TAS-I Giuseppe
Simultaneous Temperature and Strain Sensing for Cryogenic Applications Using Dual-Wavelength Fiber Bragg Gratings
 Simultaneous Temperature and Strain Sensing for Cryogenic Applications Using Dual-Wavelength Fiber Bragg Gratings Meng-Chou Wu *, William H. Prosser NASA, Langley Research Center, MS 231, Hampton, VA,
Simultaneous Temperature and Strain Sensing for Cryogenic Applications Using Dual-Wavelength Fiber Bragg Gratings Meng-Chou Wu *, William H. Prosser NASA, Langley Research Center, MS 231, Hampton, VA,
and another with a peak frequency ω 2
 Physics Qualifying Examination Part I 7-Minute Questions September 13, 2014 1. A sealed container is divided into two volumes by a moveable piston. There are N A molecules on one side and N B molecules
Physics Qualifying Examination Part I 7-Minute Questions September 13, 2014 1. A sealed container is divided into two volumes by a moveable piston. There are N A molecules on one side and N B molecules
iprom Optical Interferometry Prof. Dr. -Ing. Rainer Tutsch Institut für Produktionsmesstechnik IPROM Technische Universität Braunschweig
 Optical Interferometry Prof. Dr. -Ing. Rainer Tutsch Institut für Produktionsmesstechnik IPROM Technische Universität Braunschweig Frontiers of Metrology April 1, 01 I P NSTITUT FÜR RODUKTIONSMESSTECHNIK
Optical Interferometry Prof. Dr. -Ing. Rainer Tutsch Institut für Produktionsmesstechnik IPROM Technische Universität Braunschweig Frontiers of Metrology April 1, 01 I P NSTITUT FÜR RODUKTIONSMESSTECHNIK
Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a).
 7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
Astronomy. Optics and Telescopes
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Gravitational Waves & Precision Measurements
 Gravitational Waves & Precision Measurements Mike Smith 1 -20 2 HOW SMALL IS THAT? Einstein 1 meter 1/1,000,000 3 1,000,000 smaller Wavelength of light 10-6 meters 1/10,000 4 10,000 smaller Atom 10-10
Gravitational Waves & Precision Measurements Mike Smith 1 -20 2 HOW SMALL IS THAT? Einstein 1 meter 1/1,000,000 3 1,000,000 smaller Wavelength of light 10-6 meters 1/10,000 4 10,000 smaller Atom 10-10
2.71. Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Experiment 6: Interferometers
 Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers
 Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers Gabriele Rosi Quantum gases, fundamental interactions and cosmology conference 5-7 October 017, Pisa Outline Introduction to atom interferometry
Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers Gabriele Rosi Quantum gases, fundamental interactions and cosmology conference 5-7 October 017, Pisa Outline Introduction to atom interferometry
Fundamental Physics in Space S. Vitale, University of Trento ESO-Garching S. Vitale 1
 Fundamental Physics in Space S. Vitale, University of Trento Vitale@science.unitn.it ESO-Garching-15-09-03 S. Vitale 1 Using Space to Investigate Fundamental Laws of Physics: Quantum measurements, entanglement,
Fundamental Physics in Space S. Vitale, University of Trento Vitale@science.unitn.it ESO-Garching-15-09-03 S. Vitale 1 Using Space to Investigate Fundamental Laws of Physics: Quantum measurements, entanglement,
Postulate 2: Light propagates through empty space with a definite speed (c) independent of the speed of the source or of the observer.
 Einstein s Special Theory of Relativity 1 m E = mv E =m*c m* = KE =m*c - m c 1- v p=mv p=m*v c 9-1 Postulate 1: The laws of physics have the same form in all inertial reference frames. Postulate : Light
Einstein s Special Theory of Relativity 1 m E = mv E =m*c m* = KE =m*c - m c 1- v p=mv p=m*v c 9-1 Postulate 1: The laws of physics have the same form in all inertial reference frames. Postulate : Light
Atom interferometry in microgravity: the ICE project
 Atom interferometry in microgravity: the ICE project (4) G. Stern 1,2, R. Geiger 1, V. Ménoret 1,B. Battelier 1, R. Charrière 3, N. Zahzam 3, Y. Bidel 3, L. Mondin 4, F. Pereira 2, A. Bresson 3, A. Landragin
Atom interferometry in microgravity: the ICE project (4) G. Stern 1,2, R. Geiger 1, V. Ménoret 1,B. Battelier 1, R. Charrière 3, N. Zahzam 3, Y. Bidel 3, L. Mondin 4, F. Pereira 2, A. Bresson 3, A. Landragin
MANIPAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SCHEME OF EVAUATION MANIPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOOGY MANIPA UNIVERSITY, MANIPA SECOND SEMESTER B.Tech. END-SEMESTER EXAMINATION - MAY SUBJECT: ENGINEERING PHYSICS (PHY/) Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 5 Note: Answer
SCHEME OF EVAUATION MANIPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOOGY MANIPA UNIVERSITY, MANIPA SECOND SEMESTER B.Tech. END-SEMESTER EXAMINATION - MAY SUBJECT: ENGINEERING PHYSICS (PHY/) Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 5 Note: Answer
Gravitational Waves and LIGO: A Technical History
 Gravitational Waves and LIGO: A Technical History Stan Whitcomb IEEE SV Tech History Committee Event 11 October 2018 LIGO-G180195-v3 Goal of Talk Review a few of the technical developments that enabled
Gravitational Waves and LIGO: A Technical History Stan Whitcomb IEEE SV Tech History Committee Event 11 October 2018 LIGO-G180195-v3 Goal of Talk Review a few of the technical developments that enabled
Exploring the Gravitational Wave Universe Challenges for a LISA Successor
 Exploring the Gravitational Wave Universe Challenges for a LISA Successor H Ward University of Glasgow Cosmic Vision 2015 2025 Paris 15 th September 2004 With contributions from : P Bender, K Danzmann,
Exploring the Gravitational Wave Universe Challenges for a LISA Successor H Ward University of Glasgow Cosmic Vision 2015 2025 Paris 15 th September 2004 With contributions from : P Bender, K Danzmann,
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. Treat all balls with mass as point masses. 1.
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. Treat all balls with mass as point masses. 1.
AN OVERVIEW OF LIGO Adapted from material developed by Brock Wells Robert L. Olds Junior High School, Connell, WA August 2001
 AN OVERVIEW OF LIGO Adapted from material developed by Brock Wells Robert L. Olds Junior High School, Connell, WA August 2001 The purpose of this guide is to provide background about the LIGO project at
AN OVERVIEW OF LIGO Adapted from material developed by Brock Wells Robert L. Olds Junior High School, Connell, WA August 2001 The purpose of this guide is to provide background about the LIGO project at
Control of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
 Control of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna P. G. Maghami, T. T. Hyde NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Guidance, Navigation and Control Division Greenbelt, MD 20771 J. Kim Swales Aerospace, Inc.
Control of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna P. G. Maghami, T. T. Hyde NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Guidance, Navigation and Control Division Greenbelt, MD 20771 J. Kim Swales Aerospace, Inc.
Universe. Chapter 6. Optics and Telescopes 8/12/2015. By reading this chapter, you will learn. Tenth Edition
 Roger Freedman Robert Geller William Kaufmann III Universe Tenth Edition Chapter 6 Optics and Telescopes By reading this chapter, you will learn 6 1 How a refracting telescope uses a lens to form an image
Roger Freedman Robert Geller William Kaufmann III Universe Tenth Edition Chapter 6 Optics and Telescopes By reading this chapter, you will learn 6 1 How a refracting telescope uses a lens to form an image
Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy
 Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy An FT-IR Spectrometer is an instrument which acquires broadband NIR to FIR spectra. Unlike a dispersive instrument, i.e. grating monochromator or spectrograph, an FT-IR
Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy An FT-IR Spectrometer is an instrument which acquires broadband NIR to FIR spectra. Unlike a dispersive instrument, i.e. grating monochromator or spectrograph, an FT-IR
Particle-Wave Duality and Which-Way Information
 Particle-Wave Duality and Which-Way Information Graham Jensen and Samantha To University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S. September 25, 2013 Abstract Samantha To This experiment aimed to support
Particle-Wave Duality and Which-Way Information Graham Jensen and Samantha To University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S. September 25, 2013 Abstract Samantha To This experiment aimed to support
LISA Pathfinder measuring pico-meters and femto-newtons in space
 LISA Pathfinder measuring pico-meters and femto-newtons in space M Hewitson for the LPF team Barcelona, February 15th 2012 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space Push down to
LISA Pathfinder measuring pico-meters and femto-newtons in space M Hewitson for the LPF team Barcelona, February 15th 2012 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space Push down to
VACUUM SUPPORT FOR A LARGE INTERFEROMETRIC REFERENCE SURFACE
 VACUUM SUPPORT FOR A LARGE INTERFEROMETRIC REFERENCE SURFACE Masaki Hosoda, Robert E. Parks, and James H. Burge College of Optical Sciences University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona 85721 OVERVIEW This paper
VACUUM SUPPORT FOR A LARGE INTERFEROMETRIC REFERENCE SURFACE Masaki Hosoda, Robert E. Parks, and James H. Burge College of Optical Sciences University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona 85721 OVERVIEW This paper
TITLE: Interferometry: The Michelson Interferometer
 TITLE: Interferometry: The Michelson Interferometer Contributed by: Yolanda Flores Baboquivari High School Summary: The lesson begins with a demonstration introducing students to interference fringes formed
TITLE: Interferometry: The Michelson Interferometer Contributed by: Yolanda Flores Baboquivari High School Summary: The lesson begins with a demonstration introducing students to interference fringes formed
Measurments with Michelson interferometers
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Universe. Chapter 6. Optics and Telescopes 11/16/2014. By reading this chapter, you will learn. Tenth Edition
 Roger Freedman Robert Geller William Kaufmann III Universe Tenth Edition Chapter 6 Optics and Telescopes By reading this chapter, you will learn 6 1 How a refracting telescope uses a lens to form an image
Roger Freedman Robert Geller William Kaufmann III Universe Tenth Edition Chapter 6 Optics and Telescopes By reading this chapter, you will learn 6 1 How a refracting telescope uses a lens to form an image
Experiment 3 1. The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Optics Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab
 Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab Lab #6 - Interference Microscopes The purpose of this lab is to observe the samples provided using two different interference microscopes --
Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab Lab #6 - Interference Microscopes The purpose of this lab is to observe the samples provided using two different interference microscopes --
x Contents Segmented Mirror Telescopes Metal and Lightweight Mirrors Mirror Polishing
 Contents 1 Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes... 1 1.1 A Brief History of Optical Telescopes.................... 1 1.2 General Astronomical Requirements..................... 6 1.2.1 Angular Resolution.............................
Contents 1 Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes... 1 1.1 A Brief History of Optical Telescopes.................... 1 1.2 General Astronomical Requirements..................... 6 1.2.1 Angular Resolution.............................
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In their manuscript Dual Matter-Wave Inertial Sensors in Weightlessness Brynle Barrett et al. describe an dual species atom interferometer experiment
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In their manuscript Dual Matter-Wave Inertial Sensors in Weightlessness Brynle Barrett et al. describe an dual species atom interferometer experiment
The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Thermal And Near infrared Sensor for carbon Observation (TANSO) On board the Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT) Research Announcement
 Thermal And Near infrared Sensor for carbon Observation (TANSO) On board the Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT) Research Announcement Appendix A Outlines of GOSAT and TANSO Sensor GOSAT (Greenhouse
Thermal And Near infrared Sensor for carbon Observation (TANSO) On board the Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT) Research Announcement Appendix A Outlines of GOSAT and TANSO Sensor GOSAT (Greenhouse
The status of VIRGO. To cite this version: HAL Id: in2p
 The status of VIRGO E. Tournefier, F. Acernese, P. Amico, M. Al-Shourbagy, S. Aoudia, S. Avino, D. Babusci, G. Ballardin, R. Barillé, F. Barone, et al. To cite this version: E. Tournefier, F. Acernese,
The status of VIRGO E. Tournefier, F. Acernese, P. Amico, M. Al-Shourbagy, S. Aoudia, S. Avino, D. Babusci, G. Ballardin, R. Barillé, F. Barone, et al. To cite this version: E. Tournefier, F. Acernese,
Vibration-Free Pulse Tube Cryocooler System for Gravitational Wave Detectors I
 1 Vibration-Free Pulse Tube Cryocooler System for Gravitational Wave Detectors I - Vibration-Reduction Method and Measurement - T. Tomaru A, T. Suzuki A, T. Haruyama A, T. Shintomi A, N. Sato A, A. Yamamoto
1 Vibration-Free Pulse Tube Cryocooler System for Gravitational Wave Detectors I - Vibration-Reduction Method and Measurement - T. Tomaru A, T. Suzuki A, T. Haruyama A, T. Shintomi A, N. Sato A, A. Yamamoto
A Multipass Optics for Quantum-Well-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers
 Multipass-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers 37 A Multipass Optics for Quantum-Well-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers Markus Polanik The pump absorption of quantum-well-pumped semiconductor disk lasers can
Multipass-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers 37 A Multipass Optics for Quantum-Well-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers Markus Polanik The pump absorption of quantum-well-pumped semiconductor disk lasers can
Wave Nature of Matter
 Wave Nature of Matter Wave-Particle Duality de Broglie proposed that particles with momentum could have an associated wavelength (converse of photons having momentum) de Broglie wavelength h λ = p or p
Wave Nature of Matter Wave-Particle Duality de Broglie proposed that particles with momentum could have an associated wavelength (converse of photons having momentum) de Broglie wavelength h λ = p or p
Past and Future General Relativity Experiments: Equivalence Principle, Time Delay, and Black Holes. Irwin Shapiro 21 October 2005
 Past and Future General Relativity Experiments: Equivalence Principle, Time Delay, and Black Holes Irwin Shapiro 21 October 2005 Translation of Title (a.k.a Outline) Tests of the (Weak) Equivalence Principle
Past and Future General Relativity Experiments: Equivalence Principle, Time Delay, and Black Holes Irwin Shapiro 21 October 2005 Translation of Title (a.k.a Outline) Tests of the (Weak) Equivalence Principle
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Robust and Miniaturized Interferometric Distance Sensor for In-Situ Turning Process Monitoring
 Robust and Miniaturized Interferometric Distance Sensor for In-Situ Turning Process Monitoring F. Dreier, P. Günther, T. Pfister, J. Czarske, Technische Universität Dresden, Laboratory for Measuring and
Robust and Miniaturized Interferometric Distance Sensor for In-Situ Turning Process Monitoring F. Dreier, P. Günther, T. Pfister, J. Czarske, Technische Universität Dresden, Laboratory for Measuring and
Challenges for the next generation stellar interferometer. Markus Schöller European Southern Observatory January 29, 2009
 Challenges for the next generation stellar interferometer Markus Schöller European Southern Observatory January 29, 2009 VLTI Four 8.2m telescopes (UTs) All equipped with AO (MACAO) Six Baselines 47m-130m
Challenges for the next generation stellar interferometer Markus Schöller European Southern Observatory January 29, 2009 VLTI Four 8.2m telescopes (UTs) All equipped with AO (MACAO) Six Baselines 47m-130m
1 Naval Research Laboratory Remote Sensing Division, Code Aberdeen Ave SE Kirtland AFB, NM 87117
 Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Telescope Program at the Naval Research Laboratory Sergio R. Restaino 1, Ty Martinez 1, Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Christopher C. Wilcox 1, S. Teare 2, Robert Romeo 3,
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Telescope Program at the Naval Research Laboratory Sergio R. Restaino 1, Ty Martinez 1, Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Christopher C. Wilcox 1, S. Teare 2, Robert Romeo 3,
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer
 Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT
 5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT Gradient Index Measurement with Temperature MODEL OEK-100 PROJECT #4 50 5.1 Introduction It is possible to measure the change in index of refraction of a
5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT Gradient Index Measurement with Temperature MODEL OEK-100 PROJECT #4 50 5.1 Introduction It is possible to measure the change in index of refraction of a
NA LASER GUIDE STAR AO WITH DYNAMICAL REFOCUS
 Florence, Italy. Adaptive May 2013 Optics for Extremely Large Telescopes III ISBN: 978-88-908876-0-4 DOI: 10.12839/AO4ELT3.13893 NA LASER GUIDE STAR AO WITH DYNAMICAL REFOCUS Sebastian Rabien 1,a, Fernando
Florence, Italy. Adaptive May 2013 Optics for Extremely Large Telescopes III ISBN: 978-88-908876-0-4 DOI: 10.12839/AO4ELT3.13893 NA LASER GUIDE STAR AO WITH DYNAMICAL REFOCUS Sebastian Rabien 1,a, Fernando
Supplemental material for Bound electron nonlinearity beyond the ionization threshold
 Supplemental material for Bound electron nonlinearity beyond the ionization threshold 1. Experimental setup The laser used in the experiments is a λ=800 nm Ti:Sapphire amplifier producing 42 fs, 10 mj
Supplemental material for Bound electron nonlinearity beyond the ionization threshold 1. Experimental setup The laser used in the experiments is a λ=800 nm Ti:Sapphire amplifier producing 42 fs, 10 mj
INAF-Osservatorio astronomico di Torino Technical Report nr.156
 INAF-Osservatorio astronomico di Torino Technical Report nr.156 ISAS Optical Design Report Alberto Riva; Mario Gai; Alberto Vecchiato Pino Torinese, 26 marzo 2012 ISAS Optical Design Report Alberto Riva
INAF-Osservatorio astronomico di Torino Technical Report nr.156 ISAS Optical Design Report Alberto Riva; Mario Gai; Alberto Vecchiato Pino Torinese, 26 marzo 2012 ISAS Optical Design Report Alberto Riva
Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer
 CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.710 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.710 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light
 CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
MODERN INTERFEROMETRY
 MODERN INTERFEROMETRY * No actual laser photons were harmed during the filming of this cover. Build Michelson, Sagnac, and Mach-Zehnder Interferometers Generate and Count Interference Fringes Manually
MODERN INTERFEROMETRY * No actual laser photons were harmed during the filming of this cover. Build Michelson, Sagnac, and Mach-Zehnder Interferometers Generate and Count Interference Fringes Manually
LASER TRAPPING MICRO-PROBE FOR NANO-CMM
 LASER TRAPPING MICRO-PROBE FOR NANO-CMM T. Miyoshi, Y. Takaya and S. Takahashi Division of Production and Measurement System Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering and Systems Osaka University,
LASER TRAPPING MICRO-PROBE FOR NANO-CMM T. Miyoshi, Y. Takaya and S. Takahashi Division of Production and Measurement System Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering and Systems Osaka University,
Astrophysics & Gravitational Physics with the LISA Mission
 Astrophysics & Gravitational Physics with the LISA Mission Peter L. Bender JILA, University of Colorado, and NIST Workshop on Robotic Science from the Moon Boulder, CO 5-6 October, 2010 LISA Overview The
Astrophysics & Gravitational Physics with the LISA Mission Peter L. Bender JILA, University of Colorado, and NIST Workshop on Robotic Science from the Moon Boulder, CO 5-6 October, 2010 LISA Overview The
Optics and Telescope. Chapter Six
 Optics and Telescope Chapter Six ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap.
Optics and Telescope Chapter Six ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap.
Michelson Interferometer. crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Chapter 13: universal gravitation
 Chapter 13: universal gravitation Newton s Law of Gravitation Weight Gravitational Potential Energy The Motion of Satellites Kepler s Laws and the Motion of Planets Spherical Mass Distributions Apparent
Chapter 13: universal gravitation Newton s Law of Gravitation Weight Gravitational Potential Energy The Motion of Satellites Kepler s Laws and the Motion of Planets Spherical Mass Distributions Apparent
Experiment Design and Performance. G. Catastini TAS-I (BUOOS)
 Experiment Design and Performance G. Catastini TAS-I (BUOOS) 10 EP and the GRT Einstein s General Relativity Theory Weak Equivalence Principle: all test particles at the same space-time point in a given
Experiment Design and Performance G. Catastini TAS-I (BUOOS) 10 EP and the GRT Einstein s General Relativity Theory Weak Equivalence Principle: all test particles at the same space-time point in a given
(Refer Slide Time: 1: 19)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection
 Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection M. Tacca Nikhef - Amsterdam Nikhef- 2017 July 14th Born in Novara (Italy) Introducing Myself PostDoc Fellow @ Nikhef (since July 2017) Laurea & PhD @
Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection M. Tacca Nikhef - Amsterdam Nikhef- 2017 July 14th Born in Novara (Italy) Introducing Myself PostDoc Fellow @ Nikhef (since July 2017) Laurea & PhD @
Development of a cryogenic compact interferometric displacement sensor
 Development of a cryogenic compact interferometric displacement sensor Fabián E. Peña Arellano National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Outline of the presentation Motivation: local position sensor for
Development of a cryogenic compact interferometric displacement sensor Fabián E. Peña Arellano National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Outline of the presentation Motivation: local position sensor for
Squeezed Light for Gravitational Wave Interferometers
 Squeezed Light for Gravitational Wave Interferometers R. Schnabel, S. Chelkowski, H. Vahlbruch, B. Hage, A. Franzen, and K. Danzmann. Institut für Atom- und Molekülphysik, Universität Hannover Max-Planck-Institut
Squeezed Light for Gravitational Wave Interferometers R. Schnabel, S. Chelkowski, H. Vahlbruch, B. Hage, A. Franzen, and K. Danzmann. Institut für Atom- und Molekülphysik, Universität Hannover Max-Planck-Institut
Interferometers. PART 1: Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the most useful of all optical instru
 Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Machine Positioning Uncertainty with Laser Interferometer Feedback
 Machine Positioning Uncertainty with Laser Interferometer Feedback The purpose of this discussion is to explain the major contributors to machine positioning uncertainty in systems with laser interferometer
Machine Positioning Uncertainty with Laser Interferometer Feedback The purpose of this discussion is to explain the major contributors to machine positioning uncertainty in systems with laser interferometer
Picometre metrology. The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars
 Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
Light as Wave Motion p. 1 Huygens' Ideas p. 2 Newton's Ideas p. 8 Complex Numbers p. 10 Simple Harmonic Motion p. 11 Polarized Waves in a Stretched
 Introduction p. xvii Light as Wave Motion p. 1 Huygens' Ideas p. 2 Newton's Ideas p. 8 Complex Numbers p. 10 Simple Harmonic Motion p. 11 Polarized Waves in a Stretched String p. 16 Velocities of Mechanical
Introduction p. xvii Light as Wave Motion p. 1 Huygens' Ideas p. 2 Newton's Ideas p. 8 Complex Numbers p. 10 Simple Harmonic Motion p. 11 Polarized Waves in a Stretched String p. 16 Velocities of Mechanical
Distortion mapping correction in aspheric null testing
 Distortion mapping correction in aspheric null testing M. Novak, C. Zhao, J. H. Burge College of Optical Sciences, 1630 East University Boulevard, Tucson, AZ, 85721 ABSTRACT We describe methods to correct
Distortion mapping correction in aspheric null testing M. Novak, C. Zhao, J. H. Burge College of Optical Sciences, 1630 East University Boulevard, Tucson, AZ, 85721 ABSTRACT We describe methods to correct
Hybrid Atom-Optical Interferometry for Gravitational Wave Detection and Geophysics
 Hybrid Atom-Optical Interferometry for Gravitational Wave Detection and Geophysics Remi Geiger, SYRTE for the MIGA consortium EGAS 46, July 3rd 2014, Lille, France http://syrte.obspm.fr/tfc/capteurs_inertiels
Hybrid Atom-Optical Interferometry for Gravitational Wave Detection and Geophysics Remi Geiger, SYRTE for the MIGA consortium EGAS 46, July 3rd 2014, Lille, France http://syrte.obspm.fr/tfc/capteurs_inertiels
Sensitivity limits of atom interferometry gravity gradiometers and strainmeters. Fiodor Sorrentino INFN Genova
 Sensitivity limits of atom interferometry gravity gradiometers and strainmeters Fiodor Sorrentino INFN Genova 1 Outline AI sensors, state of the art performance Main noise sources Potential improvements
Sensitivity limits of atom interferometry gravity gradiometers and strainmeters Fiodor Sorrentino INFN Genova 1 Outline AI sensors, state of the art performance Main noise sources Potential improvements
Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. Rapport BIPM -89/1
 Bureau International des Poids et Mesures Rapport BIPM -89/1 Shape Measurements of Standard Length Scales Using Interferometry with Small Angles of Incidence by Lennart Robertsson Abstract An interferometric
Bureau International des Poids et Mesures Rapport BIPM -89/1 Shape Measurements of Standard Length Scales Using Interferometry with Small Angles of Incidence by Lennart Robertsson Abstract An interferometric
Figure measurement of a large optical flat with a Fizeau interferometer and stitching technique
 Figure measurement of a large optical flat with a Fizeau interferometer and stitching technique Chunyu Zhao a, Robert A. Sprowl a, Michael Bray b, James H. Burge a a College of Optical Sciences, the University
Figure measurement of a large optical flat with a Fizeau interferometer and stitching technique Chunyu Zhao a, Robert A. Sprowl a, Michael Bray b, James H. Burge a a College of Optical Sciences, the University
The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design
 The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design Jingquan Cheng National Radio Astronomy Observatory Charlottesville, Virginia,.USA " 4y Springer Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes 1 1.1 A Brief History
The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design Jingquan Cheng National Radio Astronomy Observatory Charlottesville, Virginia,.USA " 4y Springer Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes 1 1.1 A Brief History
1. In Young s double slit experiment, when the illumination is white light, the higherorder fringes are in color.
 TRUE-FALSE STATEMENTS: ELECTRICITY: 1. Electric field lines originate on negative charges. 2. The flux of the electric field over a closed surface is proportional to the net charge enclosed by the surface.
TRUE-FALSE STATEMENTS: ELECTRICITY: 1. Electric field lines originate on negative charges. 2. The flux of the electric field over a closed surface is proportional to the net charge enclosed by the surface.
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
The Laser Astrometric Test Of Relativity Mission
 The Laser Astrometric Test Of Relativity Mission Slava G. Turyshev, Michael Shao Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA 91009 USA Kenneth L. Nordtvedt,
The Laser Astrometric Test Of Relativity Mission Slava G. Turyshev, Michael Shao Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA 91009 USA Kenneth L. Nordtvedt,
Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna.
 Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna. 1) LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) Why? 2)How? 1 Frequency Limitation Seismic noise cannot be cancelled at low-frequency
Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna. 1) LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) Why? 2)How? 1 Frequency Limitation Seismic noise cannot be cancelled at low-frequency
High energy X-ray vortex generation using inverse Compton scattering
 22nd International Spin Symposium 9/28/216 High energy X-ray vortex generation using inverse Compton scattering Yoshitaka Taira National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
22nd International Spin Symposium 9/28/216 High energy X-ray vortex generation using inverse Compton scattering Yoshitaka Taira National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
The IPIE Adaptive Optical System Application For LEO Observations
 The IPIE Adaptive Optical System Application For LEO Observations Eu. Grishin (1), V. Shargorodsky (1), P. Inshin (2), V. Vygon (1) and M. Sadovnikov (1) (1) Open Joint Stock Company Research-and-Production
The IPIE Adaptive Optical System Application For LEO Observations Eu. Grishin (1), V. Shargorodsky (1), P. Inshin (2), V. Vygon (1) and M. Sadovnikov (1) (1) Open Joint Stock Company Research-and-Production
ANAMORPHOTIC TELESCOPE FOR EARTH OBSERVATION IN THE MID- INFRARED RANGE
 ANAMORPHOTIC TELESCOPE FOR EARTH OBSERVATION IN THE MID- INFRARED RANGE Thomas Peschel 1, Christoph Damm 1, Sebastian Scheiding 1,, Matthias Beier 1, Stefan Risse 1, Susanne Nikolov 3, Wolfgang Holota
ANAMORPHOTIC TELESCOPE FOR EARTH OBSERVATION IN THE MID- INFRARED RANGE Thomas Peschel 1, Christoph Damm 1, Sebastian Scheiding 1,, Matthias Beier 1, Stefan Risse 1, Susanne Nikolov 3, Wolfgang Holota
displacement measuring interferometery measurement uncertainty Mike Holmes and Chris Evans (contact info:
 displacement measuring interferometery measurement uncertainty Mike Holmes and Chris Evans (contact info: mholmes@zygo.com) 1 agenda heterodyne displacement measuring interferometer (DMI) overview case
displacement measuring interferometery measurement uncertainty Mike Holmes and Chris Evans (contact info: mholmes@zygo.com) 1 agenda heterodyne displacement measuring interferometer (DMI) overview case
A Fabry-Perot Interferometer System for high-speed velocity measurement. Lun K. Cheng, A.J.A. Bruinsma, W.C. Prinse* and C.
 A Fabry-Perot Interferometer System for high-speed velocity measurement Lun K. Cheng, A.J.A. Bruinsma, W.C. Prinse* and C. Smorenburg TNO Inst. of Appi. Phys., 2600 AD Deift, The Netherlands *TNO Prins
A Fabry-Perot Interferometer System for high-speed velocity measurement Lun K. Cheng, A.J.A. Bruinsma, W.C. Prinse* and C. Smorenburg TNO Inst. of Appi. Phys., 2600 AD Deift, The Netherlands *TNO Prins
