Solving Quadratic Equations by the New and Improved Factoring AC Method (by Nghi H. Nguyen)
|
|
|
- Jack Chapman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solving Quadratic Equations by the New and Improved Factoring AC Method (by Nghi H. Nguyen) So far, the ac method (YouTube.com) has been the most popular factoring method to solve a quadratic equation in general form ax² + bx + c = 0 that can be factored. Another factoring method, called the Box Method (YouTube. com) offers a similar solving approach. THE FACTORING AC METHOD. Given a factorable quadratic equation in standard form ax² + bx + c = 0. This method aims to factor this equation into 2 binomials in x by replacing in the equation the term (bx) by the 2 terms (b1x) and (b2x) that satisfy these 2 conditions: 1. The product b1*b2 = ac 2. The sum (b1 + b2) = b. Example 1. Solve: x² - 11x 102 = 0. Solution. Find 2 numbers that the product is b1*b2 = c = -102 and the sum (b1 + b2) = b = 6. Proceed by composing all factors of ac = Proceeding: (-1, 102),(1, -102),(-2, 51),(2, -51)(-3, 34)(3, -34),(-6, 17),(6, -17).OK. The last sum is: (6-17) = -11 = b. Then b1 = 6 and b2 = -17. Next, replace in the equation the term (-11x) by the 2 terms (6x) and (-17x), then group terms into common factors: x² + 6x = x(x + 6) 17(x + 6) = (x + 6)(x 17) = 0. Finally, solve the 2 binomials for x. (x + 6) = 0 x = -6 (x 17) = 0 x = 17. Example 2. Solve: 15x² 53x + 16 = 0 Solution. Find 2 numbers that their product is a*c = 15*16 = 240 and their sum = b = -53. Proceeding: (1, 240),(2, 120),(3, 80),(4, 60)(5, 48) (1, -240),(-2, -120),(-3, -80)(-4, -60),(-5, -48). OK. b1 = -5 and b2 = -48 Replace in the equation the term -53x by the 2 terms (-5x) and (-48x), then group terms: 15x² 5x 48x + 16 = 5x(3x 1) 16(3x -1) = (3x 1)(5x 16) = 0. Next, solve the 2 binomials: (3x 1) = 0 x = 1/3 (5x 16) = 0 x = 16/5 Remark. In the solving approach, in order to get the product ac = 240, we have to compose both factor pairs (1, 240) and (-1, -240). Then, we do the same thing for (2, 120) and (-2, -120) and so on. Is it possible to simplify the process if we know in advance the signs of the 2 real roots? Yes, if we apply The Rule of Signs For Real Roots of a quadratic equation into the solving approach. Page 1 of 5
2 RECALL THE RULE OF SIGN FOR REAL ROOTS. a. When a and c have different signs, both real roots have different signs. Example. The equation 5x² + 8x - 13 = 0 has 2 real roots with opposite signs: 1 and -13/5 Example. The equation 7x² 8x 15 = 0 has 2 real roots with opposite signs: (-1) and (15/7) b. When a and c have the same sign, both real roots have the same sign. - If a and b have opposite signs, both real roots are positive. Example: The equation 8x² - 11x + 3 = 0 has 2 real roots both positive: 1 and 3/8. Example: The equation 13x² 21x + 8 = 0 has 2 real roots both positive: 1 and 8/13 - If a and b have same sign, both real roots are negative. Example: The equation 8xv + 11x + 3 = 0 has 2 negative real roots: (-1) and (-3/8). Example: The equation 13x² + 23x + 10 = 0 has 2 negative real roots: (-1) and (-10/13). THE NEW IMPROVED FACTORING AC METHOD. Its approach is to factor the given quadratic equation into 2 binomials in x by replacing in the equation the term (bx) by the 2 terms (b1x) and (b2x) that satisfy these conditions: 1. b1*b2 = ac 2. b1 + b2 = b 3. Application of the Rule of Signs to find b1 and b2. A. When a = 1. Solving quadratic equation type x² + bx + c = 0 When a = 1, the product ac = c. Solving results in finding 2 numbers knowing their product (c) and their sum (-b). Using this new method, we can directly obtain the 2 real roots of the quadratic equation by composing factor pairs of c. The factor pair, whose sum equals to (b), or (-b), gives the answers. There is no need for factoring by grouping or solving the 2 binomials. a. When a and c have opposite signs, roots have opposite signs. First, compose factors of ac = c and in the same time apply the Rule of Sign. By convention, always put the negative sign (-) in front of the first number inside the factor pair. We will see later that this doesn t affect the result at all b. When a and c have same sign, both real roots have same sign. - If both roots are positive, compose factor pairs of a*c = c with all positive (+) numbers. - If both roots are negative, compose factor pairs of a*c = c with all negative numbers Example 3. Solve: x² 11x 102 = 0. Solution. Since a and c have opposite signs, roots have opposite signs. Compose the factors of a*c = c = with all first numbers being negative. Proceeding: (-1, 102),(-2, 51),(-3, 34),(-6, 17). OK!. The sum of the last pair is: 11 = -b. Consequently, these numbers (-6 and 17) are the 2 real roots of the given quadratic equation. There is no need for factoring and solving the 2 binomials for x. Page 2 of 5
3 Note. If we proceed composing factors of a*c = c = -102 differently, the outcome would be the same. Proceeding: (1, -102),(2, -51),(3, -34),(6, -17). OK. The sum of the last pair is (-11) = b. Consequently, the 2 real roots make the negative of this pair. They are: -6 and 17. Example 4. Solve x² + 31x = 0 Solution. Both roots are negative. Compose factors of c with all negative numbers. Proceeding: (-1, -108),(-2, -54),(-3, -36),(-4, -27). OK This last sum (-4, -27) = -31 = -b. Then the 2 real roots are: -4 and -27. There is no need for factoring and solving binomials. Note. If we proceed differently by composing factors of c = 108 with all positive numbers inside the factor pairs, the result will be the same. Proceeding: (1, 108),(2, 54),(3, 36),(4, 27). OK! The sum of the last pair is (4, 27) = 31 = b. Then, the 2 real roots are: -4 and -27. No factoring! B. When a is not 1 - Solving quadratic equation type ax² + bx + c = 0 In these cases, the new and improved factoring AC Method finds the 2 numbers b1 and b2 that satisfy the 2 conditions: the product (b1*b2) = ac, and the sum (b1 + b2) = b. The application of the Rule of Signs leads to these following practices: 1. If the 2 roots have different signs (a and c different signs), compose the factor pairs of the product a*c with all first numbers of the pairs being negative. 2. If the roots have same sign (a and c same sign), compose the factor pairs of the product a*c with all positive numbers if both roots are positive, or with all negative numbers if both roots are negative. 3. Stop composing factor pairs after you find the pair whose sum equals to (b), or (-b). When there isn t any factor pair of ac that equals to (b), or (-b), then, the given equation can t be factored, and consequently the quadratic formula probably should be used to solve it. 4. When a*c is a large number, composing factors may take a lot of time. You can save time by smartly composing factors: a. From the beginning, and go up the factor chain if b is relatively as large as a*c. b. From the middle of the chain if b is relatively small as compared to a*c, which is a large number. Example 5. Solve: 8x² 22x 13 = 0. Solution. Roots have opposite signs. Find 2 numbers that the product is a*c = -104, and the sum b1 + b2 = b = -22. Compose factors of a*c with first numbers of the pair being negative. Proceeding: (-1, 104),(-2, 52),(-4, 26). OK. This last sum is 22 = -b. Then: b1 = 4 and b2 = -26. Next, replace into the equation the term (-22x) by the 2 terms (4x) and (-26x). 8x² 4x + 26x 13 = 4x(2x + 1) 13(2x + 1) = (2x +1) (4x 13) = 0. 2x + 1 = 0 x = -1/2 4x 13 = 0 x = 13/4 Page 3 of 5
4 Example 6. Solve: 12x² + 5x 72 = 0. Solution. Roots have opposite signs. Find 2 numbers that the product is a*c = -864 and the sum is 5. Since b = 5 is too small as compared to ac = -864, start composing factors from the middle: Proceeding:,(-16, 54),(-18, 48),(-24, 36),(-32, 27). OK. This sum is ( ) = -5 = -b. Then (b1 + b2) = b = (32 27). Next, replace the term (5x) by the 2 terms (32x) and (-27x). 12x² + 32x 27x 72 = 4x (3x + 8) 9(3x + 8) = (3x + 8)(4x 9) = 0. 3x + 8 = 0 x = -8/3 4x 9 = 0 x = 9/4 Example 7. Solve: 24x² + 59x + 36 = 0. Solution. Both roots are negative. Product b1.b2 = 864. Sum (b1 + b2) = 59. Compose factor of a*c with all negative numbers, and start composing from the middle:. (-9, -96),(-12, -72),(-16, -54),(-18, -48),(-24, -36),(-27, -32). OK. This sum (-27-32) = -59 = -b. Then b1 = 27 and b2 = 32. Replace in the equation the term (59x) by the 2 terms (27x) and (32x). 24x² + 27x + 32x + 36 = 8x(3x + 4) + 9(3x + 4) = (3x + 4)(8x + 9) = 0 3x + 4 = 0 x = -4/3 8x + 9 = 0 x = -9/8 Example 8. Solve: 16x² 55x + 21 = 0. Solution. Both roots are positive. Find 2 numbers that product is ac = 336, and the sum (b1 + b2) = b = -41. Compose factors of ac with all numbers positive. Proceeding: (1, 336),(2, 168),(4, 82) (6, 56),(7, 48). OK. This sum is = 55 = -b. Then, b1 = -7 and b2 = -48. Next, replace in the equation the term (-55x) by the 2 terms (-7x) and (-48x). 16x² 48x 7x + 21 = 16x(x 3) - 7(x - 3) = (x - 3)(16x - 7) = 0 x 3 = 0 x = 3 16x - 7 = 0 x = 7/16. CONCLUSION AND COMMENTS. The existing factoring AC Method can be considerably improved by applying the Rule of Signs For Real Roots into the solving approach. This new and improved Factoring AC Method helps: 1. To know in advance the 2 signs (+ or -) of the 2 real roots for a better selection of the solving approach. 2. Simplify the solving process by reducing the number of permutations in half when the 2 roots have opposite signs. For example, when composing the factor pairs of ac = - 24, instead of listing all the 8 pairs: (-1, 24)(1, -24)(-2, 12)(2, -12)(-3, 8)(3, -8)(-4, 6)(4, - 6), we only need to list half of them, or 4 pairs: (-1, 24)(-2, 12)(-3, 8)(-4, 6). Page 4 of 5
5 Page 5 of 5 3. Simplify the solving process, when roots have same sign, by composing factors of the product ac with all positive numbers (or negative numbers), depending on if both roots are positive (or negative) 4. In case when a = 1, the 2 real roots can be immediately obtained from the list of the factor pairs of c. There is no need to factor by grouping and to solve the 2 binomials. (This article titled Solving Quadratic Equations by the new improved Factoring AC Method was written by Nghi H. Nguyen, co-author of the Diagonal Sum Method for solving quadratic equation)
BEST METHODS FOR SOLVING QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES. (By Nghi H Nguyen)
 BEST METHODS FOR SOLVING QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES. (By Nghi H Nguyen) I. GENERALITIES There are 3 most common methods to solve quadratic inequalities. Therefore, students sometimes are confused to select
BEST METHODS FOR SOLVING QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES. (By Nghi H Nguyen) I. GENERALITIES There are 3 most common methods to solve quadratic inequalities. Therefore, students sometimes are confused to select
Chapter 16 Review. 1. What is the solution set of n 2 + 5n 14 = 0? (A) n = {0, 14} (B) n = { 1, 14} (C) n = { 2, 7} (D) n = { 2, 7} (E) n = { 7, 2}
 Chapter 16 Review Directions: For each of the questions below, choose the best answer from the five choices given. 1. What is the solution set of n + 5n 14 = 0? (A) n = {0, 14} (B) n = { 1, 14} (C) n =
Chapter 16 Review Directions: For each of the questions below, choose the best answer from the five choices given. 1. What is the solution set of n + 5n 14 = 0? (A) n = {0, 14} (B) n = { 1, 14} (C) n =
To factor an expression means to write it as a product of factors instead of a sum of terms. The expression 3x
 Factoring trinomials In general, we are factoring ax + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers. To factor an expression means to write it as a product of factors instead of a sum of terms. The expression
Factoring trinomials In general, we are factoring ax + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers. To factor an expression means to write it as a product of factors instead of a sum of terms. The expression
A quadratic expression is a mathematical expression that can be written in the form 2
 118 CHAPTER Algebra.6 FACTORING AND THE QUADRATIC EQUATION Textbook Reference Section 5. CLAST OBJECTIVES Factor a quadratic expression Find the roots of a quadratic equation A quadratic expression is
118 CHAPTER Algebra.6 FACTORING AND THE QUADRATIC EQUATION Textbook Reference Section 5. CLAST OBJECTIVES Factor a quadratic expression Find the roots of a quadratic equation A quadratic expression is
Lesson 21 Not So Dramatic Quadratics
 STUDENT MANUAL ALGEBRA II / LESSON 21 Lesson 21 Not So Dramatic Quadratics Quadratic equations are probably one of the most popular types of equations that you ll see in algebra. A quadratic equation has
STUDENT MANUAL ALGEBRA II / LESSON 21 Lesson 21 Not So Dramatic Quadratics Quadratic equations are probably one of the most popular types of equations that you ll see in algebra. A quadratic equation has
Order of Operations Practice: 1) =
 Order of Operations Practice: 1) 24-12 3 + 6 = a) 6 b) 42 c) -6 d) 192 2) 36 + 3 3 (1/9) - 8 (12) = a) 130 b) 171 c) 183 d) 4,764 1 3) Evaluate: 12 2-4 2 ( - ½ ) + 2 (-3) 2 = 4) Evaluate 3y 2 + 8x =, when
Order of Operations Practice: 1) 24-12 3 + 6 = a) 6 b) 42 c) -6 d) 192 2) 36 + 3 3 (1/9) - 8 (12) = a) 130 b) 171 c) 183 d) 4,764 1 3) Evaluate: 12 2-4 2 ( - ½ ) + 2 (-3) 2 = 4) Evaluate 3y 2 + 8x =, when
Partial Fractions. (Do you see how to work it out? Substitute u = ax + b, so du = a dx.) For example, 1 dx = ln x 7 + C, x x (x 3)(x + 1) = a
 Partial Fractions 7-9-005 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Partial Fractions 7-9-005 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Solving Quadratic Equations
 Solving Quadratic Equations MATH 101 College Algebra J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2012 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: solve quadratic equations by factoring, solve quadratic
Solving Quadratic Equations MATH 101 College Algebra J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2012 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: solve quadratic equations by factoring, solve quadratic
General Form. Standard Form(Vertex Form) where a,b, and c are real numbers, with. where a, h, and k are real numbers, with.
 Quadratic Equations A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial equation in x. Meaning that there is at least one term that is being squared and there is NO exponent in the equation that is greater
Quadratic Equations A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial equation in x. Meaning that there is at least one term that is being squared and there is NO exponent in the equation that is greater
Section 7.1 Quadratic Equations
 Section 7.1 Quadratic Equations INTRODUCTION In Chapter 2 you learned about solving linear equations. In each of those, the highest power of any variable was 1. We will now take a look at solving quadratic
Section 7.1 Quadratic Equations INTRODUCTION In Chapter 2 you learned about solving linear equations. In each of those, the highest power of any variable was 1. We will now take a look at solving quadratic
Roots of quadratic equations
 CHAPTER Roots of quadratic equations Learning objectives After studying this chapter, you should: know the relationships between the sum and product of the roots of a quadratic equation and the coefficients
CHAPTER Roots of quadratic equations Learning objectives After studying this chapter, you should: know the relationships between the sum and product of the roots of a quadratic equation and the coefficients
To solve a radical equation, you must take both sides of an equation to a power.
 Topic 5 1 Radical Equations A radical equation is an equation with at least one radical expression. There are four types we will cover: x 35 3 4x x 1x 7 3 3 3 x 5 x 1 To solve a radical equation, you must
Topic 5 1 Radical Equations A radical equation is an equation with at least one radical expression. There are four types we will cover: x 35 3 4x x 1x 7 3 3 3 x 5 x 1 To solve a radical equation, you must
Solving Linear Equations
 Solving Linear Equations Golden Rule of Algebra: Do unto one side of the equal sign as you will do to the other Whatever you do on one side of the equal sign, you MUST do the same exact thing on the other
Solving Linear Equations Golden Rule of Algebra: Do unto one side of the equal sign as you will do to the other Whatever you do on one side of the equal sign, you MUST do the same exact thing on the other
2-7 Solving Quadratic Inequalities. ax 2 + bx + c > 0 (a 0)
 Quadratic Inequalities In One Variable LOOKS LIKE a quadratic equation but Doesn t have an equal sign (=) Has an inequality sign (>,
Quadratic Inequalities In One Variable LOOKS LIKE a quadratic equation but Doesn t have an equal sign (=) Has an inequality sign (>,
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 1: Interpreting Structure in Expressions Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: evaluating expressions using the order of operations evaluating expressions for a given value identifying parts of an expression
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: evaluating expressions using the order of operations evaluating expressions for a given value identifying parts of an expression
Multiplication of Polynomials
 Summary 391 Chapter 5 SUMMARY Section 5.1 A polynomial in x is defined by a finite sum of terms of the form ax n, where a is a real number and n is a whole number. a is the coefficient of the term. n is
Summary 391 Chapter 5 SUMMARY Section 5.1 A polynomial in x is defined by a finite sum of terms of the form ax n, where a is a real number and n is a whole number. a is the coefficient of the term. n is
SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES (CONCEPT, METHODS, AND STEPS )
 SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES (CONCEPT, METHODS, AND STEPS ) Definition. A trig inequality is an inequality in standard form: R(x) > 0 (or < 0) that contains one or a few trig functions of the variable
SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES (CONCEPT, METHODS, AND STEPS ) Definition. A trig inequality is an inequality in standard form: R(x) > 0 (or < 0) that contains one or a few trig functions of the variable
THE TRANSPOSING METHOD IN SOLVING ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS (Basic Step to improve math skills of high school students) (by Nghi H. Nguyen Jan 06, 2016)
 THE TRANSPOSING METHOD IN SOLVING ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS (Basic Step to improve math skills of high school students) (by Nghi H. Nguyen Jan 06, 2016) Most of the immigrant students who first began learning
THE TRANSPOSING METHOD IN SOLVING ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS (Basic Step to improve math skills of high school students) (by Nghi H. Nguyen Jan 06, 2016) Most of the immigrant students who first began learning
Chapter One: Pre-Geometry
 Chapter One: Pre-Geometry Index: A: Solving Equations B: Factoring (GCF/DOTS) C: Factoring (Case Two leading into Case One) D: Factoring (Case One) E: Solving Quadratics F: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Chapter One: Pre-Geometry Index: A: Solving Equations B: Factoring (GCF/DOTS) C: Factoring (Case Two leading into Case One) D: Factoring (Case One) E: Solving Quadratics F: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
LESSON 7.2 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS II
 LESSON 7.2 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS II LESSON 7.2 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS II 305 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Trinomials I a. Factoring trinomials of the form x 2 + bx + c; x 2 + bxy +
LESSON 7.2 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS II LESSON 7.2 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS II 305 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Trinomials I a. Factoring trinomials of the form x 2 + bx + c; x 2 + bxy +
Partial Fractions. (Do you see how to work it out? Substitute u = ax+b, so du = adx.) For example, 1 dx = ln x 7 +C, x 7
 Partial Fractions -4-209 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Partial Fractions -4-209 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Polynomial A monomial or sum of monomials. Binomials and Trinomial are also polynomials. Binomials are sum of two monomials Trinomials are sum of three monomials Degree
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Polynomial A monomial or sum of monomials. Binomials and Trinomial are also polynomials. Binomials are sum of two monomials Trinomials are sum of three monomials Degree
Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions
 Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions Problem 1. For the following homogeneous second order differential equations, give the general solution and the particular solution satisfying the given initial conditions.
Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions Problem 1. For the following homogeneous second order differential equations, give the general solution and the particular solution satisfying the given initial conditions.
Lesson 3.5 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 3.5 Exercises, pages 232 238 A 4. Calculate the value of the discriminant for each quadratic equation. a) 5x 2-9x + 4 = 0 b) 3x 2 + 7x - 2 = 0 In b 2 4ac, substitute: In b 2 4ac, substitute: a 5,
Lesson 3.5 Exercises, pages 232 238 A 4. Calculate the value of the discriminant for each quadratic equation. a) 5x 2-9x + 4 = 0 b) 3x 2 + 7x - 2 = 0 In b 2 4ac, substitute: In b 2 4ac, substitute: a 5,
9.4 Radical Expressions
 Section 9.4 Radical Expressions 95 9.4 Radical Expressions In the previous two sections, we learned how to multiply and divide square roots. Specifically, we are now armed with the following two properties.
Section 9.4 Radical Expressions 95 9.4 Radical Expressions In the previous two sections, we learned how to multiply and divide square roots. Specifically, we are now armed with the following two properties.
5.3. Polynomials and Polynomial Functions
 5.3 Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Polynomial Vocabulary Term a number or a product of a number and variables raised to powers Coefficient numerical factor of a term Constant term which is only a
5.3 Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Polynomial Vocabulary Term a number or a product of a number and variables raised to powers Coefficient numerical factor of a term Constant term which is only a
Unit 1 Vocabulary. A function that contains 1 or more or terms. The variables may be to any non-negative power.
 MODULE 1 1 Polynomial A function that contains 1 or more or terms. The variables may be to any non-negative power. 1 Modeling Mathematical modeling is the process of using, and to represent real world
MODULE 1 1 Polynomial A function that contains 1 or more or terms. The variables may be to any non-negative power. 1 Modeling Mathematical modeling is the process of using, and to represent real world
Roots of quadratic equations
 CHAPTER Roots of quadratic equations Learning objectives After studying this chapter, you should: know the relationships between the sum and product of the roots of a quadratic equation and the coefficients
CHAPTER Roots of quadratic equations Learning objectives After studying this chapter, you should: know the relationships between the sum and product of the roots of a quadratic equation and the coefficients
MULTIPLYING TRINOMIALS
 Name: Date: 1 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 4 Polynomials B MULTIPLYING TRINOMIALS Multiplying trinomials is the same process as multiplying binomials except for there are more terms to multiply than
Name: Date: 1 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 4 Polynomials B MULTIPLYING TRINOMIALS Multiplying trinomials is the same process as multiplying binomials except for there are more terms to multiply than
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 2: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One Variable Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: simplifying radicals working with complex numbers Introduction You can determine how far a ladder will extend from the base of
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: simplifying radicals working with complex numbers Introduction You can determine how far a ladder will extend from the base of
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Title Integration of Rational Functions by MATH 1700 MATH 1700 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 2 / 11 Rational functions A rational function is one of the form where P and Q are
Title Integration of Rational Functions by MATH 1700 MATH 1700 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 2 / 11 Rational functions A rational function is one of the form where P and Q are
Study Guide for Skills Module 3: An Approximate Method for Solving Quadratic Equations
 Chemistry 1020, Skills Module 3 Name Study Guide for Skills Module 3: An Approximate Method for Solving Quadratic Equations Reading Assignment: The module contains a review of the mathematics needed to
Chemistry 1020, Skills Module 3 Name Study Guide for Skills Module 3: An Approximate Method for Solving Quadratic Equations Reading Assignment: The module contains a review of the mathematics needed to
CH 73 THE QUADRATIC FORMULA, PART II
 1 CH THE QUADRATIC FORMULA, PART II INTRODUCTION W ay back in Chapter 55 we used the Quadratic Formula to solve quadratic equations like 6x + 1x + 0 0, whose solutions are 5 and 8. In fact, all of the
1 CH THE QUADRATIC FORMULA, PART II INTRODUCTION W ay back in Chapter 55 we used the Quadratic Formula to solve quadratic equations like 6x + 1x + 0 0, whose solutions are 5 and 8. In fact, all of the
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Title Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions MATH 1700 December 6, 2016 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions December 6, 2016 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions
Title Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions MATH 1700 December 6, 2016 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions December 6, 2016 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions
F 2k 1 = F 2n. for all positive integers n.
 Question 1 (Fibonacci Identity, 15 points). Recall that the Fibonacci numbers are defined by F 1 = F 2 = 1 and F n+2 = F n+1 + F n for all n 0. Prove that for all positive integers n. n F 2k 1 = F 2n We
Question 1 (Fibonacci Identity, 15 points). Recall that the Fibonacci numbers are defined by F 1 = F 2 = 1 and F n+2 = F n+1 + F n for all n 0. Prove that for all positive integers n. n F 2k 1 = F 2n We
6.5 Dividing Polynomials
 Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
What if the characteristic equation has complex roots?
 MA 360 Lecture 18 - Summary of Recurrence Relations (cont. and Binomial Stuff Thursday, November 13, 01. Objectives: Examples of Recurrence relation solutions, Pascal s triangle. A quadratic equation What
MA 360 Lecture 18 - Summary of Recurrence Relations (cont. and Binomial Stuff Thursday, November 13, 01. Objectives: Examples of Recurrence relation solutions, Pascal s triangle. A quadratic equation What
Math 138: Introduction to solving systems of equations with matrices. The Concept of Balance for Systems of Equations
 Math 138: Introduction to solving systems of equations with matrices. Pedagogy focus: Concept of equation balance, integer arithmetic, quadratic equations. The Concept of Balance for Systems of Equations
Math 138: Introduction to solving systems of equations with matrices. Pedagogy focus: Concept of equation balance, integer arithmetic, quadratic equations. The Concept of Balance for Systems of Equations
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Quadratics intervention Deduce quadratic roots algebraically 1 Grade 6 Objective: Deduce roots algebraically. Question 1. Factorise and solve the equation x 2 8x + 15 = 0 Question
PLC Papers Created For: Quadratics intervention Deduce quadratic roots algebraically 1 Grade 6 Objective: Deduce roots algebraically. Question 1. Factorise and solve the equation x 2 8x + 15 = 0 Question
Math 096--Quadratic Formula page 1
 Math 096--Quadratic Formula page 1 A Quadratic Formula. Use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations ax + bx + c = 0 when the equations can t be factored. To use the quadratic formula, the equation
Math 096--Quadratic Formula page 1 A Quadratic Formula. Use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations ax + bx + c = 0 when the equations can t be factored. To use the quadratic formula, the equation
POLYNOMIALS. Maths 4 th ESO José Jaime Noguera
 POLYNOMIALS Maths 4 th ESO José Jaime Noguera 1 Algebraic expressions Book, page 26 YOUR TURN: exercises 1, 2, 3. Exercise: Find the numerical value of the algebraic expression xy 2 8x + y, knowing that
POLYNOMIALS Maths 4 th ESO José Jaime Noguera 1 Algebraic expressions Book, page 26 YOUR TURN: exercises 1, 2, 3. Exercise: Find the numerical value of the algebraic expression xy 2 8x + y, knowing that
6.5 Dividing Polynomials
 Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Chapter(5( (Quadratic(Equations( 5.1 Factoring when the Leading Coefficient Equals 1
 .1 Factoring when the Leading Coefficient Equals 1 1... x 6x 8 x 10x + 9 x + 10x + 1 4. (x )( x + 1). (x + 6)(x 4) 6. x(x 6) 7. (x + )(x + ) 8. not factorable 9. (x 6)(x ) 10. (x + 1)(x ) 11. (x + 7)(x
.1 Factoring when the Leading Coefficient Equals 1 1... x 6x 8 x 10x + 9 x + 10x + 1 4. (x )( x + 1). (x + 6)(x 4) 6. x(x 6) 7. (x + )(x + ) 8. not factorable 9. (x 6)(x ) 10. (x + 1)(x ) 11. (x + 7)(x
Solving Quadratic Equations
 Concepts: Solving Quadratic Equations, Completing the Square, The Quadratic Formula, Sketching Quadratics Solving Quadratic Equations Completing the Square ax + bx + c = a x + ba ) x + c Factor so the
Concepts: Solving Quadratic Equations, Completing the Square, The Quadratic Formula, Sketching Quadratics Solving Quadratic Equations Completing the Square ax + bx + c = a x + ba ) x + c Factor so the
Linear Functions A linear function is a common function that represents a straight line
 This handout will: Define Linear and Quadratic Functions both graphically and algebraically Examine the associated equations and their components. Look at how each component could affect shape graphically
This handout will: Define Linear and Quadratic Functions both graphically and algebraically Examine the associated equations and their components. Look at how each component could affect shape graphically
review To find the coefficient of all the terms in 15ab + 60bc 17ca: Coefficient of ab = 15 Coefficient of bc = 60 Coefficient of ca = -17
 1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
Equations in Quadratic Form
 Equations in Quadratic Form MATH 101 College Algebra J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2012 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: make substitutions that allow equations to be written
Equations in Quadratic Form MATH 101 College Algebra J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2012 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: make substitutions that allow equations to be written
Solving Quadratic Equations Review
 Math III Unit 2: Polynomials Notes 2-1 Quadratic Equations Solving Quadratic Equations Review Name: Date: Period: Some quadratic equations can be solved by. Others can be solved just by using. ANY quadratic
Math III Unit 2: Polynomials Notes 2-1 Quadratic Equations Solving Quadratic Equations Review Name: Date: Period: Some quadratic equations can be solved by. Others can be solved just by using. ANY quadratic
Lecture 26. Quadratic Equations
 Lecture 26 Quadratic Equations Quadratic polynomials....................................................... 2 Quadratic polynomials....................................................... 3 Quadratic equations
Lecture 26 Quadratic Equations Quadratic polynomials....................................................... 2 Quadratic polynomials....................................................... 3 Quadratic equations
Algebra 2 Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide
 Algebra Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Algebra Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the nine specific concepts covered in the
Algebra Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Algebra Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the nine specific concepts covered in the
Herndon High School Geometry Honors Summer Assignment
 Welcome to Geometry! This summer packet is for all students enrolled in Geometry Honors at Herndon High School for Fall 07. The packet contains prerequisite skills that you will need to be successful in
Welcome to Geometry! This summer packet is for all students enrolled in Geometry Honors at Herndon High School for Fall 07. The packet contains prerequisite skills that you will need to be successful in
Quadratic Equations Part I
 Quadratic Equations Part I Before proceeding with this section we should note that the topic of solving quadratic equations will be covered in two sections. This is done for the benefit of those viewing
Quadratic Equations Part I Before proceeding with this section we should note that the topic of solving quadratic equations will be covered in two sections. This is done for the benefit of those viewing
Polynomials. Title Page. Prior Knowledge: understanding of coefficients and terms
 Polynomials Title Page Subject: Polynomials Topic: Classifying Polynomials by Degree and Number of Terms. Also a review of Coefficients. Grade(s): 8th 10th grade Prior Knowledge: understanding of coefficients
Polynomials Title Page Subject: Polynomials Topic: Classifying Polynomials by Degree and Number of Terms. Also a review of Coefficients. Grade(s): 8th 10th grade Prior Knowledge: understanding of coefficients
Sections 7.1, 7.2: Sums, differences, products of polynomials CHAPTER 7: POLYNOMIALS
 Sections 7.1, 7.2: Sums, differences, products of polynomials CHAPTER 7: POLYNOMIALS Quiz results Average 73%: high h score 100% Problems: Keeping track of negative signs x = + = + Function notation f(x)
Sections 7.1, 7.2: Sums, differences, products of polynomials CHAPTER 7: POLYNOMIALS Quiz results Average 73%: high h score 100% Problems: Keeping track of negative signs x = + = + Function notation f(x)
Lecture 17: Floyd-Hoare Logic for Partial Correctness
 Lecture 17: Floyd-Hoare Logic for Partial Correctness Aims: To look at the following inference rules Page 1 of 9 sequence; assignment and consequence. 17.1. The Deduction System for Partial Correctness
Lecture 17: Floyd-Hoare Logic for Partial Correctness Aims: To look at the following inference rules Page 1 of 9 sequence; assignment and consequence. 17.1. The Deduction System for Partial Correctness
The greatest common factor, or GCF, is the largest factor that two or more terms share.
 Unit, Lesson Factoring Recall that a factor is one of two or more numbers or expressions that when multiplied produce a given product You can factor certain expressions by writing them as the product of
Unit, Lesson Factoring Recall that a factor is one of two or more numbers or expressions that when multiplied produce a given product You can factor certain expressions by writing them as the product of
3 What is the degree of the polynomial function that generates the data shown below?
 hapter 04 Test Name: ate: 1 For the polynomial function, describe the end behavior of its graph. The leading term is down. The leading term is and down.. Since n is 1 and a is positive, the end behavior
hapter 04 Test Name: ate: 1 For the polynomial function, describe the end behavior of its graph. The leading term is down. The leading term is and down.. Since n is 1 and a is positive, the end behavior
Polynomial Functions. x n 2 a n. x n a 1. f x = a o. x n 1 a 2. x 0, , a 1
 Polynomial Functions A polynomial function is a sum of multiples of an independent variable raised to various integer powers. The general form of a polynomial function is f x = a o x n a 1 x n 1 a 2 x
Polynomial Functions A polynomial function is a sum of multiples of an independent variable raised to various integer powers. The general form of a polynomial function is f x = a o x n a 1 x n 1 a 2 x
SUMMER REVIEW PACKET. Name:
 Wylie East HIGH SCHOOL SUMMER REVIEW PACKET For students entering Regular PRECALCULUS Name: Welcome to Pre-Calculus. The following packet needs to be finished and ready to be turned the first week of the
Wylie East HIGH SCHOOL SUMMER REVIEW PACKET For students entering Regular PRECALCULUS Name: Welcome to Pre-Calculus. The following packet needs to be finished and ready to be turned the first week of the
Solving Quadratic Equations Using the Quadratic Formula
 Section 9 : Solving Quadratic Equations Using the Quadratic Fmula Quadratic Equations are equations that have an x term as the highest powered term. They are also called Second Degree Equations. The Standard
Section 9 : Solving Quadratic Equations Using the Quadratic Fmula Quadratic Equations are equations that have an x term as the highest powered term. They are also called Second Degree Equations. The Standard
Dylan Zwick. Fall Ax=b. EAx=Eb. UxrrrEb
 Math 2270 - Lecture 0: LU Factorization Dylan Zwick Fall 202 This lecture covers section 2.6 of the textbook. The Matrices L and U In elimination what we do is we take a system of equations and convert
Math 2270 - Lecture 0: LU Factorization Dylan Zwick Fall 202 This lecture covers section 2.6 of the textbook. The Matrices L and U In elimination what we do is we take a system of equations and convert
P.5 Solving Equations
 PRC Ch P_5.notebook P.5 Solving Equations What you should learn How to solve linear equations How to solve quadratic equations equations How to solve polynomial equations of degree three or higher How
PRC Ch P_5.notebook P.5 Solving Equations What you should learn How to solve linear equations How to solve quadratic equations equations How to solve polynomial equations of degree three or higher How
Lecture 27. Quadratic Formula
 Lecture 7 Quadratic Formula Goal: to solve any quadratic equation Quadratic formula 3 Plan Completing the square 5 Completing the square 6 Proving quadratic formula 7 Proving quadratic formula 8 Proving
Lecture 7 Quadratic Formula Goal: to solve any quadratic equation Quadratic formula 3 Plan Completing the square 5 Completing the square 6 Proving quadratic formula 7 Proving quadratic formula 8 Proving
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Factorising Quadratics Factorising difficult quadratic expressions 1 Grade 7 Objective: Factorise a quadratic expression of the form ax 2 + bx + c
PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Factorising Quadratics Factorising difficult quadratic expressions 1 Grade 7 Objective: Factorise a quadratic expression of the form ax 2 + bx + c
Chapter Six. Polynomials. Properties of Exponents Algebraic Expressions Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication Factoring Solving by Factoring
 Chapter Six Polynomials Properties of Exponents Algebraic Expressions Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication Factoring Solving by Factoring Properties of Exponents The properties below form the basis
Chapter Six Polynomials Properties of Exponents Algebraic Expressions Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication Factoring Solving by Factoring Properties of Exponents The properties below form the basis
Algebra I Unit Report Summary
 Algebra I Unit Report Summary No. Objective Code NCTM Standards Objective Title Real Numbers and Variables Unit - ( Ascend Default unit) 1. A01_01_01 H-A-B.1 Word Phrases As Algebraic Expressions 2. A01_01_02
Algebra I Unit Report Summary No. Objective Code NCTM Standards Objective Title Real Numbers and Variables Unit - ( Ascend Default unit) 1. A01_01_01 H-A-B.1 Word Phrases As Algebraic Expressions 2. A01_01_02
Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2
 Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2 April 11, 2016 Chapter 10 Section 1: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials A monomial is
Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2 April 11, 2016 Chapter 10 Section 1: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials A monomial is
Polynomials; Add/Subtract
 Chapter 7 Polynomials Polynomials; Add/Subtract Polynomials sounds tough enough. But, if you look at it close enough you ll notice that students have worked with polynomial expressions such as 6x 2 + 5x
Chapter 7 Polynomials Polynomials; Add/Subtract Polynomials sounds tough enough. But, if you look at it close enough you ll notice that students have worked with polynomial expressions such as 6x 2 + 5x
MathB65 Ch 4 VII, VIII, IX.notebook. November 06, 2017
 Chapter 4: Polynomials I. Exponents & Their Properties II. Negative Exponents III. Scientific Notation IV. Polynomials V. Addition & Subtraction of Polynomials VI. Multiplication of Polynomials VII. Greatest
Chapter 4: Polynomials I. Exponents & Their Properties II. Negative Exponents III. Scientific Notation IV. Polynomials V. Addition & Subtraction of Polynomials VI. Multiplication of Polynomials VII. Greatest
SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES: METHODS, AND STEPS By Nghi H. Nguyen
 DEFINITION. SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES: METHODS, AND STEPS By Nghi H. Nguyen A trig inequality is an inequality in standard form: R(x) > 0 (or < 0) that contains one or a few trig functions of
DEFINITION. SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES: METHODS, AND STEPS By Nghi H. Nguyen A trig inequality is an inequality in standard form: R(x) > 0 (or < 0) that contains one or a few trig functions of
(2) Dividing both sides of the equation in (1) by the divisor, 3, gives: =
 Dividing Polynomials Prepared by: Sa diyya Hendrickson Name: Date: Let s begin by recalling the process of long division for numbers. Consider the following fraction: Recall that fractions are just division
Dividing Polynomials Prepared by: Sa diyya Hendrickson Name: Date: Let s begin by recalling the process of long division for numbers. Consider the following fraction: Recall that fractions are just division
5-9. Complex Numbers. Key Concept. Square Root of a Negative Real Number. Key Concept. Complex Numbers VOCABULARY TEKS FOCUS ESSENTIAL UNDERSTANDING
 TEKS FOCUS 5-9 Complex Numbers VOCABULARY TEKS (7)(A) Add, subtract, and multiply complex TEKS (1)(F) Analyze mathematical relationships to connect and communicate mathematical ideas. Additional TEKS (1)(D),
TEKS FOCUS 5-9 Complex Numbers VOCABULARY TEKS (7)(A) Add, subtract, and multiply complex TEKS (1)(F) Analyze mathematical relationships to connect and communicate mathematical ideas. Additional TEKS (1)(D),
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 3 Polynomials A
 Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 3 Polynomials A 1 MATH 1 & 2 REVIEW: VOCABULARY Constant: A term that does not have a variable is called a constant. Example: the number 5 is a constant because it does
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 3 Polynomials A 1 MATH 1 & 2 REVIEW: VOCABULARY Constant: A term that does not have a variable is called a constant. Example: the number 5 is a constant because it does
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER / Quadratic Equations
 ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER 1 018/019 DR ANTHONY BROWN 31 Graphs of Quadratic Functions 3 Quadratic Equations In Chapter we looked at straight lines,
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER 1 018/019 DR ANTHONY BROWN 31 Graphs of Quadratic Functions 3 Quadratic Equations In Chapter we looked at straight lines,
1 Introduction. 2 Solving Linear Equations
 1 Introduction This essay introduces some new sets of numbers. Up to now, the only sets of numbers (algebraic systems) we know is the set Z of integers with the two operations + and and the system R of
1 Introduction This essay introduces some new sets of numbers. Up to now, the only sets of numbers (algebraic systems) we know is the set Z of integers with the two operations + and and the system R of
Statistics 100A Homework 5 Solutions
 Chapter 5 Statistics 1A Homework 5 Solutions Ryan Rosario 1. Let X be a random variable with probability density function a What is the value of c? fx { c1 x 1 < x < 1 otherwise We know that for fx to
Chapter 5 Statistics 1A Homework 5 Solutions Ryan Rosario 1. Let X be a random variable with probability density function a What is the value of c? fx { c1 x 1 < x < 1 otherwise We know that for fx to
Package Summary. Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Rational Equations. Making Math Possible 1 of 10 c Sa diyya Hendrickson
 Solving Equations Prepared by: Sa diyya Hendrickson Name: Date: Package Summary Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Rational Equations Making Math Possible 1 of 10 c Sa diyya Hendrickson Linear Equations
Solving Equations Prepared by: Sa diyya Hendrickson Name: Date: Package Summary Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Rational Equations Making Math Possible 1 of 10 c Sa diyya Hendrickson Linear Equations
Lesson 10: The Power of Algebra Finding Pythagorean Triples
 Lesson 10: The Power of Algebra Finding Pythagorean Triples Student Outcomes Students explore the difference of two squares identity x " y " = (x y)(x + y) in the context of finding Pythagorean triples.
Lesson 10: The Power of Algebra Finding Pythagorean Triples Student Outcomes Students explore the difference of two squares identity x " y " = (x y)(x + y) in the context of finding Pythagorean triples.
2x (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 2 2y. (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 4. 4xy. (1, 1)(x 1) + (1, 1)(y + 1) (1, 1)(x 1)(y + 1) 81 x y y + 7.
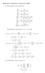 Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Chapter 2. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions 1 / 33 23 Chapter 2 Homework 2.5 p335 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 34, 38, 42, 46, 50, 52 2 / 33 23 3 / 33 23 Objectives:
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions 1 / 33 23 Chapter 2 Homework 2.5 p335 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 34, 38, 42, 46, 50, 52 2 / 33 23 3 / 33 23 Objectives:
How to use these notes
 Chapter How to use these notes These notes were prepared for the University of Utah s Math 00 refresher course. They asssume that the user has had the Math 00 course Intermediate Algebra or its equivalent
Chapter How to use these notes These notes were prepared for the University of Utah s Math 00 refresher course. They asssume that the user has had the Math 00 course Intermediate Algebra or its equivalent
Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is 10. Make an organized list.
 9.5 Study Guide For use with pages 582 589 GOAL Factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. EXAMPLE 1 Factor when b and c are positive Factor x 2 1 10x 1 24. Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is
9.5 Study Guide For use with pages 582 589 GOAL Factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. EXAMPLE 1 Factor when b and c are positive Factor x 2 1 10x 1 24. Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is
Lesson 25: Using the Quadratic Formula,
 , b ± b 4ac x = a Opening Exercise Over the years, many students and teachers have thought of ways to help us all remember the quadratic formula. Below is the YouTube link to a video created by two teachers
, b ± b 4ac x = a Opening Exercise Over the years, many students and teachers have thought of ways to help us all remember the quadratic formula. Below is the YouTube link to a video created by two teachers
Key Facts and Methods
 Intermediate Maths Key Facts and Methods Use this (as well as trying questions) to revise by: 1. Testing yourself. Asking a friend or family member to test you by reading the questions (on the lefthand
Intermediate Maths Key Facts and Methods Use this (as well as trying questions) to revise by: 1. Testing yourself. Asking a friend or family member to test you by reading the questions (on the lefthand
P3.C8.COMPLEX NUMBERS
 Recall: Within the real number system, we can solve equation of the form and b 2 4ac 0. ax 2 + bx + c =0, where a, b, c R What is R? They are real numbers on the number line e.g: 2, 4, π, 3.167, 2 3 Therefore,
Recall: Within the real number system, we can solve equation of the form and b 2 4ac 0. ax 2 + bx + c =0, where a, b, c R What is R? They are real numbers on the number line e.g: 2, 4, π, 3.167, 2 3 Therefore,
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions Part 2: Integrating Rational Functions Rational Functions Recall that a rational function is the quotient of two polynomials. x + 3 x + 2 x + 2 x
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions Part 2: Integrating Rational Functions Rational Functions Recall that a rational function is the quotient of two polynomials. x + 3 x + 2 x + 2 x
Algebra & Trig Review
 Algebra & Trig Review 1 Algebra & Trig Review This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The
Algebra & Trig Review 1 Algebra & Trig Review This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The
Newbattle Community High School National 5 Mathematics. Key Facts Q&A
 Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
Linear Models Review
 Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Chapter 1. Making algebra orderly with the order of operations and other properties Enlisting rules of exponents Focusing on factoring
 In This Chapter Chapter 1 Making Advances in Algebra Making algebra orderly with the order of operations and other properties Enlisting rules of exponents Focusing on factoring Algebra is a branch of mathematics
In This Chapter Chapter 1 Making Advances in Algebra Making algebra orderly with the order of operations and other properties Enlisting rules of exponents Focusing on factoring Algebra is a branch of mathematics
Understand the vocabulary used to describe polynomials Add polynomials Subtract polynomials Graph equations defined by polynomials of degree 2
 Section 5.1: ADDING AND SUBTRACTING POLYNOMIALS When you are done with your homework you should be able to Understand the vocabulary used to describe polynomials Add polynomials Subtract polynomials Graph
Section 5.1: ADDING AND SUBTRACTING POLYNOMIALS When you are done with your homework you should be able to Understand the vocabulary used to describe polynomials Add polynomials Subtract polynomials Graph
Solving Quadratic Equations By Graphing Answers
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with solving quadratic equations
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with solving quadratic equations
Interesting Integers!
 Interesting Integers! What You Will Learn n Some definitions related to integers. n Rules for adding and subtracting integers. n A method for proving that a rule is true. Are you ready?? Definition n Positive
Interesting Integers! What You Will Learn n Some definitions related to integers. n Rules for adding and subtracting integers. n A method for proving that a rule is true. Are you ready?? Definition n Positive
Equilibrium and Concentration
 Equilibrium and Concentration Answer Key Vocabulary: chemical equilibrium, concentration, equilibrium, equilibrium constant, reaction quotient, reversible reaction Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Equilibrium and Concentration Answer Key Vocabulary: chemical equilibrium, concentration, equilibrium, equilibrium constant, reaction quotient, reversible reaction Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Solving Quadratic Equations by Formula
 Algebra Unit: 05 Lesson: 0 Complex Numbers All the quadratic equations solved to this point have had two real solutions or roots. In some cases, solutions involved a double root, but there were always
Algebra Unit: 05 Lesson: 0 Complex Numbers All the quadratic equations solved to this point have had two real solutions or roots. In some cases, solutions involved a double root, but there were always
September 12, Math Analysis Ch 1 Review Solutions. #1. 8x + 10 = 4x 30 4x 4x 4x + 10 = x = x = 10.
 #1. 8x + 10 = 4x 30 4x 4x 4x + 10 = 30 10 10 4x = 40 4 4 x = 10 Sep 5 7:00 AM 1 #. 4 3(x + ) = 5x 7(4 x) 4 3x 6 = 5x 8 + 7x CLT 3x = 1x 8 +3x +3x = 15x 8 +8 +8 6 = 15x 15 15 x = 6 15 Sep 5 7:00 AM #3.
#1. 8x + 10 = 4x 30 4x 4x 4x + 10 = 30 10 10 4x = 40 4 4 x = 10 Sep 5 7:00 AM 1 #. 4 3(x + ) = 5x 7(4 x) 4 3x 6 = 5x 8 + 7x CLT 3x = 1x 8 +3x +3x = 15x 8 +8 +8 6 = 15x 15 15 x = 6 15 Sep 5 7:00 AM #3.
KEY CONCEPTS. Factoring is the opposite of expanding.
 KEY CONCEPTS Factoring is the opposite of expanding. To factor simple trinomials in the form x 2 + bx + c, find two numbers such that When you multiply them, their product (P) is equal to c When you add
KEY CONCEPTS Factoring is the opposite of expanding. To factor simple trinomials in the form x 2 + bx + c, find two numbers such that When you multiply them, their product (P) is equal to c When you add
Topic 7: Polynomials. Introduction to Polynomials. Table of Contents. Vocab. Degree of a Polynomial. Vocab. A. 11x 7 + 3x 3
 Topic 7: Polynomials Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Polynomials. Adding & Subtracting Polynomials 3. Multiplying Polynomials 4. Special Products of Binomials 5. Factoring Polynomials 6. Factoring
Topic 7: Polynomials Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Polynomials. Adding & Subtracting Polynomials 3. Multiplying Polynomials 4. Special Products of Binomials 5. Factoring Polynomials 6. Factoring
Chapter 9 Quadratic Functions and Equations
 Chapter 9 Quadratic Functions and Equations 1 9 1Quadratic Graphs and their properties U shaped graph such as the one at the right is called a parabola. A parabola can open upward or downward. A parabola
Chapter 9 Quadratic Functions and Equations 1 9 1Quadratic Graphs and their properties U shaped graph such as the one at the right is called a parabola. A parabola can open upward or downward. A parabola
