Digital Signal Processing, Fall 2006
|
|
|
- Lesley Walker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Digitl Sigl Processig, Fll 6 Lecture 6: Sstem structures for implemettio Zeg-u T Deprtmet of Electroic Sstems Alorg Uiversit, Demr t@om.u.d Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Course t glce Discrete-time sigls d sstems Sstem Fourier-domi represettio Smplig d recostructio Sstem lsis 5 Sstem structure 6 Filter desig -trsform DFTFFT 7, 8 3 9, Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6
2 Sstem implemettio LTI sstems it rtiol sstem fuctio e.g., > Impulse respose u u Lier costt-coefficiet differece equtio Tree equivlet represettios! o to implemet, i.e. covert to lgoritm or structure? 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Sstem implemettio Te iput-output trsformtio c e computed i differet s ec is clled implemettio A implemettio is specific descriptio of its iterl computtiol structure Te coice of implemettio cocers it computtiol requiremets memor requiremets, effects of fiite-precisio, d so o Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6
3 Prt I: Bloc digrm represettio Bloc digrm represettio of computtiol structures Sigl flo grp descriptio Bsic structures for IIR sstems Trsposed forms Bsic structures for FIR sstems 5 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Sstem implemettio Impulse respose u * u is ifiite-durtio, impossile to implemet i tis. oever, lier costt-coefficiet differece equtio provides mes for recursive computtio of te output 6 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 3
4 Bsic elemets Implemettio sed o te recurrece formul derived from differece equtio requires dders multipliers memor for storig deled sequece vlues Fig Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Emple of loc digrm represettio A secod-order differece equtio Demostrtes te compleit, te steps, te mout of resources required. 8 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6
5 5 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 9 Geerl t-order differece equtio v A cscde of to sstems! X v, v Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Rerrgemet of loc digrm A loc digrm c e rerrged i m s itout cgig overl fuctio, e.g. reversig te order of te to cscded sstems.
6 6 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Sstem fuctio decompositio v Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 I te time domi v v
7 iimum del implemettio Oe ig differece t te to implemettios cocers te umer of del elemets m, 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Direct form I d II Direct form I s so i Fig. 6.3 A direct relitio of te differece equtio Direct form II or coic direct form s so i Fig. 6.5 Tere is direct li etee te sstem fuctio differece equtio d te loc digrm Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 7
8 A emple Direct form I d direct form II implemettio Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Prt II: Sigl flo grp descriptio Bloc digrm represettio of computtiol structures Sigl flo grp descriptio Bsic structures for IIR sstems Trsposed forms Bsic structures for FIR sstems 6 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 8
9 Sigl flo grp SFG As ltertive to loc digrms it fe ottiol differeces. A etor of directed rces coectig odes. vrile 7 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Sigl flo grp odes i SFG represet ot rcig poits d dders depedig o te umer of icomig rces, ile i te digrm specil smol is used for dders d ode s ol oe icomig rc. SGF is simpler to dr. 8 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 9
10 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 9 From flo grp to sstem fuctio Fig. 6. ot direct form, cot oti ispectio. But c rite equtio for ec ode ivolve feedc, difficult to solve B -trsform lier equtios 3 3 α 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 From flo grp to sstem fuctio 3 3 Y X X α Y X X α u u X Y α α α α α α te sstem is? rel, is If α All-pss Cusl!
11 From flo grp to sstem fuctio Fig. 6.3 Fig. 6. Differet implemettios, differet mouts of computtiol resources Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Prt III: Bsic structures for IIR sstems Bloc digrm represettio of computtiol structures Sigl flo grp descriptio Bsic structures for IIR sstems Trsposed forms Bsic structures for FIR sstems Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6
12 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 3 Direct form I Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Direct form II
13 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 5 Emple.5.75 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 6 Cscde form Fctor te umertor d deomitor polomils * * d d c g g f A s
14 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 7 A emple: from d -order to st-order cscde Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 8 Prllel form prtil frctio epsio * d d e B c A C p
15 Feedc i IIR sstems u Feedc loop: closed pt ecessr ut ot sufficiet coditio for IIR sstem Feedc itroduced poles couldeccelled eros All loops must coti t lest oe uit del elemet 9 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Prt IV: Trsposed forms Bloc digrm represettio of computtiol structures Sigl flo grp descriptio Bsic structures for IIR sstems Trsposed forms Bsic structures for FIR sstems 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 5
16 Trsposed form for first-order sstem Flo grp reversl or trspositio lso provides ltertives: reversig te directios of ll rces d reversig te iput d output Resultig i sme 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Trsposed direct form II d direct form II Te trsposed direct form II implemets te eros first d te te poles, eig importt effect for fiite-precisio eistig 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 6
17 Prt V: Bsic structures for FIR sstems Bloc digrm represettio of computtiol structures Sigl flo grp descriptio Bsic structures for IIR sstems Trsposed forms Bsic structures for FIR sstems 33 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Direct form So fr, sstem fuctio s ot poles d eros. FIR sstems s specil cse. Cusl FIR sstem fuctio s ol eros ecept for poles s,,,...,, oterise Form I d form II re te sme. 3 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 7
18 8 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 35 Cscde form Fctorig te polomil sstem fuctio s Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 36 Lier-pse FIR sstems Geerlied lier-pse sstem Cusl FIR sstems ve geerlied lier-pse if stisfies te smmetr coditio,,...,, or,,...,, costts re rel d, fuctio of rel is β α ω ω β ωα ω ω j j j j j e A e e A e
19 9 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 37 Lier-pse FIR sstems if is eve iteger if Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 38 Lier pse FIR sstems is eve iteger d -
20 Discussios Implemettio of FIR d IIR sstems Use sigl loc digrm flo grp represettio to so te computtiol structures Altoug to structures m ve equivlet iputoutput crteristics for ifiite-precisio represetios of coefficiets d vriles, te m ve drmticll differet eviour e te umericl precisio is limited. 39 Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6 Summr Bloc digrm represettio of computtiol structures Sigl flo grp descriptio Bsic structures for IIR sstems Trsposed forms Bsic structures for FIR sstems Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6
21 Course t glce Discrete-time sigls d sstems Sstem Fourier-domi represettio Smplig d recostructio Sstem lsis 5 Sstem structure 6 Filter desig -trsform DFTFFT 7, 8 3 9, Digitl Sigl Processig, VI, Zeg-u T, 6
ELEG 5173L Digital Signal Processing Ch. 2 The Z-Transform
 Deprtmet of Electricl Egieerig Uiversity of Arkss ELEG 573L Digitl Sigl Processig Ch. The Z-Trsform Dr. Jigxi Wu wuj@urk.edu OUTLINE The Z-Trsform Properties Iverse Z-Trsform Z-Trsform of LTI system Z-TRANSFORM
Deprtmet of Electricl Egieerig Uiversity of Arkss ELEG 573L Digitl Sigl Processig Ch. The Z-Trsform Dr. Jigxi Wu wuj@urk.edu OUTLINE The Z-Trsform Properties Iverse Z-Trsform Z-Trsform of LTI system Z-TRANSFORM
Chapter 10: The Z-Transform Adapted from: Lecture notes from MIT, Binghamton University Dr. Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2013
 Sigls & Systems Chpter 0: The Z-Trsform Adpted from: Lecture otes from MIT, Bighmto Uiversity Dr. Hmid R. Rbiee Fll 03 Lecture 5 Chpter 0 Lecture 6 Chpter 0 Outlie Itroductio to the -Trsform Properties
Sigls & Systems Chpter 0: The Z-Trsform Adpted from: Lecture otes from MIT, Bighmto Uiversity Dr. Hmid R. Rbiee Fll 03 Lecture 5 Chpter 0 Lecture 6 Chpter 0 Outlie Itroductio to the -Trsform Properties
=> PARALLEL INTERCONNECTION. Basic Properties LTI Systems. The Commutative Property. Convolution. The Commutative Property. The Distributive Property
 Lier Time-Ivrit Bsic Properties LTI The Commuttive Property The Distributive Property The Associtive Property Ti -6.4 / Chpter Covolutio y ] x ] ] x ]* ] x ] ] y] y ( t ) + x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ x( t) * h(
Lier Time-Ivrit Bsic Properties LTI The Commuttive Property The Distributive Property The Associtive Property Ti -6.4 / Chpter Covolutio y ] x ] ] x ]* ] x ] ] y] y ( t ) + x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ x( t) * h(
Chapter 10: The Z-Transform Adapted from: Lecture notes from MIT, Binghamton University Hamid R. Rabiee Arman Sepehr Fall 2010
 Sigls & Systems Chpter 0: The Z-Trsform Adpted from: Lecture otes from MIT, Bighmto Uiversity Hmid R. Riee Arm Sepehr Fll 00 Lecture 5 Chpter 0 Outlie Itroductio to the -Trsform Properties of the ROC of
Sigls & Systems Chpter 0: The Z-Trsform Adpted from: Lecture otes from MIT, Bighmto Uiversity Hmid R. Riee Arm Sepehr Fll 00 Lecture 5 Chpter 0 Outlie Itroductio to the -Trsform Properties of the ROC of
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci. Spring 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bur Kelleci Sprig 8 OUTLINE The Z-Trsform The Regio of covergece for the Z-trsform The Iverse Z-Trsform Geometric
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bur Kelleci Sprig 8 OUTLINE The Z-Trsform The Regio of covergece for the Z-trsform The Iverse Z-Trsform Geometric
Appendix A Examples for Labs 1, 2, 3 1. FACTORING POLYNOMIALS
 Appedi A Emples for Ls,,. FACTORING POLYNOMIALS Tere re m stdrd metods of fctorig tt ou ve lered i previous courses. You will uild o tese fctorig metods i our preclculus course to ele ou to fctor epressios
Appedi A Emples for Ls,,. FACTORING POLYNOMIALS Tere re m stdrd metods of fctorig tt ou ve lered i previous courses. You will uild o tese fctorig metods i our preclculus course to ele ou to fctor epressios
Frequency-domain Characteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems
 requecy-domi Chrcteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems Prof. Siripog Potisuk LTI System descriptio Previous bsis fuctio: uit smple or DT impulse The iput sequece is represeted s lier combitio of shifted
requecy-domi Chrcteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems Prof. Siripog Potisuk LTI System descriptio Previous bsis fuctio: uit smple or DT impulse The iput sequece is represeted s lier combitio of shifted
Auto-correlation. Window Selection: Hamming. Hamming Filtered Power Spectrum. White Noise Auto-Covariance vs. Hamming Filtered Noise
 Correltio d Spectrl Alsis Applictio 4 Review of covrice idepedece cov cov with vrice : ew rdom vrile forms. d For idepedet rdom vriles - Autocorreltio Autocovrice cptures covrice where I geerl. for oise
Correltio d Spectrl Alsis Applictio 4 Review of covrice idepedece cov cov with vrice : ew rdom vrile forms. d For idepedet rdom vriles - Autocorreltio Autocovrice cptures covrice where I geerl. for oise
Discrete-Time Signals & Systems
 Chpter 2 Discrete-Time Sigls & Systems 清大電機系林嘉文 cwli@ee.thu.edu.tw 03-57352 Discrete-Time Sigls Sigls re represeted s sequeces of umbers, clled smples Smple vlue of typicl sigl or sequece deoted s x =
Chpter 2 Discrete-Time Sigls & Systems 清大電機系林嘉文 cwli@ee.thu.edu.tw 03-57352 Discrete-Time Sigls Sigls re represeted s sequeces of umbers, clled smples Smple vlue of typicl sigl or sequece deoted s x =
The z Transform. The Discrete LTI System Response to a Complex Exponential
 The Trsform The trsform geerlies the Discrete-time Forier Trsform for the etire complex ple. For the complex vrible is sed the ottio: jω x+ j y r e ; x, y Ω rg r x + y {} The Discrete LTI System Respose
The Trsform The trsform geerlies the Discrete-time Forier Trsform for the etire complex ple. For the complex vrible is sed the ottio: jω x+ j y r e ; x, y Ω rg r x + y {} The Discrete LTI System Respose
Fast Fourier Transform 1) Legendre s Interpolation 2) Vandermonde Matrix 3) Roots of Unity 4) Polynomial Evaluation
 Algorithm Desig d Alsis Victor Admchi CS 5-45 Sprig 4 Lecture 3 J 7, 4 Cregie Mello Uiversit Outlie Fst Fourier Trsform ) Legedre s Iterpoltio ) Vdermode Mtri 3) Roots of Uit 4) Polomil Evlutio Guss (777
Algorithm Desig d Alsis Victor Admchi CS 5-45 Sprig 4 Lecture 3 J 7, 4 Cregie Mello Uiversit Outlie Fst Fourier Trsform ) Legedre s Iterpoltio ) Vdermode Mtri 3) Roots of Uit 4) Polomil Evlutio Guss (777
2.1.1 Definition The Z-transform of a sequence x [n] is simply defined as (2.1) X re x k re x k r
![2.1.1 Definition The Z-transform of a sequence x [n] is simply defined as (2.1) X re x k re x k r 2.1.1 Definition The Z-transform of a sequence x [n] is simply defined as (2.1) X re x k re x k r](/thumbs/82/85448174.jpg) Z-Trsforms. INTRODUCTION TO Z-TRANSFORM The Z-trsform is coveiet d vluble tool for represetig, lyig d desigig discrete-time sigls d systems. It plys similr role i discrete-time systems to tht which Lplce
Z-Trsforms. INTRODUCTION TO Z-TRANSFORM The Z-trsform is coveiet d vluble tool for represetig, lyig d desigig discrete-time sigls d systems. It plys similr role i discrete-time systems to tht which Lplce
Lecture 2. Rational Exponents and Radicals. 36 y. b can be expressed using the. Rational Exponent, thus b. b can be expressed using the
 Lecture. Rtiol Epoets d Rdicls Rtiol Epoets d Rdicls Lier Equtios d Iequlities i Oe Vrile Qudrtic Equtios Appedi A6 Nth Root - Defiitio Rtiol Epoets d Rdicls For turl umer, c e epressed usig the r is th
Lecture. Rtiol Epoets d Rdicls Rtiol Epoets d Rdicls Lier Equtios d Iequlities i Oe Vrile Qudrtic Equtios Appedi A6 Nth Root - Defiitio Rtiol Epoets d Rdicls For turl umer, c e epressed usig the r is th
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 5
 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 5 Fll K8-5 th Semester Thir Muhmmd tmuhmmd_7@yhoo.com Cotet d Figures re from Discrete-Time Sigl Processig, e by Oppeheim, Shfer, d Buck, 999- Pretice Hll Ic. The -Trsform
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 5 Fll K8-5 th Semester Thir Muhmmd tmuhmmd_7@yhoo.com Cotet d Figures re from Discrete-Time Sigl Processig, e by Oppeheim, Shfer, d Buck, 999- Pretice Hll Ic. The -Trsform
SOLUTION OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION FOR THE EULER-BERNOULLI BEAM
 Jourl of Applied Mthemtics d Computtiol Mechics () 57-6 SOUION O DIERENIA EQUAION OR HE EUER-ERNOUI EAM Izbel Zmorsk Istitute of Mthemtics Czestochow Uiversit of echolog Częstochow Pold izbel.zmorsk@im.pcz.pl
Jourl of Applied Mthemtics d Computtiol Mechics () 57-6 SOUION O DIERENIA EQUAION OR HE EUER-ERNOUI EAM Izbel Zmorsk Istitute of Mthemtics Czestochow Uiversit of echolog Częstochow Pold izbel.zmorsk@im.pcz.pl
Important Facts You Need To Know/Review:
 Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Remarks: (a) The Dirac delta is the function zero on the domain R {0}.
 Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Assessment Center Elementary Algebra Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT)
 Assessmet Ceter Elemetr Alger Stud Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT) The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d cotet of questios o the Accuplcer Elemetr Alger test. Reviewig these smples will give
Assessmet Ceter Elemetr Alger Stud Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT) The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d cotet of questios o the Accuplcer Elemetr Alger test. Reviewig these smples will give
Unit 1. Extending the Number System. 2 Jordan School District
 Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 3
 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 3 Fall 2 2K8-5 th Semester Tahir Muhammad tmuhammad_7@yahoo.com Cotet ad Figures are from Discrete-Time Sigal Processig, 2e by Oppeheim, Shafer, ad Buc, 999-2 Pretice
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 3 Fall 2 2K8-5 th Semester Tahir Muhammad tmuhammad_7@yahoo.com Cotet ad Figures are from Discrete-Time Sigal Processig, 2e by Oppeheim, Shafer, ad Buc, 999-2 Pretice
,... are the terms of the sequence. If the domain consists of the first n positive integers only, the sequence is a finite sequence.
 Chpter 9 & 0 FITZGERALD MAT 50/5 SECTION 9. Sequece Defiitio A ifiite sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. The fuctio vlues,,, 4,...,,... re the terms of the sequece. If the domi
Chpter 9 & 0 FITZGERALD MAT 50/5 SECTION 9. Sequece Defiitio A ifiite sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. The fuctio vlues,,, 4,...,,... re the terms of the sequece. If the domi
RULES FOR MANIPULATING SURDS b. This is the addition law of surds with the same radicals. (ii)
 SURDS Defiitio : Ay umer which c e expressed s quotiet m of two itegers ( 0 ), is clled rtiol umer. Ay rel umer which is ot rtiol is clled irrtiol. Irrtiol umers which re i the form of roots re clled surds.
SURDS Defiitio : Ay umer which c e expressed s quotiet m of two itegers ( 0 ), is clled rtiol umer. Ay rel umer which is ot rtiol is clled irrtiol. Irrtiol umers which re i the form of roots re clled surds.
Orthogonality, orthogonalization, least squares
 ier Alger for Wireless Commuictios ecture: 3 Orthogolit, orthogoliztio, lest squres Ier products d Cosies he gle etee o-zero vectors d is cosθθ he l of Cosies: + cosθ If the gle etee to vectors is π/ (90º),
ier Alger for Wireless Commuictios ecture: 3 Orthogolit, orthogoliztio, lest squres Ier products d Cosies he gle etee o-zero vectors d is cosθθ he l of Cosies: + cosθ If the gle etee to vectors is π/ (90º),
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Similar idea to multiplication in N, C. Divide and conquer approach provides unexpected improvements. Naïve matrix multiplication
 Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS. Linear Equations. x l ( 3,1 ) _x-axis. Origin ( 0, 0 ) Slope = change in y change in x. Equation for l 1.
 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
Chapter #2 EEE Subsea Control and Communication Systems
 EEE 87 Chpter # EEE 87 Sube Cotrol d Commuictio Sytem Trfer fuctio Pole loctio d -ple Time domi chrcteritic Extr pole d zero Chpter /8 EEE 87 Trfer fuctio Lplce Trform Ued oly o LTI ytem Differetil expreio
EEE 87 Chpter # EEE 87 Sube Cotrol d Commuictio Sytem Trfer fuctio Pole loctio d -ple Time domi chrcteritic Extr pole d zero Chpter /8 EEE 87 Trfer fuctio Lplce Trform Ued oly o LTI ytem Differetil expreio
A GENERALIZATION OF GAUSS THEOREM ON QUADRATIC FORMS
 A GENERALIZATION OF GAU THEOREM ON QUADRATIC FORM Nicole I Brtu d Adi N Cret Deprtmet of Mth - Criov Uiversity, Romi ABTRACT A origil result cocerig the extesio of Guss s theorem from the theory of biry
A GENERALIZATION OF GAU THEOREM ON QUADRATIC FORM Nicole I Brtu d Adi N Cret Deprtmet of Mth - Criov Uiversity, Romi ABTRACT A origil result cocerig the extesio of Guss s theorem from the theory of biry
ALGEBRA. Set of Equations. have no solution 1 b1. Dependent system has infinitely many solutions
 Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Graphing Review Part 3: Polynomials
 Grphig Review Prt : Polomils Prbols Recll, tht the grph of f ( ) is prbol. It is eve fuctio, hece it is smmetric bout the bout the -is. This mes tht f ( ) f ( ). Its grph is show below. The poit ( 0,0)
Grphig Review Prt : Polomils Prbols Recll, tht the grph of f ( ) is prbol. It is eve fuctio, hece it is smmetric bout the bout the -is. This mes tht f ( ) f ( ). Its grph is show below. The poit ( 0,0)
Eigenfunction Expansion. For a given function on the internal a x b the eigenfunction expansion of f(x):
 Eigefuctio Epsio: For give fuctio o the iterl the eigefuctio epsio of f(): f ( ) cmm( ) m 1 Eigefuctio Epsio (Geerlized Fourier Series) To determie c s we multiply oth sides y Φ ()r() d itegrte: f ( )
Eigefuctio Epsio: For give fuctio o the iterl the eigefuctio epsio of f(): f ( ) cmm( ) m 1 Eigefuctio Epsio (Geerlized Fourier Series) To determie c s we multiply oth sides y Φ ()r() d itegrte: f ( )
Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
 Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Numerical Solutions of Fredholm Integral Equations Using Bernstein Polynomials
 Numericl Solutios of Fredholm Itegrl Equtios Usig erstei Polyomils A. Shiri, M. S. Islm Istitute of Nturl Scieces, Uited Itertiol Uiversity, Dhk-, gldesh Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Uiversity of Dhk, Dhk-,
Numericl Solutios of Fredholm Itegrl Equtios Usig erstei Polyomils A. Shiri, M. S. Islm Istitute of Nturl Scieces, Uited Itertiol Uiversity, Dhk-, gldesh Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Uiversity of Dhk, Dhk-,
Signals & Systems Chapter3
 Sigals & Systems Chapter3 1.2 Discrete-Time (D-T) Sigals Electroic systems do most of the processig of a sigal usig a computer. A computer ca t directly process a C-T sigal but istead eeds a stream of
Sigals & Systems Chapter3 1.2 Discrete-Time (D-T) Sigals Electroic systems do most of the processig of a sigal usig a computer. A computer ca t directly process a C-T sigal but istead eeds a stream of
M5. LTI Systems Described by Linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equations
 5. LTI Systes Descied y Lie Costt Coefficiet Diffeece Equtios Redig teil: p.34-4, 245-253 3/22/2 I. Discete-Tie Sigls d Systes Up til ow we itoduced the Fouie d -tsfos d thei popeties with oly ief peview
5. LTI Systes Descied y Lie Costt Coefficiet Diffeece Equtios Redig teil: p.34-4, 245-253 3/22/2 I. Discete-Tie Sigls d Systes Up til ow we itoduced the Fouie d -tsfos d thei popeties with oly ief peview
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
Supplemental Handout #1. Orthogonal Functions & Expansions
 UIUC Physics 435 EM Fields & Sources I Fll Semester, 27 Supp HO # 1 Prof. Steve Errede Supplemetl Hdout #1 Orthogol Fuctios & Epsios Cosider fuctio f ( ) which is defied o the itervl. The fuctio f ( )
UIUC Physics 435 EM Fields & Sources I Fll Semester, 27 Supp HO # 1 Prof. Steve Errede Supplemetl Hdout #1 Orthogol Fuctios & Epsios Cosider fuctio f ( ) which is defied o the itervl. The fuctio f ( )
FIR Filters. Lecture #7 Chapter 5. BME 310 Biomedical Computing - J.Schesser
 FIR Filters Lecture #7 Chapter 5 8 What Is this Course All About? To Gai a Appreciatio of the Various Types of Sigals ad Systems To Aalyze The Various Types of Systems To Lear the Skills ad Tools eeded
FIR Filters Lecture #7 Chapter 5 8 What Is this Course All About? To Gai a Appreciatio of the Various Types of Sigals ad Systems To Aalyze The Various Types of Systems To Lear the Skills ad Tools eeded
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing(DSP)
 Forth Clss Commictio II Electricl Dept Nd Nsih Itrodctio to Digitl Sigl ProcessigDSP Recet developmets i digitl compters ope the wy to this sject The geerl lock digrm of DSP system is show elow: Bd limited
Forth Clss Commictio II Electricl Dept Nd Nsih Itrodctio to Digitl Sigl ProcessigDSP Recet developmets i digitl compters ope the wy to this sject The geerl lock digrm of DSP system is show elow: Bd limited
Discrete-Time Signals and Systems. Discrete-Time Signals and Systems. Signal Symmetry. Elementary Discrete-Time Signals.
 Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Dr. Deepa Kudur Uiversity of oroto Referece: Sectios. -.5 of Joh G. Proakis ad Dimitris G. Maolakis, Digital Sigal Processig: Priciples, Algorithms,
Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Dr. Deepa Kudur Uiversity of oroto Referece: Sectios. -.5 of Joh G. Proakis ad Dimitris G. Maolakis, Digital Sigal Processig: Priciples, Algorithms,
Interpolation. 1. What is interpolation?
 Iterpoltio. Wht is iterpoltio? A uctio is ote give ol t discrete poits such s:.... How does oe id the vlue o t other vlue o? Well cotiuous uctio m e used to represet the + dt vlues with pssig through the
Iterpoltio. Wht is iterpoltio? A uctio is ote give ol t discrete poits such s:.... How does oe id the vlue o t other vlue o? Well cotiuous uctio m e used to represet the + dt vlues with pssig through the
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
Module 4. Signal Representation and Baseband Processing. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Sigl Represettio d Bsed Processig Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Lesso 5 Orthogolity Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Ater redig this lesso, you will ler out Bsic cocept o orthogolity d orthoormlity; Strum -
Module 4 Sigl Represettio d Bsed Processig Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Lesso 5 Orthogolity Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Ater redig this lesso, you will ler out Bsic cocept o orthogolity d orthoormlity; Strum -
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
ADVANCED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
 ADVANCED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING PROF. S. C. CHAN (email : sccha@eee.hku.hk, Rm. CYC-702) DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS MULTI-DIMENSIONAL SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS RANDOM PROCESSES AND APPLICATIONS ADAPTIVE
ADVANCED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING PROF. S. C. CHAN (email : sccha@eee.hku.hk, Rm. CYC-702) DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS MULTI-DIMENSIONAL SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS RANDOM PROCESSES AND APPLICATIONS ADAPTIVE
Section 7.3, Systems of Linear Algebraic Equations; Linear Independence, Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors (the variable vector of the system) and
 Sec. 7., Boyce & DiPrim, p. Sectio 7., Systems of Lier Algeric Equtios; Lier Idepedece, Eigevlues, Eigevectors I. Systems of Lier Algeric Equtios.. We c represet the system...... usig mtrices d vectors
Sec. 7., Boyce & DiPrim, p. Sectio 7., Systems of Lier Algeric Equtios; Lier Idepedece, Eigevlues, Eigevectors I. Systems of Lier Algeric Equtios.. We c represet the system...... usig mtrices d vectors
( ) dx ; f ( x ) is height and Δx is
 Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Indices and Logarithms
 the Further Mthemtics etwork www.fmetwork.org.uk V 7 SUMMARY SHEET AS Core Idices d Logrithms The mi ides re AQA Ed MEI OCR Surds C C C C Lws of idices C C C C Zero, egtive d frctiol idices C C C C Bsic
the Further Mthemtics etwork www.fmetwork.org.uk V 7 SUMMARY SHEET AS Core Idices d Logrithms The mi ides re AQA Ed MEI OCR Surds C C C C Lws of idices C C C C Zero, egtive d frctiol idices C C C C Bsic
Discrete Mathematics I Tutorial 12
 Discrete Mthemtics I Tutoril Refer to Chpter 4., 4., 4.4. For ech of these sequeces fid recurrece reltio stisfied by this sequece. (The swers re ot uique becuse there re ifiitely my differet recurrece
Discrete Mthemtics I Tutoril Refer to Chpter 4., 4., 4.4. For ech of these sequeces fid recurrece reltio stisfied by this sequece. (The swers re ot uique becuse there re ifiitely my differet recurrece
Westchester Community College Elementary Algebra Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER
 Westchester Commuity College Elemetry Alger Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER Courtesy of Aims Commuity College The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d cotet of questios o the Accuplcer Elemetry
Westchester Commuity College Elemetry Alger Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER Courtesy of Aims Commuity College The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d cotet of questios o the Accuplcer Elemetry
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
For students entering Honors Precalculus Summer Packet
 Hoors PreClculus Summer Review For studets eterig Hoors Preclculus Summer Pcket The prolems i this pcket re desiged to help ou review topics from previous mthemtics courses tht re importt to our success
Hoors PreClculus Summer Review For studets eterig Hoors Preclculus Summer Pcket The prolems i this pcket re desiged to help ou review topics from previous mthemtics courses tht re importt to our success
Exam. Notes: A single A4 sheet of paper (double sided; hand-written or computer typed)
 Exam February 8th, 8 Sigals & Systems (5-575-) Prof. R. D Adrea Exam Exam Duratio: 5 Mi Number of Problems: 5 Number of Poits: 5 Permitted aids: Importat: Notes: A sigle A sheet of paper (double sided;
Exam February 8th, 8 Sigals & Systems (5-575-) Prof. R. D Adrea Exam Exam Duratio: 5 Mi Number of Problems: 5 Number of Poits: 5 Permitted aids: Importat: Notes: A sigle A sheet of paper (double sided;
Content: Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, James Stewart, 2007 Chapter 1: Functions and Limits., in a set B.
 Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION NUMBER SYSTEMS AND CONVERSION
 Fudmetls of Logic Desig Chp. CHAPTE /9 INTODUCTION NUMBE SYSTEMS AND CONVESION This chpter i the book icludes: Objectives Study Guide. Digitl Systems d Switchig Circuits. Number Systems d Coversio. Biry
Fudmetls of Logic Desig Chp. CHAPTE /9 INTODUCTION NUMBE SYSTEMS AND CONVESION This chpter i the book icludes: Objectives Study Guide. Digitl Systems d Switchig Circuits. Number Systems d Coversio. Biry
(1) Functions A relationship between two variables that assigns to each element in the domain exactly one element in the range.
 -. ALGEBRA () Fuctios A reltioship etwee two vriles tht ssigs to ech elemet i the domi ectly oe elemet i the rge. () Fctorig Aother ottio for fuctio of is f e.g. Domi: The domi of fuctio Rge: The rge of
-. ALGEBRA () Fuctios A reltioship etwee two vriles tht ssigs to ech elemet i the domi ectly oe elemet i the rge. () Fctorig Aother ottio for fuctio of is f e.g. Domi: The domi of fuctio Rge: The rge of
denominator, think trig! Memorize the following two formulas; you will use them often!
 7. Bsic Itegrtio Rules Some itegrls re esier to evlute th others. The three problems give i Emple, for istce, hve very similr itegrds. I fct, they oly differ by the power of i the umertor. Eve smll chges
7. Bsic Itegrtio Rules Some itegrls re esier to evlute th others. The three problems give i Emple, for istce, hve very similr itegrds. I fct, they oly differ by the power of i the umertor. Eve smll chges
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Elemetry Lier Alger Ato & Rorres, th Editio Lecture Set Chpter : Systems of Lier Equtios & Mtrices Chpter Cotets Itroductio to System of Lier Equtios Gussi Elimitio Mtrices d Mtri Opertios Iverses; Rules
Elemetry Lier Alger Ato & Rorres, th Editio Lecture Set Chpter : Systems of Lier Equtios & Mtrices Chpter Cotets Itroductio to System of Lier Equtios Gussi Elimitio Mtrices d Mtri Opertios Iverses; Rules
COMM 602: Digital Signal Processing
 COMM 60: Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 4 -Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -Iverse Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -ve +ve Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform
COMM 60: Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 4 -Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -Iverse Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -ve +ve Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Titus Beu University Babes-Bolyai Department of Theoretical and Computational Physics Cluj-Napoca, Romania
 8. Systems of Lier Algeric Equtios Titus Beu Uiversity Bes-Bolyi Deprtmet of Theoreticl d Computtiol Physics Cluj-Npoc, Romi Biliogrphy Itroductio Gussi elimitio method Guss-Jord elimitio method Systems
8. Systems of Lier Algeric Equtios Titus Beu Uiversity Bes-Bolyi Deprtmet of Theoreticl d Computtiol Physics Cluj-Npoc, Romi Biliogrphy Itroductio Gussi elimitio method Guss-Jord elimitio method Systems
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
Repeated Root and Common Root
 Repeted Root d Commo Root 1 (Method 1) Let α, β, γ e the roots of p(x) x + x + 0 (1) The α + β + γ 0, αβ + βγ + γα, αβγ - () (α - β) (α + β) - αβ (α + β) [ (βγ + γα)] + [(α + β) + γ (α + β)] +γ (α + β)
Repeted Root d Commo Root 1 (Method 1) Let α, β, γ e the roots of p(x) x + x + 0 (1) The α + β + γ 0, αβ + βγ + γα, αβγ - () (α - β) (α + β) - αβ (α + β) [ (βγ + γα)] + [(α + β) + γ (α + β)] +γ (α + β)
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION. (2014 Admn. onwards) III Semester. B.Sc. Mathematics CORE COURSE CALCULUS AND ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION (0 Adm. owrds) III Semester B.Sc. Mthemtics CORE COURSE CALCULUS AND ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Questio Bk & Aswer Key. l l () =... 0.00 b) 0 c). l d =... c
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION (0 Adm. owrds) III Semester B.Sc. Mthemtics CORE COURSE CALCULUS AND ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Questio Bk & Aswer Key. l l () =... 0.00 b) 0 c). l d =... c
Filter banks. Separately, the lowpass and highpass filters are not invertible. removes the highest frequency 1/ 2and
 Filter bas Separately, the lowpass ad highpass filters are ot ivertible T removes the highest frequecy / ad removes the lowest frequecy Together these filters separate the sigal ito low-frequecy ad high-frequecy
Filter bas Separately, the lowpass ad highpass filters are ot ivertible T removes the highest frequecy / ad removes the lowest frequecy Together these filters separate the sigal ito low-frequecy ad high-frequecy
Z-Transform of a discrete time signal x(n) is defined as the power series
 Z-Trsform of discrete time sigl x is defied s the ower series x 3.. This reltio lso clled direct Z-Trsform. Z[ x ] 3.. x 3..3 Regio of covergece ROC of is the set of ll vlues of for which ttis fiite vlue.
Z-Trsform of discrete time sigl x is defied s the ower series x 3.. This reltio lso clled direct Z-Trsform. Z[ x ] 3.. x 3..3 Regio of covergece ROC of is the set of ll vlues of for which ttis fiite vlue.
The total number of permutations of S is n!. We denote the set of all permutations of S by
 DETERMINNTS. DEFINITIONS Def: Let S {,,, } e the set of itegers from to, rrged i scedig order. rerrgemet jjj j of the elemets of S is clled permuttio of S. S. The totl umer of permuttios of S is!. We deote
DETERMINNTS. DEFINITIONS Def: Let S {,,, } e the set of itegers from to, rrged i scedig order. rerrgemet jjj j of the elemets of S is clled permuttio of S. S. The totl umer of permuttios of S is!. We deote
DETERMINANT. = 0. The expression a 1. is called a determinant of the second order, and is denoted by : y + c 1
 NOD6 (\Dt\04\Kot\J-Advced\SMP\Mths\Uit#0\NG\Prt-\0.Determits\0.Theory.p65. INTRODUCTION : If the equtios x + b 0, x + b 0 re stisfied by the sme vlue of x, the b b 0. The expressio b b is clled determit
NOD6 (\Dt\04\Kot\J-Advced\SMP\Mths\Uit#0\NG\Prt-\0.Determits\0.Theory.p65. INTRODUCTION : If the equtios x + b 0, x + b 0 re stisfied by the sme vlue of x, the b b 0. The expressio b b is clled determit
Improving XOR-Dominated Circuits by Exploiting Dependencies between Operands. Ajay K. Verma and Paolo Ienne. csda
 Improvig XOR-Domited Circuits y Exploitig Depedecies etwee Operds Ajy K. Verm d Polo Iee csd Processor Architecture Lortory LAP & Cetre for Advced Digitl Systems CSDA Ecole Polytechique Fédérle de Luse
Improvig XOR-Domited Circuits y Exploitig Depedecies etwee Operds Ajy K. Verm d Polo Iee csd Processor Architecture Lortory LAP & Cetre for Advced Digitl Systems CSDA Ecole Polytechique Fédérle de Luse
Lincoln Land Community College Placement and Testing Office
 Licol Ld Commuity College Plcemet d Testig Office Elemetry Algebr Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT) A totl of questios re dmiistered i this test. The first type ivolves opertios with itegers d rtiol
Licol Ld Commuity College Plcemet d Testig Office Elemetry Algebr Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT) A totl of questios re dmiistered i this test. The first type ivolves opertios with itegers d rtiol
Chapter Real Numbers
 Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
 School Of Distce Eductio Questio Bk UNIVERSITY OF ALIUT SHOOL OF DISTANE EDUATION B.Sc MATHEMATIS (ORE OURSE SIXTH SEMESTER ( Admissio OMPLEX ANALYSIS Module- I ( A lytic fuctio with costt modulus is :
School Of Distce Eductio Questio Bk UNIVERSITY OF ALIUT SHOOL OF DISTANE EDUATION B.Sc MATHEMATIS (ORE OURSE SIXTH SEMESTER ( Admissio OMPLEX ANALYSIS Module- I ( A lytic fuctio with costt modulus is :
z-transform A generalization of the DTFT defined by
 The DTFT provides frequecy-domi represettio of discrete-time sigs d LTI discrete-time systems Becuse of the covergece coditio, i my cses, the DTFT of sequece my ot exist As resut, it is ot possie to mke
The DTFT provides frequecy-domi represettio of discrete-time sigs d LTI discrete-time systems Becuse of the covergece coditio, i my cses, the DTFT of sequece my ot exist As resut, it is ot possie to mke
Approximate Integration
 Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Discrete-Time Systems, LTI Systems, and Discrete-Time Convolution
 EEL5: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we begi our mathematical treatmet of discrete-time s. As show i Figure, a discrete-time operates or trasforms some iput sequece x [
EEL5: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we begi our mathematical treatmet of discrete-time s. As show i Figure, a discrete-time operates or trasforms some iput sequece x [
Fig. 1. I a. V ag I c. I n. V cg. Z n Z Y. I b. V bg
 ymmetricl Compoets equece impedces Although the followig focuses o lods, the results pply eqully well to lies, or lies d lods. Red these otes together with sectios.6 d.9 of text. Cosider the -coected lced
ymmetricl Compoets equece impedces Although the followig focuses o lods, the results pply eqully well to lies, or lies d lods. Red these otes together with sectios.6 d.9 of text. Cosider the -coected lced
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
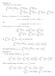 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
SM2H. Unit 2 Polynomials, Exponents, Radicals & Complex Numbers Notes. 3.1 Number Theory
 SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
Numerical Solution of Fuzzy Fredholm Integral Equations of the Second Kind using Bernstein Polynomials
 Jourl of Al-Nhri Uiversity Vol.5 (), Mrch,, pp.-9 Sciece Numericl Solutio of Fuzzy Fredholm Itegrl Equtios of the Secod Kid usig Berstei Polyomils Srmd A. Altie Deprtmet of Computer Egieerig d Iformtio
Jourl of Al-Nhri Uiversity Vol.5 (), Mrch,, pp.-9 Sciece Numericl Solutio of Fuzzy Fredholm Itegrl Equtios of the Secod Kid usig Berstei Polyomils Srmd A. Altie Deprtmet of Computer Egieerig d Iformtio
MULTIRESOLUTION TIME-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF MICROWAVE STRUCTURES USING MATLAB. Ondřej Franek, Zbyněk Raida
 MULTIRSOLUTION TIM-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF MICROWAV STRUCTURS USING MATLAB Odřej Frek, Zběk Rid Deprtmet of Rdio lectroics, Bro Uiversit of Techolog Abstrct I this pper, umericl lsis of microwve structures
MULTIRSOLUTION TIM-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF MICROWAV STRUCTURS USING MATLAB Odřej Frek, Zběk Rid Deprtmet of Rdio lectroics, Bro Uiversit of Techolog Abstrct I this pper, umericl lsis of microwve structures
 BITSAT MATHEMATICS PAPER. If log 0.0( ) log 0.( ) the elogs to the itervl (, ] () (, ] [,+ ). The poit of itersectio of the lie joiig the poits i j k d i+ j+ k with the ple through the poits i+ j k, i
BITSAT MATHEMATICS PAPER. If log 0.0( ) log 0.( ) the elogs to the itervl (, ] () (, ] [,+ ). The poit of itersectio of the lie joiig the poits i j k d i+ j+ k with the ple through the poits i+ j k, i
CITY UNIVERSITY LONDON
 CITY UNIVERSITY LONDON Eg (Hos) Degree i Civil Egieerig Eg (Hos) Degree i Civil Egieerig with Surveyig Eg (Hos) Degree i Civil Egieerig with Architecture PART EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
CITY UNIVERSITY LONDON Eg (Hos) Degree i Civil Egieerig Eg (Hos) Degree i Civil Egieerig with Surveyig Eg (Hos) Degree i Civil Egieerig with Architecture PART EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
Surds, Indices, and Logarithms Radical
 MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
Advanced Algorithmic Problem Solving Le 6 Math and Search
 Advced Algorithmic Prolem Solvig Le Mth d Serch Fredrik Heitz Dept of Computer d Iformtio Sciece Liköpig Uiversity Outlie Arithmetic (l. d.) Solvig lier equtio systems (l. d.) Chiese remider theorem (l.5
Advced Algorithmic Prolem Solvig Le Mth d Serch Fredrik Heitz Dept of Computer d Iformtio Sciece Liköpig Uiversity Outlie Arithmetic (l. d.) Solvig lier equtio systems (l. d.) Chiese remider theorem (l.5
Math 3B Midterm Review
 Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 643u Office Hours: R 11:00 m - 1:00 pm Lst updted /15/015 Here re some short otes o Sectios 7.1-7.8 i your ebook. The best idictio of wht
Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 643u Office Hours: R 11:00 m - 1:00 pm Lst updted /15/015 Here re some short otes o Sectios 7.1-7.8 i your ebook. The best idictio of wht
Section IV.6: The Master Method and Applications
 Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Northwest High School s Algebra 2
 Northwest High School s Algebr Summer Review Pcket 0 DUE August 8, 0 Studet Nme This pcket hs bee desiged to help ou review vrious mthemticl topics tht will be ecessr for our success i Algebr. Istructios:
Northwest High School s Algebr Summer Review Pcket 0 DUE August 8, 0 Studet Nme This pcket hs bee desiged to help ou review vrious mthemticl topics tht will be ecessr for our success i Algebr. Istructios:
FIR Filter Design: Part II
 EEL335: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we cosider how we might go about desigig FIR filters with arbitrary frequecy resposes, through compositio of multiple sigle-peak
EEL335: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we cosider how we might go about desigig FIR filters with arbitrary frequecy resposes, through compositio of multiple sigle-peak
Sect Simplifying Radical Expressions. We can use our properties of exponents to establish two properties of radicals: and
 128 Sect 10.3 - Simplifyig Rdicl Expressios Cocept #1 Multiplictio d Divisio Properties of Rdicls We c use our properties of expoets to estlish two properties of rdicls: () 1/ 1/ 1/ & ( Multiplictio d
128 Sect 10.3 - Simplifyig Rdicl Expressios Cocept #1 Multiplictio d Divisio Properties of Rdicls We c use our properties of expoets to estlish two properties of rdicls: () 1/ 1/ 1/ & ( Multiplictio d
 THEORY OF EQUATIONS SYNOPSIS. Polyomil Fuctio: If,, re rel d is positive iteger, the f)x) = + x + x +.. + x is clled polyomil fuctio.. Degree of the Polyomil: The highest power of x for which the coefficiet
THEORY OF EQUATIONS SYNOPSIS. Polyomil Fuctio: If,, re rel d is positive iteger, the f)x) = + x + x +.. + x is clled polyomil fuctio.. Degree of the Polyomil: The highest power of x for which the coefficiet
ECE-S352 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 3A Direct Solution of Difference Equations
 ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
Introduction to Matrix Algebra
 Itrodutio to Mtri Alger George H Olso, Ph D Dotorl Progrm i Edutiol Ledership Applhi Stte Uiversit Septemer Wht is mtri? Dimesios d order of mtri A p q dimesioed mtri is p (rows) q (olums) rr of umers,
Itrodutio to Mtri Alger George H Olso, Ph D Dotorl Progrm i Edutiol Ledership Applhi Stte Uiversit Septemer Wht is mtri? Dimesios d order of mtri A p q dimesioed mtri is p (rows) q (olums) rr of umers,
