Astrodynamics (AERO0024)
|
|
|
- Jean Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Astodynamics (AERO004). The Two-Body Poblem Gaëtan Keschen Space Stuctues & Systems Lab (S3L)
2 Y. The Two-Body Poblem.1 Justification of the -body model X. Gavitational field 3.3 Relative motion.4 Resulting obits
3 Y. The Two-Body Poblem.1 Justification of the -body model X 3 3
4 N-body poblem 4
5 Two-Body Poblem: Matlab Example Two identical masses: One is at est at the oigin of the inetial fame of efeence. The othe one has a velocity diected upwad to the ight making a 45 degees angle with the X axis. Y v 0 m 1 m X.1 Justification of the two-body model 5
6 Y x 10 5 Motion elative to the inetial fame X x 10 5 Seemingly complex motion in the inetial fame m1 m cm
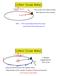
7 Y Y x 10 5 Motion elative to the cente of mass x 10 5 Motion of m elative to m 1 1 m1 m X x X x 10 5 Much less complex motion when viewed fom the c.o.m Much less complex motion when viewed fom m 1
8
9 Y.5 x 10 7 Motion of m elative to m The initial velocity is quadupled X x 10 7
10 Thee-Body Poblem: Matlab Example Thee identical masses: Two ae at est. The thid one has a velocity diected upwad to the ight making a 45 degees angle with the X axis. Y v 0 m 1 m m 3 X.1 Justification of the two-body model 10
11 Y x 10 6 Motion elative to the inetial fame m1 m m3 cm X x 10 6
12 Y x 10 5 Motion elative to the cente of mass m1 m m X What Do You Conclude? x 10 6
13 Y x 10 5 Motion elative to the inetial fame X x 10 5 Seemingly complex motion in the inetial fame m1 m cm
14 Displacement of the fist mass (x diection) Displacement of the fist mass (x diection) Why Is the 3-Body Poblem So Difficult? 16 x 105 Compaison of time seies Nominal IC 14 Petubed IC Chaotic by natue! body poblem (initial conditions petubed by 0.1%) 14 x 106 Compaison of time seies Time x body poblem (initial conditions petubed by 0.1%) Justification of the two-body model Nominal IC Petubed IC Time x
15 Y Y Why Is the 3-Body Poblem So Difficult? x Nominal IC m1 m m3 Chaotic by natue! X x x 10 5 IC petubed by 0.1% m1 m m Justification of the two-body model X x
16 Inteest in the Two-Body Poblem? Pecise obit popagation: Elaboate models ae necessay to compute the motion of satellites to the high level of accuacy equied fo many applications today (e.g., the GPS system). The - body poblem is not helpful in that context..1 Justification of the two-body model 16
17 Inteest in the Two-Body Poblem? Qualitative undestanding: The main featues of satellite and planet obits can be descibed by a easonably simple appoximation, the two-body poblem. Mission design: Some impotant quantities (ΔV and C 3 ) can be computed faily accuately using the two-body assumption. Inteplanetay tansfe: In lectue 6, we will use a sequence of -body poblems to appoximate a complex inteplanetay mission..1 Justification of the two-body model 17
18 An analytic obit popagato, based on a closed-fom solution, also pesents inteesting featues (e.g., computation time).
19 . The Two-Body Poblem. Gavitational field:..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation.. The Eath..3 Gavity models and geoid 3 What is the highest point on Eath? 19
20 Gavitational Foce The law of univesal gavitation is an empiical law descibing the gavitational attaction between bodies with mass. It was fist fomulated by Newton in Philosophiae Natualis Pincipia Mathematica (1687). He was able to elate objects falling on the Eath to the motion of the planets. Isaac Newton ( )..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 0
21 Gavitational Foce Evey point mass attacts evey othe point mass by a foce pointing along the line intesecting both points. The foce is popotional to the poduct of the two masses and invesely popotional to the squae of the distance between the point masses:..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 1
22 In Vecto Fom F mm G 1 ˆ with ˆ Newton s law of univesal gavitation
23 Gavitational Constant By measuing the mutual attaction of two bodies of known mass, the gavitational constant G can diectly be detemined fom tosion balance expeiments. Due to the small size of the gavitational foce, G is pesently only known with limited accuacy and was fist detemined many yeas afte Newton s discovey: ( ± ) m 3.kg -1.s - GmM k L ( Newton s law of univesal gavitation 3
24 Gavitational Paamete of a Celestial Body GM The gavitational paamete of the Eath has been detemined with consideable pecision fom the analysis of lase distance measuements of atificial satellites: ± km 3.s -. The uncetainty is 1 to 5e8, much smalle than the uncetainties in G and M sepaately (~1 to 1e4 each)...1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 4
25 Satellite Lase Ranging TIGO (Concepcion, Chile) LAGEOS-1 Lases measue anges fom gound stations to satellite bone eto-eflectos. Because the events of sending and eceiving a pulse can be egisteed within a few picoseconds, the distance between the gound station and the satellite is detemined within a few millimetes...1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 5
26 Acceleation of Gavity GM g eath, SL m/s g g g eath, aicaft eath, SL g g eath, ISS eath, SL % % We sense ou own weight by feeling contact foces acting on us in opposition to the foce of gavity: W=mg. If planetay gavity is the only foce acting on a body, then the body is said to be in fee fall. Thee ae, by definition, no contact foces, so thee can be no sense of weight. A peson in fee fall expeiences weightlessness: gavity is still thee, but he cannot feel it...1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 6
27 Bodies with Spatial Extent Up to now, point masses wee consideed. But an object with a spheically-symmetic distibution of mass exets the same gavitational attaction on extenal bodies as if all the object's mass wee concentated at a point at its cente. = Point mass M Sphee of mass M..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 7
28 Spheically Symmetic Mass Distibution ' M dv( ',, ) m V M Gm v dv dv ' sin v dv d d d ' R ' ' Rcos d d ' Rsin..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 8
29 Spheically Symmetic Mass Distibution R R d sind ' d ' 4 ' d ' M 0 0 R sind V Gm ' d ' R 1 R ' 0 R ' R' 4 Gm R 0 GMm ' d ' R 0 R 0 Gm d ' d ' OK!..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation 9
30 What is the Highest Point on Eath? Mount Chimboazo (6310 m), located in Ecuado, may be consideed as the highest point on Eath. It is the spot on the suface fathest fom the Eath s cente km (Chimboazo) vs km (Eveest).. The Eath 30
31 The Eath is not a Sphee.. The Eath 31
32 1 st Ode Effect: Equatoial Bulge Because ou planet otates, the centifugal foce tends to pull mateial outwads aound the Equato whee the velocity of otation is at its highest: The Eath s adius is 1km geate at the Equato compaed to the poles. The foce of gavity is weake at the Equato (g=9.78 m/s ) than it is at the poles (g=9.83 m/s )... The Eath 3
33 nd Ode Effect: Mountains and Oceans Rathe than being smooth, the suface of the Eath is elatively lumpy : Thee is about a 0 km diffeence in height between the highest mountain and the deepest pat of the ocean floo... The Eath 33
34 3 d Ode Effect: Intenal Mass Distibution The diffeent mateials that make up the layes of the Eath s cust and mantle ae fa fom homogeneously distibuted: Fo instance, the cust beneath the oceans is a lot thinne and dense than the continental cust... The Eath 34
35 The Idealized Geometical Figue of the Eath Because of its elative simplicity, a flattened ellipsoid, called the efeence ellipsoid, is typically used as the idealized Eath: Ellipsoid of evolution. The size is epesented by the adius at the equato, a. The shape of the ellipsoid is given by the flattening, f, which indicates how much the ellipsoid depats fom spheical. f=(a-b)/a, whee b is the pola adius...3 Gavity models and geoid 35
36 Most Common Refeence Ellipsoid WGS84 (Wold Geodetic System 1984, evised in 004): Oigin at the cente of mass of Eath. a= km, b= km, f=0.335 %. Refeence system used by the GPS. Official document on the couse web site (inteesting to ead!). WGS84 fou defining paametes..3 Gavity models and geoid 36
37 WGS84 Coodinate System..3 Gavity models and geoid 37
38 Longitude Point coodinates such as latitude, longitude and elevation ae defined fom the efeence ellipsoid. The meidian of zeo longitude is the IERS Refeence Meidian, which lies 5.31 east of the Geenwich Meidian...3 Gavity models and geoid 38
39 GPS Receive at the Geenwich Meidian 5.31/3600= OK!..3 Gavity models and geoid 39
40 Latitude Also called geodetic latitude..3 Gavity models and geoid 40
41 The Tue Figue of the Eath The geoid is that equipotential suface which would coincide exactly with the mean ocean suface of the Eath, if the oceans wee in equilibium, at est, and extended though the continents: It is by definition a suface to which the foce of gavity is eveywhee pependicula. It is an iegula suface but consideably smoothe than Eath's physical suface. While the latte has excusions of almost 0 km, the total vaiation in the geoid is less than 00 m...3 Gavity models and geoid 41
42 The Tue Figue of the Eath..3 Gavity models and geoid 4
43 Gavitational Modeling Spheical hamonics ae used to model the Eath gavitational model: Gavitational potential function The cuent set is EGM008 (Eath Gavity Model 008). The model compises 4.6 million tems in the spheical expansion (ode and degee 159). Geoid with a esolution appoaching 10 km (5 x5 ). Moe details in Chapte 4 (Non-Kepleian motion)...3 Gavity models and geoid 43
44 EGM008 is Available in STK Gavity models and geoid 44
45 EGM008 Made Use of Gace Satellites GRACE employs micowave anging system to measue changes in the distance between two identical satellites as they cicle Eath. The anging system detects changes as small as 10 micons ove a distance of 0 km...3 Gavity models and geoid 45
46 Geoid Definition EGM008 contains no explicit infomation about which level suface, out of the infinitely many that may be geneated fom the potential coefficients, is "the" geoid. EGM008 model is theefoe used to compute geoid undulations with espect to WGS84 ellipsoid. The esult is efeed to as WGS84-EGM08 geoid. Geoid calculato fo EGM96: Gavity models and geoid 46
47 1: ocean : efeence ellipsoid 3: local plumb 4: continent 5: geoid
48
49 GPS Receives You ae on a boat in the middle of the Atlantic ocean, what will be the height indicated by you GPS? You ae at sea level, but the height will be diffeent fom 0. The GPS satellites can only measue heights elative to the WGS84 model, which is an idealized figue of the Eath...3 Gavity models and geoid 49
50 GPS Receives Some GPS eceives can obtain the geoid height ove the WGS ellipsoid fom the cuent position. They ae then able to coect the height above WGS ellipsoid to the height above the geoid. You ae on a boat in the middle of the Atlantic ocean, will the height indicated by this GPS be equal to zeo? Not necessaily, because thee ae tides..3 Gavity models and geoid 50
51 Residual Sea Suface Slopes (EGM-96)..3 Gavity models and geoid 51
52 Residual Sea Suface Slopes (EGM-008)..3 Gavity models and geoid 5
53 Futue Impovements: GOCE, 009 (EGM96: ~0.5 m) (1mGal = 10-5 m/s )..3 Gavity models and geoid 53
54 Why So Many Effots??? 1. GPS and an advanced map of the geoid can eplace time-consuming leveling pocedues.. Physics of the Eath s inteio (gavity is diectly linked to the distibution of mass). 3. Undestanding of ocean ciculation, which plays a key ole in enegy exchanges aound the globe. 4. Computation of the motion of satellites to the level of accuacy equied today...3 Gavity models and geoid 54
55 Futhe Reading on the Couse Web Site..3 Gavity models and geoid 55
56 Digession: Geneal Relativity Einstein's theoy is the cuent desciption of gavity in moden physics. This couse will not cove the theoy of geneal elativity, but Newton's law is still an excellent appoximation of the effects of gavity if: GM v 1, and 1 c c c..3 Gavity models and geoid 56
57 Geneal Relativity: Eath-Sun Example 8 v obit 8 GM sun ~ 10, and ~ 10 c obit c c 1 yea. c OK! G= m 3.kg -1.s - obit = m (1 AU) M sun = kg c=3e8 m.s Gavity models and geoid 57
58 The Quest of a Unifying Theoy What is the elationship between the gavitational foce and othe known fundamental foces? That one body may act upon anothe at a distance though a vacuum without the mediation of anything else, by and though which thei action and foce may be conveyed fom one anothe, is to me so geat an absudity that, I believe, no man who has in philosophic mattes a competent faculty of thinking could eve fall into it. (Newton, 169) The question is not yet fully esolved today!..3 Gavity models and geoid 58
59 The Quest of a Unifying Theoy [End of digession]..3 Gavity models and geoid 59
60 10-min. beak
61 . The Two-Body Poblem 3.3 Relative motion:.3.1 Equations of motion.3. Closed-fom solution 61
62 Definition of the -Body Poblem Motion of two bodies due solely to thei own mutual gavitational attaction. Also known as Keple poblem. Assumption: two point masses (o equivalently spheically symmetic objects).??.3.1 Equations of motion 6
63 Motion of the Cente of Mass m m R 1 ˆ 1 1 R Gm m + Gm m u u 1 ˆ m 1 R 1 uˆ R G R R m R R 1 1 m 1R1 mr 0 R G m + R m m R m Inetial fame of efeence The c.o.m. of a -body R R v t system may seve as the G G0 G oigin of an inetial fame..3.1 Equations of motion 63
64 Equations of Relative Motion mm Gm m 1 1 R ˆ u mm Gm m 1 1 R ˆ 1 u + G m m R R u 1 ˆ 1 m 1 R 1 uˆ R G Inetial fame of efeence R R m R R μ is the gavitational paamete The motion of m as seen fom m 1 is the same as the motion of m 1 as seen fom m..3.1 Equations of motion 64
65 Equations of Relative Motion 3 This is a nonlinea dynamical system. How to solve it? Find constants of the motion! How many?.3. Closed-fom solution 65
66 Constant Angula Momentum h Specific angula momentum d / dt dh dt dh 0 constant= dt h.3. Closed-fom solution 66
67 The Motion Lies in a Fixed Plane hˆ h h hˆ h h The fixed plane is the obit plane and is nomal to the angula momentum vecto. constant= h.3. Closed-fom solution 67
68 Azimuth Component of the Velocity v h uˆ ( v uˆ v uˆ ) v hˆ v h v The angula momentum depends only on the azimuth component of the elative velocity.3. Closed-fom solution 68
69 Fist Integal of Motion h h h d ab c b a. c ca. b dt d h.. 3 dt h constant= e e lies in the obit plane (e.h)=0: the line defined by e is the apse line. Its nom, e, is the eccenticity..3. Closed-fom solution 69
70 Οbit Equation h e.. h. e. a. b c a b. c. h. h hh. h e. h 1 1 ecos Closed fom of the nonlinea equations of motion.3. Closed-fom solution 70
71 Conic Section in Pola Coodinates Constant: angula momentum Semi-latus ectum h 1 p 1ecos 1ecos Constant: gavitational paamete Independent vaiable: tue anomaly (=0 at the peiapsis) Constant: eccenticity.3. Closed-fom solution 71
72 Conic Section e=1 e=0 0<e<1 e>1.3. Closed-fom solution 7
73 In Summay + We can calculate fo all values of the tue anomaly. + - The obit equation is a mathematical statement of Keple s fist law. We only know the elative motion (howeve, e.g., the motion of ou sun elative to othe pats of ou galaxy is of little impotance fo missions within ou sola system). - The solution of the simple poblem of two bodies cannot be expessed in a closed fom, explicit function of time. Do we have 6 independent constants? The two vecto constants h and e povide only 5 independent constants: h.e=0.3. Closed-fom solution 73
74 . The Two-Body Poblem 3.4 Resulting obits:.4.1 Cicula obits.4. Elliptic obits.4.3 Paabolic obits.4.4 Hypebolic obits 74
75 Thee Objectives 1. Peiod. Velocity 3. Enegy 75
76 Digession: Enegy of the Obit T mv V m The gavitational foce is consevative Specific enegy v constant 76
77 Enegy of the Obit at Peiapsis vp v h p p p p p p h 1 h 1ecos (1 e) 0 1 h 1 e [End of digession] 77
78 Possible Motions in the -Body System ellipse cicle paabola hypebola 78
79 Cicula Obits (e=0) h Constant h v vcicula v cic Tcic 3/ cic Cicula obits 79
80 Obital speed (km/s) Obital Speed G( msat M ) GM ISS 7.6 HST 7.5 SPOT Altitude (km).4.1 Cicula obits 80
81 Obital peiod (min) Obital Peiod SPOT HST 95 ISS Altitude (km).4.1 Cicula obits 81
82 Hubble Space Telescope.4.1 Cicula obits 8
83 Hubble Space Telescope.4.1 Cicula obits 83
84 Two Paticula Cases km/s is the fist cosmic velocity; i.e., the minimum velocity (theoetical velocity, = 6378 km) to obit the Eath km is the altitude of the geostationay obit. It is the obit at which the satellite angula velocity is equal to that of the Eath, ω=ω E = ad/s, in inetial space (*). GEO T cic * A sideeal day, 3h56m4s, is the time it takes the Eath to complete one otation elative to inetial space. A synodic day, 4h, is the time it takes the sun to appaently otate once aound the eath. They would be identical if the eath stood still in space. 84 /3
85 Elliptic Obits (0<e<1) h 1 1 ecos The elative position vecto emains bounded. θ=0, minimum sepaation, peiapse p h (1 e) θ=π, geatest sepaation, apoapse a h (1 e) θ=π/, semi-latus ectum p e a a p p.4. Elliptic obits 85
86 Geomety of the Elliptic Obit a apse line θ b p a p.4. Elliptic obits 86
87 Angula Momentum and Enegy h 1 1 ecos a(1 e ) 1 ecos Obit equation Pola equation of an ellipse (a, semimajo axis) h a e (1 ) 1 h 1 e ellip a 0 Independent of eccenticity!.4. Elliptic obits 87
88 Vis-Viva Equation v a v ellip 1 a.4. Elliptic obits 88
89 Keple s Second Law da dt h dt hdt () t ( t dt) dt da h 1 d dt dt constant The line fom the sun to a planet sweeps out equal aeas inside the ellipse in equal lengths of time. eminde 1 Aea ABAC.4. Elliptic obits 89
90 Keple s Thid Law enclosed aea T da/ dt ab h h a e (1 ) b a 1e 3 a Tellip The elliptic obit peiod depends only on the semimajo axis and is independent of the eccentivity. T T a a The squaes of the obital peiods of the planets ae popotional to the cubes of thei mean distances fom the sun..4. Elliptic obits 90
91 STK Simulation The elliptic obit peiod depends only on the semimajo axis and is independent of the eccentivity. 91
92 OUFTI km km p a e a p a p 0.075, a 778.5km a p 3 a T s 103min v 1 a vp va 7.98km/s 6.86 km/s.4. Elliptic obits 9
93 OUFTI-1.4. Elliptic obits 93
94 OUFTI-1.4. Elliptic obits 94
95 GTO and GEO Fo an obit with a peigee at 30 km and an apogee at km, what is the velocity incement equied to each the geostationay obit? v 1 a.4. Elliptic obits 95
96 GTO and GEO Fo an obit with a peigee at 30 km and an apogee at km, what is the velocity incement equied to each the geostationay obit? a vp va a GTO p 10.13km/s 1.61km/s 4430 km vcic Answe: 1.46 km/s (apogee moto) GEO km/s.4. Elliptic obits 96
97 m/m GTO and GEO (1000,0.88) (1460,0.391) v (m/s) Isp=300s 97
98 Paabolic Obits (e=1) h 1 1 cos, 1 paab h 1 e 0 The satellite has just enough enegy to escape fom the attacting body. v v paab The satellite will coast to infinity, aiving thee with zeo velocity elative to the cental body..4.3 Paabolic obits 98
99 Escape Velocity, V esc 11. km/s is the second cosmic velocity; i.e., the minimum velocity (theoetical velocity, = 6378km) to obit the Eath. v cic v paab 11. km/s 7.9 km/s.4.3 Paabolic obits 99
100 Hypebolic Obits (e>1) h 1 1 ecos p a a a p h (1 e) h 0 (1 e) a a p a h e 1 h e hype a Hypebolic obits 100
101 C 3 Velocity v v a a Hypebolic excess speed v v v v vesc C3 v esc C 3 is a measue of the enegy fo an inteplanetay mission: 16.6 km /s (Cassini-Huygens) 8.9 km /s (Sola Obite, phase A).4.4 Hypebolic obits 101
102 Soyuz ST v-1b (Kouou Launch).4.4 Hypebolic obits 10
103 Delta II, Delta III and Atlas IIIA.4.4 Hypebolic obits 103
104 Poton.4.4 Hypebolic obits 104
105 Falcon Hypebolic obits 105
106 The Two-Body Poblem.1 JUSTIFICATION OF THE -BODY MODEL. GRAVITATIONAL FIELD..1 Newton s law of univesal gavitation.. The Eath..3 Gavity models and geoid.3 RELATIVE MOTION.3.1 Equations of motion.3. Closed-fom solution.4 RESULTING ORBITS.4.1 Cicula obits.4. Elliptic obits.4.3 Paabolic obits.4.4. Hypebolic obits 106
107 Newton s laws F ma F g mm G 1 uˆ Relative motion 3 Enegy consev. v Angula mom. h Azim. velocity Keple s 1 st law h 1 1 ecos The obit equation v h / Keple s nd law da/ dt h/ Keple s 3 d law T a /
108 Concluding Remaks Closed-fom solution fom which we deduced Keple s laws. Analytic fomulas fo obital enegy, velocity and peiod. Two-body popagato available in STK. Often used in ealy studies to pefom tending analysis. But We have lost tack of the time vaiable! 108
109 Did you Know? Compactness of the sola system: measued by the atio of the distance a of a planet fom the Sun to the adius R of the Sun. a R 00 Compactness of the hydogen atom: measued by the atio of the distance a of an electon fom the nucleus to the adius R of the nucleus. a R 54 e 109
110 Astodynamics (AERO004). The Two-Body Poblem Gaëtan Keschen Space Stuctues & Systems Lab (S3L)
AERO0025 Satellite Engineering. Lecture 2. Satellite orbits
 AERO0025 Satellite Engineeing Lectue 2 Satellite obits 1 Can the Obit Affect Mass of the satellite? Powe geneation? Amount of data that can be tansfeed to the gound? Space adiation envionment? Revisit
AERO0025 Satellite Engineeing Lectue 2 Satellite obits 1 Can the Obit Affect Mass of the satellite? Powe geneation? Amount of data that can be tansfeed to the gound? Space adiation envionment? Revisit
AERO0025 Satellite Engineering. Lecture 8. Satellite orbits
 AERO0025 Satellite Engineeing Lectue 8 Satellite obits 1 Can the Obit Affect Mass of the satellite? Powe geneation? Amount of data that can be tansfeed to the gound? Space adiation envionment? Revisit
AERO0025 Satellite Engineeing Lectue 8 Satellite obits 1 Can the Obit Affect Mass of the satellite? Powe geneation? Amount of data that can be tansfeed to the gound? Space adiation envionment? Revisit
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Between any two masses, there exists a mutual attractive force.
 YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
m1 m2 M 2 = M -1 L 3 T -2
 GAVITATION Newton s Univesal law of gavitation. Evey paticle of matte in this univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which vaies diectly as the poduct of thei masses and invesely as the squae of
GAVITATION Newton s Univesal law of gavitation. Evey paticle of matte in this univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which vaies diectly as the poduct of thei masses and invesely as the squae of
Newton s Laws, Kepler s Laws, and Planetary Orbits
 Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
F 12. = G m m 1 2 F 21 = F 12. = G m 1m 2. Review. Physics 201, Lecture 22. Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation
 Physics 201, Lectue 22 Review Today s Topics n Univesal Gavitation (Chapte 13.1-13.3) n Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation n Popeties of Gavitational Foce n Planet Obits; Keple s Laws by Newton s Law
Physics 201, Lectue 22 Review Today s Topics n Univesal Gavitation (Chapte 13.1-13.3) n Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation n Popeties of Gavitational Foce n Planet Obits; Keple s Laws by Newton s Law
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
Paths of planet Mars in sky
 Section 4 Gavity and the Sola System The oldest common-sense view is that the eath is stationay (and flat?) and the stas, sun and planets evolve aound it. This GEOCENTRIC MODEL was poposed explicitly by
Section 4 Gavity and the Sola System The oldest common-sense view is that the eath is stationay (and flat?) and the stas, sun and planets evolve aound it. This GEOCENTRIC MODEL was poposed explicitly by
Determining solar characteristics using planetary data
 Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G-type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this investigation
Detemining sola chaacteistics using planetay data Intoduction The Sun is a G-type main sequence sta at the cente of the Sola System aound which the planets, including ou Eath, obit. In this investigation
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
AY 7A - Fall 2010 Section Worksheet 2 - Solutions Energy and Kepler s Law
 AY 7A - Fall 00 Section Woksheet - Solutions Enegy and Keple s Law. Escape Velocity (a) A planet is obiting aound a sta. What is the total obital enegy of the planet? (i.e. Total Enegy = Potential Enegy
AY 7A - Fall 00 Section Woksheet - Solutions Enegy and Keple s Law. Escape Velocity (a) A planet is obiting aound a sta. What is the total obital enegy of the planet? (i.e. Total Enegy = Potential Enegy
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
AST 121S: The origin and evolution of the Universe. Introduction to Mathematical Handout 1
 Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION
 EPER S AWS OF PANETARY MOTION 1. Intoduction We ae now in a position to apply what we have leaned about the coss poduct and vecto valued functions to deive eple s aws of planetay motion. These laws wee
EPER S AWS OF PANETARY MOTION 1. Intoduction We ae now in a position to apply what we have leaned about the coss poduct and vecto valued functions to deive eple s aws of planetay motion. These laws wee
PHYSICS NOTES GRAVITATION
 GRAVITATION Newton s law of gavitation The law states that evey paticle of matte in the univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which is diectly popotional to the poduct of thei masses and invesely
GRAVITATION Newton s law of gavitation The law states that evey paticle of matte in the univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which is diectly popotional to the poduct of thei masses and invesely
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6- THE LAW OF GRAVITATION Essential Idea: The Newtonian idea of gavitational foce acting between two spheical bodies and the laws of mechanics
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6- THE LAW OF GRAVITATION Essential Idea: The Newtonian idea of gavitational foce acting between two spheical bodies and the laws of mechanics
Physics: Work & Energy Beyond Earth Guided Inquiry
 Physics: Wok & Enegy Beyond Eath Guided Inquiy Elliptical Obits Keple s Fist Law states that all planets move in an elliptical path aound the Sun. This concept can be extended to celestial bodies beyond
Physics: Wok & Enegy Beyond Eath Guided Inquiy Elliptical Obits Keple s Fist Law states that all planets move in an elliptical path aound the Sun. This concept can be extended to celestial bodies beyond
Gravitation. AP/Honors Physics 1 Mr. Velazquez
 Gavitation AP/Honos Physics 1 M. Velazquez Newton s Law of Gavitation Newton was the fist to make the connection between objects falling on Eath and the motion of the planets To illustate this connection
Gavitation AP/Honos Physics 1 M. Velazquez Newton s Law of Gavitation Newton was the fist to make the connection between objects falling on Eath and the motion of the planets To illustate this connection
KEPLER S LAWS AND PLANETARY ORBITS
 KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
Chapter 12. Kinetics of Particles: Newton s Second Law
 Chapte 1. Kinetics of Paticles: Newton s Second Law Intoduction Newton s Second Law of Motion Linea Momentum of a Paticle Systems of Units Equations of Motion Dynamic Equilibium Angula Momentum of a Paticle
Chapte 1. Kinetics of Paticles: Newton s Second Law Intoduction Newton s Second Law of Motion Linea Momentum of a Paticle Systems of Units Equations of Motion Dynamic Equilibium Angula Momentum of a Paticle
Physics 181. Assignment 4
 Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Universal Gravitation
 Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 10-: MOTION IN A GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Questions Fom Reading Activity? Gavity Waves? Essential Idea: Simila appoaches can be taken in analyzing electical
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 10-: MOTION IN A GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Questions Fom Reading Activity? Gavity Waves? Essential Idea: Simila appoaches can be taken in analyzing electical
MODULE 5 ADVANCED MECHANICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD: MOTION OF PLANETS AND SATELLITES VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLIN MODUL 5 ADVANCD MCHANICS GRAVITATIONAL FILD: MOTION OF PLANTS AND SATLLITS SATLLITS: Obital motion of object of mass m about a massive object of mass M (m
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLIN MODUL 5 ADVANCD MCHANICS GRAVITATIONAL FILD: MOTION OF PLANTS AND SATLLITS SATLLITS: Obital motion of object of mass m about a massive object of mass M (m
Recap. Centripetal acceleration: v r. a = m/s 2 (towards center of curvature)
 a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
Practice. Understanding Concepts. Answers J 2. (a) J (b) 2% m/s. Gravitation and Celestial Mechanics 287
 Pactice Undestanding Concepts 1. Detemine the gavitational potential enegy of the Eath Moon system, given that the aveage distance between thei centes is 3.84 10 5 km, and the mass of the Moon is 0.0123
Pactice Undestanding Concepts 1. Detemine the gavitational potential enegy of the Eath Moon system, given that the aveage distance between thei centes is 3.84 10 5 km, and the mass of the Moon is 0.0123
Chap 5. Circular Motion: Gravitation
 Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
Gravitation. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Chapter 13: Gravitation
 v m m F G Chapte 13: Gavitation The foce that makes an apple fall is the same foce that holds moon in obit. Newton s law of gavitation: Evey paticle attacts any othe paticle with a gavitation foce given
v m m F G Chapte 13: Gavitation The foce that makes an apple fall is the same foce that holds moon in obit. Newton s law of gavitation: Evey paticle attacts any othe paticle with a gavitation foce given
Lecture 1a: Satellite Orbits
 Lectue 1a: Satellite Obits Outline 1. Newton s Laws of Motion 2. Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation 3. Calculating satellite obital paametes (assuming cicula motion) Scala & Vectos Scala: a physical quantity
Lectue 1a: Satellite Obits Outline 1. Newton s Laws of Motion 2. Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation 3. Calculating satellite obital paametes (assuming cicula motion) Scala & Vectos Scala: a physical quantity
Physics 111. Ch 12: Gravity. Newton s Universal Gravity. R - hat. the equation. = Gm 1 m 2. F g 2 1. ˆr 2 1. Gravity G =
 ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
PHYS Dynamics of Space Vehicles
 PHYS 4110 - Dynamics of Space Vehicles Chapte 3: Two Body Poblem Eath, Moon, Mas, and Beyond D. Jinjun Shan, Pofesso of Space Engineeing Depatment of Eath and Space Science and Engineeing Room 55, Petie
PHYS 4110 - Dynamics of Space Vehicles Chapte 3: Two Body Poblem Eath, Moon, Mas, and Beyond D. Jinjun Shan, Pofesso of Space Engineeing Depatment of Eath and Space Science and Engineeing Room 55, Petie
10. Force is inversely proportional to distance between the centers squared. R 4 = F 16 E 11.
 NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Pactice Gavitation Solution nswe 1. m mv Obital speed is found fom setting which gives v whee M is the object being obited. Notice that satellite mass does not affect obital
NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Pactice Gavitation Solution nswe 1. m mv Obital speed is found fom setting which gives v whee M is the object being obited. Notice that satellite mass does not affect obital
= 1. For a hyperbolic orbit with an attractive inverse square force, the polar equation with origin at the center of attraction is
 15. Kepleian Obits Michael Fowle Peliminay: Pola Equations fo Conic Section Cuves As we shall find, Newton s equations fo paticle motion in an invese-squae cental foce give obits that ae conic section
15. Kepleian Obits Michael Fowle Peliminay: Pola Equations fo Conic Section Cuves As we shall find, Newton s equations fo paticle motion in an invese-squae cental foce give obits that ae conic section
F g. = G mm. m 1. = 7.0 kg m 2. = 5.5 kg r = 0.60 m G = N m 2 kg 2 = = N
 Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Central Force Motion
 Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Ch 13 Universal Gravitation
 Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Why do celestial objects move the way they do? Keple (1561-1630) Tycho Bahe s assistant, analyzed celestial motion mathematically Galileo (1564-1642)
Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Why do celestial objects move the way they do? Keple (1561-1630) Tycho Bahe s assistant, analyzed celestial motion mathematically Galileo (1564-1642)
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 08. Textbook Sections Lecture 8 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
Lecture 22. PE = GMm r TE = GMm 2a. T 2 = 4π 2 GM. Main points of today s lecture: Gravitational potential energy: Total energy of orbit:
 Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
History of Astronomy - Part II. Tycho Brahe - An Observer. Johannes Kepler - A Theorist
 Histoy of Astonomy - Pat II Afte the Copenican Revolution, astonomes stived fo moe obsevations to help bette explain the univese aound them Duing this time (600-750) many majo advances in science and astonomy
Histoy of Astonomy - Pat II Afte the Copenican Revolution, astonomes stived fo moe obsevations to help bette explain the univese aound them Duing this time (600-750) many majo advances in science and astonomy
Extra notes for circular motion: Circular motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and
 Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Radius of the Moon is 1700 km and the mass is 7.3x 10^22 kg Stone. Moon
 xample: A 1-kg stone is thown vetically up fom the suface of the Moon by Supeman. The maximum height fom the suface eached by the stone is the same as the adius of the moon. Assuming no ai esistance and
xample: A 1-kg stone is thown vetically up fom the suface of the Moon by Supeman. The maximum height fom the suface eached by the stone is the same as the adius of the moon. Assuming no ai esistance and
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Chap13. Universal Gravitation
 Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
Math Notes on Kepler s first law 1. r(t) kp(t)
 Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
HW6 Physics 311 Mechanics
 HW6 Physics 311 Mechanics Fall 015 Physics depatment Univesity of Wisconsin, Madison Instucto: Pofesso Stefan Westehoff By Nasse M. Abbasi June 1, 016 Contents 0.1 Poblem 1.........................................
HW6 Physics 311 Mechanics Fall 015 Physics depatment Univesity of Wisconsin, Madison Instucto: Pofesso Stefan Westehoff By Nasse M. Abbasi June 1, 016 Contents 0.1 Poblem 1.........................................
AP * PHYSICS B. Circular Motion, Gravity, & Orbits. Teacher Packet
 AP * PHYSICS B Cicula Motion, Gavity, & Obits Teache Packet AP* is a tademak of the College Entance Examination Boad. The College Entance Examination Boad was not involved in the poduction of this mateial.
AP * PHYSICS B Cicula Motion, Gavity, & Obits Teache Packet AP* is a tademak of the College Entance Examination Boad. The College Entance Examination Boad was not involved in the poduction of this mateial.
Circular Orbits. and g =
 using analyse planetay and satellite motion modelled as unifom cicula motion in a univesal gavitation field, a = v = 4π and g = T GM1 GM and F = 1M SATELLITES IN OBIT A satellite is any object that is
using analyse planetay and satellite motion modelled as unifom cicula motion in a univesal gavitation field, a = v = 4π and g = T GM1 GM and F = 1M SATELLITES IN OBIT A satellite is any object that is
ω = θ θ o = θ θ = s r v = rω
 Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
Revision Guide for Chapter 11
 Revision Guide fo Chapte 11 Contents Revision Checklist Revision Notes Momentum... 4 Newton's laws of motion... 4 Wok... 5 Gavitational field... 5 Potential enegy... 7 Kinetic enegy... 8 Pojectile... 9
Revision Guide fo Chapte 11 Contents Revision Checklist Revision Notes Momentum... 4 Newton's laws of motion... 4 Wok... 5 Gavitational field... 5 Potential enegy... 7 Kinetic enegy... 8 Pojectile... 9
Objective Notes Summary
 Objective Notes Summay An object moving in unifom cicula motion has constant speed but not constant velocity because the diection is changing. The velocity vecto in tangent to the cicle, the acceleation
Objective Notes Summay An object moving in unifom cicula motion has constant speed but not constant velocity because the diection is changing. The velocity vecto in tangent to the cicle, the acceleation
MODULE 5 ADVANCED MECHANICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD: MOTION OF PLANETS AND SATELLITES VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 5 ADVANCED MECHANICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD: MOTION OF PLANETS AND SATELLITES SATELLITES: Obital motion of object of mass m about a massive object of mass M (m
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 5 ADVANCED MECHANICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD: MOTION OF PLANETS AND SATELLITES SATELLITES: Obital motion of object of mass m about a massive object of mass M (m
Modeling Ballistics and Planetary Motion
 Discipline Couses-I Semeste-I Pape: Calculus-I Lesson: Lesson Develope: Chaitanya Kuma College/Depatment: Depatment of Mathematics, Delhi College of Ats and Commece, Univesity of Delhi Institute of Lifelong
Discipline Couses-I Semeste-I Pape: Calculus-I Lesson: Lesson Develope: Chaitanya Kuma College/Depatment: Depatment of Mathematics, Delhi College of Ats and Commece, Univesity of Delhi Institute of Lifelong
AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit 2) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit 2) Circular Motion
 AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) Cicula Motion No. kill Done 1 Know that cicula motion efes to motion in a cicle of constant adius Know that cicula motion is conveniently descibed
AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) Cicula Motion No. kill Done 1 Know that cicula motion efes to motion in a cicle of constant adius Know that cicula motion is conveniently descibed
SIO 229 Gravity and Geomagnetism. Lecture 6. J 2 for Earth. J 2 in the solar system. A first look at the geoid.
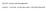 SIO 229 Gavity and Geomagnetism Lectue 6. J 2 fo Eath. J 2 in the sola system. A fist look at the geoid. The Thee Big Themes of the Gavity Lectues 1.) An ellipsoidal otating Eath Refeence body (mass +
SIO 229 Gavity and Geomagnetism Lectue 6. J 2 fo Eath. J 2 in the sola system. A fist look at the geoid. The Thee Big Themes of the Gavity Lectues 1.) An ellipsoidal otating Eath Refeence body (mass +
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department. Problem Set 10 Solutions. r s
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
TAMPINES JUNIOR COLLEGE 2009 JC1 H2 PHYSICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD
 TAMPINES JUNIOR COLLEGE 009 JC1 H PHYSICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD OBJECTIVES Candidates should be able to: (a) show an undestanding of the concept of a gavitational field as an example of field of foce and
TAMPINES JUNIOR COLLEGE 009 JC1 H PHYSICS GRAVITATIONAL FIELD OBJECTIVES Candidates should be able to: (a) show an undestanding of the concept of a gavitational field as an example of field of foce and
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Experiment 09: Angular momentum
 Expeiment 09: Angula momentum Goals Investigate consevation of angula momentum and kinetic enegy in otational collisions. Measue and calculate moments of inetia. Measue and calculate non-consevative wok
Expeiment 09: Angula momentum Goals Investigate consevation of angula momentum and kinetic enegy in otational collisions. Measue and calculate moments of inetia. Measue and calculate non-consevative wok
7.2. Coulomb s Law. The Electric Force
 Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
PS113 Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
 PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
University Physics Volume I Unit 1: Mechanics Chapter 13: Gravitation Conceptual Questions
 OpenStax Univesity Physics Volume I Univesity Physics Volume I Conceptual Questions 1. Action at a distance, such as is the case fo gavity, was once thought to be illogical and theefoe untue. What is the
OpenStax Univesity Physics Volume I Univesity Physics Volume I Conceptual Questions 1. Action at a distance, such as is the case fo gavity, was once thought to be illogical and theefoe untue. What is the
Escape Velocity. GMm ] B
![Escape Velocity. GMm ] B Escape Velocity. GMm ] B](/thumbs/84/90630003.jpg) 1 PHY2048 Mach 31, 2006 Escape Velocity Newton s law of gavity: F G = Gm 1m 2 2, whee G = 667 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 2 3 10 10 N m 2 /kg 2 is Newton s Gavitational Constant Useful facts: R E = 6 10 6 m M E
1 PHY2048 Mach 31, 2006 Escape Velocity Newton s law of gavity: F G = Gm 1m 2 2, whee G = 667 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 2 3 10 10 N m 2 /kg 2 is Newton s Gavitational Constant Useful facts: R E = 6 10 6 m M E
10. Universal Gravitation
 10. Univesal Gavitation Hee it is folks, the end of the echanics section of the couse! This is an appopiate place to complete the study of mechanics, because with his Law of Univesal Gavitation, Newton
10. Univesal Gavitation Hee it is folks, the end of the echanics section of the couse! This is an appopiate place to complete the study of mechanics, because with his Law of Univesal Gavitation, Newton
GRAVITATION. Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., New Delhi -18 PG 1
 Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa Plaza, Vikas Pui Extn., New Delhi -8 Ph. : 96905, 857, E-mail einsteinclasses00@gmail.com, PG GRAVITATION Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa Plaza, Vikas Pui Extn., New Delhi -8 Ph. : 96905, 857, E-mail einsteinclasses00@gmail.com, PG GRAVITATION Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa
Our Universe: GRAVITATION
 Ou Univese: GRAVITATION Fom Ancient times many scientists had shown geat inteest towads the sky. Most of the scientist studied the motion of celestial bodies. One of the most influential geek astonomes
Ou Univese: GRAVITATION Fom Ancient times many scientists had shown geat inteest towads the sky. Most of the scientist studied the motion of celestial bodies. One of the most influential geek astonomes
Lecture 1a: Satellite Orbits
 Lectue 1a: Satellite Obits Outline 1. Newton s Laws of Mo3on 2. Newton s Law of Univesal Gavita3on 3. Calcula3ng satellite obital paametes (assuming cicula mo3on) Scala & Vectos Scala: a physical quan3ty
Lectue 1a: Satellite Obits Outline 1. Newton s Laws of Mo3on 2. Newton s Law of Univesal Gavita3on 3. Calcula3ng satellite obital paametes (assuming cicula mo3on) Scala & Vectos Scala: a physical quan3ty
ASTR415: Problem Set #6
 ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
Lecture 3. Basic Physics of Astrophysics - Force and Energy. Forces
 Foces Lectue 3 Basic Physics of Astophysics - Foce and Enegy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Momentum is the poduct of mass and velocity - a vecto p = mv (geneally m is taken to be constant) An unbalanced foce
Foces Lectue 3 Basic Physics of Astophysics - Foce and Enegy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Momentum is the poduct of mass and velocity - a vecto p = mv (geneally m is taken to be constant) An unbalanced foce
Gravitational Potential Energy in General
 Gavitational Potential Enegy in Geneal 6.3 To exploe such concepts as how much enegy a space pobe needs to escape fom Eath s gavity, we must expand on the topic of gavitational potential enegy, which we
Gavitational Potential Enegy in Geneal 6.3 To exploe such concepts as how much enegy a space pobe needs to escape fom Eath s gavity, we must expand on the topic of gavitational potential enegy, which we
Solving Problems of Advance of Mercury s Perihelion and Deflection of. Photon Around the Sun with New Newton s Formula of Gravity
 Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Solving Poblems of Advance of Mecuy s Peihelion and Deflection of Photon Aound the Sun with New Newton s Fomula of Gavity Fu Yuhua (CNOOC Reseach Institute, E-mail:fuyh945@sina.com) Abstact: Accoding to
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
The Millikan Experiment: Determining the Elementary Charge
 LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
Astro 250: Solutions to Problem Set 1. by Eugene Chiang
 Asto 250: Solutions to Poblem Set 1 by Eugene Chiang Poblem 1. Apsidal Line Pecession A satellite moves on an elliptical obit in its planet s equatoial plane. The planet s gavitational potential has the
Asto 250: Solutions to Poblem Set 1 by Eugene Chiang Poblem 1. Apsidal Line Pecession A satellite moves on an elliptical obit in its planet s equatoial plane. The planet s gavitational potential has the
GRAVITATION. Thus the magnitude of the gravitational force F that two particles of masses m1
 GAVITATION 6.1 Newton s law of Gavitation Newton s law of gavitation states that evey body in this univese attacts evey othe body with a foce, which is diectly popotional to the poduct of thei masses and
GAVITATION 6.1 Newton s law of Gavitation Newton s law of gavitation states that evey body in this univese attacts evey othe body with a foce, which is diectly popotional to the poduct of thei masses and
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
Chapter 4. Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
F(r) = r f (r) 4.8. Central forces The most interesting problems in classical mechanics are about central forces.
 4.8. Cental foces The most inteesting poblems in classical mechanics ae about cental foces. Definition of a cental foce: (i) the diection of the foce F() is paallel o antipaallel to ; in othe wods, fo
4.8. Cental foces The most inteesting poblems in classical mechanics ae about cental foces. Definition of a cental foce: (i) the diection of the foce F() is paallel o antipaallel to ; in othe wods, fo
Physics 312 Introduction to Astrophysics Lecture 7
 Physics 312 Intoduction to Astophysics Lectue 7 James Buckley buckley@wuphys.wustl.edu Lectue 7 Eath/Moon System Tidal Foces Tides M= mass of moon o sun F 1 = GMm 2 F 2 = GMm ( + ) 2 Diffeence in gavitational
Physics 312 Intoduction to Astophysics Lectue 7 James Buckley buckley@wuphys.wustl.edu Lectue 7 Eath/Moon System Tidal Foces Tides M= mass of moon o sun F 1 = GMm 2 F 2 = GMm ( + ) 2 Diffeence in gavitational
Kepler's 1 st Law by Newton
 Astonom 10 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astonom Building This Class (Lectue 7): Gavitation Net Class: Theo of Planeta Motion HW # Due Fida! Missed nd planetaium date. (onl 5 left), including tonight Stadial
Astonom 10 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astonom Building This Class (Lectue 7): Gavitation Net Class: Theo of Planeta Motion HW # Due Fida! Missed nd planetaium date. (onl 5 left), including tonight Stadial
What Form of Gravitation Ensures Weakened Kepler s Third Law?
 Bulletin of Aichi Univ. of Education, 6(Natual Sciences, pp. - 6, Mach, 03 What Fom of Gavitation Ensues Weakened Keple s Thid Law? Kenzi ODANI Depatment of Mathematics Education, Aichi Univesity of Education,
Bulletin of Aichi Univ. of Education, 6(Natual Sciences, pp. - 6, Mach, 03 What Fom of Gavitation Ensues Weakened Keple s Thid Law? Kenzi ODANI Depatment of Mathematics Education, Aichi Univesity of Education,
Welcome to Aerospace Engineering
 Welcome to Aeospace Engineeing DESIGN-CENTERED INTRODUCTION TO AEROSPACE ENGINEERING Notes 9 Topics 1. Couse Oganization. Today's Deams in Vaious Speed Ranges 3. Designing a Flight Vehicle: Route Map of
Welcome to Aeospace Engineeing DESIGN-CENTERED INTRODUCTION TO AEROSPACE ENGINEERING Notes 9 Topics 1. Couse Oganization. Today's Deams in Vaious Speed Ranges 3. Designing a Flight Vehicle: Route Map of
1 Dark Cloud Hanging over Twentieth Century Physics
 We ae Looking fo Moden Newton by Caol He, Bo He, and Jin He http://www.galaxyanatomy.com/ Wuhan FutueSpace Scientific Copoation Limited, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China E-mail: mathnob@yahoo.com Abstact Newton
We ae Looking fo Moden Newton by Caol He, Bo He, and Jin He http://www.galaxyanatomy.com/ Wuhan FutueSpace Scientific Copoation Limited, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China E-mail: mathnob@yahoo.com Abstact Newton
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Lecture 3. Basic Physics of Astrophysics - Force and Energy. Forces
 Lectue 3 Basic Physics of Astophysics - Foce and Enegy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Foces Momentum is the poduct of mass and velocity - a vecto p = mv (geneally m is taken to be constant) An unbalanced foce
Lectue 3 Basic Physics of Astophysics - Foce and Enegy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Foces Momentum is the poduct of mass and velocity - a vecto p = mv (geneally m is taken to be constant) An unbalanced foce
Central Force Problem. Central Force Motion. Two Body Problem: Center of Mass Coordinates. Reduction of Two Body Problem 8.01 W14D1. + m 2. m 2.
 Cental oce Poblem ind the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Cental oce Motion 8.01 W14D1 Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): 1 1, ( ) G mm Linea estoing foce: ( ) k 1, Two Body
Cental oce Poblem ind the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Cental oce Motion 8.01 W14D1 Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): 1 1, ( ) G mm Linea estoing foce: ( ) k 1, Two Body
m 2 r 1 = m 1 + m 2 M r 2 = m 1 = m 1m 2
 Celestial Mechanics - A.A. 2012-13 1 Calo Nipoti, Dipatimento di Fisica e Astonomia, Univesità di Bologna 26/3/2013 2. The gavitational two-body poblem 2.1 The educed mass [LL] Two-body poblem: two inteacting
Celestial Mechanics - A.A. 2012-13 1 Calo Nipoti, Dipatimento di Fisica e Astonomia, Univesità di Bologna 26/3/2013 2. The gavitational two-body poblem 2.1 The educed mass [LL] Two-body poblem: two inteacting
Gaia s Place in Space
 Gaia s Place in Space The impotance of obital positions fo satellites Obits and Lagange Points Satellites can be launched into a numbe of diffeent obits depending on thei objectives and what they ae obseving.
Gaia s Place in Space The impotance of obital positions fo satellites Obits and Lagange Points Satellites can be launched into a numbe of diffeent obits depending on thei objectives and what they ae obseving.
To Feel a Force Chapter 7 Static equilibrium - torque and friction
 To eel a oce Chapte 7 Chapte 7: Static fiction, toque and static equilibium A. Review of foce vectos Between the eath and a small mass, gavitational foces of equal magnitude and opposite diection act on
To eel a oce Chapte 7 Chapte 7: Static fiction, toque and static equilibium A. Review of foce vectos Between the eath and a small mass, gavitational foces of equal magnitude and opposite diection act on
Electric Forces: Coulomb s Law
 Electic Foces: Coulomb s Law All the matte aound you contains chaged paticles, and it is the electic foces between these chaged paticles that detemine the stength of the mateials and the popeties of the
Electic Foces: Coulomb s Law All the matte aound you contains chaged paticles, and it is the electic foces between these chaged paticles that detemine the stength of the mateials and the popeties of the
Circular Motion & Torque Test Review. The period is the amount of time it takes for an object to travel around a circular path once.
 Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapter 7. Rotational Motion Angles, Angular Velocity and Angular Acceleration Universal Law of Gravitation Kepler s Laws
 Chapte 7 Rotational Motion Angles, Angula Velocity and Angula Acceleation Univesal Law of Gavitation Keple s Laws Angula Displacement Cicula motion about AXIS Thee diffeent measues of angles: 1. Degees.
Chapte 7 Rotational Motion Angles, Angula Velocity and Angula Acceleation Univesal Law of Gavitation Keple s Laws Angula Displacement Cicula motion about AXIS Thee diffeent measues of angles: 1. Degees.
