Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Fundamentals of Optics. Midterm II. Mar. 21, :30 20:00.
|
|
|
- Sybil Howard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Mar. 21, :3 2: Exam Type: C (A doublesided aid sheet and a nonprogrammable calculator are allowed) Exam Duration: 9 minutes Q1 Q2 Q3 Total Note: (1) Your numerical answers should be followed by appropriate units, whenever applicable. (2) Follow the sign conventions established in the lectures. (3) Unless explicitly stated in the question, explanations to your answers are optional. However, partial marks will be awarded for incorrect or incomplete answers when accompanied by correct and relevant explanations. Conversely, marks will be deducted accordingly if a wrong explanation accompanies a correct answer. (4) If, in your opinion, a question is unclear or information is missing, then make reasonable assumptions, state them in your answer, and proceed.
2 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 2 of 8 Q1 You have only two quarterwave plates and you wish to change the polarization of a collimated, horizontally polarized laser beam. Take the horizontal direction as x, and the beam propagation direction as z. Specify the number (one or two) of waveplates you will need, and the direction of the slow axis of each of the waveplates you will use in order to (1) [3 marks] Convert the laser to a circular polarization (2) [5 marks] Convert the laser to a vertical (linear) polarization (3) [5 marks] Convert the laser to a linear polarization in the cosα x + sinα y direction, where <α<π. (4) [7 marks] Write down the Jones Matrix of your polarization conversion system used in (3), in the given coordinate system. Solution: (1) Need one quarterwave plate centered on and normal to the beam path, and its slow axis should be ±45 o or ±135 o with respect to the x axis, on the xy plane. (2) Need two quarterwave plates centered on and normal to the beam path. The slow axes of both waveplates should be aligned with each other, making the combination effectively a halfwave plate, and the slow axis should be ±45 o or ±135 o with respect to the x axis, on the xy plane. (3) Need two quarterwave plates centered on and normal to the beam path. The slow axes of both waveplates should be aligned with each other, making the combination effectively a halfwave plate, and the slow axis should be ±α/2 or ± (α+π)/2 (3 marks) with respect to the x axis, on the xy plane. (4) Method 1: The Jones Matrix for the combination of two quarterwave plates with both slow axes aligned to α/2 angle with respect to the xaxis, is given by: M = R(!!)T QWP T QWP R(!) ( cos!! 2 sin!! + = 2 (!sin!! 2 cos!! 2 ) ), ( = )!cos!sin!sin cos +, e i! /2 1 + (, ) e i! /2 1 ( + cos 2,!sin ) 2 sin 2 cos 2 Note, given the other possibilities, any of the following Matrices are also OK:!cos! sin! sin! cos! cos! sin! sin!!cos! cos!!sin!!sin!!cos! +,
3 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 3 of 8 Method 2: If the input Jones Vector is [1 ] T and the output Jones Vector is [cosα, sinα] T, then the matrix M relating them must satisfy:! cos!! = M 1 sin! Also, M must be unitary (lossless system). Therefore, M = cos! sin! sin!!cos!
4 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 4 of 8 Q2 A collimated, vertically (y direction) polarized, laser beam is passing through a Faraday rotator followed by a linear polarizer with a vertical (y) transmission axis. The Faraday rotator is 2cm long, has a Verdet constant of 134 rad/(tm) at the laser wavelength, and is subject to a uniform, timevarying magnetic field expressed as B =.5sin(1πt) z Tesla, where t is time in seconds and z is the beam propagating direction. (1) [3 marks] What is the Jones vector representation of the polarization before entering the rotator? (2) [5 marks] Plot the polarization rotation angle experienced by the light beam after passing through the rotator as a function of time. Label the horizontal scale on the time axis and the maximum polarization rotation angle on the vertical scale. (3) [6 marks] What is the Jones vector representation of the polarization after exiting the rotator? (Hint: it should be a function of time.) (4) [6 marks] Assuming the input intensity of the beam is I o and the rotator is lossless, what is the intensity of the laser beam after passing through the polarizer? Express it as a function of time. Solution: (1) The Jones Vector for vertical polarization is [ 1] T. (2) The rotation angle imposed by the Faraday rotator when B is parallel to the direction of propagation is θ(t)=vbd=( 134)x[.5sin(1πt)]x.2= 1.34sin(1πt) rad. (3) Jones Matrix for the Faraday Rotator is
5 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 5 of 8 M = = = cosvbd!sinvbd sinvbd cosvbd cos[!1.34sin(1!t)]!sin[!1.34sin(1!t)] sin[!1.34sin(1!t)] cos[1.34sin(1!t)]!sin[1.34sin(1!t)] cos[!1.34sin(1!t)] sin[1.34sin(1!t)] cos[1.34sin(1!t)] Therefore the Jones vector after exiting the rotator is: cos[1.34sin(1!t)] J rot _ out = MJ in =!sin[1.34sin(1!t)] sin[1.34sin(1!t)] =!cos[1.34sin(1!t)] sin[1.34sin(1!t)] cos[1.34sin(1!t)] 1 (4) The Jones vector after passing through the polarizer is :! J out = M pol _ y J rot _ out =! sin[1.34sin(1!t)] 1 cos[1.34sin(1!t)]! = cos[1.34sin(1!t)] Therefore the intensity after passing through the polarizer is: I out = I o cos 2 [1.34sin(12!t)]
6 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 6 of 8 Q3. Three identical right angled glass prisms are used as reflectors in a periscope set up shown below. After three 9degree turns, the beam emerges in the same propagation direction as the input propagation direction. The beam enters and exits all prisms at normal incidence to the facets, and reflects internally at 45 o incidence in each prism. The refractive index of the prism is n g =1.5. The medium outside the prisms is air, and the glass material is lossless. The input is linearly polarized in the x direction. (1) [5 marks] Determine the overall transmittance of the system consisting of the three prisms. Transmittance is defined as the ratio of output power to input power. (2) [5 marks] Determine the output polarization state and express it by a Jones vector in the xyz coordinate system shown. (3) [5 marks] Determine the Jones Matrix representation of the system. (4) [5 marks] Repeat (1) for the case where the medium outside the prisms is water with refractive index n w =1.33. Solution: (1) For each prism, the beam goes through 2 normalincidence transmissions at the facets, and one total internal reflection (TIR) at 45degree incidence. (The critical angle is θ c =sin 1 (1/n g )=41.8 o ). For each normalincidence transmission, the transmittance is T facet =1[(n g 1)/(n g +1)] 2 =.96. For each total internal reflection, the transmittance is 1. Therefore, the total transmittance of the system is T 6 =.78. (2) Three qualitative remarks here: (a) The six normalincidence transmissions do not change the polarization state. So we only need to take into account the three TIRs. (b) The plane of incidence for the first TIR (xz plane) is orthogonal to the plane of incidence for the second TIR (xy plane), which is orthogonal to the plane of incidence for the third TIR (yz plane). Therefore there is a role change between TE and TM polarization in between the prisms. For example, the TM output polarization of the first TIR becomes the TE input polarization of the second TIR, and the TE output
7 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 7 of 8 polarization of the second TIR becomes the TM input polarization of the third TIR. (c) According to our sign convention, all blue E fields indicated in the diagram below are related to each other by the Fresnel coefficients, so are all the red E fields. Notice here, if the input is polarized in the xdirection, the output will be polarized in the y direction. Therefore the output polarization state is: J out =!1 or J out = 1 This is a linearly polarized state in the y direction. (3) Consider the diagram above, we note that the xcomponent of the output E field depends only on the ycomponent of the input E field, and vice versa. Also, the transmissions at normal incidence do not alter the polarization state, so we need only consider the three TIRs. Therefore, T =!r TE r TM r TE!r TM r TE r TM =!exp i! +! +! TE TM TE!exp i (! TM +! TE +! TM ) ( ) where n! TE =!2 tan!1 g sin 45 o n g cos45 o ( ) 2!1 =!.6435rad =!36.9 o
8 ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Page 8 of 8 n! TM =!2tan!1 g n g sin 45 o cos45 o ( ) 2!1 +! =1.85rad =16.3 o Therefore, T = [ ]!exp i.56!exp[ i3.6] or 1 exp( i2.5) or exp (!i2.5) 1 (4) If the surrounding medium is water, TIR will not occur because the critical angle for the waterglass interface is θ c = sin 1 (n w /n g ) = 62.5 o. With θ i =45 o, θ t = sin 1 (n i sinθ i /n t ) = 52.9 o. The Fresnel reflection coefficients for TE and TM waves are: r TE = n g cos45o! n w cos52.9 o n g cos45 o + n w cos52.9 o =.14 r TM =!n w cos45o + n g cos52.9 o n w cos45 o + n g cos52.9 o =!.19 For each normal incidence, the transmittance is T facet =1[(n g n w )/(n g + n w )] 2 =.996. For each 45degree reflection, the TE reflectance is R TE =r TE 2 =(.14) 2 =.192, and the TM reflectance is R TM =r TM 2 =(.19) 2 =3.7x1 4. Therefore, the overall transmittance for an xpolarized input is: T overall = T 6 R TM R TE R TM = !1 4 ( ) = 2.6!1 9 In other words, essentially no transmission when the surrounding is water! (If you are going to use this periscope underwater, better put it in a sealed, waterproof enclosure.)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics. Final Exam. April 16, 2007.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE426F Optical Engineering. Final Exam. Dec. 17, 2003.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
Polarizers and Retarders
 Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
Chap. 5. Jones Calculus and Its Application to Birefringent Optical Systems
 Chap. 5. Jones Calculus and Its Application to Birefringent Optical Systems - The overall optical transmission through many optical components such as polarizers, EO modulators, filters, retardation plates.
Chap. 5. Jones Calculus and Its Application to Birefringent Optical Systems - The overall optical transmission through many optical components such as polarizers, EO modulators, filters, retardation plates.
Problem 8.0 Make Your Own Exam Problem for Midterm II by April 13
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Problem Set 8: Electromagnetic Waves at Boundaries
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Problem Set 8: Electromagnetic Waves at Boundaries
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Lecture 5: Polarization. Polarized Light in the Universe. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Polarizers. Retarders. Outline
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection
 Lecture 4: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht
Lecture 4: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht
Optics and Optical Design. Chapter 6: Polarization Optics. Lectures 11 13
 Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11 13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x direction y x z Components
Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11 13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x direction y x z Components
Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University,
Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media. Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces
 Lecture 5: Crystal Optics Outline 1 Homogeneous, Anisotropic Media 2 Crystals 3 Plane Waves in Anisotropic Media 4 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media 5 Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces Christoph
Lecture 5: Crystal Optics Outline 1 Homogeneous, Anisotropic Media 2 Crystals 3 Plane Waves in Anisotropic Media 4 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media 5 Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces Christoph
Optics and Optical Design. Chapter 6: Polarization Optics. Lectures 11-13
 Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11-13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x-direction y x z Components
Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11-13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x-direction y x z Components
[D] indicates a Design Question
![[D] indicates a Design Question [D] indicates a Design Question](/thumbs/77/76276479.jpg) EP421 Assignment 4: Polarization II: Applications of Optical Anisotropy use of the Jones Calculus (Handed Out: Friday 1 November 2013 Due Back: Friday 8 November 2013) 1. Optic Axis of Birefringent Crystals
EP421 Assignment 4: Polarization II: Applications of Optical Anisotropy use of the Jones Calculus (Handed Out: Friday 1 November 2013 Due Back: Friday 8 November 2013) 1. Optic Axis of Birefringent Crystals
1. Consider the biconvex thick lens shown in the figure below, made from transparent material with index n and thickness L.
 Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
16. More About Polarization
 16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 6: Polarization Original: Professor McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the basics of polarization and learn to use common optical elements
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 6: Polarization Original: Professor McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the basics of polarization and learn to use common optical elements
Speed of Light in Glass
 Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Lecture 4: Anisotropic Media. Dichroism. Optical Activity. Faraday Effect in Transparent Media. Stress Birefringence. Form Birefringence
 Lecture 4: Anisotropic Media Outline Dichroism Optical Activity 3 Faraday Effect in Transparent Media 4 Stress Birefringence 5 Form Birefringence 6 Electro-Optics Dichroism some materials exhibit different
Lecture 4: Anisotropic Media Outline Dichroism Optical Activity 3 Faraday Effect in Transparent Media 4 Stress Birefringence 5 Form Birefringence 6 Electro-Optics Dichroism some materials exhibit different
Fresnel s law, theory of reflection
 Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP Used concepts Electromagnetic theory of light, reflection coefficient, reflection factor, Brewster s law, law of refraction, polarisation, degree of polarisation.
Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP Used concepts Electromagnetic theory of light, reflection coefficient, reflection factor, Brewster s law, law of refraction, polarisation, degree of polarisation.
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
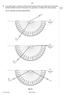 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials
 Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 3--997 Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 3--997 Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
Surface Plasmon Wave
 Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Quarter wave plates and Jones calculus for optical system
 2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6 1 Quarter wave plates and Jones calculus for optical system T. Johnson 2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6
2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6 1 Quarter wave plates and Jones calculus for optical system T. Johnson 2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 2002
 151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
Homework 1. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2017 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich
 Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 13.10.2017; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2017 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to establish
Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 13.10.2017; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2017 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to establish
Advanced Test Equipment Rentals ATEC (2832)
 Established 98 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (83) 9.5. THE AGILENT 869A POLARIZATION CONTROLLER A number of polarization controllers have been developed for the commercial
Established 98 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (83) 9.5. THE AGILENT 869A POLARIZATION CONTROLLER A number of polarization controllers have been developed for the commercial
Matrices in Polarization Optics. Polarized Light - Its Production and Analysis
 Matrices in Polarization Optics Polarized Light - Its Production and Analysis For all electromagnetic radiation, the oscillating components of the electric and magnetic fields are directed at right angles
Matrices in Polarization Optics Polarized Light - Its Production and Analysis For all electromagnetic radiation, the oscillating components of the electric and magnetic fields are directed at right angles
Waves in Linear Optical Media
 1/53 Waves in Linear Optical Media Sergey A. Ponomarenko Dalhousie University c 2009 S. A. Ponomarenko Outline Plane waves in free space. Polarization. Plane waves in linear lossy media. Dispersion relations
1/53 Waves in Linear Optical Media Sergey A. Ponomarenko Dalhousie University c 2009 S. A. Ponomarenko Outline Plane waves in free space. Polarization. Plane waves in linear lossy media. Dispersion relations
Experiment 8. Fresnel Coefficients. 8.1 Introduction. References
 Experiment 8 Fresnel Coefficients References Optics by Eugene Hecht, Chapter 4 Introduction to Modern Optics by Grant Fowles, Chapter 2 Principles of Optics by Max Born and Emil Wolf, Chapter 1 Optical
Experiment 8 Fresnel Coefficients References Optics by Eugene Hecht, Chapter 4 Introduction to Modern Optics by Grant Fowles, Chapter 2 Principles of Optics by Max Born and Emil Wolf, Chapter 1 Optical
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT
 ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (EO) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (EO) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A
 Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces
 Lecture 1: Foundations of Optics Outline 1 Electromagnetic Waves 2 Material Properties 3 Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces 4 Fresnel Equations 5 Brewster Angle 6 Total Internal Reflection Christoph
Lecture 1: Foundations of Optics Outline 1 Electromagnetic Waves 2 Material Properties 3 Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces 4 Fresnel Equations 5 Brewster Angle 6 Total Internal Reflection Christoph
Lecture 9. Transmission and Reflection. Reflection at a Boundary. Specific Boundary. Reflection at a Boundary
 Lecture 9 Reflection at a Boundary Transmission and Reflection A boundary is defined as a place where something is discontinuous Half the work is sorting out what is continuous and what is discontinuous
Lecture 9 Reflection at a Boundary Transmission and Reflection A boundary is defined as a place where something is discontinuous Half the work is sorting out what is continuous and what is discontinuous
Deviations from Malus Law
 From: Steve Scott, Jinseok Ko, Howard Yuh To: MSE Enthusiasts Re: MSE Memo #18a: Linear Polarizers and Flat Glass Plates Date: January 16, 2004 This memo discusses three issues: 1. When we measure the
From: Steve Scott, Jinseok Ko, Howard Yuh To: MSE Enthusiasts Re: MSE Memo #18a: Linear Polarizers and Flat Glass Plates Date: January 16, 2004 This memo discusses three issues: 1. When we measure the
Testing stress birefringence of an optical window. Chiayu Ai and. James C. Wyant. WYKO Corp., 2650 E. Elvira Road, Tucson, AZ ABSTRACT
 Testing stress birefringence of an optical window Chiayu Ai and James C. Wyant WYKO Corp., 2650 E. Elvira Road, Tucson, AZ 85706 ABSTRACT This paper describes a method to measure the birefringence of an
Testing stress birefringence of an optical window Chiayu Ai and James C. Wyant WYKO Corp., 2650 E. Elvira Road, Tucson, AZ 85706 ABSTRACT This paper describes a method to measure the birefringence of an
Polarization. Polarization. Physics Waves & Oscillations 4/3/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones. Two problems to be considered today:
 4/3/26 Physics 422 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 34 Polarization of Light Spring 26 Semester Matthew Jones Polarization (,)= cos (,)= cos + Unpolarizedlight: Random,, Linear polarization: =,± Circular polarization:
4/3/26 Physics 422 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 34 Polarization of Light Spring 26 Semester Matthew Jones Polarization (,)= cos (,)= cos + Unpolarizedlight: Random,, Linear polarization: =,± Circular polarization:
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Important announcements Homework #2 is due Feb. 12 Mid-term exam Feb 28
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Important announcements Homework #2 is due Feb. 12 Mid-term exam Feb 28
Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 30, 2017 Today s Topics. Begin Modern Optics Ch. 2: The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time
 Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
PHY410 Optics Exam #3
 PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Lecture Outline. Scattering at an Interface Sunrises & Sunsets Rainbows Polarized Sunglasses 8/9/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics.
 Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics Topic 3i Scattering at an Interface: Examples Examples These notes may
Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics Topic 3i Scattering at an Interface: Examples Examples These notes may
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Physics 5c Lecture 6 eflection and efraction (&L Sections. 3) Administravia! Laser safety video at the end of this lecture! Because you ll be doing take-home lab using a laser pointer! Lecture
Wave Phenomena Physics 5c Lecture 6 eflection and efraction (&L Sections. 3) Administravia! Laser safety video at the end of this lecture! Because you ll be doing take-home lab using a laser pointer! Lecture
Midterm Exam Solutions
 SIMG-455 Midterm Exam Solutions 1. We used the Argand diagram (also called the phasor diagram) to represent temporal oscillatory motion. (a) Use the Argand diagram to demonstrate that the superposition
SIMG-455 Midterm Exam Solutions 1. We used the Argand diagram (also called the phasor diagram) to represent temporal oscillatory motion. (a) Use the Argand diagram to demonstrate that the superposition
Summary of Beam Optics
 Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
17. Jones Matrices & Mueller Matrices
 7. Jones Matrices & Mueller Matrices Jones Matrices Rotation of coordinates - the rotation matrix Stokes Parameters and unpolarized light Mueller Matrices R. Clark Jones (96-24) Sir George G. Stokes (89-93)
7. Jones Matrices & Mueller Matrices Jones Matrices Rotation of coordinates - the rotation matrix Stokes Parameters and unpolarized light Mueller Matrices R. Clark Jones (96-24) Sir George G. Stokes (89-93)
Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time.
 L e c t u r e 8 1 Polarization Polarized light Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time. Imagine two harmonic, linearly polarized light
L e c t u r e 8 1 Polarization Polarized light Light for which the orientation of the electric field is constant although its magnitude and sign vary in time. Imagine two harmonic, linearly polarized light
Jones calculus for optical system
 2/14/17 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6 1 Jones calculus for optical system T. Johnson Key concepts in the course so far What is meant by an electro-magnetic response? What characterises
2/14/17 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6 1 Jones calculus for optical system T. Johnson Key concepts in the course so far What is meant by an electro-magnetic response? What characterises
Assignment , 7.1, 7.2, 7.5, 7.11, 7.12, 7.15, TIR and FTIR
 LC45-summer, 1 1. 1.1, 7.1, 7., 7.5, 7.11, 7.1, 7.15, 7.1 1.1. TIR and FTIR a) B considering the electric field component in medium B in Figure 1. (b), eplain how ou can adjust the amount of transmitted
LC45-summer, 1 1. 1.1, 7.1, 7., 7.5, 7.11, 7.1, 7.15, 7.1 1.1. TIR and FTIR a) B considering the electric field component in medium B in Figure 1. (b), eplain how ou can adjust the amount of transmitted
Tutorial 7: Solutions
 Tutorial 7: Solutions 1. (a) A point source S is a perpendicular distance R away from the centre of a circular hole of radius a in an opaque screen. f the distance to the periphery is (R + l), show that
Tutorial 7: Solutions 1. (a) A point source S is a perpendicular distance R away from the centre of a circular hole of radius a in an opaque screen. f the distance to the periphery is (R + l), show that
Homework 1. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2018 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich
 Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 12 October 2018; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2018 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to
Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 12 October 2018; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2018 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction What We (OK, Brian) Did Last Time Discussed EM waves in vacuum and in matter Maxwell s equations Wave equation Plane waves E t = c E B t
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction What We (OK, Brian) Did Last Time Discussed EM waves in vacuum and in matter Maxwell s equations Wave equation Plane waves E t = c E B t
Model 556X User s Manual. Optical Isolator
 Model 556X User s Manual Optical Isolator 550031 Rev. A 2 Is a registered trademark of New Focus Inc. Warranty New Focus, Inc. guarantees its products to be free of defects for one year from the date of
Model 556X User s Manual Optical Isolator 550031 Rev. A 2 Is a registered trademark of New Focus Inc. Warranty New Focus, Inc. guarantees its products to be free of defects for one year from the date of
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Physics 5c Lecture 6 eflection and efraction (&L Sections. 3) Administravia Laser safety video at the end of this lecture ecause you ll be doing take-home lab using a laser pointer Lecture
Wave Phenomena Physics 5c Lecture 6 eflection and efraction (&L Sections. 3) Administravia Laser safety video at the end of this lecture ecause you ll be doing take-home lab using a laser pointer Lecture
LECTURE 23: LIGHT. Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle
 LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT. Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle
 LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
Chap. 2. Polarization of Optical Waves
 Chap. 2. Polarization of Optical Waves 2.1 Polarization States - Direction of the Electric Field Vector : r E = E xˆ + E yˆ E x x y ( ω t kz + ϕ ), E = E ( ωt kz + ϕ ) = E cos 0 x cos x y 0 y - Role :
Chap. 2. Polarization of Optical Waves 2.1 Polarization States - Direction of the Electric Field Vector : r E = E xˆ + E yˆ E x x y ( ω t kz + ϕ ), E = E ( ωt kz + ϕ ) = E cos 0 x cos x y 0 y - Role :
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 102: Lecture 15 Electromagnetic Waves Energy & Polarization Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 1 Checkpoint 1.1, 1.2 y E x loop in xy plane loop in xz plane A B C Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 2 Propagation
Physics 102: Lecture 15 Electromagnetic Waves Energy & Polarization Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 1 Checkpoint 1.1, 1.2 y E x loop in xy plane loop in xz plane A B C Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 2 Propagation
βi β r medium 1 θ i θ r y θ t β t
 W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes Date:November 7, 997 0. Reections and Refractions of Plane Waves. Hr Ei Hi βi β r Er medium θ i θ r μ, ε y θ t μ, ε medium x z Ht β t Et Perpendicular Case (Transverse Electric
W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes Date:November 7, 997 0. Reections and Refractions of Plane Waves. Hr Ei Hi βi β r Er medium θ i θ r μ, ε y θ t μ, ε medium x z Ht β t Et Perpendicular Case (Transverse Electric
Modulators. Tuesday, 11/14/2006 Physics 158 Peter Beyersdorf. Document info 17. 1
 Modulators Tuesday, 11/14/2006 Physics 158 Peter Beyersdorf Document info 17. 1 Class Outline Birefringence Optical Activity Faraday Rotation Optical Modulators Electrooptic Modulators Accoustooptic Modulators
Modulators Tuesday, 11/14/2006 Physics 158 Peter Beyersdorf Document info 17. 1 Class Outline Birefringence Optical Activity Faraday Rotation Optical Modulators Electrooptic Modulators Accoustooptic Modulators
Chiroptical Spectroscopy
 Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Physics 214 Course Overview
 Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Typical anisotropies introduced by geometry (not everything is spherically symmetric) temperature gradients magnetic fields electrical fields
 Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
PHYS 102 Exams. PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A)
 PHYS 102 Exams PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A) The next two questions pertain to the situation described below. A metal ring, in the page, is in a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page as
PHYS 102 Exams PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A) The next two questions pertain to the situation described below. A metal ring, in the page, is in a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page as
4: birefringence and phase matching
 /3/7 4: birefringence and phase matching Polarization states in EM Linear anisotropic response χ () tensor and its symmetry properties Working with the index ellipsoid: angle tuning Phase matching in crystals
/3/7 4: birefringence and phase matching Polarization states in EM Linear anisotropic response χ () tensor and its symmetry properties Working with the index ellipsoid: angle tuning Phase matching in crystals
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light
 1. Purpose: IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light Analyze elliptically polarized light; determine the orientation of the vibration ellipse and the ratio of its semi-axes. 2. Apparatus: Gaertner Scientific
1. Purpose: IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light Analyze elliptically polarized light; determine the orientation of the vibration ellipse and the ratio of its semi-axes. 2. Apparatus: Gaertner Scientific
Polarimetry in the E-ELT era. Polarized Light in the Universe. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Polarizers. Retarders. Fundamentals of Polarized Light
 Polarimetry in the E-ELT era Fundamentals of Polarized Light 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Polarimetry in the E-ELT era Fundamentals of Polarized Light 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 36 Date:
 Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with
 Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with n = 1.71 4 30 λ 0 (λ 0 in µm), where λ 0 is the wavelength in vacuum, was used to disperse
Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with n = 1.71 4 30 λ 0 (λ 0 in µm), where λ 0 is the wavelength in vacuum, was used to disperse
POLARIZATION AND BIREFRINGENCE
 UNIT 3 POLARIZATION AND BIREFRINGENCE Name Lab Partner(s) Date Lab Section # TA signature Be sure to have your TA check your lab work and sign this sheet before you leave. Save it until the end of the
UNIT 3 POLARIZATION AND BIREFRINGENCE Name Lab Partner(s) Date Lab Section # TA signature Be sure to have your TA check your lab work and sign this sheet before you leave. Save it until the end of the
LC circuit: Energy stored. This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters
 Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Conceptual Physics. Luis A. Anchordoqui. Department of Physics and Astronomy Lehman College, City University of New York. Lesson VI October 3, 2017
 Conceptual Physics Luis A. Anchordoqui Department of Physics and Astronomy Lehman College, City University of New York Lesson VI October 3, 2017 https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.07445 L. A. Anchordoqui (CUNY)
Conceptual Physics Luis A. Anchordoqui Department of Physics and Astronomy Lehman College, City University of New York Lesson VI October 3, 2017 https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.07445 L. A. Anchordoqui (CUNY)
POLARISATION. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion.
 POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Optical circulator analysis and optimization: a mini-project for physical optics
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Optical circulator analysis and optimization: a mini-project for physical optics Zhujun Wan Zhujun Wan, "Optical circulator analysis
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Optical circulator analysis and optimization: a mini-project for physical optics Zhujun Wan Zhujun Wan, "Optical circulator analysis
UE SPM-PHY-S Polarization Optics
 UE SPM-PHY-S07-101 Polarization Optics N. Fressengeas Laboratoire Matériaux Optiques, Photonique et Systèmes Unité de Recherche commune à l Université Paul Verlaine Metz et à Supélec Document à télécharger
UE SPM-PHY-S07-101 Polarization Optics N. Fressengeas Laboratoire Matériaux Optiques, Photonique et Systèmes Unité de Recherche commune à l Université Paul Verlaine Metz et à Supélec Document à télécharger
Chapter 9 - Polarization
 Chapter 9 - Polarization Gabriel Popescu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Beckman Institute Quantitative Light Imaging Laboratory http://light.ece.uiuc.edu Principles of Optical Imaging Electrical
Chapter 9 - Polarization Gabriel Popescu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Beckman Institute Quantitative Light Imaging Laboratory http://light.ece.uiuc.edu Principles of Optical Imaging Electrical
Jones vector & matrices
 Jones vector & matrices Department of Physics 1 Matrix treatment of polarization Consider a light ray with an instantaneous E-vector as shown y E k, t = xe x (k, t) + ye y k, t E y E x x E x = E 0x e i
Jones vector & matrices Department of Physics 1 Matrix treatment of polarization Consider a light ray with an instantaneous E-vector as shown y E k, t = xe x (k, t) + ye y k, t E y E x x E x = E 0x e i
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - DISCLAIMER - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - General Information: This is a midterm from a previous semester. This means: This midterm contains problems that are of
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - DISCLAIMER - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - General Information: This is a midterm from a previous semester. This means: This midterm contains problems that are of
PHYS 110B - HW #5 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS 0B - HW #5 Fall 005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased [.] Imagine a prism made of lucite (n.5) whose cross-section is a
PHYS 0B - HW #5 Fall 005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased [.] Imagine a prism made of lucite (n.5) whose cross-section is a
Determination of Cauchy s Contants
 8. Determination of Cauchy s Contants 8.1 Objective: To determine Cauchy s Constants using a prism and spectrometer. Apparatus: Glass prism, spectrometer and mercury vapour lamp. 8. Theory: The wavelength
8. Determination of Cauchy s Contants 8.1 Objective: To determine Cauchy s Constants using a prism and spectrometer. Apparatus: Glass prism, spectrometer and mercury vapour lamp. 8. Theory: The wavelength
Physics 208 Final Exam
 Physics 208 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work, with partial credit. See the last pages of the exam for formula sheets. Please be clear and well-organized, so that we can easily follow each step
Physics 208 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work, with partial credit. See the last pages of the exam for formula sheets. Please be clear and well-organized, so that we can easily follow each step
BISTABLE twisted nematic (BTN) liquid crystal displays
 JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL 1, NO 2, DECEMBER 2005 217 Analytic Solution of Film Compensated Bistable Twisted Nematic Liquid Crystal Displays Fushan Zhou and Deng-Ke Yang Abstract In this paper,
JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL 1, NO 2, DECEMBER 2005 217 Analytic Solution of Film Compensated Bistable Twisted Nematic Liquid Crystal Displays Fushan Zhou and Deng-Ke Yang Abstract In this paper,
Chapter 14 Matrix Treatment of Polarization
 Chapter 4 Matri Treatment of Polarization Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Naer Eradat Spring 29 5//29 Matri Treatment of Polarization Polarization Polarization
Chapter 4 Matri Treatment of Polarization Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Naer Eradat Spring 29 5//29 Matri Treatment of Polarization Polarization Polarization
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
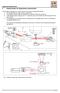 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Devlin et al. 10.1073/pnas.1611740113 Optical Characterization We deposit blanket TiO films via ALD onto silicon substrates to prepare samples for spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE)
Supporting Information Devlin et al. 10.1073/pnas.1611740113 Optical Characterization We deposit blanket TiO films via ALD onto silicon substrates to prepare samples for spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE)
4. Integrated Photonics. (or optoelectronics on a flatland)
 4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Discussion 2A
 EECS 16A Spring 218 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Discussion 2A 1. Visualizing Matrices as Operations This problem is going to help you visualize matrices as operations. For example, when
EECS 16A Spring 218 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Discussion 2A 1. Visualizing Matrices as Operations This problem is going to help you visualize matrices as operations. For example, when
OBSERVATIONS OF THE GOOS-HÄNCHEN AND IMBERT-FEDOROV SHIFTS VIA WEAK MEASUREMENT. A Thesis. Presented to the. Faculty of. San Diego State University
 OBSERVATIONS OF THE GOOS-HÄNCHEN AND IMBERT-FEDOROV SHIFTS VIA WEAK MEASUREMENT A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of San Diego State University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
OBSERVATIONS OF THE GOOS-HÄNCHEN AND IMBERT-FEDOROV SHIFTS VIA WEAK MEASUREMENT A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of San Diego State University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
PHYS 450 Spring semester Lecture 13: Polarized Light. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University. Historical Timeline
 PHYS 450 Spring semester 2017 Lecture 13: Polarized Light Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University Lecture 13 1 Historical Timeline 1669 Bartholinus describes image doubling properties
PHYS 450 Spring semester 2017 Lecture 13: Polarized Light Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University Lecture 13 1 Historical Timeline 1669 Bartholinus describes image doubling properties
Lecture 8: Polarimetry 2. Polarizers and Retarders. Polarimeters. Scattering Polarization. Zeeman Effect. Outline
 Lecture 8: Polarimetry 2 Outline 1 Polarizers and Retarders 2 Polarimeters 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht University, C.U.Keller@uu.nl Observational Astrophysics
Lecture 8: Polarimetry 2 Outline 1 Polarizers and Retarders 2 Polarimeters 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht University, C.U.Keller@uu.nl Observational Astrophysics
Innovation and Development of Study Field. nano.tul.cz
 Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
