Lecture 13. Poisson Distribution. Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.5. STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 16, 2014
|
|
|
- Garry Vincent Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 13 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.5 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 16, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 13.1
2 Agenda
3 Review So far, we have seen discrete probability distributions of the number of successes in a sequence of random experiments with specified sample size. Bernoulli distribution: independent trial (sampling with replacement), sample size =
4 Review So far, we have seen discrete probability distributions of the number of successes in a sequence of random experiments with specified sample size. Bernoulli distribution: independent trial (sampling with replacement), sample size = 1 Binomial distribution: independent trials (sampling with replacement), sample size = n 13.3
5 Review So far, we have seen discrete probability distributions of the number of successes in a sequence of random experiments with specified sample size. Bernoulli distribution: independent trial (sampling with replacement), sample size = 1 Binomial distribution: independent trials (sampling with replacement), sample size = n Hypergeometric distribution: dependent trials (sampling without replacement), sample size = n 13.3
6 Review So far, we have seen discrete probability distributions of the number of successes in a sequence of random experiments with specified sample size. Bernoulli distribution: independent trial (sampling with replacement), sample size = 1 Binomial distribution: independent trials (sampling with replacement), sample size = n Hypergeometric distribution: dependent trials (sampling without replacement), sample size = n 13.3
7 Review So far, we have seen discrete probability distributions of the number of successes in a sequence of random experiments with specified sample size. Bernoulli distribution: independent trial (sampling with replacement), sample size = 1 Binomial distribution: independent trials (sampling with replacement), sample size = n Hypergeometric distribution: dependent trials (sampling without replacement), sample size = n The Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space does not have a (fixed) sample size 13.3
8 : Characteristics of the : Let X be a Poisson r.v. The definition of X: The number of successes 13.4
9 : Characteristics of the : Let X be a Poisson r.v. The definition of X: The number of successes The support: x = 0, 1, 2, 13.4
10 : Characteristics of the : Let X be a Poisson r.v. The definition of X: The number of successes The support: x = 0, 1, 2, Its parameter(s) and definition(s): λ: the average number of successes 13.4
11 : Characteristics of the : Let X be a Poisson r.v. The definition of X: The number of successes The support: x = 0, 1, 2, Its parameter(s) and definition(s): λ: the average number of successes The probability mass function (pmf): p X (x) = e λ λ x x! 13.4
12 : Characteristics of the : Let X be a Poisson r.v. The definition of X: The number of successes The support: x = 0, 1, 2, Its parameter(s) and definition(s): λ: the average number of successes The probability mass function (pmf): p X (x) = e λ λ x x! The expected value: E[X] = λ 13.4
13 : Characteristics of the : Let X be a Poisson r.v. The definition of X: The number of successes The support: x = 0, 1, 2, Its parameter(s) and definition(s): λ: the average number of successes The probability mass function (pmf): p X (x) = e λ λ x x! The expected value: E[X] = λ The variance: Var(X) = λ 13.4
14 Poisson approximation to Binomial Distribution If X Binomial(n, p) and n > 100 and p <.01 then we can approximate the distribution X by using X Poisson(n p) 13.5
15 Example 33 Let us say a certain disease has a 0.14 % of occurring. Let us sample 1,000 people. Find the exact and approximate probabilities that 0 people have the disease and at most 5 people have the disease. Solution. Set-up: Let X be the number of people have the disease in the sample (n = 1000). Which distribution to use? 1 The sample size is fixed (n = 1000 Binomial or Hypergeometric What are the parameters? n = 1000, p =
16 Example 33 Let us say a certain disease has a 0.14 % of occurring. Let us sample 1,000 people. Find the exact and approximate probabilities that 0 people have the disease and at most 5 people have the disease. Solution. Set-up: Let X be the number of people have the disease in the sample (n = 1000). Which distribution to use? 1 The sample size is fixed (n = 1000 Binomial or Hypergeometric 2 One person have the disease is independent to others Binomial What are the parameters? n = 1000, p =
17 Example 33 cont d Any approximation? Since n = 1000 > 100 and p =.0014 <.01. We can use Poisson X to approximate Binomial distribution X Exact probabilities X Binomial(n = 1000, p =.0014) P(X = 0) = ( ) (.0014) 0 (1.0014) =.2464 P(X 5) = 5 ( 1000 ) x=0 x (.0014) x (1.0014) 1000 x =.9986 Approximate probabilities X Poisson(λ = n p = 1.4) P(X = 0) P(X = 0) = e ! =.2466 P(X 5) P(X 5) = 5 x=0 e 1.4 λ x x! =
18 Example 34 Suppose earthquakes occur in the western US with a rate of 2 per week. Let X be the number of earthquakes in the western US this week. Let Y be the number of earthquakes in the western US this month (assume a 4 week period of time). Find the probability that X is 3 and Y is 12. Let Z be the number of weeks in a 4 week period that have a week with 3 earthquakes in the western US. Find the probability that Z is 4. Is this the same as the probability that Y is 12? Does this make sense? Solution. Set-up: X be the number of earthquakes in the western US this week. Y be the number of earthquakes in the western US in a 4 week period. Z be the number of weeks in a 4 week period that have a week with 3 earthquakes in the western US. 13.8
19 Example 34 cont d Solution. Which distribution to use? X and Y 1 No set sample size Z What are the parameters? X : λ = 2 per week Y : λ = 8 per 4 weeks Z : n = 4, p = P(X = 3) 13.9
20 Example 34 cont d Solution. Which distribution to use? X and Y Z 1 No set sample size 2 Number of events in a given time interval with specified occurrence rate Poisson What are the parameters? X : λ = 2 per week Y : λ = 8 per 4 weeks Z : n = 4, p = P(X = 3) 13.9
21 Example 34 cont d Solution. Which distribution to use? X and Y Z 1 No set sample size 2 Number of events in a given time interval with specified occurrence rate Poisson 1 The sample size is fixed n = 4 Binomial or Hypergeometric What are the parameters? X : λ = 2 per week Y : λ = 8 per 4 weeks Z : n = 4, p = P(X = 3) 13.9
22 Example 34 cont d Solution. Which distribution to use? X and Y Z 1 No set sample size 2 Number of events in a given time interval with specified occurrence rate Poisson 1 The sample size is fixed n = 4 Binomial or Hypergeometric 2 Whether in a given week with 3 earthquakes is independent to other weeks Binomial What are the parameters? X : λ = 2 per week Y : λ = 8 per 4 weeks Z : n = 4, p = P(X = 3) 13.9
23 Example 34 cont d X Poisson(λ = 2) Y Poisson(λ = 8) P(X = 3) = e ! =.1804 P(Y = 12) = e ! =.0481 P(Z = 4) = ( 4 4) (.1804) 4 (1.1804) 4 4 =.0011 The probability that Z is 4 is much lower than the probability that Y is 12. This makes sense since there are more options for Y being 12. The probability that Z is 4 means that 4 weeks in a row there were 3 earthquakes. However with Y being 12 that just means 12 earthquakes happened in 4 weeks. We could have had 12, 0, 0, 0 or 7, 2, 1, 2, etc 13.10
24 Example 35 PRP has on average 4 telephone calls per minute. Let X be the number of phone calls in the next minute. Find the probability that X is at least 3 Solution. Which distribution to use? 1 No set sample size What are the parameters? λ = 4 per minute X Poisson(λ = 4) P(X 3) = 1 [P(X = 0) + P(X = 1) + P(X = 2)] = 1 [ e ! + e ! + e ! ] = =
25 Example 35 PRP has on average 4 telephone calls per minute. Let X be the number of phone calls in the next minute. Find the probability that X is at least 3 Solution. Which distribution to use? 1 No set sample size 2 Number of events in a given time interval with specified occurrence rate Poisson What are the parameters? λ = 4 per minute X Poisson(λ = 4) P(X 3) = 1 [P(X = 0) + P(X = 1) + P(X = 2)] = 1 [ e ! + e ! + e ! ] = =
26 In today s lecture, we Introduced the Poisson distribution Used when measuring rate of success" Different from Bernoulli, Binomial, and Hypergeometric distributions, the sample size is not fixed Poisson approximation to Binomial Appropriate when n > 100 and p <
Lecture 14. Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.6. STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 23, Whitney Huang Purdue University
 Lecture 14 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.6 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 23, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 14.1 Agenda 14.2 Review So far, we have covered Bernoulli
Lecture 14 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.6 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 23, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 14.1 Agenda 14.2 Review So far, we have covered Bernoulli
Bernoulli and Binomial Distributions. Notes. Bernoulli Trials. Bernoulli/Binomial Random Variables Bernoulli and Binomial Distributions.
 Lecture 11 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.3 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 16, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 11.1 Agenda 1 2 11.2 Bernoulli trials Many problems in
Lecture 11 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 5.3 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 16, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 11.1 Agenda 1 2 11.2 Bernoulli trials Many problems in
Lecture 20. Poisson Processes. Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models March 26, 2014
 Lecture 20 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 12.1 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models March 26, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 20.1 Agenda 1 2 20.2 For a specified event that occurs
Lecture 20 Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 12.1 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models March 26, 2014 Whitney Huang Purdue University 20.1 Agenda 1 2 20.2 For a specified event that occurs
Math/Stat 352 Lecture 8
 Math/Stat 352 Lecture 8 Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Commonly Used Distributions: Poisson, hypergeometric, geometric, and negative binomial. 1 The Poisson Distribution Poisson random variable counts the number
Math/Stat 352 Lecture 8 Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Commonly Used Distributions: Poisson, hypergeometric, geometric, and negative binomial. 1 The Poisson Distribution Poisson random variable counts the number
Chapters 3.2 Discrete distributions
 Chapters 3.2 Discrete distributions In this section we study several discrete distributions and their properties. Here are a few, classified by their support S X. There are of course many, many more. For
Chapters 3.2 Discrete distributions In this section we study several discrete distributions and their properties. Here are a few, classified by their support S X. There are of course many, many more. For
Binomial and Poisson Probability Distributions
 Binomial and Poisson Probability Distributions Esra Akdeniz March 3, 2016 Bernoulli Random Variable Any random variable whose only possible values are 0 or 1 is called a Bernoulli random variable. What
Binomial and Poisson Probability Distributions Esra Akdeniz March 3, 2016 Bernoulli Random Variable Any random variable whose only possible values are 0 or 1 is called a Bernoulli random variable. What
Week 6, 9/24/12-9/28/12, Notes: Bernoulli, Binomial, Hypergeometric, and Poisson Random Variables
 Week 6, 9/24/12-9/28/12, Notes: Bernoulli, Binomial, Hypergeometric, and Poisson Random Variables 1 Monday 9/24/12 on Bernoulli and Binomial R.V.s We are now discussing discrete random variables that have
Week 6, 9/24/12-9/28/12, Notes: Bernoulli, Binomial, Hypergeometric, and Poisson Random Variables 1 Monday 9/24/12 on Bernoulli and Binomial R.V.s We are now discussing discrete random variables that have
STAT 430/510 Probability Lecture 12: Central Limit Theorem and Exponential Distribution
 STAT 430/510 Probability Lecture 12: Central Limit Theorem and Exponential Distribution Pengyuan (Penelope) Wang June 15, 2011 Review Discussed Uniform Distribution and Normal Distribution Normal Approximation
STAT 430/510 Probability Lecture 12: Central Limit Theorem and Exponential Distribution Pengyuan (Penelope) Wang June 15, 2011 Review Discussed Uniform Distribution and Normal Distribution Normal Approximation
Conditional distributions (discrete case)
 Conditional distributions (discrete case) The basic idea behind conditional distributions is simple: Suppose (XY) is a jointly-distributed random vector with a discrete joint distribution. Then we can
Conditional distributions (discrete case) The basic idea behind conditional distributions is simple: Suppose (XY) is a jointly-distributed random vector with a discrete joint distribution. Then we can
Lecture 16. STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models February 23, Whitney Huang Purdue University. Relationship between Discrete
 Lecture 6 STAT 5 Introduction to Probability Models February 3, 04 between Whitney Huang Purdue University 6. Agenda Distributions between 6. Choosing a Distribution between 6.3 In some of our examples,
Lecture 6 STAT 5 Introduction to Probability Models February 3, 04 between Whitney Huang Purdue University 6. Agenda Distributions between 6. Choosing a Distribution between 6.3 In some of our examples,
Mathematical Statistics 1 Math A 6330
 Mathematical Statistics 1 Math A 6330 Chapter 3 Common Families of Distributions Mohamed I. Riffi Department of Mathematics Islamic University of Gaza September 28, 2015 Outline 1 Subjects of Lecture 04
Mathematical Statistics 1 Math A 6330 Chapter 3 Common Families of Distributions Mohamed I. Riffi Department of Mathematics Islamic University of Gaza September 28, 2015 Outline 1 Subjects of Lecture 04
Probability Theory and Simulation Methods. April 6th, Lecture 19: Special distributions
 April 6th, 2018 Lecture 19: Special distributions Week 1 Chapter 1: Axioms of probability Week 2 Chapter 3: Conditional probability and independence Week 4 Chapters 4, 6: Random variables Week 9 Chapter
April 6th, 2018 Lecture 19: Special distributions Week 1 Chapter 1: Axioms of probability Week 2 Chapter 3: Conditional probability and independence Week 4 Chapters 4, 6: Random variables Week 9 Chapter
Stat 100a, Introduction to Probability.
 Stat 100a, Introduction to Probability. Outline for the day: 1. Geometric random variables. 2. Negative binomial random variables. 3. Moment generating functions. 4. Poisson random variables. 5. Continuous
Stat 100a, Introduction to Probability. Outline for the day: 1. Geometric random variables. 2. Negative binomial random variables. 3. Moment generating functions. 4. Poisson random variables. 5. Continuous
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 7 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 14, 2012 Reminders Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 7 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 14, 2012 Reminders Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
Lecture 4: Random Variables and Distributions
 Lecture 4: Random Variables and Distributions Goals Random Variables Overview of discrete and continuous distributions important in genetics/genomics Working with distributions in R Random Variables A
Lecture 4: Random Variables and Distributions Goals Random Variables Overview of discrete and continuous distributions important in genetics/genomics Working with distributions in R Random Variables A
STAT 430/510: Lecture 15
 STAT 430/510: Lecture 15 James Piette June 23, 2010 Updates HW4 is up on my website. It is due next Mon. (June 28th). Starting today back at section 6.4... Conditional Distribution: Discrete Def: The conditional
STAT 430/510: Lecture 15 James Piette June 23, 2010 Updates HW4 is up on my website. It is due next Mon. (June 28th). Starting today back at section 6.4... Conditional Distribution: Discrete Def: The conditional
Chapter 5. Chapter 5 sections
 1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Lecture 3. Discrete Random Variables
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 3. Discrete Random Variables January 23, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 3 January 23, 2013 1 / 14 Agenda Random Variable: Motivation and Definition
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 3. Discrete Random Variables January 23, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 3 January 23, 2013 1 / 14 Agenda Random Variable: Motivation and Definition
p. 4-1 Random Variables
 Random Variables A Motivating Example Experiment: Sample k students without replacement from the population of all n students (labeled as 1, 2,, n, respectively) in our class. = {all combinations} = {{i
Random Variables A Motivating Example Experiment: Sample k students without replacement from the population of all n students (labeled as 1, 2,, n, respectively) in our class. = {all combinations} = {{i
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 14: Continuous random variables Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin www.cs.cmu.edu/
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 14: Continuous random variables Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin www.cs.cmu.edu/
Statistics for Economists. Lectures 3 & 4
 Statistics for Economists Lectures 3 & 4 Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University 1 CHAPTER 2- Discrete Distributions 2.1. Random variables of the Discrete Type Definition 2.1.1: Given a random experiment with
Statistics for Economists Lectures 3 & 4 Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University 1 CHAPTER 2- Discrete Distributions 2.1. Random variables of the Discrete Type Definition 2.1.1: Given a random experiment with
Topic 3 - Discrete distributions
 Topic 3 - Discrete distributions Basics of discrete distributions Mean and variance of a discrete distribution Binomial distribution Poisson distribution and process 1 A random variable is a function which
Topic 3 - Discrete distributions Basics of discrete distributions Mean and variance of a discrete distribution Binomial distribution Poisson distribution and process 1 A random variable is a function which
1 Bernoulli Distribution: Single Coin Flip
 STAT 350 - An Introduction to Statistics Named Discrete Distributions Jeremy Troisi Bernoulli Distribution: Single Coin Flip trial of an experiment that yields either a success or failure. X Bern(p),X
STAT 350 - An Introduction to Statistics Named Discrete Distributions Jeremy Troisi Bernoulli Distribution: Single Coin Flip trial of an experiment that yields either a success or failure. X Bern(p),X
Chapter 2: Discrete Distributions. 2.1 Random Variables of the Discrete Type
 Chapter 2: Discrete Distributions 2.1 Random Variables of the Discrete Type 2.2 Mathematical Expectation 2.3 Special Mathematical Expectations 2.4 Binomial Distribution 2.5 Negative Binomial Distribution
Chapter 2: Discrete Distributions 2.1 Random Variables of the Discrete Type 2.2 Mathematical Expectation 2.3 Special Mathematical Expectations 2.4 Binomial Distribution 2.5 Negative Binomial Distribution
Lecture 2: Discrete Probability Distributions
 Lecture 2: Discrete Probability Distributions IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge February 1st, 2011 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture
Lecture 2: Discrete Probability Distributions IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge February 1st, 2011 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture
Random Variables. Lecture 6: E(X ), Var(X ), & Cov(X, Y ) Random Variables - Vocabulary. Random Variables, cont.
 Lecture 6: E(X ), Var(X ), & Cov(X, Y ) Sta230/Mth230 Colin Rundel February 5, 2014 We have been using them for a while now in a variety of forms but it is good to explicitly define what we mean Random
Lecture 6: E(X ), Var(X ), & Cov(X, Y ) Sta230/Mth230 Colin Rundel February 5, 2014 We have been using them for a while now in a variety of forms but it is good to explicitly define what we mean Random
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variables
 MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY STT 351 SECTION 2 FALL 2008 LECTURE NOTES Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variables Nao Mimoto Contents 1 Random Variables 2 2 Probability Distributions for Discrete Variables 3 3 Expected
MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY STT 351 SECTION 2 FALL 2008 LECTURE NOTES Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variables Nao Mimoto Contents 1 Random Variables 2 2 Probability Distributions for Discrete Variables 3 3 Expected
BNAD 276 Lecture 5 Discrete Probability Distributions Exercises 1 11
 1 / 15 BNAD 276 Lecture 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 1 11 Phuong Ho May 14, 2017 Exercise 1 Suppose we have the probability distribution for the random variable X as follows. X f (x) 20.20 25.15
1 / 15 BNAD 276 Lecture 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 1 11 Phuong Ho May 14, 2017 Exercise 1 Suppose we have the probability distribution for the random variable X as follows. X f (x) 20.20 25.15
STAT509: Discrete Random Variable
 University of South Carolina September 16, 2014 Motivation So far, we have already known how to calculate probabilities of events. Suppose we toss a fair coin three times, we know that the probability
University of South Carolina September 16, 2014 Motivation So far, we have already known how to calculate probabilities of events. Suppose we toss a fair coin three times, we know that the probability
What s for today. More on Binomial distribution Poisson distribution. c Mikyoung Jun (Texas A&M) stat211 lecture 7 February 8, / 16
 What s for today More on Binomial distribution Poisson distribution c Mikyoung Jun (Texas A&M) stat211 lecture 7 February 8, 2011 1 / 16 Review: Binomial distribution Question: among the following, what
What s for today More on Binomial distribution Poisson distribution c Mikyoung Jun (Texas A&M) stat211 lecture 7 February 8, 2011 1 / 16 Review: Binomial distribution Question: among the following, what
BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION
 BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION The binomial distribution is a particular type of discrete pmf. It describes random variables which satisfy the following conditions: 1 You perform n identical experiments (called
BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION The binomial distribution is a particular type of discrete pmf. It describes random variables which satisfy the following conditions: 1 You perform n identical experiments (called
Special distributions
 Special distributions August 22, 2017 STAT 101 Class 4 Slide 1 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation 2 Bernoulli and binomial 3 Poisson 4 Uniform 5 Exponential 6 Normal STAT 101 Class 4 Slide 2 What distributions
Special distributions August 22, 2017 STAT 101 Class 4 Slide 1 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation 2 Bernoulli and binomial 3 Poisson 4 Uniform 5 Exponential 6 Normal STAT 101 Class 4 Slide 2 What distributions
STAT 430/510 Probability
 STAT 430/510 Probability Hui Nie Lecture 16 June 24th, 2009 Review Sum of Independent Normal Random Variables Sum of Independent Poisson Random Variables Sum of Independent Binomial Random Variables Conditional
STAT 430/510 Probability Hui Nie Lecture 16 June 24th, 2009 Review Sum of Independent Normal Random Variables Sum of Independent Poisson Random Variables Sum of Independent Binomial Random Variables Conditional
STAT Chapter 5 Continuous Distributions
 STAT 270 - Chapter 5 Continuous Distributions June 27, 2012 Shirin Golchi () STAT270 June 27, 2012 1 / 59 Continuous rv s Definition: X is a continuous rv if it takes values in an interval, i.e., range
STAT 270 - Chapter 5 Continuous Distributions June 27, 2012 Shirin Golchi () STAT270 June 27, 2012 1 / 59 Continuous rv s Definition: X is a continuous rv if it takes values in an interval, i.e., range
Relationship between probability set function and random variable - 2 -
 2.0 Random Variables A rat is selected at random from a cage and its sex is determined. The set of possible outcomes is female and male. Thus outcome space is S = {female, male} = {F, M}. If we let X be
2.0 Random Variables A rat is selected at random from a cage and its sex is determined. The set of possible outcomes is female and male. Thus outcome space is S = {female, male} = {F, M}. If we let X be
ST 371 (V): Families of Discrete Distributions
 ST 371 (V): Families of Discrete Distributions Certain experiments and associated random variables can be grouped into families, where all random variables in the family share a certain structure and a
ST 371 (V): Families of Discrete Distributions Certain experiments and associated random variables can be grouped into families, where all random variables in the family share a certain structure and a
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 10: Expectation and Variance Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin www.cs.cmu.edu/ psarkar/teaching
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 10: Expectation and Variance Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin www.cs.cmu.edu/ psarkar/teaching
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 3: Probability Distributions
 Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 3: Probability Distributions James V. Lambers Department of Mathematics The University of Southern Mississippi James V. Lambers Statistical Data Analysis
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 3: Probability Distributions James V. Lambers Department of Mathematics The University of Southern Mississippi James V. Lambers Statistical Data Analysis
Common Discrete Distributions
 Common Discrete Distributions Statistics 104 Autumn 2004 Taken from Statistics 110 Lecture Notes Copyright c 2004 by Mark E. Irwin Common Discrete Distributions There are a wide range of popular discrete
Common Discrete Distributions Statistics 104 Autumn 2004 Taken from Statistics 110 Lecture Notes Copyright c 2004 by Mark E. Irwin Common Discrete Distributions There are a wide range of popular discrete
Special Discrete RV s. Then X = the number of successes is a binomial RV. X ~ Bin(n,p).
 Sect 3.4: Binomial RV Special Discrete RV s 1. Assumptions and definition i. Experiment consists of n repeated trials ii. iii. iv. There are only two possible outcomes on each trial: success (S) or failure
Sect 3.4: Binomial RV Special Discrete RV s 1. Assumptions and definition i. Experiment consists of n repeated trials ii. iii. iv. There are only two possible outcomes on each trial: success (S) or failure
Random Variable. Discrete Random Variable. Continuous Random Variable. Discrete Random Variable. Discrete Probability Distribution
 Random Variable Theoretical Probability Distribution Random Variable Discrete Probability Distributions A variable that assumes a numerical description for the outcome of a random eperiment (by chance).
Random Variable Theoretical Probability Distribution Random Variable Discrete Probability Distributions A variable that assumes a numerical description for the outcome of a random eperiment (by chance).
Practice Problem - Skewness of Bernoulli Random Variable. Lecture 7: Joint Distributions and the Law of Large Numbers. Joint Distributions - Example
 A little more E(X Practice Problem - Skewness of Bernoulli Random Variable Lecture 7: and the Law of Large Numbers Sta30/Mth30 Colin Rundel February 7, 014 Let X Bern(p We have shown that E(X = p Var(X
A little more E(X Practice Problem - Skewness of Bernoulli Random Variable Lecture 7: and the Law of Large Numbers Sta30/Mth30 Colin Rundel February 7, 014 Let X Bern(p We have shown that E(X = p Var(X
To find the median, find the 40 th quartile and the 70 th quartile (which are easily found at y=1 and y=2, respectively). Then we interpolate:
 Joel Anderson ST 37-002 Lecture Summary for 2/5/20 Homework 0 First, the definition of a probability mass function p(x) and a cumulative distribution function F(x) is reviewed: Graphically, the drawings
Joel Anderson ST 37-002 Lecture Summary for 2/5/20 Homework 0 First, the definition of a probability mass function p(x) and a cumulative distribution function F(x) is reviewed: Graphically, the drawings
4. Discrete Probability Distributions. Introduction & Binomial Distribution
 4. Discrete Probability Distributions Introduction & Binomial Distribution Aim & Objectives 1 Aims u Introduce discrete probability distributions v Binomial distribution v Poisson distribution 2 Objectives
4. Discrete Probability Distributions Introduction & Binomial Distribution Aim & Objectives 1 Aims u Introduce discrete probability distributions v Binomial distribution v Poisson distribution 2 Objectives
POISSON RANDOM VARIABLES
 POISSON RANDOM VARIABLES Suppose a random phenomenon occurs with a mean rate of occurrences or happenings per unit of time or length or area or volume, etc. Note: >. Eamples: 1. Cars passing through an
POISSON RANDOM VARIABLES Suppose a random phenomenon occurs with a mean rate of occurrences or happenings per unit of time or length or area or volume, etc. Note: >. Eamples: 1. Cars passing through an
More on Distribution Function
 More on Distribution Function The distribution of a random variable X can be determined directly from its cumulative distribution function F X. Theorem: Let X be any random variable, with cumulative distribution
More on Distribution Function The distribution of a random variable X can be determined directly from its cumulative distribution function F X. Theorem: Let X be any random variable, with cumulative distribution
success and failure independent from one trial to the next?
 , section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Notes by Tim Pilachowski Definition of Bernoulli trials which make up a binomial experiment: The number of trials in an experiment is fixed. There are exactly two
, section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Notes by Tim Pilachowski Definition of Bernoulli trials which make up a binomial experiment: The number of trials in an experiment is fixed. There are exactly two
Statistics for Engineers Lecture 2 Discrete Distributions
 Statistics for Engineers Lecture 2 Discrete Distributions Chong Ma Department of Statistics University of South Carolina chongm@email.sc.edu January 18, 2017 Chong Ma (Statistics, USC) STAT 509 Spring
Statistics for Engineers Lecture 2 Discrete Distributions Chong Ma Department of Statistics University of South Carolina chongm@email.sc.edu January 18, 2017 Chong Ma (Statistics, USC) STAT 509 Spring
Lecture 4: Bernoulli Process
 Lecture 4: Bernoulli Process Hyang-Won Lee Dept. of Internet & Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University Lecture 4 Hyang-Won Lee 1 / 12 Stochastic Process A stochastic process is a mathematical model of a probabilistic
Lecture 4: Bernoulli Process Hyang-Won Lee Dept. of Internet & Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University Lecture 4 Hyang-Won Lee 1 / 12 Stochastic Process A stochastic process is a mathematical model of a probabilistic
Closed book and notes. 120 minutes. Cover page, five pages of exam. No calculators.
 IE 230 Seat # Closed book and notes. 120 minutes. Cover page, five pages of exam. No calculators. Score Final Exam, Spring 2005 (May 2) Schmeiser Closed book and notes. 120 minutes. Consider an experiment
IE 230 Seat # Closed book and notes. 120 minutes. Cover page, five pages of exam. No calculators. Score Final Exam, Spring 2005 (May 2) Schmeiser Closed book and notes. 120 minutes. Consider an experiment
Random Variables Example:
 Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Binomial random variable
 Binomial random variable Toss a coin with prob p of Heads n times X: # Heads in n tosses X is a Binomial random variable with parameter n,p. X is Bin(n, p) An X that counts the number of successes in many
Binomial random variable Toss a coin with prob p of Heads n times X: # Heads in n tosses X is a Binomial random variable with parameter n,p. X is Bin(n, p) An X that counts the number of successes in many
Continuous Probability Spaces
 Continuous Probability Spaces Ω is not countable. Outcomes can be any real number or part of an interval of R, e.g. heights, weights and lifetimes. Can not assign probabilities to each outcome and add
Continuous Probability Spaces Ω is not countable. Outcomes can be any real number or part of an interval of R, e.g. heights, weights and lifetimes. Can not assign probabilities to each outcome and add
Things to remember when learning probability distributions:
 SPECIAL DISTRIBUTIONS Some distributions are special because they are useful They include: Poisson, exponential, Normal (Gaussian), Gamma, geometric, negative binomial, Binomial and hypergeometric distributions
SPECIAL DISTRIBUTIONS Some distributions are special because they are useful They include: Poisson, exponential, Normal (Gaussian), Gamma, geometric, negative binomial, Binomial and hypergeometric distributions
Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics
 Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification SS8, IN2345 Tobias Neckel Scientific Computing in Computer Science TUM Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics Concept of Building Block: Prerequisites:
Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification SS8, IN2345 Tobias Neckel Scientific Computing in Computer Science TUM Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics Concept of Building Block: Prerequisites:
STAT 430/510: Lecture 16
 STAT 430/510: Lecture 16 James Piette June 24, 2010 Updates HW4 is up on my website. It is due next Mon. (June 28th). Starting today back at section 6.7 and will begin Ch. 7. Joint Distribution of Functions
STAT 430/510: Lecture 16 James Piette June 24, 2010 Updates HW4 is up on my website. It is due next Mon. (June 28th). Starting today back at section 6.7 and will begin Ch. 7. Joint Distribution of Functions
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 8 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 16, 2012 Reminders Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 8 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 16, 2012 Reminders Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
Lecture 2: Probability and Distributions
 Lecture 2: Probability and Distributions Ani Manichaikul amanicha@jhsph.edu 17 April 2007 1 / 65 Probability: Why do we care? Probability helps us by: Allowing us to translate scientific questions info
Lecture 2: Probability and Distributions Ani Manichaikul amanicha@jhsph.edu 17 April 2007 1 / 65 Probability: Why do we care? Probability helps us by: Allowing us to translate scientific questions info
Sampling Distributions
 Sampling Distributions Mathematics 47: Lecture 9 Dan Sloughter Furman University March 16, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Sampling Distributions March 16, 2006 1 / 10 Definition We call the probability
Sampling Distributions Mathematics 47: Lecture 9 Dan Sloughter Furman University March 16, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Sampling Distributions March 16, 2006 1 / 10 Definition We call the probability
More Discrete Distribu-ons. Keegan Korthauer Department of Sta-s-cs UW Madison
 More Discrete Distribu-ons Keegan Korthauer Department of Sta-s-cs UW Madison 1 COMMON DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS Bernoulli Binomial Poisson Geometric 2 Some Common Distribu-ons Probability Distribu-ons Discrete
More Discrete Distribu-ons Keegan Korthauer Department of Sta-s-cs UW Madison 1 COMMON DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS Bernoulli Binomial Poisson Geometric 2 Some Common Distribu-ons Probability Distribu-ons Discrete
MATH : EXAM 2 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE
 MATH 3342-004: EXAM 2 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE INFO: WHEN: Friday (03/11) at 10:00am DURATION: 50 mins PROBLEM COUNT: Appropriate for a 50-min exam BONUS COUNT: At least one TOPICS CANDIDATE FOR THE EXAM:
MATH 3342-004: EXAM 2 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE INFO: WHEN: Friday (03/11) at 10:00am DURATION: 50 mins PROBLEM COUNT: Appropriate for a 50-min exam BONUS COUNT: At least one TOPICS CANDIDATE FOR THE EXAM:
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 13: Expectation and Variance and joint distributions Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 13: Expectation and Variance and joint distributions Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin
ACM 116: Lecture 2. Agenda. Independence. Bayes rule. Discrete random variables Bernoulli distribution Binomial distribution
 1 ACM 116: Lecture 2 Agenda Independence Bayes rule Discrete random variables Bernoulli distribution Binomial distribution Continuous Random variables The Normal distribution Expected value of a random
1 ACM 116: Lecture 2 Agenda Independence Bayes rule Discrete random variables Bernoulli distribution Binomial distribution Continuous Random variables The Normal distribution Expected value of a random
Probability: Why do we care? Lecture 2: Probability and Distributions. Classical Definition. What is Probability?
 Probability: Why do we care? Lecture 2: Probability and Distributions Sandy Eckel seckel@jhsph.edu 22 April 2008 Probability helps us by: Allowing us to translate scientific questions into mathematical
Probability: Why do we care? Lecture 2: Probability and Distributions Sandy Eckel seckel@jhsph.edu 22 April 2008 Probability helps us by: Allowing us to translate scientific questions into mathematical
3 Multiple Discrete Random Variables
 3 Multiple Discrete Random Variables 3.1 Joint densities Suppose we have a probability space (Ω, F,P) and now we have two discrete random variables X and Y on it. They have probability mass functions f
3 Multiple Discrete Random Variables 3.1 Joint densities Suppose we have a probability space (Ω, F,P) and now we have two discrete random variables X and Y on it. They have probability mass functions f
Stat Lecture 20. Last class we introduced the covariance and correlation between two jointly distributed random variables.
 Stat 260 - Lecture 20 Recap of Last Class Last class we introduced the covariance and correlation between two jointly distributed random variables. Today: We will introduce the idea of a statistic and
Stat 260 - Lecture 20 Recap of Last Class Last class we introduced the covariance and correlation between two jointly distributed random variables. Today: We will introduce the idea of a statistic and
Bernoulli and Binomial
 Bernoulli and Binomial Will Monroe July 1, 217 image: Antoine Taveneaux with materials by Mehran Sahami and Chris Piech Announcements: Problem Set 2 Due this Wednesday, 7/12, at 12:3pm (before class).
Bernoulli and Binomial Will Monroe July 1, 217 image: Antoine Taveneaux with materials by Mehran Sahami and Chris Piech Announcements: Problem Set 2 Due this Wednesday, 7/12, at 12:3pm (before class).
Lecture 10: Probability distributions TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019
 Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
Midterm #1. Lecture 10: Joint Distributions and the Law of Large Numbers. Joint Distributions - Example, cont. Joint Distributions - Example
 Midterm #1 Midterm 1 Lecture 10: and the Law of Large Numbers Statistics 104 Colin Rundel February 0, 01 Exam will be passed back at the end of class Exam was hard, on the whole the class did well: Mean:
Midterm #1 Midterm 1 Lecture 10: and the Law of Large Numbers Statistics 104 Colin Rundel February 0, 01 Exam will be passed back at the end of class Exam was hard, on the whole the class did well: Mean:
Bernoulli Trials, Binomial and Cumulative Distributions
 Bernoulli Trials, Binomial and Cumulative Distributions Sec 4.4-4.6 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 9-3339 Cathy Poliak,
Bernoulli Trials, Binomial and Cumulative Distributions Sec 4.4-4.6 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 9-3339 Cathy Poliak,
Probability Theory. Patrick Lam
 Probability Theory Patrick Lam Outline Probability Random Variables Simulation Important Distributions Discrete Distributions Continuous Distributions Most Basic Definition of Probability: number of successes
Probability Theory Patrick Lam Outline Probability Random Variables Simulation Important Distributions Discrete Distributions Continuous Distributions Most Basic Definition of Probability: number of successes
Chapter (4) Discrete Probability Distributions Examples
 Chapter (4) Discrete Probability Distributions Examples Example () Two balanced dice are rolled. Let X be the sum of the two dice. Obtain the probability distribution of X. Solution When the two balanced
Chapter (4) Discrete Probability Distributions Examples Example () Two balanced dice are rolled. Let X be the sum of the two dice. Obtain the probability distribution of X. Solution When the two balanced
Homework 4 Math 11, UCSD, Winter 2018 Due on Tuesday, 13th February
 PID: Last Name, First Name: Section: Approximate time spent to complete this assignment: hour(s) Homework 4 Math 11, UCSD, Winter 2018 Due on Tuesday, 13th February Readings: Chapters 16.6-16.7 and the
PID: Last Name, First Name: Section: Approximate time spent to complete this assignment: hour(s) Homework 4 Math 11, UCSD, Winter 2018 Due on Tuesday, 13th February Readings: Chapters 16.6-16.7 and the
Conditional Probability
 Conditional Probability Idea have performed a chance experiment but don t know the outcome (ω), but have some partial information (event A) about ω. Question: given this partial information what s the
Conditional Probability Idea have performed a chance experiment but don t know the outcome (ω), but have some partial information (event A) about ω. Question: given this partial information what s the
Probability Distributions Columns (a) through (d)
 Discrete Probability Distributions Columns (a) through (d) Probability Mass Distribution Description Notes Notation or Density Function --------------------(PMF or PDF)-------------------- (a) (b) (c)
Discrete Probability Distributions Columns (a) through (d) Probability Mass Distribution Description Notes Notation or Density Function --------------------(PMF or PDF)-------------------- (a) (b) (c)
Random Variable And Probability Distribution. Is defined as a real valued function defined on the sample space S. We denote it as X, Y, Z,
 Random Variable And Probability Distribution Introduction Random Variable ( r.v. ) Is defined as a real valued function defined on the sample space S. We denote it as X, Y, Z, T, and denote the assumed
Random Variable And Probability Distribution Introduction Random Variable ( r.v. ) Is defined as a real valued function defined on the sample space S. We denote it as X, Y, Z, T, and denote the assumed
Lecture 08: Poisson and More. Lisa Yan July 13, 2018
 Lecture 08: Poisson and More Lisa Yan July 13, 2018 Announcements PS1: Grades out later today Solutions out after class today PS2 due today PS3 out today (due next Friday 7/20) 2 Midterm announcement Tuesday,
Lecture 08: Poisson and More Lisa Yan July 13, 2018 Announcements PS1: Grades out later today Solutions out after class today PS2 due today PS3 out today (due next Friday 7/20) 2 Midterm announcement Tuesday,
STAT 430/510: Lecture 10
 STAT 430/510: Lecture 10 James Piette June 9, 2010 Updates HW2 is due today! Pick up your HW1 s up in stat dept. There is a box located right when you enter that is labeled "Stat 430 HW1". It ll be out
STAT 430/510: Lecture 10 James Piette June 9, 2010 Updates HW2 is due today! Pick up your HW1 s up in stat dept. There is a box located right when you enter that is labeled "Stat 430 HW1". It ll be out
Twelfth Problem Assignment
 EECS 401 Not Graded PROBLEM 1 Let X 1, X 2,... be a sequence of independent random variables that are uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. Consider a sequence defined by (a) Y n = max(x 1, X 2,..., X
EECS 401 Not Graded PROBLEM 1 Let X 1, X 2,... be a sequence of independent random variables that are uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. Consider a sequence defined by (a) Y n = max(x 1, X 2,..., X
INF FALL NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING. Jan Tore Lønning
 1 INF4080 2018 FALL NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING Jan Tore Lønning 2 Probability distributions Lecture 5, 5 September Today 3 Recap: Bayes theorem Discrete random variable Probability distribution Discrete
1 INF4080 2018 FALL NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING Jan Tore Lønning 2 Probability distributions Lecture 5, 5 September Today 3 Recap: Bayes theorem Discrete random variable Probability distribution Discrete
Discrete Random Variables
 CPSC 53 Systems Modeling and Simulation Discrete Random Variables Dr. Anirban Mahanti Department of Computer Science University of Calgary mahanti@cpsc.ucalgary.ca Random Variables A random variable is
CPSC 53 Systems Modeling and Simulation Discrete Random Variables Dr. Anirban Mahanti Department of Computer Science University of Calgary mahanti@cpsc.ucalgary.ca Random Variables A random variable is
The Binomial distribution. Probability theory 2. Example. The Binomial distribution
 Probability theory Tron Anders Moger September th 7 The Binomial distribution Bernoulli distribution: One experiment X i with two possible outcomes, probability of success P. If the experiment is repeated
Probability theory Tron Anders Moger September th 7 The Binomial distribution Bernoulli distribution: One experiment X i with two possible outcomes, probability of success P. If the experiment is repeated
Lecture 10: Normal RV. Lisa Yan July 18, 2018
 Lecture 10: Normal RV Lisa Yan July 18, 2018 Announcements Midterm next Tuesday Practice midterm, solutions out on website SCPD students: fill out Google form by today Covers up to and including Friday
Lecture 10: Normal RV Lisa Yan July 18, 2018 Announcements Midterm next Tuesday Practice midterm, solutions out on website SCPD students: fill out Google form by today Covers up to and including Friday
Basics on Probability. Jingrui He 09/11/2007
 Basics on Probability Jingrui He 09/11/2007 Coin Flips You flip a coin Head with probability 0.5 You flip 100 coins How many heads would you expect Coin Flips cont. You flip a coin Head with probability
Basics on Probability Jingrui He 09/11/2007 Coin Flips You flip a coin Head with probability 0.5 You flip 100 coins How many heads would you expect Coin Flips cont. You flip a coin Head with probability
Continuous Random Variables. What continuous random variables are and how to use them. I can give a definition of a continuous random variable.
 Continuous Random Variables Today we are learning... What continuous random variables are and how to use them. I will know if I have been successful if... I can give a definition of a continuous random
Continuous Random Variables Today we are learning... What continuous random variables are and how to use them. I will know if I have been successful if... I can give a definition of a continuous random
15 Discrete Distributions
 Lecture Note 6 Special Distributions (Discrete and Continuous) MIT 4.30 Spring 006 Herman Bennett 5 Discrete Distributions We have already seen the binomial distribution and the uniform distribution. 5.
Lecture Note 6 Special Distributions (Discrete and Continuous) MIT 4.30 Spring 006 Herman Bennett 5 Discrete Distributions We have already seen the binomial distribution and the uniform distribution. 5.
Lecture 12. Poisson random variables
 18.440: Lecture 12 Poisson random variables Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Poisson random variable definition Poisson random variable properties Poisson random variable problems 2 Outline Poisson random
18.440: Lecture 12 Poisson random variables Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Poisson random variable definition Poisson random variable properties Poisson random variable problems 2 Outline Poisson random
3.4. The Binomial Probability Distribution
 3.4. The Binomial Probability Distribution Objectives. Binomial experiment. Binomial random variable. Using binomial tables. Mean and variance of binomial distribution. 3.4.1. Four Conditions that determined
3.4. The Binomial Probability Distribution Objectives. Binomial experiment. Binomial random variable. Using binomial tables. Mean and variance of binomial distribution. 3.4.1. Four Conditions that determined
Topic 3: The Expectation of a Random Variable
 Topic 3: The Expectation of a Random Variable Course 003, 2016 Page 0 Expectation of a discrete random variable Definition: The expected value of a discrete random variable exists, and is defined by EX
Topic 3: The Expectation of a Random Variable Course 003, 2016 Page 0 Expectation of a discrete random variable Definition: The expected value of a discrete random variable exists, and is defined by EX
Discrete Distributions
 Chapter 2 Discrete Distributions 2.1 Random Variables of the Discrete Type An outcome space S is difficult to study if the elements of S are not numbers. However, we can associate each element/outcome
Chapter 2 Discrete Distributions 2.1 Random Variables of the Discrete Type An outcome space S is difficult to study if the elements of S are not numbers. However, we can associate each element/outcome
18.175: Lecture 13 Infinite divisibility and Lévy processes
 18.175 Lecture 13 18.175: Lecture 13 Infinite divisibility and Lévy processes Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Poisson random variable convergence Extend CLT idea to stable random variables Infinite divisibility
18.175 Lecture 13 18.175: Lecture 13 Infinite divisibility and Lévy processes Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Poisson random variable convergence Extend CLT idea to stable random variables Infinite divisibility
SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 12, STAT 4351
 SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 2, STAT 435 Welcome to your 2th homework. It looks like this is the last one! As usual, try to find mistakes and get extra points! Now let us look at your problems.. Problem 7.22.
SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 2, STAT 435 Welcome to your 2th homework. It looks like this is the last one! As usual, try to find mistakes and get extra points! Now let us look at your problems.. Problem 7.22.
Brief Review of Probability
 Maura Department of Economics and Finance Università Tor Vergata Outline 1 Distribution Functions Quantiles and Modes of a Distribution 2 Example 3 Example 4 Distributions Outline Distribution Functions
Maura Department of Economics and Finance Università Tor Vergata Outline 1 Distribution Functions Quantiles and Modes of a Distribution 2 Example 3 Example 4 Distributions Outline Distribution Functions
Lecture 18: Central Limit Theorem. Lisa Yan August 6, 2018
 Lecture 18: Central Limit Theorem Lisa Yan August 6, 2018 Announcements PS5 due today Pain poll PS6 out today Due next Monday 8/13 (1:30pm) (will not be accepted after Wed 8/15) Programming part: Java,
Lecture 18: Central Limit Theorem Lisa Yan August 6, 2018 Announcements PS5 due today Pain poll PS6 out today Due next Monday 8/13 (1:30pm) (will not be accepted after Wed 8/15) Programming part: Java,
STAT 516 Midterm Exam 2 Friday, March 7, 2008
 STAT 516 Midterm Exam 2 Friday, March 7, 2008 Name Purdue student ID (10 digits) 1. The testing booklet contains 8 questions. 2. Permitted Texas Instruments calculators: BA-35 BA II Plus BA II Plus Professional
STAT 516 Midterm Exam 2 Friday, March 7, 2008 Name Purdue student ID (10 digits) 1. The testing booklet contains 8 questions. 2. Permitted Texas Instruments calculators: BA-35 BA II Plus BA II Plus Professional
Expectation of Random Variables
 1 / 19 Expectation of Random Variables Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay February 13, 2015 2 / 19 Expectation of Discrete
1 / 19 Expectation of Random Variables Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay February 13, 2015 2 / 19 Expectation of Discrete
n(1 p i ) n 1 p i = 1 3 i=1 E(X i p = p i )P(p = p i ) = 1 3 p i = n 3 (p 1 + p 2 + p 3 ). p i i=1 P(X i = 1 p = p i )P(p = p i ) = p1+p2+p3
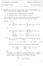 Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
Math 151. Rumbos Spring Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 3
 Math 151. Rumbos Spring 2014 1 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 3 1. Suppose that a book with n pages contains on average λ misprints per page. What is the probability that there will be at least
Math 151. Rumbos Spring 2014 1 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 3 1. Suppose that a book with n pages contains on average λ misprints per page. What is the probability that there will be at least
A Probability Primer. A random walk down a probabilistic path leading to some stochastic thoughts on chance events and uncertain outcomes.
 A Probability Primer A random walk down a probabilistic path leading to some stochastic thoughts on chance events and uncertain outcomes. Are you holding all the cards?? Random Events A random event, E,
A Probability Primer A random walk down a probabilistic path leading to some stochastic thoughts on chance events and uncertain outcomes. Are you holding all the cards?? Random Events A random event, E,
