Lecture 36 Date:
|
|
|
- Elizabeth Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 36 Date: Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave
2 Introduction One can t expect plane waves to be incident normally on a plane in all types of applications. Therefore one must consider the general problem of a plane wave propagating along a specified axis that is arbitrarily located relative to a rectangular coordinate system. The most general form of a plane wave in a lossless media is given by: ( r, t) o cos(. r t) Where: aˆ aˆ aˆ r xaˆ yaˆ zaˆ x x y y z z x y z x y z
3 Introduction (contd.) ( r, t) o cos(. r t) One can deduce Maxwell s equations in the following form: H H. H 0. 0 They show two things: (i), H and β are orthogonal, (ii) and H lie on the same plane. r x y y cons tant x y z The corresponding magnetic field is: H aˆ
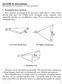
4 Reflection at Oblique Incidence The plane defined by the propagation vector β and a unit normal vector a n to the boundary is called the plane of incidence. The angle between β and a n is the angle of incidence. cos( x y y t) i io ix iy iz i cos( x y y t) r ro rx ry rz r β r β t cos( x y y t) t to tx ty tz t β i Where: β i, β r and β t will have normal and tangential components to the plane of incidence.
5 Reflection at Oblique Incidence (contd.) β rz = β cosθ r β sinθ i β sinθ r β sinθ t β iz = β cosθ i β tz = β cosθ t From boundary condition we can write: the tangential component of must be continuous at z = 0. i tan z r tan z t tan z ( 0) ( 0) ( 0) This boundary condition can be satisfied if: i r t ix rx tx x iy ry ty y
6 Reflection at Oblique Incidence (contd.) First condition implies that the frequency remains unchanged. From second and third conditions we can write: β sinθ i = β sinθ r β sinθ i = β sinθ t Where, θ r is the angle of reflection and θ t is the angle of transmission. We know, for lossless media: θ i = θ sin r t u sin u i
7 Reflection at Oblique Incidence (contd.) sint u sin u i Snell s Law n sin n i sin t n and n are the refractive indices of the media After these general preliminaries on oblique incidence, let us consider two special cases (i) the field perpendicular to the plane of incidence, (ii) the field parallel to it. Any other polarization may be considered as a linear combination of these two cases.
8 Parallel Polarization Consider following figure: field lies in the xz-plane, the plane of incidence. It illustrates the case of Parallel Polarization. r t H t In medium the incident and reflected waves are: H r i i ( aˆ cos aˆ sin ) e j x z is io x i z i ( sin cos ) i r r ( aˆ cos aˆ sin ) e j x z rs ro x r z r ( sin cos ) H i io j x z ( sini cos i) H is e a ˆ y io j x z ( sinr cos r) H rs e a ˆ y
9 Parallel Polarization (contd.) The transmitted fields in medium are given by: t t ( aˆ cos aˆ sin ) e j x z ts to x t z t to j x z ( sint cos t) H ts e a ˆ ( sin cos ) We know: θ i = θ r and tangential components of electric and magnetic fields are continuous at the boundary z=0. Therefore: cos cos io ro i to t y io ro to
10 Parallel Polarization (contd.) Simplification gives: cos cos cos cos ro t i io t i to cosi cos cos io t i Fresnel s quations For θ i = θ t = 0, we get: ro io to io
11 Parallel Polarization (contd.) Furthermore, the expressions for reflection coefficient and transmission coefficient can be written in terms of angle of incidence. u cost sin t sin i u In addition: cos t cosi The reflection coefficient Γ equals zero when there is no reflection (only the parallel component is not reflected), and the incident angle at which this happens is called Brewster s Angle θ B. The Brewster s Angle is also known as polarizing angle. At this angle, the perpendicular component of will be reflected. Brewster s concept is utilized in laser tube used in surgical procedures.
12 Parallel Polarization (contd.) For Brewster s Angle, set Γ = 0: cos cos sin t sin B t B sin B For a lossless and nonmagnetic medium: There is a Brewster Angle for any combination of ε and ε. sin B sin B
13 Perpendicular Polarization The field is perpendicular to the plane of incidence (the xz-plane). In this situation we get Perpendicular Polarization. Here, H field is parallel to the plane of incidence. H r t e a j ( x sin iz cos i is io ) ˆ y r H t e a j ( x sin rz cos r rs io ) ˆ y i H a a e io ( sin i cos i) is ( ˆ cos ˆ sin ) j x z x i z i H i H a a e ro ( sin r cos r) rs ( ˆ cos ˆ sin ) j x z x r z r
14 Perpendicular Polarization (contd.) The transmitted fields in medium are given by: e a j ( x sin tz cos t ts to ) ˆ y H a a e to ( sin t cos t) ts ( ˆ cos ˆ sin ) j x z x t z t Again, θ i = θ r and tangential components of electric and magnetic fields are continuous at the boundary z=0. Therefore: io ro to cos cos io ro i to t
15 Perpendicular Polarization (contd.) Simplification gives: cos cos cos cos ro i t io i t to cosi cos cos io i t Fresnel s quations for perpendicular polarization For θ i = θ t = 0, we get: ro io to io
16 Perpendicular Polarization (contd.) Simplification for Brewster s Angle in Perpendicular Polarization gives: cos cos B t sin B sin t sin B For nonmagnetic media, μ = μ = μ 0 and therefore: sin B Brewster s Angle doesn t exist as sine of an angle is never greater than unity
17 Perpendicular Polarization (contd.) If μ μ and ε = ε then: sin B sin B Theoretically possible but rarely occurs in practice
18 Applications of RF/Microwaves The use of RF/microwaves has greatly expanded. xamples include telecommunications, radio astronomy, land surveying, radar, meteorology, UHF television, terrestrial microwave links, solid-state devices, heating, medicine, and identification systems. Features that make microwaves attractive for communications include wide available bandwidths (capacities to carry information) and directive properties for short wavelengths. Currently, there are three main techniques to carry energy over long distances: (a) microwave links, (b) coaxial cables, and (c) fibre optics. A microwave system normally consists of a transmitter (including a microwave oscillator, waveguides, amplifiers, and transmitting antenna) and a receiver subsystem (including a receiver antenna, transmission line or waveguide, and amplifiers). A microwave network is usually an interconnection of various microwave components and devices.
19 Applications of RF/Microwaves (contd.) Common microwave components include: Coaxial cables, which are transmission lines for interconnecting microwave components. Waveguide sections, which may be straight, curved, or twisted. Antenna, which transmit or receive M waves efficiently. Terminators, which are designed to absorb the input power and therefore acts as one port network. Attenuators, which are designed to absorb some of the M power passing through the device, thereby decreasing the power level of the microwave signal. Directional couplers, with a mechanism to couple between different ports. Isolators, which allow energy flow in only one direction. Circulators, which are designed to establish various entry/exit points where power can be either fed or extracted. Filters, which suppress unwanted signals and/or separate signals of different frequencies.
20 RF/Microwave Circuit A microwave circuit consists of microwave components such as sources, transmission lines, waveguides, attenuators, circulators, and filters. One way of analyzing, such circuits, are to relate the input and output variables of each component. At RF/microwave frequencies, where current and voltage are not well defined, it is a common practice to use S-parameters for analysis. S-parameters are defined in terms of wave variables which are more easily measurable at high frequencies than voltage and current.
21 RF/Microwave Circuit (contd.) Let us consider following -port network: The traveling waves are related to the S-parameters as: b Sa Sa b Sa Sa where, a and a are incident waves at port and respectively; while b and b represent the reflected waves.
22 RF/Microwave Circuit (contd.) In matrix form: b S S a b S S a The off-diagonal terms represent transmission coefficients, while the diagonal terms represent reflection coefficients. If the network is reciprocal, it will have the same transmission characteristic in either direction. S S If the network is symmetric, then: S S For matched two port network: S S 0
23 RF/Microwave Circuit (contd.) Γ L The input reflection coefficient in terms of the S-parameters and the load Z L : b S S L i S a S L ZL Zo L ZL Zo
24 RF/Microwave Circuit (contd.) Similarly, the output reflection coefficient (with V g = 0) can be expressed in terms of the generator impedance Z g : b S S g o S a S g Zg Zin g Zg Zin
25 xample S-parameters are obtained for a microwave transistor operating at.5 GHz: S = 0.85 < 30, S = 0.07 < 56, S =.68 < 0, S = 0.85 < 40. Determine the input reflection coefficient when Z L = Z o = 75Ω. L Z Z L L Z Z o o 0 S S S S i L SL
βi β r medium 1 θ i θ r y θ t β t
 W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes Date:November 7, 997 0. Reections and Refractions of Plane Waves. Hr Ei Hi βi β r Er medium θ i θ r μ, ε y θ t μ, ε medium x z Ht β t Et Perpendicular Case (Transverse Electric
W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes Date:November 7, 997 0. Reections and Refractions of Plane Waves. Hr Ei Hi βi β r Er medium θ i θ r μ, ε y θ t μ, ε medium x z Ht β t Et Perpendicular Case (Transverse Electric
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Today in Physics 218: impedance of the vacuum, and Snell s Law
 Today in Physics 218: impedance of the vacuum, and Snell s Law The impedance of linear media Spacecloth Reflection and transmission of electromagnetic plane waves at interfaces: Snell s Law and the first
Today in Physics 218: impedance of the vacuum, and Snell s Law The impedance of linear media Spacecloth Reflection and transmission of electromagnetic plane waves at interfaces: Snell s Law and the first
Reflection/Refraction
 Reflection/Refraction Page Reflection/Refraction Boundary Conditions Interfaces between different media imposed special boundary conditions on Maxwell s equations. It is important to understand what restrictions
Reflection/Refraction Page Reflection/Refraction Boundary Conditions Interfaces between different media imposed special boundary conditions on Maxwell s equations. It is important to understand what restrictions
LECTURE 23: LIGHT. Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle
 LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT. Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle
 LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
Four Ports. 1 ENGN4545/ENGN6545: Radiofrequency Engineering L#16
 Four Ports Theorems of four port networks 180 o and 90 o Hybrids Directional couplers Transmission line transformers, Four port striplines Rat-races, Wilkinsons, Magic-T s Circulators, Diplexers and Filter
Four Ports Theorems of four port networks 180 o and 90 o Hybrids Directional couplers Transmission line transformers, Four port striplines Rat-races, Wilkinsons, Magic-T s Circulators, Diplexers and Filter
Waves in Linear Optical Media
 1/53 Waves in Linear Optical Media Sergey A. Ponomarenko Dalhousie University c 2009 S. A. Ponomarenko Outline Plane waves in free space. Polarization. Plane waves in linear lossy media. Dispersion relations
1/53 Waves in Linear Optical Media Sergey A. Ponomarenko Dalhousie University c 2009 S. A. Ponomarenko Outline Plane waves in free space. Polarization. Plane waves in linear lossy media. Dispersion relations
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
FINAL EXAM IN FYS-3007
 Page 1 of 4 pages + chart FINAL EXAM IN FYS-007 Exam in : Fys-007 Microwave Techniques Date : Tuesday, May 1, 2011 Time : 09.00 1.00 Place : Åsgårdveien 9 Approved remedies : All non-living and non-communicating
Page 1 of 4 pages + chart FINAL EXAM IN FYS-007 Exam in : Fys-007 Microwave Techniques Date : Tuesday, May 1, 2011 Time : 09.00 1.00 Place : Åsgårdveien 9 Approved remedies : All non-living and non-communicating
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation
 III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
Lecture 23 Date:
 Lecture 3 Date:.04.05 Incidence, Reflectn, and Transmissn of Plane Waves Wave Incidence For many applicatns, [such as fiber optics, wire line transmissn, wireless transmissn], it s necessary to know what
Lecture 3 Date:.04.05 Incidence, Reflectn, and Transmissn of Plane Waves Wave Incidence For many applicatns, [such as fiber optics, wire line transmissn, wireless transmissn], it s necessary to know what
Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with
 Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with n = 1.71 4 30 λ 0 (λ 0 in µm), where λ 0 is the wavelength in vacuum, was used to disperse
Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with n = 1.71 4 30 λ 0 (λ 0 in µm), where λ 0 is the wavelength in vacuum, was used to disperse
Polarized Light. Nikki Truss. Abstract:
 Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
ECE Microwave Engineering
 ECE 537-635 Microwave Engineering Fall 8 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Adapted from notes by Prof. Jeffery T. Williams Notes Power Dividers and Circulators Power Dividers and Couplers A power divider
ECE 537-635 Microwave Engineering Fall 8 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Adapted from notes by Prof. Jeffery T. Williams Notes Power Dividers and Circulators Power Dividers and Couplers A power divider
5. Circulators and Isolators
 9/9/006 Circulators and Isolators / 5. Circulators and Isolators Q: All the devices we have studied thus far are reciprocal. Are there such things as non-reciprocal microwave devices? A: HO: The Circulator
9/9/006 Circulators and Isolators / 5. Circulators and Isolators Q: All the devices we have studied thus far are reciprocal. Are there such things as non-reciprocal microwave devices? A: HO: The Circulator
Lecture 12. Microwave Networks and Scattering Parameters
 Lecture Microwave Networs and cattering Parameters Optional Reading: teer ection 6.3 to 6.6 Pozar ection 4.3 ElecEng4FJ4 LECTURE : MICROWAE NETWORK AND -PARAMETER Microwave Networs: oltages and Currents
Lecture Microwave Networs and cattering Parameters Optional Reading: teer ection 6.3 to 6.6 Pozar ection 4.3 ElecEng4FJ4 LECTURE : MICROWAE NETWORK AND -PARAMETER Microwave Networs: oltages and Currents
Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 8 Electromagnetic Waves Overview. The most remarkable conclusion of Maxwell s work on electromagnetism in the 860 s was that waves could exist in the fields themselves, traveling with the speed
Physics 8 Electromagnetic Waves Overview. The most remarkable conclusion of Maxwell s work on electromagnetism in the 860 s was that waves could exist in the fields themselves, traveling with the speed
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides
 1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
Lecture Outline. Scattering at an Interface Sunrises & Sunsets Rainbows Polarized Sunglasses 8/9/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics.
 Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics Topic 3i Scattering at an Interface: Examples Examples These notes may
Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics Topic 3i Scattering at an Interface: Examples Examples These notes may
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction
 Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
PHY3128 / PHYM203 (Electronics / Instrumentation) Transmission Lines
 Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
EM Waves. From previous Lecture. This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization. Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves
 EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
Ref: J. D. Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics; A. Sommerfeld: Electrodynamics.
 2 Fresnel Equations Contents 2. Laws of reflection and refraction 2.2 Electric field parallel to the plane of incidence 2.3 Electric field perpendicular to the plane of incidence Keywords: Snell s law,
2 Fresnel Equations Contents 2. Laws of reflection and refraction 2.2 Electric field parallel to the plane of incidence 2.3 Electric field perpendicular to the plane of incidence Keywords: Snell s law,
3 December Lesson 5.5
 Preparation Assignments for Homework #8 Due at the start of class. Reading Assignments Please see the handouts for each lesson for the reading assignments. 3 December Lesson 5.5 A uniform plane wave is
Preparation Assignments for Homework #8 Due at the start of class. Reading Assignments Please see the handouts for each lesson for the reading assignments. 3 December Lesson 5.5 A uniform plane wave is
APPLICATION OF BILAYER ANISOTROPIC STRUC- TURES FOR DESIGNING LOW-PASS FILTERS AND PO- LARIZERS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 29, 95 108, 2013 APPLICATION OF BILAYER ANISOTROPIC STRUC- TURES FOR DESIGNING LOW-PASS FILTERS AND PO- LARIZERS Amir Raeesi *, Ali Abdolali, and Hossein Mirzaei
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 29, 95 108, 2013 APPLICATION OF BILAYER ANISOTROPIC STRUC- TURES FOR DESIGNING LOW-PASS FILTERS AND PO- LARIZERS Amir Raeesi *, Ali Abdolali, and Hossein Mirzaei
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 11. Transmission Lines. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EEE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 11 Transmission ines Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 1 1 11.1 Introduction Wave propagation in unbounded media is used in
EEE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 11 Transmission ines Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 1 1 11.1 Introduction Wave propagation in unbounded media is used in
Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media. Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces
 Lecture 5: Crystal Optics Outline 1 Homogeneous, Anisotropic Media 2 Crystals 3 Plane Waves in Anisotropic Media 4 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media 5 Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces Christoph
Lecture 5: Crystal Optics Outline 1 Homogeneous, Anisotropic Media 2 Crystals 3 Plane Waves in Anisotropic Media 4 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media 5 Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces Christoph
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
ECE 3300 Standing Waves
 Standing Waves ECE3300 Lossless Transmission Lines Lossless Transmission Line: Transmission lines are characterized by: and Zo which are a function of R,L,G,C To minimize loss: Use high conductivity materials
Standing Waves ECE3300 Lossless Transmission Lines Lossless Transmission Line: Transmission lines are characterized by: and Zo which are a function of R,L,G,C To minimize loss: Use high conductivity materials
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
Today in Physics 218: Fresnel s equations
 Today in Physics 8: Fresnel s equations Transmission and reflection with E parallel to the incidence plane The Fresnel equations Total internal reflection Polarization on reflection nterference R 08 06
Today in Physics 8: Fresnel s equations Transmission and reflection with E parallel to the incidence plane The Fresnel equations Total internal reflection Polarization on reflection nterference R 08 06
Preliminary Topics in EM
 ECE 53 1 st Century Electromagnetics Instructor: Office: Phone: E Mail: Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf A 337 (915) 747 6958 rcrumpf@utep.edu Lecture #1 Preliminary Topics in EM Lecture 1 1 Lecture Outline Maxwell
ECE 53 1 st Century Electromagnetics Instructor: Office: Phone: E Mail: Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf A 337 (915) 747 6958 rcrumpf@utep.edu Lecture #1 Preliminary Topics in EM Lecture 1 1 Lecture Outline Maxwell
ECE 604, Lecture 17. October 30, In this lecture, we will cover the following topics: Reflection and Transmission Single Interface Case
 ECE 604, Lecture 17 October 30, 2018 In this lecture, we will cover the following topics: Duality Principle Reflection and Transmission Single Interface Case Interesting Physical Phenomena: Total Internal
ECE 604, Lecture 17 October 30, 2018 In this lecture, we will cover the following topics: Duality Principle Reflection and Transmission Single Interface Case Interesting Physical Phenomena: Total Internal
( z) ( ) ( )( ) ω ω. Wave equation. Transmission line formulas. = v. Helmholtz equation. Exponential Equation. Trig Formulas = Γ. cos sin 1 1+Γ = VSWR
 Wave equation 1 u tu v u(, t f ( vt + g( + vt Helmholt equation U + ku jk U Ae + Be + jk Eponential Equation γ e + e + γ + γ Trig Formulas sin( + y sin cos y+ sin y cos cos( + y cos cos y sin sin y + cos
Wave equation 1 u tu v u(, t f ( vt + g( + vt Helmholt equation U + ku jk U Ae + Be + jk Eponential Equation γ e + e + γ + γ Trig Formulas sin( + y sin cos y+ sin y cos cos( + y cos cos y sin sin y + cos
Propagation of EM Waves in material media
 Propagation of EM Waves in material media S.M.Lea 09 Wave propagation As usual, we start with Maxwell s equations with no free charges: D =0 B =0 E = B t H = D t + j If we now assume that each field has
Propagation of EM Waves in material media S.M.Lea 09 Wave propagation As usual, we start with Maxwell s equations with no free charges: D =0 B =0 E = B t H = D t + j If we now assume that each field has
Module 5 : Plane Waves at Media Interface. Lecture 36 : Reflection & Refraction from Dielectric Interface (Contd.) Objectives
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Reflection and Refraction with Parallel Polarization. Reflection and Refraction for Normal Incidence. Lossy Media Interface. Reflection and Refraction
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Reflection and Refraction with Parallel Polarization. Reflection and Refraction for Normal Incidence. Lossy Media Interface. Reflection and Refraction
Lecture 17 Date:
 Lecture 17 Date: 09.03.017 The Quadrature Hybrid We began our discussion of dividers and couplers by considering important general properties of three- and four-port networks. This was followed by an analysis
Lecture 17 Date: 09.03.017 The Quadrature Hybrid We began our discussion of dividers and couplers by considering important general properties of three- and four-port networks. This was followed by an analysis
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
Fresnel s law, theory of reflection
 Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP Used concepts Electromagnetic theory of light, reflection coefficient, reflection factor, Brewster s law, law of refraction, polarisation, degree of polarisation.
Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP Used concepts Electromagnetic theory of light, reflection coefficient, reflection factor, Brewster s law, law of refraction, polarisation, degree of polarisation.
Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces
 Lecture 1: Foundations of Optics Outline 1 Electromagnetic Waves 2 Material Properties 3 Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces 4 Fresnel Equations 5 Brewster Angle 6 Total Internal Reflection Christoph
Lecture 1: Foundations of Optics Outline 1 Electromagnetic Waves 2 Material Properties 3 Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces 4 Fresnel Equations 5 Brewster Angle 6 Total Internal Reflection Christoph
and Ee = E ; 0 they are separated by a dielectric material having u = io-s S/m, µ, = µ, 0
 602 CHAPTER 11 TRANSMISSION LINES 11.10 Two identical pulses each of magnitude 12 V and width 2 µs are incident at t = 0 on a lossless transmission line of length 400 m terminated with a load. If the two
602 CHAPTER 11 TRANSMISSION LINES 11.10 Two identical pulses each of magnitude 12 V and width 2 µs are incident at t = 0 on a lossless transmission line of length 400 m terminated with a load. If the two
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
Chapter 4 Reflection and Transmission of Waves
 4-1 Chapter 4 Reflection and Transmission of Waves ECE 3317 Dr. Stuart Long www.bridgat.com www.ranamok.com Boundary Conditions 4- -The convention is that is the outward pointing normal at the boundary
4-1 Chapter 4 Reflection and Transmission of Waves ECE 3317 Dr. Stuart Long www.bridgat.com www.ranamok.com Boundary Conditions 4- -The convention is that is the outward pointing normal at the boundary
Program WAVES Version 1D C.W. Trueman Updated March 23, 2004
 Program WAVES Version 1D C.W. Trueman Updated March 23, 2004 Program WAVES animates plane wave incidence on a dielectric half space. These notes describe how to use the program and outline a series of
Program WAVES Version 1D C.W. Trueman Updated March 23, 2004 Program WAVES animates plane wave incidence on a dielectric half space. These notes describe how to use the program and outline a series of
Lecture 19 Date:
 Lecture 19 Date: 8.10.014 The Quadrature Hybrid We began our discussion of dividers and couplers by considering important general properties of three- and fourport networks. This was followed by an analysis
Lecture 19 Date: 8.10.014 The Quadrature Hybrid We began our discussion of dividers and couplers by considering important general properties of three- and fourport networks. This was followed by an analysis
Wavepackets. Outline. - Review: Reflection & Refraction - Superposition of Plane Waves - Wavepackets - ΔΔk Δx Relations
 Wavepackets Outline - Review: Reflection & Refraction - Superposition of Plane Waves - Wavepackets - ΔΔk Δx Relations 1 Sample Midterm (one of these would be Student X s Problem) Q1: Midterm 1 re-mix (Ex:
Wavepackets Outline - Review: Reflection & Refraction - Superposition of Plane Waves - Wavepackets - ΔΔk Δx Relations 1 Sample Midterm (one of these would be Student X s Problem) Q1: Midterm 1 re-mix (Ex:
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.)
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction What We (OK, Brian) Did Last Time Discussed EM waves in vacuum and in matter Maxwell s equations Wave equation Plane waves E t = c E B t
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction What We (OK, Brian) Did Last Time Discussed EM waves in vacuum and in matter Maxwell s equations Wave equation Plane waves E t = c E B t
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
Microwave Network Analysis
 Prof. Dr. Mohammad Tariqul Islam titareq@gmail.my tariqul@ukm.edu.my Microwave Network Analysis 1 Text Book D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 3 rd edition, 2005 by John-Wiley & Sons. Fawwaz T. ILABY,
Prof. Dr. Mohammad Tariqul Islam titareq@gmail.my tariqul@ukm.edu.my Microwave Network Analysis 1 Text Book D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 3 rd edition, 2005 by John-Wiley & Sons. Fawwaz T. ILABY,
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON. SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2018
 ENG018 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING MODULE NO: EEE6002 Date: 17 January 2018 Time: 2.00 4.00 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are six questions.
ENG018 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING MODULE NO: EEE6002 Date: 17 January 2018 Time: 2.00 4.00 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are six questions.
EECS 117 Lecture 3: Transmission Line Junctions / Time Harmonic Excitation
 EECS 117 Lecture 3: Transmission Line Junctions / Time Harmonic Excitation Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 3 p. 1/23 Transmission Line
EECS 117 Lecture 3: Transmission Line Junctions / Time Harmonic Excitation Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 3 p. 1/23 Transmission Line
4. Integrated Photonics. (or optoelectronics on a flatland)
 4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
Plane Waves Part II. 1. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when
 Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
444 Index Boundary condition at transmission line short circuit, 234 for normal component of B, 170, 180 for normal component of D, 169, 180 for tange
 Index A. see Magnetic vector potential. Acceptor, 193 Addition of complex numbers, 19 of vectors, 3, 4 Admittance characteristic, 251 input, 211 line, 251 Ampere, definition of, 427 Ampere s circuital
Index A. see Magnetic vector potential. Acceptor, 193 Addition of complex numbers, 19 of vectors, 3, 4 Admittance characteristic, 251 input, 211 line, 251 Ampere, definition of, 427 Ampere s circuital
Scattering Parameters
 Berkeley Scattering Parameters Prof. Ali M. Niknejad U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2016 by Ali M. Niknejad September 7, 2017 1 / 57 Scattering Parameters 2 / 57 Scattering Matrix Voltages and currents are
Berkeley Scattering Parameters Prof. Ali M. Niknejad U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2016 by Ali M. Niknejad September 7, 2017 1 / 57 Scattering Parameters 2 / 57 Scattering Matrix Voltages and currents are
Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Physics 214 Course Overview
 Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 30, 2017 Today s Topics. Begin Modern Optics Ch. 2: The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time
 Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
Microwave Network Analysis Lecture 1: The Scattering Parameters
 Microwave Network Analysis Lecture : The Scattering Parameters ELC 305a Fall 0 Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Outline Review on Network
Microwave Network Analysis Lecture : The Scattering Parameters ELC 305a Fall 0 Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Outline Review on Network
Problem set 3. Electromagnetic waves
 Second Year Electromagnetism Michaelmas Term 2017 Caroline Terquem Problem set 3 Electromagnetic waves Problem 1: Poynting vector and resistance heating This problem is not about waves but is useful to
Second Year Electromagnetism Michaelmas Term 2017 Caroline Terquem Problem set 3 Electromagnetic waves Problem 1: Poynting vector and resistance heating This problem is not about waves but is useful to
Waves. Daniel S. Weile. ELEG 648 Waves. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware. Plane Waves Reflection of Waves
 Waves Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Waves Outline Outline Introduction Let s start by introducing simple solutions to Maxwell s equations
Waves Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Waves Outline Outline Introduction Let s start by introducing simple solutions to Maxwell s equations
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
Lecture 13 Date:
 ecture 3 Date: 6.09.204 The Signal Flow Graph (Contd.) Impedance Matching and Tuning Tpe Matching Network Example Signal Flow Graph (contd.) Splitting Rule Now consider the three equations SFG a a b 2
ecture 3 Date: 6.09.204 The Signal Flow Graph (Contd.) Impedance Matching and Tuning Tpe Matching Network Example Signal Flow Graph (contd.) Splitting Rule Now consider the three equations SFG a a b 2
Contents. Transmission Lines The Smith Chart Vector Network Analyser (VNA) ü structure ü calibration ü operation. Measurements
 Contents Transmission Lines The Smith Chart Vector Network Analyser (VNA) ü structure ü calibration ü operation Measurements Göran Jönsson, EIT 2015-04-27 Vector Network Analysis 2 Waves on Lines If the
Contents Transmission Lines The Smith Chart Vector Network Analyser (VNA) ü structure ü calibration ü operation Measurements Göran Jönsson, EIT 2015-04-27 Vector Network Analysis 2 Waves on Lines If the
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017
 Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Electromagnetic Waves. Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
ECE357H1F ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS FINAL EXAM. 28 April Examiner: Prof. Sean V. Hum. Duration: hours
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE357H1F ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS FINAL EXAM 28 April 15 Examiner:
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE357H1F ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS FINAL EXAM 28 April 15 Examiner:
Summary of Beam Optics
 Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
Lecture 9. Transmission and Reflection. Reflection at a Boundary. Specific Boundary. Reflection at a Boundary
 Lecture 9 Reflection at a Boundary Transmission and Reflection A boundary is defined as a place where something is discontinuous Half the work is sorting out what is continuous and what is discontinuous
Lecture 9 Reflection at a Boundary Transmission and Reflection A boundary is defined as a place where something is discontinuous Half the work is sorting out what is continuous and what is discontinuous
A Review of Basic Electromagnetic Theories
 A Review of Basic Electromagnetic Theories Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820)
A Review of Basic Electromagnetic Theories Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820)
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff
 Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Module 6 : Wave Guides. Lecture 40 : Introduction of Parallel Waveguide. Objectives. In this course you will learn the following
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide. Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide Wave Guide is a structure which can guide Electro Magnetic Energy.
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide. Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide Wave Guide is a structure which can guide Electro Magnetic Energy.
Innovation and Development of Study Field. nano.tul.cz
 Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations
 Electromagnetic Waves ECEN 3410 Prof. Wagner Final Review Questions 1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations 1. Describe the integral form of charge conservation within a volume V through a surface S, and give
Electromagnetic Waves ECEN 3410 Prof. Wagner Final Review Questions 1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations 1. Describe the integral form of charge conservation within a volume V through a surface S, and give
TC 412 Microwave Communications. Lecture 6 Transmission lines problems and microstrip lines
 TC 412 Microwave Communications Lecture 6 Transmission lines problems and microstrip lines RS 1 Review Input impedance for finite length line Quarter wavelength line Half wavelength line Smith chart A
TC 412 Microwave Communications Lecture 6 Transmission lines problems and microstrip lines RS 1 Review Input impedance for finite length line Quarter wavelength line Half wavelength line Smith chart A
DIRECTIONAL COUPLERS
 DIRECTIONAL COUPLERS Ing. rvargas@inictel.gob.pe INICTEL Abstract This paper analyzes two types of Directional Couplers. First, magnetic coupling between a transmission line and a secondary circuit is
DIRECTIONAL COUPLERS Ing. rvargas@inictel.gob.pe INICTEL Abstract This paper analyzes two types of Directional Couplers. First, magnetic coupling between a transmission line and a secondary circuit is
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic waves
 Chapter 9. lectromagnetic waves 9.1.1 The (classical or Mechanical) waves equation Given the initial shape of the string, what is the subsequent form, The displacement at point z, at the later time t,
Chapter 9. lectromagnetic waves 9.1.1 The (classical or Mechanical) waves equation Given the initial shape of the string, what is the subsequent form, The displacement at point z, at the later time t,
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 lectromagnetic Waves (H&L Sections 9.5 7) What We Did Last Time! Studied spherical waves! Wave equation of isotropic waves! Solution e! Intensity decreases with! Doppler
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 lectromagnetic Waves (H&L Sections 9.5 7) What We Did Last Time! Studied spherical waves! Wave equation of isotropic waves! Solution e! Intensity decreases with! Doppler
GLE 594: An introduction to applied geophysics
 GL 594: An introduction to applied geophysics Ground Penetrating Radar Fall 005 Ground Penetrating Radar Reading Today: 309-316 Next class: 316-39 Introduction to GPR Using the reflection (and sometimes
GL 594: An introduction to applied geophysics Ground Penetrating Radar Fall 005 Ground Penetrating Radar Reading Today: 309-316 Next class: 316-39 Introduction to GPR Using the reflection (and sometimes
Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves
 9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
ECE 107: Electromagnetism
 ECE 107: Electromagnetism Set 2: Transmission lines Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Outline Transmission
ECE 107: Electromagnetism Set 2: Transmission lines Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Outline Transmission
Effects of Loss Factor on Plane Wave Propagation through a Left-Handed Material Slab
 Vol. 113 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 Effects of Loss Factor on Plane Wave Propagation through a Left-Handed Material Slab C. Sabah Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department, University
Vol. 113 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 Effects of Loss Factor on Plane Wave Propagation through a Left-Handed Material Slab C. Sabah Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department, University
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Total Internal Reflection & Metal Mirrors
 Phys 531 Lecture 7 15 September 2005 Total Internal Reflection & Metal Mirrors Last time, derived Fresnel relations Give amplitude of reflected, transmitted waves at boundary Focused on simple boundaries:
Phys 531 Lecture 7 15 September 2005 Total Internal Reflection & Metal Mirrors Last time, derived Fresnel relations Give amplitude of reflected, transmitted waves at boundary Focused on simple boundaries:
Solutions: Homework 7
 Solutions: Homework 7 Ex. 7.1: Frustrated Total Internal Reflection a) Consider light propagating from a prism, with refraction index n, into air, with refraction index 1. We fix the angle of incidence
Solutions: Homework 7 Ex. 7.1: Frustrated Total Internal Reflection a) Consider light propagating from a prism, with refraction index n, into air, with refraction index 1. We fix the angle of incidence
EE 5337 Computational Electromagnetics. Preliminary Topics
 Instructor Dr. Raymond Rumpf (915) 747 6958 rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 5337 Computational Electromagnetics Lecture #3 Preliminary Topics Lecture 3These notes may contain copyrighted material obtained under fair
Instructor Dr. Raymond Rumpf (915) 747 6958 rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 5337 Computational Electromagnetics Lecture #3 Preliminary Topics Lecture 3These notes may contain copyrighted material obtained under fair
Lab 8 - Polarization
 Lab 8 Polarization L8-1 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - Polarization OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate
Lab 8 Polarization L8-1 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - Polarization OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate
EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF INHOMOGENEOUS GRATINGS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 69, 21 34, 2007 EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF INHOMOGENEOUS GRATINGS M. Khalaj-Amirhosseini College of Electrical Engineering Iran University of Science
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 69, 21 34, 2007 EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF INHOMOGENEOUS GRATINGS M. Khalaj-Amirhosseini College of Electrical Engineering Iran University of Science
CBSE 12th Physics 2016 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board ARYAN INSTITUTE
 CBSE 12th Physics 2016 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board CBSE 12th Physics 2016 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board TIME - 3HR. QUESTIONS - 26 THE MARKS ARE MENTIONED ON EACH QUESTION SECTION-A Q.1. A point charge +Q
CBSE 12th Physics 2016 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board CBSE 12th Physics 2016 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board TIME - 3HR. QUESTIONS - 26 THE MARKS ARE MENTIONED ON EACH QUESTION SECTION-A Q.1. A point charge +Q
