Calculation of Initial Stiffness of Semirigid Connections with Consideration of Rotational Constraint on Angle from Beam Contact Surface
|
|
|
- Emil Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Calulaion of Iniial Siffness of Semirigid Conneions wih Consideraion of Roaional Consrain on Angle from Beam Cona Surfae X.G. Lin Osaka Insiue of Tehnology, Japan K. Asada Oayashi Corporaion, Japan SUMMARY: The ojeive of his paper is o derive a new formula o improve iniial siffness alulaion of semi-rigid seel eam-o-olumn onneions wih op and sea flange angles. In order o improve prediion of iniial siffness, deformaion of he onneion from FEM model is losely examined and some deformaion haraerisis are oserved suh as how and when angle an e separaed from eam in he viiniy of ol. Based on hose oservaions, some mehanial assumpions are made aou how horizonal arm of angle is en and hen a new iniial siffness orreion faor is proposed. The iniial siffness formula is furher modified o allow a small separaion eween angle and olumn a ol loaions when angle sars o fail. The new formula also inludes we angle onriuion. When iniial siffness alulaed using he formula proposed here is ompared wih la es resuls, mos of daa shows heir differene remains wihin 1%. Keywords: semirigid onneion, high srengh ol, seel frame, iniial siffness 1. INTRODUCTION Afer many weld fraures were oserved in rigid (welded) onneions of uilding sruures during Hyogo- ken-namu Earhquake of Japan (on January 17, 1995), sruural engineers are geing more and more ineres in designing semi-rigid (oled) eam-o-olumn onneions wih angle or spli ee eause semi-rigid onneions allow more deformaion and asor more energy and an preven possile rual weld fraure failure given y rigid onneions during an earhquake. Bu displaemens of frames are no welome in general and have o e alulaed and onrolled. So design of semi-rigidly joined seel frames will e more hallenging han design of rigidly joined seel frames. Therefore aurae alulaions of displaemens or iniial siffness are needed in design of semi-rigid eam-o-olumn onneions. In order o esimae iniial siffness of semi-rigid eam-o-olumn onneions for displaemen alulaion, C.Faella(1999), N.Kishi and Wai-Fan Chen (199) have developed and inrodued several formulas for he siffness alulaion. In heir work, he verial arm of an angle (op or sea) used o e simplified as anilever eams and deformaion in horizonal direion of he verial arms was assumed uniformed or same. Auhors of his paper has pulished an iniial siffness reduion faor in he pas, whih ries o onsider deformaion differene in he horizonal direion of he angles. Alhough he iniial siffness reduion faor is an improvemen in iniial siffness alulaion, u i sill has following limiaions: (1) he siffness orreion faor proposed earlier o onsider roaional onsrain on eam ona surfae is deermined ased on averaged numerial resuls while i ould vary from one sruure o anoher sruure; (2) earlier siffness formula is ased on assumpion ha failure ours in angle insead of ol and angle never separae from olumn a ol loaions; () earlier siffness formula is only verified y angle ension ess; (4) earlier siffness formula doesn' oun onriuion from we angle and an no e used in he onneion wih we angle in addiion o op and sea angles. In his sudy, some -D finie elemen modeling and analysis using ABAQUS are ondued. In ABAQUS nonlinear analysis he separaion eween angle and olumn or eam a ol loaion is
2 onsidered and also plasi deformaion in angle is inluded. Based on numerial simulaion resuls, a new iniial siffness orreion faor is proposed and he iniial siffness formula is furher modified afer allowing a small separaion eween angle and olumn a ol loaions when angle saring o fail. In finie elemen modeling and analysis, we angle onriuion is ompared wih op and sea angles. A new formula is derived o inlude we angle onriuion. Before finie elemen modeling and analysis of differen join onfiguraions, eigh physial es speimens are uil and esed. Among hem, 4 are flange angle onneions and 4 are we angle onneions. Resuls alulaed using he proposed iniial siffness formula is ompared wih ending es resuls and he auray is verified. 2. BENDING TEST OF SEMIRIGID BEAM-TO-COLUMN CONNECTION This paper is o sudy appliaion of op and sea flange angle as well as doule we angle o eam-oolumn onneion. In order o sudy individual onriuion of hem, op and sea flange angle is used in some ess and doule we angle is used in some oher ess. Fig. 1 shows piures for wo ypial semi-rigid eam-o-olumn onneions. The firs onneion onsiss of wo eams, one ener plae and four flange angles. Column is replaed y a ener plae o exlude olumn onriuion and make sudy fous on angles onriuion. The seond onneion onsiss of wo eams, one ener plae and wo op flange angles and four we angles. The use of op flange angle in he seond ype of onneion is o keep eams having he same roaion ener (he op orner of eams) and has lile onriuion in siffness eause i is loaed in ompressive side. (a) Top and sea flange angle onneion () Doule we angle onneion Figure 1. Bending es speimens (a) Flange angle () We angle Figure 2. Conneion deails for speimen of oh ypes
3 Tale 2.1. Deails of ending es speimens Speimen Angle hikness Angle widh g 1 g 2 g Speimen Angle hikness Angle Widh g 1 g 2 L WL L WL L WL L WL P (kn) L15-7 δ P (kn) WL15-2 δ Tale 2.2. Resuls of ending ess Iniial siffness Speimen Loading Unloading (kn/mm) (kn/mm) 125 P (kn) δ P (kn) L15-6 WL15- δ P (kn) Figure. Load versus displaemen urves for ending ess Yield srengh (kn) Speimen L2-7 δ P (kn) Loading (kn/mm) WL2-25 δ Iniial siffness Unloading (kn/mm) Yield srengh (kn) L WL L WL L WL L WL All es speimens are made of JIS seel grade SS4. Angles have wo hikness of 15 mm and 2 mm. Angles are u from eiher L-2x2x2 or L-2x2x15. Fig. 2 shows all major dimensions for all differen angles. Beam is H-294x2x8x12. Cener plae is 6 mm hik. High srengh ols are M22 of eiher F1T or S1T. All ol holes have 2 mm learane. More deailed daa of all eigh speimens are lised in Tale 2.1. All loading es are ondued using Amsler ype universal esing mahine. For eah of ess, a verial load is applied o ener plae and load is inreased slowly unil angles deformaion ge ino large plasi range. Beams are unloaded wie during esing. One unloading is performed in elasi range and anoher in plasi range. Only verial displaemen in ener plae is used in siffness alulaion. Sine axial fore in eam is no desired, roller suppors are used o give eams free moving in axial direion. Fig. presens some of ypial load-defleion urves. Tale 2.2 summarizes alulaed iniial siffness and yield srengh. In Tale 2.2, iniial siffness is alulaed wie. One is alulaed ased on elasi
4 loading urve slope and anoher is ased on elasi unloading urve slope. Beause defleion is very small from elasi loading urve and i is no easy o measure i auraely, iniial siffness ased on unloading urve is hosen for laer omparison wih iniial siffness prediion. The yield srengh is deermined using general yielding alulaion. I is easily noied ha iniial siffness of eah speimen depends mainly on angle hikness and numer of ols. All eams remains in elasi range. When iniial siffness is alulaed using es daa, eam deformaion is required and i is alulaed using elasi heoreial alulaion insead of es measuremen.. IMPROVEMENT OF STIFFNESS PREDICTION FOR FLANGE ANGLE CONNECTION Fig. 4 is a piure of semi-rigid eam-o-olumn onneion. In he pas, for ensional siffness sudy auhors of his paper proposed mehanial mehanism illusraed in Fig. 5. Eqn..1 is he ension siffness formula developed ased on his mehanism. The main feaure of his formula is onsideraion of angle deformaion in he viiniy of ols and inrodues an angle siffness reduion oeffiien in widh direion. K a ( B B B ) K r 1 f 1 2 f 2 2 ( 1.4).65B f E (.1), 1, K,.12 (1 ) K is heoreial siffness of uni widh of he rigid segmen, is hikness of he angle and E is elasi modulus of seel and is oeffiien of shear deformaion. Br and C is widh and lengh of he rigid segmen respeively. Bf is he widh of he flexile segmen, is a siffness reduion oeffiien, whih is a siffness raio eween he rigid segmen and he flexile segmen wih same widh. In he righ end of mehanial mehanism illusraed in Fig. 5 if eam flange and angle do no separae, he righ end anno roae and i will e similar o a fixed end. Afer flange and angle separae, he righ end will roae even i ould ge some resisane from ona surfaes. Compared wih fixed end, is siffness will e redued. A orreion faor a is refleing he siffness reduion. Auhors of his paper adoped average value of numerial resuls of he orreion faor in previous sudy. Bu differen eam-o-olumn onneion should have differen orreion faor. Use of average value ould resul in error in he alulaion. In addiion, rigid segmen lengh alulaion up o he fron of ol is anoher one required furher invesigaion eause i is only good for he failure where ols have lile deformaion and angle auses he failure. When ol sreh inreases, inauray will inrease. Figure 4. Semi-rigid onneion Figure 5. Segmenal eam model for verial arm of op angle
5 (a) L15-7 () L2-7 Figure 6. Separaion paern in he viiniy of ol area Ks Figure 7. Segmenal eam model for horizonal arm of op angle In order o improve siffness prediion, his paper ondus FEM modeling and analysis on es speimens and sudies he way how angle deforms in he finie elemen models. Fig. 6 shows angle ona separaion urves on he verial arm. Compared wih 15 mm hik L15-7, 2 mm hik L2-7 shows a lower separaion urve, whih exends ino he ol hole. In he horizonal arms, separaion lines show similar rend, u hey do no pass ol holes a all and all sop in he fron of ols. In order o develop orreion faor formula, roaional siffness Ks is required o alulae firs aording o Fig. 7. Beause ona separaion urves are similar in he verial arm and horizonal arm, afer lengh C is modified in Fig. 5, new mehanial mehanism is oained as in Fig. 7. To use his new mehanial mehanism, roaional siffness an e derived as follow. K s ( B r B 1 f 1 B 2 f 2 ) K s (.52).65B f E (.2), 1, Ks (1 ), In he aove formula,,,, are ona parameers in he horizonal arm and hey have definiion similar o hose in Eqn..1. Ks is roaional siffness of uni widh of rigid segmen. Formula for is a simplified one and he error inrodued y his simplifiaion is igger han same alulaion in he verial arm. To use esalished aove, orreion faor a an e esimaed as follow. a , ( Ba / B ) ( B / B a 1/ ) (.)
6 T1 T2 T T4 B 4 Mode1 Mode2 Mode Mode 4 Figure 8. Failure modes for semi-rigid onneion Figure 9. Model for parameer l Figure 1. Separaion haraerisi in he we B a B B g 2 r f 1 B f 2.5( B ),, B B B r 1 f 1 B 2 f 2 g.5b (.7 ) 1, B B B r 1 f 1 B 2 f 2 (.4) B and B are equivalen widh of horizonal arm and verial arm. Regarding o parameer l, i an e aken as zero if ol does no sreh and angle fails firs. I is oserved from numerial resuls in Fig. 6 ha when angle is hiker, ol may have some small srehing and make ona separaion urve pass ol and reah he area ehind ol. This ype of failure is mode in Fig. 8. In general here are four ypes of onneion failure modes as illusraed in Fig. 8. In order o ahieve enough deformaion ailiy in onneion design, failure mode 1 and 2 should e avoided. Failure mode 4 is he es one. Therefore all sudies ondued y auhors of his paper are aou how o do iniial siffness alulaion on failure mode 4. Failure mode has less apaiy of deformaion han mode 4, u muh eer han mode 1 and 2. Mode is a possile rue failure mode in sruural design and should e inluded in iniial siffness invesigaion. This paper ries o modify exising siffness alulaion formula o over oh 4 and failure modes. The sraegy is o use yield srengh differene eween mode 4 and o move ona separaion urve owards rear edge of ol head. When he differene (T4-T) reahes 2% of T4, move he ona separaion urve o he rear edge of ol head. This will e exreme ase. Based on all earlier reasoning, parameer l alulaion an e expressed as Eqn..5. Fig. 9 shows he relaionship eween l and f. Le When. B is he size of ol head as indiaed in Fig. 5. B 5 (.7), ( T4 T ) / T (.5) 4 4. WEB ANGLE CONTRIBUTION AND STIFFNESS PREDICTION OF SPECIMENS Fig. 1 shows we deformaion and ona separaion urve from finie elemen analysis. Alhough sress disriuion of we is more ompliaed han op or sea angle, ona separaion urve is sill
7 showing similar haraerisis. Cona separaion line around ol is urve, no a sraigh line. The lengh of rigid segmen is geing longer when i is away from roaion ener. Considering ha he oom ol has more onriuion, lengh of rigid segmen a oom ol is aken as C in Eqn..1. Tha means his will e he lengh of rigid segmen for all oher rigid segmens. In Fig. 11, he ona area of we angle is divided ino many small areas y ols and resulan reaion fore is assumed o e a ol ener. Then we ension siffness onriuion from eah of areas an e alulaed in a similar way used for op and sea angles using Eqn..1 and.5. Based on all assumpion made aove, for a semi-rigid onneion wih oh flange angles (op and sea) and doule we angles he roaional siffness an e alulaed in Eqn i is he disane from ol o he infleion poin in flange angle K ( H 1.5)( H 1.5 ) K K K K (4.1) i ( B / B ) 2 / 2 a i (4.2) 1/ EBa ( Ba / B ) 6Ks In order o verify he auray of iniial siffness prediion esalished in his sudy, all alulaed resuls are ompared wih la es resuls. In iniial siffness prediion using Eqn. 4.1, he firs porion of Eqn. 4.1 is used for semi-rigid onneions wih op and sea angles. The seond porion of Eqn. 4.1 is used for semi-rigid onneions wih doule we angles. Fig. 12 shows all omparison eween siffness alulaion using Eqn. 4.1 and la es resuls. In he omparison of semi-rigid onneions wih op and sea angles, when ol posiion parameer g 1 is higher, siffness prediion ends o e higher. Siffness prediion is lower when g 1 is smaller. All speimen shows differene less han 1%. For semi-rigid onneions wih doule we angles, he highes siffness onneion is showing highes differene, aou 2% higher. All oher ases have differene wihin 1%. Figure 11. Segmenal eam model for we angle K pre /K es L15-7 L15-6 L2-7 L2-6 (a) Top and sea flange angle onneion K pre /K es WL15-2 WL15- WL2-2 WL2- () Doule we angle onneion Figure 12. Comparison of predied iniial siffness wih es resuls
8 5. CONCLUDING REMARKS 1) In order o improve siffness prediion auray, his paper sudies ona separaion haraerisi of flange angle and we angle and proposes new formula for orreion faor alulaion. 2) This paper modifies earlier siffness alulaion and makes alulaion also valid for he onneion where small deformaion of ol is expeed. ) This paper inrodues a mehod o alulae we angle siffness onriuion. 4) 7 of 8 es resuls prove prediion error wihin 1% and only 1 es resul shows 2% differene eween prediion and es resuls. REFERENCES Lin, X.G. and Hamamoo, N. (28). Prediion of Iniial Siffness of Semirigid Seel Beam-o-Column Conneions wih Bols and Angles. Proeedings of he 1 h World Conferene on Earhquake Engineering, Paper No Kishi, N. and Chen, W.F. (199). Momen-roaion relaions of semirigid onneions wih angles. Journal of Sruural Engineering. 116:7, Fealla, C., Piluso, V. and Rizzano, G. (1999). Sruural Seel Semirigid Conneions: Theory, Design and Sofware. CRC Press LLC, U.S.A. Azizinamini, A., Bordurn, J.H. and Radziminski, J.B. (1987). Iniial Siffness of Semi-rigid Seel Beam-o-Column Conneions. Journal of Consruional Seel Researh. No.8, Lin, X.G. and Sugimoo, H. (24). Experimenal Sudy on Inelasi Behavior and Ulimae Srengh of Seel Beam-o-Column Conneions wih Bols and Angles. Proeedings of he 1 h World Conferene on Earhquake Engineering. Paper No Tanuma, Y. and Hashimoo, K. (1999). Momen-roaion ehaviour of semirigid onneions wih angles. Journal of Sruural and Consruion Engineering. No.515, Tanaka, H. and Tanaka, A. (1975). Design formulas for he srengh of -su onneion. Seel Consruion Engineering. 11:12, 5-1.
Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Shotcrete Lining Reinforced with Steel Fibre and Steel Sets
 IACSIT Inernaional Journal of Engineering and Tehnology, Vol. 5, No. 6, Deember 2013 Nonlinear Finie Elemen Analysis of Shoree Lining Reinfored wih Seel Fibre and Seel Ses Jeong Soo Kim, Moon Kyum Kim,
IACSIT Inernaional Journal of Engineering and Tehnology, Vol. 5, No. 6, Deember 2013 Nonlinear Finie Elemen Analysis of Shoree Lining Reinfored wih Seel Fibre and Seel Ses Jeong Soo Kim, Moon Kyum Kim,
5.2 Design for Shear (Part I)
 5. Design or Shear (Par I) This seion overs he ollowing opis. General Commens Limi Sae o Collapse or Shear 5..1 General Commens Calulaion o Shear Demand The objeive o design is o provide ulimae resisane
5. Design or Shear (Par I) This seion overs he ollowing opis. General Commens Limi Sae o Collapse or Shear 5..1 General Commens Calulaion o Shear Demand The objeive o design is o provide ulimae resisane
Concrete damaged plasticity model
 Conree damaged asiiy model Conree damaged asiiy model is a maerial model for he analysis of onree sruures mainly under dynami loads suh as earhquakes(only aes an be analyzed under he dynami loads like
Conree damaged asiiy model Conree damaged asiiy model is a maerial model for he analysis of onree sruures mainly under dynami loads suh as earhquakes(only aes an be analyzed under he dynami loads like
Shear failure of plain concrete in strain localized area
 Shear failure of plain onree in srain loalized area Y. Kaneko & H. Mihashi Tohoku Universiy, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan S. Ishihara Asanuma Corporaion, Takasuki, Osaka, Japan ABSTRACT: The objeive of his paper
Shear failure of plain onree in srain loalized area Y. Kaneko & H. Mihashi Tohoku Universiy, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan S. Ishihara Asanuma Corporaion, Takasuki, Osaka, Japan ABSTRACT: The objeive of his paper
Hybrid probabilistic interval dynamic analysis of vehicle-bridge interaction system with uncertainties
 1 APCOM & SCM 11-14 h Deember, 13, Singapore Hybrid probabilisi inerval dynami analysis of vehile-bridge ineraion sysem wih unerainies Nengguang iu 1, * Wei Gao 1, Chongmin Song 1 and Nong Zhang 1 Shool
1 APCOM & SCM 11-14 h Deember, 13, Singapore Hybrid probabilisi inerval dynami analysis of vehile-bridge ineraion sysem wih unerainies Nengguang iu 1, * Wei Gao 1, Chongmin Song 1 and Nong Zhang 1 Shool
Numerical Simulation of Thermal Stresses in Prismatic Concrete Beams Reinforced with FRP Bars under Low Temperatures
 Cemisry and Maerials Resear, Vol.5 013 Speial Issue for Inernaional Congress on Maerials & Sruural Sabiliy, Raba, Moroo, 7-30 November 013 Numerial Simulaion of Termal Sresses in Prismai Conree Beams Reinfored
Cemisry and Maerials Resear, Vol.5 013 Speial Issue for Inernaional Congress on Maerials & Sruural Sabiliy, Raba, Moroo, 7-30 November 013 Numerial Simulaion of Termal Sresses in Prismai Conree Beams Reinfored
1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 5 Creep and Shrinkage Deformation
 1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures pring 24 Prof. Oral Buyukozurk Massahuses Insiue of Tehnology Ouline 5 1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures (3--9 Ouline 5 and hrinkage Deformaion
1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures pring 24 Prof. Oral Buyukozurk Massahuses Insiue of Tehnology Ouline 5 1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures (3--9 Ouline 5 and hrinkage Deformaion
ERRATA. Figure GL. 2 TRANSVERSE CROSS SECTION OF A SCREW SLOT
 srew slo: a semi-hollow in an exrusion inended o reain a srew arallel o he axis of he exrusion. (See Figure GL.). Figure GL. TRANSVERSE CROSS SECTION OF A SCREW SLOT self-drilling srew: a srew ha drills
srew slo: a semi-hollow in an exrusion inended o reain a srew arallel o he axis of he exrusion. (See Figure GL.). Figure GL. TRANSVERSE CROSS SECTION OF A SCREW SLOT self-drilling srew: a srew ha drills
Analysis of Tubular Linear Permanent Magnet Motor for Drilling Application
 Analysis of Tubular Linear Permanen Magne Moor for Drilling Appliaion Shujun Zhang, Lars Norum, Rober Nilssen Deparmen of Eleri Power Engineering Norwegian Universiy of Siene and Tehnology, Trondheim 7491
Analysis of Tubular Linear Permanen Magne Moor for Drilling Appliaion Shujun Zhang, Lars Norum, Rober Nilssen Deparmen of Eleri Power Engineering Norwegian Universiy of Siene and Tehnology, Trondheim 7491
(Radiation Dominated) Last Update: 21 June 2006
 Chaper Rik s Cosmology uorial: he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe Chaper he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe (Radiaion Dominaed) Las Updae: 1 June 006 1. Inroduion n In Chaper
Chaper Rik s Cosmology uorial: he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe Chaper he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe (Radiaion Dominaed) Las Updae: 1 June 006 1. Inroduion n In Chaper
Flexural Behaviour of Precast, Prestressed Ribbed RPC Bottom Panels
 Send Orders for Reprins o reprins@benhamsiene.ae 98 The Open Civil Engineering Journal 2015 9 98-106 Open Aess Flexural Behaviour of Preas Presressed Ribbed RPC Boom Panels Zheng Wenzhong* Lu Xueyuan and
Send Orders for Reprins o reprins@benhamsiene.ae 98 The Open Civil Engineering Journal 2015 9 98-106 Open Aess Flexural Behaviour of Preas Presressed Ribbed RPC Boom Panels Zheng Wenzhong* Lu Xueyuan and
Tensile and Compressive Damage Coupling for Fully-reversed Bending Fatigue of Fibre-reinforced Composites
 Van Paepegem, W. and Degriek, J. (00. Tensile and Compressive Damage Coupling for Fully-reversed Bending Faigue of Fibrereinfored Composies. Faigue and Fraure of Engineering Maerials & Sruures, 5(6, 547-56.
Van Paepegem, W. and Degriek, J. (00. Tensile and Compressive Damage Coupling for Fully-reversed Bending Faigue of Fibrereinfored Composies. Faigue and Fraure of Engineering Maerials & Sruures, 5(6, 547-56.
ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS IN FIRE
 ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS IN FIRE Dr Zhaohui Huang Universiy of Sheffield 6 May 2005 1 VULCAN layered slab elemens: connecion o beam elemens Plae Elemen Slab nodes y x Reference Plane h
ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS IN FIRE Dr Zhaohui Huang Universiy of Sheffield 6 May 2005 1 VULCAN layered slab elemens: connecion o beam elemens Plae Elemen Slab nodes y x Reference Plane h
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Poisson s Raio For a slender bar subjeced o axial loading: ε x x y 0 The elongaion in he x-direcion i is accompanied by a conracion in he oher direcions. Assuming ha he maerial is isoropic (no direcional
Poisson s Raio For a slender bar subjeced o axial loading: ε x x y 0 The elongaion in he x-direcion i is accompanied by a conracion in he oher direcions. Assuming ha he maerial is isoropic (no direcional
A comparative Study of Contact Problems Solution Based on the Penalty and Lagrange Multiplier Approaches
 Journal of he Serbian Soiey for ompuaional Mehanis / Vol. / o., 2007 / pp. 74-83 A omparaive Sudy of ona Problems Soluion Based on he Penaly and Lagrange Muliplier Approahes S. Vulovi, M. Zivovi,. Grujovi,
Journal of he Serbian Soiey for ompuaional Mehanis / Vol. / o., 2007 / pp. 74-83 A omparaive Sudy of ona Problems Soluion Based on he Penaly and Lagrange Muliplier Approahes S. Vulovi, M. Zivovi,. Grujovi,
κt π = (5) T surrface k BASELINE CASE
 II. BASELINE CASE PRACICAL CONSIDERAIONS FOR HERMAL SRESSES INDUCED BY SURFACE HEAING James P. Blanhard Universi of Wisonsin Madison 15 Engineering Dr. Madison, WI 5376-169 68-63-391 blanhard@engr.is.edu
II. BASELINE CASE PRACICAL CONSIDERAIONS FOR HERMAL SRESSES INDUCED BY SURFACE HEAING James P. Blanhard Universi of Wisonsin Madison 15 Engineering Dr. Madison, WI 5376-169 68-63-391 blanhard@engr.is.edu
A Numerical Hydraulic Fracture Model Using the Extended Finite Element Method
 nernaional Conferene on Mehanial and ndusrial Engineering (CME'2013) Augus 28-29, 2013 Penang (Malaysia) A Numerial Hydrauli Fraure Model Using he Exended Finie Elemen Mehod Ashkan. Mahdavi, and Soheil.
nernaional Conferene on Mehanial and ndusrial Engineering (CME'2013) Augus 28-29, 2013 Penang (Malaysia) A Numerial Hydrauli Fraure Model Using he Exended Finie Elemen Mehod Ashkan. Mahdavi, and Soheil.
Active Structural Acoustic Control of Sound Power Radiation from a Soft-Core Sandwich Panel
 Aive Sruural Aousi Conrol of Sound Power Radiaion fro a Sof-Core Sandwih Panel Kiran SAHU 1 ; Jukka TUHKURI ; 1 Aalo Universiy Finland ABSTRACT In his paper aive onrol of haroni sound ransied hrough a
Aive Sruural Aousi Conrol of Sound Power Radiaion fro a Sof-Core Sandwih Panel Kiran SAHU 1 ; Jukka TUHKURI ; 1 Aalo Universiy Finland ABSTRACT In his paper aive onrol of haroni sound ransied hrough a
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Curling Stress Equation for Transverse Joint Edge of a Concrete Pavement Slab Based on Finite-Element Method Analysis
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 155 35 Curling Sress Equaion for Transverse Join Edge of a Concree Pavemen Slab Based on Finie-Elemen Mehod Analysis TATSUO NISHIZAWA, TADASHI FUKUDA, SABURO MATSUNO, AND
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 155 35 Curling Sress Equaion for Transverse Join Edge of a Concree Pavemen Slab Based on Finie-Elemen Mehod Analysis TATSUO NISHIZAWA, TADASHI FUKUDA, SABURO MATSUNO, AND
Derivation of longitudinal Doppler shift equation between two moving bodies in reference frame at rest
 Deriaion o longiudinal Doppler shi equaion beween wo moing bodies in reerene rame a res Masanori Sao Honda Eleronis Co., d., Oyamazuka, Oiwa-ho, Toyohashi, ihi 44-393, Japan E-mail: msao@honda-el.o.jp
Deriaion o longiudinal Doppler shi equaion beween wo moing bodies in reerene rame a res Masanori Sao Honda Eleronis Co., d., Oyamazuka, Oiwa-ho, Toyohashi, ihi 44-393, Japan E-mail: msao@honda-el.o.jp
LIGHT and SPECIAL RELATIVITY
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT LIGHT and SPECIAL RELATIVITY LENGTH CONTRACTION RELATIVISTIC ADDITION OF VELOCITIES Time is a relaie quaniy: differen obserers an measuremen differen ime
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT LIGHT and SPECIAL RELATIVITY LENGTH CONTRACTION RELATIVISTIC ADDITION OF VELOCITIES Time is a relaie quaniy: differen obserers an measuremen differen ime
Mass Transfer Coefficients (MTC) and Correlations I
 Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
The Nottingham eprints service makes this work by researchers of the University of Nottingham available open access under the following conditions.
 Hyde, Chrisopher J. and Hyde, T.H. and Sun, Wei and Beker, A.A. () Damage mehanis based prediions of reep rak growh in 36 sainless seel. Engineering Fraure Mehanis, 77 (). pp. 385-4. ISSN 3-7944 Aess from
Hyde, Chrisopher J. and Hyde, T.H. and Sun, Wei and Beker, A.A. () Damage mehanis based prediions of reep rak growh in 36 sainless seel. Engineering Fraure Mehanis, 77 (). pp. 385-4. ISSN 3-7944 Aess from
Numerical simulation of damage in glass subjected to static indentation
 8 ème Congrès Français de Méanique Grenoble, 7- aoû 007 Numerial simulaion of damage in glass subjeed o sai indenaion Jewan Ismail, Fahmi Zaïri, Moussa Naï-Abdelaziz & Ziouni Azari Laboraoire de Méanique
8 ème Congrès Français de Méanique Grenoble, 7- aoû 007 Numerial simulaion of damage in glass subjeed o sai indenaion Jewan Ismail, Fahmi Zaïri, Moussa Naï-Abdelaziz & Ziouni Azari Laboraoire de Méanique
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration
 rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
An Inventory Model for Weibull Time-Dependence. Demand Rate with Completely Backlogged. Shortages
 Inernaional Mahemaial Forum, 5, 00, no. 5, 675-687 An Invenory Model for Weibull Time-Dependene Demand Rae wih Compleely Baklogged Shorages C. K. Tripahy and U. Mishra Deparmen of Saisis, Sambalpur Universiy
Inernaional Mahemaial Forum, 5, 00, no. 5, 675-687 An Invenory Model for Weibull Time-Dependene Demand Rae wih Compleely Baklogged Shorages C. K. Tripahy and U. Mishra Deparmen of Saisis, Sambalpur Universiy
This document is meant to encapsulate the discussion from Thursday July 9 th 2009 on the review of the paper:
 This doumen is mean o enapsulae he disussion from Thursday July 9 h 2009 on he review of he paper: No seady sae flows below he yield sress. A rue yield sress a las? -Møller, Fall, Bonn (ArXiv: 0904.1467v1
This doumen is mean o enapsulae he disussion from Thursday July 9 h 2009 on he review of he paper: No seady sae flows below he yield sress. A rue yield sress a las? -Møller, Fall, Bonn (ArXiv: 0904.1467v1
Constant Acceleration
 Objecive Consan Acceleraion To deermine he acceleraion of objecs moving along a sraigh line wih consan acceleraion. Inroducion The posiion y of a paricle moving along a sraigh line wih a consan acceleraion
Objecive Consan Acceleraion To deermine he acceleraion of objecs moving along a sraigh line wih consan acceleraion. Inroducion The posiion y of a paricle moving along a sraigh line wih a consan acceleraion
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) - State Feedback Design
 Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
DESIGN OF TENSION MEMBERS
 CHAPTER Srcral Seel Design LRFD Mehod DESIGN OF TENSION MEMBERS Third Ediion A. J. Clark School of Engineering Deparmen of Civil and Environmenal Engineering Par II Srcral Seel Design and Analysis 4 FALL
CHAPTER Srcral Seel Design LRFD Mehod DESIGN OF TENSION MEMBERS Third Ediion A. J. Clark School of Engineering Deparmen of Civil and Environmenal Engineering Par II Srcral Seel Design and Analysis 4 FALL
Research of Tire Rolling Radius Based On the Finite Vibration Unit Model
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, -ISSN: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 4 (Aril. 2013), V1 PP 49-53 Researh of Tire Rollinius Based On he Finie Vibraion Uni Model Wang Liiang, Han Zongi,
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, -ISSN: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 4 (Aril. 2013), V1 PP 49-53 Researh of Tire Rollinius Based On he Finie Vibraion Uni Model Wang Liiang, Han Zongi,
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
Combined Bending with Induced or Applied Torsion of FRP I-Section Beams
 Combined Bending wih Induced or Applied Torsion of FRP I-Secion Beams MOJTABA B. SIRJANI School of Science and Technology Norfolk Sae Universiy Norfolk, Virginia 34504 USA sirjani@nsu.edu STEA B. BONDI
Combined Bending wih Induced or Applied Torsion of FRP I-Secion Beams MOJTABA B. SIRJANI School of Science and Technology Norfolk Sae Universiy Norfolk, Virginia 34504 USA sirjani@nsu.edu STEA B. BONDI
A state space approach to calculating the Beveridge Nelson decomposition
 Eonomis Leers 75 (00) 3 7 www.elsevier.om/ loae/ eonbase A sae spae approah o alulaing he Beveridge Nelson deomposiion James C. Morley* Deparmen of Eonomis, Washingon Universiy, Campus Box 08, Brookings
Eonomis Leers 75 (00) 3 7 www.elsevier.om/ loae/ eonbase A sae spae approah o alulaing he Beveridge Nelson deomposiion James C. Morley* Deparmen of Eonomis, Washingon Universiy, Campus Box 08, Brookings
The Relativistic Field of a Rotating Body
 The Relaivisi Field of a Roaing Body Panelis M. Pehlivanides Alani IKE, Ahens 57, Greee ppexl@eemail.gr Absra Based on he pahs of signals emanaing from a roaing poin body, e find he equaions and properies
The Relaivisi Field of a Roaing Body Panelis M. Pehlivanides Alani IKE, Ahens 57, Greee ppexl@eemail.gr Absra Based on he pahs of signals emanaing from a roaing poin body, e find he equaions and properies
OPTIMUM DESIGN OF STIFFENED PANEL USING THE METHOD OF MATHEMATICAL PROGRAMMING
 ICA 000 COGRE OPTIMUM EIG OF TIFFEE PAEL UIG THE METHO OF MATHEMATICAL PROGRAMMIG o. Ing. Anonín Píš!k C. Ing. P"esl Hobza Insiue of Aerospae Engineering Faul of Mehanial Engineering rno Universi of Tehnolog
ICA 000 COGRE OPTIMUM EIG OF TIFFEE PAEL UIG THE METHO OF MATHEMATICAL PROGRAMMIG o. Ing. Anonín Píš!k C. Ing. P"esl Hobza Insiue of Aerospae Engineering Faul of Mehanial Engineering rno Universi of Tehnolog
mywbut.com Lesson 11 Study of DC transients in R-L-C Circuits
 mywbu.om esson Sudy of DC ransiens in R--C Ciruis mywbu.om Objeives Be able o wrie differenial equaion for a d iruis onaining wo sorage elemens in presene of a resisane. To develop a horough undersanding
mywbu.om esson Sudy of DC ransiens in R--C Ciruis mywbu.om Objeives Be able o wrie differenial equaion for a d iruis onaining wo sorage elemens in presene of a resisane. To develop a horough undersanding
Phys 221 Fall Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko Brooks/Cole
 Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1-3
 A.P. Physics B Uni 1 Tes Reiew Physics Basics, Moemen, and Vecors Chapers 1-3 * In sudying for your es, make sure o sudy his reiew shee along wih your quizzes and homework assignmens. Muliple Choice Reiew:
A.P. Physics B Uni 1 Tes Reiew Physics Basics, Moemen, and Vecors Chapers 1-3 * In sudying for your es, make sure o sudy his reiew shee along wih your quizzes and homework assignmens. Muliple Choice Reiew:
Economics 202 (Section 05) Macroeconomic Theory Practice Problem Set 7 Suggested Solutions Professor Sanjay Chugh Fall 2013
 Deparmen of Eonomis Boson College Eonomis 0 (Seion 05) Maroeonomi Theory Praie Problem Se 7 Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Fall 03. Lags in Labor Hiring. Raher han supposing ha he represenaive
Deparmen of Eonomis Boson College Eonomis 0 (Seion 05) Maroeonomi Theory Praie Problem Se 7 Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Fall 03. Lags in Labor Hiring. Raher han supposing ha he represenaive
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Introduction. σ 2 (1)
 Holzforshung 2018; aop Yuxin Wen, Ping Yang, Jian Zhao and Dong Zhao* Theoreial and experimenal onsideraions on he neural axis of wood beams wih a hole in differen loaions hps://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0174
Holzforshung 2018; aop Yuxin Wen, Ping Yang, Jian Zhao and Dong Zhao* Theoreial and experimenal onsideraions on he neural axis of wood beams wih a hole in differen loaions hps://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0174
Biol. 356 Lab 8. Mortality, Recruitment, and Migration Rates
 Biol. 356 Lab 8. Moraliy, Recruimen, and Migraion Raes (modified from Cox, 00, General Ecology Lab Manual, McGraw Hill) Las week we esimaed populaion size hrough several mehods. One assumpion of all hese
Biol. 356 Lab 8. Moraliy, Recruimen, and Migraion Raes (modified from Cox, 00, General Ecology Lab Manual, McGraw Hill) Las week we esimaed populaion size hrough several mehods. One assumpion of all hese
Lab #2: Kinematics in 1-Dimension
 Reading Assignmen: Chaper 2, Secions 2-1 hrough 2-8 Lab #2: Kinemaics in 1-Dimension Inroducion: The sudy of moion is broken ino wo main areas of sudy kinemaics and dynamics. Kinemaics is he descripion
Reading Assignmen: Chaper 2, Secions 2-1 hrough 2-8 Lab #2: Kinemaics in 1-Dimension Inroducion: The sudy of moion is broken ino wo main areas of sudy kinemaics and dynamics. Kinemaics is he descripion
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to understand
 Insrucional Objecives A he end of his lesson, he sudens should be able o undersand Sress concenraion and he facors responsible. Deerminaion of sress concenraion facor; experimenal and heoreical mehods.
Insrucional Objecives A he end of his lesson, he sudens should be able o undersand Sress concenraion and he facors responsible. Deerminaion of sress concenraion facor; experimenal and heoreical mehods.
Simulation-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010
 Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Design of Air Turbine Flow Passage and Analysis of Energy Efficiency
 Available online a www.sienedire.om Energy Proedia 7 (0 ) 7 0 Inernaional Conferene on Fuure Elerial Power and Energy Sysems Design of Air Turbine Flow Passage and Analysis of Energy Effiieny PAN Hong-gang
Available online a www.sienedire.om Energy Proedia 7 (0 ) 7 0 Inernaional Conferene on Fuure Elerial Power and Energy Sysems Design of Air Turbine Flow Passage and Analysis of Energy Effiieny PAN Hong-gang
Lecture 4 Kinetics of a particle Part 3: Impulse and Momentum
 MEE Engineering Mechanics II Lecure 4 Lecure 4 Kineics of a paricle Par 3: Impulse and Momenum Linear impulse and momenum Saring from he equaion of moion for a paricle of mass m which is subjeced o an
MEE Engineering Mechanics II Lecure 4 Lecure 4 Kineics of a paricle Par 3: Impulse and Momenum Linear impulse and momenum Saring from he equaion of moion for a paricle of mass m which is subjeced o an
Exponential model. The Gibbs sampler is described for ecological examples by Clark et al. (2003, 2004) and
 APPEDIX: GIBBS SAMPLER FOR BAYESIA SAE-SPACE MODELS Eponenial model he Gis sampler is descried or ecological eamples Clark e al. (3 4) and Wikle (3). I involves alernael sampling rom each o he condiional
APPEDIX: GIBBS SAMPLER FOR BAYESIA SAE-SPACE MODELS Eponenial model he Gis sampler is descried or ecological eamples Clark e al. (3 4) and Wikle (3). I involves alernael sampling rom each o he condiional
THE RECIPROCITY THEOREM APPLIED TO FIND THE BEST COUPLING INCIDENCE
 THE RECIPROCITY THEOREM APPLIED TO FIND THE BEST COUPLING INCIDENCE RECHERCHE DE LA DIRECTION D INCIDENCE DE PLUS FORT COUPLAGE A L AIDE DU THEOREME DE RECIPROCITE Jean-Pierre ADAM 1, Jean-Chrisophe JOLY
THE RECIPROCITY THEOREM APPLIED TO FIND THE BEST COUPLING INCIDENCE RECHERCHE DE LA DIRECTION D INCIDENCE DE PLUS FORT COUPLAGE A L AIDE DU THEOREME DE RECIPROCITE Jean-Pierre ADAM 1, Jean-Chrisophe JOLY
The Role of Pitch Filter in Pulse-by-Pulse Reoptimization of the LP Synthesis Filter. Allam Mousa
 An-Najah Univ. J. Res. (N. S), Vol. 6 (2), 2002 The Role of Pih Filer in Pulse-by-Pulse Reopimizaion of he LP Synhesis Filer Allam Mousa Deparmen of Elerial Enineerin, An-Najah Naional Universiy, Nablus,
An-Najah Univ. J. Res. (N. S), Vol. 6 (2), 2002 The Role of Pih Filer in Pulse-by-Pulse Reopimizaion of he LP Synhesis Filer Allam Mousa Deparmen of Elerial Enineerin, An-Najah Naional Universiy, Nablus,
BUCKLING AND REDUCED STIFFNESS CRITERIA FOR FRP CYLINDRICAL SHELLS UNDER COMPRESSION
 Asia-Paifi Conferene on FRP in Sruures (APFIS 7) S.T. Smih (ed) 7 Inernaional Insiue for FRP in Consruion BUCKLIG AD REDUCED STIFFESS CRITERIA FOR FRP CYLIDRICAL SHELLS UDER COMPRESSIO K. Masumoo 1, S.
Asia-Paifi Conferene on FRP in Sruures (APFIS 7) S.T. Smih (ed) 7 Inernaional Insiue for FRP in Consruion BUCKLIG AD REDUCED STIFFESS CRITERIA FOR FRP CYLIDRICAL SHELLS UDER COMPRESSIO K. Masumoo 1, S.
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Lecture Notes Note 17
 EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
Load carrying capacity of masonry bridges: numerical evaluation of the influence of fill and spandrels
 Load arrying apaiy of masonry bridges: numerial evaluaion of he influene of fill and spandrels A. Cavihi and L. Gambaroa Deparmen of Sruural and Geoehnial Engineering, Universiy of Genova, Ialy ABSTRACT.
Load arrying apaiy of masonry bridges: numerial evaluaion of he influene of fill and spandrels A. Cavihi and L. Gambaroa Deparmen of Sruural and Geoehnial Engineering, Universiy of Genova, Ialy ABSTRACT.
Stability of an ideal (flat) plate. = k. critical stresses σ* (or N*) take the. Thereof infinitely many solutions: Critical stresses are given as:
 . Buckling of plaes Linear and nonlinear heor of uckling, uckling under direc sresses (class secions), uckling under shear, local loading and Eurocode approach. Saili of an ideal (fla) plae various loading
. Buckling of plaes Linear and nonlinear heor of uckling, uckling under direc sresses (class secions), uckling under shear, local loading and Eurocode approach. Saili of an ideal (fla) plae various loading
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 47 (2013 ) 33 38
 Available online a www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Physics Procedia 47 3 ) 33 38 Scienific Workshop on Nuclear Fission Dynamics and he Emission of Promp Neurons and Gamma Rays, Biarriz, France, 8-3 November
Available online a www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Physics Procedia 47 3 ) 33 38 Scienific Workshop on Nuclear Fission Dynamics and he Emission of Promp Neurons and Gamma Rays, Biarriz, France, 8-3 November
Optimal Transform: The Karhunen-Loeve Transform (KLT)
 Opimal ransform: he Karhunen-Loeve ransform (KL) Reall: We are ineresed in uniary ransforms beause of heir nie properies: energy onservaion, energy ompaion, deorrelaion oivaion: τ (D ransform; assume separable)
Opimal ransform: he Karhunen-Loeve ransform (KL) Reall: We are ineresed in uniary ransforms beause of heir nie properies: energy onservaion, energy ompaion, deorrelaion oivaion: τ (D ransform; assume separable)
On the Distribution of the Break-Date Estimator Implied by the Perron-Type Statistics When the Form of Break is Misspecified
 Xavier Universiy Exhii Fauly Sholarship Eonomis 1-24-27 On he Disriuion of he Break-Dae Esimaor Implied y he Perron-ype Saisis When he Form of Break is Misspeified Ami Sen Xavier Universiy - Cininnai Follow
Xavier Universiy Exhii Fauly Sholarship Eonomis 1-24-27 On he Disriuion of he Break-Dae Esimaor Implied y he Perron-ype Saisis When he Form of Break is Misspeified Ami Sen Xavier Universiy - Cininnai Follow
Entropy ISSN
 Enropy 003, 5, 467 48 Enropy ISSN 099-4300 www.mdpi.org/enropy/ Full paper CONVECIVE HEAING OF SOLID SURFACE: ENROPY GENERAION DUE O EMPERAURE FIELD AND HERMAL DISPLACEMEN Yagoub Nassar Al-Nassar Mehanial
Enropy 003, 5, 467 48 Enropy ISSN 099-4300 www.mdpi.org/enropy/ Full paper CONVECIVE HEAING OF SOLID SURFACE: ENROPY GENERAION DUE O EMPERAURE FIELD AND HERMAL DISPLACEMEN Yagoub Nassar Al-Nassar Mehanial
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
EE40 Summer 2005: Lecture 2 Instructor: Octavian Florescu 1. Measuring Voltages and Currents
 Announemens HW # Due oday a 6pm. HW # posed online oday and due nex Tuesday a 6pm. Due o sheduling onflis wih some sudens, lasses will resume normally his week and nex. Miderm enaively 7/. EE4 Summer 5:
Announemens HW # Due oday a 6pm. HW # posed online oday and due nex Tuesday a 6pm. Due o sheduling onflis wih some sudens, lasses will resume normally his week and nex. Miderm enaively 7/. EE4 Summer 5:
Inverted Pendulum-type Personal Mobility Considering Human Vibration Sensitivity
 (IJACSA) Inernaional Journal of Advaned Compuer Siene and Appliaions, Vol. 5, No. 3, 14 Invered Pendulum-ype Personal Mobiliy Considering Human Vibraion Sensiiviy Misaki Masuda Shool of Siene for Open
(IJACSA) Inernaional Journal of Advaned Compuer Siene and Appliaions, Vol. 5, No. 3, 14 Invered Pendulum-ype Personal Mobiliy Considering Human Vibraion Sensiiviy Misaki Masuda Shool of Siene for Open
Molecular Motion in Isotropic Turbulence
 Moleular Moion in Isoropi Turbulene Jing Fan, Jian-Zheng Jiang, and Fei Fei Laboraory of High Temperaure Gas Dynamis, Insiue of Mehanis Chinese Aademy of Sienes, Being 9, China Absra Moleular moion in
Moleular Moion in Isoropi Turbulene Jing Fan, Jian-Zheng Jiang, and Fei Fei Laboraory of High Temperaure Gas Dynamis, Insiue of Mehanis Chinese Aademy of Sienes, Being 9, China Absra Moleular moion in
The Contradiction within Equations of Motion with Constant Acceleration
 The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
Program: RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, RF-DYNAM Pro, DYNAM Pro. Category: Isotropic Linear Elasticity, Dynamics, Member
 Verificaion Example Program: RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, RF-DYNAM Pro, DYNAM Pro Caegory: Isoropic Linear Elasiciy, Dynamics, Member Verificaion Example: 0104 Canilever Beam wih Periodic Exciaion 0104 Canilever Beam
Verificaion Example Program: RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, RF-DYNAM Pro, DYNAM Pro Caegory: Isoropic Linear Elasiciy, Dynamics, Member Verificaion Example: 0104 Canilever Beam wih Periodic Exciaion 0104 Canilever Beam
v A Since the axial rigidity k ij is defined by P/v A, we obtain Pa 3
 The The rd rd Inernaional Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 14 Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech Augus Republic, 1 Sepember 1-, 14 In-plane and Ou-of-plane Deflecion of J-shaped
The The rd rd Inernaional Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 14 Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech Augus Republic, 1 Sepember 1-, 14 In-plane and Ou-of-plane Deflecion of J-shaped
Traveling Waves. Chapter Introduction
 Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
SIMULATION STUDY OF STOCHASTIC CHANNEL REDISTRIBUTION
 Developmens in Business Simulaion and Experienial Learning, Volume 3, 3 SIMULATIO STUDY OF STOCHASTIC CHAEL REDISTRIBUTIO Yao Dong-Qing Towson Universiy dyao@owson.edu ABSTRACT In his paper, we invesigae
Developmens in Business Simulaion and Experienial Learning, Volume 3, 3 SIMULATIO STUDY OF STOCHASTIC CHAEL REDISTRIBUTIO Yao Dong-Qing Towson Universiy dyao@owson.edu ABSTRACT In his paper, we invesigae
Effect of Aggregate Gradation on Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus of Cement Treated Aggregate Base Material for Highway Pavement
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 07, Issue 10 (Oober. 2017), V2 PP 79-89 www.iosrjen.org Effe of Aggregae Gradaion on Compressive Srengh and Elasi Modulus
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 07, Issue 10 (Oober. 2017), V2 PP 79-89 www.iosrjen.org Effe of Aggregae Gradaion on Compressive Srengh and Elasi Modulus
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Timed Circuits. Asynchronous Circuit Design. Timing Relationships. A Simple Example. Timed States. Timing Sequences. ({r 6 },t6 = 1.
 Timed Circuis Asynchronous Circui Design Chris J. Myers Lecure 7: Timed Circuis Chaper 7 Previous mehods only use limied knowledge of delays. Very robus sysems, bu exremely conservaive. Large funcional
Timed Circuis Asynchronous Circui Design Chris J. Myers Lecure 7: Timed Circuis Chaper 7 Previous mehods only use limied knowledge of delays. Very robus sysems, bu exremely conservaive. Large funcional
On Measuring Pro-Poor Growth. 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growth: A Short Review of the Literature
 On Measuring Pro-Poor Growh 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growh: A Shor eview of he Lieraure During he pas en years or so here have been various suggesions concerning he way one should check
On Measuring Pro-Poor Growh 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growh: A Shor eview of he Lieraure During he pas en years or so here have been various suggesions concerning he way one should check
Econ107 Applied Econometrics Topic 7: Multicollinearity (Studenmund, Chapter 8)
 I. Definiions and Problems A. Perfec Mulicollineariy Econ7 Applied Economerics Topic 7: Mulicollineariy (Sudenmund, Chaper 8) Definiion: Perfec mulicollineariy exiss in a following K-variable regression
I. Definiions and Problems A. Perfec Mulicollineariy Econ7 Applied Economerics Topic 7: Mulicollineariy (Sudenmund, Chaper 8) Definiion: Perfec mulicollineariy exiss in a following K-variable regression
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuits
 Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 6.1: Definition of. Laplace Transform. In this chapter we use the Laplace transform to convert a
 Boye/DiPrima 9 h ed, Ch 6.: Definiion of Laplae Transform Elemenary Differenial Equaions and Boundary Value Problems, 9 h ediion, by William E. Boye and Rihard C. DiPrima, 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, In.
Boye/DiPrima 9 h ed, Ch 6.: Definiion of Laplae Transform Elemenary Differenial Equaions and Boundary Value Problems, 9 h ediion, by William E. Boye and Rihard C. DiPrima, 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, In.
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
Electrical and current self-induction
 Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
MOMENTUM CONSERVATION LAW
 1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
Amit Mehra. Indian School of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA Vijay Mookerjee
 RESEARCH ARTICLE HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT FOR PROGRAMMERS USING OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE Ami Mehra Indian Shool of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA {Ami_Mehra@isb.edu} Vijay Mookerjee Shool of Managemen, Uniersiy
RESEARCH ARTICLE HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT FOR PROGRAMMERS USING OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE Ami Mehra Indian Shool of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA {Ami_Mehra@isb.edu} Vijay Mookerjee Shool of Managemen, Uniersiy
A semi-analytical model for polymers subjected to high strain rates
 5 h European LS-DYNA Users Conferene Maerial Tehnology A semi-analyial model for polymers subjeed o high srain raes Auhors: A. Haufe, DYNAmore GmbH P.A. Du Bois, Consuling Engineer S. Kolling & M. Feuh,
5 h European LS-DYNA Users Conferene Maerial Tehnology A semi-analyial model for polymers subjeed o high srain raes Auhors: A. Haufe, DYNAmore GmbH P.A. Du Bois, Consuling Engineer S. Kolling & M. Feuh,
A New Formulation of Electrodynamics
 . Eleromagnei Analysis & Appliaions 1 457-461 doi:1.436/jemaa.1.86 Published Online Augus 1 hp://www.sirp.org/journal/jemaa A New Formulaion of Elerodynamis Arbab I. Arbab 1 Faisal A. Yassein 1 Deparmen
. Eleromagnei Analysis & Appliaions 1 457-461 doi:1.436/jemaa.1.86 Published Online Augus 1 hp://www.sirp.org/journal/jemaa A New Formulaion of Elerodynamis Arbab I. Arbab 1 Faisal A. Yassein 1 Deparmen
Properties of Two Carbon Composite Materials Using LTM25 Epoxy Resin
 NASA Tehnial Memorandum 110286 Properies of Two Carbon Composie Maerials Using LTM25 Epoxy Resin Juan R. Cruz Langley Researh Cener, Hampon, Virginia C. H. Shah and A. S. Posyn Norhrop Grumman Corporaion,
NASA Tehnial Memorandum 110286 Properies of Two Carbon Composie Maerials Using LTM25 Epoxy Resin Juan R. Cruz Langley Researh Cener, Hampon, Virginia C. H. Shah and A. S. Posyn Norhrop Grumman Corporaion,
Analysis of Members with Axial Loads and Moments. (Length effects Disregarded, Short Column )
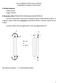 Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
New Oscillation Criteria For Second Order Nonlinear Differential Equations
 Researh Inveny: Inernaional Journal Of Engineering And Siene Issn: 78-47, Vol, Issue 4 (Feruary 03), Pp 36-4 WwwResearhinvenyCom New Osillaion Crieria For Seond Order Nonlinear Differenial Equaions Xhevair
Researh Inveny: Inernaional Journal Of Engineering And Siene Issn: 78-47, Vol, Issue 4 (Feruary 03), Pp 36-4 WwwResearhinvenyCom New Osillaion Crieria For Seond Order Nonlinear Differenial Equaions Xhevair
This is an example to show you how SMath can calculate the movement of kinematic mechanisms.
 Dec :5:6 - Kinemaics model of Simple Arm.sm This file is provided for educaional purposes as guidance for he use of he sofware ool. I is no guaraeed o be free from errors or ommissions. The mehods and
Dec :5:6 - Kinemaics model of Simple Arm.sm This file is provided for educaional purposes as guidance for he use of he sofware ool. I is no guaraeed o be free from errors or ommissions. The mehods and
Chapter 12: Velocity, acceleration, and forces
 To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
RECHARGING LARGE CAPACITOR BANKS. H. R. Shaylor Brookhaven National Laboratory
 RECHARGING LARGE CAPACIOR BANKS H. R. Shaylor Brookhaven Naional Laboraory he power bill for a large lina suh as ha proposed for he AGS onversion would be in he order of $100, 000 per year. his is for
RECHARGING LARGE CAPACIOR BANKS H. R. Shaylor Brookhaven Naional Laboraory he power bill for a large lina suh as ha proposed for he AGS onversion would be in he order of $100, 000 per year. his is for
1. The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object from t = 0 to t = T. a
 Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Chapter Floating Point Representation
 Chaper 01.05 Floaing Poin Represenaion Afer reading his chaper, you should be able o: 1. conver a base- number o a binary floaing poin represenaion,. conver a binary floaing poin number o is equivalen
Chaper 01.05 Floaing Poin Represenaion Afer reading his chaper, you should be able o: 1. conver a base- number o a binary floaing poin represenaion,. conver a binary floaing poin number o is equivalen
Dynamic Analysis of Loads Moving Over Structures
 h Inernaional ongress of roaian ociey of echanics epember, 18-, 3 Bizovac, roaia ynamic nalysis of Loads oving Over rucures Ivica Kožar, Ivana Šimac Keywords: moving load, direc acceleraion mehod 1. Inroducion
h Inernaional ongress of roaian ociey of echanics epember, 18-, 3 Bizovac, roaia ynamic nalysis of Loads oving Over rucures Ivica Kožar, Ivana Šimac Keywords: moving load, direc acceleraion mehod 1. Inroducion
MAC1105-College Algebra
 . Inverse Funcions I. Inroducion MAC5-College Algera Chaper -Inverse, Eponenial & Logarihmic Funcions To refresh our undersnading of "Composiion of a funcion" or "Composie funcion" which refers o he comining
. Inverse Funcions I. Inroducion MAC5-College Algera Chaper -Inverse, Eponenial & Logarihmic Funcions To refresh our undersnading of "Composiion of a funcion" or "Composie funcion" which refers o he comining
Designing A Fanlike Structure
 Designing A Fnlike Sruure To proeed wih his lesson, lik on he Nex buon here or he op of ny pge. When you re done wih his lesson, lik on he Conens buon here or he op of ny pge o reurn o he lis of lessons.
Designing A Fnlike Sruure To proeed wih his lesson, lik on he Nex buon here or he op of ny pge. When you re done wih his lesson, lik on he Conens buon here or he op of ny pge o reurn o he lis of lessons.
RC, RL and RLC circuits
 Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
From Particles to Rigid Bodies
 Rigid Body Dynamics From Paricles o Rigid Bodies Paricles No roaions Linear velociy v only Rigid bodies Body roaions Linear velociy v Angular velociy ω Rigid Bodies Rigid bodies have boh a posiion and
Rigid Body Dynamics From Paricles o Rigid Bodies Paricles No roaions Linear velociy v only Rigid bodies Body roaions Linear velociy v Angular velociy ω Rigid Bodies Rigid bodies have boh a posiion and
3. Differential Equations
 3. Differenial Equaions 3.. inear Differenial Equaions of Firs rder A firs order differenial equaion is an equaion of he form d() d ( ) = F ( (),) (3.) As noed above, here will in general be a whole la
3. Differenial Equaions 3.. inear Differenial Equaions of Firs rder A firs order differenial equaion is an equaion of he form d() d ( ) = F ( (),) (3.) As noed above, here will in general be a whole la
Problem 1 / 25 Problem 2 / 10 Problem 3 / 15 Problem 4 / 30 Problem 5 / 20 TOTAL / 100
 Deparmen of Applied Eonomis Johns Hopkins Universiy Eonomis 60 Maroeonomi Theory and Poliy Miderm Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Summer 0 NAME: The Exam has a oal of five (5) problems and
Deparmen of Applied Eonomis Johns Hopkins Universiy Eonomis 60 Maroeonomi Theory and Poliy Miderm Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Summer 0 NAME: The Exam has a oal of five (5) problems and
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
