Dynamic Power Allocation in MIMO Fading Systems Without Channel Distribution Information
|
|
|
- Stephany Jenkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 Dynamc Powr Allocaon n MIMO Fadng Sysms Whou Channl Dsrbuon Informaon Hao Yu and Mchal J. Nly Unvrsy of Souhrn Calforna Absrac Ths papr consdrs dynamc powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms wh unknown channl sa dsrbuons. Frs, h dal cas of prfc nsananous channl sa nformaon a h ransmr (CSIT) s rad. Usng h drf-plus-pnaly mhod, a dynamc powr allocaon polcy s dvlopd and shown o approach opmaly, rgardlss of h channl sa dsrbuon and whou rqurng knowldg of hs dsrbuon. Nx, h cas of dlayd and quanzd channl sa nformaon s consdrd. Opmal uly s fundamnally dffrn n hs cas, and a dffrn onln algorhm s dvlopd ha s basd on convx projcons. Th proposd algorhm for hs dlayd-csit cas s shown o hav an O( ) opmaly gap, whr s h quanzaon rror of CSIT. I. INTRODUCTION Durng h pas dcad, h mulpl-npu mulpl-oupu (MIMO) chnqu has bn rcognzd as on of h mos mporan chnqus for ncrasng h capabls of wrlss communcaon sysms. In h wrlss fadng channl, whr h channl changs ovr m, h problm of powr allocaon s o drmn h ransm covaranc of h ransmr o maxmz h rgodc capacy subjc o boh long rm and shor rm powr consrans. I s ofn rasonabl o assum ha nsananous channl sa nformaon (CSI) s avalabl a h rcvr hrough ranng. Mos works on powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms also assum ha sascal nformaon abou h channl sa, rfrrd o as channl dsrbuon nformaon (CDI), s avalabl a h ransmr. Undr h assumpon of prfc nsananous channl sa nformaon a h rcvr (CSIR) and prfc channl dsrbuon nformaon a h ransmr (CDIT), pror work on powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms can b cagorzd no wo cass: Prfc nsananous channl sa nformaon a h ransmr (dal-csit): In h dal cas of prfc CSIT, opmal powr allocaon s known o b a warfllng soluon []. Compuaon of war-lvls nvolvs a on-dmnsonal ngral quaon for fadng channls wh..d. Raylgh nrs or a mul-dmnsonal ngral quaon for gnral fadng channls []. No CSIT: If CSIT s unavalabl, h opmal powr allocaon s n gnral sll opn. If h channl marx has..d. Raylgh nrs, hn h opmal powr allocaon s known o b h dny ransm covaranc scald o Hao Yu and Mchal J. Nly ar wh h Dparmn of Elcrcal Engnrng, Unvrsy of Souhrn Calforna, Los Angls, USA. Ths work s suppord n par by h NSF gran CCF sasfy h powr consran []. Th opmal powr allocaon n MIMO fadng channls wh corrlad Raylgh nrs s oband n [3], [4]. Th powr allocaon n MIMO fadng channls s furhr consdrd n [5] undr a mor gnral channl corrlaon modl. Ths pror work rls on accura CDIT and/or on rsrcv channl dsrbuon assumpons. I can b dffcul o accuraly sma h CDI, spcally whn hr ar complcad corrlaons. Soluons ha bas dcsons on prfc CDIT can b subopmal du o msmachs. Ths papr dsgns algorhms ha do no rqur pror knowldg of h channl dsrbuon, y prform arbrarly clos o h opmal valu ha can b achvd by havng hs knowldg. Furhr, h convrgnc m s compud and shown o b sgnfcanly smallr han h m rqurd o accuraly sma h channl dsrbuon. Th dal-csit assumpon s rasonabl n m-dvson duplx (TDD) sysms wh symmrc TDD wrlss channls. Howvr, n frquncy-dvson duplx (FDD) scnaros and ohr scnaros whou channl symmry, h CSI mus b smad a h rcvr, quanzd, and rpord back o h ransmr wh a m dlay. Ths papr frs consdrs h dal-csit cas and dvlops a soluon ha dos no rqur CDIT. Nx, h cas of dlayd and quanzd CSIT s consdrd and a fundamnally dffrn algorhm s dvlopd for ha cas. Th lar algorhm agan dos no us CDIT, bu achvs a uly whn O( ) of h bs uly ha can b achvd vn wh prfc CDIT, whr s h quanzaon rror. Ths shows ha dlayd bu accura CSIT (wh 0) s almos as good as havng prfc CDIT. A. Rlad work and our conrbuons In h dal CSIT cas, h proposd dynamc powr allocaon polcy s an adapon of h gnral drf-plus-pnaly algorhm for sochasc nwork opmzaon [6], [7]. In hs MIMO conx, h currn papr shows h algorhm provds srong sampl pah and convrgnc m guarans. Th dynamc of h drf-plus-pnaly algorhm s smlar o ha of h sochasc dual subgradn algorhm, alhough h opmaly analyss and prformanc bounds ar dffrn. Th sochasc dual subgradn algorhm has bn appld n opmzaon of h wrlss fadng channl whou CDI,.g., downlnk powr schdulng n sngl annna cllular sysms [8], powr allocaon n sngl annna broadcas OFDM channls [9], schdulng and rsourc allocaon n
2 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 random accss channls [0], powr allocaon n mul-carrr MIMO nworks []. In h dlayd and quanzd CSIT cas, h suaon s smlar o h scnaro of onln convx opmzaon [] xcp ha w ar unabl o obsrv ru hsory rward funcons du o channl quanzaon. Th proposd dynamc powr allocaon polcy can b vwd as an onln algorhm wh naccura hsory nformaon. Th currn papr analyzs h prformanc loss du o CSI quanzaon rror and provds srong sampl pah and convrgnc m guarans of hs algorhm. Accordng o h auhors knowldg, onln convx opmzaon wh naccura hsory nformaon has no bn sudd bfor. Th analyss n hs MIMO conx can b xndd o mor gnral onln convx opmzaon wh naccura hsory nformaon. Onln opmzaon has bn appld n powr allocaon n wrlss fadng channls whou CDIT and wh dlayd and accura CSIT,.g., subopmal onln powr allocaon n sngl annna sngl usr channls [3], subopmal onln powr allocaon n sngl annna mulpl usr channls [4]. A clos rlad rcn work s [5], whr onln powr allocaon n MIMO sysms s consdrd. Th onln algorhm n [5] s dffrn from our algorhm and follows a marx xponnal larnng schm rqurng h compuaon of marx xponnals a ach slo. In conras, our onln algorhm only nvolvs a smpl projcon a ach slo and a closd-form soluon of hs projcon s drvd n hs papr. Work [5] also consdrs h ffc of mprfc CSIT by assumng CSIT s unbasd,.., xpcd CSIT rror condonal on obsrvd prvous CSIT s zro. Ths assumpon of mprfc CSIT s suabl o modl h CSIT masurmn rror or fdback rror bu can no capur h CSI quanzaon rror. In conras, h currn papr only rqurs ha CSIT rror s boundd. II. SIGNAL MODEL AND PROBLEM FORMULATIONS A. Sgnal modl Consdr a pon-o-pon MIMO fadng channl ha opras n slod m wh normalzd m slos {,,...}. Thr ar N T annnas a h ransmr and N R annnas a h rcvr. Th channl can b modld as y() =H()x()+z() whr {,,...} s h m ndx, z() C N R s h addv nos vcor, x() C N T s h ransmd sgnal vcor, H() C N R N T s h channl marx, and y() C N R s h rcvd sgnal vcor. Assum ha nos vcors z() ar ndpndn and dncally dsrbud (..d.) ovr m slos and ar normalzd crcularly symmrc complx Gaussan random vcors wh E[z()z H ()] = I NR, whr I NR dnos an N R N R dny marx. Assum ha channl marcs H() ar..d. across m and hav a fxd bu arbrary probably dsrbuon, possbly on wh corrlaons bwn nrs of h marx. Assum hr xss If h sz of h dny marx s clar, w ofn smply wr I. a consan B>0 such ha khk F appl B wh probably on, whr k k F dnos h Frobnus norm of marcs. Assum ha h rcvr can rack channl marcs H() xacly hrough ranng. In symmrc TDD scnaros, s rasonabl o assum h ransmr has prfc CSIT. In mor gnral scnaros, h channl marx H() s masurd a h rcvr a ach slo, a quanzd vrson H() s crad as a funcon of H(), and hs quanzd vrson s fd back o h ransmr wh on slo of dlay. W assum ha h quanzaon rror s boundd,.., hr xss >0 such ha kh() H()k F appl for all. Du o h on slo dlay, a slo h ransmr only knows H( ). Snc channls ar..d. ovr slos, hs dlayd nformaon s ndpndn of h currn (and unknown) H(). Rmarkably, urns ou ha h oudad nformaon s sll usful. B. Opmal powr allocaon wh prfc CDIT If h channl marx s fxd a H and h ransm covaranc s fxd a Q, h MIMO capacy s gvn by []: log d(i + HQH H ) whr suprscrp H dnos Hrman ranspos and d( ) dnos h drmnan opraor of marcs. If H s random hn h avrag capacy, formally calld h rgodc capacy [6], s gvn by E H log d(i + HQH H ). W consdr wo yps of powr consrans a h ransmr: An avrag powr consran E H [r(q)] appl P and an nsananous powr consran r(q) appl P, whr r( ) dnos h rac opraor of marcs. Th dal-csit problm s o choos Q as a (possbly random) funcon of h obsrvd H o maxmz h rgodc capacy subjc o powr consrans: max Q(H) E H log d(i + HQ(H)H H ) () s.. E H [r(q(h))] appl P, () Q(H) Q, 8H, (3) whr Q s a s ha nforcs h nsananous powr consran: Q = Q S N T + : r(q) appl P (4) whr S N T + dnos h N T N T posv smdfn marx spac. To avod rvals s assumd ha P P. In ()-(3) w us noaon Q(H) o mphasz ha Q can dpnd on H,.., adapv o channl ralzaons. If h ransmr has no CSIT, h opmal powr allocaon problm s dffrn, gvn as follows. max Q E H log d(i + HQH H ) (5) s.. E H [r(q)] appl P, (6) Q Q, (7) whr s Q s dfnd n (4). Agan assum P P. Snc h nsananous CSIT s unavalabl, h ransm covaranc A boundd Frobnus norm always holds n h physcal world bcaus h channl anuas h sgnal. Parcular modls such as Raylgh and Rcan fadng vola hs assumpon n ordr o hav smplr dsrbuon funcons.
3 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 canno adap o H. By h convxy of hs problm and Jnsn s nqualy, a randomzd Q can b shown o b uslss. I suffcs o consdr a consan Q. Snc P P, hs mpls h problm s quvaln o a problm ha rmovs h consran (6) and ha changs h consran (7) o: Q Q = {Q S N T + : r(q) appl P } Th problms ()-(3) and (5)-(7) ar fundamnally dffrn and hav dffrn opmal objcv funcon valus. Opmaly for hs problms s dfnd by h channl dsrbuon nformaon (CDI). In hs papr, h problms ar solvd va dynamc algorhms ha do no rqur CDI. Th algorhms ar dffrn for h wo cass, and us dffrn chnqus. C. Lnar algbra and marx drvavs Rcall ha f A C m n and B C n m hn r(ab) = r(ba). Ths subscon prsns addonal usful facs abou Frobnus norms and complx marcs. Proofs ar gvn n [7] for complnss. Fac. For any A, B C m n and C C n k w hav: ) kak F = ka H k F = ka T k = k Ak F. ) ka + Bk F applkak F + kbk F. 3) kack F applkak F kck F. 4) r(a H B) applkak F kbk F. Fac. For any A S n + w hav kak F appl r(a). Fac 3 ([8]). Th funcon f : S n +! R dfnd by f(q) = log d(i + HQH H ) s concav and s gradn s gvn by r Q f(q) =H H (I + HQH H ) H, 8Q S n +. Th nx fac s h complx marx vrson of h frs ordr condon for concav funcons of ral numbr varabls,.., f(y) appl f(x)+f 0 (x)(y x), 8x, y domf f f s concav. Fac 4. L funcon f(q) :S n +! R b a concav funcon and hav gradn r Q f(q) S n a pon Q. Thn, f( b Q) appl f(q)+r [r Q f(q)] H ( b Q Q), 8 b Q S n +. III. IDEAL CSIT CASE Consdr h cas of prfc nsananous CSIT, calld h dal-csit cas. Th problm o solv s ()-(3). A h bgnnng of ach slo {,,...} h channl H() s known and a covaranc marx Q() can b chosn basd on hs nformaon. Ths s don whou usng CDI va h drfplus-pnaly chnqu of [7]. For ach slo {,,...} dfn h rward R(): R() = log d(i + H()Q()H() H ) (8) Th avrag powr consran () s nforcd va a vrual quu Z() wh Z(0) = 0 and wh upda: Z( + ) = max[z()+r(q()) P ] In h drf-plus-pnaly algorhm, vry slo a marx Q() Q s slcd o maxmz VR() Z()r(Q()), whr V s a posv wgh. Ths rsuls n Algorhm blow. Algorhm Dynamc powr allocaon wh dal CSIT L V > 0 b a consan paramr and Z(0) = 0. A ach m {,,...}, obsrv H() and Z(). Thn do h followng: Choos ransm covaranc Q() Qo maxmz: V log d(i + H()Q()H() H ) Z()r(Q()) Upda Z( + ) = max[z()+r(q()) P ]. Dfn R op as h opmal avrag uly n (). Th valu R op dpnds on h (unknown) dsrbuon for H(). Fx > 0 and dfn V =(P + P ) /( ). A horm n [7] nsurs ha, rgardlss of h dsrbuon of H(): X E[R( )] R op, 8 >0 (9) lm! X E[r(Q( ))] appl P (0) Ths holds for arbrarly small valus of > and so h algorhm coms arbrarly clos o opmaly. Noc ha Algorhm dos no us channl dsrbuon nformaon (.., no CDI). Th nx subscons show how o solv h covaranc slcon problm for choosng Q() n Algorhm, and shows ha h spcal srucur of hs MIMO problm producs a sampl pah guaran ha s sgnfcanly srongr han (0) and ha dmonsras convrgnc m ha s ypcally much fasr han h m ha would b rqurd o accuraly sma h CDI nformaon. A. Transm covaranc updas n Algorhm Ths subscon shows h Q() slcon n Algorhm can b asly solvd and has an (almos) closd-form soluon. Th convx program nvolvd n h ransm covaranc upda of Algorhm s n h form max log d(i + HQH H Z ) r(q) () Q V s.. r(q) appl P () Q S N T + (3) Ths convx program s smlar o h convnonal problm of ransm covaranc dsgn wh a drmnsc channl H, xcp ha objcv () has an addonal pnaly rm (Z/V )r(q). I s wll known ha, whou hs pnaly rm, h soluon s o dagonalz h channl marx and alloca powr ovr gn-mods accordng o a war-fllng chnqu []. Th nx horm shows ha h opmal soluon o problm ()-(3) has a smlar srucur. Thorm. Consdr h SVD H H H = U H U, whr U s a unary marx and s a dagonal marx wh non-ngav nrs,..., N T. Thn h opmal soluon o ()-(3) s
4 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 gvn by Q = U H U, whr s a dagonal marx wh nrs,..., N T gvn by: = max µ, 8 {,...,NT }, whr µ s chosn such ha P N T = appl P, µ 0 and µ P N T = P =0. Th xac µ can b drmnd wh complxy O(N T log N T ), dscrbd n Algorhm. Proof: S Appndx A. Algorhm Algorhm o solv problm ()-(3) ) Chck f P N T = max{ Z/V } appl P holds. If ys, l µ = 0 and = max{ Z/V }, 8 {,,...,N T } and rmna h algorhm; ls, connu o h nx sp. ) Sor all, {,,...,N T } n a dcrasng ordr such ha () () (N T ). Dfn S 0 =0. 3) For =o N T L S = S +. L µ = () S +P (Z/V ). If µ > 0 and () appl hn rmna h loop; ls, connu (+) o h nx raon n h loop. 4) L = max, 8 {,,...,NT } and rmna h algorhm. Th complxy of Algorhm s domnad by h sorng of all n sp (). Rcall ha h war-fllng soluon of powr allocaon n mulpl paralll channls can also b found by an xac algorhm (s Scon 6 n [9]), whch s smlar o Algorhm. Th man dffrnc s ha Algorhm has a frs sp o vrfy f µ =0. Ths s bcaus unlk h powr allocaon n mulpl paralll channls, whr h opmal soluon always uss full powr, h opmal soluon o problm ()-(3) may no us full powr for larg Z du o h pnaly rm (Z/V )r(q) n objcv (). B. Drmnsc bounds Rcall ha kh()k F appl B for all, for som consan B. Lmma. In Algorhm, f Z() VB, hn Q() =0. Proof: Suppos h SVD of H H ()H() s gvn by H H ()H() =U H U, whr dagonal marx has nonngav dagonal nrs,..., N T. No ha r(h H ()H()) (b) appl kh()k F appl B whr (a) follows from r(h H ()H()) = P N T = ; and (b) follows from Fac. By Thorm, Q() =U H U, whr s a dagonal marx wh nrs,..., N T gvn by = max µ +Z()/V, 8 {,,...,NT }, whr µ 0. Snc appl B, 8 {,,...,N T }, w know ha f Z() VB, hn µ+z()/v appl 0 for all µ 0 and hnc = 8 {,,...,N T }. (a) appl Lmma. L Z() b yldd by Algorhm. For all slos {,,...}, w hav Z() appl VB +(P P ). Proof: By Lmma, Z() can no ncras f Z() VB. If Z() appl VB, hn Z(+) s a mos VB +(P P ) by h upda quaon of Z(+) and h nsananous powr consran. C. Prformanc of Algorhm (dal-csit) Thorm. Fx >0 and dfn V =(P + P ) /( ). Undr Algorhm w hav for all >0: X X E[R( )] R op r(q( )) appl P + B (P + P ) + (P P ) In parcular, h sampl pah m avrag powr s whn of s rqurd consran P whnvr (/ ). Proof: Th frs nqualy s h sam as (9). I rmans o prov h scond nqualy. For all slos h Algorhm upda for Z( ) sasfs: Z( + ) = max[z( )+r(q( )) P ] Z( )+r(q( )) P Rarrangng rms gvs: r(q( )) P appl Z( + ) Z( ). Fx >0. Summng ovr {..., } and dvdng by gvs: X Z() Z(0) r(q( )) P appl appl (VB +(P P )) whr h las nqualy holds bcaus Z(0) = 0 and Z() appl VB +(P P ) by Lmma. Thorm provds a sampl pah guaran on avrag powr, whch s much srongr han h guran n (0). I also shows ha convrgnc m o rach an -approxma soluon s O(/ ). Typcally, hs s dramacally mor ffcn han h convrgnc m rqurd o oban vn a coars sma of h jon dsrbuon for h nrs of H(). Indd, f ach channl nry h j wr quanzd no / dsnc lvls, hr would b (/ ) N T N R dffrn possbl (quanzd) marx ralzaons. Wang for (/ ) N T N R slos would a bs allow ach ralzaon o appar onc, whch s sll no nough for accura smaon of h probabls assocad wh ach ralzaon. Forunaly, Thorm shows ha such smaon s no ndd. IV. DELAYED AND QUANTIZED CSIT CASE Consdr h cas of dlayd and quanzd CSIT. A h bgnnng of ach slo {,,...}, channl H() s unknown and only quanzd channls of prvous slos H( ), {,..., } ar known.
5 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 Ths s smlar o h scnaro of onln opmzaon whr h dcson makr slcs x() X a ach slo o maxmz an unknown rward funcon f (x) basd on h nformaon of prvous rward funcons f (x( )), {,..., }. Th goal s o mnmz avrag rgr max P xx f (x) P f (x( )). Th bs known avrag rgr of onln opmzaon wh Lpschz connuous and convx rward funcons s O( p ) n []. Ths s dffrn from convnonal onln opmzaon bcaus a ach slo, h rwards of prvous slos,.., R( ) = log d(i + H( )Q( )H H ( )), {,..., }, ar sll unknown du o h fac ha h rpord channls H( ) ar h quanzd vrsons. Nvrhlss, an onln algorhm whou usng CDIT s dvlopd n Algorhm 3. Algorhm 3 Dynamc Powr Allocaon wh Dlayd and Quanzd CSIT L >0 b a consan paramr and Q(0) Qb arbrary. A ach m {,,...}, obsrv H( ) and do h followng: L D( ) = H H ( )(I NR + H( )Q( ) H H ( )) H( ). Choos ransm covaranc Q() =P Q Q( ) + D( ), whr P Q [ ] s h projcon ono convx s Q = {Q S N T + : r(q) appl P }. Dfn Q Q as an opmal soluon o problm (5)-(7), whch dpnds on h (unknown) dsrbuon for H(). Dfn R op () = log d(i + H()Q H H ()) as h uly a slo aand by Q. If h channl s no quanzd,.., H( ) = H( ), 8 {,,...}, hn D( ) s h gradn of R( ) a pon Q( ). Fx >0 and ak =. Th rsuls n [] nsur ha, rgardlss of h dsrbuon of H(): X R( ) X R op ( ) P N R B 4, 8 >0 (4) X r(q( )) appl P,8 >0 (5) Th nx subscons analyz h prformanc of Algorhm 3 wh quanzd channls and shows ha h prformanc dgrads lnarly wh rspc o h quanzaon rror. If = hn (4) and (5) ar rcovrd. A. Transm Covaranc Updas n Algorhm 3 Ths subscon shows h Q() slcon n Algorhm 3 can b asly solvd and has an (almos) closd-form soluon. Th projcon opraor nvolvd n Algorhm 3 by dfnon s mn kq Xk F (6) s.. r(q) appl P (7) Q S N T + (8) whr X = Q( ) + D( ) s an Hrman marx a ach m. Whou consran r(q) appl P, h projcon of Hrman marx X ono h posv smdfn con S n + s smply akng h gnvalu xpanson of X and droppng rms assocad wh ngav gnvalus (s Scon 8... n [0]). Work [] consdrd h projcon ono h nrscon of h posv smdfn con S n + and an affn subspac gvn by {Q : r(a Q)=b, {,,...,p}, r(b j Q) appl d j,j {,,...,m}} and dvlopd h dual-basd rav numrcal algorhm o calcula h projcon. Problm (6)- (8) s a spcal cas, whr h affn subspac s gvn by r(q) appl P, of h projcon consdrd n []. Insad of solvng problm (6)-(8) usng numrcal algorhms, hs subscon shows ha problm (6)-(8) has an (almos) closd-form soluon. Thorm 3. Consdr SVD X = U H U, whr U s a unary marx and s a dagonal marx wh nrs,..., N T. Thn h opmal soluon o problm (6)-(8) s gvn by Q = U H U, whr s a dagonal marx wh nrs,..., N T gvn by, = max[ µ ], 8 {,,...,N T }, whr µ s chosn such ha P N T = appl P, µ 0 and µ P N T = P =0. Th xac µ can b drmnd wh complxy O(N T log N T ), dscrbd n Algorhm 4. Proof: Th proof s skchd as follows. Frs, problm (6)-(8) s rducd o a smplr convx program wh a ral vcor varabl by characrzng h srucur of s opmal soluon. Thn, an (almos) closd-form soluon o h smplr convx program s oband by sudyng s KKT condons. S Appndx B for dals. Algorhm 4 Algorhm o solv problm (6)-(8) ) Chck f P N T = max[ ] appl P holds. If ys, l µ =0 and = max[ ], 8 {,,...,N T } and rmna h algorhm; ls, connu o h nx sp. ) Sor all, {,,...,N T } n a dcrasng ordr such ha () () (N T ). Dfn S 0 =0. 3) For =o N T L S = S +. L µ = S P. If µ () µ > 0 and (+) µ appl hn rmna h loop; ls, connu o h nx raon n h loop. 4) L = max[ µ ], 8 {,,...,N T } and rmna h algorhm.
6 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 B. Propry of D( ) Dfn D( ) = H H ( )(I NR + H( )Q( )H H ( )) H( ), whch s h gradn of R( ) a pon Q( ) and s unknown o h ransmr du o h unavalably of H( ). Th nx lmma rlas D( ) and D( ). Lmma 3. For all slos {,,...}, w hav ) kd( )k F appl p N R B. ) kd( ) D( )kf appl ( ), whr ( ) = p NR B + p N R (B + )+(B + ) N R P (B + ) sasfyng ( )! 0 as!.., ( ) O( ). 3) k D( )k F appl ( )+ p N R B Proof: S full vrson [7] for dals. C. Prformanc of Algorhm 3 Thorm 4. Fx >0 and dfn =. Undr Algorhm 3, w hav for all >0: X R( ) X R op ( ) X r(q( )) appl P ( ) P P ( ( )+ p N R B ) whr ( ) s h consan dfnd n Lmma 3. In parcular, h sampl pah m avrag uly s whn + ( ) P of h opmal m avrag uly for problm (5)-(7) whnvr (/ ). Proof: Th scond nqualy rvally follows from h fac ha Q() Q, 8 {,...}. I rmans o prov h frs nqualy. Ths proof xnds h rgr analyss of convnonal onln convx opmzaon [] by consdrng nxac gradn D( ). For all slos {,,...}, h ransm covaranc upda n Algorhm 3 sasfs: kq( ) Q k F =kp Q Q( ) + D( ) (a) applkq( ) + D( ) Q k F Q k F =kq( ) Q k F + r D H ( )(Q( ) Q ) + k D( )k F =kq( ) Q k F + r D H ( )(Q( ) Q ) + r ( D( ) D( )) H (Q( ) Q ) + k D( )k F, whr (a) follows from h non-xpansv propry of projcons ono convx ss. Dfn () =kq( + ) Q k F kq() Q k F. Rarrangng rms n h las quaon and dvdng by facor mpls r D H ( )(Q( ) Q ) ( ) k D( )k F r ( D( ) D( )) H (Q( ) Q ) (9) Dfn f(q) = log d(i+h( )QH H ( )). By Fac 3, f( ) s concav ovr Q. No ha D( ) = r Q f(q( )) by Fac 3 and Q Q. By Fac 4, w hav f(q( )) f(q ) r(d H ( )(Q( ) Q )). (0) No ha f(q( )) = R( ) and f(q )=R op ( ). Combnng (9) and (0) ylds R( ) R op ( ) ( ) k D( )k F (a) (b) r ( D( ) D( )) H (Q( ) Q ) ( ) k D( )k F k D( ) D( )k F kq( ) Q k F ( ) ( ( )+p N R B ) ( ) P whr (a) follows from Fac and (b) follows from Lmma 3 and h fac ha kq( ) Q k F applkq( )k F +kq k F appl r(q( )) + r(q ) appl P, whch s mpld by Fac, Fac and fac Q( ), Q Q. Rplacng wh ylds for all {,...}, R( ) R op ( ) ( ) p ( ( )+ NR B ) ( ) P. Fx >0. Summng ovr {,..., }, dvdng by facor and nong ha P ( ) s a lscop sum gvs P R( ) P Rop ( ) (kq() Q k F kq(0) Q k F ) ( ( )+p N R B ) ( ) P P ( ( )+p N R B ) ( ) P, whr h las nqualy follows bcaus kq(0) Q k F appl kq(0)k F + kq k F appl r(q(0)) + r(q ) appl P and kq() Q k F 0. Thorm 4 provs a sampl pah guaran on h avrag uly. I shows ha h convrgnc m o rach an + ( ) P approxma soluon s O(/ ). No ha f = hn quaons (4) and (5) ar rcovrd by Thorm 4. Thorm 4 also solas h ffcs of dlay and quanzaon. Th obsrvaon s ha h ffc of CSIT dlay vanshs as Algorhm 3 runs for a suffcnly long m. In som sns, dlayd bu accura CSIT s almos as good as prfc CDIT. In conras, h ffc of CSIT quanzaon dos no vansh as Algorhm 3 runs for a suffcnly long m. Th prformanc dgradaon du o quanzaon scals lnarly wh rspc o h quanzaon rror snc ( ) O( ). Inuvly, hs s rasonabl snc h powr allocaon basd on quanzd CSIT s acually opmzng anohr dffrn MIMO sysm.
7 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 D. Exnsons ) T -Slo Dlayd and Quanzd CSIT: Thus far, w hav assumd ha CSIT s dlayd by on slo. In fac, f CSIT s dlayd by T slos, w can modfy h upda of ransm covarancs n Algorhm 3 as Q() =P Q [Q( T )+ D( T )]. AT -slo vrson of Thorm 4 can b smlarly provn. ) Algorhm 3 wh Tm Varyng : Algorhm 3 can b xndd o hav m varyng sp sz () = p a m. Th full vrson [7] provs ha such an algorhm P P Rop ( ) ylds R( ) Pp p ( ( )+ p NR B ) ( ) P for all >0. Ths shows h convrgnc m o an + ( ) P approxma soluon s agan O(/ ). Howvr, an advanag of m varyng sp szs s h prformanc auomacally gs mprovd as h algorhm runs and hr s no nd o rsar h algorhm wh a dffrn consan sp sz f a br prformanc s dmandd. V. SIMULATIONS Consdr a MIMO sysm whr boh h ransmr and h rcvr hav wo annnas. Th powr consrans ar P = 5and P = 0. Th channl has appl wo ralzaons wh j0.84 qual probably 0.5,.., H =0.5 j.58 j.83 j.97 and appl j.3 H = j.69 j0.07 j.86. If h channl s quanzd, hy ar quanzd as H and H, rspcvly. Th algorhms n hs papr can b asly appld o xampls wh nfn possbl oucoms for h channl marx. Ths smpl xampl of wo possbls s consdrd bcaus an offln opmal soluon basd on prfc CDIT can only b compud whn h numbr of sampls s small. 3 Fgur compars h prformanc of Algorhm wh prfc CSIT and h opmal soluon o problm ()-(3). In h smulaon, w ak V = 000. Fgur compars h prformanc of Algorhm 3 wh on slo dlayd and quanzd CSIT and h opmal soluon o problm (5)-(7). To sudy h ffc of quanzaon rror, w consdr 3 dffrn quanzaon lvls. Cas : H appl appl = j j.5 j.8 j.9 and H j.3 = j.6 j0 j.8 ; Cas appl appl : H j =0.5 j.5 j j and H j.5 = j.5 j0 j ; appl appl Cas 3: H = 0.5 and H =. In h smulaon, w ak Q(0) = 0 and = 0 3. I can b obsrvd ha prformanc bcoms wors as CSIT quanzaon gs coarsr, whl h avrag powr consrans ar srcly sasfd vn wh quanzd CSIT. 3 Ths s known as h curs of dmnsonaly for sochasc opmzaon du o h larg sampl sz. Tha s, vn wh prfc CDIT, problm ()-(3) and problm (5)-(7) can b numrcally hard o solv whn h sampl sz of H s larg. In conras, h dynamc algorhms proposd n hs papr can dal wh problms vn wh an nfn numbr of sampls and h prformanc guarans ar ndpndn of h sampl sz. Uly Avrag Powr Uly Prformanc of Algorhm Slos: Avrag Powr Algorhm Algorhm opmal soluon o problm () (3) opmal soluon o problm () (3) Slos: Fg.. Prformanc of Algorhm. Prformanc of Algorhm Slos: x quanzaon cas opmal soluon o problm (5) (7) quanzaon cas quanzaon cas quanzaon cas 3 quanzaon cas quanzaon cas Slos: x 0 5 Fg.. Prformanc of Algorhm 3. VI. CONCLUSION Ths papr consdrs dynamc powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms whou CDIT. In h cas of dal CSIT, h proposd dynamc powr polcy can approach opmaly. In h cas of dlayd and quanzd CSIT, h proposd dynamc powr allocaon polcy can achv O( ) sub-opmaly, whr s h quanzaon rror. APPENDIX A PROOF OF THEOREM Th proof mhod s an xnson of Scon 3. n [], whch gvs h srucur of h opmal ransm covaranc n drmnsc MIMO channls. No ha log d(i + HQH H ) (a) = log d(i + QH H H) (b) = log d(i + QU H U) (c) = log d(i + / UQU H / ), whr (a) and (c) follows from h lmnary dny
8 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 log d(i n + AB) = log d(i n + BA), 8A, B C n n ; and (b) follows from h fac ha H H H = U H U. Dfn Q = UQU H, whch s smdfn posv f and only f Q s. No ha r( Q)=r(UQU H )=r(q) by h fac ha r(ab) =r(ba), 8A C m n, B C n m. Thus, problm ()-(3) s quvaln o max Q log d(i + / Q / ) Z V r( Q) () s.. r( Q) appl P () Q S N T + (3) Fac 5 (Hadamard s Inqualy, Thorm 7.8. n []). For all A S n +, d(a) appl Q n = A wh qualy f A s dagonal. Th nx clam can b provn usng Hadamard s nqualy. Clam. Problm ()-(3) has a dagonal opmal soluon. Proof: Suppos problm ()-(3) has a non-dagonal opmal soluon gvn by marx Q. Consdr a dagonal marx Q b whos nrs ar dncal o h dagonal nrs of Q. No ha r( Q) b = r( Q). To show Q b s a soluon no wors han Q, suffcs o show ha log d(i + / Q b / ) log d(i + / Q / ). Ths s ru bcas d(i + / Q b / ) = Q N T = ( + Q b ) = Q N T = ( + Q ) d(i + / Q / ), whr h las nqualy follows from Hadamard s nqualy. Thus, Q b s a soluon no wors han Q and hnc opmal. By Clam, w can consdr Q = = dag(,,..., NT ) and problm ()-(3) s quvaln o max s.. XN T log( + ) = N T Z V XN T (4) = X appl P (5) = 8 {,,...,N T } (6) No ha problm (4)-(6) sasfs Slar s condon. So h opmal soluon o problm (4)-(6) s characrzd by KKT condons [0]. Th rmanng par s smlar o h drvaon of h war-fllng soluon of powr allocaon n paralll channls,.g., h proof of Exampl 5. n [0]. Inroducng Lagrang mulplrs µ R + for nqualy consran P N T = appl P and = [,..., NT ] T R N T + for nqualy consrans {,,...,N T }. L = [,..., N T ] T and (µ, ) b any prmal and dual opmal pons wh zro dualy gap. By KKT condons, w hav + + µ = 8 {,,...,N T }; P N T = appl P ; µ 0; µ P N T = P = 0; 8 {,,...,N T }; 8 {,,...,N T }; = 8 {,,...,N T }. Elmnang, 8 {,,...,N T } n all quaons ylds µ +, 8 {,,...,N T }; P N T = appl P ; µ 0; µ P N T = P = 0; 8 {,,...,N T };(µ + ) = 8 {,,...,N T }. For all {,,...,N T }, w consdr µ < and µ sparaly: ) If µ <, hn µ + holds only whn > whch by (µ +Z/V + ) mpls ha µ + =.., =. ) If µ, hn > 0 s mpossbl, bcaus > 0 mpls ha µ + > whch oghr wh > 0 conradc h slacknss condon (µ + ) =0. Thus, f µ, w mus hav =0. Summarzng boh cass, w hav = max, 8 {,,...,NT }, whr µ s chosn such ha P n = appl P, µ 0 and µ P N T = P =0. To fnd such µ, w frs chck f µ = 0. If µ = 0 s ru, h slacknss condon µ P N T = = 0 s guarand o hold and w nd o furhr rqur P N T P = = NT = max appl P. Thus µ =0f and only f P N T = max Z/V appl P. Thus, Algorhm chcks f P N T = max Z/V appl P holds a h frs sp and f hs s ru, hn w conclud µ =0and w ar don! Ohrws, w know µ > 0. By h slacknss condon µ P N T = P = w mus hav P N T = = P NT = max = P. To fnd µ > 0 such ha P NT = max = P, w could apply a bscon sarch by nong ha all ar dcrasng wh rspc o µ. Anohr algorhm of fndng µ s nsprd by h obsrvaon ha f j k, 8j, k {,,...,N T }, hn j k. Thus, w frs sor all n a dcrasng ordr, say s h prmuaon such ha () () (N T ); and hn squnally chck f {,,...,N T } s h ndx such ha () µ 0 and (+) µ appl 0. To chck hs, w frs assum s ndd such an ndx and solv h quaon = P o oban µ ; (No ha n P j= (j) Algorhm, o avod rcalculang h paral sum P j= (j) for ach, w nroduc h paramr S = P j= and (j) upda S ncrmnally. By dong hs, h complxy of ach raon n h loop s only O().) hn vrfy h assumpon by chckng f 0 and () appl 0. (+) Ths algorhm s dscrbd n Algorhm. APPENDIX B PROOF OF THEOREM 3 Clam. If b s an opmal soluon o h followng convx program: mn k k F (7) s.. r( ) appl P (8) S N T + (9) hn b Q = U H b U s an opmal soluon o problm (6)-(8).
9 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 Proof: Ths clam can b provn by conradcon. L b b an opmal soluon o convx program (7)-(9) and dfn Q b = U H U. b Assum ha hr xss Q S N T + such ha Q 6= Q b and s a soluon o problm (6)-(8) ha s srcly br han Q. b Consdr = UQU H and rach a conradcon by showng s srcly br han b as follows: No ha r( )=r(u QU H )=r( Q) appl P, whr h las nqualy follows from h assumpon ha Q s soluon o problm (6)-(8). Also no ha S N T + snc Q S N T +. Thus, s fasbl o problm (7)-(9). No ha k (a) k F = ku H U U H (b) Uk F = kq (c) Xk F < kq b (d) Xk F = kuqu b H UXU H () k F = k b k F, whr (a) and (d) follow from h fac Frobnus norm s unary nvaran 4 ; (b) follows from h fac ha = UQU H and X = U H U; (c) follows from h fac ha Q s srcly br han Q; b and () follows from h fac ha Q b = U H U b and X = U H U. Thus, s srcly br han. b A conradcon! Clam 3. Th opmal soluon o problm (7)-(9) mus b a dagonal marx. Proof: Ths clam can b provn by conradcon. Assum ha problm (7)-(9) has an opmal soluon ha s no dagonal. Snc s posv smdfn, all h dagonal nrs of ar non-ngav. Dfn b as a dagonal marx whos h -h dagonal nry s qual o h -h dagonal nry of for all {,,...,N T }. No ha r( b )=r( ) appl P and b S n +. Thus, b s fasbl o problm (7)-(9). No ha k b k F < k k F snc s dagonal. Thus, b s a soluon srcly br han. A conradcon! So h opmal soluon o problm (7)-(9) mus b a dagonal marx. By h abov wo clams, suffcs o assum ha h opmal soluon o problm (6)-(8) has h srucur ˆQ = U H U, whr s a marx wh non-ngav nrs. To solv problm (6)-(8), suffcs o consdr h followng convx program. mn s.. XN T ( ) (30) = XN T appl P (3) = 8 {,,...,N T } (3) No ha problm (30)-(3) sasfs Slar s condon. So h opmal soluon o problm (30)-(3) s characrzd by KKT condons [0]. Th rmanng par s smlar o h proof of Thorm and can b found n h full vrson [7]. REFERENCES [] S. K. Jayawra and H. V. Poor, Capacy of mulpl-annna sysms wh boh rcvr and ransmr channl sa nformaon, IEEE Transacons on Informaon Thory, vol. 49, no. pp , 003. [3] S. A. Jafar, S. Vshwanah, and A. Goldsmh, Channl capacy and bamformng for mulpl ransm and rcv annnas wh covaranc fdback, n Procdngs of IEEE Inrnaonal Confrnc on Communcaons (ICC), 00. [4] E. Jorswck and H. Boch, Channl capacy and capacy-rang of bamformng n MIMO wrlss sysms undr corrlad fadng wh covaranc fdback, IEEE Transacons on Wrlss Communcaons, vol. 3, no. 5, pp , 004. [5] V. V. Vravall, Y. Lang, and A. M. Sayd, Corrlad MIMO wrlss channls: capacy, opmal sgnalng, and asympocs, IEEE Transacons on Informaon Thory, vol. 5, no. 6, pp , 005. [6] M. J. Nly, Dynamc powr allocaon and roung for sall and wrlss nworks wh m varyng channls, Ph.D. dssraon, Massachuss Insu of Tchnology, 003. [7], Sochasc nwork opmzaon wh applcaon o communcaon and quung sysms. Morgan & Claypool Publshrs, 0 vol. 3, no.. [8] J.-W. L, R. R. Mazumdar, and N. B. Shroff, Opporunsc powr schdulng for dynamc mul-srvr wrlss sysms, IEEE Transacons on Wrlss Communcaons, vol. 5, no. 6, pp , 006. [9] A. Rbro, Ergodc sochasc opmzaon algorhms for wrlss communcaon and nworkng, IEEE Transacons on Sgnal Procssng, vol. 58, no., pp , 00. [0] Y. Hu and A. Rbro, Adapv dsrbud algorhms for opmal random accss channls, IEEE Transacons on Wrlss Communcaons, vol. no. 8, pp , 0. [] J. Lu, Y. T. Hou, Y. Sh, and H. D. Shral, On prformanc opmzaon for mul-carrr mmo ad hoc nworks, n Procdngs of h 0h ACM nrnaonal symposum on Mobl ad hoc nworkng and compung (MobHoc), 009, pp [] M. Znkvch, Onln convx programmng and gnralzd nfnsmal gradn ascn, n Procdngs of h 0h Inrnaonal Confrnc on Machn Larnng (ICML), 003. [3] N. Buchbndr, L. Lwn-Eyan, I. Mnach, J. S. Naor, and A. Orda, Dynamc powr allocaon undr arbrary varyng channls-an onln approach, n Procdngs of IEEE Annual Jon Confrnc of h IEEE Compur and Communcaons Socs (INFOCOM), 009. [4], Dynamc powr allocaon undr arbrary varyng channls h mul-usr cas, n Procdngs of IEEE Annual Jon Confrnc of h IEEE Compur and Communcaons Socs (INFOCOM), 00. [5] I. Sakogannaks, P. Mrkopoulos, and C. Toua, Adapv powr allocaon and conrol n m-varyng mul-carrr MIMO nworks, arxv prprn arxv: , 05. [6] A. Goldsmh, Wrlss communcaons. Cambrdg Unvrsy Prss, 005. [7] H. Yu and M. J. Nly, Dynamc powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms whou channl dsrbuon nformaon, arxv prprn arxv:5.0849, 05. [8] A. Fn, S. Hanly, and R. Mahar, Drvavs of muual nformaon n gaussan vcor channls wh applcaons, n Procdngs of IEEE Inrnaonal Symposum on Informaon Thory (ISIT), 007, pp [9] D. P. Palomar and M. A. Lagunas, Jon ransm-rcv spac-m qualzaon n spaally corrlad MIMO channls: A bamformng approach, IEEE Journal on Slcd Aras n Communcaons, vol., no. 5, pp , 003. [0] S. Boyd and L. Vandnbrgh, Convx Opmzaon. Cambrdg Unvrsy Prss, 004. [] S. Boyd and L. Xao, Las-squars covaranc marx adjusmn, SIAM Journal on Marx Analyss and Applcaons, vol. 7, no., pp , 005. [] R. A. Horn and C. R. Johnson, Marx Analyss. Cambrdg Unvrsy Prss, 985. [] I. E. Tlaar, Capacy of mul-annna gaussan channls, Europan ransacons on lcommuncaons, vol. no. 6, pp , Tha s kauk F = kak F for all A C n n and all unary marx U.
Consider a system of 2 simultaneous first order linear equations
 Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Summary: Solving a Homogeneous System of Two Linear First Order Equations in Two Unknowns
 Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
State Observer Design
 Sa Obsrvr Dsgn A. Khak Sdgh Conrol Sysms Group Faculy of Elcrcal and Compur Engnrng K. N. Toos Unvrsy of Tchnology Fbruary 2009 1 Problm Formulaon A ky assumpon n gnvalu assgnmn and sablzng sysms usng
Sa Obsrvr Dsgn A. Khak Sdgh Conrol Sysms Group Faculy of Elcrcal and Compur Engnrng K. N. Toos Unvrsy of Tchnology Fbruary 2009 1 Problm Formulaon A ky assumpon n gnvalu assgnmn and sablzng sysms usng
The Variance-Covariance Matrix
 Th Varanc-Covaranc Marx Our bggs a so-ar has bn ng a lnar uncon o a s o daa by mnmzng h las squars drncs rom h o h daa wh mnsarch. Whn analyzng non-lnar daa you hav o us a program l Malab as many yps o
Th Varanc-Covaranc Marx Our bggs a so-ar has bn ng a lnar uncon o a s o daa by mnmzng h las squars drncs rom h o h daa wh mnsarch. Whn analyzng non-lnar daa you hav o us a program l Malab as many yps o
innovations shocks white noise
 Innovaons Tm-srs modls ar consrucd as lnar funcons of fundamnal forcasng rrors, also calld nnovaons or shocks Ths basc buldng blocks sasf var σ Srall uncorrlad Ths rrors ar calld wh nos In gnral, f ou
Innovaons Tm-srs modls ar consrucd as lnar funcons of fundamnal forcasng rrors, also calld nnovaons or shocks Ths basc buldng blocks sasf var σ Srall uncorrlad Ths rrors ar calld wh nos In gnral, f ou
Advanced Queueing Theory. M/G/1 Queueing Systems
 Advand Quung Thory Ths slds ar rad by Dr. Yh Huang of Gorg Mason Unvrsy. Sudns rgsrd n Dr. Huang's ourss a GMU an ma a sngl mahn-radabl opy and prn a sngl opy of ah sld for hr own rfrn, so long as ah sld
Advand Quung Thory Ths slds ar rad by Dr. Yh Huang of Gorg Mason Unvrsy. Sudns rgsrd n Dr. Huang's ourss a GMU an ma a sngl mahn-radabl opy and prn a sngl opy of ah sld for hr own rfrn, so long as ah sld
Boosting and Ensemble Methods
 Boosng and Ensmbl Mhods PAC Larnng modl Som dsrbuon D ovr doman X Eampls: c* s h arg funcon Goal: Wh hgh probably -d fnd h n H such ha rrorh,c* < d and ar arbrarly small. Inro o ML 2 Wak Larnng
Boosng and Ensmbl Mhods PAC Larnng modl Som dsrbuon D ovr doman X Eampls: c* s h arg funcon Goal: Wh hgh probably -d fnd h n H such ha rrorh,c* < d and ar arbrarly small. Inro o ML 2 Wak Larnng
9. Simple Rules for Monetary Policy
 9. Smpl Ruls for Monar Polc John B. Talor, Ma 0, 03 Woodford, AR 00 ovrvw papr Purpos s o consdr o wha xn hs prscrpon rsmbls h sor of polc ha conomc hor would rcommnd Bu frs, l s rvw how hs sor of polc
9. Smpl Ruls for Monar Polc John B. Talor, Ma 0, 03 Woodford, AR 00 ovrvw papr Purpos s o consdr o wha xn hs prscrpon rsmbls h sor of polc ha conomc hor would rcommnd Bu frs, l s rvw how hs sor of polc
Frequency Response. Response of an LTI System to Eigenfunction
 Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
t=0 t>0: + vr - i dvc Continuation
 hapr Ga Dlay and rcus onnuaon s rcu Equaon >: S S Ths dffrnal quaon, oghr wh h nal condon, fully spcfs bhaor of crcu afr swch closs Our n challng: larn how o sol such quaons TUE/EE 57 nwrk analys 4/5 NdM
hapr Ga Dlay and rcus onnuaon s rcu Equaon >: S S Ths dffrnal quaon, oghr wh h nal condon, fully spcfs bhaor of crcu afr swch closs Our n challng: larn how o sol such quaons TUE/EE 57 nwrk analys 4/5 NdM
Ergodic Capacity of a SIMO System Over Nakagami-q Fading Channel
 DUET Journal Vol., Issu, Jun Ergodc apac of a SIO Ssm Ovr Nakagam-q Fadng hannl d. Sohdul Islam * and ohammad akbul Islam Dp. of Elcrcal and Elcronc Engnrng, Islamc Unvrs of Tchnolog (IUT, Gazpur, Bangladsh
DUET Journal Vol., Issu, Jun Ergodc apac of a SIO Ssm Ovr Nakagam-q Fadng hannl d. Sohdul Islam * and ohammad akbul Islam Dp. of Elcrcal and Elcronc Engnrng, Islamc Unvrs of Tchnolog (IUT, Gazpur, Bangladsh
Supplementary Figure 1. Experiment and simulation with finite qudit. anharmonicity. (a), Experimental data taken after a 60 ns three-tone pulse.
 Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
ELEN E4830 Digital Image Processing
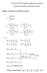 ELEN E48 Dgal Imag Procssng Mrm Eamnaon Sprng Soluon Problm Quanzaon and Human Encodng r k u P u P u r r 6 6 6 6 5 6 4 8 8 4 P r 6 6 P r 4 8 8 6 8 4 r 8 4 8 4 7 8 r 6 6 6 6 P r 8 4 8 P r 6 6 8 5 P r /
ELEN E48 Dgal Imag Procssng Mrm Eamnaon Sprng Soluon Problm Quanzaon and Human Encodng r k u P u P u r r 6 6 6 6 5 6 4 8 8 4 P r 6 6 P r 4 8 8 6 8 4 r 8 4 8 4 7 8 r 6 6 6 6 P r 8 4 8 P r 6 6 8 5 P r /
SIMEON BALL AND AART BLOKHUIS
 A BOUND FOR THE MAXIMUM WEIGHT OF A LINEAR CODE SIMEON BALL AND AART BLOKHUIS Absrac. I s shown ha h paramrs of a lnar cod ovr F q of lngh n, dmnson k, mnmum wgh d and maxmum wgh m sasfy a cran congrunc
A BOUND FOR THE MAXIMUM WEIGHT OF A LINEAR CODE SIMEON BALL AND AART BLOKHUIS Absrac. I s shown ha h paramrs of a lnar cod ovr F q of lngh n, dmnson k, mnmum wgh d and maxmum wgh m sasfy a cran congrunc
Lecture 4 : Backpropagation Algorithm. Prof. Seul Jung ( Intelligent Systems and Emotional Engineering Laboratory) Chungnam National University
 Lcur 4 : Bacpropagaon Algorhm Pro. Sul Jung Inllgn Sm and moonal ngnrng Laboraor Chungnam Naonal Unvr Inroducon o Bacpropagaon algorhm 969 Mn and Papr aac. 980 Parr and Wrbo dcovrd bac propagaon algorhm.
Lcur 4 : Bacpropagaon Algorhm Pro. Sul Jung Inllgn Sm and moonal ngnrng Laboraor Chungnam Naonal Unvr Inroducon o Bacpropagaon algorhm 969 Mn and Papr aac. 980 Parr and Wrbo dcovrd bac propagaon algorhm.
Problem 1: Consider the following stationary data generation process for a random variable y t. e t ~ N(0,1) i.i.d.
 A/CN C m Sr Anal Profor Òcar Jordà Wnr conomc.c. Dav POBLM S SOLIONS Par I Analcal Quon Problm : Condr h followng aonar daa gnraon proc for a random varabl - N..d. wh < and N -. a Oban h populaon man varanc
A/CN C m Sr Anal Profor Òcar Jordà Wnr conomc.c. Dav POBLM S SOLIONS Par I Analcal Quon Problm : Condr h followng aonar daa gnraon proc for a random varabl - N..d. wh < and N -. a Oban h populaon man varanc
CIVL 8/ D Boundary Value Problems - Triangular Elements (T6) 1/8
 CIVL 8/7 -D Boundar Valu Problm - rangular Elmn () /8 SI-ODE RIAGULAR ELEMES () A quadracall nrpolad rangular lmn dfnd b nod, hr a h vrc and hr a h mddl a ach d. h mddl nod, dpndng on locaon, ma dfn a
CIVL 8/7 -D Boundar Valu Problm - rangular Elmn () /8 SI-ODE RIAGULAR ELEMES () A quadracall nrpolad rangular lmn dfnd b nod, hr a h vrc and hr a h mddl a ach d. h mddl nod, dpndng on locaon, ma dfn a
Analysis of decentralized potential field based multi-agent navigation via primal-dual Lyapunov theory
 Analyss of dcnralzd ponal fld basd mul-agn navgaon va prmal-dual Lyapunov hory Th MIT Faculy has mad hs arcl opnly avalabl. Plas shar how hs accss bnfs you. Your sory mars. Caon As Publshd Publshr Dmarogonas,
Analyss of dcnralzd ponal fld basd mul-agn navgaon va prmal-dual Lyapunov hory Th MIT Faculy has mad hs arcl opnly avalabl. Plas shar how hs accss bnfs you. Your sory mars. Caon As Publshd Publshr Dmarogonas,
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 16 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 16 Apr 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 16 Apr 2016](/thumbs/91/106796584.jpg) Th Cauchy problm for a combuson modl n porous mda J. C. da Moa M. M. Sanos. A. Sanos arxv:64.4798v [mah.ap] 6 Apr 6 Absrac W prov h xsnc of a global soluon o h Cauchy problm for a nonlnar racon-dffuson
Th Cauchy problm for a combuson modl n porous mda J. C. da Moa M. M. Sanos. A. Sanos arxv:64.4798v [mah.ap] 6 Apr 6 Absrac W prov h xsnc of a global soluon o h Cauchy problm for a nonlnar racon-dffuson
FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS
 FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS hp://www.cs.umass.du/c/orn/faultolransysms ar 4 Analyss Mhods Chapr HW Faul Tolranc ar.4.1 Duplx Sysms Boh procssors xcu h sam as If oupus ar n agrmn - rsul s assumd o b corrc If
FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS hp://www.cs.umass.du/c/orn/faultolransysms ar 4 Analyss Mhods Chapr HW Faul Tolranc ar.4.1 Duplx Sysms Boh procssors xcu h sam as If oupus ar n agrmn - rsul s assumd o b corrc If
Wave Superposition Principle
 Physcs 36: Was Lcur 5 /7/8 Wa Suroson Prncl I s qu a common suaon for wo or mor was o arr a h sam on n sac or o xs oghr along h sam drcon. W wll consdr oday sral moran cass of h combnd ffcs of wo or mor
Physcs 36: Was Lcur 5 /7/8 Wa Suroson Prncl I s qu a common suaon for wo or mor was o arr a h sam on n sac or o xs oghr along h sam drcon. W wll consdr oday sral moran cass of h combnd ffcs of wo or mor
Chapter 9 Transient Response
 har 9 Transn sons har 9: Ouln N F n F Frs-Ordr Transns Frs-Ordr rcus Frs ordr crcus: rcus conan onl on nducor or on caacor gornd b frs-ordr dffrnal quaons. Zro-nu rsons: h crcu has no ald sourc afr a cran
har 9 Transn sons har 9: Ouln N F n F Frs-Ordr Transns Frs-Ordr rcus Frs ordr crcus: rcus conan onl on nducor or on caacor gornd b frs-ordr dffrnal quaons. Zro-nu rsons: h crcu has no ald sourc afr a cran
Guaranteed Cost Control for a Class of Uncertain Delay Systems with Actuator Failures Based on Switching Method
 49 Inrnaonal Journal of Conrol, Ru Wang Auomaon, and Jun and Zhao Sysms, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 49-5, Ocobr 7 Guarand Cos Conrol for a Class of Uncran Dlay Sysms wh Acuaor Falurs Basd on Swchng Mhod Ru Wang
49 Inrnaonal Journal of Conrol, Ru Wang Auomaon, and Jun and Zhao Sysms, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 49-5, Ocobr 7 Guarand Cos Conrol for a Class of Uncran Dlay Sysms wh Acuaor Falurs Basd on Swchng Mhod Ru Wang
Safety and Reliability of Embedded Systems. (Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Stochastic Reliability Analysis
 (Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons of Falurs ovr Tm Rlably Modlng Exampls of Dsrbuon Funcons Th xponnal
(Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons of Falurs ovr Tm Rlably Modlng Exampls of Dsrbuon Funcons Th xponnal
Applying Software Reliability Techniques to Low Retail Demand Estimation
 Applyng Sofwar Rlably Tchnqus o Low Ral Dmand Esmaon Ma Lndsy Unvrsy of Norh Txas ITDS Dp P.O. Box 30549 Dnon, TX 7603-549 940 565 3174 lndsym@un.du Robr Pavur Unvrsy of Norh Txas ITDS Dp P.O. Box 30549
Applyng Sofwar Rlably Tchnqus o Low Ral Dmand Esmaon Ma Lndsy Unvrsy of Norh Txas ITDS Dp P.O. Box 30549 Dnon, TX 7603-549 940 565 3174 lndsym@un.du Robr Pavur Unvrsy of Norh Txas ITDS Dp P.O. Box 30549
Chapter 13 Laplace Transform Analysis
 Chapr aplac Tranorm naly Chapr : Ouln aplac ranorm aplac Tranorm -doman phaor analy: x X σ m co ω φ x X X m φ x aplac ranorm: [ o ] d o d < aplac Tranorm Thr condon Unlaral on-dd aplac ranorm: aplac ranorm
Chapr aplac Tranorm naly Chapr : Ouln aplac ranorm aplac Tranorm -doman phaor analy: x X σ m co ω φ x X X m φ x aplac ranorm: [ o ] d o d < aplac Tranorm Thr condon Unlaral on-dd aplac ranorm: aplac ranorm
Safety and Reliability of Embedded Systems. (Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Stochastic Reliability Analysis
 Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms (Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons
Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms (Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons
Control Systems (Lecture note #6)
 6.5 Corol Sysms (Lcur o #6 Las Tm: Lar algbra rw Lar algbrac quaos soluos Paramrzao of all soluos Smlary rasformao: compao form Egalus ad gcors dagoal form bg pcur: o brach of h cours Vcor spacs marcs
6.5 Corol Sysms (Lcur o #6 Las Tm: Lar algbra rw Lar algbrac quaos soluos Paramrzao of all soluos Smlary rasformao: compao form Egalus ad gcors dagoal form bg pcur: o brach of h cours Vcor spacs marcs
Theoretical Seismology
 Thorcal Ssmology Lcur 9 Sgnal Procssng Fourr analyss Fourr sudd a h Écol Normal n Pars, augh by Lagrang, who Fourr dscrbd as h frs among Europan mn of scnc, Laplac, who Fourr rad lss hghly, and by Mong.
Thorcal Ssmology Lcur 9 Sgnal Procssng Fourr analyss Fourr sudd a h Écol Normal n Pars, augh by Lagrang, who Fourr dscrbd as h frs among Europan mn of scnc, Laplac, who Fourr rad lss hghly, and by Mong.
Lucas Test is based on Euler s theorem which states that if n is any integer and a is coprime to n, then a φ(n) 1modn.
 Modul 10 Addtonal Topcs 10.1 Lctur 1 Prambl: Dtrmnng whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or compost s known as prmalty tstng. Thr ar prmalty tsts whch mrly tll us whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or not, wthout gvng us th factors
Modul 10 Addtonal Topcs 10.1 Lctur 1 Prambl: Dtrmnng whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or compost s known as prmalty tstng. Thr ar prmalty tsts whch mrly tll us whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or not, wthout gvng us th factors
Lecture 1: Numerical Integration The Trapezoidal and Simpson s Rule
 Lcur : Numrical ngraion Th Trapzoidal and Simpson s Rul A problm Th probabiliy of a normally disribud (man µ and sandard dviaion σ ) vn occurring bwn h valus a and b is B A P( a x b) d () π whr a µ b -
Lcur : Numrical ngraion Th Trapzoidal and Simpson s Rul A problm Th probabiliy of a normally disribud (man µ and sandard dviaion σ ) vn occurring bwn h valus a and b is B A P( a x b) d () π whr a µ b -
Transient Analysis of Two-dimensional State M/G/1 Queueing Model with Multiple Vacations and Bernoulli Schedule
 Inrnaonal Journal of Compur Applcaons (975 8887) Volum 4 No.3, Fbruary 22 Transn Analyss of Two-dmnsonal Sa M/G/ Quung Modl wh Mulpl Vacaons and Brnoull Schdul Indra Assoca rofssor Dparmn of Sascs and
Inrnaonal Journal of Compur Applcaons (975 8887) Volum 4 No.3, Fbruary 22 Transn Analyss of Two-dmnsonal Sa M/G/ Quung Modl wh Mulpl Vacaons and Brnoull Schdul Indra Assoca rofssor Dparmn of Sascs and
CPSC 211 Data Structures & Implementations (c) Texas A&M University [ 259] B-Trees
![CPSC 211 Data Structures & Implementations (c) Texas A&M University [ 259] B-Trees CPSC 211 Data Structures & Implementations (c) Texas A&M University [ 259] B-Trees](/thumbs/74/70718364.jpg) CPSC 211 Daa Srucurs & Implmnaions (c) Txas A&M Univrsiy [ 259] B-Trs Th AVL r and rd-black r allowd som variaion in h lnghs of h diffrn roo-o-laf pahs. An alrnaiv ida is o mak sur ha all roo-o-laf pahs
CPSC 211 Daa Srucurs & Implmnaions (c) Txas A&M Univrsiy [ 259] B-Trs Th AVL r and rd-black r allowd som variaion in h lnghs of h diffrn roo-o-laf pahs. An alrnaiv ida is o mak sur ha all roo-o-laf pahs
CONTINUOUS TIME DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING
 Eon. 511b Sprng 1993 C. Sms I. Th Opmaon Problm CONTINUOUS TIME DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING W onsdr h problm of maxmng subj o and EU(C, ) d (1) j ^ d = (C, ) d + σ (C, ) dw () h(c, ), (3) whr () and (3) hold for
Eon. 511b Sprng 1993 C. Sms I. Th Opmaon Problm CONTINUOUS TIME DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING W onsdr h problm of maxmng subj o and EU(C, ) d (1) j ^ d = (C, ) d + σ (C, ) dw () h(c, ), (3) whr () and (3) hold for
Engineering Circuit Analysis 8th Edition Chapter Nine Exercise Solutions
 Engnrng rcu naly 8h Eon hapr Nn Exrc Soluon. = KΩ, = µf, an uch ha h crcu rpon oramp. a For Sourc-fr paralll crcu: For oramp or b H 9V, V / hoo = H.7.8 ra / 5..7..9 9V 9..9..9 5.75,.5 5.75.5..9 . = nh,
Engnrng rcu naly 8h Eon hapr Nn Exrc Soluon. = KΩ, = µf, an uch ha h crcu rpon oramp. a For Sourc-fr paralll crcu: For oramp or b H 9V, V / hoo = H.7.8 ra / 5..7..9 9V 9..9..9 5.75,.5 5.75.5..9 . = nh,
Implementation of the Extended Conjugate Gradient Method for the Two- Dimensional Energized Wave Equation
 Lonardo Elcronc Jornal of raccs and Tchnolos ISSN 58-078 Iss 9 Jl-Dcmbr 006 p. -4 Implmnaon of h Endd Cona Gradn Mhod for h Two- Dmnsonal Enrd Wav Eqaon Vcor Onoma WAZIRI * Snda Ass REJU Mahmacs/Compr
Lonardo Elcronc Jornal of raccs and Tchnolos ISSN 58-078 Iss 9 Jl-Dcmbr 006 p. -4 Implmnaon of h Endd Cona Gradn Mhod for h Two- Dmnsonal Enrd Wav Eqaon Vcor Onoma WAZIRI * Snda Ass REJU Mahmacs/Compr
A Note on Estimability in Linear Models
 Intrnatonal Journal of Statstcs and Applcatons 2014, 4(4): 212-216 DOI: 10.5923/j.statstcs.20140404.06 A Not on Estmablty n Lnar Modls S. O. Adymo 1,*, F. N. Nwob 2 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatcs and Statstcs,
Intrnatonal Journal of Statstcs and Applcatons 2014, 4(4): 212-216 DOI: 10.5923/j.statstcs.20140404.06 A Not on Estmablty n Lnar Modls S. O. Adymo 1,*, F. N. Nwob 2 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatcs and Statstcs,
Homework: Introduction to Motion
 Homwork: Inroducon o Moon Dsanc vs. Tm Graphs Nam Prod Drcons: Answr h foowng qusons n h spacs provdd. 1. Wha do you do o cra a horzona n on a dsancm graph? 2. How do you wak o cra a sragh n ha sops up?
Homwork: Inroducon o Moon Dsanc vs. Tm Graphs Nam Prod Drcons: Answr h foowng qusons n h spacs provdd. 1. Wha do you do o cra a horzona n on a dsancm graph? 2. How do you wak o cra a sragh n ha sops up?
Gaussian Random Process and Its Application for Detecting the Ionospheric Disturbances Using GPS
 Journal of Global Posonng Sysms (005) Vol. 4, No. 1-: 76-81 Gaussan Random Procss and Is Applcaon for Dcng h Ionosphrc Dsurbancs Usng GPS H.. Zhang 1,, J. Wang 3, W. Y. Zhu 1, C. Huang 1 (1) Shangha Asronomcal
Journal of Global Posonng Sysms (005) Vol. 4, No. 1-: 76-81 Gaussan Random Procss and Is Applcaon for Dcng h Ionosphrc Dsurbancs Usng GPS H.. Zhang 1,, J. Wang 3, W. Y. Zhu 1, C. Huang 1 (1) Shangha Asronomcal
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Rcap: Maxmum 3-Sasfably Maxmum 3-Sasfably: Analyss CS 580: Algorhm Dsgn and Analyss Jrmah Block Purdu Unvrsy Sprng 2018 Announcmns: Homwork 6 dadln xndd o Aprl 24 h a 11:59 PM Cours Evaluaon Survy: Lv
Rcap: Maxmum 3-Sasfably Maxmum 3-Sasfably: Analyss CS 580: Algorhm Dsgn and Analyss Jrmah Block Purdu Unvrsy Sprng 2018 Announcmns: Homwork 6 dadln xndd o Aprl 24 h a 11:59 PM Cours Evaluaon Survy: Lv
On the Derivatives of Bessel and Modified Bessel Functions with Respect to the Order and the Argument
 Inrnaional Rsarch Journal of Applid Basic Scincs 03 Aailabl onlin a wwwirjabscom ISSN 5-838X / Vol 4 (): 47-433 Scinc Eplorr Publicaions On h Driais of Bssl Modifid Bssl Funcions wih Rspc o h Ordr h Argumn
Inrnaional Rsarch Journal of Applid Basic Scincs 03 Aailabl onlin a wwwirjabscom ISSN 5-838X / Vol 4 (): 47-433 Scinc Eplorr Publicaions On h Driais of Bssl Modifid Bssl Funcions wih Rspc o h Ordr h Argumn
Dr. Junchao Xia Center of Biophysics and Computational Biology. Fall /21/2016 1/23
 BIO53 Bosascs Lcur 04: Cral Lm Thorm ad Thr Dsrbuos Drvd from h Normal Dsrbuo Dr. Juchao a Cr of Bophyscs ad Compuaoal Bology Fall 06 906 3 Iroduco I hs lcur w wll alk abou ma cocps as lsd blow, pcd valu
BIO53 Bosascs Lcur 04: Cral Lm Thorm ad Thr Dsrbuos Drvd from h Normal Dsrbuo Dr. Juchao a Cr of Bophyscs ad Compuaoal Bology Fall 06 906 3 Iroduco I hs lcur w wll alk abou ma cocps as lsd blow, pcd valu
Bethe-Salpeter Equation Green s Function and the Bethe-Salpeter Equation for Effective Interaction in the Ladder Approximation
 Bh-Salp Equaon n s Funcon and h Bh-Salp Equaon fo Effcv Inacon n h Ladd Appoxmaon Csa A. Z. Vasconcllos Insuo d Físca-UFRS - upo: Físca d Hadons Sngl-Pacl Popagao. Dagam xpanson of popagao. W consd as
Bh-Salp Equaon n s Funcon and h Bh-Salp Equaon fo Effcv Inacon n h Ladd Appoxmaon Csa A. Z. Vasconcllos Insuo d Físca-UFRS - upo: Físca d Hadons Sngl-Pacl Popagao. Dagam xpanson of popagao. W consd as
EE243 Advanced Electromagnetic Theory Lec # 10: Poynting s Theorem, Time- Harmonic EM Fields
 Appl M Fall 6 Nuruhr Lcur # r 9/6/6 4 Avanc lcromagnc Thory Lc # : Poynng s Thorm Tm- armonc M Fls Poynng s Thorm Consrvaon o nrgy an momnum Poynng s Thorm or Lnar sprsv Ma Poynng s Thorm or Tm-armonc
Appl M Fall 6 Nuruhr Lcur # r 9/6/6 4 Avanc lcromagnc Thory Lc # : Poynng s Thorm Tm- armonc M Fls Poynng s Thorm Consrvaon o nrgy an momnum Poynng s Thorm or Lnar sprsv Ma Poynng s Thorm or Tm-armonc
Chap 2: Reliability and Availability Models
 Chap : lably ad valably Modls lably = prob{s s fully fucog [,]} Suppos from [,] m prod, w masur ou of N compos, of whch N : # of compos oprag corrcly a m N f : # of compos whch hav fald a m rlably of h
Chap : lably ad valably Modls lably = prob{s s fully fucog [,]} Suppos from [,] m prod, w masur ou of N compos, of whch N : # of compos oprag corrcly a m N f : # of compos whch hav fald a m rlably of h
10/7/14. Mixture Models. Comp 135 Introduction to Machine Learning and Data Mining. Maximum likelihood estimation. Mixture of Normals in 1D
 Comp 35 Introducton to Machn Larnng and Data Mnng Fall 204 rofssor: Ron Khardon Mxtur Modls Motvatd by soft k-mans w dvlopd a gnratv modl for clustrng. Assum thr ar k clustrs Clustrs ar not rqurd to hav
Comp 35 Introducton to Machn Larnng and Data Mnng Fall 204 rofssor: Ron Khardon Mxtur Modls Motvatd by soft k-mans w dvlopd a gnratv modl for clustrng. Assum thr ar k clustrs Clustrs ar not rqurd to hav
CSE 245: Computer Aided Circuit Simulation and Verification
 CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
A universal saturation controller design for mobile robots
 A unvrsal sauraon conrollr sgn for mobl robos K.D. Do,,Z.P.Jang an J. Pan Dparmn of Elcrcal an Compur Engnrng, Polychnc Unvrsy, NY, USA. Emal: uc@mch.uwa.u.au, zjang@conrol.poly.u Dparmn of Mchancal Engnrng,
A unvrsal sauraon conrollr sgn for mobl robos K.D. Do,,Z.P.Jang an J. Pan Dparmn of Elcrcal an Compur Engnrng, Polychnc Unvrsy, NY, USA. Emal: uc@mch.uwa.u.au, zjang@conrol.poly.u Dparmn of Mchancal Engnrng,
Grand Canonical Ensemble
 Th nsmbl of systms mmrsd n a partcl-hat rsrvor at constant tmpratur T, prssur P, and chmcal potntal. Consdr an nsmbl of M dntcal systms (M =,, 3,...M).. Thy ar mutually sharng th total numbr of partcls
Th nsmbl of systms mmrsd n a partcl-hat rsrvor at constant tmpratur T, prssur P, and chmcal potntal. Consdr an nsmbl of M dntcal systms (M =,, 3,...M).. Thy ar mutually sharng th total numbr of partcls
Dynamic Team Decision Theory. EECS 558 Project Shrutivandana Sharma and David Shuman December 10, 2005
 Dynamc Team Decson Theory EECS 558 Proec Shruvandana Sharma and Davd Shuman December 0, 005 Oulne Inroducon o Team Decson Theory Decomposon of he Dynamc Team Decson Problem Equvalence of Sac and Dynamc
Dynamc Team Decson Theory EECS 558 Proec Shruvandana Sharma and Davd Shuman December 0, 005 Oulne Inroducon o Team Decson Theory Decomposon of he Dynamc Team Decson Problem Equvalence of Sac and Dynamc
Soft k-means Clustering. Comp 135 Machine Learning Computer Science Tufts University. Mixture Models. Mixture of Normals in 1D
 Comp 35 Machn Larnng Computr Scnc Tufts Unvrsty Fall 207 Ron Khardon Th EM Algorthm Mxtur Modls Sm-Suprvsd Larnng Soft k-mans Clustrng ck k clustr cntrs : Assocat xampls wth cntrs p,j ~~ smlarty b/w cntr
Comp 35 Machn Larnng Computr Scnc Tufts Unvrsty Fall 207 Ron Khardon Th EM Algorthm Mxtur Modls Sm-Suprvsd Larnng Soft k-mans Clustrng ck k clustr cntrs : Assocat xampls wth cntrs p,j ~~ smlarty b/w cntr
Dynamic Controllability with Overlapping Targets: Or Why Target Independence May Not be Good for You
 Dynamc Conrollably wh Ovrlappng Targs: Or Why Targ Indpndnc May No b Good for You Ncola Acoclla Unvrsy of Rom La Sapnza Govann D Barolomo Unvrsy of Rom La Sapnza and Unvrsy of Tramo Andrw Hughs Hall Vandrbl
Dynamc Conrollably wh Ovrlappng Targs: Or Why Targ Indpndnc May No b Good for You Ncola Acoclla Unvrsy of Rom La Sapnza Govann D Barolomo Unvrsy of Rom La Sapnza and Unvrsy of Tramo Andrw Hughs Hall Vandrbl
Reduced The Complexity of Soft Input Soft Output Maximum A posteriori Decoder of Linear Block Code By Using Parallel Trellises Structure
 Journal of Babylon nvrsy/engnrng Scncs/ No.4/ Vol.25: 27 Rducd Th Complxy of Sof Inpu Sof upu Maxmum A posror Dcodr of Lnar Block Cod By sng Paralll Trllss Srucur Samr Abdul Cahm Khohr Hadr Jabbar Abd
Journal of Babylon nvrsy/engnrng Scncs/ No.4/ Vol.25: 27 Rducd Th Complxy of Sof Inpu Sof upu Maxmum A posror Dcodr of Lnar Block Cod By sng Paralll Trllss Srucur Samr Abdul Cahm Khohr Hadr Jabbar Abd
Geo-LANMAR Routing: Asymptotic Analysis of a Scalable Routing Scheme with Group Motion Support
 Go-LANMAR Roung: Asympoc Analyss of a Scalabl Roung Schm wh Group Moon Suppor Florano D Rango, Maro Grla, Bao Zhou, Salvaor Marano D.E.I.S. Dparmn, Unvrsy of alabra, Ialy, 8736 -mal: drango, marano @ds.uncal.
Go-LANMAR Roung: Asympoc Analyss of a Scalabl Roung Schm wh Group Moon Suppor Florano D Rango, Maro Grla, Bao Zhou, Salvaor Marano D.E.I.S. Dparmn, Unvrsy of alabra, Ialy, 8736 -mal: drango, marano @ds.uncal.
Least squares and motion. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD
 Las squars ad moo uo Vascoclos ECE Dparm UCSD Pla for oda oda w wll dscuss moo smao hs s rsg wo was moo s vr usful as a cu for rcogo sgmao comprsso c. s a gra ampl of las squars problm w wll also wrap
Las squars ad moo uo Vascoclos ECE Dparm UCSD Pla for oda oda w wll dscuss moo smao hs s rsg wo was moo s vr usful as a cu for rcogo sgmao comprsso c. s a gra ampl of las squars problm w wll also wrap
Prediction of channel information in multi-user OFDM systems
 Prcon of channl nforaon n ul-usr OFD syss Ja-oon Jon an Yong-wan L School of Elcrcal Engnrng an INC Soul Naonal Unvrsy. Kwanak P. O. Box 34, Soul, 5-600 Kora Absrac Channl nforaon s nspnsabl o ploy avanc
Prcon of channl nforaon n ul-usr OFD syss Ja-oon Jon an Yong-wan L School of Elcrcal Engnrng an INC Soul Naonal Unvrsy. Kwanak P. O. Box 34, Soul, 5-600 Kora Absrac Channl nforaon s nspnsabl o ploy avanc
Final Exam : Solutions
 Comp : Algorihm and Daa Srucur Final Exam : Soluion. Rcuriv Algorihm. (a) To bgin ind h mdian o {x, x,... x n }. Sinc vry numbr xcp on in h inrval [0, n] appar xacly onc in h li, w hav ha h mdian mu b
Comp : Algorihm and Daa Srucur Final Exam : Soluion. Rcuriv Algorihm. (a) To bgin ind h mdian o {x, x,... x n }. Sinc vry numbr xcp on in h inrval [0, n] appar xacly onc in h li, w hav ha h mdian mu b
Convergence of Quintic Spline Interpolation
 Inrnaonal Journal o ompur Applcaons 97 8887 Volum 7 No., Aprl onvrgnc o Qunc Spln Inrpolaon Y.P. Dub Dparmn O Mamacs, L.N..T. Jabalpur 8 Anl Sukla Dparmn O Mamacs Gan Ganga ollg O Tcnog, Jabalpur 8 ASTRAT
Inrnaonal Journal o ompur Applcaons 97 8887 Volum 7 No., Aprl onvrgnc o Qunc Spln Inrpolaon Y.P. Dub Dparmn O Mamacs, L.N..T. Jabalpur 8 Anl Sukla Dparmn O Mamacs Gan Ganga ollg O Tcnog, Jabalpur 8 ASTRAT
Comparative Study of Finite Element and Haar Wavelet Correlation Method for the Numerical Solution of Parabolic Type Partial Differential Equations
 ISS 746-7659, England, UK Journal of Informaon and Compung Scnc Vol., o. 3, 6, pp.88-7 Comparav Sudy of Fn Elmn and Haar Wavl Corrlaon Mhod for h umrcal Soluon of Parabolc Typ Paral Dffrnal Equaons S.
ISS 746-7659, England, UK Journal of Informaon and Compung Scnc Vol., o. 3, 6, pp.88-7 Comparav Sudy of Fn Elmn and Haar Wavl Corrlaon Mhod for h umrcal Soluon of Parabolc Typ Paral Dffrnal Equaons S.
Physics 160 Lecture 3. R. Johnson April 6, 2015
 Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
8. Queueing systems. Contents. Simple teletraffic model. Pure queueing system
 8. Quug sysms Cos 8. Quug sysms Rfrshr: Sml lraffc modl Quug dscl M/M/ srvr wag lacs Alcao o ack lvl modllg of daa raffc M/M/ srvrs wag lacs lc8. S-38.45 Iroduco o Tlraffc Thory Srg 5 8. Quug sysms 8.
8. Quug sysms Cos 8. Quug sysms Rfrshr: Sml lraffc modl Quug dscl M/M/ srvr wag lacs Alcao o ack lvl modllg of daa raffc M/M/ srvrs wag lacs lc8. S-38.45 Iroduco o Tlraffc Thory Srg 5 8. Quug sysms 8.
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SPECTRAL PEAK FREQUENCIES OF A CAUSAL AR(P) PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS OF ROOTS OF THE ASSOCIATED AR POLYNOMIAL.
 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SPECTRAL PEAK FREQUENCIES OF A CAUSAL AR(P) PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS OF ROOTS OF THE ASSOCIATED AR POLYNOMIAL A Wrng Proc Prsnd o T Faculy of Darmn of Mamacs San Jos Sa Unvrsy In Paral
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SPECTRAL PEAK FREQUENCIES OF A CAUSAL AR(P) PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS OF ROOTS OF THE ASSOCIATED AR POLYNOMIAL A Wrng Proc Prsnd o T Faculy of Darmn of Mamacs San Jos Sa Unvrsy In Paral
Midterm exam 2, April 7, 2009 (solutions)
 Univrsiy of Pnnsylvania Dparmn of Mahmaics Mah 26 Honors Calculus II Spring Smsr 29 Prof Grassi, TA Ashr Aul Midrm xam 2, April 7, 29 (soluions) 1 Wri a basis for h spac of pairs (u, v) of smooh funcions
Univrsiy of Pnnsylvania Dparmn of Mahmaics Mah 26 Honors Calculus II Spring Smsr 29 Prof Grassi, TA Ashr Aul Midrm xam 2, April 7, 29 (soluions) 1 Wri a basis for h spac of pairs (u, v) of smooh funcions
Review - Probabilistic Classification
 Mmoral Unvrsty of wfoundland Pattrn Rcognton Lctur 8 May 5, 6 http://www.ngr.mun.ca/~charlsr Offc Hours: Tusdays Thursdays 8:3-9:3 PM E- (untl furthr notc) Gvn lablld sampls { ɛc,,,..., } {. Estmat Rvw
Mmoral Unvrsty of wfoundland Pattrn Rcognton Lctur 8 May 5, 6 http://www.ngr.mun.ca/~charlsr Offc Hours: Tusdays Thursdays 8:3-9:3 PM E- (untl furthr notc) Gvn lablld sampls { ɛc,,,..., } {. Estmat Rvw
Yutaka Suzuki Faculty of Economics, Hosei University. Abstract
 Equlbrum ncnvs and accumulaon of rlaonal sklls n a dynamc modl of hold up Yuaka uzuk Faculy of Economcs, Hos Unvrsy Absrac W consruc a dynamc modl of Holdup by applyng a framwork n capal accumulaon gams,
Equlbrum ncnvs and accumulaon of rlaonal sklls n a dynamc modl of hold up Yuaka uzuk Faculy of Economcs, Hos Unvrsy Absrac W consruc a dynamc modl of Holdup by applyng a framwork n capal accumulaon gams,
Chapter 7 Stead St y- ate Errors
 Char 7 Say-Sa rror Inroucon Conrol ym analy an gn cfcaon a. rann ron b. Sably c. Say-a rror fnon of ay-a rror : u c a whr u : nu, c: ouu Val only for abl ym chck ym ably fr! nu for ay-a a nu analy U o
Char 7 Say-Sa rror Inroucon Conrol ym analy an gn cfcaon a. rann ron b. Sably c. Say-a rror fnon of ay-a rror : u c a whr u : nu, c: ouu Val only for abl ym chck ym ably fr! nu for ay-a a nu analy U o
1. Inverse Matrix 4[(3 7) (02)] 1[(0 7) (3 2)] Recall that the inverse of A is equal to:
![1. Inverse Matrix 4[(3 7) (02)] 1[(0 7) (3 2)] Recall that the inverse of A is equal to: 1. Inverse Matrix 4[(3 7) (02)] 1[(0 7) (3 2)] Recall that the inverse of A is equal to:](/thumbs/84/89365453.jpg) Rfrncs Brnank, B. and I. Mihov (1998). Masuring monary policy, Quarrly Journal of Economics CXIII, 315-34. Blanchard, O. R. Proi (00). An mpirical characrizaion of h dynamic ffcs of changs in govrnmn spnding
Rfrncs Brnank, B. and I. Mihov (1998). Masuring monary policy, Quarrly Journal of Economics CXIII, 315-34. Blanchard, O. R. Proi (00). An mpirical characrizaion of h dynamic ffcs of changs in govrnmn spnding
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 0 Canoncal Transformaons (Chaper 9) Wha We Dd Las Tme Hamlon s Prncple n he Hamlonan formalsm Dervaon was smple δi δ Addonal end-pon consrans pq H( q, p, ) d 0 δ q ( ) δq ( ) δ
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 0 Canoncal Transformaons (Chaper 9) Wha We Dd Las Tme Hamlon s Prncple n he Hamlonan formalsm Dervaon was smple δi δ Addonal end-pon consrans pq H( q, p, ) d 0 δ q ( ) δq ( ) δ
Published in: Proceedings of the Twenty Second Nordic Seminar on Computational Mechanics
 Downloadd from vbn.aau.dk on: aprl 09, 019 Aalborg Unvrs Implmnaon of Moldng Consrans n Topology Opmzaon Marx, S.; Krsnsn, Andrs Schmd Publshd n: Procdngs of h Twny Scond Nordc Smnar on Compuaonal Mchancs
Downloadd from vbn.aau.dk on: aprl 09, 019 Aalborg Unvrs Implmnaon of Moldng Consrans n Topology Opmzaon Marx, S.; Krsnsn, Andrs Schmd Publshd n: Procdngs of h Twny Scond Nordc Smnar on Compuaonal Mchancs
Charging of capacitor through inductor and resistor
 cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
Valuation and Analysis of Basket Credit Linked Notes with Issuer Default Risk
 Valuaon and Analy of Ba Crd Lnd o wh ur Dfaul R Po-Chng Wu * * Dparmn of Banng and Fnanc Kanan Unvry Addr: o. Kanan Rd. Luchu Shang aoyuan 33857 awan R.O.C. E-mal: pcwu@mal.nu.du.w l.: 886-3-34500 x. 67
Valuaon and Analy of Ba Crd Lnd o wh ur Dfaul R Po-Chng Wu * * Dparmn of Banng and Fnanc Kanan Unvry Addr: o. Kanan Rd. Luchu Shang aoyuan 33857 awan R.O.C. E-mal: pcwu@mal.nu.du.w l.: 886-3-34500 x. 67
Robust decentralized control with scalar output of multivariable structurally uncertain plants with state delay 1
 rprns of h 8h IFAC World Congrss lano Ial Augus 8 - Spmbr obus dcnralzd conrol wh scalar oupu of mulvarabl srucurall uncran plans wh sa dla Elzava arshva Absrac h problm of a robus conrol ssm dsgn for
rprns of h 8h IFAC World Congrss lano Ial Augus 8 - Spmbr obus dcnralzd conrol wh scalar oupu of mulvarabl srucurall uncran plans wh sa dla Elzava arshva Absrac h problm of a robus conrol ssm dsgn for
Microscopic Flow Characteristics Time Headway - Distribution
 CE57: Traffic Flow Thory Spring 20 Wk 2 Modling Hadway Disribuion Microscopic Flow Characrisics Tim Hadway - Disribuion Tim Hadway Dfiniion Tim Hadway vrsus Gap Ahmd Abdl-Rahim Civil Enginring Dparmn,
CE57: Traffic Flow Thory Spring 20 Wk 2 Modling Hadway Disribuion Microscopic Flow Characrisics Tim Hadway - Disribuion Tim Hadway Dfiniion Tim Hadway vrsus Gap Ahmd Abdl-Rahim Civil Enginring Dparmn,
Solution in semi infinite diffusion couples (error function analysis)
 Soluon n sem nfne dffuson couples (error funcon analyss) Le us consder now he sem nfne dffuson couple of wo blocks wh concenraon of and I means ha, n a A- bnary sysem, s bondng beween wo blocks made of
Soluon n sem nfne dffuson couples (error funcon analyss) Le us consder now he sem nfne dffuson couple of wo blocks wh concenraon of and I means ha, n a A- bnary sysem, s bondng beween wo blocks made of
Conventional Hot-Wire Anemometer
 Convnonal Ho-Wr Anmomr cro Ho Wr Avanag much mallr prob z mm o µm br paal roluon array o h nor hghr rquncy rpon lowr co prormanc/co abrcaon roc I µm lghly op p layr 8µm havly boron op ch op layr abrcaon
Convnonal Ho-Wr Anmomr cro Ho Wr Avanag much mallr prob z mm o µm br paal roluon array o h nor hghr rquncy rpon lowr co prormanc/co abrcaon roc I µm lghly op p layr 8µm havly boron op ch op layr abrcaon
AR(1) Process. The first-order autoregressive process, AR(1) is. where e t is WN(0, σ 2 )
 AR() Procss Th firs-ordr auorgrssiv procss, AR() is whr is WN(0, σ ) Condiional Man and Varianc of AR() Condiional man: Condiional varianc: ) ( ) ( Ω Ω E E ) var( ) ) ( var( ) var( σ Ω Ω Ω Ω E Auocovarianc
AR() Procss Th firs-ordr auorgrssiv procss, AR() is whr is WN(0, σ ) Condiional Man and Varianc of AR() Condiional man: Condiional varianc: ) ( ) ( Ω Ω E E ) var( ) ) ( var( ) var( σ Ω Ω Ω Ω E Auocovarianc
CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 Collg Physcs Studnt s Manual Chaptr 33 CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS 33. THE FOUR BASIC FORCES 4. (a) Fnd th rato of th strngths of th wak and lctromagntc forcs undr ordnary crcumstancs. (b) What dos that
Collg Physcs Studnt s Manual Chaptr 33 CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS 33. THE FOUR BASIC FORCES 4. (a) Fnd th rato of th strngths of th wak and lctromagntc forcs undr ordnary crcumstancs. (b) What dos that
Gauge Theories. Elementary Particle Physics Strong Interaction Fenomenology. Diego Bettoni Academic year
 Gau Thors Elmary Parcl Physcs Sro Iraco Fomoloy o Bo cadmc yar - Gau Ivarac Gau Ivarac Whr do Laraas or Hamloas com from? How do w kow ha a cra raco should dscrb a acual hyscal sysm? Why s h lcromac raco
Gau Thors Elmary Parcl Physcs Sro Iraco Fomoloy o Bo cadmc yar - Gau Ivarac Gau Ivarac Whr do Laraas or Hamloas com from? How do w kow ha a cra raco should dscrb a acual hyscal sysm? Why s h lcromac raco
Lecture 12: Introduction to nonlinear optics II.
 Lcur : Iroduco o olar opcs II r Kužl ropagao of srog opc sgals propr olar ffcs Scod ordr ffcs! Thr-wav mxg has machg codo! Scod harmoc grao! Sum frqucy grao! aramrc grao Thrd ordr ffcs! Four-wav mxg! Opcal
Lcur : Iroduco o olar opcs II r Kužl ropagao of srog opc sgals propr olar ffcs Scod ordr ffcs! Thr-wav mxg has machg codo! Scod harmoc grao! Sum frqucy grao! aramrc grao Thrd ordr ffcs! Four-wav mxg! Opcal
Lectures 9-11: Fourier Transforms
 Lcurs 9-: ourr Transforms Rfrncs Jordan & Smh Ch7, Boas Ch5 scon 4, Kryszg Ch Wb s hp://wwwjhudu/sgnals/: go o Connuous Tm ourr Transform Proprs PHY6 Inroducon o ourr Transforms W hav sn ha any prodc funcon
Lcurs 9-: ourr Transforms Rfrncs Jordan & Smh Ch7, Boas Ch5 scon 4, Kryszg Ch Wb s hp://wwwjhudu/sgnals/: go o Connuous Tm ourr Transform Proprs PHY6 Inroducon o ourr Transforms W hav sn ha any prodc funcon
CHAPTER CHAPTER14. Expectations: The Basic Tools. Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano
 Expcaions: Th Basic Prpard by: Frnando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano CHAPTER CHAPTER14 2006 Prnic Hall Businss Publishing Macroconomics, 4/ Olivir Blanchard 14-1 Today s Lcur Chapr 14:Expcaions: Th Basic Th
Expcaions: Th Basic Prpard by: Frnando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano CHAPTER CHAPTER14 2006 Prnic Hall Businss Publishing Macroconomics, 4/ Olivir Blanchard 14-1 Today s Lcur Chapr 14:Expcaions: Th Basic Th
NAME: ANSWER KEY DATE: PERIOD. DIRECTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the letter of the correct answer.
 R A T T L E R S S L U G S NAME: ANSWER KEY DATE: PERIOD PREAP PHYSICS REIEW TWO KINEMATICS / GRAPHING FORM A DIRECTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Chs h r f h rr answr. Us h fgur bw answr qusns 1 and 2. 0 10 20
R A T T L E R S S L U G S NAME: ANSWER KEY DATE: PERIOD PREAP PHYSICS REIEW TWO KINEMATICS / GRAPHING FORM A DIRECTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Chs h r f h rr answr. Us h fgur bw answr qusns 1 and 2. 0 10 20
V.Abramov - FURTHER ANALYSIS OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR LARGE CLIENT/SERVER COMPUTER NETWORKS
 R&RATA # Vol.) 8, March FURTHER AALYSIS OF COFIDECE ITERVALS FOR LARGE CLIET/SERVER COMPUTER ETWORKS Vyacheslav Abramov School of Mahemacal Scences, Monash Unversy, Buldng 8, Level 4, Clayon Campus, Wellngon
R&RATA # Vol.) 8, March FURTHER AALYSIS OF COFIDECE ITERVALS FOR LARGE CLIET/SERVER COMPUTER ETWORKS Vyacheslav Abramov School of Mahemacal Scences, Monash Unversy, Buldng 8, Level 4, Clayon Campus, Wellngon
Almost unbiased exponential estimator for the finite population mean
 Almos ubasd poal smaor for f populao ma Rajs Sg, Pakaj aua, ad rmala Saa, Scool of Sascs, DAVV, Idor (M.P., Ida (rsgsa@aoo.com Flor Smaradac ar of Dparm of Mamacs, Uvrs of Mco, Gallup, USA (smarad@um.du
Almos ubasd poal smaor for f populao ma Rajs Sg, Pakaj aua, ad rmala Saa, Scool of Sascs, DAVV, Idor (M.P., Ida (rsgsa@aoo.com Flor Smaradac ar of Dparm of Mamacs, Uvrs of Mco, Gallup, USA (smarad@um.du
Node Placement and Mobility Control in Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks
 Prprns of h 18h IFAC Worl Congrss o Placmn an Mobly Conrol n Mobl Wrlss Snsor works Mnchol Km an Song-Lyun Km School of Elcrcal an Elcronc Engnrng, Yons Unvrsy, 50 Yons-ro, Soamun-gu, Soul 120-749, Kora
Prprns of h 18h IFAC Worl Congrss o Placmn an Mobly Conrol n Mobl Wrlss Snsor works Mnchol Km an Song-Lyun Km School of Elcrcal an Elcronc Engnrng, Yons Unvrsy, 50 Yons-ro, Soamun-gu, Soul 120-749, Kora
MATCHED FILTER BOUND OPTIMIZATION FOR MULTIUSER DOWNLINK TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING
 MATCHED FILTER BOUND OPTIMIZATION FOR MULTIUSER DOWNLINK TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING Guspp Montalbano? and Drk T. M. Slock?? Insttut Eurécom 2229 Rout ds Crêts, B.P. 193, 06904 Sopha Antpols CEDEX, Franc E-Mal:
MATCHED FILTER BOUND OPTIMIZATION FOR MULTIUSER DOWNLINK TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING Guspp Montalbano? and Drk T. M. Slock?? Insttut Eurécom 2229 Rout ds Crêts, B.P. 193, 06904 Sopha Antpols CEDEX, Franc E-Mal:
The Fourier Transform
 /9/ Th ourr Transform Jan Baptst Josph ourr 768-83 Effcnt Data Rprsntaton Data can b rprsntd n many ways. Advantag usng an approprat rprsntaton. Eampls: osy ponts along a ln Color spac rd/grn/blu v.s.
/9/ Th ourr Transform Jan Baptst Josph ourr 768-83 Effcnt Data Rprsntaton Data can b rprsntd n many ways. Advantag usng an approprat rprsntaton. Eampls: osy ponts along a ln Color spac rd/grn/blu v.s.
Real-Time Scheduling for Event-Triggered and Time-Triggered Flows in Industrial Wireless Sensor-Actuator Networks
 Ral-Tm Schdulng or Evn-Trggrd and Tm-Trggrd Flows n Indusral Wrlss Snsor-Acuaor Nworks X Jn, Abusad Saullah, Chnang Lu, and Png Zng Absrac Wrlss snsor-acuaor nworks nabl an cn and cos-cv approach or ndusral
Ral-Tm Schdulng or Evn-Trggrd and Tm-Trggrd Flows n Indusral Wrlss Snsor-Acuaor Nworks X Jn, Abusad Saullah, Chnang Lu, and Png Zng Absrac Wrlss snsor-acuaor nworks nabl an cn and cos-cv approach or ndusral
Chapter 10. The singular integral Introducing S(n) and J(n)
 Chaptr Th singular intgral Our aim in this chaptr is to rplac th functions S (n) and J (n) by mor convnint xprssions; ths will b calld th singular sris S(n) and th singular intgral J(n). This will b don
Chaptr Th singular intgral Our aim in this chaptr is to rplac th functions S (n) and J (n) by mor convnint xprssions; ths will b calld th singular sris S(n) and th singular intgral J(n). This will b don
Continous system: differential equations
 /6/008 Coious sysm: diffrial quaios Drmiisic modls drivaivs isad of (+)-( r( compar ( + ) R( + r ( (0) ( R ( 0 ) ( Dcid wha hav a ffc o h sysm Drmi whhr h paramrs ar posiiv or gaiv, i.. giv growh or rducio
/6/008 Coious sysm: diffrial quaios Drmiisic modls drivaivs isad of (+)-( r( compar ( + ) R( + r ( (0) ( R ( 0 ) ( Dcid wha hav a ffc o h sysm Drmi whhr h paramrs ar posiiv or gaiv, i.. giv growh or rducio
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci. Spring 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Aoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kllci Spring 08 OUTLINE Th Laplac Tranform Rgion of convrgnc for Laplac ranform Invr Laplac ranform Gomric valuaion
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Aoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kllci Spring 08 OUTLINE Th Laplac Tranform Rgion of convrgnc for Laplac ranform Invr Laplac ranform Gomric valuaion
Probabilistic Reasoning; Graphical models
 Ovrvw. robablsc Rasonng/Graphcal modls. Imporanc Samplng 3. Markov Chan Mon Carlo: Gbbs Samplng 4. Samplng n prsnc of Drmnsm 5. Rao-Blackwllsaon 6. AND/OR mporanc samplng Ovrvw. robablsc Rasonng/Graphcal
Ovrvw. robablsc Rasonng/Graphcal modls. Imporanc Samplng 3. Markov Chan Mon Carlo: Gbbs Samplng 4. Samplng n prsnc of Drmnsm 5. Rao-Blackwllsaon 6. AND/OR mporanc samplng Ovrvw. robablsc Rasonng/Graphcal
4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b
![4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b 4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b](/thumbs/71/65779443.jpg) 4. Th Uniform Disribuion Df n: A c.r.v. has a coninuous uniform disribuion on [a, b] whn is pdf is f x a x b b a Also, b + a b a µ E and V Ex4. Suppos, h lvl of unblivabiliy a any poin in a Transformrs
4. Th Uniform Disribuion Df n: A c.r.v. has a coninuous uniform disribuion on [a, b] whn is pdf is f x a x b b a Also, b + a b a µ E and V Ex4. Suppos, h lvl of unblivabiliy a any poin in a Transformrs
Robustness Experiments with Two Variance Components
 Naonal Insue of Sandards and Technology (NIST) Informaon Technology Laboraory (ITL) Sascal Engneerng Dvson (SED) Robusness Expermens wh Two Varance Componens by Ana Ivelsse Avlés avles@ns.gov Conference
Naonal Insue of Sandards and Technology (NIST) Informaon Technology Laboraory (ITL) Sascal Engneerng Dvson (SED) Robusness Expermens wh Two Varance Componens by Ana Ivelsse Avlés avles@ns.gov Conference
ADAPTIVE PRE-EMPTIVE CONTROL OF VACUUM DEWATERING IN PAPER MANUFACTURING 1. Petar Bjegovic 3 Perry Y. Li 2
 Copyrgh 2002 IFC 5h Trnnal World Congrss arclona Span DPTIVE PRE-EMPTIVE CONTROL OF VCUUM DEWTERING IN PPER MNUFCTURING Par jgoc 3 Prry Y. L 2 Dparmn of Mchancal Engnrng Unrsy of Mnnsoa Church S. SE Mnnapols
Copyrgh 2002 IFC 5h Trnnal World Congrss arclona Span DPTIVE PRE-EMPTIVE CONTROL OF VCUUM DEWTERING IN PPER MNUFCTURING Par jgoc 3 Prry Y. L 2 Dparmn of Mchancal Engnrng Unrsy of Mnnsoa Church S. SE Mnnapols
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Relative controllability of nonlinear systems with delays in control
 Relave conrollably o nonlnear sysems wh delays n conrol Jerzy Klamka Insue o Conrol Engneerng, Slesan Techncal Unversy, 44- Glwce, Poland. phone/ax : 48 32 37227, {jklamka}@a.polsl.glwce.pl Keywor: Conrollably.
Relave conrollably o nonlnear sysems wh delays n conrol Jerzy Klamka Insue o Conrol Engneerng, Slesan Techncal Unversy, 44- Glwce, Poland. phone/ax : 48 32 37227, {jklamka}@a.polsl.glwce.pl Keywor: Conrollably.
Poisson process Markov process
 E2200 Quuing hory and lraffic 2nd lcur oion proc Markov proc Vikoria Fodor KTH Laboraory for Communicaion nwork, School of Elcrical Enginring 1 Cour oulin Sochaic proc bhind quuing hory L2-L3 oion proc
E2200 Quuing hory and lraffic 2nd lcur oion proc Markov proc Vikoria Fodor KTH Laboraory for Communicaion nwork, School of Elcrical Enginring 1 Cour oulin Sochaic proc bhind quuing hory L2-L3 oion proc
IMPROVED RATIO AND PRODUCT TYPE ESTIMATORS OF FINITE POPULATION MEAN IN SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING
 REVISTA IVESTIGAIO OPERAIOAL VOL. 6, O., 7-76, 6 IMPROVED RATIO AD PRODUT TPE ESTIMATORS OF FIITE POPULATIO MEA I SIMPLE RADOM SAMPLIG Gajndra K. Vshwaarma, Ravndra Sngh, P.. Gupa, Sarla Par Dparmn of
REVISTA IVESTIGAIO OPERAIOAL VOL. 6, O., 7-76, 6 IMPROVED RATIO AD PRODUT TPE ESTIMATORS OF FIITE POPULATIO MEA I SIMPLE RADOM SAMPLIG Gajndra K. Vshwaarma, Ravndra Sngh, P.. Gupa, Sarla Par Dparmn of
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
