Finitely Large Phased Arrays of Microstrip Antennas Analysis and Design
|
|
|
- Carmel Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I Preface The paper in this RN report has been submitted to the proceedings of the 4th International Workshop Scientific Computing in Electrical Engineering (SCEE). This workshop was organized by the Eindhoven University of Technology from the 23th till the 28th of June, 22. poster about the research described in the paper was presented at this workshop. Details are described in two internal reports of Thales Nederland B.V., namely Finitely Large Phased rrays of Microstrip ntennas by D.J. Bekers (ER ) and Planar rray of Narrow Ring-Shaped Microstrips in Half Space by W. Dijkstra (ER ).
2 II
3 Finitely Large Phased rrays of Microstrip ntennas nalysis and Design Dave J. Bekers 1, Stef J.L. van Eijndhoven, lphons.f. van de Ven, Peter-Paul Borsboom 2, and Evert W. Kolk 3 1 Eindhoven University of Technology, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, P.O. Box 513, 56 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands 2 Thales Nederland B.V., Department JRS, P.O. Box 42, 755 GD Hengelo, The Netherlands 3 Thales ir Defense, Haneau de Roussigny, 9147 Limours, France bstract. This paper focuses on the development of a model to obtain qualitative insight in the behaviour of large, but finite, phased arrays of microstrip antennas. This model concerns a finite array of simple elements, namely perfectly conducting, infinitely thin, narrow rings, excited by voltage gaps and positioned in free or half space. The currents on the rings, and from that the electromagnetic field, are calculated by a moment method. Dimension analysis is carried out to reduce numerical effort and to acquire insight in the behaviour of the array. The qualitative analysis shows promising results and although numerically a brute force method has been applied, CPU times are still acceptable. 1 Problem Description Currently, Thales Nederland is realizing new radar systems consisting of large phased arrays of microstrip antennas. These arrays consist of about 1 antenna elements positioned on an antenna face of about 16 m 2. The systems scan in azimuth by rotation and in elevation by phase shifts. narrow main lobe and low side lobe level, an impedance match with the feeding network of the array, and a low cross polarization are design goals. To analyse such arrays, either a finite array model (or element-by-element approach) or an infinite array model is used at Thales Nederland. The infinite array model requires much less computation time and data storage demand than the finite array model. However, since it cannot account for edge effects and differences between the antenna elements, the need for a finite array model still exists to meet the design goals. Since the actual geometry of the antenna elements is complicated, simulation of a finite array taking into account in detail these elements will require too much computing resources to be realistically feasible. Therefore, we have decided to develop a model based on simple elements that will enable us to find the characteristics that describe the qualitative behaviour of large phased arrays.
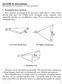
4 D D O N O > N = 5? H H > = 5? H H 2 Dave J. Bekers et al. 2 Modelling The main requirements on our model are the following. Firstly, the arrays are finite such that boundary effects can be incorporated. Secondly, computation times should be in the order of hours. Thirdly, the algorithm should be based on analytical expressions to provide insight in the characteristics or characteristic parameters of an array. The qualitative model concerns a finite planar array of simple elements in free space or above an infinitely wide ground plate. Considering the radiating part of the actual antenna elements, i.e. a rectangular microstrip loop, we have chosen perfectly conducting, infinitely thin, narrow ring-shaped microstrips, shortly rings, as elements; see Fig. 1. The reasons for this choice are twofold. ring is the most simple loop geometry and the modes on this geometry can be described analytically. The rings are excited by voltage gaps at a certain frequency with corresponding wavelength λ and wave number k. On each ring, the gap is uniform with respect to the width and can be positioned arbitrarily. The widths 2b q of the rings are all of the same order, but much smaller than the wavelength, the radii a q, and the distances between the rings. In other words, kb q 1, β q = b q /a q 1, and b p /(L pq a p a q ) 1, where L pq is the distance between the centers c p and c q of ring p and q; see Fig. 1. If a ground plate is present, the rings are situated above this plate at height h. ϑ ϑ ϑ ψ ϑ ψ Fig. 1. Geometry of an array of two rings. Since the excitation is time harmonic, the electromagnetic field is so also, and therefore, a (spatial) time-harmonic representation of this field is used. The time dependence is suppressed. The total electric field is written as the sum of a scattered electric field E scat and an excitation field E ex. The scattered electric field is expressed in terms of the unknown current density
5 Finitely Large Phased rrays of Microstrip ntennas 3 J on the rings by an integro-differential operator acting on the current, E scat = LJ. (1) The operator L can be factorized as L = DT, where D is the differential operator jωµ(i+ ) and T is the integral operator described by a Green s kernel, where T J is the magnetic vector potential. The condition that the tangential component of the total electric field is zero at the surface S of the rings yields an equation for the current, (LJ) tan = (E ex ) tan, on S. (2) Here, ( ) tan is a trace operator that restricts a vector field to the surface S and projects this field tangentially on S. Equation (2) is solved by a moment method expanding the unknown current into a finite number of expansion functions with unknown coefficients. Once the current is known, the electromagnetic far field can be calculated analytically. 3 nalytical spects Let the surface of the q-th ring be S q. On each S q, a polar parameter representation is chosen, the orientation of which is described by the angle ψ q ; see Figure 1. The voltage gap on S q is positioned in ϑ q = π. Hence, ψ q determines not only the orientation of the parameter representation, but also the position of the gap. Two tangent vectors e rq and e ϑq correspond in the usual way to this representation. Together with the corresponding normal, they form a local coordinate system on S q, which is extended straightforwardly to global coordinate system. It is assumed that the current J q = J Sq is directed along the centerlines of the rings and that it is uniform with respect to the width b q, J q (r q, ϑ q ) = w(ϑ q )e ϑq. (3) The basis of this assumption is that the wavelength is much larger than the widths of the rings. Expressing LJ q, i.e. the scattered electric field induced by ring q, into the system of S p, we calculate (LJ q ) tan on S p straightforwardly by putting the axial coordinate equal to zero and omitting the axial component. Then, a differential operator D rp ϑ p is determined such that (LJ q ) tan Sp = D rp ϑ p (T J q Sp ), (4) where Sp denotes the restriction to S p. Hence, the projection of the trace operator is incorporated in D rpϑ p. The impedance matrix component for a test function v p and an expansion function J q is given by <v p, (LJ q ) tan Sp >, (5)
6 4 Dave J. Bekers et al. where <, > is the inner product on functions defined from S to the tangent space of S. It is shown that the variation of (LJ q ) tan Sp in r p is of order β p with respect to its variation in ϑ p. This implies that (LJ q ) tan Sp depends only weakly on r p. Therefore, the test function v p is chosen uniform with respect to r p and tangentially directed only. This means v p (r p, ϑ p ) = v(ϑ p )e ϑp. (6) Then, the impedance matrix component (5) turns into <v p, (LJ q ) tan Sp > = v p (ϑ p ) (D rpϑ p [T J q Sp ]) ϑp dσ(r p, ϑ p ). (7) ϑ p r p Neglecting terms of order β p, we reverse the differential operator D rpϑ p and the integral with respect to r p. This leads to averaging of the Green s kernel with respect to the radial source and observation coordinates. In case p = q, the averaged kernel has a logarithmic singularity, otherwise it is regular. Requiring that the test function v p and the expansion function w q have square integrable second and first generalized derivatives, respectively, we transfer the reversed differential operator to v p. The resulting differential operator incorporates the Helmholtz operator. Together with the periodic boundary conditions, this operator induces a Sturm-Liouville problem for v p, the eigen functions of which are chosen as test functions. Then, the expansion functions are chosen equal to the test functions. The resulting impedance matrix component is a double integral, which can be rewritten to a single integral in case p = q by use of properties of inner product and convolution. Choosing a finite number of test and expansion functions on each S p, we obtain an impedance matrix built up of blocks, which describe the self and mutual coupling of the rings. The blocks on the diagonal are diagonal matrices describing the self coupling of each ring, while the other blocks are dense matrices describing the mutual coupling between each pair of rings. The expansion coefficients are calculated by an LU-factorization of the impedance matrix. 4 Numerical Results The first result we show is used for validation of the implementation. We show the real and imaginary part of the current through one ring in free space, excited at a frequency of 3 GHz; see Fig. 2. We can compare the result with known results from literature: the current through a wire loop excited by a voltage gap at the same frequency; see [2, Fig. 2 and 3] and [4]. Here, we use a rule of thumb found by Kraus [3, p. 238], which states that the results for a thin strip of width w and a wire with cross-sectional radius w/4 are equivalent. Two expansion functions show already an accurate result for the real part of the current. Four expansion functions show a quite accurate result
7 Finitely Large Phased rrays of Microstrip ntennas 5 for the imaginary part of the current, except near the voltage gap in ϑ = π. The reason for the latter is the following. It can be shown that since the current has a square integrable generalized derivative, the excitation field should be square integrable. However, the delta functions that describe the voltage gaps are not square integrable. Furthermore, the expansion functions do not only have square integrable generalized derivatives, but are even continuously differentiable. Figure 3 shows the effect of a ground plate. Figure 3.(a) shows the current amplitude for a ring in free space, and at h = λ/4, h = λ/2, and h = λ above a ground plate. The current is normalized on the maximum amplitude in free space. Due to interference, the amplitude for h = λ/4 is lower than for free space, and for h = λ/2 and h = λ higher. Due to space attenuation, the amplitude for h = λ is lower than for h = λ/2. Figure 3.(b) shows the far field components in the yz-plane for free space and for h = λ/4. Here, a spherical coordinate is chosen that is related to the cartesian coordinate system in Fig. 1 in the usual way. The influence of the ground plate can be observed from the behaviour of the φ-component, i.e. the cross-polarization, that vanishes at θ = 9 o (endfire) for the ground plate, but not for free space. Figure 4 shows results for two line arrays of 7 identical rings with spacings 7λ/15 and 3λ/5. Here, 8 expansion functions per ring is a suitable choice. The orientation of the local coordinate systems on the rings is such that ψ q =. s aforementioned, the voltage gaps, all of equal amplitude, are positioned in ϑ q = π. The centers of the rings are positioned on the positive x-axis, where the center of the first ring is in the origin; see Fig. 1. The CPU time of a Matlab implementation on a HP PC with Windows NT, an Intel Pentium IV processor at 1.6 GHz, and 256 Mb of RM is 366 sec. Figures 4.(a)-(b) show the normalized radiation intensities in the xz and yz-plane (H and E-plane) together with the intensity of one ring. In the xz-plane, one main lobe and several side lobes are observed for both spacings, where the number of lobes is related to the spacing. In the E-plane, only one lobe is observed. These results are in qualitative correspondence with results from literature; see [1, Chapter 3]. Besides that the array with larger spacing has more side lobes, also its maximal radiation intensity is higher. This effect is due to the degree of mutual coupling. Influence of mutual coupling on the current is shown in Fig. 4.(c)-(f). For smaller spacing, the amplitudes of the currents differ significantly from the amplitude on one ring, while for larger spacing, they differ only slightly. In particular, the maxima of the amplitudes for the spacing 7λ/15 are significantly lower than the maximum for one ring. For the spacing 3λ/5, these maxima are both slightly higher and lower than the maximum for one ring. The phases differ for both spacings from the phase on one ring.
8 6 Dave J. Bekers et al. 5 Conclusions We have developed a tool for analysing finite arrays of rings that is easy to handle. The algorithm is based on analytic expressions as required. The validation has been successful; results have shown to be in qualitative correspondence with literature and practice. lthough numerically, a brute force method has been applied, the CPU times are acceptable. However, to analyse large arrays of about 1 elements or more, they should be reduced. The accuracy is sufficient for qualitative analysis. 6 Prospects Research on characteristics of arrays and essential aspects of the antenna elements will be topic of further research. transparent relation should be established between excitation, geometry, and scattered field. Finally, feedback should be provided to the hardware designers of Thales Nederland. References 1. Stutzman, W.L., Thiele, G..: ntenna Theory and Design. Wiley, New York (1998, 2nd, ed.) 2. Poljak, D.: Finite Element Integral Equation Modelling of a Thin Wire Loop ntenna. Commun. Numer. Meth. Engng. 14 (1998) Kraus, J.: ntennas. McGraw-Hill, New York (195). 4. Champagne, N.J., Williams, J.T., Wilton, D.R.: The use of curved segments for numerically modeling thin wire antennas and scatterers. IEEE Trans. nt. Prop. 4 (1992)
9 Finitely Large Phased rrays of Microstrip ntennas 7 Real part of current () 3.5 x Imaginary part of current ().5 x pi pi/2 pi/2 pi (a) 3 pi pi/2 pi/2 pi (b) Fig. 2. The total current on a ring excited by a voltage gap of 1 V at a frequency of 3 GHz.; a =.637 λ, b =.27 λ, c = (,, ), and ψ =. (a) Real part; 2 expansion functions of cosine type. (b) Imaginary part; blue, red, black: 4, 6, and 8 expansion functions of cosine type. Normalized absolute current (db) pi pi/2 pi/2 pi Normalized far field components (db) θ (deg) (a) (b) Fig. 3. ring excited by a voltage gap of 1 V with 8 expansion functions of cosine type; ka = 2π/5, β = 1/4, c = (,, ), ψ =. (a) Current amplitudes normalized on the maximum amplitude in free space; blue: free space; green: h = λ/4; red: h = λ/2; black: h = λ. (b) Far field components in the yz-plane normalized on the maximum of E θ ; blue: free space; black: h = λ/4; solid lines: E θ -components (co-polarization); dashed lines: E φ -components (cross-polarization).
10 8 Dave J. Bekers et al. Normalized radiation intensity (db) Normalized radiation intensity (db) θ (deg) (a) θ (deg) (b) Normalized absolute current (db) Normalized absolute current (db) pi pi/2 pi/2 pi (c) 1 pi pi/2 pi/2 pi (d) Phase (rad) Phase (rad) pi pi/2 pi/2 pi (e) 3 pi pi/2 pi/2 pi (f) Fig. 4. Results for line arrays of 7 rings of equal radii (ka q = 2π/6) and widths (β q = 3/5), with voltage gaps of equal amplitude (1 V), and positioned in free space. (a)-(b): Radiation intensities in the xz and yz-plane, resp., normalized on the maximum intensity of one ring; blue: one ring; black: spacing 7λ/15 (c q = 7λ(q 1)/15); red: spacing 3λ/5 (c q = 3λ(q 1)/5). (c)-(f): Current amplitudes and phases for spacings 7λ/15 ((c), (e)) and 3λ/5 ((d), (f)); blue: one ring; green/red/black/purple: from first ring to center ring.
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 && & 44&, &&7 4/ 00
 ! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
DESIGNS of antenna arrays are often based on simulations
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE 2006 2821 Eigencurrent Analysis of Resonant Behavior in Finite Antenna Arrays Dave J. Bekers, Member, IEEE, Stephanus J. L. van
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE 2006 2821 Eigencurrent Analysis of Resonant Behavior in Finite Antenna Arrays Dave J. Bekers, Member, IEEE, Stephanus J. L. van
Analysis of eddy currents in a gradient coil
 Analysis of eddy currents in a gradient coil J.M.B. Kroot Eindhoven University of Technology P.O.Box 53; 56 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands Abstract To model the z-coil of an MRI-scanner, a set of circular
Analysis of eddy currents in a gradient coil J.M.B. Kroot Eindhoven University of Technology P.O.Box 53; 56 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands Abstract To model the z-coil of an MRI-scanner, a set of circular
CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE DUAL INVERTED-F ANTENNA
 CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE DUAL INVERTED-F ANTENNA 4.1. Introduction The previous chapter presented the Inverted-F Antenna (IFA) and its variations as antenna designs suitable for use in hand-held
CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE DUAL INVERTED-F ANTENNA 4.1. Introduction The previous chapter presented the Inverted-F Antenna (IFA) and its variations as antenna designs suitable for use in hand-held
4.4 Microstrip dipole
 4.4 Microstrip dipole Basic theory Microstrip antennas are frequently used in today's wireless communication systems. Thanks to their low profile, they can be mounted to the walls of buildings, to the
4.4 Microstrip dipole Basic theory Microstrip antennas are frequently used in today's wireless communication systems. Thanks to their low profile, they can be mounted to the walls of buildings, to the
Short Wire Antennas: A Simplified Approach Part I: Scaling Arguments. Dan Dobkin version 1.0 July 8, 2005
 Short Wire Antennas: A Simplified Approach Part I: Scaling Arguments Dan Dobkin version 1.0 July 8, 2005 0. Introduction: How does a wire dipole antenna work? How do we find the resistance and the reactance?
Short Wire Antennas: A Simplified Approach Part I: Scaling Arguments Dan Dobkin version 1.0 July 8, 2005 0. Introduction: How does a wire dipole antenna work? How do we find the resistance and the reactance?
Aperture Antennas 1 Introduction
 1 Introduction Very often, we have antennas in aperture forms, for example, the antennas shown below: Pyramidal horn antenna Conical horn antenna 1 Paraboloidal antenna Slot antenna Analysis Method for.1
1 Introduction Very often, we have antennas in aperture forms, for example, the antennas shown below: Pyramidal horn antenna Conical horn antenna 1 Paraboloidal antenna Slot antenna Analysis Method for.1
On the Modal Superposition Lying under the MoM Matrix Equations
 42 P. HAZDRA, P. HAMOUZ, ON THE MODAL SUPERPOSITION LYING UNDER THE MOM MATRIX EQUATIONS On the Modal Superposition Lying under the MoM Matrix Equations Pavel HAZDRA 1, Pavel HAMOUZ 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic
42 P. HAZDRA, P. HAMOUZ, ON THE MODAL SUPERPOSITION LYING UNDER THE MOM MATRIX EQUATIONS On the Modal Superposition Lying under the MoM Matrix Equations Pavel HAZDRA 1, Pavel HAMOUZ 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, , 2011
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 173 183, 2011 STUDY OF THE RADIATED POLARIZATIO OF A ATEA ARRAY WITH CIRCULAR GEOMETRY K. Louertani 1, *, R. Guinvarc h 2,. Ribière-Tharaud 3, and M. Hélier
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 173 183, 2011 STUDY OF THE RADIATED POLARIZATIO OF A ATEA ARRAY WITH CIRCULAR GEOMETRY K. Louertani 1, *, R. Guinvarc h 2,. Ribière-Tharaud 3, and M. Hélier
A Novel Single-Source Surface Integral Method to Compute Scattering from Dielectric Objects
 SUBMITTED TO IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS ON NOVEMBER 18, 2016 1 A Novel Single-Source Surface Integral Method to Compute Scattering from Dielectric Objects Utkarsh R. Patel, Student
SUBMITTED TO IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS ON NOVEMBER 18, 2016 1 A Novel Single-Source Surface Integral Method to Compute Scattering from Dielectric Objects Utkarsh R. Patel, Student
The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetics with MATLAB Simulations
 The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetics with MATLAB Simulations Atef Z. Elsherbeni and Veysel Demir SciTech Publishing, Inc Raleigh, NC scitechpublishing.com Contents Preface Author
The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetics with MATLAB Simulations Atef Z. Elsherbeni and Veysel Demir SciTech Publishing, Inc Raleigh, NC scitechpublishing.com Contents Preface Author
Array Antennas. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 Array Antennas An array antenna is a group of antenna elements with excitations coordinated in some way to achieve desired properties for the combined radiation pattern. When designing an array
Chapter 6 Array Antennas An array antenna is a group of antenna elements with excitations coordinated in some way to achieve desired properties for the combined radiation pattern. When designing an array
Focusing Characteristic Analysis of Circular Fresnel Zone Plate Lens
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University, Vol.35, Nos.l&2, pp.53-6, March 200 Focusing Characteristic Analysis of Circular Fresnel Zone Plate Lens Tae Yong KIM! and Yukio KAGAWA 2 (Received
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University, Vol.35, Nos.l&2, pp.53-6, March 200 Focusing Characteristic Analysis of Circular Fresnel Zone Plate Lens Tae Yong KIM! and Yukio KAGAWA 2 (Received
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6
 ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 1 Leaky Modes v TM 1 Mode SW 1 v= utan u ε R 2 R kh 0 n1 r = ( ) 1 u Splitting point ISW f = f s f > f s We will examine the solutions as the
ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 1 Leaky Modes v TM 1 Mode SW 1 v= utan u ε R 2 R kh 0 n1 r = ( ) 1 u Splitting point ISW f = f s f > f s We will examine the solutions as the
3.2 Numerical Methods for Antenna Analysis
 ECEn 665: Antennas and Propagation for Wireless Communications 43 3.2 Numerical Methods for Antenna Analysis The sinusoidal current model for a dipole antenna is convenient because antenna parameters can
ECEn 665: Antennas and Propagation for Wireless Communications 43 3.2 Numerical Methods for Antenna Analysis The sinusoidal current model for a dipole antenna is convenient because antenna parameters can
Finite Element Method (FEM)
 Finite Element Method (FEM) The finite element method (FEM) is the oldest numerical technique applied to engineering problems. FEM itself is not rigorous, but when combined with integral equation techniques
Finite Element Method (FEM) The finite element method (FEM) is the oldest numerical technique applied to engineering problems. FEM itself is not rigorous, but when combined with integral equation techniques
ELECTROMAGNETIC band-gap (EBG) materials are. Analysis of Directive Radiation From a Line Source in a Metamaterial Slab With Low Permittivity
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH 2006 1017 Analysis of Directive Radiation From a Line Source in a Metamaterial Slab With Low Permittivity Giampiero Lovat, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH 2006 1017 Analysis of Directive Radiation From a Line Source in a Metamaterial Slab With Low Permittivity Giampiero Lovat, Member, IEEE,
IMPACT OF FINITE GROUND PLANE EDGE DIFFRA- CTIONS ON RADIATION PATTERNS OF APERTURE ANTENNAS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 55, 1 21, 2013 IMPACT OF FINITE GROUND PLANE EDGE DIFFRA- CTIONS ON RADIATION PATTERNS OF APERTURE ANTENNAS Nafati A. Aboserwal, Constantine A. Balanis *,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 55, 1 21, 2013 IMPACT OF FINITE GROUND PLANE EDGE DIFFRA- CTIONS ON RADIATION PATTERNS OF APERTURE ANTENNAS Nafati A. Aboserwal, Constantine A. Balanis *,
FAST AND ACCURATE RADAR CROSS SECTION COM- PUTATION USING CHEBYSHEV APPROXIMATION IN BOTH BROAD FREQUENCY BAND AND ANGULAR DOMAINS SIMULTANEOUSLY
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 13, 121 129, 2010 FAST AND ACCURATE RADAR CROSS SECTION COM- PUTATION USING CHEBYSHEV APPROXIMATION IN BOTH BROAD FREQUENCY BAND AND ANGULAR DOMAINS
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 13, 121 129, 2010 FAST AND ACCURATE RADAR CROSS SECTION COM- PUTATION USING CHEBYSHEV APPROXIMATION IN BOTH BROAD FREQUENCY BAND AND ANGULAR DOMAINS
Application of AWE for RCS frequency response calculations using Method of Moments
 NASA Contractor Report 4758 Application of AWE for RCS frequency response calculations using Method of Moments C.J.Reddy Hampton University, Hampton, Virginia M.D.Deshpande ViGYAN Inc., Hampton, Virginia
NASA Contractor Report 4758 Application of AWE for RCS frequency response calculations using Method of Moments C.J.Reddy Hampton University, Hampton, Virginia M.D.Deshpande ViGYAN Inc., Hampton, Virginia
Microstrip Antennas. Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay. (022)
 Microstrip Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay gkumar@ee.iitb.ac.in (022) 2576 7436 Rectangular Microstrip Antenna (RMSA) Y Top View W x X L Side View r Ground plane
Microstrip Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay gkumar@ee.iitb.ac.in (022) 2576 7436 Rectangular Microstrip Antenna (RMSA) Y Top View W x X L Side View r Ground plane
SPHERICAL NEAR-FIELD ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS
 SPHERICAL NEAR-FIELD ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS Edited by J.E.Hansen Peter Peregrinus Ltd. on behalf of the Institution of Electrical Engineers Contents Contributing authors listed Preface v xiii 1 Introduction
SPHERICAL NEAR-FIELD ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS Edited by J.E.Hansen Peter Peregrinus Ltd. on behalf of the Institution of Electrical Engineers Contents Contributing authors listed Preface v xiii 1 Introduction
Part I. The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn
 9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
Research Article Electromagnetic Radiation from Arbitrarily Shaped Microstrip Antenna Using the Equivalent Dipole-Moment Method
 Antennas and Propagation Volume 2012, Article ID 181235, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/181235 Research Article Electromagnetic Radiation from Arbitrarily Shaped Microstrip Antenna Using the Equivalent Dipole-Moment
Antennas and Propagation Volume 2012, Article ID 181235, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/181235 Research Article Electromagnetic Radiation from Arbitrarily Shaped Microstrip Antenna Using the Equivalent Dipole-Moment
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves
 5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
A cylinder in a magnetic field (Jackson)
 Problem 1. A cylinder in a magnetic field (Jackson) A very long hollow cylinder of inner radius a and outer radius b of permeability µ is placed in an initially uniform magnetic field B o at right angles
Problem 1. A cylinder in a magnetic field (Jackson) A very long hollow cylinder of inner radius a and outer radius b of permeability µ is placed in an initially uniform magnetic field B o at right angles
Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation
 Chapter 7 Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation Classical array antenna theory focuses on the problem of pattern synthesis. There is a vast body of work in the literature on methods
Chapter 7 Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation Classical array antenna theory focuses on the problem of pattern synthesis. There is a vast body of work in the literature on methods
Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit Cell
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
Electromagnetic Scattering from a PEC Wedge Capped with Cylindrical Layers with Dielectric and Conductive Properties
 0. OZTURK, ET AL., ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM A PEC WEDGE CAPPED WIT CYLINDRICAL LAYERS... Electromagnetic Scattering from a PEC Wedge Capped with Cylindrical Layers with Dielectric and Conductive
0. OZTURK, ET AL., ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM A PEC WEDGE CAPPED WIT CYLINDRICAL LAYERS... Electromagnetic Scattering from a PEC Wedge Capped with Cylindrical Layers with Dielectric and Conductive
A Plane Wave Expansion of Spherical Wave Functions for Modal Analysis of Guided Wave Structures and Scatterers
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 51, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2003 2801 A Plane Wave Expansion of Spherical Wave Functions for Modal Analysis of Guided Wave Structures and Scatterers Robert H.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 51, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2003 2801 A Plane Wave Expansion of Spherical Wave Functions for Modal Analysis of Guided Wave Structures and Scatterers Robert H.
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff
 Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna
 352 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna M. Hosseini 2, A. Pirhadi 1,2, and M. Hakkak
352 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna M. Hosseini 2, A. Pirhadi 1,2, and M. Hakkak
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematics of light transmission and reflection from a slab confined between
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure. Schematics of light transmission and reflection from a slab confined between two infinite media. Supplementary Figure. Reflectivity of a magneto-electric slab
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure. Schematics of light transmission and reflection from a slab confined between two infinite media. Supplementary Figure. Reflectivity of a magneto-electric slab
APPLICATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD INTEGRAL EQUATION TO DIFFRACTION AND REFLECTION BY A CONDUCTING SHEET
 In: International Journal of Theoretical Physics, Group Theory... ISSN: 1525-4674 Volume 14, Issue 3 pp. 1 12 2011 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. APPLICATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD INTEGRAL EQUATION TO DIFFRACTION
In: International Journal of Theoretical Physics, Group Theory... ISSN: 1525-4674 Volume 14, Issue 3 pp. 1 12 2011 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. APPLICATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD INTEGRAL EQUATION TO DIFFRACTION
SPHERICAL RESONATOR WITH DB-BOUNDARY CON- DITIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 3 37, 2009 SPHERICAL RESONATOR WITH DB-BOUNDARY CON- DITIONS I. V. Lindell and A. H. Sihvola Electromagnetics Group Department of Radio Science and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 3 37, 2009 SPHERICAL RESONATOR WITH DB-BOUNDARY CON- DITIONS I. V. Lindell and A. H. Sihvola Electromagnetics Group Department of Radio Science and
Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, ISBN:
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING FROM THE SERRATIONS OF COMPACT RANGES 1
 Paper presented at Antenna Measurement Techniques Association 29 th Annual Symposium (AMTA 2007), St. Louis, MO, USA, 4-9 November 2007, Proceedings pp. 150-155 (Session 5). POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING
Paper presented at Antenna Measurement Techniques Association 29 th Annual Symposium (AMTA 2007), St. Louis, MO, USA, 4-9 November 2007, Proceedings pp. 150-155 (Session 5). POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
Theoretical study of two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 3 journal of September 2005 physics pp. 501 512 Theoretical study of two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 3 journal of September 2005 physics pp. 501 512 Theoretical study of two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate
Prüfung Regelungstechnik I (Control Systems I) Übersetzungshilfe / Translation aid (English) To be returned at the end of the exam!
 Prüfung Regelungstechnik I (Control Systems I) Prof. Dr. Lino Guzzella 29. 8. 2 Übersetzungshilfe / Translation aid (English) To be returned at the end of the exam! Do not mark up this translation aid
Prüfung Regelungstechnik I (Control Systems I) Prof. Dr. Lino Guzzella 29. 8. 2 Übersetzungshilfe / Translation aid (English) To be returned at the end of the exam! Do not mark up this translation aid
A GENERALIZED COUPLED-LINE DUAL-BAND WILKINSON POWER DIVIDER WITH EXTENDED PORTS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 19, 197 14, 1 A GENERALIZED COUPLED-LINE DUAL-BAND WILKINSON POWER DIVIDER WITH EXTENDED PORTS J. C. Li *, Y. L. Wu, Y. A. Liu, J. Y. Shen, S. L. Li, and C.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 19, 197 14, 1 A GENERALIZED COUPLED-LINE DUAL-BAND WILKINSON POWER DIVIDER WITH EXTENDED PORTS J. C. Li *, Y. L. Wu, Y. A. Liu, J. Y. Shen, S. L. Li, and C.
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic-Thermal Analysis Study Based on HFSS-ANSYS Link
 Syracuse University SURFACE Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Technical Reports College of Engineering and Computer Science 5-9-2011 Electromagnetic-Thermal Analysis Study Based on HFSS-ANSYS
Syracuse University SURFACE Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Technical Reports College of Engineering and Computer Science 5-9-2011 Electromagnetic-Thermal Analysis Study Based on HFSS-ANSYS
The below identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO 31 October 2018 The below identified patent application is available
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO 31 October 2018 The below identified patent application is available
Extinction properties of a sphere with negative permittivity and permeability
 PERGAMON Solid State Communications 116 (2000) 411 415 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Extinction properties of a sphere with negative permittivity and permeability R. Ruppin* Department of Physics and Applied
PERGAMON Solid State Communications 116 (2000) 411 415 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Extinction properties of a sphere with negative permittivity and permeability R. Ruppin* Department of Physics and Applied
Resonances and dipole moments in dielectric, magnetic, and magnetodielectric cylinders an overview
 Appl Phys A (2011) 103: 789 793 DOI 10.1007/s00339-010-6219-6 Resonances and dipole moments in dielectric, magnetic, and magnetodielectric cylinders an overview A. Dirksen S. Arslanagic O. Breinbjerg Received:
Appl Phys A (2011) 103: 789 793 DOI 10.1007/s00339-010-6219-6 Resonances and dipole moments in dielectric, magnetic, and magnetodielectric cylinders an overview A. Dirksen S. Arslanagic O. Breinbjerg Received:
ANALYSIS OF LINEAR TAPERED WAVEGUIDE BY TWO APPROACHES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 64, 19 38, 006 ANALYSIS OF LINEAR TAPERED WAVEGUIDE BY TWO APPROACHES S. Dwari, A. Chakraborty, and S. Sanyal Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 64, 19 38, 006 ANALYSIS OF LINEAR TAPERED WAVEGUIDE BY TWO APPROACHES S. Dwari, A. Chakraborty, and S. Sanyal Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication
2 Hallén s integral equation for the thin wire dipole antenna
 Ú Ð Ð ÓÒÐ Ò Ø ØØÔ»» Ѻ Ö Ùº º Ö ÁÒغ º ÁÒ Ù ØÖ Ð Å Ø Ñ Ø ÎÓк ÆÓº ¾ ¾¼½½µ ½ ¹½ ¾ ÆÙÑ Ö Ð Ñ Ø Ó ÓÖ Ò ÐÝ Ó Ö Ø ÓÒ ÖÓÑ Ø Ò Û Ö ÔÓÐ ÒØ ÒÒ Ëº À Ø ÑÞ ¹Î ÖÑ ÞÝ Ö Åº Æ Ö¹ÅÓ Êº Ë Þ ¹Ë Ò µ Ô ÖØÑ ÒØ Ó Ð ØÖ Ð Ò Ò
Ú Ð Ð ÓÒÐ Ò Ø ØØÔ»» Ѻ Ö Ùº º Ö ÁÒغ º ÁÒ Ù ØÖ Ð Å Ø Ñ Ø ÎÓк ÆÓº ¾ ¾¼½½µ ½ ¹½ ¾ ÆÙÑ Ö Ð Ñ Ø Ó ÓÖ Ò ÐÝ Ó Ö Ø ÓÒ ÖÓÑ Ø Ò Û Ö ÔÓÐ ÒØ ÒÒ Ëº À Ø ÑÞ ¹Î ÖÑ ÞÝ Ö Åº Æ Ö¹ÅÓ Êº Ë Þ ¹Ë Ò µ Ô ÖØÑ ÒØ Ó Ð ØÖ Ð Ò Ò
Surface Impedance Absorbing Boundary for Terminating FDTD Simulations
 135 ACS JOURNAL, Vol. 29, No. 12, DCMBR 214 Surface Impedance Absorbing Boundary for Terminating FDTD Simulations Yunlong Mao 1,2, Atef Z. lsherbeni 2,SiLi 1,2, and Tao Jiang 1 1 College of Information
135 ACS JOURNAL, Vol. 29, No. 12, DCMBR 214 Surface Impedance Absorbing Boundary for Terminating FDTD Simulations Yunlong Mao 1,2, Atef Z. lsherbeni 2,SiLi 1,2, and Tao Jiang 1 1 College of Information
Chapter 4 Layered Substrates 4.1 Introduction
 Chapter 4 Layered Substrates 4.1 Introduction The significant result of the previous chapter is that guided mode (surface wave) losses can be avoided on substrates with thicknesses of an odd integral multiple
Chapter 4 Layered Substrates 4.1 Introduction The significant result of the previous chapter is that guided mode (surface wave) losses can be avoided on substrates with thicknesses of an odd integral multiple
On the Existence of Superdirective Radiation Modes in Thin-Wire Nanoloops
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION. On the Existence of Superdirective Radiation Modes in Thin-Wire Nanoloops Mario F. Pantoja, Jogender Nagar 2, Bingqian Lu 2, and Douglas H. Werner 2 Department of Electromagnetism
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. On the Existence of Superdirective Radiation Modes in Thin-Wire Nanoloops Mario F. Pantoja, Jogender Nagar 2, Bingqian Lu 2, and Douglas H. Werner 2 Department of Electromagnetism
A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 121 134, 2008 A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER Y. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Li School of Electronic Engineering Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 121 134, 2008 A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER Y. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Li School of Electronic Engineering Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
A half submerged metal sphere (UIC comprehensive
 Problem 1. exam) A half submerged metal sphere (UIC comprehensive A very light neutral hollow metal spherical shell of mass m and radius a is slightly submerged by a distance b a below the surface of a
Problem 1. exam) A half submerged metal sphere (UIC comprehensive A very light neutral hollow metal spherical shell of mass m and radius a is slightly submerged by a distance b a below the surface of a
USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION
 October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
AN INDEPENDENT LOOPS SEARCH ALGORITHM FOR SOLVING INDUCTIVE PEEC LARGE PROBLEMS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 23, 53 63, 2012 AN INDEPENDENT LOOPS SEARCH ALGORITHM FOR SOLVING INDUCTIVE PEEC LARGE PROBLEMS T.-S. Nguyen *, J.-M. Guichon, O. Chadebec, G. Meunier, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 23, 53 63, 2012 AN INDEPENDENT LOOPS SEARCH ALGORITHM FOR SOLVING INDUCTIVE PEEC LARGE PROBLEMS T.-S. Nguyen *, J.-M. Guichon, O. Chadebec, G. Meunier, and
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides
 1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
3.4-7 First check to see if the loop is indeed electromagnetically small. Ie sinθ ˆφ H* = 2. ˆrr 2 sinθ dθ dφ =
 ECE 54/4 Spring 17 Assignment.4-7 First check to see if the loop is indeed electromagnetically small f 1 MHz c 1 8 m/s b.5 m λ = c f m b m Yup. (a) You are welcome to use equation (-5), but I don t like
ECE 54/4 Spring 17 Assignment.4-7 First check to see if the loop is indeed electromagnetically small f 1 MHz c 1 8 m/s b.5 m λ = c f m b m Yup. (a) You are welcome to use equation (-5), but I don t like
METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS Philip M. Morse PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Herman Feshbach PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PART II: CHAPTERS 9
METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS Philip M. Morse PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Herman Feshbach PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PART II: CHAPTERS 9
Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques
 Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques F. D Agostino, M. Migliozzi University of Salerno, Italy ANTENNAE REGIONS The REACTIVE NEAR-FIELD REGION is the
Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques F. D Agostino, M. Migliozzi University of Salerno, Italy ANTENNAE REGIONS The REACTIVE NEAR-FIELD REGION is the
Supplementary Material for. Resonant Transparency and Non-Trivial Excitations in Toroidal Metamaterials
 Supplementary Material for Resonant Transparency and Non-Trivial Excitations in Toroidal Metamaterials V. A. Fedotov 1, A. V. Rogacheva 1, V. Savinov 1, D. P. Tsai 2,3, N. I. Zheludev 1, 4 1 Optoelectronics
Supplementary Material for Resonant Transparency and Non-Trivial Excitations in Toroidal Metamaterials V. A. Fedotov 1, A. V. Rogacheva 1, V. Savinov 1, D. P. Tsai 2,3, N. I. Zheludev 1, 4 1 Optoelectronics
Asymptotic Waveform Evaluation(AWE) Technique for Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Analysis
 NASA Technical Memorandum 110292 Asymptotic Waveform Evaluation(AWE Technique for Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Analysis C. R. Cockrell and F.B. Beck NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia
NASA Technical Memorandum 110292 Asymptotic Waveform Evaluation(AWE Technique for Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Analysis C. R. Cockrell and F.B. Beck NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia
Power Absorption of Near Field of Elementary Radiators in Proximity of a Composite Layer
 Power Absorption of Near Field of Elementary Radiators in Proximity of a Composite Layer M. Y. Koledintseva, P. C. Ravva, J. Y. Huang, and J. L. Drewniak University of Missouri-Rolla, USA M. Sabirov, V.
Power Absorption of Near Field of Elementary Radiators in Proximity of a Composite Layer M. Y. Koledintseva, P. C. Ravva, J. Y. Huang, and J. L. Drewniak University of Missouri-Rolla, USA M. Sabirov, V.
J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian University Xi an, Shaanxi , P. R.
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
THEORY AND DESIGN OF HIGH ORDER SOUND FIELD MICROPHONES USING SPHERICAL MICROPHONE ARRAY
 THEORY AND DESIGN OF HIGH ORDER SOUND FIELD MICROPHONES USING SPHERICAL MICROPHONE ARRAY Thushara D. Abhayapala, Department of Engineering, FEIT & Department of Telecom Eng, RSISE The Australian National
THEORY AND DESIGN OF HIGH ORDER SOUND FIELD MICROPHONES USING SPHERICAL MICROPHONE ARRAY Thushara D. Abhayapala, Department of Engineering, FEIT & Department of Telecom Eng, RSISE The Australian National
The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE135 Engineering Electromagnetics Exam II April 12, Z T E = η/ cos θ, Z T M = η cos θ
 The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE135 Engineering Electromagnetics Exam II April 12, 2012 Time: 2 hours. Closed book, closed notes. Calculator provided. For oblique incidence of
The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE135 Engineering Electromagnetics Exam II April 12, 2012 Time: 2 hours. Closed book, closed notes. Calculator provided. For oblique incidence of
ON THE EXISTENCE OF THE NEAR ZONE INVERSE DOPPLER EFFECT
 ON THE EXISTENCE OF THE NEAR ZONE INVERSE DOPPLER EFFECT Yehuda Ben-Shimol* and Dan Censor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, P.O.B. 653, Beer-Sheva,
ON THE EXISTENCE OF THE NEAR ZONE INVERSE DOPPLER EFFECT Yehuda Ben-Shimol* and Dan Censor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, P.O.B. 653, Beer-Sheva,
Module 7 : Antenna. Lecture 52 : Array Synthesis. Objectives. In this course you will learn the following. Array specified by only its nulls.
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Array specified by only its nulls. Radiation pattern of a general array. Array synthesis. Criterion for choosing number of elements in synthesized
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Array specified by only its nulls. Radiation pattern of a general array. Array synthesis. Criterion for choosing number of elements in synthesized
AN FFT-BASED APPROACH IN ACCELERATION OF DISCRETE GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD FOR AN- TENNA ANALYSIS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 29, 17 28, 2013 AN FFT-BASED APPROACH IN ACCELERATION OF DISCRETE GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD FOR AN- TENNA ANALYSIS Salma Mirhadi *, Mohammad Soleimani, and Ali
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 29, 17 28, 2013 AN FFT-BASED APPROACH IN ACCELERATION OF DISCRETE GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD FOR AN- TENNA ANALYSIS Salma Mirhadi *, Mohammad Soleimani, and Ali
Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX
 Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX Antony A. Stark and Urs Graf Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, University of Cologne aas@cfa.harvard.edu 1 October 2013 This memorandum
Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX Antony A. Stark and Urs Graf Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, University of Cologne aas@cfa.harvard.edu 1 October 2013 This memorandum
Electromagnetic Shielding
 Electromagnetic Shielding SALVATORE CELOZZI RODOLFO ARANEO GIAMPIERO LOVAT Electrical Engineering Department "La Sapienza" University Rome, Italy IEEE Press iwiley- 'INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC.,
Electromagnetic Shielding SALVATORE CELOZZI RODOLFO ARANEO GIAMPIERO LOVAT Electrical Engineering Department "La Sapienza" University Rome, Italy IEEE Press iwiley- 'INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC.,
Written Examination. Antennas and Propagation (AA ) June 22, 2018.
 Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 7-8 June, 8. Problem ( points A circular loop of radius a = cm is positioned at a height h over a perfectly electric conductive ground plane as in figure,
Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 7-8 June, 8. Problem ( points A circular loop of radius a = cm is positioned at a height h over a perfectly electric conductive ground plane as in figure,
ST.JOSEPH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING,DEPARTMENT OF ECE
 EC6403 -ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS CLASS/SEM: II ECE/IV SEM UNIT I - STATIC ELECTRIC FIELD Part A - Two Marks 1. Define scalar field? A field is a system in which a particular physical function has a value
EC6403 -ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS CLASS/SEM: II ECE/IV SEM UNIT I - STATIC ELECTRIC FIELD Part A - Two Marks 1. Define scalar field? A field is a system in which a particular physical function has a value
Microwave multipactor breakdown in open two-wire transmission systems
 Microwave multipactor breakdown in open two-wire transmission systems Joel Rasch*, D. Anderson*, V. E. Semenov, E. Rakova, J. F. Johansson, M. Lisak* and J. Puech *Chalmers University of Technology Outline
Microwave multipactor breakdown in open two-wire transmission systems Joel Rasch*, D. Anderson*, V. E. Semenov, E. Rakova, J. F. Johansson, M. Lisak* and J. Puech *Chalmers University of Technology Outline
A far-field based T-matrix method for three dimensional acoustic scattering
 ANZIAM J. 50 (CTAC2008) pp.c121 C136, 2008 C121 A far-field based T-matrix method for three dimensional acoustic scattering M. Ganesh 1 S. C. Hawkins 2 (Received 14 August 2008; revised 4 October 2008)
ANZIAM J. 50 (CTAC2008) pp.c121 C136, 2008 C121 A far-field based T-matrix method for three dimensional acoustic scattering M. Ganesh 1 S. C. Hawkins 2 (Received 14 August 2008; revised 4 October 2008)
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017
 Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING BY MIXED CONDUCTING/DIELECTRIC OBJECTS USING HIGHER-ORDER MOM
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 66, 51 63, 2006 ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING BY MIXED CONDUCTING/DIELECTRIC OBJECTS USING HIGHER-ORDER MOM S. G. Wang, X. P. Guan, D. W. Wang, X. Y. Ma, and Y.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 66, 51 63, 2006 ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING BY MIXED CONDUCTING/DIELECTRIC OBJECTS USING HIGHER-ORDER MOM S. G. Wang, X. P. Guan, D. W. Wang, X. Y. Ma, and Y.
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Physics Letters A.
 Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
RADIATING ELEMENTS MAY BE: DIPOLES, SLOTS, POLYRODS, LOOPS, HORNS, HELIX, SPIRALS, LOG PERIODIC STRUCTURES AND EVEN DISHES Dipoles simple structures,
 ANTENNA ARRAYS Array - collection of radiating elements An array may be: 1D (linear), 2D (planar), 3D (frequency selective) structure of radiating elements Purpose More directivity, Steereable beams Radiation
ANTENNA ARRAYS Array - collection of radiating elements An array may be: 1D (linear), 2D (planar), 3D (frequency selective) structure of radiating elements Purpose More directivity, Steereable beams Radiation
MONTE CARLO INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE FOR THE ANALYSIS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM CONDUCTING SURFACES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 79, 91 106, 2008 MONTE CARLO INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE FOR THE ANALYSIS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM CONDUCTING SURFACES M. Mishra and N. Gupta Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 79, 91 106, 2008 MONTE CARLO INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE FOR THE ANALYSIS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM CONDUCTING SURFACES M. Mishra and N. Gupta Department
NASA Contractor Report. Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements
 NASA Contractor Report Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements M. D.Deshpande VIGYAN Inc., Hampton, VA C. J. Reddy
NASA Contractor Report Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements M. D.Deshpande VIGYAN Inc., Hampton, VA C. J. Reddy
Circuit analysis of magnetic couplings between circular turn and spiral coil
 Computer Applications in Electrical Engineering Vol. 1 014 Circuit analysis of magnetic couplings between circular turn and spiral coil Mirosław Wciślik, Tomasz Kwaśniewski Kielce University of Technology
Computer Applications in Electrical Engineering Vol. 1 014 Circuit analysis of magnetic couplings between circular turn and spiral coil Mirosław Wciślik, Tomasz Kwaśniewski Kielce University of Technology
Closed-Form Evaluation of Mutual Coupling in a Planar Array of Circular Apertures
 NASA Technical Paper 3552 Closed-Form Evaluation of Mutual Coupling in a Planar Array of Circular Apertures M. C. Bailey Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NASA Technical Paper 3552 Closed-Form Evaluation of Mutual Coupling in a Planar Array of Circular Apertures M. C. Bailey Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia National Aeronautics and Space Administration
REALIZATION OF A MATCHING REGION BETWEEN A RADOME AND A GROUND PLANE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, 1 1, 21 REALIZATION OF A MATCHING REGION BETWEEN A RADOME AND A GROUND PLANE D. Sjöberg and M. Gustafsson Department of Electrical and Information
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, 1 1, 21 REALIZATION OF A MATCHING REGION BETWEEN A RADOME AND A GROUND PLANE D. Sjöberg and M. Gustafsson Department of Electrical and Information
While the poor efficiency of the small antennas discussed in the last unit limits their
 Unit 3 Linear Wire Antennas and Antenna Arrays While the poor efficiency of the small antennas discussed in the last unit limits their practicality, the ideas encountered in analyzing them are very useful
Unit 3 Linear Wire Antennas and Antenna Arrays While the poor efficiency of the small antennas discussed in the last unit limits their practicality, the ideas encountered in analyzing them are very useful
APPLICATION OF INTEGRAL EQUATION METHOD TO METAL-PLATE LENS STRUCTURES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 54, 245 262, 2005 APPLICATION OF INTEGRAL EQUATION METHOD TO METAL-PLATE LENS STRUCTURES A. Matsushima, Y. Nakamura, and S. Tomino Department of Electrical and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 54, 245 262, 2005 APPLICATION OF INTEGRAL EQUATION METHOD TO METAL-PLATE LENS STRUCTURES A. Matsushima, Y. Nakamura, and S. Tomino Department of Electrical and
Sound radiation from a loudspeaker, from a spherical pole cap, and from a piston in an infinite baffle1
 Sound radiation from a loudspeaker, from a spherical pole cap, and from a piston in an infinite baffle1 Ronald M. Aarts, Philips Research Europe HTC 36 (WO-02), NL-5656 AE Eindhoven, The Netherlands, Also
Sound radiation from a loudspeaker, from a spherical pole cap, and from a piston in an infinite baffle1 Ronald M. Aarts, Philips Research Europe HTC 36 (WO-02), NL-5656 AE Eindhoven, The Netherlands, Also
Microstrip Coupler with Complementary Split-Ring Resonator (CSRR)
 Microstrip Coupler with Complementary Split-Ring Resonator (CSRR) E-242 Course Project Report Submitted by, EMIL MATHEW JOSEPH 4810-411-091-07049 Guided by, Prof. K J VINOY Department of Electrical and
Microstrip Coupler with Complementary Split-Ring Resonator (CSRR) E-242 Course Project Report Submitted by, EMIL MATHEW JOSEPH 4810-411-091-07049 Guided by, Prof. K J VINOY Department of Electrical and
Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines
 Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Aspects of the Scattering and Impedance Properties of Chaotic Microwave Cavities
 Vol. 109 (2006) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Quantum Chaos and Localisation Phenomena, Warsaw, Poland, May 19 22, 2005 Aspects of the Scattering and Impedance Properties
Vol. 109 (2006) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Quantum Chaos and Localisation Phenomena, Warsaw, Poland, May 19 22, 2005 Aspects of the Scattering and Impedance Properties
Modeling and Analysis of a Long Thin Stripline in a Stripline Environment
 Modeling and Analysis of a Long Thin Stripline in a Stripline Environment Dave Bekers Revised Edition: September 2002 (First Edition: May 2002) iii Preface The research described in this report has been
Modeling and Analysis of a Long Thin Stripline in a Stripline Environment Dave Bekers Revised Edition: September 2002 (First Edition: May 2002) iii Preface The research described in this report has been
TRADITIONALLY, the singularity present in the method of
 1200 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 4, APRIL 2006 Evaluation Integration of the Thin Wire Kernel Donald R. Wilton, Fellow, IEEE, Nathan J. Champagne, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
1200 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 4, APRIL 2006 Evaluation Integration of the Thin Wire Kernel Donald R. Wilton, Fellow, IEEE, Nathan J. Champagne, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
A Dash of Maxwell s. In Part 4, we derived our third form of Maxwell s. A Maxwell s Equations Primer. Part 5 Radiation from a Small Wire Element
 A Dash of Maxwell s by Glen Dash Ampyx LLC A Maxwell s Equations Primer Part 5 Radiation from a Small Wire Element In Part 4, we derived our third form of Maxwell s Equations, which we called the computational
A Dash of Maxwell s by Glen Dash Ampyx LLC A Maxwell s Equations Primer Part 5 Radiation from a Small Wire Element In Part 4, we derived our third form of Maxwell s Equations, which we called the computational
Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay. Poisson s and Laplace s Equations
 Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
DIRECTIVITY OPTIMIZATION IN PLANAR SUB-ARRAYED MONOPULSE ANTENNA
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 4, 1 7, 2008 DIRECTIVITY OPTIMIZATION IN PLANAR SUB-ARRAYED MONOPULSE ANTENNA P. Rocca, L. Manica, and A. Massa ELEDIA Department of Information Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 4, 1 7, 2008 DIRECTIVITY OPTIMIZATION IN PLANAR SUB-ARRAYED MONOPULSE ANTENNA P. Rocca, L. Manica, and A. Massa ELEDIA Department of Information Engineering
APPLICATION OF BILAYER ANISOTROPIC STRUC- TURES FOR DESIGNING LOW-PASS FILTERS AND PO- LARIZERS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 29, 95 108, 2013 APPLICATION OF BILAYER ANISOTROPIC STRUC- TURES FOR DESIGNING LOW-PASS FILTERS AND PO- LARIZERS Amir Raeesi *, Ali Abdolali, and Hossein Mirzaei
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 29, 95 108, 2013 APPLICATION OF BILAYER ANISOTROPIC STRUC- TURES FOR DESIGNING LOW-PASS FILTERS AND PO- LARIZERS Amir Raeesi *, Ali Abdolali, and Hossein Mirzaei
AN EXPRESSION FOR THE RADAR CROSS SECTION COMPUTATION OF AN ELECTRICALLY LARGE PERFECT CONDUCTING CYLINDER LOCATED OVER A DIELECTRIC HALF-SPACE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 267 272, 27 AN EXPRESSION FOR THE RADAR CROSS SECTION COMPUTATION OF AN ELECTRICALLY LARGE PERFECT CONDUCTING CYLINDER LOCATED OVER A DIELECTRIC HALF-SPACE
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 267 272, 27 AN EXPRESSION FOR THE RADAR CROSS SECTION COMPUTATION OF AN ELECTRICALLY LARGE PERFECT CONDUCTING CYLINDER LOCATED OVER A DIELECTRIC HALF-SPACE
Scattering of ECRF waves by edge density fluctuations and blobs
 PSFC/JA-14-7 Scattering of ECRF waves by edge density fluctuations and blobs A. K. Ram and K. Hizanidis a June 2014 Plasma Science and Fusion Center, Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA
PSFC/JA-14-7 Scattering of ECRF waves by edge density fluctuations and blobs A. K. Ram and K. Hizanidis a June 2014 Plasma Science and Fusion Center, Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA
Lecture 8 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture 8 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Scattering Introduction - Consider a localized object that contains charges
Lecture 8 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Scattering Introduction - Consider a localized object that contains charges
