Gaussian and Mean Curvatures
|
|
|
- Aubrey Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gaussian and Mean Curvatures (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 31, 2017 We have learned that the two principal curvatures (and vectors) determine the local shape of a point on a surface. One characterizes the rate of maximum bending of the surface and the tangent direction in which it occurs, while the other characterizes the rate and tangent direction of minimum bending. The rate of surface bending along any tangent direction at the same point is determined by the two principal curvatures according to Euler s formula. Our main focus will nevertheless be on two new measures of the curving a surface its Gaussian and mean curvatures that turn out to have greater geometrical significance than the principal curvatures. 1 Definition Let κ 1 and κ 2 be the principal curvatures of a surface patch σ(u,v). The Gaussian curvature of σ is K = κ 1 κ 2, and its mean curvature is H = 1 2 (κ 1 +κ 2 ). To compute K and H, we use the first and second fundamental forms of the surface: Edu 2 +2Fdudv +Gdv 2 and Ldu 2 +2Mdudv +Ndv 2. Again, we adopt the matrix notation: ( ) E F F 1 = F G and F 2 = ( L M M N ). By definition, the principal curvatures are the eigenvalues of F 1 1 F 2. Hence the determinant of this matrix is the product κ 1 κ 2, i.e., the Gaussian curvature K. So K = det(f 1 1 F 2 ) = det(f 1 ) 1 det(f 2 ) = LN M2.. (1) EG F2 The material is mostly adapted from the book Elementary Differential Geometry by Andrew Pressley, Springer- Verlag,
2 The trace of the matrix is the sum of its eigenvalues, thus, twice the mean curvature H. After some calculation, we obtain H = 1 2 trace(f 1 1 F 2 ) = 1 LG 2MF +NE 2 EG F 2. (2) An equivalent way to obtain K and H uses the fact that the principal curvatures are also the roots of det(f 2 κf 1 ) = 0, which expands into a quadratic equation (EG F 2 )κ 2 (LG 2MF +NE)κ+LN M 2 = 0. The product K and the sum 2H of the two roots, can be determined directly from the coefficients. The results are the same as in (1) and (2). Conversely, given the Gaussian and mean curvatures K and H, we can easily find the principal curvatures κ 1 and κ 2, which are the roots of i.e., H ± H 2 K. κ 2 2Hκ+K = 0, Example 1. We have considered the surface of revolution (see Example 1 in the notes titled Surface Curvatures ) σ(u,v) = (f(u)cosv,f(u)sinv,g(u)), where we assume, without loss of generality, that f > 0 and f 2 + ġ 2 = 1 everywhere. Here a dot denotes d/du. The coefficients of the first and second fundamental forms were determined: So the Gaussian curvatures is E = 1, F = 0, G = f 2, L = f g fġ, M = 0, N = fġ. LN M2 K = EG F 2 = ( f g fġ)fġ f 2 = ( f g fġ)ġ. f Meanwhile, differentiate f 2 +ġ 2 = 1: Thus, f f +ġ g = 0. ( f g fġ)ġ = f 2 f 2 fġ = f( f 2 +ġ 2 ) = f. So the Gaussian curvature gets simplified to K = f f. 2
3 Example 2. Here we compute the Gaussian and mean curvatures of a Monge patch z = f(x,y). Namely, the patch is described by σ(x,y) = (x,y,f(x,y)). First, we obtain the first and second derivatives: σ x = (1,0,f x ), σ y = (0,1,f y ), σ xx = (0,0,f xx ), σ xy = (0,0,f xy ), σ yy = (0,0,f yy ). Immediately, the coefficients of the first fundamental form are determined So is the unit normal to the patch: E = 1+f 2 x, F = f xf y, G = 1+f 2 y. ˆn = σ x σ y σ x σ y = ( f x, f y,1). 1+fx 2 +fy 2 With the normal ˆn, we obtain the coefficients of the second fundamental form: L = σ xx ˆn = M = σ xy ˆn = N = σ yy ˆn = f xx 1+f 2 x +f 2 y f xy 1+f 2 x +f2 y f yy 1+f 2 x +f2 y,,. Plug the expressions for E,F,G,L,M,N into (1) and (2). A few more steps of symbolic manipulation yield: K = LN M2 EG F 2 = f xxf yy f 2 xy (1+f 2 x +f2 y )2, H = 1 LG 2MF +NE 2 EG F 2 = f xx(1+fy) 2f 2 xy f x f y +f yy (1+fx) 2. 2(1+fx 2 +fy) 2 3/2 2 Classification of Surface Points The Gaussian curvature is independent of the choice of the unit normal ˆn. To see why, suppose ˆn is changed to ˆn. Then the signs of the coefficients of L,M,N change, so do the signs of both principal curvatures κ 1 and κ 2, which are the roots of det(f 2 κf 1 ). Their product K = κ 1 κ 2 is unaffected. The mean curvature H = (κ 1 + κ 2 )/2, nevertheless, has its sign depending on the choice of ˆn. Thesign of K at a point p on a surfaces has an important geometric meaning, which is detailed below. 1. K > 0 The principal curvatures κ 1 and κ 2 have the same sign. The normal curvature κ in any tangent direction t is equal to κ 1 cos 2 θ + κ 2 sin 2 θ, where θ is the angle between t and the principal vector corresponding to κ 1. So κ has the same sign as that of κ 1 and κ 2. The surface is bending away from its tangent plane in all tangent directions at p. The quadratic approximation of the surface near p is the paraboloid z = 1 2 (κ 1x 2 +κ 2 y 2 ). 3
4 We call p an elliptic point of the surface. The left figure below plots an elliptic paraboloid z = x 2 +2y 2 with principal curvatures 2 and 4 at the origin. 2. K < 0 The principal curvatures κ 1 and κ 2 have opposite signs at p. The quadratic approximation of the surface near p is a hyperboloid. The point is said to be a hyperbolic point of the surface. The right figure above plots a hyperbolic paraboloid z = x 2 2y 2 with principal curvatures 2 and 4 at the origin. 3. K = 0 There are two cases: (a) Only one principal curvature, say, κ 1, is zero. In this case, the quadratic approximation is the cylinder z = 1 2 κ 2y 2. The point p is called a parabolic point of the surface. (b) Both principal curvatures are zero. The quadratic approximation is the plane z = 0. The point p is a planar point of the surface. One cannot determine the shape of the surface near p without examining the third or higher order derivatives. For example, a point in the plane and the origin of a monkey saddle z = x 3 3xy 2 (shown below) are both planar points, but they have quite different shapes. 4
5 A torus is the surface swept by a circle of radius a originally in the yz-plane and centered on the y-axis at a distance b, b > a, from the origin, when the circle revolves about the z-axis. It is easy to derive the following implicit equation for the torus: ( ) 2 x 2 +y 2 b +z 2 = a 2. z p p b a y x a The torus is a good example which has all three types of points. At points on the outer half of the torus, the torus bends away from from its tangent plane; hence K > 0. At each point on the inner half, the torus bends toward its tangent plane in the horizontal direction, but away from it in the orthogonal direction; hence K < 0. On the two circles, swept respectively by the top and bottom points of the original circle, every point has K = 0. A surface S is flat if its Gaussian curvature is zero everywhere. A plane is flat. Let it be the xy-plane with the parametrization (x,y,0). We can easily show that the plane has zero Gaussian curvature. A circular cylinder, treated in Example 3 of the notes Surface Curvatures, has one principal curvature equal to zero and the other equal to the inverse of the radius of its cross section. So a circular cylinder is also flat, even though it is so obviously curved. A surface is minimal provided its mean curvature is zero everywhere. Minimal surfaces have Gaussian curvature K 0. This is because H = (κ 1 +κ 2 )/2 = 0 implies κ 1 = κ 2. The catenoid (cosucoshv,sinucoshv,v) plotted over [0,2π] [ 2,2] below is a minimal surface. 5
6 3 The Gauss Map The standard unit normal ˆn to a surface patch σ measures the direction of its tangent plane. The change rate of ˆn in a tangent direction, i.e., the normal curvature, indicates the degree of variation of surface geometry in that direction at the point. To make the notion of change of geometry independent of any tangent direction, we can measure by the rate of change of ˆn per unit area. Note that ˆn is a point of the unit sphere S 2 centered at the origin. The Gauss map from a surface patch σ(u,v) : U R 3 to the unit sphere S 2 sends a point p = σ(u,v) to the point ˆn(u,v) of S 2. The Gauss map may be a many-to-one mapping since multiple points on the patch can have the same unit normal. ˆn(q) q ˆn(p) p σ(r) Gauss map ˆn(p) ˆn(q) N(R) unit sphere Let R U be a region in the patch s domain. The amount by which ˆn varies over the corresponding region σ(r) on the surface is measured by the area of the image region N(R) on the unit sphere. The rate of change of ˆn per unit area is the limit of the ratio of the area A N (R) of N(R) to the area Aσ(R) of the surface region σ(r), as R shrinks to a point. To be more precise, we consider R to be a closed disk of radius δ centered at (u,v) U. This ratio is A N (R) lim δ 0 Aσ(R). It can beshown [2, pp ] that the above ratio is the absolute value of thegaussian curvature at p, i.e., A N (R) lim δ 0 Aσ(R) = K. The integral of the Gaussian curvature K over a surface S, KdS, S is called the total Gaussian curvature of S. It is the algebraic area of the image of the region on the unit sphere under the Gauss map. Note the use of the word algebraic since Gaussian curvature can be either positive or negative, Suppose the patch S = σ(u,v) is defined over the domain [a,b] [c,d]. Then the total Gaussian curvature is computed as d b c a K(u,v) EG F 2 dudv. Example 3. If the Gaussian curvature K of a surface S is constant, then the total Gaussian curvature is KA(S), where A(S) is the area of the surface. Thus a sphere of radius r has total Gaussian curvature 1 r 2 4πr 2 = 4π, which is independent of the radius r. 6
7 Example 4. Without any computation, we can determine that an ellipsoid also has total curvature 4π. The Gauss map is bijective (one-to-one and onto) since every point on the ellipsoid has a distinct normal. The image region covers the unit sphere. Because the Gaussian curvature is everywhere positive on the ellipsoid, the area of the unit sphere, 4π, is the total Gaussian curvature of the ellipsoid. References [1] B. O Neill. Elementary Differential Geometry. Academic Press, Inc., [2] A. Pressley. Elementary Differential Geometry. Springer-Verlag London,
Dierential Geometry Curves and surfaces Local properties Geometric foundations (critical for visual modeling and computing) Quantitative analysis Algo
 Dierential Geometry Curves and surfaces Local properties Geometric foundations (critical for visual modeling and computing) Quantitative analysis Algorithm development Shape control and interrogation Curves
Dierential Geometry Curves and surfaces Local properties Geometric foundations (critical for visual modeling and computing) Quantitative analysis Algorithm development Shape control and interrogation Curves
Geodesics. (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia. Nov 2, 2017
 Geodesics (om S 477/577 Notes Yan-Bin Jia Nov 2, 2017 Geodesics are the curves in a surface that make turns just to stay on the surface and never move sideways. A bug living in the surface and following
Geodesics (om S 477/577 Notes Yan-Bin Jia Nov 2, 2017 Geodesics are the curves in a surface that make turns just to stay on the surface and never move sideways. A bug living in the surface and following
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring Final exam May 3rd. Suggested solutions
 alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 12.1 & 12.2 Vectors in the Plane
 MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013
 Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013 1 Rectangular Space Coordinates; Vectors in the Three-Dimensional Space (a) Cartesian coordinates of a point (b) sphere (c) symmetry about a point, a line, and a
Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013 1 Rectangular Space Coordinates; Vectors in the Three-Dimensional Space (a) Cartesian coordinates of a point (b) sphere (c) symmetry about a point, a line, and a
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
CHAPTER 3. Gauss map. In this chapter we will study the Gauss map of surfaces in R 3.
 CHAPTER 3 Gauss map In this chapter we will study the Gauss map of surfaces in R 3. 3.1. Surfaces in R 3 Let S R 3 be a submanifold of dimension 2. Let {U i, ϕ i } be a DS on S. For any p U i we have a
CHAPTER 3 Gauss map In this chapter we will study the Gauss map of surfaces in R 3. 3.1. Surfaces in R 3 Let S R 3 be a submanifold of dimension 2. Let {U i, ϕ i } be a DS on S. For any p U i we have a
Chapter 5. The Second Fundamental Form
 Chapter 5. The Second Fundamental Form Directional Derivatives in IR 3. Let f : U IR 3 IR be a smooth function defined on an open subset of IR 3. Fix p U and X T p IR 3. The directional derivative of f
Chapter 5. The Second Fundamental Form Directional Derivatives in IR 3. Let f : U IR 3 IR be a smooth function defined on an open subset of IR 3. Fix p U and X T p IR 3. The directional derivative of f
Lectures in Discrete Differential Geometry 2 Surfaces
 Lectures in Discrete Differential Geometry 2 Surfaces Etienne Vouga February 4, 24 Smooth Surfaces in R 3 In this section we will review some properties of smooth surfaces R 3. We will assume that is parameterized
Lectures in Discrete Differential Geometry 2 Surfaces Etienne Vouga February 4, 24 Smooth Surfaces in R 3 In this section we will review some properties of smooth surfaces R 3. We will assume that is parameterized
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework
 MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
Parametric Curves. (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia. Oct 3, 2017
 Parametric Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 3, 2017 1 Introduction A curve in R 2 (or R 3 ) is a differentiable function α : [a,b] R 2 (or R 3 ). The initial point is α[a] and the final point
Parametric Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 3, 2017 1 Introduction A curve in R 2 (or R 3 ) is a differentiable function α : [a,b] R 2 (or R 3 ). The initial point is α[a] and the final point
Math 10C - Fall Final Exam
 Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
Lecture 11: Differential Geometry
 Lecture 11: Differential Geometry c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 2000 Last modified on February 28, 2000 at 8:45 PM Contents 11.1 Introduction..............................................
Lecture 11: Differential Geometry c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 2000 Last modified on February 28, 2000 at 8:45 PM Contents 11.1 Introduction..............................................
Geometric Modelling Summer 2016
 Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 Exercises Benjamin Karer M.Sc. http://gfx.uni-kl.de/~gm Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 1 Dierential Geometry Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling
Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 Exercises Benjamin Karer M.Sc. http://gfx.uni-kl.de/~gm Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 1 Dierential Geometry Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling
Practice problems for Exam 1. a b = (2) 2 + (4) 2 + ( 3) 2 = 29
 Practice problems for Exam.. Given a = and b =. Find the area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides a and b. A = a b a ı j k b = = ı j + k = ı + 4 j 3 k Thus, A = 9. a b = () + (4) + ( 3)
Practice problems for Exam.. Given a = and b =. Find the area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides a and b. A = a b a ı j k b = = ı j + k = ı + 4 j 3 k Thus, A = 9. a b = () + (4) + ( 3)
Review problems for the final exam Calculus III Fall 2003
 Review problems for the final exam alculus III Fall 2003 1. Perform the operations indicated with F (t) = 2t ı 5 j + t 2 k, G(t) = (1 t) ı + 1 t k, H(t) = sin(t) ı + e t j a) F (t) G(t) b) F (t) [ H(t)
Review problems for the final exam alculus III Fall 2003 1. Perform the operations indicated with F (t) = 2t ı 5 j + t 2 k, G(t) = (1 t) ı + 1 t k, H(t) = sin(t) ı + e t j a) F (t) G(t) b) F (t) [ H(t)
d F = (df E 3 ) E 3. (4.1)
 4. The Second Fundamental Form In the last section we developed the theory of intrinsic geometry of surfaces by considering the covariant differential d F, that is, the tangential component of df for a
4. The Second Fundamental Form In the last section we developed the theory of intrinsic geometry of surfaces by considering the covariant differential d F, that is, the tangential component of df for a
9.1 Mean and Gaussian Curvatures of Surfaces
 Chapter 9 Gauss Map II 9.1 Mean and Gaussian Curvatures of Surfaces in R 3 We ll assume that the curves are in R 3 unless otherwise noted. We start off by quoting the following useful theorem about self
Chapter 9 Gauss Map II 9.1 Mean and Gaussian Curvatures of Surfaces in R 3 We ll assume that the curves are in R 3 unless otherwise noted. We start off by quoting the following useful theorem about self
Index. Bertrand mate, 89 bijection, 48 bitangent, 69 Bolyai, 339 Bonnet s Formula, 283 bounded, 48
 Index acceleration, 14, 76, 355 centripetal, 27 tangential, 27 algebraic geometry, vii analytic, 44 angle at a corner, 21 on a regular surface, 170 angle excess, 337 angle of parallelism, 344 angular velocity,
Index acceleration, 14, 76, 355 centripetal, 27 tangential, 27 algebraic geometry, vii analytic, 44 angle at a corner, 21 on a regular surface, 170 angle excess, 337 angle of parallelism, 344 angular velocity,
14.1. Multiple Integration. Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane. Iterated Integrals. Iterated Integrals. MAC2313 Calculus III - Chapter 14
 14 Multiple Integration 14.1 Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane Objectives Evaluate an iterated integral. Use an iterated integral to find the area of a plane region. Copyright Cengage Learning.
14 Multiple Integration 14.1 Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane Objectives Evaluate an iterated integral. Use an iterated integral to find the area of a plane region. Copyright Cengage Learning.
ν(u, v) = N(u, v) G(r(u, v)) E r(u,v) 3.
 5. The Gauss Curvature Beyond doubt, the notion of Gauss curvature is of paramount importance in differential geometry. Recall two lessons we have learned so far about this notion: first, the presence
5. The Gauss Curvature Beyond doubt, the notion of Gauss curvature is of paramount importance in differential geometry. Recall two lessons we have learned so far about this notion: first, the presence
Visualisations of Gussian and Mean Curvatures by Using Mathematica and webmathematica
 6 th International Conference on Applied Informatics Eger, Hungary, January 27 31, 2004. Visualisations of Gussian and Mean Curvatures by Using Mathematica and webmathematica Vladimir Benič, Sonja Gorjanc
6 th International Conference on Applied Informatics Eger, Hungary, January 27 31, 2004. Visualisations of Gussian and Mean Curvatures by Using Mathematica and webmathematica Vladimir Benič, Sonja Gorjanc
Math 118, Fall 2014 Final Exam
 Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES 5. The Second Fundamental Form of a Surface
 DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES 5. The Second Fundamental Form of a Surface The main idea of this chapter is to try to measure to which extent a surface S is different from a plane, in other
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES 5. The Second Fundamental Form of a Surface The main idea of this chapter is to try to measure to which extent a surface S is different from a plane, in other
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1
 Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
On divergence representations of the Gaussian and the mean curvature of surfaces and applications
 Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Math. Model. in Geoph., 17 (014), 35 45 c 014 NCC Publisher On divergence representations of the Gaussian and the mean curvature of surfaces and applications A.G. Megrabov Abstract.
Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Math. Model. in Geoph., 17 (014), 35 45 c 014 NCC Publisher On divergence representations of the Gaussian and the mean curvature of surfaces and applications A.G. Megrabov Abstract.
Peter Alfeld Math , Fall 2005
 WeBWorK assignment due 9/2/05 at :59 PM..( pt) Consider the parametric equation x = 2(cosθ + θsinθ) y = 2(sinθ θcosθ) What is the length of the curve for θ = 0 to θ = 7 6 π? 2.( pt) Let a = (-2 4 2) and
WeBWorK assignment due 9/2/05 at :59 PM..( pt) Consider the parametric equation x = 2(cosθ + θsinθ) y = 2(sinθ θcosθ) What is the length of the curve for θ = 0 to θ = 7 6 π? 2.( pt) Let a = (-2 4 2) and
Dr. Back. Nov. 3, 2009
 Dr. Back Nov. 3, 2009 Please Don t Rely on this File! In you re expected to work on these topics mostly without computer aid. But seeing a few better pictures can help understanding the concepts. A copy
Dr. Back Nov. 3, 2009 Please Don t Rely on this File! In you re expected to work on these topics mostly without computer aid. But seeing a few better pictures can help understanding the concepts. A copy
Math 263 Final. (b) The cross product is. i j k c. =< c 1, 1, 1 >
 Math 63 Final Problem 1: [ points, 5 points to each part] Given the points P : (1, 1, 1), Q : (1,, ), R : (,, c 1), where c is a parameter, find (a) the vector equation of the line through P and Q. (b)
Math 63 Final Problem 1: [ points, 5 points to each part] Given the points P : (1, 1, 1), Q : (1,, ), R : (,, c 1), where c is a parameter, find (a) the vector equation of the line through P and Q. (b)
Math 115 ( ) Yum-Tong Siu 1. Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives
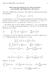 Math 115 006-007 Yum-Tong Siu 1 Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives The Case of High-Order Derivatives. The context is to find the extremal for the functional
Math 115 006-007 Yum-Tong Siu 1 Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives The Case of High-Order Derivatives. The context is to find the extremal for the functional
Vectors, dot product, and cross product
 MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
G G. G. x = u cos v, y = f(u), z = u sin v. H. x = u + v, y = v, z = u v. 1 + g 2 x + g 2 y du dv
 1. Matching. Fill in the appropriate letter. 1. ds for a surface z = g(x, y) A. r u r v du dv 2. ds for a surface r(u, v) B. r u r v du dv 3. ds for any surface C. G x G z, G y G z, 1 4. Unit normal N
1. Matching. Fill in the appropriate letter. 1. ds for a surface z = g(x, y) A. r u r v du dv 2. ds for a surface r(u, v) B. r u r v du dv 3. ds for any surface C. G x G z, G y G z, 1 4. Unit normal N
Unit Speed Curves. Recall that a curve Α is said to be a unit speed curve if
 Unit Speed Curves Recall that a curve Α is said to be a unit speed curve if The reason that we like unit speed curves that the parameter t is equal to arc length; i.e. the value of t tells us how far along
Unit Speed Curves Recall that a curve Α is said to be a unit speed curve if The reason that we like unit speed curves that the parameter t is equal to arc length; i.e. the value of t tells us how far along
MATH 2083 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be on Wednesday, May 4 from 10:00am-12:00pm.
 MATH 2083 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be on Wednesday, May 4 from 10:00am-12:00pm. Bring a calculator and something to write with. Also, you will be allowed to bring in one 8.5 11 sheet of paper
MATH 2083 FINAL EXAM REVIEW The final exam will be on Wednesday, May 4 from 10:00am-12:00pm. Bring a calculator and something to write with. Also, you will be allowed to bring in one 8.5 11 sheet of paper
Boundary value problems
 1 Introduction Boundary value problems Lecture 5 We have found that the electric potential is a solution of the partial differential equation; 2 V = ρ/ǫ 0 The above is Poisson s equation where ρ is the
1 Introduction Boundary value problems Lecture 5 We have found that the electric potential is a solution of the partial differential equation; 2 V = ρ/ǫ 0 The above is Poisson s equation where ρ is the
Final Exam Topic Outline
 Math 442 - Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Final Exam Topic Outline 30th November 2010 David Dumas Note: There is no guarantee that this outline is exhaustive, though I have tried to include
Math 442 - Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Final Exam Topic Outline 30th November 2010 David Dumas Note: There is no guarantee that this outline is exhaustive, though I have tried to include
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2, Math 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
1 Vectors and the Scalar Product
 1 Vectors and the Scalar Product 1.1 Vector Algebra vector in R n : an n-tuple of real numbers v = a 1, a 2,..., a n. For example, if n = 2 and a 1 = 1 and a 2 = 1, then w = 1, 1 is vector in R 2. Vectors
1 Vectors and the Scalar Product 1.1 Vector Algebra vector in R n : an n-tuple of real numbers v = a 1, a 2,..., a n. For example, if n = 2 and a 1 = 1 and a 2 = 1, then w = 1, 1 is vector in R 2. Vectors
Intrinsic Surface Geometry
 Chapter 7 Intrinsic Surface Geometry The second fundamental form of a regular surface M R 3 helps to describe precisely how M sits inside the Euclidean space R 3. The first fundamental form of M, on the
Chapter 7 Intrinsic Surface Geometry The second fundamental form of a regular surface M R 3 helps to describe precisely how M sits inside the Euclidean space R 3. The first fundamental form of M, on the
Hyperbolic Geometry on Geometric Surfaces
 Mathematics Seminar, 15 September 2010 Outline Introduction Hyperbolic geometry Abstract surfaces The hemisphere model as a geometric surface The Poincaré disk model as a geometric surface Conclusion Introduction
Mathematics Seminar, 15 September 2010 Outline Introduction Hyperbolic geometry Abstract surfaces The hemisphere model as a geometric surface The Poincaré disk model as a geometric surface Conclusion Introduction
and y c from x 0 to x 1
 Math 44 Activity 9 (Due by end of class August 6). Find the value of c, c, that minimizes the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region between the graphs of y 4 and y c from to about the line
Math 44 Activity 9 (Due by end of class August 6). Find the value of c, c, that minimizes the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region between the graphs of y 4 and y c from to about the line
Lecture 10. (2) Functions of two variables. Partial derivatives. Dan Nichols February 27, 2018
 Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
1 Vectors and 3-Dimensional Geometry
 Calculus III (part ): Vectors and 3-Dimensional Geometry (by Evan Dummit, 07, v..55) Contents Vectors and 3-Dimensional Geometry. Functions of Several Variables and 3-Space..................................
Calculus III (part ): Vectors and 3-Dimensional Geometry (by Evan Dummit, 07, v..55) Contents Vectors and 3-Dimensional Geometry. Functions of Several Variables and 3-Space..................................
MA304 Differential Geometry
 MA304 Differential Geoetry Hoework 4 solutions Spring 018 6% of the final ark 1. The paraeterised curve αt = t cosh t for t R is called the catenary. Find the curvature of αt. Solution. Fro hoework question
MA304 Differential Geoetry Hoework 4 solutions Spring 018 6% of the final ark 1. The paraeterised curve αt = t cosh t for t R is called the catenary. Find the curvature of αt. Solution. Fro hoework question
(a) The points (3, 1, 2) and ( 1, 3, 4) are the endpoints of a diameter of a sphere.
 MATH 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Problem. a) The points,, ) and,, 4) are the endpoints of a diameter of a sphere. i) Determine the center and radius of the sphere. ii) Find an equation for the sphere.
MATH 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Problem. a) The points,, ) and,, 4) are the endpoints of a diameter of a sphere. i) Determine the center and radius of the sphere. ii) Find an equation for the sphere.
MTH 234 Exam 1 February 20th, Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Practice Problems for the Final Exam
 Math 114 Spring 2017 Practice Problems for the Final Exam 1. The planes 3x + 2y + z = 6 and x + y = 2 intersect in a line l. Find the distance from the origin to l. (Answer: 24 3 ) 2. Find the area of
Math 114 Spring 2017 Practice Problems for the Final Exam 1. The planes 3x + 2y + z = 6 and x + y = 2 intersect in a line l. Find the distance from the origin to l. (Answer: 24 3 ) 2. Find the area of
Calculus III (MAC )
 Calculus III (MAC2-) Test (25/9/7) Name (PRINT): Please show your work. An answer with no work receives no credit. You may use the back of a page if you need more space for a problem. You may not use any
Calculus III (MAC2-) Test (25/9/7) Name (PRINT): Please show your work. An answer with no work receives no credit. You may use the back of a page if you need more space for a problem. You may not use any
Partial Derivatives. w = f(x, y, z).
 Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of Several Variables So far we have focused our attention of functions of one variable. These functions model situations in which a variable depends on another independent
Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of Several Variables So far we have focused our attention of functions of one variable. These functions model situations in which a variable depends on another independent
Exercises for Multivariable Differential Calculus XM521
 This document lists all the exercises for XM521. The Type I (True/False) exercises will be given, and should be answered, online immediately following each lecture. The Type III exercises are to be done
This document lists all the exercises for XM521. The Type I (True/False) exercises will be given, and should be answered, online immediately following each lecture. The Type III exercises are to be done
EXAM 2 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS, MATH 233 WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 18, 2000
 EXAM 2 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS, MATH 233 WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 18, 2000 This examination has 30 multiple choice questions. Problems are worth one point apiece, for a total of 30 points for the whole examination.
EXAM 2 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS, MATH 233 WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 18, 2000 This examination has 30 multiple choice questions. Problems are worth one point apiece, for a total of 30 points for the whole examination.
1 Geometry of R Conic Sections Parametric Equations More Parametric Equations Polar Coordinates...
 Contents 1 Geometry of R 2 2 1.1 Conic Sections............................................ 2 1.2 Parametric Equations........................................ 3 1.3 More Parametric Equations.....................................
Contents 1 Geometry of R 2 2 1.1 Conic Sections............................................ 2 1.2 Parametric Equations........................................ 3 1.3 More Parametric Equations.....................................
MTHE 227 Problem Set 2 Solutions
 MTHE 7 Problem Set Solutions 1 (Great Circles). The intersection of a sphere with a plane passing through its center is called a great circle. Let Γ be the great circle that is the intersection of the
MTHE 7 Problem Set Solutions 1 (Great Circles). The intersection of a sphere with a plane passing through its center is called a great circle. Let Γ be the great circle that is the intersection of the
Math Review for Exam Compute the second degree Taylor polynomials about (0, 0) of the following functions: (a) f(x, y) = e 2x 3y.
 Math 35 - Review for Exam 1. Compute the second degree Taylor polynomial of f e x+3y about (, ). Solution. A computation shows that f x(, ), f y(, ) 3, f xx(, ) 4, f yy(, ) 9, f xy(, ) 6. The second degree
Math 35 - Review for Exam 1. Compute the second degree Taylor polynomial of f e x+3y about (, ). Solution. A computation shows that f x(, ), f y(, ) 3, f xx(, ) 4, f yy(, ) 9, f xy(, ) 6. The second degree
Chapter 14. Basics of The Differential Geometry of Surfaces. Introduction. Parameterized Surfaces. The First... Home Page. Title Page.
 Chapter 14 Basics of The Differential Geometry of Surfaces Page 649 of 681 14.1. Almost all of the material presented in this chapter is based on lectures given by Eugenio Calabi in an upper undergraduate
Chapter 14 Basics of The Differential Geometry of Surfaces Page 649 of 681 14.1. Almost all of the material presented in this chapter is based on lectures given by Eugenio Calabi in an upper undergraduate
Solutions to Test #1 MATH 2421
 Solutions to Test # MATH Pulhalskii/Kawai (#) Decide whether the following properties are TRUE or FALSE for arbitrary vectors a; b; and c: Circle your answer. [Remember, TRUE means that the statement is
Solutions to Test # MATH Pulhalskii/Kawai (#) Decide whether the following properties are TRUE or FALSE for arbitrary vectors a; b; and c: Circle your answer. [Remember, TRUE means that the statement is
Algebraic Curves. (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia. Oct 17, 2017
 Algebraic Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 17, 2017 An algebraic curve is a curve which is described by a polynomial equation: f(x,y) = a ij x i y j = 0 in x and y. The degree of the curve
Algebraic Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 17, 2017 An algebraic curve is a curve which is described by a polynomial equation: f(x,y) = a ij x i y j = 0 in x and y. The degree of the curve
Homework for Math , Spring 2008
 Homework for Math 4530 1, Spring 2008 Andrejs Treibergs, Instructor April 18, 2008 Please read the relevant sections in the text Elementary Differential Geometry by Andrew Pressley, Springer, 2001. You
Homework for Math 4530 1, Spring 2008 Andrejs Treibergs, Instructor April 18, 2008 Please read the relevant sections in the text Elementary Differential Geometry by Andrew Pressley, Springer, 2001. You
Review Sheet for the Final
 Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r (t) = 3 cos t, 0, 3 sin t, r ( 3π
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P 3, 3π, r t) 3 cos t, 4t, 3 sin t 3 ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. olution:
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P 3, 3π, r t) 3 cos t, 4t, 3 sin t 3 ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. olution:
Pullbacks, Isometries & Conformal Maps
 Pullbacks, Isometries & Conformal Maps Outline 1. Pullbacks Let V and W be vector spaces, and let T : V W be an injective linear transformation. Given an inner product, on W, the pullback of, is the inner
Pullbacks, Isometries & Conformal Maps Outline 1. Pullbacks Let V and W be vector spaces, and let T : V W be an injective linear transformation. Given an inner product, on W, the pullback of, is the inner
MAC2313 Final A. (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
MATH PROBLEM SET 6
 MATH 431-2018 PROBLEM SET 6 DECEMBER 2, 2018 DUE TUESDAY 11 DECEMBER 2018 1. Rotations and quaternions Consider the line l through p 0 := (1, 0, 0) and parallel to the vector v := 1 1, 1 that is, defined
MATH 431-2018 PROBLEM SET 6 DECEMBER 2, 2018 DUE TUESDAY 11 DECEMBER 2018 1. Rotations and quaternions Consider the line l through p 0 := (1, 0, 0) and parallel to the vector v := 1 1, 1 that is, defined
e x3 dx dy. 0 y x 2, 0 x 1.
 Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
1 Functions of Several Variables Some Examples Level Curves / Contours Functions of More Variables... 6
 Contents 1 Functions of Several Variables 1 1.1 Some Examples.................................. 2 1.2 Level Curves / Contours............................. 4 1.3 Functions of More Variables...........................
Contents 1 Functions of Several Variables 1 1.1 Some Examples.................................. 2 1.2 Level Curves / Contours............................. 4 1.3 Functions of More Variables...........................
Lectures on Quantum sine-gordon Models
 Lectures on Quantum sine-gordon Models Juan Mateos Guilarte 1, 1 Departamento de Física Fundamental (Universidad de Salamanca) IUFFyM (Universidad de Salamanca) Universidade Federal de Matto Grosso Cuiabá,
Lectures on Quantum sine-gordon Models Juan Mateos Guilarte 1, 1 Departamento de Física Fundamental (Universidad de Salamanca) IUFFyM (Universidad de Salamanca) Universidade Federal de Matto Grosso Cuiabá,
Math 5378, Differential Geometry Solutions to practice questions for Test 2
 Math 5378, Differential Geometry Solutions to practice questions for Test 2. Find all possible trajectories of the vector field w(x, y) = ( y, x) on 2. Solution: A trajectory would be a curve (x(t), y(t))
Math 5378, Differential Geometry Solutions to practice questions for Test 2. Find all possible trajectories of the vector field w(x, y) = ( y, x) on 2. Solution: A trajectory would be a curve (x(t), y(t))
ENGI Partial Differentiation Page y f x
 ENGI 3424 4 Partial Differentiation Page 4-01 4. Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, be found unambiguously by differentiation: y f x, the rate of change of the dependent variable can
ENGI 3424 4 Partial Differentiation Page 4-01 4. Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, be found unambiguously by differentiation: y f x, the rate of change of the dependent variable can
Vector Functions & Space Curves MATH 2110Q
 Vector Functions & Space Curves Vector Functions & Space Curves Vector Functions Definition A vector function or vector-valued function is a function that takes real numbers as inputs and gives vectors
Vector Functions & Space Curves Vector Functions & Space Curves Vector Functions Definition A vector function or vector-valued function is a function that takes real numbers as inputs and gives vectors
CS Tutorial 5 - Differential Geometry I - Surfaces
 236861 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 5 Differential Geometry II Surfaces c 2009 Parameterized surfaces A parameterized surface X : U R 2 R 3 a differentiable map 1 X from an open set U R 2 to R
236861 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 5 Differential Geometry II Surfaces c 2009 Parameterized surfaces A parameterized surface X : U R 2 R 3 a differentiable map 1 X from an open set U R 2 to R
3.1 Classic Differential Geometry
 Spring 2015 CSCI 599: Digital Geometry Processing 3.1 Classic Differential Geometry Hao Li http://cs599.hao-li.com 1 Spring 2014 CSCI 599: Digital Geometry Processing 3.1 Classic Differential Geometry
Spring 2015 CSCI 599: Digital Geometry Processing 3.1 Classic Differential Geometry Hao Li http://cs599.hao-li.com 1 Spring 2014 CSCI 599: Digital Geometry Processing 3.1 Classic Differential Geometry
GEOMETRY HW (t, 0, e 1/t2 ), t > 0 1/t2, 0), t < 0. (0, 0, 0), t = 0
 GEOMETRY HW CLAY SHONKWILER Consider the map.5.0 t, 0, e /t ), t > 0 αt) = t, e /t, 0), t < 0 0, 0, 0), t = 0 a) Prove that α is a differentiable curve. Proof. If we denote αt) = xt), yt), zt0), then it
GEOMETRY HW CLAY SHONKWILER Consider the map.5.0 t, 0, e /t ), t > 0 αt) = t, e /t, 0), t < 0 0, 0, 0), t = 0 a) Prove that α is a differentiable curve. Proof. If we denote αt) = xt), yt), zt0), then it
Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 2016
 MA34 Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 26 Example Sheet d n+ = d n cot θ n r θ n r = Θθ n i. 2. 3. 4. Possible answers include: and with opposite orientation: 5..
MA34 Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 26 Example Sheet d n+ = d n cot θ n r θ n r = Θθ n i. 2. 3. 4. Possible answers include: and with opposite orientation: 5..
Math 433 Outline for Final Examination
 Math 433 Outline for Final Examination Richard Koch May 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length of a curve;. the definition of T (s), N(s), B(s), and κ(s) for
Math 433 Outline for Final Examination Richard Koch May 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length of a curve;. the definition of T (s), N(s), B(s), and κ(s) for
MTH 277 Test 4 review sheet Chapter , 14.7, 14.8 Chalmeta
 MTH 77 Test 4 review sheet Chapter 13.1-13.4, 14.7, 14.8 Chalmeta Multiple Choice 1. Let r(t) = 3 sin t i + 3 cos t j + αt k. What value of α gives an arc length of 5 from t = 0 to t = 1? (a) 6 (b) 5 (c)
MTH 77 Test 4 review sheet Chapter 13.1-13.4, 14.7, 14.8 Chalmeta Multiple Choice 1. Let r(t) = 3 sin t i + 3 cos t j + αt k. What value of α gives an arc length of 5 from t = 0 to t = 1? (a) 6 (b) 5 (c)
Math 11 Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam
 Math 11 Fall 218 Practice Final Exam Disclaimer: This practice exam should give you an idea of the sort of questions we may ask on the actual exam. Since the practice exam (like the real exam) is not long
Math 11 Fall 218 Practice Final Exam Disclaimer: This practice exam should give you an idea of the sort of questions we may ask on the actual exam. Since the practice exam (like the real exam) is not long
Mathematics 117 Lecture Notes for Curves and Surfaces Module
 Mathematics 117 Lecture Notes for Curves and Surfaces Module C.T.J. Dodson, Department of Mathematics, UMIST These notes supplement the lectures and provide practise exercises. We begin with some material
Mathematics 117 Lecture Notes for Curves and Surfaces Module C.T.J. Dodson, Department of Mathematics, UMIST These notes supplement the lectures and provide practise exercises. We begin with some material
PRACTICE PROBLEMS. Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1. Mixed partial derivatives.
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1.1. Let Show that f is C 1 and yet How is that possible? 1. Mixed partial derivatives f(x, y) = {xy x
PRACTICE PROBLEMS Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1.1. Let Show that f is C 1 and yet How is that possible? 1. Mixed partial derivatives f(x, y) = {xy x
ENGI 4430 Surface Integrals Page and 0 2 r
 ENGI 4430 Surface Integrals Page 9.01 9. Surface Integrals - Projection Method Surfaces in 3 In 3 a surface can be represented by a vector parametric equation r x u, v ˆi y u, v ˆj z u, v k ˆ where u,
ENGI 4430 Surface Integrals Page 9.01 9. Surface Integrals - Projection Method Surfaces in 3 In 3 a surface can be represented by a vector parametric equation r x u, v ˆi y u, v ˆj z u, v k ˆ where u,
William P. Thurston. The Geometry and Topology of Three-Manifolds
 William P. Thurston The Geometry and Topology of Three-Manifolds Electronic version 1.1 - March 00 http://www.msri.org/publications/books/gt3m/ This is an electronic edition of the 1980 notes distributed
William P. Thurston The Geometry and Topology of Three-Manifolds Electronic version 1.1 - March 00 http://www.msri.org/publications/books/gt3m/ This is an electronic edition of the 1980 notes distributed
Review for Exam 1. (a) Find an equation of the line through the point ( 2, 4, 10) and parallel to the vector
 Calculus 3 Lia Vas Review for Exam 1 1. Surfaces. Describe the following surfaces. (a) x + y = 9 (b) x + y + z = 4 (c) z = 1 (d) x + 3y + z = 6 (e) z = x + y (f) z = x + y. Review of Vectors. (a) Let a
Calculus 3 Lia Vas Review for Exam 1 1. Surfaces. Describe the following surfaces. (a) x + y = 9 (b) x + y + z = 4 (c) z = 1 (d) x + 3y + z = 6 (e) z = x + y (f) z = x + y. Review of Vectors. (a) Let a
53. Flux Integrals. Here, R is the region over which the double integral is evaluated.
 53. Flux Integrals Let be an orientable surface within 3. An orientable surface, roughly speaking, is one with two distinct sides. At any point on an orientable surface, there exists two normal vectors,
53. Flux Integrals Let be an orientable surface within 3. An orientable surface, roughly speaking, is one with two distinct sides. At any point on an orientable surface, there exists two normal vectors,
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Chapter 12 Review Vector. MATH 126 (Section 9.5) Vector and Scalar The University of Kansas 1 / 30
 Chapter 12 Review Vector MATH 126 (Section 9.5) Vector and Scalar The University of Kansas 1 / 30 iclicker 1: Let v = PQ where P = ( 2, 5) and Q = (1, 2). Which of the following vectors with the given
Chapter 12 Review Vector MATH 126 (Section 9.5) Vector and Scalar The University of Kansas 1 / 30 iclicker 1: Let v = PQ where P = ( 2, 5) and Q = (1, 2). Which of the following vectors with the given
1 Geometry of R Conic Sections Parametric Equations More Parametric Equations Polar Coordinates...
 Contents 1 Geometry of R 1.1 Conic Sections............................................ 1. Parametric Equations........................................ 3 1.3 More Parametric Equations.....................................
Contents 1 Geometry of R 1.1 Conic Sections............................................ 1. Parametric Equations........................................ 3 1.3 More Parametric Equations.....................................
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12. Show all your work on the standard
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12. Show all your work on the standard
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math 21a, Spring 2003
 SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math a, Spring 3 Problem ) ( points) Circle for each of the questions the correct letter. No justifications are needed. Your score will be C W where C is the number of
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math a, Spring 3 Problem ) ( points) Circle for each of the questions the correct letter. No justifications are needed. Your score will be C W where C is the number of
, where s is the arclength parameter. Prove that. κ = w = 1 κ (θ) + 1. k (θ + π). dγ dθ. = 1 κ T. = N dn dθ. = T, N T = 0, N = T =1 T (θ + π) = T (θ)
 Here is a collection of old exam problems: 1. Let β (t) :I R 3 be a regular curve with speed = dβ, where s is the arclength parameter. Prove that κ = d β d β d s. Let β (t) :I R 3 be a regular curve such
Here is a collection of old exam problems: 1. Let β (t) :I R 3 be a regular curve with speed = dβ, where s is the arclength parameter. Prove that κ = d β d β d s. Let β (t) :I R 3 be a regular curve such
Math 234 Final Exam (with answers) Spring 2017
 Math 234 Final Exam (with answers) pring 217 1. onsider the points A = (1, 2, 3), B = (1, 2, 2), and = (2, 1, 4). (a) [6 points] Find the area of the triangle formed by A, B, and. olution: One way to solve
Math 234 Final Exam (with answers) pring 217 1. onsider the points A = (1, 2, 3), B = (1, 2, 2), and = (2, 1, 4). (a) [6 points] Find the area of the triangle formed by A, B, and. olution: One way to solve
Tangent Plane. Linear Approximation. The Gradient
 Calculus 3 Lia Vas Tangent Plane. Linear Approximation. The Gradient The tangent plane. Let z = f(x, y) be a function of two variables with continuous partial derivatives. Recall that the vectors 1, 0,
Calculus 3 Lia Vas Tangent Plane. Linear Approximation. The Gradient The tangent plane. Let z = f(x, y) be a function of two variables with continuous partial derivatives. Recall that the vectors 1, 0,
Gauss s Law. Name. I. The Law: , where ɛ 0 = C 2 (N?m 2
 Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
MATHEMATICS 317 December 2010 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATI 317 December 1 Final Eam olutions 1. Let r(t) = ( 3 cos t, 3 sin t, 4t ) be the position vector of a particle as a function of time t. (a) Find the velocity of the particle as a function of time
MATHEMATI 317 December 1 Final Eam olutions 1. Let r(t) = ( 3 cos t, 3 sin t, 4t ) be the position vector of a particle as a function of time t. (a) Find the velocity of the particle as a function of time
Intro Vectors 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2011/2012, 4th quarter. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
Classical differential geometry of two-dimensional surfaces
 Classical differential geometry of two-dimensional surfaces 1 Basic definitions This section gives an overview of the basic notions of differential geometry for twodimensional surfaces. It follows mainly
Classical differential geometry of two-dimensional surfaces 1 Basic definitions This section gives an overview of the basic notions of differential geometry for twodimensional surfaces. It follows mainly
CALCULUS ON MANIFOLDS. 1. Riemannian manifolds Recall that for any smooth manifold M, dim M = n, the union T M =
 CALCULUS ON MANIFOLDS 1. Riemannian manifolds Recall that for any smooth manifold M, dim M = n, the union T M = a M T am, called the tangent bundle, is itself a smooth manifold, dim T M = 2n. Example 1.
CALCULUS ON MANIFOLDS 1. Riemannian manifolds Recall that for any smooth manifold M, dim M = n, the union T M = a M T am, called the tangent bundle, is itself a smooth manifold, dim T M = 2n. Example 1.
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
Things you should have learned in Calculus II
 Things you should have learned in Calculus II 1 Vectors Given vectors v = v 1, v 2, v 3, u = u 1, u 2, u 3 1.1 Common Operations Operations Notation How is it calculated Other Notation Dot Product v u
Things you should have learned in Calculus II 1 Vectors Given vectors v = v 1, v 2, v 3, u = u 1, u 2, u 3 1.1 Common Operations Operations Notation How is it calculated Other Notation Dot Product v u
