and u and v are orthogonal if and only if u v = 0. u v = x1x2 + y1y2 + z1z2. 1. In R 3 the dot product is defined by
|
|
|
- Albert Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Linear Algebra [] 4.2 The Dot Product and Projections. In R 3 the dot product is defined by u v = u v cos θ. 2. For u = (x, y, z) and v = (x2, y2, z2), we have u v = xx2 + yy2 + zz2. 3. cos θ = u v u v, and u and v are orthogonal if and only if u v =.
2 Linear Algebra [2] 4.3 Planes A nonzero vector n is called a normal to a plane if it is orthogonal to every vector in the plane. A point P is on the plane with normal n through the point P if and only if n ( PP ) =.
3 Linear Algebra [3] and If n = (a, b, c), P(x, y, z) and P (x, y, z), then PP = OP OP = (x x, y y, z z) (a, b, c) (x x, y y, z z) =. Hence, the plane through P(x, y, z) with normal n = (a, b, c) is given by a(x x) + b(y y) + c(z z) =. Eg. An equation of the plane through P(,, 3) with normal n = (3,, 2) is 3(x ) (y + ) + 2(z 3) =. This simplifies to 3x y + 2z =.
4 Linear Algebra [4] 7. Orthogonality in R n Given X = x. and Y = xn X and Y is defined by y. in R n, the dot product of yn X Y = X T Y = xy + x2y2 + + xnyn. The length X of X is defined by X = X X = x 2 + x x2 n.
5 Linear Algebra [5] Eg. If X = and Y = 2 2, then 2 X Y = [ 2 ] 2 = =, 2 and X 2 = = 7 and X = 7.
6 Linear Algebra [6] Thm.. X Y = Y X 2. X (Y + Z) = X Y + X Z, (X + Y ) Z = X Z + Y Z. 3. (kx) Y = X (ky ) = k(x Y ), k R. 4. X, and X = X = O. 5. kx = k X, k R.
7 Linear Algebra [7] Eg. X + Y 2 = (X + Y ) (X + Y ) = X X + X Y + Y X + Y Y = X 2 + Y 2 + 2(X Y ). X X has length. Indeed, X X = X X =.
8 Linear Algebra [8] Def.. Two vectors X and Y are orthogonal if X Y =. 2. A set {X, X2, Xm} of nonzero vectors in R n is called an orthogonal set if Xi Xj = for i j. 3. An orthogonal set {X, X2,, Xm} is orthonormal if Xi = for all i. Rmk. If {X, X2,, Xm} is orthogonal, then { } X X, X2 X2,, Xm Xm is orthonormal.
9 Linear Algebra [9] Eg. X = form an orthogonal set and X 2 =, 3 4 2, X2 = and X3 = X2 3 2 = and X = 2 2 form an orthonormal set.
10 Linear Algebra [] Thm. Every orthogonal set of vectors in R n is linearly independent. Proof. Let {X, X2,, Xm} be orthogonal. Consider rx + r2x2 + + rmxm = O. = Xi O = Xi (rx + r2x2 + + rmxm) = r(xi X) + r2(xi X2) + + rm(xi Xm) = ri Xi 2. Hence ri = for each i.
11 Linear Algebra [] Thm. If {X, X2,, Xn} is an orthogonal basis of R n, then X = X X X 2 X + X X 2 X2 2 X X X n Xn 2 X n for every X in R n. Proof. If X = rx + r2x2 + + rnxn, then X Xi = ri(xi Xi) = ri Xi 2. Therefore, ri = X X i Xi 2.
12 Linear Algebra [2] Eg. X = 2, X2 = orthogonal basis of R 3. X = 3 and X3 = 3 = rx + r2x2 + r3x3. 4 form an 4 r = X X X 2 = 2, r 2 = X X 2 X2 2 = 3, r 3 = X X 3 X3 2 =. Hence, X = 2 X + 3 X 2.
13 Linear Algebra [3] Projections Def. If U is a subspace of R n, we define the orthogonal complement U of U by U = {X R n X Y = for all Y U}. Observe that if U = span{x,, Xm}, then U = {X R n X Xi = for all i}.
14 Linear Algebra [4] Eg. Find U if U = span, 2 x y Solution. Let X = U. z w 2 3 in R 4. Then X = and X = yield x y + 2z =, x 2z + 3w =.
15 Linear Algebra [5] [ ] [ ], x y = s z w 2 4 +t 3 3. U = span 2 4, 3 3.
16 Linear Algebra [6] Def. Let {X, X2,, Xm} be an orthogonal basis of a subspace U of R n. Given X in R n, we define proj U (X) = X X X 2 X + X X 2 X2 2 X X X m Xm 2 X m and call it the orthogonal projection of X on U.
17 Linear Algebra [7] Thm. If U is a subspace of R n and X R n, write P = proj U (X). Then. P U and X P U. 2. X P X Y for all Y U. 3. dim U + dim U = n. Proof.. Clearly, P U. (X P ) Xi = X Xi P Xi = X Xi X X i Xi 2 X i Xi = Thus X P U.
18 Linear Algebra [8] 2. Write X Y = (X P ) + (P Y ). Then P Y is in U and X P U. X Y 2 = (X P ) + (P Y ) 2 = X P 2 + P Y 2 + 2(X P ) (P Y ) = X P 2 + P Y 2 X P Let {X,, Xm} and {Y,, Yk} be orthogonal basis of U and U, respectively. Then {X,, Xm, Y,, Yn} is orthogonal, so linearly independent. If X R n, then X = P + (X P ). Thus {X,, Xm, Y,, Yn} spans R n.
19 Linear Algebra [9] Eg. Let U = span,. If X = 3 2, find the vector in U closest to X and express X as the sum of a vector in U and a vector in U. Solution. Note that, is orthogonal.
20 Linear Algebra [2] P = proj U (X) = X X X 2 X + X X 2 X2 2 X 2 = 4 3 X + 3 X 2 = = 3 X = P + (X P ) =
21 Linear Algebra [2] Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization Algorithm Question : Given a basis B = {Y,, Ym} of U, how can we obtain an orthogonal basis from B? Answer : Construct X,, Xm in U as follows. X = Y, X2 = Y2 Y 2 X X 2 X, X3 = Y3 Y 3 X X 2 X Y 3 X2 X2 2 X 2, Xm = Ym Y m X X 2 X Y m X2 X2 2 X 2 Y m Xm Xm 2 X m. Then {X,, Xm} is an orthogonal basis of U.
22 Linear Algebra [22] Proof. Let U = span{x}, U2 = span{x, X2},, Um = span{x,, Xm }. {X} is orthogonal. X2 = Y2 proj U (Y 2), X2 U {X, X2} is orthogonal. X3 = Y3 proj (Y U 2 3), X3 U 2 {X, X2, X3} is orthogonal. Continue the process. Xm = Ym proj (Y U m m), Xm U m {X,, Xm} is orthogonal.
23 Linear Algebra [23] Eg. Let U be the subspace of R 4 with basis {Y, Y2, Y3}, where Y =, Y2 = Find an orthogonal basis., Y3 =. Solution. X = Y, X2 = Y2 Y 2 X X 2 X = ( 2 3 ) = ,
24 Linear Algebra [24] X3 = Y3 Y 3 X X 2 X Y 3 X2 X2 2 X 2 Thus = ( 3 ), 2, ( 2 5 ) 2 = 3 is an orthogonal basis
25 Linear Algebra [25] How can we get an orthonormal basis? 3, 5 2,
Worksheet for Lecture 25 Section 6.4 Gram-Schmidt Process
 Worksheet for Lecture Name: Section.4 Gram-Schmidt Process Goal For a subspace W = Span{v,..., v n }, we want to find an orthonormal basis of W. Example Let W = Span{x, x } with x = and x =. Give an orthogonal
Worksheet for Lecture Name: Section.4 Gram-Schmidt Process Goal For a subspace W = Span{v,..., v n }, we want to find an orthonormal basis of W. Example Let W = Span{x, x } with x = and x =. Give an orthogonal
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
Vectors. Vectors and the scalar multiplication and vector addition operations:
 Vectors Vectors and the scalar multiplication and vector addition operations: x 1 x 1 y 1 2x 1 + 3y 1 x x n 1 = 2 x R n, 2 2 y + 3 2 2x = 2 + 3y 2............ x n x n y n 2x n + 3y n I ll use the two terms
Vectors Vectors and the scalar multiplication and vector addition operations: x 1 x 1 y 1 2x 1 + 3y 1 x x n 1 = 2 x R n, 2 2 y + 3 2 2x = 2 + 3y 2............ x n x n y n 2x n + 3y n I ll use the two terms
Chapter 4 Euclid Space
 Chapter 4 Euclid Space Inner Product Spaces Definition.. Let V be a real vector space over IR. A real inner product on V is a real valued function on V V, denoted by (, ), which satisfies () (x, y) = (y,
Chapter 4 Euclid Space Inner Product Spaces Definition.. Let V be a real vector space over IR. A real inner product on V is a real valued function on V V, denoted by (, ), which satisfies () (x, y) = (y,
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Math 261 Lecture Notes: Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 and 6.4 Orthogonal Sets and Projections
 Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./ Orthonormal Sets A set of vectors {u, u,...,
Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./ Orthonormal Sets A set of vectors {u, u,...,
Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review. Give complete answers to each of the following questions. Show all of your work.
 Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review Give complete answers to each of the following questions Show all of your work Note: You might struggle with some of these questions, either because it has
Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review Give complete answers to each of the following questions Show all of your work Note: You might struggle with some of these questions, either because it has
MTH 2310, FALL Introduction
 MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
Solutions to Review Problems for Chapter 6 ( ), 7.1
 Solutions to Review Problems for Chapter (-, 7 The Final Exam is on Thursday, June,, : AM : AM at NESBITT Final Exam Breakdown Sections % -,7-9,- - % -9,-,7,-,-7 - % -, 7 - % Let u u and v Let x x x x,
Solutions to Review Problems for Chapter (-, 7 The Final Exam is on Thursday, June,, : AM : AM at NESBITT Final Exam Breakdown Sections % -,7-9,- - % -9,-,7,-,-7 - % -, 7 - % Let u u and v Let x x x x,
Projection Theorem 1
 Projection Theorem 1 Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality Lemma. (Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality) For all x, y in an inner product space, [ xy, ] x y. Equality holds if and only if x y or y θ. Proof. If y θ, the inequality
Projection Theorem 1 Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality Lemma. (Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality) For all x, y in an inner product space, [ xy, ] x y. Equality holds if and only if x y or y θ. Proof. If y θ, the inequality
Linear Models Review
 Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
MATH 260 LINEAR ALGEBRA EXAM III Fall 2014
 MAH 60 LINEAR ALGEBRA EXAM III Fall 0 Instructions: the use of built-in functions of your calculator such as det( ) or RREF is permitted ) Consider the table and the vectors and matrices given below Fill
MAH 60 LINEAR ALGEBRA EXAM III Fall 0 Instructions: the use of built-in functions of your calculator such as det( ) or RREF is permitted ) Consider the table and the vectors and matrices given below Fill
Chapter 6: Orthogonality
 Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Lecture 10: Vector Algebra: Orthogonal Basis
 Lecture 0: Vector Algebra: Orthogonal Basis Orthogonal Basis of a subspace Computing an orthogonal basis for a subspace using Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization Process Orthogonal Set Any set of vectors that
Lecture 0: Vector Algebra: Orthogonal Basis Orthogonal Basis of a subspace Computing an orthogonal basis for a subspace using Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization Process Orthogonal Set Any set of vectors that
v = w if the same length and the same direction Given v, we have the negative v. We denote the length of v by v.
 Linear Algebra [1] 4.1 Vectors and Lines Definition scalar : magnitude vector : magnitude and direction Geometrically, a vector v can be represented by an arrow. We denote the length of v by v. zero vector
Linear Algebra [1] 4.1 Vectors and Lines Definition scalar : magnitude vector : magnitude and direction Geometrically, a vector v can be represented by an arrow. We denote the length of v by v. zero vector
Section 6.2, 6.3 Orthogonal Sets, Orthogonal Projections
 Section 6. 6. Orthogonal Sets Orthogonal Projections Main Ideas in these sections: Orthogonal set = A set of mutually orthogonal vectors. OG LI. Orthogonal Projection of y onto u or onto an OG set {u u
Section 6. 6. Orthogonal Sets Orthogonal Projections Main Ideas in these sections: Orthogonal set = A set of mutually orthogonal vectors. OG LI. Orthogonal Projection of y onto u or onto an OG set {u u
orthogonal relations between vectors and subspaces Then we study some applications in vector spaces and linear systems, including Orthonormal Basis,
 5 Orthogonality Goals: We use scalar products to find the length of a vector, the angle between 2 vectors, projections, orthogonal relations between vectors and subspaces Then we study some applications
5 Orthogonality Goals: We use scalar products to find the length of a vector, the angle between 2 vectors, projections, orthogonal relations between vectors and subspaces Then we study some applications
Section 6.1. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality
 Section 6. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Almost solve the equation Ax = b Problem: In the real world, data is imperfect. x v u But due to measurement error, the measured x is not
Section 6. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Almost solve the equation Ax = b Problem: In the real world, data is imperfect. x v u But due to measurement error, the measured x is not
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T. KEMP)
 MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
Math 416, Spring 2010 Gram-Schmidt, the QR-factorization, Orthogonal Matrices March 4, 2010 GRAM-SCHMIDT, THE QR-FACTORIZATION, ORTHOGONAL MATRICES
 Math 46, Spring 00 Gram-Schmidt, the QR-factorization, Orthogonal Matrices March 4, 00 GRAM-SCHMIDT, THE QR-FACTORIZATION, ORTHOGONAL MATRICES Recap Yesterday we talked about several new, important concepts
Math 46, Spring 00 Gram-Schmidt, the QR-factorization, Orthogonal Matrices March 4, 00 GRAM-SCHMIDT, THE QR-FACTORIZATION, ORTHOGONAL MATRICES Recap Yesterday we talked about several new, important concepts
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH M Test #1. July 11, 2013 Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 222 3. M Test # July, 23 Solutions. For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 222 3. M Test # July, 23 Solutions. For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For
Linear Algebra Massoud Malek
 CSUEB Linear Algebra Massoud Malek Inner Product and Normed Space In all that follows, the n n identity matrix is denoted by I n, the n n zero matrix by Z n, and the zero vector by θ n An inner product
CSUEB Linear Algebra Massoud Malek Inner Product and Normed Space In all that follows, the n n identity matrix is denoted by I n, the n n zero matrix by Z n, and the zero vector by θ n An inner product
LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN
 LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN c W W L Chen, 1997, 2008. This chapter is available free to all individuals, on the understanding that it is not to be used for financial gain, and may be downloaded and/or photocopied,
LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN c W W L Chen, 1997, 2008. This chapter is available free to all individuals, on the understanding that it is not to be used for financial gain, and may be downloaded and/or photocopied,
Homework 5. (due Wednesday 8 th Nov midnight)
 Homework (due Wednesday 8 th Nov midnight) Use this definition for Column Space of a Matrix Column Space of a matrix A is the set ColA of all linear combinations of the columns of A. In other words, if
Homework (due Wednesday 8 th Nov midnight) Use this definition for Column Space of a Matrix Column Space of a matrix A is the set ColA of all linear combinations of the columns of A. In other words, if
Two Posts to Fill On School Board
 Y Y 9 86 4 4 qz 86 x : ( ) z 7 854 Y x 4 z z x x 4 87 88 Y 5 x q x 8 Y 8 x x : 6 ; : 5 x ; 4 ( z ; ( ) ) x ; z 94 ; x 3 3 3 5 94 ; ; ; ; 3 x : 5 89 q ; ; x ; x ; ; x : ; ; ; ; ; ; 87 47% : () : / : 83
Y Y 9 86 4 4 qz 86 x : ( ) z 7 854 Y x 4 z z x x 4 87 88 Y 5 x q x 8 Y 8 x x : 6 ; : 5 x ; 4 ( z ; ( ) ) x ; z 94 ; x 3 3 3 5 94 ; ; ; ; 3 x : 5 89 q ; ; x ; x ; ; x : ; ; ; ; ; ; 87 47% : () : / : 83
Announcements Monday, November 20
 Announcements Monday, November 20 You already have your midterms! Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be awarded depends on many factors, and
Announcements Monday, November 20 You already have your midterms! Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be awarded depends on many factors, and
1.6 and 5.3. Curve Fitting One of the broadest applications of linear algebra is to curve fitting, especially in determining unknown coefficients in
 16 and 53 Curve Fitting One of the broadest applications of linear algebra is to curve fitting, especially in determining unknown coefficients in functions You should know that, given two points in the
16 and 53 Curve Fitting One of the broadest applications of linear algebra is to curve fitting, especially in determining unknown coefficients in functions You should know that, given two points in the
MTH 2032 SemesterII
 MTH 202 SemesterII 2010-11 Linear Algebra Worked Examples Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2011 ii Contents Table of Contents
MTH 202 SemesterII 2010-11 Linear Algebra Worked Examples Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2011 ii Contents Table of Contents
Chapter 6. Orthogonality and Least Squares
 Chapter 6 Orthogonality and Least Squares Section 6.1 Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Recall: This course is about learning to: Solve the matrix equation Ax = b Solve the matrix equation
Chapter 6 Orthogonality and Least Squares Section 6.1 Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Recall: This course is about learning to: Solve the matrix equation Ax = b Solve the matrix equation
MA 265 FINAL EXAM Fall 2012
 MA 265 FINAL EXAM Fall 22 NAME: INSTRUCTOR S NAME:. There are a total of 25 problems. You should show work on the exam sheet, and pencil in the correct answer on the scantron. 2. No books, notes, or calculators
MA 265 FINAL EXAM Fall 22 NAME: INSTRUCTOR S NAME:. There are a total of 25 problems. You should show work on the exam sheet, and pencil in the correct answer on the scantron. 2. No books, notes, or calculators
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 34: Review for Test 2.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 34: Review for Test 2. Topics for Test 2 Linear transformations (Leon 4.1 4.3) Matrix transformations Matrix of a linear mapping Similar matrices Orthogonality (Leon 5.1
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 34: Review for Test 2. Topics for Test 2 Linear transformations (Leon 4.1 4.3) Matrix transformations Matrix of a linear mapping Similar matrices Orthogonality (Leon 5.1
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH M Test #2 Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 3. M Test # Solutions. (8 pts) For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For this
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 3. M Test # Solutions. (8 pts) For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For this
There are two things that are particularly nice about the first basis
 Orthogonality and the Gram-Schmidt Process In Chapter 4, we spent a great deal of time studying the problem of finding a basis for a vector space We know that a basis for a vector space can potentially
Orthogonality and the Gram-Schmidt Process In Chapter 4, we spent a great deal of time studying the problem of finding a basis for a vector space We know that a basis for a vector space can potentially
6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares
 Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares CSIE NCU 1 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares 6.1 Inner product, length, and orthogonality. 2 6.2 Orthogonal sets... 8 6.3 Orthogonal projections... 13
Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares CSIE NCU 1 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares 6.1 Inner product, length, and orthogonality. 2 6.2 Orthogonal sets... 8 6.3 Orthogonal projections... 13
Math Linear Algebra
 Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Orthonormal Bases; Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition
 Orthonormal Bases; Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 205 Motivation When working with an inner product space, the most
Orthonormal Bases; Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 205 Motivation When working with an inner product space, the most
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II
 Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Math 1180, Notes, 14 1 C. v 1 v n v 2. C A ; w n. A and w = v i w i : v w = i=1
 Math 8, 9 Notes, 4 Orthogonality We now start using the dot product a lot. v v = v v n then by Recall that if w w ; w n and w = v w = nx v i w i : Using this denition, we dene the \norm", or length, of
Math 8, 9 Notes, 4 Orthogonality We now start using the dot product a lot. v v = v v n then by Recall that if w w ; w n and w = v w = nx v i w i : Using this denition, we dene the \norm", or length, of
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 191 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture 1: Inner Products, Length, Orthogonality Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 191Applied Linear Algebra p.1/ Motivation Not all linear systems have
Math 191 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture 1: Inner Products, Length, Orthogonality Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 191Applied Linear Algebra p.1/ Motivation Not all linear systems have
MATH 31 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL
 MATH 3 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL MAIN TOPICS FOR THE FINAL EXAM:. Vectors. Dot product. Cross product. Geometric applications. 2. Row reduction. Null space, column space, row space, left
MATH 3 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL MAIN TOPICS FOR THE FINAL EXAM:. Vectors. Dot product. Cross product. Geometric applications. 2. Row reduction. Null space, column space, row space, left
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning:
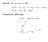 Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Vector spaces. DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis.
 Vector spaces DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Vector space Consists of: A set V A scalar
Vector spaces DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Vector space Consists of: A set V A scalar
The Gram-Schmidt Process 1
 The Gram-Schmidt Process In this section all vector spaces will be subspaces of some R m. Definition.. Let S = {v...v n } R m. The set S is said to be orthogonal if v v j = whenever i j. If in addition
The Gram-Schmidt Process In this section all vector spaces will be subspaces of some R m. Definition.. Let S = {v...v n } R m. The set S is said to be orthogonal if v v j = whenever i j. If in addition
MTH 309Y 37. Inner product spaces. = a 1 b 1 + a 2 b a n b n
 MTH 39Y 37. Inner product spaces Recall: ) The dot product in R n : a. a n b. b n = a b + a 2 b 2 +...a n b n 2) Properties of the dot product: a) u v = v u b) (u + v) w = u w + v w c) (cu) v = c(u v)
MTH 39Y 37. Inner product spaces Recall: ) The dot product in R n : a. a n b. b n = a b + a 2 b 2 +...a n b n 2) Properties of the dot product: a) u v = v u b) (u + v) w = u w + v w c) (cu) v = c(u v)
LINEAR ALGEBRA 1, 2012-I PARTIAL EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 LINEAR ALGEBRA, -I PARTIAL EXAM SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem (a) For each of the two matrices below, (i) determine whether it is diagonalizable, (ii) determine whether it is orthogonally diagonalizable,
LINEAR ALGEBRA, -I PARTIAL EXAM SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem (a) For each of the two matrices below, (i) determine whether it is diagonalizable, (ii) determine whether it is orthogonally diagonalizable,
Transpose & Dot Product
 Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
1. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer.
 MATH 5 Practice Problem Set Spring 7. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer. () Determine all the values of a for which the system has infinitely many solutions: x +
MATH 5 Practice Problem Set Spring 7. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer. () Determine all the values of a for which the system has infinitely many solutions: x +
Homework 11 Solutions. Math 110, Fall 2013.
 Homework 11 Solutions Math 110, Fall 2013 1 a) Suppose that T were self-adjoint Then, the Spectral Theorem tells us that there would exist an orthonormal basis of P 2 (R), (p 1, p 2, p 3 ), consisting
Homework 11 Solutions Math 110, Fall 2013 1 a) Suppose that T were self-adjoint Then, the Spectral Theorem tells us that there would exist an orthonormal basis of P 2 (R), (p 1, p 2, p 3 ), consisting
OWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
x 3y 2z = 6 1.2) 2x 4y 3z = 8 3x + 6y + 8z = 5 x + 3y 2z + 5t = 4 1.5) 2x + 8y z + 9t = 9 3x + 5y 12z + 17t = 7
 Linear Algebra and its Applications-Lab 1 1) Use Gaussian elimination to solve the following systems x 1 + x 2 2x 3 + 4x 4 = 5 1.1) 2x 1 + 2x 2 3x 3 + x 4 = 3 3x 1 + 3x 2 4x 3 2x 4 = 1 x + y + 2z = 4 1.4)
Linear Algebra and its Applications-Lab 1 1) Use Gaussian elimination to solve the following systems x 1 + x 2 2x 3 + 4x 4 = 5 1.1) 2x 1 + 2x 2 3x 3 + x 4 = 3 3x 1 + 3x 2 4x 3 2x 4 = 1 x + y + 2z = 4 1.4)
ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment NOTRequiredJustHWformatOfQuizReviewForExam3part2 due 12/31/2014 at 07:10pm CST
 me me ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment NOTRequiredJustHWformatOfQuizReviewForExam3part2 due 12/31/2014 at 07:10pm CST 1. (1 pt) local/library/ui/eigentf.pg A is n n an matrices.. There are an infinite number
me me ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment NOTRequiredJustHWformatOfQuizReviewForExam3part2 due 12/31/2014 at 07:10pm CST 1. (1 pt) local/library/ui/eigentf.pg A is n n an matrices.. There are an infinite number
Transpose & Dot Product
 Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
MATH. 20F SAMPLE FINAL (WINTER 2010)
 MATH. 20F SAMPLE FINAL (WINTER 2010) You have 3 hours for this exam. Please write legibly and show all working. No calculators are allowed. Write your name, ID number and your TA s name below. The total
MATH. 20F SAMPLE FINAL (WINTER 2010) You have 3 hours for this exam. Please write legibly and show all working. No calculators are allowed. Write your name, ID number and your TA s name below. The total
Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality
 Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Linear Algebra MATH 2076 Linear Algebra,, Chapter 6, Section 1 1 / 13 Algebraic Definition for Dot Product u 1 v 1 u 2 Let u =., v = v 2. be vectors in Rn. The
Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Linear Algebra MATH 2076 Linear Algebra,, Chapter 6, Section 1 1 / 13 Algebraic Definition for Dot Product u 1 v 1 u 2 Let u =., v = v 2. be vectors in Rn. The
Section 6.4. The Gram Schmidt Process
 Section 6.4 The Gram Schmidt Process Motivation The procedures in 6 start with an orthogonal basis {u, u,..., u m}. Find the B-coordinates of a vector x using dot products: x = m i= x u i u i u i u i Find
Section 6.4 The Gram Schmidt Process Motivation The procedures in 6 start with an orthogonal basis {u, u,..., u m}. Find the B-coordinates of a vector x using dot products: x = m i= x u i u i u i u i Find
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET
 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
Lecture 13: Orthogonal projections and least squares (Section ) Thang Huynh, UC San Diego 2/9/2018
 Lecture 13: Orthogonal projections and least squares (Section 3.2-3.3) Thang Huynh, UC San Diego 2/9/2018 Orthogonal projection onto subspaces Theorem. Let W be a subspace of R n. Then, each x in R n can
Lecture 13: Orthogonal projections and least squares (Section 3.2-3.3) Thang Huynh, UC San Diego 2/9/2018 Orthogonal projection onto subspaces Theorem. Let W be a subspace of R n. Then, each x in R n can
The Gram Schmidt Process
 u 2 u The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple
u 2 u The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple
The Gram Schmidt Process
 The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple case
The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple case
Orthogonal Complements
 Orthogonal Complements Definition Let W be a subspace of R n. If a vector z is orthogonal to every vector in W, then z is said to be orthogonal to W. The set of all such vectors z is called the orthogonal
Orthogonal Complements Definition Let W be a subspace of R n. If a vector z is orthogonal to every vector in W, then z is said to be orthogonal to W. The set of all such vectors z is called the orthogonal
Math 413/513 Chapter 6 (from Friedberg, Insel, & Spence)
 Math 413/513 Chapter 6 (from Friedberg, Insel, & Spence) David Glickenstein December 7, 2015 1 Inner product spaces In this chapter, we will only consider the elds R and C. De nition 1 Let V be a vector
Math 413/513 Chapter 6 (from Friedberg, Insel, & Spence) David Glickenstein December 7, 2015 1 Inner product spaces In this chapter, we will only consider the elds R and C. De nition 1 Let V be a vector
Answer Keys For Math 225 Final Review Problem
 Answer Keys For Math Final Review Problem () For each of the following maps T, Determine whether T is a linear transformation. If T is a linear transformation, determine whether T is -, onto and/or bijective.
Answer Keys For Math Final Review Problem () For each of the following maps T, Determine whether T is a linear transformation. If T is a linear transformation, determine whether T is -, onto and/or bijective.
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Answer any eight)
 Name of the student : Roll No : CS65: Linear Algebra and Random Processes Exam - Course Instructor : Prashanth L.A. Date : Sep-24, 27 Duration : 5 minutes INSTRUCTIONS: The test will be evaluated ONLY
Name of the student : Roll No : CS65: Linear Algebra and Random Processes Exam - Course Instructor : Prashanth L.A. Date : Sep-24, 27 Duration : 5 minutes INSTRUCTIONS: The test will be evaluated ONLY
Then x 1,..., x n is a basis as desired. Indeed, it suffices to verify that it spans V, since n = dim(v ). We may write any v V as r
 Practice final solutions. I did not include definitions which you can find in Axler or in the course notes. These solutions are on the terse side, but would be acceptable in the final. However, if you
Practice final solutions. I did not include definitions which you can find in Axler or in the course notes. These solutions are on the terse side, but would be acceptable in the final. However, if you
Miderm II Solutions To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce
![Miderm II Solutions To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce Miderm II Solutions To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce](/thumbs/88/117490958.jpg) Miderm II Solutions Problem. [8 points] (i) [4] Find the inverse of the matrix A = To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce We have A = 2 2 (ii) [2] Possibly
Miderm II Solutions Problem. [8 points] (i) [4] Find the inverse of the matrix A = To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce We have A = 2 2 (ii) [2] Possibly
2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution.
 1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
10 Orthogonality Orthogonal subspaces
 10 Orthogonality 10.1 Orthogonal subspaces In the plane R 2 we think of the coordinate axes as being orthogonal (perpendicular) to each other. We can express this in terms of vectors by saying that every
10 Orthogonality 10.1 Orthogonal subspaces In the plane R 2 we think of the coordinate axes as being orthogonal (perpendicular) to each other. We can express this in terms of vectors by saying that every
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET
 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
Announcements Wednesday, November 15
 3π 4 Announcements Wednesday, November 15 Reviews today: Recitation Style Solve and discuss Practice problems in groups Preparing for the exam tips and strategies It is not mandatory Eduardo at Culc 141,
3π 4 Announcements Wednesday, November 15 Reviews today: Recitation Style Solve and discuss Practice problems in groups Preparing for the exam tips and strategies It is not mandatory Eduardo at Culc 141,
Problem Set (T) If A is an m n matrix, B is an n p matrix and D is a p s matrix, then show
 MTH 0: Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology - Kanpur Problem Set Problems marked (T) are for discussions in Tutorial sessions (T) If A is an m n matrix,
MTH 0: Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology - Kanpur Problem Set Problems marked (T) are for discussions in Tutorial sessions (T) If A is an m n matrix,
MAT Linear Algebra Collection of sample exams
 MAT 342 - Linear Algebra Collection of sample exams A-x. (0 pts Give the precise definition of the row echelon form. 2. ( 0 pts After performing row reductions on the augmented matrix for a certain system
MAT 342 - Linear Algebra Collection of sample exams A-x. (0 pts Give the precise definition of the row echelon form. 2. ( 0 pts After performing row reductions on the augmented matrix for a certain system
x = t 1 x 1 + t 2 x t k x k
 Def.: Given vectors x,...,x k in R n, the set of all their linear combinations is called their span, and is denoted by span(x,...,x k ) Thm.: span(x,...,x k ) is a subspace of R n Def.: If V is a subspace
Def.: Given vectors x,...,x k in R n, the set of all their linear combinations is called their span, and is denoted by span(x,...,x k ) Thm.: span(x,...,x k ) is a subspace of R n Def.: If V is a subspace
A Primer in Econometric Theory
 A Primer in Econometric Theory Lecture 1: Vector Spaces John Stachurski Lectures by Akshay Shanker May 5, 2017 1/104 Overview Linear algebra is an important foundation for mathematics and, in particular,
A Primer in Econometric Theory Lecture 1: Vector Spaces John Stachurski Lectures by Akshay Shanker May 5, 2017 1/104 Overview Linear algebra is an important foundation for mathematics and, in particular,
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2018 Lecture Notes Note 25
 EECS 6 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 8 Lecture Notes Note 5 5. Speeding up OMP In the last lecture note, we introduced orthogonal matching pursuit OMP, an algorithm that can extract
EECS 6 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 8 Lecture Notes Note 5 5. Speeding up OMP In the last lecture note, we introduced orthogonal matching pursuit OMP, an algorithm that can extract
Chapter 2. Vectors and Vector Spaces
 2.2. Cartesian Coordinates and Geometrical Properties of Vectors 1 Chapter 2. Vectors and Vector Spaces Section 2.2. Cartesian Coordinates and Geometrical Properties of Vectors Note. There is a natural
2.2. Cartesian Coordinates and Geometrical Properties of Vectors 1 Chapter 2. Vectors and Vector Spaces Section 2.2. Cartesian Coordinates and Geometrical Properties of Vectors Note. There is a natural
Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems
 Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems Heinrich Voss voss@tu-harburg.de Hamburg University of Technology Institute of Numerical Simulation TUHH Heinrich Voss Numerical Linear Algebra
Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems Heinrich Voss voss@tu-harburg.de Hamburg University of Technology Institute of Numerical Simulation TUHH Heinrich Voss Numerical Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra. Session 12
 Linear Algebra. Session 12 Dr. Marco A Roque Sol 08/01/2017 Example 12.1 Find the constant function that is the least squares fit to the following data x 0 1 2 3 f(x) 1 0 1 2 Solution c = 1 c = 0 f (x)
Linear Algebra. Session 12 Dr. Marco A Roque Sol 08/01/2017 Example 12.1 Find the constant function that is the least squares fit to the following data x 0 1 2 3 f(x) 1 0 1 2 Solution c = 1 c = 0 f (x)
ECS130 Scientific Computing. Lecture 1: Introduction. Monday, January 7, 10:00 10:50 am
 ECS130 Scientific Computing Lecture 1: Introduction Monday, January 7, 10:00 10:50 am About Course: ECS130 Scientific Computing Professor: Zhaojun Bai Webpage: http://web.cs.ucdavis.edu/~bai/ecs130/ Today
ECS130 Scientific Computing Lecture 1: Introduction Monday, January 7, 10:00 10:50 am About Course: ECS130 Scientific Computing Professor: Zhaojun Bai Webpage: http://web.cs.ucdavis.edu/~bai/ecs130/ Today
1. Subspaces A subset M of Hilbert space H is a subspace of it is closed under the operation of forming linear combinations;i.e.,
 Abstract Hilbert Space Results We have learned a little about the Hilbert spaces L U and and we have at least defined H 1 U and the scale of Hilbert spaces H p U. Now we are going to develop additional
Abstract Hilbert Space Results We have learned a little about the Hilbert spaces L U and and we have at least defined H 1 U and the scale of Hilbert spaces H p U. Now we are going to develop additional
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Linear Algebra Practice Problems Page of 7 Linear Algebra Practice Problems These problems cover Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 7 of Elementary Linear Algebra, 6th ed, by Ron Larson and David Falvo (ISBN-3 = 978--68-78376-2,
Linear Algebra Practice Problems Page of 7 Linear Algebra Practice Problems These problems cover Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 7 of Elementary Linear Algebra, 6th ed, by Ron Larson and David Falvo (ISBN-3 = 978--68-78376-2,
Conceptual Questions for Review
 Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Practice Final Exam. Solutions.
 MATH Applied Linear Algebra December 6, 8 Practice Final Exam Solutions Find the standard matrix f the linear transfmation T : R R such that T, T, T Solution: Easy to see that the transfmation T can be
MATH Applied Linear Algebra December 6, 8 Practice Final Exam Solutions Find the standard matrix f the linear transfmation T : R R such that T, T, T Solution: Easy to see that the transfmation T can be
Exercise Solutions to Functional Analysis
 Exercise Solutions to Functional Analysis Note: References refer to M. Schechter, Principles of Functional Analysis Exersize that. Let φ,..., φ n be an orthonormal set in a Hilbert space H. Show n f n
Exercise Solutions to Functional Analysis Note: References refer to M. Schechter, Principles of Functional Analysis Exersize that. Let φ,..., φ n be an orthonormal set in a Hilbert space H. Show n f n
7. Dimension and Structure.
 7. Dimension and Structure 7.1. Basis and Dimension Bases for Subspaces Example 2 The standard unit vectors e 1, e 2,, e n are linearly independent, for if we write (2) in component form, then we obtain
7. Dimension and Structure 7.1. Basis and Dimension Bases for Subspaces Example 2 The standard unit vectors e 1, e 2,, e n are linearly independent, for if we write (2) in component form, then we obtain
MATH 369 Linear Algebra
 Assignment # Problem # A father and his two sons are together 00 years old. The father is twice as old as his older son and 30 years older than his younger son. How old is each person? Problem # 2 Determine
Assignment # Problem # A father and his two sons are together 00 years old. The father is twice as old as his older son and 30 years older than his younger son. How old is each person? Problem # 2 Determine
Solutions: Problem Set 3 Math 201B, Winter 2007
 Solutions: Problem Set 3 Math 201B, Winter 2007 Problem 1. Prove that an infinite-dimensional Hilbert space is a separable metric space if and only if it has a countable orthonormal basis. Solution. If
Solutions: Problem Set 3 Math 201B, Winter 2007 Problem 1. Prove that an infinite-dimensional Hilbert space is a separable metric space if and only if it has a countable orthonormal basis. Solution. If
MATH 1120 (LINEAR ALGEBRA 1), FINAL EXAM FALL 2011 SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE VERSION
 MATH (LINEAR ALGEBRA ) FINAL EXAM FALL SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE VERSION Problem (a) For each matrix below (i) find a basis for its column space (ii) find a basis for its row space (iii) determine whether
MATH (LINEAR ALGEBRA ) FINAL EXAM FALL SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE VERSION Problem (a) For each matrix below (i) find a basis for its column space (ii) find a basis for its row space (iii) determine whether
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 10 November 23, Linear models
 DS-GA 2 Lecture notes November 23, 2 Linear functions Linear models A linear model encodes the assumption that two quantities are linearly related. Mathematically, this is characterized using linear functions.
DS-GA 2 Lecture notes November 23, 2 Linear functions Linear models A linear model encodes the assumption that two quantities are linearly related. Mathematically, this is characterized using linear functions.
MATH 167: APPLIED LINEAR ALGEBRA Least-Squares
 MATH 167: APPLIED LINEAR ALGEBRA Least-Squares October 30, 2014 Least Squares We do a series of experiments, collecting data. We wish to see patterns!! We expect the output b to be a linear function of
MATH 167: APPLIED LINEAR ALGEBRA Least-Squares October 30, 2014 Least Squares We do a series of experiments, collecting data. We wish to see patterns!! We expect the output b to be a linear function of
Math Real Analysis II
 Math 4 - Real Analysis II Solutions to Homework due May Recall that a function f is called even if f( x) = f(x) and called odd if f( x) = f(x) for all x. We saw that these classes of functions had a particularly
Math 4 - Real Analysis II Solutions to Homework due May Recall that a function f is called even if f( x) = f(x) and called odd if f( x) = f(x) for all x. We saw that these classes of functions had a particularly
3. For a given dataset and linear model, what do you think is true about least squares estimates? Is Ŷ always unique? Yes. Is ˆβ always unique? No.
 7. LEAST SQUARES ESTIMATION 1 EXERCISE: Least-Squares Estimation and Uniqueness of Estimates 1. For n real numbers a 1,...,a n, what value of a minimizes the sum of squared distances from a to each of
7. LEAST SQUARES ESTIMATION 1 EXERCISE: Least-Squares Estimation and Uniqueness of Estimates 1. For n real numbers a 1,...,a n, what value of a minimizes the sum of squared distances from a to each of
Announcements Wednesday, November 15
 Announcements Wednesday, November 15 The third midterm is on this Friday, November 17. The exam covers 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.5. About half the problems will be conceptual, and the other half computational.
Announcements Wednesday, November 15 The third midterm is on this Friday, November 17. The exam covers 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.5. About half the problems will be conceptual, and the other half computational.
REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE
 REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE PHILIP BROCOUM Let V be a finite dimensional real linear space. Definition 1. A function, : V V R is a bilinear form in V if for all x 1, x, x, y 1, y, y V and all k R,
REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE PHILIP BROCOUM Let V be a finite dimensional real linear space. Definition 1. A function, : V V R is a bilinear form in V if for all x 1, x, x, y 1, y, y V and all k R,
MATH 22A: LINEAR ALGEBRA Chapter 4
 MATH 22A: LINEAR ALGEBRA Chapter 4 Jesús De Loera, UC Davis November 30, 2012 Orthogonality and Least Squares Approximation QUESTION: Suppose Ax = b has no solution!! Then what to do? Can we find an Approximate
MATH 22A: LINEAR ALGEBRA Chapter 4 Jesús De Loera, UC Davis November 30, 2012 Orthogonality and Least Squares Approximation QUESTION: Suppose Ax = b has no solution!! Then what to do? Can we find an Approximate
MIDTERM I LINEAR ALGEBRA. Friday February 16, Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MIDTERM I LIEAR ALGEBRA MATH 215 Friday February 16, 2018. ame PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIOS Please answer the all of the questions, and show your work. You must explain your answers to get credit. You will be
MIDTERM I LIEAR ALGEBRA MATH 215 Friday February 16, 2018. ame PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIOS Please answer the all of the questions, and show your work. You must explain your answers to get credit. You will be
4.4. Orthogonality. Note. This section is awesome! It is very geometric and shows that much of the geometry of R n holds in Hilbert spaces.
 4.4. Orthogonality 1 4.4. Orthogonality Note. This section is awesome! It is very geometric and shows that much of the geometry of R n holds in Hilbert spaces. Definition. Elements x and y of a Hilbert
4.4. Orthogonality 1 4.4. Orthogonality Note. This section is awesome! It is very geometric and shows that much of the geometry of R n holds in Hilbert spaces. Definition. Elements x and y of a Hilbert
Math 18, Linear Algebra, Lecture C00, Spring 2017 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam
 Math 8, Linear Algebra, Lecture C, Spring 7 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam. The augmentedmatrix of a linear system has been transformed by row operations into 5 4 8. Determine if the system
Math 8, Linear Algebra, Lecture C, Spring 7 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam. The augmentedmatrix of a linear system has been transformed by row operations into 5 4 8. Determine if the system
MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix
 MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix Definition: Let L : V 1 V 2 be a linear operator. The null space N (L) of L is the subspace of V 1 defined by N (L) = {x
MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix Definition: Let L : V 1 V 2 be a linear operator. The null space N (L) of L is the subspace of V 1 defined by N (L) = {x
Designing Information Devices and Systems II
 EECS 16B Fall 2016 Designing Information Devices and Systems II Linear Algebra Notes Introduction In this set of notes, we will derive the linear least squares equation, study the properties symmetric
EECS 16B Fall 2016 Designing Information Devices and Systems II Linear Algebra Notes Introduction In this set of notes, we will derive the linear least squares equation, study the properties symmetric
